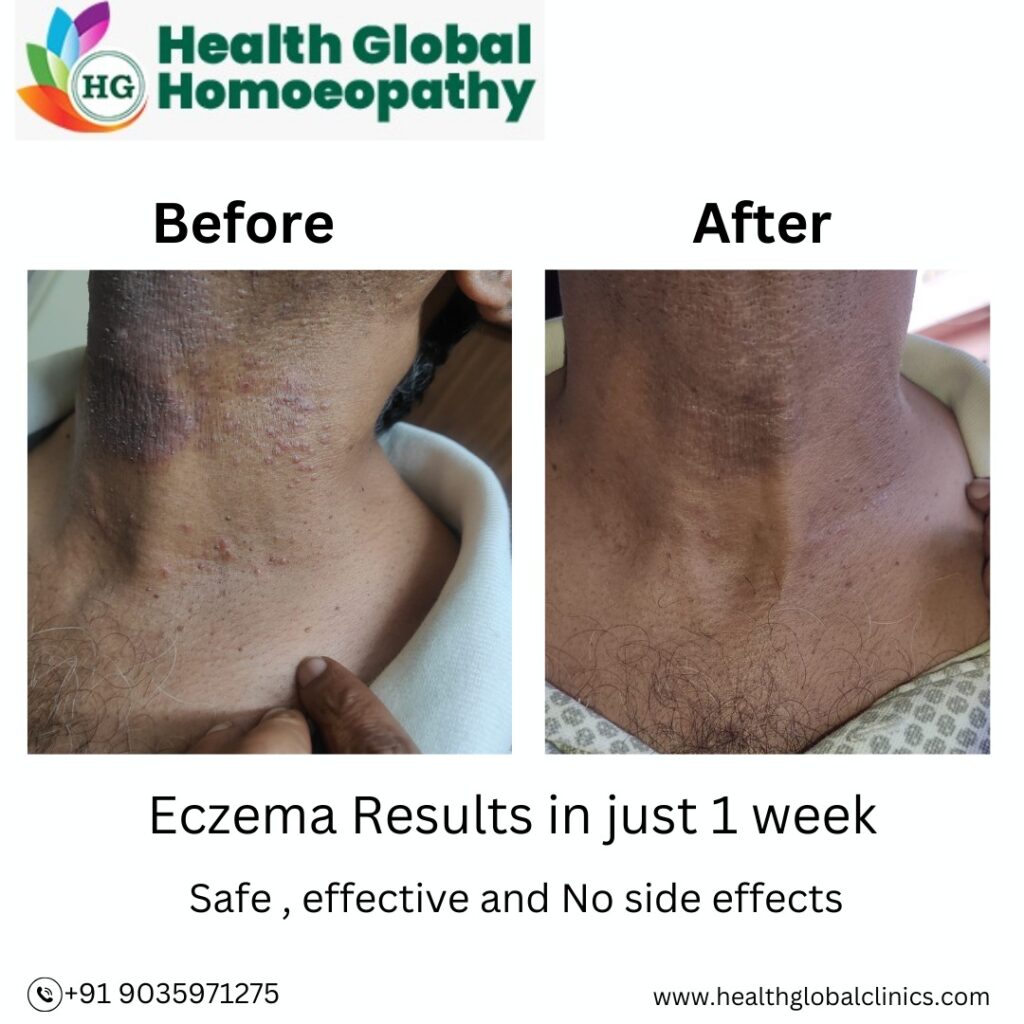
Eczema
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by itching, redness, and dryness. It affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact their quality of life. This blog explores eczema’s types, causes, pathophysiology, and how homeopathic treatment can provide relief.
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a term for a group of conditions that cause the skin to become inflamed, irritated, and itchy. It is not contagious but often runs in families with a history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever.
Types of Eczema
- Atopic Dermatitis:
- The most common form of eczema.
- Associated with other allergic conditions like asthma or hay fever.
- Symptoms include dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
- Contact Dermatitis:
- Caused by direct skin contact with irritants or allergens.
- Divided into irritant and allergic contact dermatitis.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema:
- Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet.
- Triggers include stress, seasonal changes, or prolonged exposure to water.
- Nummular Eczema:
- Appears as round, coin-shaped spots on the skin.
- Often triggered by dry skin or environmental factors.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis:
- Affects areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp and face.
- Commonly referred to as dandruff when affecting the scalp.
- Stasis Dermatitis:
- Occurs in the lower legs due to poor blood flow.
- Often seen in people with varicose veins or chronic venous insufficiency.
Causes of Eczema
Eczema’s exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors:
- Genetics: A family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma.
- Environmental Triggers: Allergens, irritants (like soap or detergents), weather changes, and stress.
- Immune System Dysfunction: An overactive immune response to triggers.
- Skin Barrier Defects: Making the skin more prone to irritants and dehydration.
Pathophysiology of Eczema
Eczema results from a complex interplay of genetic, immune, and environmental factors:
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction:
- Mutations in the filaggrin protein impair the skin’s barrier function, leading to moisture loss and increased permeability to allergens and irritants.
- Immune Dysregulation:
- An overactive immune system triggers inflammation, causing redness, itching, and swelling.
- T-helper cells (Th2) dominate, producing cytokines that exacerbate inflammation.
- Microbial Imbalanc
- Dysbiosis of the skin microbiome, such as overgrowth of Staphylococcus aureus, worsens symptoms.
Homeopathic Treatment for Eczema
Homeopathy offers a holistic and individualized approach to managing eczema by addressing the root cause rather than just the symptoms. These are the homeopathic remedies for eczema
- Commonly Used Remedies:
- Graphites: For thick, oozing eczema with cracked skin.
- Sulphur: For intensely itchy, burning, and red skin.
- Rhus Toxicodendron: For blistery, itchy eczema that worsens in wet weather.
- Mezereum: For eczema with oozing and crusting, especially on the scalp.
- Holistic Approach:
- Treats the individual as a whole, considering their physical, emotional, and mental health.
- Lifestyle modifications and dietary advice are often part of the treatment plan.
- Long-Term Benefits:
- Strengthens the immune system.
- Reduces the recurrence of flare-ups.Do not self medicate these homeopathic remedies for eczema
Conclusion
Eczema can be challenging to live with, but understanding its types, causes, and pathophysiology is the first step toward effective management. Homeopathy provides a safe, natural, and holistic approach to treating eczema, addressing the condition’s root causes and improving overall well-being.