Skin Diseases
Understanding Skin Problems: Causes, Types, and Treatments
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that speeds up the life cycle of skin cells, causing them to build up rapidly on the surface of the skin. These extra skin cells form scales and red patches that are often itchy and sometimes painful. Here’s an in-depth look at psoriasis:
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, inflammatory disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. It is not contagious and often fluctuates in severity, with periods of flares and remission.
Causes:
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it involves a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors:
- Immune System: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, speeding up their production and causing an accumulation on the skin’s surface.
- Genetics: Psoriasis tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component. If a close relative has psoriasis, your risk of developing the condition is higher.
- Triggers: Various factors can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis, including:
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can trigger flare-ups.
- Infections: Certain infections, like strep throat, can trigger psoriasis, especially in children.
- Injury to the Skin: Cuts, scrapes, or severe sunburns can trigger a type of psoriasis known as the Koebner phenomenon.
- Medications: Some medications, like lithium or beta-blockers, can worsen psoriasis.
- Climate: Cold, dry weather can exacerbate symptoms.
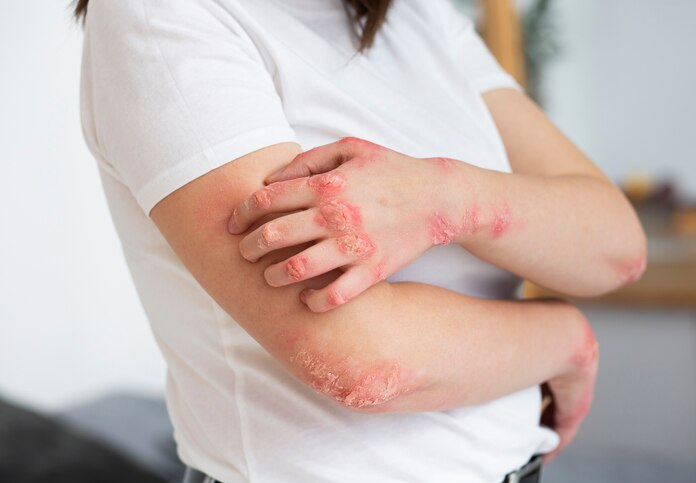

Types of Psoriasis:
- Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris):
- The most common form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales. These plaques can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
- Guttate Psoriasis:
- Appears as small, dot-like lesions and often starts in childhood or young adulthood. It can be triggered by a bacterial infection like strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis:
- Occurs in body folds, such as under the breasts, in the groin, or around the buttocks. It is characterized by smooth, red patches of skin that worsen with friction and sweating.
- Pustular Psoriasis:
- Characterized by white pustules (blisters of noninfectious pus) surrounded by red skin. It can occur on the hands and feet or cover most of the body (generalized pustular psoriasis).
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis:
- A severe and rare form that leads to widespread redness and scaling, covering large areas of the body. It can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
- Nail Psoriasis:
- Affects the fingernails and toenails, leading to pitting, abnormal nail growth, and discoloration. In severe cases, the nails may crumble or detach from the nail bed.
- Psoriatic Arthritis:
A type of arthritis that affects some people with psoriasis. It causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, and can lead to joint damage if untreated.
Homeopathic treatment
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on quality of life, particularly due to its visible symptoms and associated discomfort. Managing stress, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following a tailored treatment plan can help keep symptoms under control.
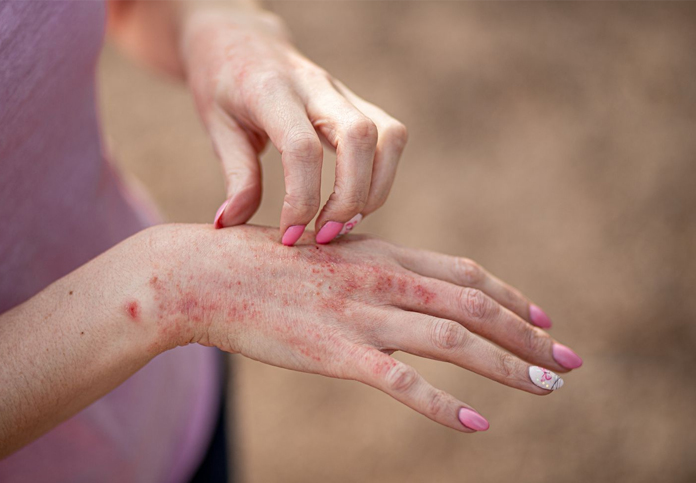
Symptoms:
- Red Patches of Skin: Covered with thick, silvery scales.
