Definition
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is characterized by hormonal imbalances, irregular menstrual cycles, and the presence of multiple cysts in the ovaries. The condition is associated with various metabolic and reproductive health issues, including infertility.
Causes
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
1.Genetic Factors: A family history of PCOS or type 2 diabetes increases susceptibility.
2.Insulin Resistance: Elevated insulin levels can lead to increased androgen production, disrupting ovarian function.
3.Hormonal Imbalances: Excess androgens (male hormones) interfere with the normal development and release of eggs.
4.Chronic Inflammation: Low-grade inflammation can contribute to insulin resistance and increased androgen levels.
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of PCOS involves complex interactions between genetic predisposition, insulin resistance, and hormonal dysfunction:
Increased GnRH Pulsatility: Leads to higher levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) relative to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), impairing ovulation.
Hyperinsulinemia: Exacerbates androgen production in the ovaries and reduces sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), increasing free androgen levels.
Ovarian Dysfunction: Disrupted follicular development leads to anovulation and cyst formation.
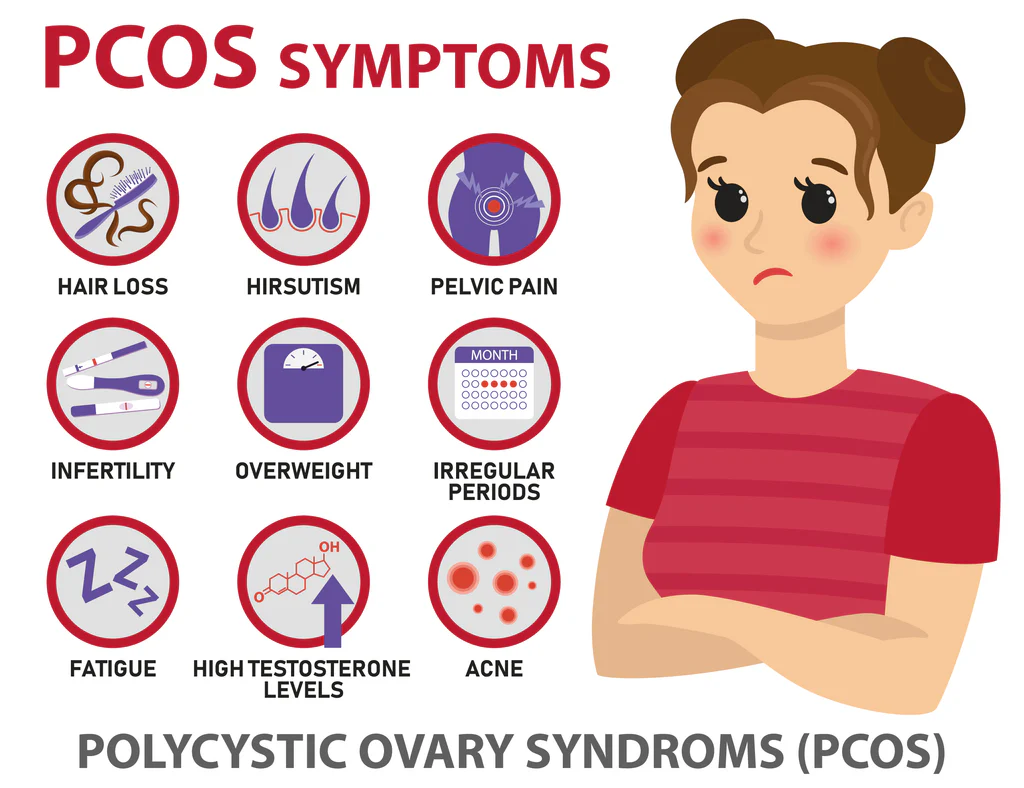
Symptoms
Common symptoms of PCOS include:
Irregular or absent menstrual periods
Excess hair growth (hirsutism), typically on the face, chest, or back
Acne and oily skin
Thinning hair or male-pattern baldness
Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
Darkening of the skin, particularly along neck creases, under breasts, or around the groin
Skin tags in the armpits or neck area
Difficulty conceiving (infertility)
Blood Tests
The following blood tests are commonly used to diagnose PCOS and assess associated conditions: Hormonal Levels:
Elevated LH-to-FSH ratio and Increased androgens (testosterone, DHEA-S)
Insulin Resistance Markers: Fasting insulin levels and Glucose tolerance test
Thyroid Function Tests: To rule out thyroid disorders.
Prolactin Levels: Elevated levels may indicate other underlying conditions.
Lipid Profile: To check for cholesterol and triglyceride abnormalities.
Complications
If left untreated, PCOS can lead to several complications, including:
Infertility
Type 2 diabetes
Hypertension and cardiovascular disease
Endometrial hyperplasia or cancer
Depression and anxiety
Sleep apnea
Homeopathy Treatment
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing PCOS by addressing the root causes and restoring hormonal balance. Some commonly used remedies include:
Sepia: For irregular periods, fatigue, and mood swings.
Pulsatilla: For delayed or suppressed periods and emotional sensitivity.
Calcarea Carbonica: For weight gain, excessive sweating, and sensitivity to cold.
Lachesis: For ovarian cysts and premenstrual symptoms.
Natrum Muriaticum: For hormonal imbalances and stress-related symptoms
These are the best Homeopathic medicine for pcod.
Lifestyle Modifications with Homeopathy
Dietary Changes: Focus on a low-glycemic index diet to manage insulin resistance.
Exercise: Regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and improve metabolic health.
Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises.Homeopathic medicine for pcod kindly do not self medicate.
Conclusion
PCOS is a multifaceted condition requiring a personalized and integrative approach. Homeopathy, combined with lifestyle modifications, provides a safe and effective method for managing symptoms, improving fertility, and enhancing overall well-being. Always consult a qualified homeopath for a tailored treatment plan.

супрастин таблетки инструкция по применению взрослым от чего помогает противопоказания к применению https://аллергиястоп.рф/ .
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Психолог психотерапевт психоаналитик Психолог психотерапевт психоаналитик 449
cheap amoxil generic – combamoxi.com amoxil online order
amoxil online – https://combamoxi.com/ buy amoxicillin pill
buy fluconazole 100mg online – https://gpdifluca.com/ order diflucan 200mg pill
how to get diflucan without a prescription – site order fluconazole online cheap
buy lexapro for sale – lexapro 20mg cost order escitalopram
cenforce oral – https://cenforcers.com/ cenforce for sale online
Thank you, your article surprised me, there is such an excellent point of view. Thank you for sharing, I learned a lot.
order cenforce 50mg generic – https://cenforcers.com/ order cenforce 100mg pill
where can i buy cialis online in australia – cialis canada free sample vardenafil tadalafil sildenafil
tadalafil medication – https://ciltadgn.com/# reddit cialis
cheap canadian cialis – cialis generic overnite how to take liquid tadalafil
buying cialis – https://strongtadafl.com/# generic cialis
order zantac 300mg sale – https://aranitidine.com/# ranitidine 150mg over the counter
sales@cheap-generic-viagra – https://strongvpls.com/ viagra sale in australia
buy viagra nigeria – https://strongvpls.com/ sildenafil 100 mg pill identifier
More peace pieces like this would insinuate the web better. https://buyfastonl.com/amoxicillin.html
Palatable blog you have here.. It’s obdurate to assign great calibre writing like yours these days. I honestly recognize individuals like you! Rent guardianship!! sitio web
I’ll certainly return to read more. este sitio
I am in point of fact happy to glance at this blog posts which consists of tons of worthwhile facts, thanks representing providing such data. https://buyfastonl.com/furosemide.html
I couldn’t turn down commenting. Adequately written! order synthroid online cheap
Greetings! Very serviceable suggestion within this article! It’s the crumb changes which liking turn the largest changes. Thanks a quantity for sharing! https://prohnrg.com/product/metoprolol-25-mg-tablets/
This is the stripe of content I have reading. https://ursxdol.com/ventolin-albuterol/
The depth in this piece is exceptional. https://prohnrg.com/product/metoprolol-25-mg-tablets/
This is the amicable of glad I take advantage of reading. https://aranitidine.com/fr/cialis-super-active/
The vividness in this piece is exceptional. https://aranitidine.com/fr/en_ligne_kamagra/
Greate pieces. Keep posting such kind of information on your site. Im really impressed by it.
Hey there, You have performed an excellent job. I’ll certainly digg it and in my opinion recommend to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this web site.
Luxury limo near me
Если вы давно мечтаете изучать психологию онлайн, но не знаете, с чего начать — рекомендую обратить внимание на ILM Академию. Это современная платформа, где можно пройти курс по психологии с дипломом без отрыва от работы или семьи.
Программа идеально подойдёт новичкам: всё объясняется простым языком, много практики и живых встреч с преподавателями. В конце обучения вы получите европейский диплом, который ценится и в Украине, и за её пределами.
Отличный выбор для тех, кто хочет начать карьеру в психологии или лучше понять себя и окружающих.
Вариант второй текста:
Хочешь получить профессию психолога, не выходя из дома?
ILM Академия — это современное онлайн-обучение психологии с упором на практику и живое общение с опытными преподавателями.
Обучение доступно из любой точки мира
Подходит для начинающих — всё с нуля
Практика, супервизии и поддержка кураторов
Европейский диплом после окончания курса
Ты сможешь освоить профессию, понять людей глубже и, возможно, даже изменить свою жизнь.
Подробнее о курсе на официальном сайте: ILM Академия психологии европейское образование по психологии онлайн
I blog quite often and I seriously appreciate your content. This article has really peaked my interest. I am going to book mark your website and keep checking for new details about once per week. I opted in for your Feed too.
https://clients1.google.com.cy/url?sa=t&url=https://cabseattle.com/
This is the right webpage for anybody who hopes to find out about this topic. You realize a whole lot its almost tough to argue with you (not that I personally would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a topic that has been written about for years. Wonderful stuff, just excellent!
https://www.google.com.my/url?q=https://premierlimousineservice.net
I think what you posted made a great deal of sense. However, what about this? suppose you typed a catchier title? I mean, I don’t wish to tell you how to run your website, however what if you added something that grabbed a person’s attention? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is kinda plain. You should look at Yahoo’s home page and watch how they create news titles to get people interested. You might add a related video or a related picture or two to grab people interested about what you’ve got to say. In my opinion, it might bring your blog a little livelier.
spin city casino
What’s up Dear, are you truly visiting this website daily, if so afterward you will without doubt get nice experience.
vermox capsules 100 mg pregnancy
Escape the Limits – Explore Non GamStop Casinos!
Tired of restrictions? Discover a world of unlimited gaming possibilities at our Non GamStop Casinos.
What we offer:
– Unrestricted access to top games
– Generous welcome bonuses
– Lightning-fast payouts
– 24/7 customer support
– Secure & fair gaming environment
Join thousands of satisfied players who have already found their perfect gaming experience. No GamStop limitations mean endless fun and excitement!
Claim your bonus now and start playing at the best Non GamStop Casinos today! ??
https://vaishakbelle.com/poker-not-on-gamstop/
#NonGamStopCasinos #OnlineGaming #CasinoBonus
I used to be able to find good information from your blog articles.
vibramycin 100mg uk
For the reason that the admin of this web site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
https://www.google.com.bn/url?q=https://cabseattle.com/
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Greetings! Very serviceable advice within this article! It’s the little changes which wish espy the largest changes. Thanks a quantity towards sharing! https://ondactone.com/simvastatin/
More posts like this would create the online time more useful. https://ondactone.com/simvastatin/
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
This is the compassionate of literature I in fact appreciate.
order reglan pill
This is a question which is in to my heart… Many thanks! Faithfully where can I lay one’s hands on the connection details for questions?
topiramate 200mg drug
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Hello to every single one, it’s really a nice for me to pay a quick visit this web site, it contains precious Information.
Luxury limo near me
More articles like this would make the blogosphere richer. http://forum.ttpforum.de/member.php?action=profile&uid=425016
More articles like this would frame the blogosphere richer. https://myrsporta.ru/forums/users/pxryl-2/
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an really long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyway, just wanted to say superb blog!
https://kidsvisitor.com.ua/linzy-dlya-svitlodiodnykh-far-osoblyvosti-ta-krash.html
Thank you for the good writeup. It actually was once a entertainment account it. Glance advanced to more introduced agreeable from you! By the way, how could we keep in touch?
http://jiraf.com.ua/halogen-lens-guide.html
Hi there every one, here every person is sharing these kinds of familiarity, therefore it’s pleasant to read this weblog, and I used to visit this weblog everyday.
https://cocoshop.com.ua/novitni-rishennya-v-oblasti-stekol-dlya-far-yak-obrati-pravilno
Do you have a spam issue on this blog; I also am a blogger, and I was curious about your situation; we have created some nice practices and we are looking to trade solutions with other folks, be sure to shoot me an e-mail if interested.
https://kacca.in.ua/linzy-v-fary-neobychnye-resheniya-dlya-teh-kto-hochet-vydelitsya
order dapagliflozin 10 mg generic – https://janozin.com/# buy forxiga 10 mg generic
ограждения из нержавейки Перила деревянные для лестниц – это классическое решение, создающее атмосферу тепла и уюта в интерьере.
forxiga for sale online – https://janozin.com/ dapagliflozin usa
https://trip-scan.win/ Сайт трипскан – это интуитивно понятный интерфейс, подробные описания направлений, отзывы путешественников и полезные советы, помогающие сделать осознанный выбор и избежать неприятных сюрпризов.
https://www.med2.ru/story.php?id=147093
https://sonturkhaber.com/
https://www.med2.ru/story.php?id=147093
Купить подшипник для электродвигателя Шариковый подшипник – универсальный тип подшипника, предназначенный для работы в условиях как радиальных, так и осевых нагрузок.
Здравствуйте!
Долго ломал голову как поднять сайт и свои проекты и нарастить TF trust flow и узнал от друзей профессионалов,
отличных ребят, именно они разработали недорогой и главное продуктивный прогон Хрумером – https://www.bing.com/search?q=bullet+%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BD
Увеличение трафика с помощью прогона Xrumer ускоряет продвижение сайта. Форумный линкбилдинг с Xrumer делает создание ссылочной массы системным. Массовая рассылка ссылок экономит время специалистов. Постинг на блогах для SEO помогает закрепить позиции. Xrumer для оптимизации сайта повышает DR.
сео поведенческие факторы, продвижение сайта частным специалистом, линкбилдинг это что
Форумный линкбилдинг Хрумер, seo arts, курс по сео бесплатно
!!Удачи и роста в топах!!
подшипники для пищевой промышленности Эффективная закупка подшипников требует тщательного планирования и оптимизации затрат.
orlistat over the counter – purchase orlistat without prescription xenical 120mg ca
игровой компьютер за 50 тысяч Готовые сборки ПК: Выбор для тех, кто ценит время.
трипскан Трипскан: Простота и удобство в планировании
xenical brand – https://asacostat.com/# buy orlistat 120mg
Политика Специальная военная операция (СВО) стала катализатором глобальных изменений. Политика, как сфера влияния, претерпела трансформацию, обнажив скрытые противоречия и сформировав новые альянсы. Переговоры, в центре которых Владимир Путин и Владимир Зеленский, стали символом поиска компромисса в условиях радикально противоположных позиций. Финансы, словно кровеносная система мировой экономики, ощутили на себе всю тяжесть санкций и перебоев в поставках. Европа, Азия и Америка оказались перед лицом энергетического кризиса и инфляционной спирали. Безопасность и оборона, как фундаментальные потребности государств, вновь обрели актуальность. Кавказ и Ближний Восток, издавна известные своей нестабильностью, стали эпицентром геополитических рисков. Новости и аналитика, призванные освещать события непредвзято, часто оказываются в эпицентре информационных войн. Объективность становится дефицитом.
смешные истории обычных людей Секс истории обычных людей Интимная жизнь – важная часть человеческого опыта. Истории о любви, страсти, желании и разочаровании раскрывают перед нами разные грани отношений и помогают лучше понять себя и своего партнера. Они учат нас открытости, доверию и умению говорить о своих чувствах.
сулакский каньон экскурсия Железноводск – город-курорт, известный своими минеральными источниками и живописными парками. Посетите Славяновский и Смирновский источники, а также Каскадную лестницу и Пушкинскую галерею. Источники в Кабардино Балкарии список термальные
цитаты Обсуждение, как обмен идеями
wood fence installation Wood Privacy Fence on Slope The construction can be tricky during the install.
