Acne: Causes, Types, and Homeopathic Treatment
Acne is a widespread skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum) and dead skin cells. This leads to the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes cysts or nodules. While it affects people of all ages, acne is most commonly seen during adolescence. This article delves into the causes, types, and treatment options for acne, with a special focus on the effectiveness of homeopathy.
Causes of Acne
Acne develops due to several contributing factors, including:
Excess Oil Production:
Sebaceous glands produce too much oil, clogging the pores.Clogged Hair Follicles:
Dead skin cells mix with excess oil, forming a plug in the hair follicle, which can lead to acne formation.Bacteria:
The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) thrives in clogged pores, contributing to inflammation and infection.Hormones:
Androgens, hormones that surge during puberty, cause the sebaceous glands to produce more oil. Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or the use of birth control can also trigger acne.Inflammation:
When the clogged pores break down, bacteria spill into surrounding tissue, causing redness, swelling, and inflammation.
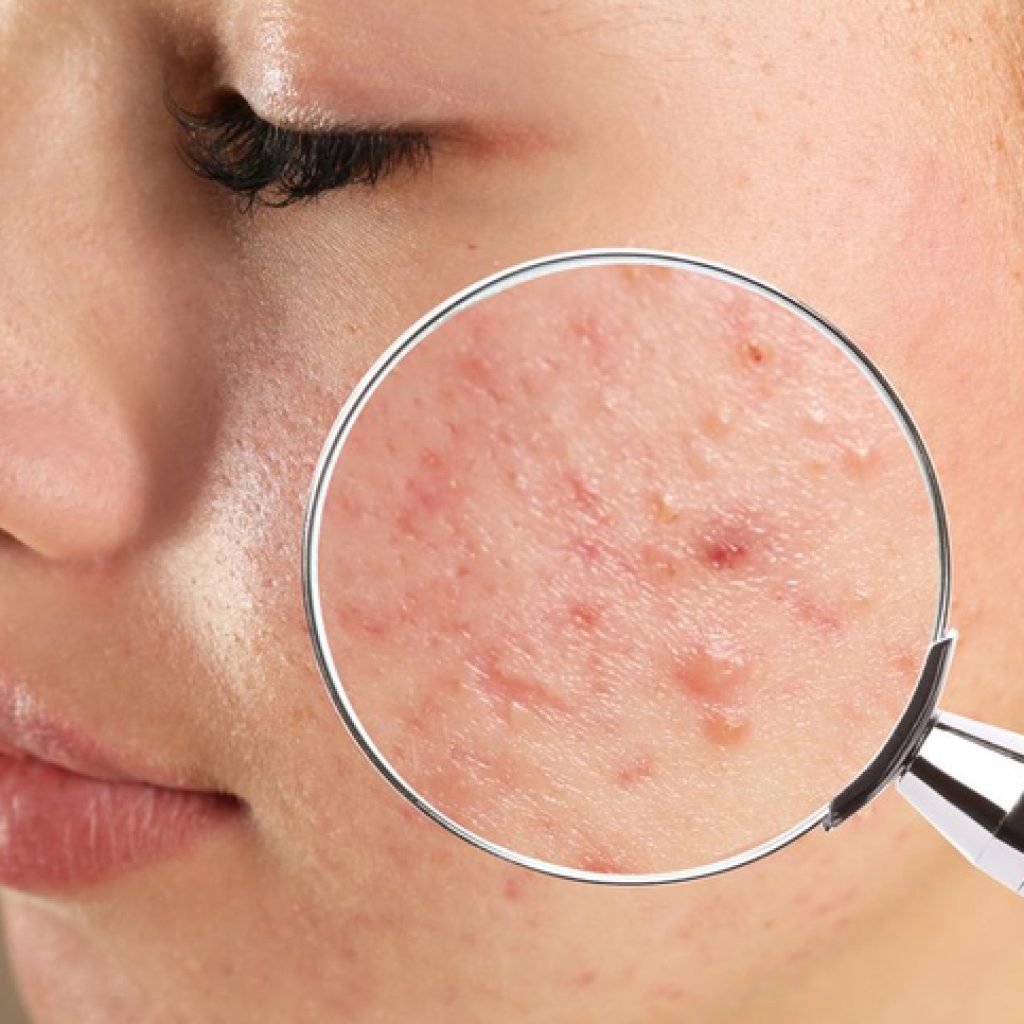
What is Acne?
Acne is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects areas with a high concentration of oil glands, such as the face, chest, back, and shoulders. It can range in severity from mild forms like blackheads and whiteheads to more severe conditions involving cysts and nodules.
Causes of Acne
Acne develops due to several contributing factors, including:
Excess Oil Production:
Sebaceous glands produce too much oil, clogging the pores.Clogged Hair Follicles:
Dead skin cells mix with excess oil, forming a plug in the hair follicle, which can lead to acne formation.Bacteria:
The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) thrives in clogged pores, contributing to inflammation and infection.Hormones:
Androgens, hormones that surge during puberty, cause the sebaceous glands to produce more oil. Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or the use of birth control can also trigger acne.Inflammation:
When the clogged pores break down, bacteria spill into surrounding tissue, causing redness, swelling, and inflammation.