- Dry, Cracked Skin: That may bleed.
- Itching, Burning, or Soreness: In the affected areas.
- Thickened or Ridged Nails: With pitting or discoloration.
- Stiff, Swollen Joints: If psoriatic arthritis develops.
Psoriasis being an autoimmune disease cannot be completely cured but with effective medicines and the treatment the disease can be kept under control. Homeopathic med are safe effective and have no side effects .homeopathic medicines focus on the root cause and tries to correct the skin inflammation. gradually you will start to see the changes to see the normal skin.
There are very effective homeopathic remedies for psoriasis, these are listed below ars alb, mezerium,graphites,kali ars and so many.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition characterized by the loss of pigment, resulting in white patches on the skin. It occurs when the cells responsible for producing melanin (the pigment that gives skin its colour) are destroyed. Here’s a detailed overview of vitiligo:
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks and destroys melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin. The loss of these cells leads to the development of white or depigmented patches on the skin, which can occur anywhere on the body.
Causes:
The exact cause of vitiligo is not completely understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, autoimmune, and environmental factors:
- Autoimmune Response: In vitiligo, the immune system mistakenly targets and destroys melanocytes, leading to loss of skin color.
- Genetics: There is a genetic predisposition to vitiligo, and it is more likely to occur in individuals with a family history of the condition or other autoimmune disorders.
Environmental Triggers: Factors such as sunburn, exposure to certain chemicals, or significant emotional stress may trigger the onset of vitiligo in predisposed individuals.

Types of Vitiligo:
- Non-Segmental Vitiligo (NSV):
- The most common form, also known as generalized vitiligo, where white patches appear symmetrically on both sides of the body. It can affect the face, neck, hands, and other areas.
- Subtypes:
- Acrofacial Vitiligo: Affects the fingers, toes, and facial features.
- Universal Vitiligo: Extensive loss of skin color across most of the body.
- Segmental Vitiligo:
- This type tends to affect one side or segment of the body. It often appears at a younger age, progresses for a few years, and then stabilizes. It is less common and typically more localized.
- Focal Vitiligo:
- Characterized by one or a few patches in a small area. It does not spread widely and is less common.
Symptoms:
- White or Depigmented Patches: The primary symptom is the development of milky-white patches on the skin. These patches may appear anywhere on the body but are most common on areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, and feet.
- Premature Greying: Hair on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or beard may turn white or gray prematurely.
- Mucous Membranes: Loss of colour in the tissues lining the inside of the mouth and nose.
- Eye Colour Changes: Some people with vitiligo may experience changes in the colour of their retinas or iris.
Diagnosis:
Vitiligo is usually diagnosed through a physical examination by a doctor. A Wood’s lamp (a special type of ultraviolet light) may be used to highlight areas of depigmentation. In some cases, a skin biopsy or blood tests may be performed to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment:
Vitiligo can have a significant emotional and psychological impact, especially due to its visible nature.Homeopathic medicines are selected after complete detailed medical history of the pts with relevant blood test done. Homeopathic medicines when administered it helps in production of pigments. Some important homeopathic remedies like hydrocotyle and asf are seen to give good results.
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a general term that refers to inflammation of the skin, which can cause redness, swelling, itching, and sometimes blistering or peeling. There are several types of dermatitis, each with different causes and characteristics. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
Types of Dermatitis:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema):
- What It Is: A chronic condition that usually begins in childhood and is associated with other atopic conditions like asthma and hay fever. It causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
- Causes: The exact cause is unknown but involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The immune system overreacts to allergens or irritants, leading to inflammation.
- Symptoms: Dry, red patches of skin, often on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, and the bends of the elbows and knees. Itching can be severe, leading to scratching and skin damage.

- Contact Dermatitis:
- What It Is: Inflammation caused by direct contact with an irritant or allergen. It can be either irritant contact dermatitis or allergic contact dermatitis.
- Causes:
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Caused by direct damage to the skin by substances like detergents, acids, or solvents.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Caused by an allergic reaction to substances like nickel, poison ivy, latex, or fragrances.
- Symptoms: Redness, itching, swelling, and blisters at the site of contact. The reaction can occur immediately or after repeated exposure.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis:
- What It Is: A common skin condition that affects areas of the body with a high concentration of sebaceous (oil) glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. It is often associated with dandruff.