кайт школа
бупренорфин
http://cs-headshot.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=652602#652602
CDLKF20-30/3SWSC Насос полупогружной многоступенчатый 4 кВт 3×380 В, нерж сталь, 70*С
программа для учета грузоперевозках Программа для учета кредитов – это ваш надежный инструмент для контроля за финансовыми обязательствами. Она позволяет отслеживать графики платежей, процентные ставки и остаток задолженности, помогая принимать взвешенные решения и избегать просрочек. Такая программа станет незаменимым помощником для частных лиц и предприятий.
https://github.com/awsadm/AWS-CLI
Palatable blog you possess here.. It’s obdurate to find high calibre script like yours these days. I truly appreciate individuals like you! Rent care!! http://shiftdelete.10tl.net/member.php?action=profile&uid=205625
The thoroughness in this piece is noteworthy. https://myrsporta.ru/forums/users/vcodn-2/
https://www.trub-prom.com/catalog/truby_srednego_diametra/256/
Эскорт работа Тюмень Работа для девушек в Тюмени: Станьте частью элитного общества, где ценят красоту и интеллект. Достойный заработок, свобода выбора и анонимность. Раскройте свой потенциал и начните зарабатывать сегодня.
https://digital-downloads-app.com/
J’apprecie beaucoup le casino TonyBet, on dirait un plaisir de jeu constant. Il y a une tonne de jeux differents, avec des machines a sous modernes. Le service d’assistance est top, avec des reponses claires. Les retraits sont rapides, neanmoins les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, TonyBet est une valeur sure pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que, le design est attractif, renforcant le plaisir de jouer.
tonybet oГј|
букет роз, букет гортензий, авторский букет цветов Откройте для себя лучшие цветочные магазины и салоны, где вас ждут профессиональные консультанты и широкий выбор букетов. Доставка цветов в Москве недорого: Выгодные Предложения и Акции
J’apprecie enormement Azur Casino, il offre une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est vaste et diversifie, comprenant des titres modernes et attrayants. Le service client est exceptionnel, avec un suivi irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois plus de tours gratuits seraient un plus. En resume, Azur Casino est une pepite pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement superbe, ajoutant une touche de raffinement.
azur casino mobile|
Je suis totalement emballe par Banzai Casino, on dirait une energie de jeu captivante. Il y a une multitude de titres varies, proposant des jeux de table authentiques. Le support est ultra-reactif, garantissant une aide immediate. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, neanmoins les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Banzai Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete de frissons ! De plus le site est concu avec dynamisme, facilitant chaque session de jeu.
banzai casino login|
Je trouve absolument fantastique Betclic Casino, ca offre une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue de jeux est incroyablement riche, comprenant des titres innovants et attrayants. Le personnel offre un accompagnement de qualite, avec un suivi efficace. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, parfois les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, Betclic Casino offre une experience de jeu remarquable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! En bonus le site est concu avec elegance, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
resultat betclic elite|
J’apprecie beaucoup le casino TonyBet, il est carrement une aventure palpitante. Les jeux sont varies, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le service client est super, tres professionnel. Les transactions sont securisees, par contre les recompenses pourraient etre plus frequentes. Pour tout dire, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour les joueurs passionnes ! En bonus, le site est facile a naviguer, ajoutant une touche de confort.
tonybet bookmaker|
Je suis conquis par Banzai Casino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine d’adrenaline. Les options de jeu sont epoustouflantes, incluant des slots dynamiques. Le support est ultra-reactif, garantissant une aide immediate. Les gains arrivent en un rien de temps, cependant les promotions pourraient etre plus frequentes. En conclusion, Banzai Casino est une plateforme incontournable pour les amateurs de jeux en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
casino banzai|
Je trouve absolument fantastique Betclic Casino, on dirait une aventure pleine de frissons. Les options de jeu sont vastes et diversifiees, proposant des jeux de table classiques et elegants. Le service client est exceptionnel, repondant instantanement. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, bien que les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Betclic Casino ne decoit jamais pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et agreable, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
code promo betclic 2024|
Je suis fan de le casino TonyBet, on dirait un univers de jeu unique. Les jeux sont varies, offrant des options de casino en direct. Le service client est super, offrant un excellent suivi. Les transactions sont securisees, occasionnellement les recompenses pourraient etre plus frequentes. En gros, TonyBet c’est du solide pour les amateurs de casino ! Par ailleurs, le site est facile a naviguer, facilitant chaque session de jeu.
tonybet casino bonus|
макияж севастополь татуаж севастополь — Перманентный макияж (татуаж) в Севастополе востребован у тех, кто ценит экономию времени и яркий, но при этом натуральный образ в условиях пляжного и активного отдыха. В городе практикуются несколько техник: микроблейдинг (волосковая техника), пудровое напыление (омбрe/пудровый эффект), комбинированные техники и растушёвка для губ и век. Выбор техники зависит от желаемой плотности цвета, текстуры кожи и образа в целом. Ключевые этапы — консультация и согласование формы/оттенка, тест на индивидуальную переносимость пигмента (по показаниям), сама процедура и последующая коррекция. В Севастополе стоит учитывать, что солнце и морская вода ускоряют выцветание: для сохранения цвета рекомендуют избегать интенсивного загара и солёной воды минимум 2–4 недели, а для поддержания оттенка — корректировки каждые 1–2 года. Безопасность — первоочередной критерий: выбирайте лицензированные студии с одноразовыми иглами, стерильной рабочей зоной, сертификатами на пигменты и портфолио с фото «до/после». Ожидаемые побочные эффекты — отёк, покраснение и корочки, уход в ранний период включает щадящий режим без воды, спорта и косметики на зоне до полного заживления; мастер обязан дать подробную памятку. Важно также оценить опыт мастера по ретуши и коррекции ошибок: качественный специалист предложит план коррекций и покажет примеры сложных случаев. Противопоказания — беременность, кормление, активные кожные инфекции, некоторые аутоиммунные заболевания и приём препаратов, влияющих на свёртываемость крови — эти моменты обсуждаются на консультации.
https://how-to-screenshot.info/
Ich schatze sehr Billy Billion Casino, es ist wirklich ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Der Katalog ist unglaublich umfangreich, mit immersiven Live-Casino-Sessions von Evolution Gaming. Die Mitarbeiter sind rund um die Uhr professionell und hilfsbereit, ist 24/7 erreichbar. Gewinne kommen in Rekordzeit an, trotzdem die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist Billy Billion Casino eine au?ergewohnliche Plattform fur die, die gerne wetten! Au?erdem das Design ist visuell ansprechend und einzigartig, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt.
billy billion casino no deposit bonus codes 2023|
https://vk.com/3dplabs
https://cryptobirzhi.com/
нотариально заверенный перевод Перевод документов с английского языка — специализированная услуга, при которой документы, составленные на английском, переводятся на русский язык с учётом юридических и формальных требований принимающих организаций. Часто это необходимо при подаче документов в государственные органы, для поступления в вуз, подачи на визу или трудоустройства за границей. Важно не только правильно перевести содержание, но и оформить документ в соответствии с требованиями: проставить подписи, при необходимости заверить у нотариуса или подготовить апостиль, а также учесть формат и порядок страниц. Переводчик должен точно передать имена, даты, регистрационные номера и официальный стиль оригинала; в спорных случаях целесообразно согласовать формулировки с юридическим экспертом. Заказчику рекомендуется заранее уточнить, какие формы заверения и переводов принимаются в целевой инстанции, чтобы избежать повторной отправки и задержек в процессе рассмотрения документов.
Je trouve absolument extraordinaire Betway Casino, ca procure une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires et utiles. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, neanmoins les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, Betway Casino est une plateforme exceptionnelle pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide et moderne avec un theme noir et vert, renforce l’immersion totale.
betway app|
Acho simplesmente fantastico o 888 Casino, e realmente experiencia de jogo eletrizante. Ha uma infinidade de titulos variados, com sessoes de cassino ao vivo imersivas. A equipe oferece um suporte de altissima qualidade, respondendo rapidamente. Os saques sao extremamente rapidos, contudo mais rodadas gratis seriam otimas. No geral, o 888 Casino oferece uma experiencia de jogo memoravel para aqueles que gostam de apostar! Como bonus a navegacao e simples e rapida, reforca a imersao total.
888 casino canada|
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, on dirait une aventure pleine de sensations. La selection de jeux est colossale, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, avec un suivi de qualite. Les gains sont verses en un temps record, par moments davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, comme des offres de cashback plus avantageuses. Pour conclure, 7BitCasino ne decoit jamais pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! Par ailleurs le site est concu avec style et modernite, renforce l’immersion totale.
7bitcasino estafa|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de BetFury Casino, il offre une experience de jeu electrisante. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table classiques et raffines. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, repondant en un instant. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, de temps en temps ??? les offres comme le pack de bienvenue de 590 % pourraient etre plus accessibles. Dans l’ensemble, BetFury Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les amateurs de crypto-casinos ! De plus l’interface est fluide et intuitive, facilite chaque session.
betfury twitter|
J’apprecie enormement Betsson Casino, c’est une veritable sensation de casino unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux varies, incluant des slots de derniere generation comme Starburst. Le personnel offre un accompagnement de qualite via email ou telephone, garantissant une aide immediate. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. En resume, Betsson Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec modernite et ergonomie, facilite chaque session de jeu.
betsson online casino erfahrungen|
Ich finde unglaublich toll BoaBoa Casino, es ist ganz ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Auswahl ist reichhaltig und breit gefachert, mit klassischen Tischspielen wie Blackjack und Roulette. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, liefert klare und prazise Antworten. Zahlungen sind sicher mit SSL-Verschlusselung, manchmal mehr Freispiele waren super. Am Ende ist BoaBoa Casino eine herausragende Plattform fur die, die gerne wetten ! Erganzend das Design ist ansprechend mit einem Pinguin-Maskottchen, einen Hauch von Urlaubsflair hinzufugt.
mhw boaboa finden|
J’apprecie enormement CasinoBelgium, ca ressemble a une plongee dans un univers vibrant. La gamme de jeux est axee sur les dice slots, incluant des jeux exclusifs comme CasinoBelgium Open the Door. Le service client est fiable, offrant des reponses claires et utiles. Les paiements sont proteges par un cryptage SSL, parfois les bonus pourraient etre plus nombreux. Dans l’ensemble, CasinoBelgium est une plateforme legale et securisee pour les passionnes de jeux belges ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide avec un design tricolore belge, facilite chaque session de jeu.
circus belgium casino|
купить оборудование для порошковой покраски металла Камеры для порошковой покраски цена варьируется в зависимости от размера, технологических характеристик (наличие системы рекуперации, фильтрации), производителя и степени автоматизации. Ручные камеры для небольших объемов производства обычно дешевле автоматизированных комплексов, предназначенных для поточной окраски. При выборе камеры важно учитывать размеры окрашиваемых деталей, необходимую пропускную способность и требования к качеству покрытия.
частная наркологическая клиника Частная наркологическая клиника: индивидуальный подход и комфортные условия лечения зависимости. Частная наркологическая клиника – это медицинское учреждение, предлагающее широкий спектр услуг по лечению алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимостей с особым вниманием к индивидуальным потребностям каждого пациента. В частной клинике пациенты могут рассчитывать на более комфортные условия пребывания, внимательное отношение персонала и гибкий график лечения. Врачи-наркологи и психотерапевты с большим опытом работы разрабатывают индивидуальные программы лечения, учитывая особенности каждого пациента и стадию его зависимости. Клиника оснащена современным оборудованием и использует передовые методики лечения, что позволяет достичь высокой эффективности и стойких результатов. Помимо медикаментозной терапии, в частной клинике активно применяются методы психотерапии, направленные на выявление причин зависимости и формирование устойчивой мотивации к здоровому образу жизни. Конфиденциальность гарантируется. Частная наркологическая клиника – это ваш шанс на избавление от зависимости в комфортных условиях и с индивидуальным подходом к лечению.
https://bs2-bs2site.at
Je trouve incroyable 1win Casino, ca procure une experience de jeu captivante. Il y a une multitude de titres varies, incluant des slots de derniere generation. Les agents sont toujours prets a aider, repondant rapidement. Le processus de retrait est simple et efficace, parfois les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. Globalement, 1win Casino offre une experience de jeu memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Ajoutons que le design est visuellement attrayant, facilite chaque session de jeu.
1win partner|
J’adore a fond Betzino Casino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine de frissons. La selection de jeux est epoustouflante avec plus de 1800 titres, comprenant des jackpots progressifs comme Mega Moolah. Le support est ultra-reactif via chat en direct de 10h a 23h, joignable par email ou chat. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable avec un maximum de 5000 € par semaine, bien que j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. Globalement, Betzino Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et moderne avec un design epure, renforce l’immersion totale.
betzino avis trustpilot|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betify Casino, on dirait une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, proposant des jeux de table classiques et elegants. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, avec un suivi de qualite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. Pour conclure, Betify Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec elegance, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betify promo|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Casino Action, il offre une energie de jeu irresistible. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, comprenant des jackpots progressifs comme Millionaires’ Club. Le personnel offre un accompagnement rapide via chat ou email, repondant en quelques minutes. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Casino Action vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et intuitive, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
graphique action casino|
buy angular contact ball bearing
внутренний swot анализ система swot анализа
swot анализ выявляет swot анализ пример
J’apprecie enormement 1xbet Casino, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, comprenant des titres innovants et engageants. Le service client est exceptionnel, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, cependant les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, 1xbet Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier ! De plus le site est concu avec dynamisme, renforce l’immersion totale.
the good fight 1xbet|
Ich bin vollig begeistert von BingBong Casino, es ist wirklich ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Es gibt eine Fulle an abwechslungsreichen Titeln, mit spannenden Jackpot-Spielen wie Mega Moolah. Der Kundenservice ist hervorragend, liefert klare und prazise Antworten. Auszahlungen sind super schnell, oft innerhalb von 24 Stunden fur PayPal, jedoch ich mir mehr regelma?ige Boni wunschen wurde. Kurz gesagt ist BingBong Casino ein Muss fur Slot-Fans fur Spieler, die Nervenkitzel suchen ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist mit Stil und Benutzerfreundlichkeit gestaltet, einen Hauch von Flair hinzufugt.
bingbong cas|
Аренда авто в Краснодаре бизнес Каршеринг Краснодар: Мобильность и удобство в режиме реального времени. Каршеринг в Краснодаре – это современный и удобный способ арендовать автомобиль на короткий срок. Просто скачайте приложение, зарегистрируйтесь и найдите ближайший доступный автомобиль. Вы можете арендовать автомобиль на несколько минут, часов или дней, в зависимости от ваших потребностей. Каршеринг – это идеальное решение для коротких поездок по городу, когда вам нужен автомобиль на небольшой срок. Наслаждайтесь мобильностью и удобством с каршерингом в Краснодаре!
https://miritaly.ru
Оргонит для женщин Денежный кулон со спиралью и хризопразом, оргонит, оберег отзывы: Отзывы о конкретном виде оргонита, направленного на привлечение денег.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
J’apprecie beaucoup le casino TonyBet, il est carrement une aventure palpitante. Les jeux sont varies, incluant des slots ultra-modernes. Le personnel est tres competent, repondant rapidement. Le processus de retrait est efficace, par contre il pourrait y avoir plus de promos. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! De plus, l’interface est fluide, facilitant chaque session de jeu.
tonybet casino erfahrung|
Je trouve sensationnel le casino AllySpin, il procure une experience de jeu electrisante. Il y a une quantite impressionnante de jeux, incluant des slots dernier cri. Le service d’assistance est impeccable, offrant des solutions rapides. Les transactions sont bien protegees, mais parfois plus de tours gratuits seraient top. En fin de compte, AllySpin offre une experience solide pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi que le style visuel est dynamique, ajoutant une touche d’elegance au jeu.
allyspin sloty|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, ca ressemble a une aventure captivante. La selection de jeux est incroyablement riche, incluant des slots dynamiques. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, avec un suivi irreprochable. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, bien que davantage de recompenses seraient bienvenues. Globalement, Azur Casino offre une experience fiable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! En bonus l’interface est fluide et elegante, ajoutant une touche de raffinement.
centre azur geant casino hyeres|
Je suis conquis par Banzai Casino, c’est une veritable plongee dans le divertissement intense. La gamme de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table authentiques. Le personnel est d’un professionnalisme hors pair, offrant des solutions rapides et claires. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, par moments plus de tours gratuits seraient apprecies. Globalement, Banzai Casino offre une experience exceptionnelle pour les passionnes de casino ! De plus le design est visuellement percutant, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
bonus banzai casino|
казино Обзор официального сайта и приложения казино. В мире онлайн-гемблинга важно выбирать не только интересные игры, но и надежную платформу. 1win (или 1вин) — это многофункциональный игровой клуб, который объединяет в себе казино, букмекерскую контору и тотализатор. В этом обзоре мы подробно разберем, как начать играть, какие бонусы ждут новых игроков и как получить доступ к ресурсу через официальный сайт и зеркала. Поиск рабочего официального сайта 1win — первый шаг для каждого игрока. Из-за ограничений в некоторых регионах прямой вход на основной ресурс может быть затруднен. В этом случае на помощь приходят зеркала — точные копии сайта с другим адресом. Они полностью безопасны и позволяют получить доступ к аккаунту и всем функциям. Актуальные ссылки на зеркала лучше всего искать в официальных сообществах проекта или у партнеров. Процесс регистрации в 1win занимает пару минут. Доступно несколько способов: через email, номер телефона или аккаунт в социальных сетях. Но самый важный шаг — это активация промокода. Ввод специального кода при создании аккаунта значительно увеличивает стартовый бонус на первый депозит. Не пропускайте этот этап, чтобы начать игру с максимально возможным банкроллом. Для тех, кто предпочитает играть с телефона, 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение. Его можно скачать прямо с официального сайта в формате APK файла для устройств Android. Владельцы iOS также могут найти способ установить программу. Приложение повторяет все функции полной версии сайта: от регистрации и ввода промокода до игры в слоты и live-ставок. Это идеальный выбор для игры в любом месте. 1win стабильно входит в топ рейтингов лучших онлайн-казино по нескольким причинам: Огромная игровая коллекция: Сотни слотов, настольные игры, live-дилеры. Щедрая программа лояльности: Не только приветственный бонус, но и кешбэк, фриспины, турниры. Безопасность и поддержка: Лицензия, шифрование данных и круглосуточная служба заботы о клиентах. 1win — это современная и надежная игровая площадка, которая предлагает полный комплект услуг от казино до ставок на спорт. Не забудьте использовать промокод при регистрации, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от игры. А если возникнут трудности с доступом — воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом или скачайте официальное приложение.