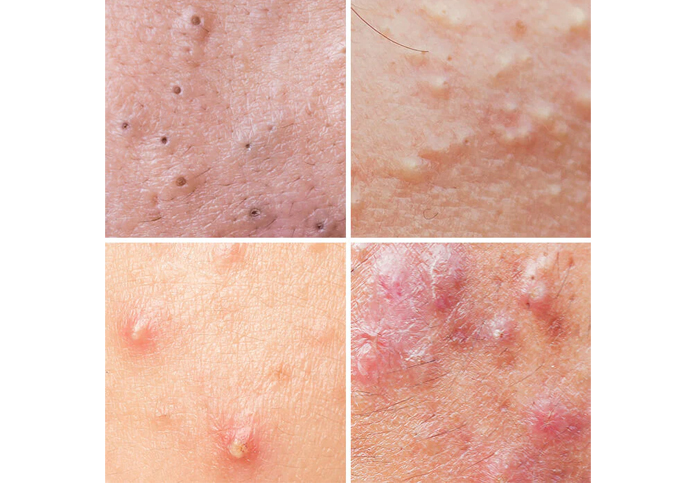
Types of Acne
There are different types of acne, each varying in appearance and severity:
Comedonal Acne:
- Blackheads: Open comedones where the plug is exposed to air, causing it to turn black.
- Whiteheads: Closed comedones where the follicle remains closed, leading to small, white bumps under the skin.
Inflammatory Acne:
- Papules: Small, red bumps that are tender to the touch.
- Pustules: Papules with a white or yellow center filled with pus.
Nodulocystic Acne:
- Nodules: Large, painful lumps deep beneath the skin’s surface.
- Cysts: Deep, painful, pus-filled lesions that may lead to scarring.
Symptoms of Acne
The symptoms of acne can vary based on the type and severity, but commonly include:
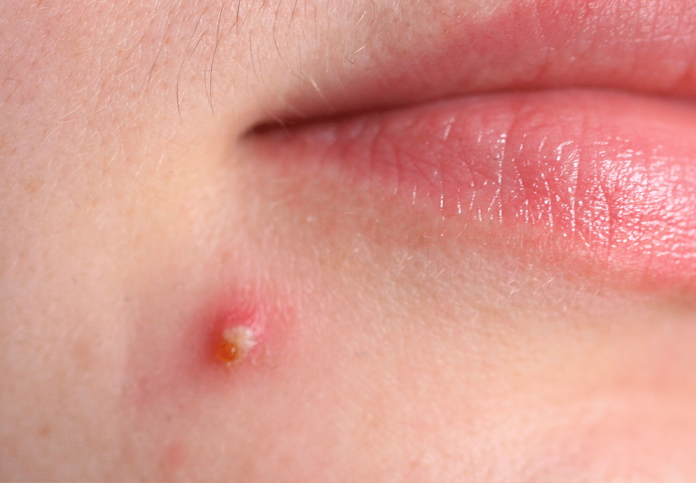
- Pimples: Red, raised spots with a white center that form due to infected or inflamed blocked pores.
- Blackheads and Whiteheads: Non-inflamed clogged pores that appear as small bumps.
- Cysts and Nodules: Larger, painful lesions beneath the skin that can lead to scarring.
- Oily Skin: Excessive oil production leading to a greasy appearance.
- Scarring: Severe acne, particularly cystic acne, can leave permanent scars.
Risk Factors for Acne
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing acne:
- Age: Most common during adolescence, though it can occur at any age.
- Hormonal Changes: Such as puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or the use of oral contraceptives.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition increases the likelihood of developing acne.
- Medications: Certain drugs like corticosteroids, androgens, or lithium can exacerbate acne.
- Diet: Diets high in refined sugars, dairy products, or processed foods may worsen acne, though more research is required.
- Stress: Stress can trigger hormonal changes, potentially worsening acne.
Diagnosis of Acne
Acne is usually diagnosed through a visual examination. A healthcare professional will classify acne based on the type and number of lesions present, and whether scarring is visible. This helps determine the severity and appropriate treatment options.
Homeopathic Treatment for Acne
Homeopathy offers a natural, effective approach to treating acne, focusing on individual symptoms and underlying causes. It has shown a 96% success rate in treating acne, with remedies aimed at reducing inflammation, promoting skin healing, and preventing future outbreaks.
Common Homeopathic Remedies for Acne:
- Beri Beri Aquifolium: Known for improving skin clarity and tone.
- Hepar Sulph: Effective in treating pustular acne and reducing inflammation.
- Silicea: Used for deep, cystic acne, helping to heal skin from within.
- Pulsatilla: Helps treat acne caused by hormonal changes, especially in women.
Homeopathic treatment is individualized, meaning that remedies are tailored to each person’s unique set of symptoms and medical history. This personalized approach helps address the root cause of acne and enhances overall skin health.