- Causes: The exact cause is not known, but it may be related to a yeast (Malassezia) on the skin, genetics, or an abnormal immune response.
- Symptoms: Red, greasy, scaly patches on the scalp, eyebrows, sides of the nose, eyelids, and ears. It can cause dandruff in the scalp and cradle cap in infants.
- Nummular Dermatitis:
- What It Is: Also known as discoid eczema, it appears as round, coin-shaped spots on the skin.
- Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but it may be triggered by dry skin, environmental factors, or injury to the skin.
- Symptoms: Itchy, circular patches that can be red, scaly, and sometimes ooze fluid. These patches commonly appear on the arms, legs, hands, and torso.
- Stasis Dermatitis:
- What It Is: A skin inflammation that occurs on the lower legs due to poor circulation and venous insufficiency.
- Causes: The condition is often associated with chronic venous insufficiency, where blood pools in the veins of the legs, leading to swelling and skin changes.
- Symptoms: Swollen legs, itching, scaling, and brownish discoloration of the skin. In severe cases, ulcers can form.
- Perioral Dermatitis:
- What It Is: A facial rash that usually occurs around the mouth, and sometimes the eyes and nose.
- Causes: The exact cause is unclear, but it may be related to the use of topical steroids, cosmetics, or skin care products.
- Symptoms: Red bumps, scaling, and itching around the mouth, nose, and eyes.
General Symptoms of Dermatitis:
- Redness and Swelling: Inflamed skin is common in all forms of dermatitis.
- Itching: A hallmark symptom that can range from mild to severe.
- Blisters or Cracking: In some cases, the skin may blister or crack, especially if scratched.
- Dry or Scaly Skin: Chronic dermatitis often leads to dry, scaly patches.
Treatment : Homeopathy has good role in treating dermatitis, medicines used are graphites,sep, nat mur and many.homeopathy has shown promising results in managing dermatitis ,these remedies can help address underlying causes ,reduce symptoms and promote healthy skin function.A comprehensive assessment of your symptoms with medical history and a tailored remedy plan to address the underlying causes will be given.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Regular Moisturizing: Helps maintain skin hydration an prevent flare-ups.
- Gentle Skin Care: Using mild soaps, avoiding hot water, and wearing soft fabrics can minimize irritation.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger or exacerbate dermatitis, so techniques like meditation or yoga may help.
Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum) and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes cysts or nodules. It can affect people of all ages, though it is most common during adolescence. Here’s an in-depth overview:
What is Acne?
Acne is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects areas of the skin with the highest concentration of oil glands, including the face, chest, back, and shoulders. It ranges in severity from mild, consisting mainly of whiteheads and blackheads, to severe, characterized by deep, painful cysts and nodules.
Causes:
Several factors contribute to the development of acne:
- Excess Oil Production:
- Sebaceous glands in the skin produce more oil than necessary, leading to the clogging of pores.
- Clogged Hair Follicles:
- Dead skin cells and excess oil accumulate in the hair follicles, forming a soft plug. This creates an environment where bacteria can thrive.
- Bacteria:
- Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) is the bacteria that live on the skin and contribute to inflammation and infection in clogged pores.
- Hormones:
- Androgens, hormones that increase during puberty, cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and produce more sebum. Hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, or when starting or stopping birth control pills can also trigger or worsen acne.
- Inflammation:
- When the walls of the clogged pores break down, bacteria can spill into the surrounding tissue, causing redness, swelling, and inflammation.
Types of Acne:
- Comedonal Acne:
- Blackheads: Open comedones where the plug of sebum and dead skin cells is exposed to air, turning it black.
- Whiteheads: Closed comedones where the follicle is closed, leading to a small, white bump under the skin.
- Inflammatory Acne:
- Papules: Small, red, tender bumps caused by inflammation.
- Pustules: Similar to papules but with a white or yellow center (pus).
- Nodulocystic Acne:
- Nodules: Large, painful lumps beneath the surface of the skin, formed deep within the hair follicles.
- Cysts: Deep, painful, pus-filled lumps beneath the skin’s surface, which can result in scarring.