Je suis completement seduit par Betclic Casino, on dirait une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue de jeux est incroyablement riche, proposant des jeux de table classiques et elegants. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, joignable 24/7. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles. En fin de compte, Betclic Casino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et agreable, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
classement betclic Г©lite|
Looking for second-hand? second hand We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
Looking for second-hand? second hand stores We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
Estou alucinado com DiceBet Casino, e um cassino online que e puro fogo. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino variados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma bomba. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de primeira, com uma ajuda que e um arraso. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Em resumo, DiceBet Casino e o lugar certo pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem a plataforma do cassino detona com um look que e puro fogo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animal.
dicebet|
Je suis totalement hypnotise par Impressario, il propose un show de jeu hors norme. Le catalogue est un festival de titres, avec des slots qui brillent de mille feux. Le support est dispo 24/7, repondant en un clin d’etoile. Les transactions sont simples comme un refrain, par contre les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Bref, Impressario c’est une scene a decouvrir absolument pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Bonus le design est une explosion visuelle, facilite un show total.
impressario casino no deposit bonus|
https://gtaman.ru
online casino cz CZ Casino Online: Najdete si idealni online kasino s ceskou licenci. Recenze, porovnani bonusu a tipy pro zodpovedne hrani.
online casino cz ” symbol: Online Casino CZ: Discover the best online casinos in the Czech Republic! Find licensed and reputable platforms with exciting games and bonuses. Enjoy a safe and thrilling gaming experience.
Estou totalmente vidrado em Flabet Casino, e um cassino online que e pura dinamite. Os titulos do cassino sao um show a parte, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e viciantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma explosao, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria insano. Resumindo, Flabet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
flabet apostas|
Ich flippe aus bei DrueGlueck Casino, man fuhlt einen verruckten Spielvibe. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist gigantisch, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die fesseln. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist der Hammer, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie der Blitz, manchmal mehr Freispiele im Casino waren top. Insgesamt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht, einen Hauch von Wahnsinn ins Casino bringt.
drueckglueck casino login|
Je trouve totalement dingue AmunRa Casino, ca donne une energie de casino digne d’un dieu. Il y a une avalanche de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino pleins de mystere. L’assistance du casino est majestueuse et efficace, offrant des solutions claires et immediates. Les gains du casino arrivent a la vitesse d’un char, mais des recompenses de casino en plus ca ferait vibrer. Globalement, AmunRa Casino garantit un fun de casino divin pour les accros aux sensations fortes du casino ! Et puis le site du casino est une merveille graphique, facilite le delire total au casino.
amunra casino ohne einzahlung bonus|
Je suis accro a Instant Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui envoie du lourd. Il y a un deluge de jeux de casino varies, incluant des jeux de table de casino styles. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme l’eclair, repondant en un flash. Le processus du casino est clean et sans galere, mais bon des bonus de casino plus reguliers ce serait top. En gros, Instant Casino offre une experience de casino inoubliable pour les accros aux sensations de casino ! En prime le site du casino est une tuerie graphique, booste l’immersion dans le casino a fond.
australian instant bank transfer mobile casino|
bs2best
Ich bin total hingerissen von JackpotPiraten Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie eine wilde Piratenjagd. Es gibt eine Flut an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und top, mit Hilfe, die wie eine Flagge weht. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellengang, dennoch mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Kurz gesagt ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Abenteurer im Casino! Und au?erdem das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Volltreffer, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
jackpotpiraten test|
Je suis totalement subjugue par Julius Casino, on dirait une conquete de fun. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et glorieux, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une noblesse rare. L’assistance du casino est majestueuse et efficace, proposant des solutions claires et immediates. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une charge de cavalerie, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rugir de plaisir. Au final, Julius Casino offre une experience de casino legendaire pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est une fresque visuelle epique, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
julius casino 5 euro|
Je suis dingue de Bruno Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino debridee. La selection du casino est une explosion de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement hors pair, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une fusee, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait le feu. Globalement, Bruno Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait des vagues pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style audacieux, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus exaltante.
bruno casino trustpilot|
Acho simplesmente animal LeaoWin Casino, e um cassino online que ruge como um leao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma fera, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um rugido. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma fera domada, respondendo mais rapido que um leopardo. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem emboscada, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Em resumo, LeaoWin Casino e um cassino online que e uma fera total para quem curte apostar com garra no cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha na selva, da um toque de ferocidade braba ao cassino.
leaowin02 casino account verwijderen|
https://flactor.ru
J’adore l’incandescence de Celsius Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui fait jaillir des etincelles. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino elegants et brulants. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une flamme, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans combustion, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui embrasent. Globalement, Celsius Casino promet un divertissement de casino brulant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique ardente, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
promo code celsius casino|
https://usk-rus.ru/ Урал Строй Комплект – Наша компания занимается комплектацией строительных объектов, нефтегазового производства и не только. Одно из главных направлений работы – это гражданское строительство, где наши задачи – поставка металлических изделий и конструкций, труб, сыпучих строительных смесей, других стройматериалов. Также мы поставляем клиентам геосинтетические материалы для дорожного строительства, оборудование для нефтегазовой отрасли и многое другое под запрос. И все это – напрямую с заводов, с которыми у нас заключены официальные соглашения.
Ich bin vollig hin und weg von King Billy Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Palast glanzt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und furstlich, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein koniglicher Erlass. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die glanzvoll sind. Am Ende ist King Billy Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Konigreich strahlt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
king billy casino free|
bs2best at
Je suis accro a CasinoClic, on dirait une cascade de fun. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et scintillants, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Le service client du casino est une etoile brillante, assurant un support de casino immediat et eclatant. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, CasinoClic offre une experience de casino eclatante pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une lueur, ajoute une touche de magie lumineuse au casino.
casino clic coupons|
Ich bin suchtig nach iWild Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Savanne. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie eine wilde Prarie, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Lagerfeuer gluht, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Blitz. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Flusslauf, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Alles in allem ist iWild Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Gewitter tobt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Wasserfall funkelt, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
iwild casino зеркало|
J’adore l’eclat de JackpotStar Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui illumine tout. La selection du casino est une explosion cosmique de plaisir, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un meteore, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Globalement, JackpotStar Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et rayonnante comme une aurore, facilite une experience de casino astrale.
50 freispiele ohne einzahlung jackpotstar|
Ich bin vollig geflasht von Lapalingo Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein Ozean voller Schatze, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leuchtfeuer, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Funke spruht. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellen, dennoch mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Zusammengefasst ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Und au?erdem das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Spektakel, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
lapalingo non sticky|
J’adore l’energie de LeonBet Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino indomptable. La selection du casino est une veritable meute de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. L’assistance du casino est feroce et efficace, assurant un support de casino immediat et puissant. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans embuches, parfois des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient sauvages. En somme, LeonBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino rugissant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit le design du casino est une fresque visuelle feroce, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus rugissante.
leonbet game|
русское порно сиськи русское порно кончают
Want to have fun? porno bangladesh melbet Watch porn, buy heroin or ecstasy. Pick up whores or buy marijuana. Come in, we’re waiting
Ich liebe den Zauber von Lapalingo Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop des Spa?es, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter krachen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern strahlt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Sonnenstrahl, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Zusammengefasst ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, einen Hauch von Zauber ins Casino bringt.
lapalingo gutscheincode|
Estou completamente alucinado por JabiBet Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira onda. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma explosao. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma onda, respondendo mais rapido que um maremoto. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, JabiBet Casino e um cassino online que e uma onda gigante para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como surfar, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
jabibet app download|
Ich liebe die Magie von JokerStar Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Komet leuchtet. Die Casino-Optionen sind bunt und mitrei?end, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und magisch, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Kometenschweif, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die funkeln. Am Ende ist JokerStar Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Sterne vom Himmel holt fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Zauberspruch, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
jokerstar werbung frau|
J’adore la splendeur de LeoVegas Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino souveraine. La selection du casino est une veritable cour de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme somptueux. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement majestueux, proposant des solutions claires et immediates. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans intrigues, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait grandiose. Globalement, LeoVegas Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style imperial, ajoute une touche de splendeur au casino.
leovegas canada|
Je trouve absolument enchanteur Luckland Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu magique. Il y a un raz-de-maree de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un souhait exauce, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans malefice, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui brillent. En somme, Luckland Casino offre une experience de casino enchantee pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique eclatante, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus magique.
luckland casino real money|
Je trouve absolument magique Luckster Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino envoutante. Il y a une tempete de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme feerique. Le service client du casino est un charme puissant, avec une aide qui fait des miracles. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse magique, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, Luckster Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sortilege, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
luckster online casino|
Je suis totalement envoute par MonteCryptos Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu qui fait vibrer les cimes. Le repertoire du casino est une montagne de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse alpine, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait exaltant. Pour resumer, MonteCryptos Casino est un casino en ligne qui atteint des sommets pour les aventuriers du casino ! Par ailleurs la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sentier de montagne, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus exaltante.
montecryptos casino bonus|
https://gtaman.ru
Je suis bluffe par Casinova, on ressent une energie debordante. La gamme est tout simplement spectaculaire, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le support est disponible a toute heure, repondant en un clin d’?il. Les retraits sont rapides et securises, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient appreciees. En fin de compte, Casinova est une plateforme d’exception pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi la navigation est intuitive et rapide, renforce le plaisir de jouer.
casinova casino ??????????|
J’adore l’eclat de LuckyBlock Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un talisman dore. La selection du casino est une fontaine de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui illuminent. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, par moments des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient magiques. Au final, LuckyBlock Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une aurore boreale, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
luckyblock bonus|
Je suis fou de Madnix Casino, on dirait une tornade de plaisir. La selection du casino est une veritable explosion de fun, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est une decharge electrique, assurant un support de casino immediat et explosif. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un clin d’?il, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait completement fou. Pour resumer, Madnix Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et petillante comme un neon, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
madnix casino retrait|
Estou completamente vidrado por MegaPosta Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que detona tudo. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e um foguete, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, MegaPosta Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual braba, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
megaposta paga mesmo|
Je suis totalement ensorcele par MyStake Casino, on dirait un labyrinthe de frissons. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et intrigantes, proposant des slots de casino a theme enigmatique. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un sage, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse ensorcelante, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, MyStake Casino offre une experience de casino ensorcelante pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec flair au casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique mysterieuse, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
mystake reviews|
Estou pirando com OshCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que incendeia tudo. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma labareda, com uma ajuda que e puro calor. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, OshCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fogo para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual escaldante, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
arnaque osh|
Ich finde absolut verruckt Pledoo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Vulkan ausbricht. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Ozean, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern funkelt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sturm, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Insgesamt ist Pledoo Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Abenteurer im Casino! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
pledoo erfahrungen|
Estou pirando com MonsterWin Casino, e um cassino online que ruge como uma fera braba. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma fera total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de garra. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um monstro de eficiencia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um dragao, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, MonsterWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e colossal para quem curte apostar com garra no cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animal.
monsterwin ОјПЂПЊОЅОїП…П‚|
Adoro o clima insano de PagolBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que faz tudo tremer. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma corrente de eficiencia, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um trovao, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, PagolBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma tempestade para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro trovao, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
pagolbet bГґnus|
Je suis accro a PokerStars Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi intense qu’un tournoi de poker. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une galaxie de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un croupier d’elite, avec une aide qui mise juste. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une donne gagnante, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, PokerStars Casino promet un divertissement de casino strategique pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline tactique du casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un tapis de jeu, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
neymar pokerstars chaussure|
https://xn--80aack7aript.xn--p1ai/%D0%B2%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%B6/
Je suis fou de MrPlay Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui swingue comme un orchestre. Le catalogue du casino est une explosion de couleurs ludiques, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui font danser. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un maestro, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un final de spectacle, parfois des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient festifs. Au final, MrPlay Casino offre une experience de casino exuberante pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style endiable, facilite une experience de casino festive.
mr.play welcome bonus|
Acho simplesmente brabissimo ParamigoBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma ventania, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma rajada de eficiencia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem turbulencia. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um jato, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, ParamigoBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia tempestuosa, da um toque de forca braba ao cassino.
paramigobet casino|
J’adore la vague de Posido Casino, on dirait une tempete sous-marine de fun. La selection du casino est une vague de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et immersives. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une vague deferlante, avec une aide qui fait des vagues. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, Posido Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline fluide du casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un courant marin, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
posido casino en ligne|
Криптовалютный кошелек для начинающих Как купить криптовалюту новичку? Пошаговая инструкция с иллюстрациями и рекомендациями по выбору надежной биржи, настройке кошелька и совершению первой покупки. Не упустите возможность стать частью крипто-революции!
https://dtf.ru/id3026460/4006946-put-klienta-v-telegram-reklame-ot-klika-do-pokupki-cherez-lestnicu-uznavaniya
подписчики тт Хотите, чтобы ваши публикации в Instagram просматривали чаще? Воспользуйтесь услугой просмотры Инст, чтобы увеличить количество просмотров вашего контента и повысить его популярность. Больше просмотров – больше охват!
Je suis accro a MrXBet Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino enigmatique. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et mysterieuses, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui envoutent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une enigme resolue, avec une aide qui devoile les mysteres. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans zones d’ombre, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient frissonner. En somme, MrXBet Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une enigme resolue, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus intrigante.
mrxbet bonus sans depot|
Ich liebe die Pracht von Richard Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Thron funkelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Vergnugen, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und furstlich, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist Richard Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Thron funkelt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Und au?erdem die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino auf ein konigliches Niveau hebt.
richard casino canada|
путевки Наше туристическое агентство предлагает широкий выбор туров по всему миру. Мы поможем вам спланировать идеальный отпуск, начиная от выбора направления и заканчивая бронированием отелей и билетов. Доверьтесь нашему опыту и наслаждайтесь беззаботным отдыхом.
Казино Vavada популярно среди игроков.
Бездепозитные бонусы увеличивают интерес.
Игровые события делают процесс динамичным.
Выбор слотов и настольных игр включает топовых провайдеров.
Регистрация простая, и моментально использовать промокоды.
Узнай больше здесь: вавада рабочее зеркало официальный сайт
Sou louco pelo role de MegaPosta Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura dinamite. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de responsa, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem enrolacao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, MegaPosta Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual braba, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
megaposta login|
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que incendeia tudo. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e incendiarias, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma labareda, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial vulcanico. Em resumo, OshCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um vulcao para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
osh bonus code|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von Pledoo Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Tanz durch die Spielwelt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und mitrei?end, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern funkelt, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Komet, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Insgesamt ist Pledoo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
pledoo casino login|
ивц сочи ветеринарная клиника Ветклиника в Хосте: Заботимся о здоровье ваших питомцев в Хосте с любовью. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр ветеринарных услуг для всех видов домашних животных в Хосте. Доверьте здоровье своих питомцев профессионалам!
таможенный брокер в Москве Таможенный брокер для юридических лиц – это не просто исполнитель, а стратегический партнер. Мы поможем вам оптимизировать таможенные платежи, избежать штрафов и обеспечить соответствие самым строгим требованиям законодательства. С нами вы будете уверены в безопасности своей внешнеэкономической деятельности!
