Respiratory System
Understanding Respiratory System Problems: Causes, Types, and Treatments
Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic Rhinitis is an inflammatory condition of the nasal passages triggered by allergens. It is commonly referred to as hay fever and can cause symptoms similar to those of a cold, but without the accompanying fever or body aches.
Types of Allergic Rhinitis
- Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis:
- Also known as hay fever.
- Caused by airborne allergens such as pollen from trees, grasses, or weeds.
- Symptoms typically occur during specific seasons when these allergens are prevalent.
- Perennial Allergic Rhinitis:
- Occurs year-round.
- Triggered by indoor allergens like dust mites, pet dander, mold, and cockroach droppings.
- Symptoms are persistent and can be exacerbated by indoor environments.
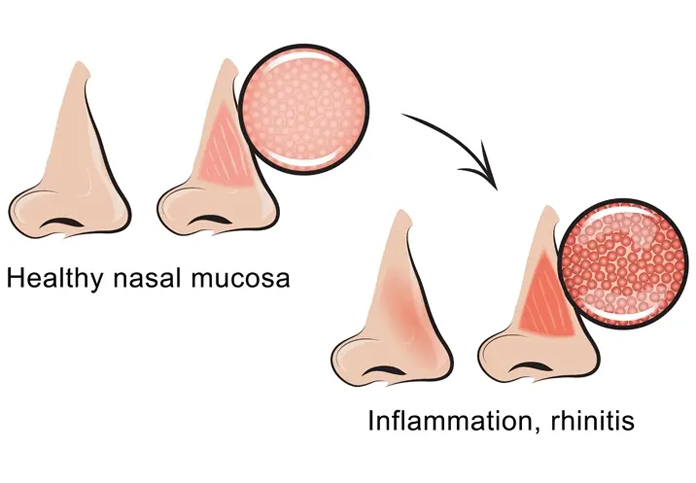
Symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis
- Nasal Symptoms:
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Itchy nose or throat
- Other Symptoms:
- Postnasal drip (mucus dripping down the back of the throat)
- Coughing
- Fatigue or feeling generally unwell
- Headaches
- Irritability or difficulty concentrating
Causes and Triggers
- Pollen: From trees, grasses, and weeds during certain seasons.
- Dust Mites: Tiny organisms that live in household dust.
- Pet Dander: Skin flakes, urine, and saliva from pets.
- Mold: Found in damp or humid areas, both indoors and outdoors.
- Cockroach Droppings: Can be a source of allergens in urban areas.
Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis
- Medical History:
- Evaluation of symptoms, their duration, and triggers.
- Physical Examination:
- Examination of the nose, throat, and eyes to check for signs of inflammation or infection.
- Allergy Testing:
- Skin Prick Test: Small amounts of allergens are introduced into the skin to check for reactions.
- Blood Tests: Measure levels of specific IgE antibodies against allergens.
- Nasal Endoscopy:
- A procedure to examine the nasal passages and sinuses using a thin, flexible tube with a camera.
Treatment for Allergic Rhinitis
- Avoidance of Triggers:
- Pollen: Keep windows closed during high pollen seasons, use air purifiers, and shower after being outdoors.
- Dust Mites: Use dust-mite-proof pillow and mattress covers, and wash bedding in hot water.
- Pet Dander: Keep pets out of sleeping areas, and clean frequently.
- Mold: Use dehumidifiers and clean areas prone to mold growth.
- Medications:homeopathy has always given very good results in allergy cases, remedies like ars alb, allium cepa , sabadilla are very helpful.
- .
- Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Saline Nasal Rinses: Help clear allergens and mucus from the nasal passages.
Complications of Allergic Rhinitis
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses due to prolonged nasal congestion.
- Ear Infections: Can occur if fluid builds up in the middle ear.
- Asthma: Allergic rhinitis can exacerbate asthma symptoms or contribute to asthma development.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which can lead to difficulty breathing. It is typically marked by recurring symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. Asthma can affect people of all ages, and its severity can vary from mild to life-threatening.
Symptoms of Asthma
- Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound during breathing, especially when exhaling.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling breathless.
- Chest Tightness: A sensation of pressure or tightness in the chest.
- Coughing: Persistent coughing, particularly at night or early in the morning.
Causes and Triggers
- Genetic Factors:
- A family history of asthma or other allergic conditions can increase the risk.
- Environmental Factors:
- Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, mold, pet dander, and cockroach droppings.
- Air Pollution: Exposure to pollutants, such as tobacco smoke, vehicle emissions, and industrial pollutants.
- Weather Conditions: Cold air, humidity, and changes in weather can trigger asthma symptoms.
- Respiratory Infections:
- Viral infections, particularly in early childhood, can increase the risk of developing asthma or worsen symptoms.
- Physical Activity:
- Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB) can occur during or after physical activity, particularly in cold or dry air.
- Irritants:
- Tobacco Smoke: Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Strong Odors: Fragrances, cleaning products, and fumes.
- Emotional Stress:
- Stress and strong emotions can trigger or exacerbate asthma symptoms.
Diagnosis of Asthma
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
- Evaluation of symptoms, their frequency, and triggers.
- Physical examination to check for signs of wheezing or other respiratory issues.
- Spirometry:
- A test that measures how much air you can inhale and exhale and how quickly you can exhale. It helps determine lung function and airway obstruction.
- Peak Flow Measurement:
- Measures how fast you can exhale air from your lungs, which can help monitor asthma control.
- Allergy Testing:
- Identifies potential allergens that may trigger asthma symptoms.
Treatment for Asthma
Homeopathy has been very successful in treating asthma cases, remedies like ars alb, nat sulph,blata has given immense results.
- Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Monitoring Symptoms: Keeping track of symptoms, medication use, and peak flow measurements to manage asthma effectively.
- Action Plan: Developing an asthma action plan with your healthcare provider to handle worsening symptoms and emergencies.
Management and Prevention
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider to monitor and adjust treatment as needed.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to known asthma triggers.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and managing stress can help control asthma.
- Vaccinations: Getting vaccinated against flu and other respiratory infections to prevent exacerbations.