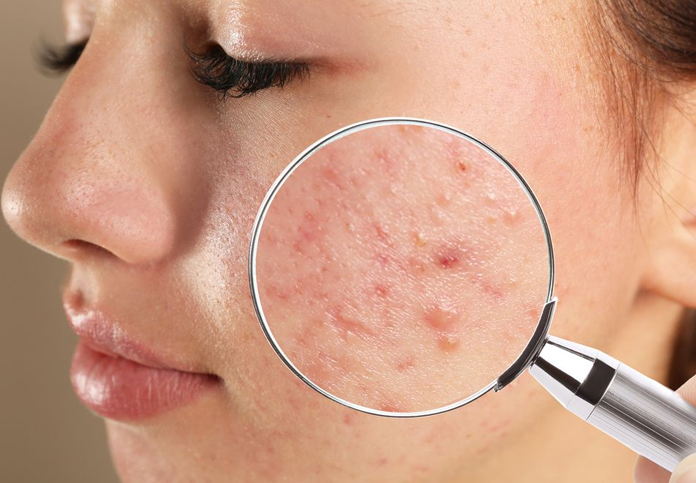
Symptoms:
- Pimples: Red, raised spots with a white center that develop when blocked hair follicles become inflamed or infected.
- Blackheads and Whiteheads: Non-inflamed clogged pores that appear as small bumps.
- Cysts and Nodules: Large, painful, and potentially scarring lesions.
- Oily Skin: Excess oil production can lead to a greasy appearance.
- Scarring: Severe acne, especially cystic acne, can lead to permanent scarring.
Risk Factors:
- Age: Most common during adolescence, but can occur at any age.
- Hormonal Changes: Including puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and use of oral contraceptives.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition to acne can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including corticosteroids, androgens, or lithium, can exacerbate acne.
- Diet: Some studies suggest that diets high in refined sugars, dairy products, and processed foods may worsen acne, though more research is needed.
- Stress: Stress can exacerbate acne by triggering hormonal changes.
Diagnosis:
Acne is usually diagnosed through a visual examination by a doctor The severity of acne can be classified based on the number and type of lesions, and whether scarring is present.
Treatment Options:
Homeopathy has 96% success rate in treating acne. Medicines are selected on the individual symptoms. Commonly used medicines are beri beri aquifolium, hepar sulph, silicea, puls.Homoeopathy offers a natural effective approach to reduce acne and inflammation promotes healthy skin healing and repair,it enhance skin clarity and tone.
Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nails. It presents as an itchy, non-infectious rash with small, flat-topped, purple or reddish-purple bumps (papules). The exact cause of lichen planus is not well understood, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues.
Common Symptoms:
- Skin: The rash typically appears on the wrists, lower back, and ankles but can occur anywhere on the body. It is often itchy and may have a lacy white pattern known as Wickham’s striae.
- Mucous Membranes: Lichen planus can affect the mouth, causing white patches, ulcers, or painful sores. It can also affect the genital area.
- Hair: In some cases, lichen planus can lead to hair loss if it affects the scalp (lichen planopilaris).
- Nails: The condition can cause thinning, ridging, splitting, or loss of nails.
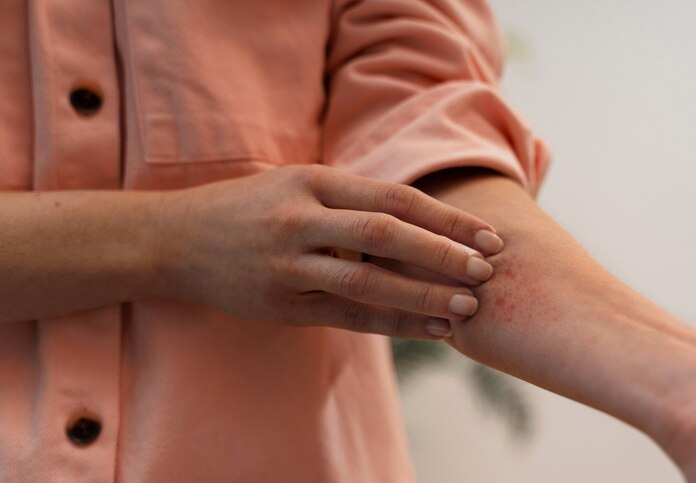

Potential Triggers:
- Medications: Certain drugs, including NSAIDs, beta-blockers, and ACE inhibitors, can trigger lichen planus in some individuals.
- Infections: Some infections, like hepatitis C, have been associated with lichen planus.
- Allergic Reactions: Reactions to certain metals or chemicals might also trigger the condition.
Diagnosis:
Lichen planus is diagnosed through a clinical examination, often supported by a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. Blood tests might be done to rule out related conditions or triggers, such as hepatitis C.