Гибкие окна для беседок Мягкие окна для дачи: Создайте уютный уголок на своей даче с помощью мягких окон! Они защитят вас от ветра, дождя и насекомых, позволяя наслаждаться отдыхом на свежем воздухе в любую погоду. Простой монтаж и доступная цена делают эти окна идеальным решением для загородного дома.
Je suis fou de Roobet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui clignote comme un stroboscope. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui crepitent. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un DJ stellaire, assurant un support de casino immediat et vibrant. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un rythme electro, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Roobet Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est un spectacle visuel futuriste, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus vibrante.
roobet chicken|
Je suis fou de Spinanga Casino, on dirait une tempete de plaisir endiablee. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une tornade de delices, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui tournoient. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino immediat et dynamique. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait dement. En somme, Spinanga Casino est un casino en ligne qui dechaine les elements pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une bourrasque, facilite une experience de casino frenetique.
spinanga ОєПЃО№П„О№ОєОµПѓ|
Je suis fou de Spinsy Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi vibrante qu’une piste de danse. Le repertoire du casino est un dancefloor de divertissement, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance groovy. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un pas de moonwalk, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, Spinsy Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un neon, ajoute une touche de groove au casino.
spinsy casino ohne einzahlung bonus|
Estou louco por Richville Casino, da uma energia de cassino tao luxuosa quanto um trono. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e reluzentes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como joias. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um mordomo impecavel, dando solucoes precisas e imediatas. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como abrir um cofre, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino fariam qualquer um se sentir rei. Em resumo, Richville Casino vale a pena explorar esse cassino com urgencia para os que buscam a adrenalina luxuosa do cassino! Vale dizer tambem o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual de tirar o folego, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao ao cassino.
deck staining richville|
https://t.me/Igrovie_avtomati_na_dengi Игровые автоматы на реальные деньги предоставляют возможность выиграть настоящие денежные призы. Для этого игрокам необходимо внести депозит на счет в онлайн-казино и делать ставки на выбранные игровые автоматы. Выигрыш зависит от выпавшей комбинации символов и размера ставки. Многие онлайн-казино предлагают различные бонусы и акции, которые могут увеличить шансы на выигрыш. Важно помнить, что игра на реальные деньги сопряжена с риском потери средств, поэтому необходимо играть ответственно и не ставить больше, чем вы можете позволить себе проиграть.
https://t.me/perevedem_document Перевод Документов: Мост между Языками и Культурами В современном мире глобализации, где границы стираются, а сотрудничество между странами и культурами становится все более тесным, перевод документов приобретает огромное значение. Это не просто замена слов одного языка словами другого, а кропотливая работа по передаче смысла, контекста и нюансов оригинала, чтобы обеспечить полное и точное понимание информации. Когда необходим перевод документов? Международный бизнес: контракты, договоры, финансовые отчеты, маркетинговые материалы – все это требует качественного перевода для успешного ведения дел за рубежом. Юридические вопросы: судебные документы, свидетельства, доверенности, нотариальные акты должны быть переведены с соблюдением строгих юридических норм и терминологии. Медицинская сфера: медицинские заключения, инструкции к лекарствам, результаты исследований – точность перевода здесь критически важна для здоровья пациентов. Техническая документация: инструкции по эксплуатации, технические спецификации, чертежи – перевод должен быть понятным и однозначным для специалистов. Образование и наука: дипломы, аттестаты, научные статьи, исследования – для признания образования за рубежом и обмена знаниями необходим качественный перевод. Почему важно обращаться к профессионалам? Точность и соответствие: профессиональные переводчики обладают глубокими знаниями языка и предметной области, что гарантирует точность и соответствие перевода оригиналу. Соблюдение терминологии: использование правильной терминологии – залог того, что перевод будет понятен специалистам в соответствующей области. Культурная адаптация: профессиональный переводчик адаптирует текст с учетом культурных особенностей целевой аудитории, чтобы избежать недопонимания или неловких ситуаций. Конфиденциальность: профессиональные бюро переводов гарантируют конфиденциальность ваших документов. Как выбрать бюро переводов? Опыт и репутация: изучите опыт работы бюро, ознакомьтесь с отзывами клиентов. Специализация: убедитесь, что бюро специализируется на переводах в нужной вам области. Наличие профессиональных переводчиков: узнайте, работают ли в бюро переводчики с соответствующим образованием и опытом. Стоимость и сроки: сравните цены и сроки выполнения заказа в разных бюро. В заключение, перевод документов – это важный инструмент для преодоления языковых барьеров и успешного взаимодействия в современном мире. Доверяйте перевод ваших документов профессионалам, чтобы быть уверенными в качестве и точности результата. Если вам нужно перевести конкретный документ, просто предоставьте его мне, и я постараюсь вам помочь!
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
Углубление колодца Продолжение предыдущего ответа: от 80 см до 1,2 метра, в зависимости от типа грунта и климатических условий. Заливка отмостки – это важный этап строительства, который позволяет защитить дом от негативного воздействия окружающей среды.
Estou completamente vidrado por SpinFest Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que explode como um festival de cores. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque dancante. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma escola de samba, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, SpinFest Casino e um cassino online que e uma folia sem fim para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual cheio de cores, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
spinfest de|
Acho simplesmente intergalactico SpeiCasino, e um cassino online que decola como um foguete espacial. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como nebulosas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. No fim das contas, SpeiCasino e um cassino online que e uma supernova de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo cosmico no cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma aurora boreal, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
spei party|
Je suis fou de RubyVegas Casino, on dirait une mine de plaisirs etincelants. Le repertoire du casino est un filon de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent comme des gemmes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un eclat de lumiere, avec une aide qui rayonne comme un diamant. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une gemme polie, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient precieux. En somme, RubyVegas Casino promet un divertissement de casino etincelant pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus le design du casino est un eclat visuel precieux, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
Acho simplesmente alucinante RioPlay Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao animada quanto um desfile na Sapucai. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e dancantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com gingado. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria um arraso. Resumindo, RioPlay Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de carnaval, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
roblox lite rioplay atualizado apk|
печатьнахолсте Портрет Вид искусства в котором художник изображает человека.
https://impossible-studio.ghost.io/kak-vybrat-luchshii-vpn-siervis-podrobnoie-rukovodstvo/ Новый лонгрид про Youtuber VPN! Узнайте, как смотреть YouTube и другие платформы без лагов и блокировок. Подключайте до 5 устройств на одной подписке, тестируйте сервис бесплатно 3 дня и платите всего 290? в первый месяц вместо 2000? у конкурентов. Серверы в Европе — ваши данные защищены от российских властей.
микрозайм онлайн на карту без процентов первый Спасибо за быстрое решение вопроса! 30 микрозаймы онлайн на высоте!
курсовая на заказ срочно курсовые контрольные на заказ
срочно онлайн займ отказа онлайн займ на карту без отказа
кредитные займы онлайн оформить займ онлайн
Estou completamente enfeiticado por SpellWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um feitico lancado. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino fascinantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. O servico do cassino e confiavel e encantador, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem truques, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No fim das contas, SpellWin Casino e um cassino online que e um portal de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo mistico no cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como uma pocao reluzente, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel magico.
spellwin bonus|
Acho simplesmente magico SpinGenei Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma lampada de Aladim. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um lampiao de delicias, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como pocoes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e encantador, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem truques. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem maldicoes, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, SpinGenei Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma lampada magica, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais encantadora.
spingenie|
Adoro o brilho estelar de SSSXWin Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como uma supernova em chamas. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma galaxia de emocoes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia reluzente, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. Em resumo, SSSXWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os astronautas do cassino! E mais o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
sssxwin casino las vegas|
Ich liebe den Glanz von SlotClub Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Wirbelwind durch die Nacht rast. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Lichtspektakel, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Lichtimpuls, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallen. Insgesamt ist SlotClub Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
slotclub spielothek|
Sou louco pela vibe de AFun Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que gira como um carrossel enlouquecido. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de folia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela da festa, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, AFun Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro axe, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
casino online afun|
Adoro o frenesi de AFun Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura euforia. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de energia, respondendo mais rapido que um estalo de confete. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como serpentinas, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. Em resumo, AFun Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma folia total para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo vibrante, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de uma festa.
afun golpe|
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
anГЎlise betorspin|
Estou alucinado com BRCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma escola de samba na avenida. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de prazeres, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de responsa, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. Resumindo, BRCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carnaval total para os folioes do cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro axe, adiciona um toque de folia ao cassino.
br77 game e confiГЎvel|
Ich bin suchtig nach Trickz Casino, es pulsiert mit einer verhexten Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Hexenwerk, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Zaubertrick funkeln. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein magischer Assistent, mit Hilfe, die wie eine Illusion verblufft. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Tauschung, manchmal mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein magischer Volltreffer. Am Ende ist Trickz Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und funkelt wie ein Zauberstab, das Casino-Erlebnis total verhext.
trickz casino bonus|
Je suis accro a VBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui explose comme un geyser. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est une torche d’efficacite, assurant un support de casino immediat et incandescent. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans cendres, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui envoient du feu. En somme, VBet Casino est un casino en ligne qui eclate comme un volcan pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une flamme, ajoute une touche de feu au casino.
vbet league|
Estou pirando com AFun Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que gira como um carrossel enlouquecido. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um espetaculo de luzes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que pulsam como batidas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um malabarista, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem pausa. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, AFun Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os folioes do cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro axe, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de uma festa.
afun gold|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os astronautas do cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin slots|
Adoro o balanco de BRCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um pandeiro. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro axe, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, BRCasino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os folioes do cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma fantasia de carnaval, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
br77 pneus|
Ich liebe den Zauber von Trickz Casino, es pulsiert mit einer verhexten Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Hexenwerk, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und verhext, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein magischer Funke. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Zaubertrick, ab und zu mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein magischer Volltreffer. Insgesamt ist Trickz Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zirkus der Magie strahlt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Zauberspruch, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
trickz casino guru|
Estou completamente hipnotizado por Bet558 Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma estrela em colisao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um universo de prazeres, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco profundo. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria estelar. No geral, Bet558 Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma supernova para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! E mais o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
bet558 download|
J’adore la fraicheur de ViggoSlots Casino, on dirait une tempete de neige pleine de frissons. Le repertoire du casino est un iceberg de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un vent de toundra, avec une aide qui brille comme un cristal de glace. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un flocon de neige, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent comme l’aurore. Dans l’ensemble, ViggoSlots Casino offre une experience de casino vivifiante pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un chemin dans la neige, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
viggoslots android|
Sou louco pela energia de BacanaPlay Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um desfile de carnaval. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de carnaval. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de swing, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. Na real, BacanaPlay Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carnaval total para os folioes do cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma fantasia de carnaval, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
codigo promocional bacanaplay|
Je suis fou de ViggoSlots Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi vivifiante qu’un vent polaire. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une toundra de delices, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et glacees. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse malgre le froid, repondant en un eclair glacial. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une avalanche, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, ViggoSlots Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique polaire, ajoute une touche de fraicheur au casino.
viggoslots fi|
Ich finde absolut rasant Turbonino Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Hochgeschwindigkeitsrennen. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen mitrei?en. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Boxenstopp, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Rennwagen, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist Turbonino Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Boxenstopp, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
turbonino erfahrungen|
Acho simplesmente alucinante Bet4Slot Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura adrenalina giratoria. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de giro, com slots de cassino tematicos de aventura. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carrossel, com uma ajuda que roda como uma roda-gigante. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma montanha-russa, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, Bet4Slot Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro giro para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um giro de piao, adiciona um toque de adrenalina giratoria ao cassino.
bet4slot cassino online login|
Sou louco pela energia de BetPrimeiro Casino, parece uma cratera cheia de adrenalina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao de delicias, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e inflamados. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Resumindo, BetPrimeiro Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro magma para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma brasa ardente, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
anГЎlise betprimeiro|
I’m crazy about Wazamba Casino, it feels like a safari through a jackpot jungle. Its collection is a canopy of thrilling entertainment, offering live casino sessions that roar like a lion. The casino’s customer service is a tribal chief of efficiency, with help that shines like a tribal torch. Casino payments are secure and smooth, however the casino offers could be more generous. In the end, Wazamba Casino is a casino you can’t miss for fans of modern casino slots! Additionally the casino interface is smooth and vibrant like a tropical sunrise, making you want to dive back into the casino endlessly.
wazamba cassino Г© confiГЎvel|
Je suis fou de Tortuga Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi intrepide qu’un equipage pirate. L’eventail de jeux du casino est un coffre de butin, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un vent de tempete, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une carte au tresor, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Tortuga Casino promet un divertissement de casino epique pour les pirates du casino ! De surcroit le design du casino est une fresque visuelle de haute mer, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
code promo tortuga casino|
J’adore le frisson de Unibet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui resonne comme un crescendo. Le repertoire du casino est une partition de divertissement, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance musicale. Le service client du casino est un maestro virtuose, repondant en un eclair melodique. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Unibet Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter le design du casino est une fresque visuelle harmonieuse, facilite une experience de casino enchanteresse.
unibet parrainage|
Игровая платформа Вавада часто выбирается игроками.
Бездепы и промокоды помогают стартовать новичкам.
Соревнования дают шанс выиграть крупные призы.
Подборка развлечений обновляется постоянно.
Создать аккаунт легко, и бонусы становятся доступны сразу.
Узнай больше по ссылке: https://jennychendds.com
https://mobilebloger.ru/ru-ru/
Estou completamente vidrado por Bet4Slot Casino, parece uma montanha-russa de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um carrossel de delicias, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de rotacao. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que roda como uma roda-gigante. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um giro de roleta, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, Bet4Slot Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro giro para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um giro de piao, torna a experiencia de cassino um carrossel inesquecivel.
bet4slot 1 cream|
Estou pirando com BetPrimeiro Casino, parece uma cratera cheia de adrenalina. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e escaldantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque vulcanico. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma chama de eficiencia, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao vulcanica. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma corrente de lava, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No fim das contas, BetPrimeiro Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro magma para quem curte apostar com estilo ardente no cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como lava derretida, torna a experiencia de cassino uma erupcao inesquecivel.
betprimeiro cГіdigo promocional|
ivibet casino Casinos ohne Steuer
Je trouve absolument enivrant Unibet Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino digne d’un chef d’orchestre. Il y a une vague de jeux de casino captivants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui chantent comme un ch?ur. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une portee musicale, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait melodique. En somme, Unibet Casino offre une experience de casino envoutante pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline rythmee du casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une salle de concert, ajoute une touche de musique au casino.
unibet offre de bienvenue|
http://www.evakuatorhelp.ru Профессиональная и оперативная помощь на дорогах – это наш профиль! Мы предоставляем полный спектр услуг: от эвакуации автотранспорта до мелкого ремонта, выполненного непосредственно на дороге. Работаем быстро, качественно и по доступным ценам. Где бы вы ни находились и что бы ни случилось с вашим автомобилем – мы всегда рядом и готовы помочь! Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
Je suis totalement submerge par Winamax Casino, on dirait une tempete sous-marine de plaisir. Il y a une maree de jeux de casino captivants, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et immersives. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et limpide, assurant un support de casino immediat et fluide. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse de maree, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient nager de joie. Dans l’ensemble, Winamax Casino promet un divertissement de casino aquatique pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style oceanique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus fluide.
winamax bug|
Ich bin suchtig nach Wunderino Casino, es pulsiert mit einer verhexten Casino-Energie. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und bezaubernd, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zauberspruch wirkt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Zaubertrick, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein magischer Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist Wunderino Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feenlicht verzaubert fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in magische Hohen hebt.
chris tall – laugh stories|
Страхование Прогнозы экономики – это попытки предсказать будущее состояние экономики на основе анализа текущих данных и тенденций. Они основываются на моделях и предположениях, которые могут быть неточными, поэтому прогнозы экономики следует рассматривать с осторожностью. Тем не менее, прогнозы экономики могут быть полезны для планирования бизнеса, инвестиций и личных финансов.
https://korolevachiana.github.io/FiveText/index.html Если вы устали от предсказуемых сюжетов и шаблонных персонажей, творчество Королевы Чианы станет для вас настоящим открытием. Её проза – это глоток свежего воздуха в мире современной литературы. Каждая история – это оригинальная идея, воплощенная в жизнь с безупречным мастерством. Книги Королевы Чианы заставляют задуматься о важных жизненных ценностях и пересмотреть свои взгляды на мир.
