Neurological Disorders
Understanding Neurological Disorders: Causes, Types, and Treatments
Headache
Headaches are a common issue that can range from mild and occasional to severe and chronic. They can be caused by a variety of factors and can manifest in different types. Here’s a detailed overview of headaches, including their causes, types, symptoms, and treatments:
Causes of Headaches
- Primary Headaches:
- Tension: Often related to muscle tension and stress.
- Migraine: Often triggered by genetic and environmental factors.
- Cluster: Severe pain usually around one eye, potentially linked to irregularities in the biological clock.
- Secondary Headaches:
- Medical Conditions: Such as infections (e.g., sinusitis, meningitis), high blood pressure, or neurological conditions.
- Trauma: Head injuries or concussions.
- Medication Overuse: Frequent use of pain relief medications can lead to rebound headaches.
- Substance Withdrawal: Such as from caffeine or alcohol.
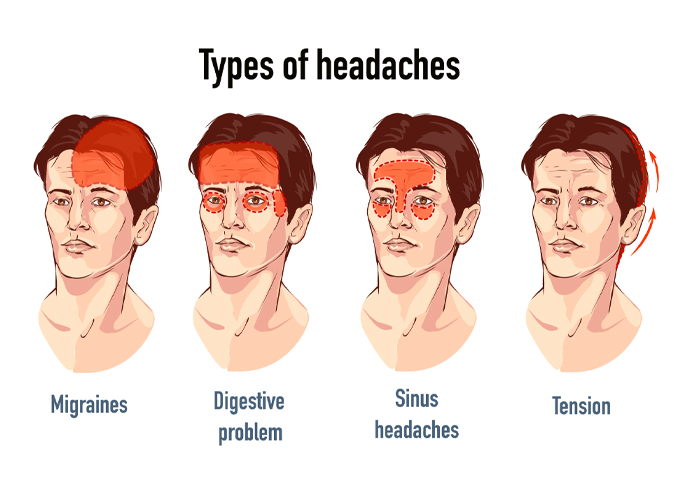
Types of Headaches
- Tension-Type Headaches:
- Characteristics: Mild to moderate pain, often described as a tight band around the head.
- Symptoms: Dull, aching pain; pressure or tightness in the forehead, temples, or neck.
- Duration: Can last from 30 minutes to several days.
- Migraine Headaches:
- Characteristics: Intense, throbbing pain, often on one side of the head.
- Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, aura (visual disturbances) in some cases.
- Duration: Can last from a few hours to several days.
- Cluster Headaches:
- Characteristics: Severe, sharp pain usually around one eye or temple.
- Symptoms: Redness or watering of the eye, nasal congestion, or a runny nose on the affected side.
- Duration: Typically occur in clusters over weeks or months, with each headache lasting 15 minutes to 3 hours.
- Sinus Headaches:
- Characteristics: Pain in the forehead, cheeks, and nose area.
- Symptoms: Accompanied by nasal congestion, facial swelling, and sometimes fever.
- Duration: Often linked to sinus infections or inflammation.
- Medication Overuse Headaches:
- Characteristics: Result from frequent use of headache medications.
- Symptoms: Daily or almost daily headaches.
- Duration: Persistent as long as medication use continues.
- Rebound Headaches:
- Characteristics: Similar to medication overuse headaches but specifically triggered by pain relief medications.
- Symptoms: Persistent headache that improves when medication is taken but returns once it wears off.
Symptoms of Headaches
- Pain: Varies from dull and aching to sharp and throbbing.
- Nausea/Vomiting: Common with migraines.
- Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to light, sound, or smells.
- Visual Disturbances: Such as seeing flashes of light or blind spots, particularly with migraines.
- Neck or Shoulder Pain: Often associated with tension-type headaches.
Treatment for Headaches
- Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration.
- Rest: Ensure adequate sleep and manage stress.
- Cold or Warm Compresses: Apply to the head or neck to relieve pain.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress-related headaches.
- Medications:Homeopathic remedies like spigelia , sangunaria, iris versicolor, and many other remedies are helpful and a constitutional approach with mental emotional modalities and physical modalities is very important to reduce the frequency and intensity of the headache and follows the cure.
- Behavioral Therapies:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Can be useful for managing chronic headaches, particularly tension-type headaches.
- Biofeedback: Helps in learning to control physiological functions to reduce headache frequency and intensity.
- Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: May help some individuals with chronic headaches.
- Massage Therapy: Can alleviate tension and reduce headache frequency.
- Avoidance of Triggers:
- Dietary Changes: Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger migraines or other headaches.
- Stress Management: Techniques to reduce stress and its impact on headache frequency.