Treatment:Homoeopathic approach for lichen planus is individualised ,gentle and holistic approach to alleviate symptoms and promote healing by addressing the underlying causes and triggers .There are med like ars alb, hydrocotyle and merc sol which are helpful.we need to assess the symptoms, medical history and constitution to recommend the most suitable remedy.homeopathic remedies can help to reduce the inflammation and itching ,improve the skin health and appearance, and enhance overall well being.
Prognosis:
Lichen planus can last for several months to years, and while it often resolves on its own, some cases may recur or persist. In rare cases, especially when it affects the mucous membranes, it may increase the risk of developing certain cancers, such as oral cancer.
Tinea
Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nails. It presents as an itchy, non-infectious rash with small, flat-topped, purple or reddish-purple bumps (papules). The exact cause of lichen planus is not well understood, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues.
Causes:
- Fungal Infection: Tinea is caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments.
- Contagion: It can be spread through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or object (like towels, clothing, or surfaces).
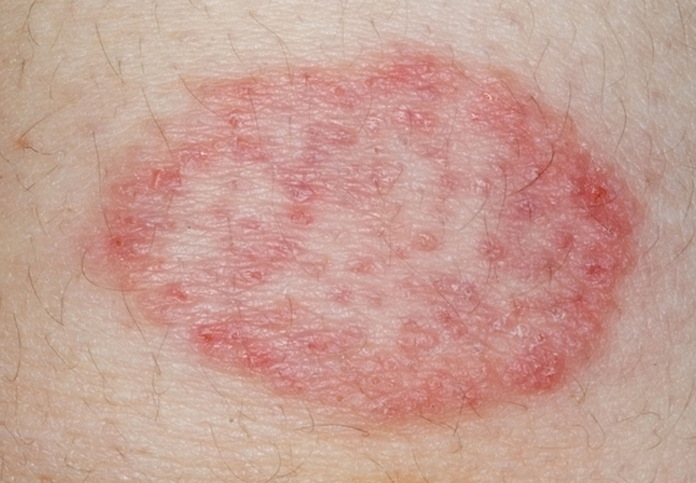
Common Types of Tinea:
- Tinea Corporis (Body Ringworm):
- Location: Affects the skin on the body, usually the arms, legs, or torso.
- Symptoms: Red, circular, itchy rash with a clear or scaly center. The edges of the rash may be slightly raised.
- Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot):
- Location: Affects the feet, especially between the toes.
- Symptoms: Itchy, scaly, and cracked skin. It may cause blisters and burning sensations.
- Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch):
- Location: Affects the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks.
- Symptoms: Red, itchy rash that may be ring-shaped and have a clear center. It is more common in males.
- Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm):
- Location: Affects the scalp.
- Symptoms: Scaly, itchy patches on the scalp that can lead to hair loss in the affected areas. It is more common in children.
- Tinea Unguium (Onychomycosis):
- Location: Affects the nails, particularly toenails.
- Symptoms: Thickened, discolored, and brittle nails. The nails may crumble and become distorted.
- Tinea Barbae:
- Location: Affects the beard area, including the chin and upper lip.
- Symptoms: Red, scaly, and itchy patches, sometimes with hair loss in the affected areas.
Risk Factors:
- Moisture: Excessive sweating or damp skin increases the risk.
- Close Contact: Engaging in sports, using communal showers, or living in crowded conditions.
- Immunocompromised State: Conditions that weaken the immune system can increase susceptibility.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination: The appearance of the rash is often characteristic.
- Microscopic Examination: Skin scrapings may be examined under a microscope.
- Fungal Culture: Sometimes used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment:
- Tinea can be frustrating and persistent condition, but homeopathy offers a natural and effective approach to promote healing and prevent recurrence.Homeopathy has wider approach for fungal infection remedies like sulphur, tellurium, graphites are helpful,further evaluation is done on pt case history to give the constitution med .
Prevention:
- Personal Hygiene: Regularly wash and dry skin thoroughly, especially in areas prone to moisture.
- Avoid Sharing Items: Do not share towels, shoes, or other personal items.
- Wear Protective Footwear: Use sandals in communal showers or locker rooms.
Prognosis:
With appropriate treatment, most cases of tinea resolve within a few weeks. However, recurrence is possible, especially in individuals with continued exposure to risk factors.
Urticaria
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of red, itchy raised rashes on the skin. These rashes can vary in size and may join together to form larger areas of swelling. Urticaria can affect any part of the body and can range from mild to severe.
Causes and Triggers:
- Allergic Reactions: Foods, medications, insect stings, or pollen can trigger urticaria in susceptible individuals.