Ich bin vollig begeistert von Wheelz Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Adrenalinschub auf Hochstgeschwindigkeit. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und elektrisierend, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Turbo-Boost glanzt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Fahrticket, dennoch die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist Wheelz Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und funkelt wie ein Freizeitpark bei Nacht, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
wheelz aaron fotheringham|
Estou completamente fascinado por VikingLuck Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao feroz quanto uma tempestade nordica. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um escudo de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como runas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um trovao de Thor. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura epica. Em resumo, VikingLuck Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro Valhalla, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um guerreiro ao campo de batalha.
viking luck casino online|
перевод документов рядом сайты бюро переводов
Ich bin total begeistert von Trickz Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zauberstab funkelt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein Zauberkoffer voller Wunder, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und verhext, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, ab und zu mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein zauberhafter Gewinn. Am Ende ist Trickz Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zirkus der Magie strahlt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein magischer Zirkus leuchtet, das Casino-Erlebnis total verhext.
trickz casino kokemuksia|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como supernovas. Na real, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os astronautas do cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin avaliação|
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: blackjack envolvente, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi bem prestativo, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou em minutos, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Enfim, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Vale experimentar.
chauvet dj 4play|
Me encantei pelo ritmo de BR4Bet Casino, e uma onda de diversao que cintila como um farol. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que reluzem como chamas. O atendimento e solido como um farol. oferecendo respostas claras como um farol. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma lanterna. mesmo assim mais bonus regulares seriam radiantes. Ao final, BR4Bet Casino e um clarao de emocoes para os exploradores de jogos online! Como extra o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. elevando a imersao ao nivel de uma fogueira.
br4bet esta fora do ar|
Sou louco pela velocidade de F12.Bet Casino, e um cassino online que acelera como um carro de corrida. Tem um pit stop de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo lives que explodem como largadas. O time do cassino e digno de um piloto. com ajuda que ronca como um motor. O processo e claro e sem freadas. mesmo assim mais bonus regulares seriam velozes. Para encurtar, F12.Bet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo veloz! Como extra a plataforma acelera com um visual veloz. adicionando um toque de velocidade ao cassino.
f12 bet Г© confiavel|
Curto demais a quadra de MarjoSports Casino, e um cassino online que acelera como um contra-ataque fulminante. O leque do cassino e um estadio de delicias. oferecendo lives que explodem como penaltis. O suporte e um apito preciso. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo e claro e sem impedimentos. mas mais bonus regulares seriam esportivos. No geral, MarjoSports Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o design e um espetaculo visual de torcida. dando vontade de voltar como um craque.
marjosports bonus de cadastro|
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque me impressionou bastante. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: slots modernos, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que vale elogio. Fiz saque em Ethereum e o dinheiro entrou na mesma hora, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino me conquistou. Eu ja voltei varias vezes.
4play bet br|
Je trouve absolument cartoon Simsinos Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui rebondit comme un toon. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui sautent comme des toons. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. avec une aide qui rebondit comme un toon. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans fondu. mais des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rebondir. Au final, Simsinos Casino resonne comme un storyboard de plaisir pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! De plus le design du casino est une fresque visuelle cartoon. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto colore.
simsinos casino erfahrungen|
Sou louco pela torcida de MarjoSports Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um craque. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com caca-niqueis modernos que driblam como craques. O atendimento e solido como um campo. com ajuda que marca gol como um penalti. As transacoes sao faceis como um apito. as vezes mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. Em sintese, MarjoSports Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a interface e fluida e vibra como um estadio. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um gol.
marjosports show da sorte|
Je suis envoute par BankOnBet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi securisee qu’un vault blinde. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et securisees. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui accumulent. Les agents verrouillent les problemes. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. The process is clear like a balance sheet. parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient fructifier. Au final, BankOnBet Casino est un casino en ligne qui securise les victoires pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! What’s more la plateforme du casino brille par son style rentable. ajoute une touche de luxe bancaire au casino.
bankonbet casino spiele|
Sou louco pela matriz de PlayPix Casino, oferece uma aventura que glitcha como um render 8-bit. O catalogo de jogos e uma tela de emocoes. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque cibernetico. O time do cassino e digno de um programador. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. Os saques processam como servidores. entretanto mais bonus seriam um diferencial de matriz. Para encurtar, PlayPix Casino garante um jogo que reluz como pixels para quem curte apostar com estilo cibernetico! Vale dizer a plataforma reluz com um visual glitch. amplificando o jogo com vibracao digital.
tv playpix apk|
Je suis accro a BankOnBet Casino, on dirait une chambre forte pleine de jackpots. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un tresor de delices. proposant des slots de casino a theme financier. L’assistance du casino est fiable et discrete. assurant un support de casino immediat et securise. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides. mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un investissement. Pour resumer, BankOnBet Casino est un vault de thrills pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! En plus la navigation est simple comme un compte. amplifiant le jeu avec style securise.
bankonbet casino sign up|
Estou alucinado com Brazino Casino, parece um abismo de adrenalina subaquatica. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como conchas. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como aguas cristalinas. O atendimento e solido como um coral. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. Os pagamentos sao lisos como um coral. ocasionalmente mais bonus regulares seriam aquaticos. Em resumo, Brazino Casino promete uma diversao que e uma mare para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja o visual e uma explosao de corais. criando uma experiencia de cassino subaquatica.
brazino777 clip|
Казино Вавада привлекает внимание тысяч игроков.
Бонусы и бездепы делают процесс комфортным.
Игровые турниры дают дополнительные возможности.
Подборка игр включают топовые разработки.
Создать аккаунт можно быстро, и можно начать играть без задержек.
Узнай подробности прямо здесь: онлайн казино вавада
pure cocaine in prague cocaine prague
Estou completamente hipnotizado por IJogo Casino, oferece uma aventura que se entrelaca como uma rede tropical. A colecao e uma teia de entretenimento. com caca-niqueis que se enroscam como teias. Os agentes sao rapidos como uma cobra. oferecendo respostas claras como um labirinto resolvido. Os saques sao velozes como um cacador na selva. de vez em quando mais bonus seriam um diferencial enredado. No fim das contas, IJogo Casino e um enredo de emocoes para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer o design e fluido como um emaranhado. dando vontade de voltar como um cipo.
ijogo com como sacar|
Je trouve absolument legendaire Casinia Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi noble qu’un tournoi de chevaliers. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. proposant des slots de casino a theme medieval. Le service client du casino est un chevalier fidele. avec une aide qui brille comme une couronne. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse chevaleresque. neanmoins plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait legendaire. Pour resumer, Casinia Casino offre une experience de casino noble pour les explorateurs de melodies en ligne! Ajoutons le site du casino est une merveille graphique noble. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus noble.
casinia casino testbericht|
1xbet bonus code eg 1xbet Bangladesh Promo Code: Unlock Exclusive Bonuses and Enhanced Betting Opportunities In the vibrant landscape of online betting in Bangladesh, 1xbet stands out as a leading platform, offering a diverse range of sporting events, casino games, and other exciting opportunities. To amplify the thrill and maximize your winning potential, 1xbet provides a variety of promo codes tailored specifically for Bangladeshi players. These codes unlock exclusive bonuses, free bets, and enhanced odds, giving you a significant advantage in your betting journey. Types of 1xbet Promo Codes Available in Bangladesh: 1xbet Promo Code Bangladesh: This is a general promo code that can be used by both new and existing players in Bangladesh. It typically unlocks a welcome bonus, deposit bonus, or free bet. 1xbet Promo Code Registration Bangladesh: This code is exclusively for new players registering on the 1xbet platform in Bangladesh. It offers an enhanced welcome bonus to kickstart their betting adventure. 1xbet Free Promo Code Bangladesh: This code grants Bangladeshi players a free bet, allowing them to place a wager without risking their own funds. 1xbet Free Bet Promo Code Bangladesh: Similar to the previous code, this one provides a free bet opportunity, often tied to specific sporting events or promotions. 1xbet Bonus Promo Code Bangladesh: This code unlocks a bonus on your deposit, increasing your betting balance and giving you more chances to win. Promo Code for 1xbet Bangladesh Today: This code is a time-sensitive offer, valid only for a specific day. It usually provides a daily bonus, free bet, or enhanced odds on selected events. 1xbet Promo Code for Registration Bangladesh: This code is another registration-specific code, offering a larger welcome bonus than the standard registration bonus. How to Find and Use 1xbet Promo Codes in Bangladesh: 1xbet promo codes are widely available through various channels, including: Official 1xbet Website: Regularly check the 1xbet website for the latest promo code offers. Affiliate Websites: Many affiliate websites dedicated to online betting provide exclusive 1xbet promo codes for Bangladeshi players. Social Media: Follow 1xbet’s official social media accounts to stay updated on new promo code releases. Email Newsletters: Subscribe to 1xbet’s email newsletters to receive promo codes directly in your inbox. To use a promo code, simply enter it in the designated field during registration or when making a deposit. The bonus or free bet will be automatically credited to your account. Maximize Your Winnings with 1xbet Promo Codes: By utilizing 1xbet promo codes, Bangladeshi players can significantly enhance their betting experience and increase their chances of winning. Whether you’re a seasoned bettor or a newcomer to the world of online betting, these codes offer a valuable advantage. So, keep an eye out for the latest 1xbet promo codes and unlock a world of exclusive bonuses and thrilling betting opportunities.
Me enredei no caos de IJogo Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino enredada. As opcoes sao ricas e se entrelacam como vinhas. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O suporte e um fio guia. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. As transacoes sao simples como um fio solto. as vezes mais giros gratis seriam intrincados. Ao final, IJogo Casino promete uma diversao que e uma teia para os cacadores de vitorias intrincadas! De lambuja o design e um espetaculo visual enredado. dando vontade de voltar como um cipo.
ijogo com game|
Galera, vim dividir com voces sobre o Bingoemcasa porque superou minhas expectativas. O site tem um ar amigavel que lembra um salao cheio de energia. As salas de bingo sao super animadas, e ainda testei blackjack e poker tambem, todos rodaram sem travar. O atendimento no chat foi muito atencioso, o que ja me deixou bem a vontade. As retiradas foram instantaneas, inclusive testei PIX e funcionou perfeito. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que podiam ter bonus semanais, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Resumindo, o Bingoemcasa e divertido de verdade. Vale testar sem medo
bingoemcasa site|
Je suis accro a Casinia Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino chevaleresque. Le repertoire du casino est un donjon de divertissement. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent comme des armures. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un destrier. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. se deroulent comme une quete. parfois des tours gratuits pour une melodie epique. Globalement, Casinia Casino promet un divertissement de casino legendaire pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline royale du casino! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et vibre comme une cour royale. ajoute une touche de grandeur au casino.
casinia kaszinГі|
code promo 1xbet gabon code promo 1xbet cote d’ivoire Le monde des paris sportifs en ligne est en constante evolution, et 1xbet s’est etabli comme un leader mondial, offrant une plateforme complete et diversifiee aux parieurs du monde entier. En Cote d’Ivoire, l’enthousiasme pour les paris sportifs est palpable, et 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire propose une gamme allechante de promotions pour ameliorer l’experience de pari de ses utilisateurs. Au c?ur de ces promotions se trouvent les codes promotionnels, des cles magiques qui debloquent des bonus exclusifs et des opportunites de pari ameliorees. Qu’est-ce qu’un code promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire? Un code promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire est une combinaison unique de lettres et de chiffres qui peuvent etre entres lors de l’inscription ou du depot pour activer un bonus specifique. Ces bonus peuvent inclure: Bonus de bienvenue: Un bonus offert aux nouveaux utilisateurs lors de leur premier depot. Bonus de depot: Un bonus accorde sur les depots ulterieurs. Paris gratuits: La possibilite de placer un pari sans risquer son propre argent. Cotes ameliorees: Des cotes plus elevees sur certains evenements sportifs. Ou trouver les codes promo 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire? Les codes promotionnels 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire sont disponibles via plusieurs canaux, notamment: Le site Web officiel de 1xbet: Consultez regulierement le site Web de 1xbet pour les dernieres offres. Les sites Web affilies: De nombreux sites Web affilies proposent des codes promotionnels exclusifs pour les joueurs ivoiriens. Les reseaux sociaux: Suivez les comptes de medias sociaux officiels de 1xbet pour rester informe des nouvelles versions de code promotionnel. Les newsletters par e-mail: Abonnez-vous aux newsletters par e-mail de 1xbet pour recevoir les codes promotionnels directement dans votre boite de reception. L’utilisation efficace des codes promotionnels 1xbet Cote d’Ivoire peut considerablement augmenter vos chances de gagner et rendre votre experience de pari plus agreable. Gardez un ?il sur les derniers codes et profitez des avantages qu’ils offrent.
жилье вахта Оператор лазерных установок вахтой – это работа оператором лазерных установок вахтовым методом. Она предполагает управление лазерными установками на удаленном объекте в течение вахты. Оператор лазерных установок вахты должен иметь высокую квалификацию, опыт работы и знать современные лазерные технологии.
buy weed prague cocaine in prague
Je suis totalement pixelise par RollBit Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui deroule comme un ruban de pixels. La selection du casino est une chaine de plaisirs. proposant des slots de casino a theme numerique. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un flux de donnees. repondant en un flash pixelise. arrivent comme un concerto cubique. occasionnellement des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient derouler. A la fin, RollBit Casino est un casino en ligne qui deroule une symphonie de bits pour les fans de symphonies de bits! Bonus est une cadence visuelle envoutante. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto cubique.
rollbit price prediction|
Estou alucinado com XPBet Casino, e um redemoinho de diversao que se repete. O catalogo de jogos e um espiral de prazeres. incluindo mesas com charme de roda. O servico e confiavel como um ciclo. oferecendo respostas claras como uma roda. As transacoes sao simples como um giro. de vez em quando queria mais promocoes que giram como espirais. Resumindo, XPBet Casino e um loop de emocoes para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De lambuja o design e um espetaculo visual de vortice. fazendo o cassino pulsar como uma roda.
xp bet.|
Je suis seduit par Boomerang Casino, on dirait un cercle de frissons qui boucle. vibre avec un cercle de jeux varies. avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et circulaires. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un lanceur. assurant un support de casino immediat et boomerang. se deroulent comme une rhapsodie de ricochets. tout de meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En conclusion, Boomerang Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! De surcroit resonne avec une melodie graphique arque. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto circulaire.
boomerang casino verificatiemethoden|
Curto demais a vibracao de DonaldBet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um malabarista em acao. O catalogo de jogos e um picadeiro de prazeres. oferecendo lives que explodem como fogos de artificio. O time do cassino e digno de um diretor de circo. com ajuda que ilumina como um refletor. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um palhaco. em alguns momentos queria promocoes que explodem como fogos. No fim das contas, DonaldBet Casino e uma explosao de adrenalina para os fas de adrenalina vibrante! Como extra o layout e vibrante como um refletor. tornando cada sessao ainda mais vibrante.
afiliados donaldbet|
Curto demais a vibracao de JonBet Casino, oferece uma aventura que vibra como uma corda de harpa. A colecao e uma onda sonora de entretenimento. com caca-niqueis modernos que ecoam como sinos. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. As transacoes sao simples como um reverb. entretanto mais recompensas fariam o coracao ecoar. No fim das contas, JonBet Casino garante um jogo que ressoa como um sino para os exploradores de jogos online! De bonus a plataforma vibra com um visual ressonante. dando vontade de voltar como uma vibracao.
jonbet paga?|
Je suis fou de Boomerang Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui ricoche comme un projectile. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et boomerang. comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un lanceur. joignable par chat ou email. fluisent comme une sonate arque. occasionnellement des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient circulaires. Globalement, Boomerang Casino promet un divertissement de casino arque pour les explorateurs de melodies en ligne! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique circulaire. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto circulaire.
boomerang casino bonus terms|
Sou louco pela chama de DonaldBet Casino, oferece uma aventura que brilha como uma lona de circo. Tem um turbilhao de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como holofotes. O atendimento e solido como uma lona. oferecendo respostas claras como um picadeiro. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um palhaco. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de circo. No geral, DonaldBet Casino e um picadeiro de emocoes para quem curte apostar com estilo circense! Alem disso o design e fluido como uma acrobacia. tornando cada sessao ainda mais vibrante.
donaldbet app|
психолог для всех Психолог для всех – это не просто профессия, это призвание помогать людям. Специалист, обладающий широким спектром знаний и навыков, готов поддержать в любой жизненной ситуации: от профессионального выгорания до проблем в личных отношениях. Это не просто советчик, это компас, помогающий найти верное направление и обрести уверенность в себе.
Где купить реплику Баленсьяга Реплики одежды Диор позволяют ощутить парижский шик и безупречный вкус, не тратя десятки тысяч долларов. Они идеально подходят для тех, кто ценит элегантность и стремится выглядеть модно, не переплачивая за лейбл.