- Infections: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections can trigger hives.
- Autoimmune Reactions: The body’s immune system may mistakenly attack healthy tissue, leading to chronic urticaria.
- Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate or trigger symptoms.
- Physical Stimuli: Pressure, temperature changes, sunlight, and exercise can trigger physical urticaria.
- Idiopathic: In many cases, no identifiable cause is found.
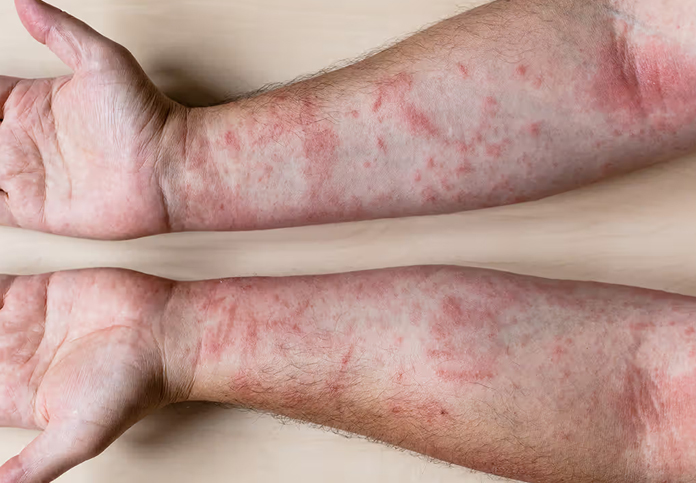
Types of Urticaria:
- Acute Urticaria:
- Duration: Lasts less than six weeks.
- Causes: Often triggered by an allergic reaction to foods (e.g., nuts, shellfish), medications (e.g., antibiotics, NSAIDs), insect stings, or infections. Stress, exercise, or exposure to heat or cold can also trigger acute urticaria.
- Symptoms: Sudden appearance of welts that may change shape and size, disappear, and reappear within minutes or hours. The welts are often itchy and may cause a burning or stinging sensation.
- Chronic Urticaria:
- Duration: Persists for more than six weeks, often months or years.
- Causes: The exact cause is often unknown (idiopathic), but it may be associated with autoimmune conditions, infections, or chronic diseases. In some cases, physical factors like pressure, temperature, or sunlight may trigger symptoms.
- Symptoms: Similar to acute urticaria but recurring or persisting for longer periods. The itching and welts can significantly affect the quality of life.
- Physical Urticaria:
- Triggered by: Physical stimuli such as cold, heat, pressure, vibration, sunlight, or water.
- Symptoms: The appearance of welts and itching in response to specific physical triggers.
Symptoms:
- Welts (Hives): Red or skin-colored, raised areas that can vary in size and shape. They may merge to form larger areas.
- Itching: Often intense and can worsen with scratching.
- Swelling: The skin around the welts may become swollen (angioedema), particularly around the eyes, lips, hands, feet, and throat.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: In some cases, the welts may cause discomfort beyond itching.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination: Diagnosis is often based on the appearance of the welts and patient history.
- Allergy Testing: Skin prick tests or blood tests to identify potential allergens.
- Blood Tests: To check for underlying conditions, especially in chronic cases.
- Physical Challenge Tests: To identify physical triggers (e.g., cold, heat, pressure).
Treatment:Homeopathy has personalised approach for urticaria,offer a natural and effective approach to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. After the treatment gradually pts will notice frequency and intensity of the urticaria coming down,reduces itching,redness and swelling. Success rate is 96% . few of the remedies which are helpful apis , urtrica urens,rhus tox.constitution approach is very important to cure the case.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are cosmetic treatments that use a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin, removing its outer layers. This process promotes the growth of new, smoother skin, helping to reduce fine lines, wrinkles, acne scars, and uneven pigmentation. They are commonly used for facial rejuvenation and improving skin texture.
Homoeopathic HydraFacial
The Homoeopathic HydraFacial is a non-invasive skincare treatment that combines the principles of homeopathy with modern facial technology. It uses gentle, homeopathic remedies tailored to individual skin types, along with a multi-step process that includes cleansing, exfoliation, extraction, and hydration. The treatment deeply nourishes the skin with homeopathic serums, promoting natural healing and rejuvenation without harsh chemicals. Unlike traditional facials, this method is designed to restore balance and enhance the skin’s vitality, making it ideal for sensitive skin. It helps in reducing fine lines, improving skin tone, and providing a radiant, refreshed complexion.