J’apprecie enormement 7BitCasino, ca procure une energie de jeu irresistible. La selection de jeux est colossale, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Les agents sont disponibles 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, par moments plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, notamment des bonus sans depot. Globalement, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino bewertung|
Ich bin total begeistert von King Billy Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Konig regiert. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die verzaubern. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zepter glanzt, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren koniglich. Insgesamt ist King Billy Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Kronungsfest funkelt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, einen Hauch von Majestat ins Casino bringt.
billy king casino|
Je kiffe grave Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. Les options sont ultra-riches et captivantes, avec des slots qui claquent grave. L’assistance est au top du top, garantissant un support direct et carre. Les paiements sont fluides et blindes, des fois des recompenses en plus ca ferait kiffer. Dans le fond, Gamdom garantit un fun intergalactique pour les aventuriers du jeu ! A noter aussi le site est une tuerie graphique, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
hack gamdom|
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, c’est une veritable sensation de casino unique. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, incluant des slots de pointe. Le personnel offre un accompagnement irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies sont instantanees, par moments davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. Globalement, 7BitCasino offre une experience de jeu securisee et equitable pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! De plus la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino opiniones|
J’adore l’energie de DBosses, ca offre une aventure palpitante. La gamme est tout simplement epoustouflante, avec des slots modernes et immersifs. Le personnel offre un suivi irreprochable, avec une aide personnalisee. Le processus est clair et sans complications, de temps a autre les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, DBosses garantit un divertissement de haut niveau pour les fans de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et moderne, renforce l’envie de revenir.
dbosses casino|
Je trouve absolument sensationnel BetFury Casino, ca ressemble a une energie de jeu irresistible. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, incluant des slots de derniere generation. Le personnel offre un accompagnement de qualite, avec un suivi exemplaire. Les retraits sont instantanes, parfois les offres comme le pack de bienvenue de 590 % pourraient etre plus accessibles. Pour conclure, BetFury Casino est une plateforme revolutionnaire pour les adeptes de divertissement innovant ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement percutant avec un theme sombre, amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betfury baixar app|
Je suis a fond dans Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. La gamme est une vraie pepite, proposant des sessions live qui tabassent. Le support est dispo 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en mode TGV, mais bon des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. Bref, Gamdom offre une experience de ouf pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! Et puis le design est une bombe visuelle, facilite le delire total.
gamdom code 2021|
Achou totalmente epico DiceBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que explode tudo. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao, com jogos de cassino perfeitos para criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de primeira, com uma ajuda que e um arraso. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Em resumo, DiceBet Casino vale cada segundo explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como brincadeira, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
dicebet reclame aqui|
J’adore le show de Impressario, il propose un show de jeu hors norme. Le catalogue est un festival de titres, proposant des sessions live qui en mettent plein la vue. Le support est dispo 24/7, garantissant un support direct et brillant. Les transactions sont simples comme un refrain, de temps en temps des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. Dans le fond, Impressario est un must pour les joueurs stars pour les amateurs de slots qui brillent ! En prime le design est une explosion visuelle, donne envie de revenir pour un rappel.
impressario casino|
Je suis scotche par Impressario, il propose un show de jeu hors norme. Les options sont variees et eblouissantes, proposant des sessions live qui en mettent plein la vue. Les agents sont rapides comme des cometes, repondant en un clin d’etoile. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, mais bon plus de tours gratos ca ferait vibrer. En gros, Impressario c’est une scene a decouvrir absolument pour les accros aux sensations eclatantes ! Bonus la navigation est simple comme une melodie, ajoute un max de charisme.
impressario casino no deposit bonus code|
Adoro de verdade o 888 Casino, e realmente sensacao unica de cassino. A selecao de jogos e impressionante, oferecendo jogos de mesa classicos e elegantes. O atendimento ao cliente e excepcional, garantindo ajuda imediata. O processo de retirada e simples e confiavel, em alguns momentos as ofertas poderiam ser mais generosas. De modo geral, o 888 Casino nunca decepciona para os jogadores em busca de adrenalina! Como bonus o design e visualmente impactante, reforca a imersao total.
888 live casino|
Adoro o role insano de Flabet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que detona tudo. Os titulos do cassino sao um show a parte, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e viciantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem treta, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, Flabet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro gas para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, da um toque de classe insana ao cassino.
flabet patrocinio|
J’adore a fond Instant Casino, ca donne une energie de casino survoltee. Les options de jeu en casino sont ultra-riches, offrant des machines a sous de casino uniques. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme l’eclair, repondant en un flash. Les gains du casino arrivent a la vitesse lumiere, des fois des recompenses de casino en plus ca ferait kiffer. Dans le fond, Instant Casino est un spot de casino a ne pas rater pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! En prime l’interface du casino est fluide et ultra-cool, facilite le delire total au casino.
instant casino paga mesmo|
Je suis completement conquis par 1xbet Casino, on dirait une experience de jeu exaltante. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, incluant des slots de pointe. Les agents sont toujours disponibles et efficaces, repondant en un clin d’?il. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. Dans l’ensemble, 1xbet Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec dynamisme, facilite chaque session de jeu.
1xbet yeni giris|
Ich bin suchtig nach DrueGlueck Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Adrenalinkick. Es gibt eine Flut an abwechslungsreichen Casino-Titeln, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die fesseln. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist der Hammer, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Auszahlungen im Casino sind blitzschnell, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren der Hit. Am Ende ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Online-Casino, das alles sprengt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total intensiviert.
drueckglueck test|
J’apprecie enormement 1xbet Casino, il offre une aventure pleine de frissons. La selection de jeux est monumentale, incluant des slots de pointe. Le service client est exceptionnel, joignable 24/7. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Globalement, 1xbet Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour ceux qui aiment parier ! En bonus le design est visuellement percutant, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
1xbet казино|
Adoro de verdade o 888 Casino, e realmente aventura cheia de emocoes. A gama de jogos e simplesmente fenomenal, contendo titulos inovadores e atraentes. A equipe oferece um suporte de altissima qualidade, oferecendo respostas rapidas e precisas. Os ganhos sao pagos em tempo recorde, no entanto mais recompensas seriam bem-vindas. Para concluir, o 888 Casino vale totalmente a pena para os fas de emocoes fortes! Note tambem que a navegacao e simples e rapida, reforca a imersao total.
888 casino big win|
Acho completamente fora da curva Flabet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e um estouro. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma loucura, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um fogo. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um trovao, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita plus. No geral, Flabet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro gas para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de vibe, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
apostas esportivas apostas esportivas flabet|
Je trouve completement fou Instant Casino, il propose une experience de casino explosive. Les options de jeu en casino sont ultra-riches, comprenant des jeux de casino tailles pour les cryptos. Le service client du casino est une bombe, garantissant un support de casino direct et efficace. Le processus du casino est clean et sans galere, des fois j’aimerais plus de promos de casino qui dechirent. Au final, Instant Casino garantit un fun de casino supersonique pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Et puis le site du casino est une tuerie graphique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus kiffante.
21dukes casino instant play|
Je suis totalement subjugue par Julius Casino, il propose une aventure de casino digne d’un empereur. Il y a un deferlement de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une noblesse rare. L’assistance du casino est majestueuse et efficace, proposant des solutions claires et immediates. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse triomphale, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Julius Casino promet un divertissement de casino heroique pour les conquerants du casino ! A noter le design du casino est une fresque visuelle epique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus triomphante.
casino julius avis|
Je trouve sensationnel le casino AllySpin, ca donne une plongee dans le divertissement. La selection de jeux est immense, proposant des experiences de casino en direct. Le service client est remarquable, garantissant un suivi de qualite. Les retraits sont super rapides, mais parfois les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. Pour faire court, AllySpin offre une experience solide pour ceux qui aiment les defis ! Notons aussi que la navigation est fluide, ajoutant une touche d’elegance au jeu.
avis allyspin|
Sou viciado no role de LeaoWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e indomavel. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e instintivos. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma aguia, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, LeaoWin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro rugido para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro rugido, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
leaowin02 casino bonus code 2024|
Je suis fan de le casino TonyBet, ca ressemble a une experience de jeu incroyable. La selection de machines est vaste, comprenant des titres innovants. Le service client est super, repondant rapidement. On recupere ses gains vite, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient bien. En resume, TonyBet ne decoit pas pour les amateurs de casino ! Ajoutons que, la plateforme est intuitive, ajoutant une touche de confort.
tonybet review|
Je suis epoustoufle par le casino AllySpin, on dirait une aventure palpitante. Il y a une quantite impressionnante de jeux, proposant des experiences de casino en direct. Le service client est remarquable, avec des reponses precises et utiles. Les gains arrivent vite, par moments j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles. Pour faire court, AllySpin vaut vraiment le detour pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi que le style visuel est dynamique, renforcant l’immersion.
allyspin sloty|
Adoro o clima feroz de LeaoWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura selva. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e instintivos. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma fera domada, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem emboscada, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, LeaoWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, da um toque de ferocidade braba ao cassino.
is leaowin02 casino legaal in nederland|
buy xtc prague plug in prague
buy coke in telegram cocain in prague from brazil
трипскан Tripscan зеркало: “Tripscan зеркало” относится к альтернативным веб-адресам или копиям сайта Tripscan, которые создаются для обеспечения доступности сервиса в случае блокировок основного домена или технических проблем. Зеркала сайта Tripscan позволяют пользователям получить доступ к тем же функциям и данным, что и на основном сайте, даже если основной домен по каким-либо причинам недоступен. Использование зеркал является распространенной практикой для онлайн-сервисов, которые сталкиваются с проблемами доступа из-за цензуры, блокировок или технических сбоев. Пользователи могут найти актуальные зеркала Tripscan на форумах, в социальных сетях или через поисковые системы. Важно убедиться в подлинности зеркала перед вводом личной информации, чтобы избежать мошенничества.
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, ca procure une experience de jeu electrisante. La selection de jeux est colossale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service client est remarquable, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies sont instantanees, occasionnellement plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. En fin de compte, 7BitCasino offre une experience de jeu securisee et equitable pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! De plus le design est visuellement attrayant avec une touche vintage, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino code|
Je suis totalement conquis par BetFury Casino, c’est une veritable immersion dans un univers vibrant. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, incluant des slots de derniere generation. Les agents sont toujours professionnels et efficaces, garantissant une aide via chat ou email. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, de temps en temps ??? les offres comme le pack de bienvenue de 590 % pourraient etre plus accessibles. Dans l’ensemble, BetFury Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour les joueurs en quete de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et intuitive, ajoute une touche de sophistication a l’experience.
betfury cashback|
купить промышленные подшипники bbcr Подшипник для конвейера: Этот запрос указывает на потребность в подшипниках, предназначенных для использования в конвейерных системах. Подшипники для конвейеров должны обладать высокой надежностью, износостойкостью и способностью выдерживать высокие нагрузки. Они могут быть шариковыми, роликовыми или игольчатыми, в зависимости от типа конвейера и условий эксплуатации. При выборе подшипников для конвейерных систем необходимо учитывать тип транспортируемого груза, скорость движения ленты, температурный режим и наличие агрессивных сред. Важно учитывать тип конвейера (ленточный, роликовый, цепной и т.д.), нагрузку на подшипник, скорость движения конвейера и условия эксплуатации (температура, влажность, наличие агрессивных веществ). Рекомендуется приобретать подшипники у специализированных поставщиков, имеющих опыт работы с конвейерными системами.
Je trouve completement barre Gamdom, ca donne une energie de jeu demente. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, avec des slots qui claquent grave. Le service client est une tuerie, garantissant un support direct et carre. Les paiements sont fluides et blindes, par contre les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, Gamdom offre une experience de ouf pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! Et puis le design est une bombe visuelle, ajoute un max de swag.
gamdom redeem gift card|
сайт трипскан Tripscan win: Фраза “Tripscan win” используется для обозначения успеха или преимущества, которое получает пользователь, используя сервис Tripscan. В контексте планирования путешествий, “win” означает нахождение наиболее выгодных предложений, экономию времени и денег, а также получение положительного опыта от организации поездки. “Tripscan win” может использоваться в рекламных кампаниях, отзывах пользователей и других маркетинговых материалах для подчеркивания конкурентных преимуществ сервиса и привлечения новых клиентов. Фраза имеет позитивный оттенок и ассоциируется с успехом, достижением целей и удовлетворением потребностей.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de 7BitCasino, ca procure une aventure pleine de sensations. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le personnel offre un accompagnement irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, bien que les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. En resume, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec style et modernite, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
promo code 7bitcasino|
Je suis accro a DBosses, c’est une plateforme qui electrise. Le catalogue est d’une diversite impressionnante, proposant des sessions live vibrantes. Les agents sont rapides et devoues, joignable via chat ou email. Les retraits sont fluides et ultra-rapides, de temps a autre plus de tours gratuits seraient top. En resume, DBosses garantit un divertissement de haut niveau pour les passionnes de sensations fortes ! Notons aussi le design est captivant et elegant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus exaltante.
dbosses casino bonus|
pr товаров и услуг Маркетинг консультации / Консультации маркетинг / Консультация по маркетингу: Пользователь заинтересован в получении экспертной оценки текущей маркетинговой стратегии и рекомендаций по ее улучшению. Важно предложить бесплатные консультации или аудиты, чтобы продемонстрировать свою экспертность и помочь клиентам определиться с дальнейшей стратегией продвижения. Необходимо предоставить возможность получить ответы на вопросы о различных аспектах маркетинга, таких как: выбор целевой аудитории, разработка стратегии продвижения, выбор каналов коммуникации и т.д.
Je trouve incroyable 1win Casino, il offre une energie de jeu irresistible. La selection est incroyablement riche, offrant des experiences de casino en direct immersives. Le personnel est professionnel et attentionne, offrant des solutions claires et efficaces. Les transactions sont bien protegees, parfois plus de tours gratuits seraient un plus. Pour conclure, 1win Casino est une plateforme exceptionnelle pour les passionnes de jeux en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est visuellement attrayant, ajoute une touche d’elegance a l’experience.
1win promo code|
Adoro o clima insano de DiceBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino alucinante. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e vibrantes, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes claras na hora. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um cometa, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, DiceBet Casino e o lugar certo pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino detona com um look que e puro fogo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
dicebet reclame aqui|
Je trouve absolument fantastique Betify Casino, c’est une veritable plongee dans un univers palpitant. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, incluant des slots de derniere generation. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, joignable 24/7. Les gains sont verses en un temps record, cependant les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino ne decoit jamais pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et agreable, facilite chaque session de jeu.
penalty shoot out street betify|
Je kiffe a fond Impressario, il propose un show de jeu hors norme. La selection de jeux est juste monumentale, avec des slots qui brillent de mille feux. Le service client est digne d’un gala, garantissant un support direct et brillant. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, mais bon j’aimerais plus de promos qui envoutent. Au final, Impressario est un must pour les joueurs stars pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Bonus le design est une explosion visuelle, donne envie de revenir pour un rappel.
impressario casino|
ламинирование бровей севастополь Хотите красивые брови, которые не нужно подкрашивать каждый день? Татуаж бровей Севастополь – это то, что вам нужно! В нашем салоне мы делаем татуаж бровей в различных техниках, чтобы удовлетворить все ваши пожелания. Наши мастера имеют большой опыт работы и используют только качественные материалы. Татуаж бровей – это отличный способ сэкономить время и всегда выглядеть превосходно! Запишитесь на бесплатную консультацию, и мы поможем вам выбрать идеальный вариант!
coke in prague buy coke in prague
Ich liebe den Zauber von Lapalingo Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop des Spa?es, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellen, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Spektakel, einen Hauch von Zauber ins Casino bringt.
no deposit lapalingo|
buy coke in prague plug in prague
Ich bin suchtig nach iWild Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Urwald tobt. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Sturm toben. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Dornen, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein wilder Gewinn. Alles in allem ist iWild Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Wildnis beherrscht fur Spieler, die auf wilde Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
50 freispiele ohne einzahlung iwild|
Adoro o clima explosivo de JabiBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e puro tsunami. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo a parte, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma explosao. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma mare de qualidade, com uma ajuda que e pura correnteza. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que arrasam. No geral, JabiBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma mare cheia para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como surfar, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
jabibet apk|
Je trouve absolument grandiose LeoVegas Casino, on dirait une tempete de fun majestueux. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est digne d’un monarque, avec une aide qui inspire le respect. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un couronnement, quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient royaux. Dans l’ensemble, LeoVegas Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline majestueuse du casino ! Par ailleurs la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sceptre, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
leovegas affiliates|
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Estou completamente alucinado por JabiBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e uma mare alta. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma tempestade, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma mare de qualidade, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. No fim das contas, JabiBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
jabibet login|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von Platin Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Edelstein strahlt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und glanzvoll, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und prazise, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Schatten, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein glitzernder Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist Platin Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Extra die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch glanzvoller macht.
platin casino owner|
Je suis fou de Luckster Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu ensorcelante. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs magiques, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui enchantent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un sortilege, avec une aide qui fait des miracles. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans malefice, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Luckster Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline enchantee du casino ! En plus le design du casino est une explosion visuelle feerique, facilite une experience de casino enchanteresse.
luckster casino review|
Je trouve absolument enivrant Lucky8 Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino ensorcelante. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le service client du casino est une etoile porte-bonheur, repondant en un eclair magique. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Lucky8 Casino offre une experience de casino envoutante pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit le design du casino est une explosion visuelle feerique, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
lucky8 casino official site|
Je suis fou de Luckster Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un sort. Le repertoire du casino est une cascade de divertissement, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et ensorcelantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un sortilege, assurant un support de casino immediat et ensorcelant. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un coup de baguette, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Globalement, Luckster Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sortilege, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
luckster login|
Ich finde absolut magisch LuckyNiki Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Sternenstaub funkelt. Es gibt eine Woge an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein leuchtender Talisman, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sternenschauer, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren zauberhaft. Insgesamt ist LuckyNiki Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Ubrigens die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Nordlicht, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
luckyniki erfahrungsbericht|
J’adore l’eclat de LuckyBlock Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu petillante comme une etoile. La selection du casino est une fontaine de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme chanceux. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. Globalement, LuckyBlock Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique lumineuse, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
luckyblock webapp|
Je suis accro a Madnix Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino totalement folle. Il y a une avalanche de jeux de casino captivants, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement qui fait des etincelles, avec une aide qui claque comme un coup de tonnerre. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans court-circuit, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait completement fou. En somme, Madnix Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait trembler les murs pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit la plateforme du casino brille par son style completement fou, ajoute une touche de folie au casino.
chat madnix|
оказание pr услуг Запуск нового продукта на рынок Запуск нового продукта на рынок – это сложный и ответственный процесс, требующий тщательной подготовки и планирования. Успех запуска во многом зависит от того, насколько хорошо вы изучили рынок, определили целевую аудиторию и разработали эффективную маркетинговую стратегию. Этапы запуска нового продукта: Исследование рынка: Анализ рынка, определение целевой аудитории, изучение конкурентов. Разработка продукта: Создание продукта, отвечающего потребностям целевой аудитории и превосходящего конкурентов. Разработка маркетинговой стратегии: Определение целей запуска, позиционирование продукта, выбор каналов коммуникации. Создание маркетинговых материалов: Разработка рекламных материалов, контента для сайта и социальных сетей, презентаций для клиентов. Предпродажная подготовка: Обучение персонала, подготовка отдела продаж к работе с новым продуктом. Запуск продукта: Организация рекламной кампании, публикация пресс-релизов, проведение презентаций и других мероприятий. Мониторинг и анализ: Отслеживание результатов запуска, анализ продаж, отзывов клиентов и внесение корректировок в стратегию. Ключевые факторы успеха: Качественный продукт: Продукт должен быть полезным, интересным и отвечать потребностям целевой аудитории. Четкое позиционирование: Продукт должен иметь четкое позиционирование и выгодно отличаться от конкурентов. Эффективная маркетинговая стратегия: Стратегия должна быть направлена на привлечение внимания целевой аудитории и стимулирование продаж. Квалифицированный персонал: Персонал должен быть обучен работе с новым продуктом и уметь эффективно продавать его. Постоянный мониторинг и анализ: Необходимо постоянно отслеживать результаты запуска и вносить корректировки в стратегию. Запуск нового продукта – это возможность для роста вашего бизнеса. Подготовьтесь к нему тщательно, и успех не заставит себя ждать!
ремонт духовки вдома Львів
врач психиатр запись на прием Психиатр и психотерапевт, частная практика. Индивидуальный подход и полная конфиденциальность.
проектирование автоматического пожаротушения Система газового пожаротушения Система газового пожаротушения (СГП) — это комплекс технических средств, предназначенных для обнаружения пожара на ранней стадии, оповещения о нем и автоматического тушения с помощью огнетушащих газов. СГП применяется для защиты помещений с ценным оборудованием, архивов, музеев, серверных комнат и других объектов, где использование воды или порошка может привести к невосстановимым повреждениям. Основными компонентами СГП являются: Датчики обнаружения пожара: Тепловые, дымовые, газовые, комбинированные. Прибор приемно-контрольный пожарный (ППКП): Обрабатывает сигналы от датчиков, определяет наличие пожара и управляет исполнительными устройствами. Модули газового пожаротушения (МГП): Содержат огнетушащий газ под давлением и выпускают его в защищаемое помещение при поступлении сигнала от ППКП. Система трубопроводов и распылителей: Доставляет огнетушащий газ к очагу возгорания и равномерно распределяет его по защищаемому объему. Система оповещения о пожаре: Звуковые и световые извещатели, предназначенные для эвакуации людей из защищаемого помещения. Система управления эвакуацией: Автоматическое открывание дверей, включение аварийного освещения. Система контроля доступа: Запрет доступа в помещение во время тушения пожара. Принцип действия СГП: Датчики обнаруживают признаки пожара (дым, тепло, газ). ППКП анализирует сигналы от датчиков и, при подтверждении наличия пожара, формирует сигнал на запуск системы пожаротушения. МГП активируются и выпускают огнетушащий газ в защищаемое помещение. Газ снижает концентрацию кислорода в помещении до уровня, при котором горение становится невозможным. Система оповещения о пожаре оповещает людей о необходимости эвакуации. Преимущества СГП: Высокая эффективность тушения: Быстро и надежно ликвидирует пожар. Безопасность для оборудования и ценностей: Не повреждает защищаемые объекты. Автоматическая работа: Не требует участия человека в процессе тушения. Возможность применения в труднодоступных местах. Недостатки СГП: Высокая стоимость: СГП дороже водяных и порошковых систем пожаротушения. Требования к герметичности помещения: Для эффективной работы СГП необходимо обеспечить герметичность помещения. Опасность для людей: Высокая концентрация огнетушащего газа может быть опасна для здоровья. Система газового пожаротушения – это надежное и эффективное средство защиты имущества и жизни людей от пожара.
Je suis captive par Casinova, on ressent une energie debordante. Le catalogue est d’une richesse incroyable, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Les agents sont rapides et professionnels, joignable via chat ou email. Le processus est clair et sans accroc, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient appreciees. Pour conclure, Casinova est une plateforme d’exception pour ceux qui aiment parier avec style ! De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ajoute une touche de classe.
mr casinova|
Je suis accro a Lucky31 Casino, on dirait une pluie d’etoiles filantes. Le repertoire du casino est un tourbillon de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement scintillant, avec une aide qui fait des merveilles. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans sortilege, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Globalement, Lucky31 Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! A noter le design du casino est une explosion visuelle feerique, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
avis casino lucky31|
Je suis accro a CasinoClic, on dirait une cascade de fun. Le repertoire du casino est une veritable comete de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui electrisent. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient vibrer. Dans l’ensemble, CasinoClic promet un divertissement de casino electrisant pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! En plus l’interface du casino est fluide et rayonnante comme une aurore, ajoute une touche de magie lumineuse au casino.
casino clic code|
https://2news.com.ua/ Новости Украины
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e um terremoto. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma chama. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma labareda, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial vulcanico. Na real, OshCasino e um cassino online que e uma erupcao de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
osh casino sister sites|
Ich finde absolut verruckt Pledoo Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Tanz durch die Spielwelt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und mitrei?end, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter knistern. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern funkelt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Insgesamt ist Pledoo Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Abenteurer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Polarlicht, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
pledoo caisno|
продвижение компании в интернете Услуги PR (Public Relations): Создание и поддержание позитивной репутации вашего бренда Услуги PR (Public Relations) – это стратегически важный инструмент для создания и поддержания позитивной репутации вашей компании в глазах общественности, включая клиентов, партнеров, инвесторов и других заинтересованных лиц. PR – это не только работа со СМИ, но и активное взаимодействие с вашей целевой аудиторией через различные каналы коммуникации. В отличие от рекламы, которая является платным способом продвижения, PR – это получение бесплатного упоминания о вашей компании в СМИ и других источниках информации. Это более эффективный и надежный способ завоевать доверие аудитории. Основные задачи PR: Формирование позитивного имиджа: Создание благоприятного впечатления о вашей компании, продукте или личности в глазах общественности. Повышение узнаваемости бренда: Увеличение осведомленности о вашей компании и ее продуктах. Управление репутацией: Реагирование на негативные отзывы, предотвращение кризисных ситуаций и восстановление репутации после кризисов. Установление доверительных отношений: Создание прочных связей с целевой аудиторией, инвесторами и партнерами. Поддержка маркетинговых кампаний: Усиление эффекта от рекламных кампаний за счет PR-активностей. Основные инструменты PR: Пресс-релизы: Распространение информации о ваших новостях, событиях и достижениях в СМИ. Пресс-конференции: Организация мероприятий для общения с журналистами и ответов на их вопросы. Интервью: Предоставление интервью представителям СМИ для распространения информации о вашей компании. Публикации статей: Публикация экспертных статей и других материалов о вашей компании в СМИ. Организация мероприятий: Организация и участие в мероприятиях для повышения
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, e um cassino online que detona como um vulcao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tremores, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que incendeiam. Em resumo, OshCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro magma, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
osh affiliate|
Sou louco pelo role de MegaPosta Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira explosao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um estouro, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma verdadeira faisca, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem enrolacao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, MegaPosta Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia explosiva, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
megaposta|
Ich bin suchtig nach PlayJango Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Flut voller Spa?, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und strahlend, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Am Ende ist PlayJango Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
playjango trustpilot|
Acho simplesmente intergalactico Bet558 Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma estrela em colisao. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como nebulosas, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro meteoro, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura cosmica. Na real, Bet558 Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
bet558 com login|
Je suis accro a PokerStars Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un tapis vert. Le repertoire du casino est un tournoi de divertissement, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino immediat et precis. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un jeu de cartes, parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un full house. Globalement, PokerStars Casino est un casino en ligne qui domine le jeu pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec flair au casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique etoilee, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
pokerstars service client|
Ich bin suchtig nach PlayJango Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk explodiert. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Flut voller Spa?, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter knistern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leuchtfeuer, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Komet, dennoch die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Am Ende ist PlayJango Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Polarlicht, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
opiniones playjango|
Sou viciado no role de MonsterWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que e um monstro. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brutais, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e selvagens. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um dragao, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, MonsterWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e colossal para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia selvagem, da um toque de ferocidade braba ao cassino.
monsterwin bonus|
J’adore la ferveur de PokerStars Casino, on dirait un ciel etoile de sensations. Le repertoire du casino est un tournoi de divertissement, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance tactique. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un croupier d’elite, repondant en un eclair strategique. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse fulgurante, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient vibrer. Pour resumer, PokerStars Casino offre une experience de casino palpitante pour les strateges du casino ! Bonus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel captivant, ajoute une touche de panache au casino.
pokerstars avis|
Acho simplesmente brabissimo ParamigoBet Casino, e um cassino online que e um verdadeiro furacao. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e vibrantes, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um trovao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um ciclone, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Em resumo, ParamigoBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma tempestade para os aventureiros do cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual avassaladora, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
paramigobet casino bonus|
консультации маркетинг Консультация по маркетингу Консультация по маркетингу – это возможность получить экспертное мнение и практические рекомендации по развитию вашего бизнеса от опытного маркетолога. Это возможность посмотреть на свой бизнес со стороны, выявить проблемные зоны и получить инструменты для их решения. Что вы получите на консультации: Анализ текущей ситуации: Оценка вашего текущего маркетингового положения, выявление сильных и слабых сторон, определение возможностей для роста. Определение целей: Помощь в определении четких и измеримых маркетинговых целей. Разработка стратегии: Разработка индивидуальной маркетинговой стратегии, учитывающей особенности вашего бизнеса и целевую аудиторию. Выбор инструментов: Подбор оптимальных маркетинговых инструментов для достижения ваших целей (SEO, контекстная реклама, SMM, контент-маркетинг и др.). Рекомендации по улучшению: Предоставление практических рекомендаций по улучшению вашего сайта, рекламных кампаний, контента и других аспектов маркетинга. Ответы на вопросы: Ответы на все ваши вопросы по маркетингу, развеивание сомнений и помощь в принятии правильных решений. Когда необходима консультация: Вы не знаете, с чего начать маркетинговое продвижение. Вы тратите деньги на рекламу, но не видите результатов. Вы хотите увеличить продажи, но не знаете, как это сделать. Вы хотите выйти на новый рынок. Вы хотите улучшить свой сайт и привлечь больше посетителей. Вы хотите повысить узнаваемость своего бренда. Консультация по маркетингу – это инвестиция в ваш успех. Получите профессиональную помощь и выведите свой бизнес на новый уровень!
Adoro a erupcao de BetPrimeiro Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um vulcao em furia. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e escaldantes, com slots de cassino tematicos de erupcao. O servico do cassino e confiavel e ardente, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma corrente de lava, mas queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como vulcoes. No fim das contas, BetPrimeiro Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os vulcanologos do cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo vulcanico, eleva a imersao no cassino ao calor de um vulcao.
betprimeiro paga|
Je trouve absolument envoutant Posido Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui ondule comme une mer dechainee. L’eventail de jeux du casino est un ocean de delices, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et immersives. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une vague deferlante, repondant en un eclat d’ecume. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eclaboussent. Pour resumer, Posido Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait des vagues pour les navigateurs du casino ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est un spectacle visuel aquatique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus fluide.
posido connexion|
Sou viciado no role de ParamigoBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que faz tudo voar. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo avassalador, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, respondendo mais rapido que um trovao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um ciclone, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, ParamigoBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro vento para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
paramigobet bedrägeri|
J’adore l’exuberance de MrPlay Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui swingue comme un orchestre. Les options de jeu au casino sont variees et festives, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un maestro, avec une aide qui fait swinguer. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient festifs. Au final, MrPlay Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline festive du casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique festive, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
mr.play arvostelu|
Je suis accro a Posido Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi fluide qu’un courant oceanique. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et fluides, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et immersives. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un capitaine, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eclaboussent. Globalement, Posido Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait des vagues pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une mer turquoise, ajoute une touche d’eclat marin au casino.
posido casino auszahlung|
https://kitehurghada.ru/
Je suis accro a PlazaRoyal Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un trone. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un tresor couronne, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le service client du casino est digne d’un monarque, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse princiere, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Pour resumer, PlazaRoyal Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Par ailleurs le design du casino est un spectacle visuel royal, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
royal plaza baku casino|
J’adore le frisson de MrXBet Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino enigmatique. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et mysterieuses, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. L’assistance du casino est fiable et perspicace, avec une aide qui devoile les mysteres. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une cle trouvee, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, MrXBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino enigmatique pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec flair au casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style captivant, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
mrxbet 5|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Richard Casino, es pulsiert mit einer luxuriosen Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen verzaubern. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und furstlich, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Alles in allem ist Richard Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Thron funkelt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
promo code richard casino|
J’adore l’eclat de ParisVegasClub, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un cabaret. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un veritable show lumineux, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un metteur en scene, assurant un support de casino immediat et eclatant. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une replique, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, ParisVegasClub c’est un casino a rejoindre sans tarder pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! De surcroit la plateforme du casino brille par son style eblouissant, ajoute une touche de panache au casino.
paris vegas club germany|
Je suis totalement submerge par Winamax Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui plonge dans les abysses. L’eventail de jeux du casino est un ocean de delices, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance marine. Le service client du casino est une perle rare, assurant un support de casino immediat et fluide. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une goutte d’eau, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Winamax Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait des vagues pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel aquatique, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
ice bank winamax|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Richard Casino, es pulsiert mit einer luxuriosen Casino-Energie. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und prachtig, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett leuchten. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und furstlich, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein kaiserlicher Befehl, ab und zu wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie Juwelen glanzen. Zusammengefasst ist Richard Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Palast strahlt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Zusatzlich die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und prunkvoll wie ein Thronsaal, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
richard mille casino|
Ищешь знакомства в Ростове-на-Дону? Вступай в наш активный Telegram-чат с реальными людьми для общения и новых встреч. Знакомства Ростов В чате дружелюбная атмосфера, много участников, возможность найти друзей или романтику, интересные темы и обсуждения. Присоединяйся и начинай знакомиться прямо сейчас!
ball bearing Cylindrical Bearings Cylindrical bearings are specialized for applications where radial and axial loads are present. Their design incorporates cylindrical rollers that provide a larger contact area compared to traditional ball bearings, reducing the stress on each roller and enhancing load capacity. These bearings are commonly used in heavy machinery, automotive components, and industrial equipment due to their ability to withstand high radial loads and allow for axial movement. Explore our range of cylindrical bearings, which come in various dimensions and designs tailored to meet your specific operational requirements. Ensure the reliability and performance of your machinery with our top-quality cylindrical bearings.
Sou viciado no role de OshCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que incendeia tudo. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de fogo. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma labareda, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, OshCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
casino osh avis|
Ich bin suchtig nach Platin Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Schatz funkelt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Juwelensafe, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Diamant leuchten. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein geschliffener Diamant. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Edelstein, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein glitzernder Gewinn. Am Ende ist Platin Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Schatz strahlt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Und au?erdem die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch glanzvoller macht.
platin casino cГіdigo de casino|
Estou completamente vidrado por MegaPosta Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que detona tudo. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma bomba total, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, MegaPosta Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale falar tambem a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro gas, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino toda hora.
megaposta.|
https://t.me/insta_akki
Хотите узнать секреты Вавада?
Каждый игрок может получить уникальные возможности.
Мы подготовили подборку полезных материалов, которые помогут вам играть эффективнее.
Вся информация доступна по ссылке: https://kmural.ru/news_importer/inc/kak_otugrat_veydzgher_h40_v_vavada__rabochie_strategii.html.
Начните играть с выгодой прямо сейчас!
https://kitehurghada.ru/
Je trouve absolument dement Spinanga Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui tourbillonne comme un ouragan dechaine. La selection du casino est une spirale de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Le service client du casino est une bourrasque d’efficacite, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une brise, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait dement. Dans l’ensemble, Spinanga Casino offre une experience de casino virevoltante pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! A noter le design du casino est un spectacle visuel tumultueux, facilite une experience de casino frenetique.
spinanga|
Нужна лабораторная? заказ лабораторная работа Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужен чертеж? стоимость чертежей на заказ выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Нужна презентация? заказать проект презентацию Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
J’adore la frenesie de Spinanga Casino, on dirait une tempete de plaisir endiablee. La selection du casino est une spirale de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et hypnotiques. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un cyclone, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait dement. Globalement, Spinanga Casino offre une experience de casino virevoltante pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique orageuse, facilite une experience de casino frenetique.
spinanga casino login|
Estou louco por Richville Casino, da uma energia de cassino tao luxuosa quanto um trono. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um cofre de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um mordomo impecavel, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro de luxo, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria chique. No fim das contas, Richville Casino vale a pena explorar esse cassino com urgencia para os nobres do cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passeio de carruagem, eleva a imersao no cassino ao apice.
richville apartments|
Ich bin suchtig nach SlotClub Casino, es pulsiert mit einer schillernden Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Welle an packenden Casino-Titeln, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Schalter, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist SlotClub Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
slotclub testbericht|
buy cocaine prague vhq cocaine in prague
prague drugstore cocain in prague from brazil
https://fixme.com.ua/
https://t.me/bonus_dragon_money
Je suis fou de Spinanga Casino, on dirait une tempete de plaisir endiablee. Le repertoire du casino est un tourbillon de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui tournoient. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, avec une aide qui fait tourbillonner. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un cyclone, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient explosifs. Globalement, Spinanga Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline frenetique du casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un ouragan, facilite une experience de casino frenetique.
spinanga casino opinie|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que orbita como um cometa reluzente. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
betorspin reclame aqui|
Estou louco por Richville Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao sofisticada quanto uma mansao de ouro. A gama do cassino e um verdadeiro palacio de delicias, com slots de cassino tematicos de luxo. O servico do cassino e confiavel e majestoso, respondendo rapido como um brinde de champanhe. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como abrir um cofre, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria opulento. Resumindo, Richville Casino vale a pena explorar esse cassino com urgencia para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passeio de carruagem, eleva a imersao no cassino ao apice.
paver cleaning contractor richville|
Ich bin total hingerissen von SlotClub Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Neonlicht explodiert. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Regenbogen, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Flackern, ab und zu die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem ist SlotClub Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Lichtspiel glitzert fur Spieler, die auf leuchtende Casino-Kicks stehen! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Lichtschalter, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
slotclub РїСЂРѕРјРѕРєРѕРґ|
обзор новых казино Сравнение онлайн казино Выбираете онлайн казино? Сравните их! Мы сравниваем казино по различным параметрам: репутация, лицензия, ассортимент игр, бонусы, способы оплаты, скорость выплат и качество службы поддержки. Сравнение поможет вам сделать правильный выбор и найти идеальное казино для себя.
Estou pirando com SpinWiz Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao encantadora quanto um feitico de varinha. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um grimorio de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro genio, com uma ajuda que reluz como um encantamento. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, SpinWiz Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro feitico para os magos do cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passe de magica, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais encantadora.
spinwiz Г© confiГЎvel|
https://fixme.com.ua/
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que orbita como um cometa reluzente. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como supernovas. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os astronautas do cassino! Vale dizer tambem o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin suporte|
Estou completamente alucinado por SpeiCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao reluzente quanto uma supernova. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro foguete, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma nave espacial, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como estrelas. Resumindo, SpeiCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
spei sport|
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin Г© legal|
Estou pirando com SpinWiz Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um portal magico. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um feitico de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de feiticaria. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma vassoura magica, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, SpinWiz Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os magos do cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino reluz com um visual que e puro feitico, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais encantadora.
spinwiz Г© confiavel|
Estou completamente alucinado por SpeiCasino, parece uma galaxia cheia de diversao estelar. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um universo de delicias, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, SpeiCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho estelar para os astronautas do cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma aurora boreal, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
download spei|
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como supernovas. Na real, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin suporte|
Adoro o encanto de SpinGenei Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma lampada de Aladim. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e encantadoras, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que brilha como uma varinha magica. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma lampada magica, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial encantado. No geral, SpinGenei Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo mistico no cassino! Vale dizer tambem o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual encantado, torna a experiencia de cassino um conto de fadas.
ontario slot games |
Je trouve absolument eblouissant Riviera Casino, on dirait une escapade glamour au bord de la mer. La selection du casino est une promenade de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme mediterraneen. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un hors-bord, assurant un support de casino immediat et elegant. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une brise marine, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. Au final, Riviera Casino est un casino en ligne qui brille comme une plage doree pour les navigateurs du casino ! De surcroit la plateforme du casino brille par son style raffine, facilite une experience de casino luxueuse.
casino riviera beach|
Estou alucinado com SpellWin Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma pocao encantada. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um feitico de prazeres, com slots de cassino tematicos de fantasia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro encantamento, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma runa, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura magica. No fim das contas, SpellWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para quem curte apostar com estilo mistico no cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual encantado, torna a experiencia de cassino um conto de fadas.
spellwin kasyno|
fastest deposit casinos
https://finance-info.ru/
Прокат авто Краснодар на месяц
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No geral, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin.|
J’adore l’intensite de Stake Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui explose comme un volcan en eruption. Il y a une explosion de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme explosif. Le service client du casino est une flamme vive, repondant en un eclair brulant. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans cendres, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, Stake Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait trembler le sol pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline enflammee du casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style explosif, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus enflammee.
drake stake|
Je suis fou de Riviera Casino, on dirait une escapade glamour au bord de la mer. Il y a une vague de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance cotiere. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un hors-bord, assurant un support de casino immediat et elegant. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans tempete, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent comme le soleil. Au final, Riviera Casino offre une experience de casino luxueuse pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style raffine, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
golden riviera casino online|
Adoro o charme de SpellWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao fascinante quanto um grimorio antigo. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e hipnotizantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem truques, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, SpellWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo mistico, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais encantadora.
spellwin no deposit bonus codes|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os astronautas do cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin roulette|
Adoro o brilho de SpinSala Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um holofote. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de glamour. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro holofote, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um foguete, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, SpinSala Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como um letreiro de neon, adiciona um toque de glamour reluzente ao cassino.
spinsala casino no deposit bonus|
Трансы Екатеринбурга Трансы Екатеринбург
Estou completamente vidrado por SupremaBet Casino, parece um reinado de diversao avassaladora. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um imperio de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como cetros. O servico do cassino e confiavel e majestoso, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago imperial. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um falcao real, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, SupremaBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro cetro para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo soberano, adiciona um toque de grandeza ao cassino.
supremabet – suprema bet ltda|
catherinewburton Customers appreciate their creativity, trust, and professional approach to services.
Estou pirando com SpinSala Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro brilho estelar. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um palco de delicias, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de glamour. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem apagar. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem sombras, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial reluzente. No geral, SpinSala Casino vale demais girar nesse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma coreografia de luzes, adiciona um toque de glamour reluzente ao cassino.
spinsala uk|
1win — это букмекер и онлайн?казино с акциями на старте.
Фрибеты и коды дают дополнительный банк на старте.
Создать аккаунт просто, а затем можно активировать предложение.
Каталог развлечений и спорта регулярно обновляются.
Чтобы использовать актуальный код, смотри подробности здесь — 1вин промокод, активируй по инструкции.
Играйте ответственно, чтобы процесс оставался комфортным.
Нужна презентация? генератор красивых презентаций Создавайте убедительные презентации за минуты. Умный генератор формирует структуру, дизайн и иллюстрации из вашего текста. Библиотека шаблонов, фирстиль, графики, экспорт PPTX/PDF, совместная работа и комментарии — всё в одном сервисе.
Проблемы с откачкой? насос для откачки воды в шахте сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
justvotenoon2 Inspiring designs and trusted solutions define the identity of these.
Je suis accro a VBet Casino, on dirait une eruption de plaisirs incandescents. Le repertoire du casino est un magma de divertissement, proposant des slots de casino a theme volcanique. Le service client du casino est une torche d’efficacite, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une coulee de lave, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait volcanique. Globalement, VBet Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! En plus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel brulant, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
vbet georgia|
broodbase – I enjoyed browsing here, everything looks smooth and perfectly balanced.
Je suis fou de VBet Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino digne d’un cratere. Le repertoire du casino est un magma de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, avec une aide qui jaillit comme une flamme. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse eruptive, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui envoient du feu. Globalement, VBet Casino est un casino en ligne qui eclate comme un volcan pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un cratere en fusion, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
1 selection lost- acca free bet vbet|
Je trouve absolument glacial ViggoSlots Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui brille comme une banquise illuminee. La selection du casino est une tempete de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance arctique. Le service client du casino est un flocon d’efficacite, avec une aide qui brille comme un cristal de glace. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une avalanche, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient frissonner. Au final, ViggoSlots Casino est un casino en ligne qui brille comme une banquise pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style givre, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
viggoslots stop sms|
Ich bin suchtig nach Turbonino Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Blitz uber die Piste schie?t. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Geschwindigkeitsspektakel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen mitrei?en. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Turbo-Motor lauft, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Schaltvorgang, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Volltreffer. Kurz gesagt ist Turbonino Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Uberholmanover glanzt fur Spieler, die auf rasante Casino-Kicks stehen! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Boxenstopp, den Spielspa? im Casino auf die Pole-Position hebt.
turbonino casino bonus|
Je suis fou de ViggoSlots Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme un glacier sous l’aurore. Il y a une avalanche de jeux de casino captivants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui scintillent comme la neige. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Pour resumer, ViggoSlots Casino est un casino en ligne qui brille comme une banquise pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit le design du casino est un spectacle visuel arctique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus glaciale.
viggoslots analyse|
габапентин эффект Габапентин: Будьте внимательны! Побочные эффекты габапентина могут быть разнообразными и проявляться в разной степени. Важно помнить, что не все пациенты испытывают побочные эффекты, а их выраженность может быть различной. При возникновении любых нежелательных реакций необходимо проконсультироваться с врачом.
схемы оптимизации налогов ндс Оптимизация НДС: законные способы и эффективные стратегии Оптимизация налогообложения НДС – это комплекс мер, направленных на снижение суммы налога, подлежащей уплате в бюджет. Важно отметить, что оптимизация не должна приводить к нарушению налогового законодательства. Законные методы включают использование налоговых вычетов, применение льгот, и грамотное ведение бухгалтерского учета. Например, своевременное оформление всех необходимых документов, подтверждающих право на вычет, поможет уменьшить базу НДС.
Je suis fou de Unibet Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui vibre comme une note aigue d’une symphonie. La selection du casino est une symphonie de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et vibrantes. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une note staccato, avec une aide qui resonne comme une symphonie. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse virtuose, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient chanter. Globalement, Unibet Casino c’est un casino a rejoindre sans tarder pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style symphonique, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
le cheval vainqueur de unibet turf|
I’m totally enchanted by Wazamba Casino, it pulses with a casino energy as fierce as a tribal drum. The selection is a wild expedition of fun, offering live casino sessions that roar like a lion. The casino team delivers support worthy of a jungle king, ensuring immediate casino support as bold as a warrior. Casino transactions are as simple as a tribal dance, however I’d love more casino promotions that roar like a waterfall. In summary, Wazamba Casino is a gem for casino fans for fans of modern casino slots! Plus casino navigation is intuitive like a tribal path, making you want to dive back into the casino endlessly.
wazamba mobil|
banehmagic – Strong aesthetics and purpose, they seem genuinely committed to excellence.
catherinewburton – Her website feels graceful, content is elegant and thoughtfully crafted.
габапентин от чего помогает Габапентин: Что говорят пациенты? Отзывы о габапентине разнятся. Некоторые пациенты отмечают значительное облегчение боли и улучшение качества жизни, другие жалуются на побочные эффекты, такие как сонливость, головокружение и нарушение координации. Важно помнить, что эффективность и переносимость препарата индивидуальны и зависят от особенностей организма.
Je suis fou de Unibet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un orchestre en feu. Il y a une vague de jeux de casino captivants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui chantent comme un ch?ur. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, repondant en un eclair melodique. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un tempo allegro, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Unibet Casino offre une experience de casino envoutante pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! A noter le design du casino est une fresque visuelle harmonieuse, ajoute une touche de musique au casino.
unibet contact tГ©lГ©phone|
I’m crazy about Wazamba Casino, it’s an online casino that roars like a jungle beast. The casino’s game lineup is a rainforest of delights, offering live casino sessions that roar like a lion. The casino support is available 24/7, reachable via chat or email. The casino process is transparent with no hidden traps, still extra casino rewards would make hearts pound. Overall, Wazamba Casino is an online casino that thrives like a jungle oasis for those chasing the adrenaline rush of the casino! As a bonus the casino site is a graphical wonder, making every casino session even wilder.
wazamba no deposit bonus|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que orbita como um cometa reluzente. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin codigo de bonus|
Je trouve absolument palpitant Tortuga Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui navigue comme un galion au vent. Le repertoire du casino est une carte au tresor de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui rugissent comme la mer. Le service client du casino est un capitaine aguerri, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un abordage, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui pillent les c?urs. En somme, Tortuga Casino promet un divertissement de casino epique pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique pirate, facilite une experience de casino epique.
tortuga casino enligne|
https://dzen.ru/110km
кайт школа египет Кайт Египет: откройте для себя мир кайтсерфинга в самых живописных местах Красного моря.
недорогие значок с логотипом значки на заказ с логотипом
производство значков на заказ сделать значки
https://detivetra.ru/
знаки на заказ значки свой дизайн на заказ
Ich bin vollig begeistert von Wheelz Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Turbo-Rollercoaster vibriert. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Fahrgeschaft-Spektakel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die wie ein Looping mitrei?en. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Loopingstart, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der die Kurve kriegt. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Achterbahn-Drop, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Volltreffer. Alles in allem ist Wheelz Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf rasante Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
wheelz / wheelzgames spielbank|
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de diversao, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. Na real, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin security|
Adoro o impulso de WinGameBR Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro combustivel cosmico. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um lancamento orbital. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um cometa, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como supernovas. No geral, WinGameBR Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, adiciona um toque de brilho cosmico ao cassino.
wingame br sports betting|
Hey there! This is kind of off topic but I need some advice from an established blog. Is it difficult to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure where to start. Do you have any tips or suggestions? Cheers
https://http-kra40.cc
Heya! I understand this is somewhat off-topic however I had to ask. Does managing a well-established website such as yours take a lot of work? I’m brand new to blogging but I do write in my diary everyday. I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my personal experience and thoughts online. Please let me know if you have any kind of recommendations or tips for brand new aspiring blog owners. Thankyou!
kra40 cc
Estou completamente apaixonado por BR4Bet Casino, parece um festival de luzes cheio de adrenalina. A colecao e um facho de diversao. com slots tematicos de aventuras radiantes. Os agentes voam como claroes. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques sao velozes como um clarao. as vezes mais bonus regulares seriam radiantes. Para encurtar, BR4Bet Casino e uma fogueira de adrenalina para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. dando vontade de voltar como uma chama eterna.
br4bet casino|
motocitee – The brand identity feels cohesive, visual language is consistent throughout.
motocitee – Impressive attention to detail, I love the user interface design.
trendingnewsfeed – Headlines gave me what I wanted without all the fluff or filler content.
apkcontainer – The interface is pretty clean, I didn’t feel lost browsing through apps.
sunnyflowercases – Overall, cute designs, good UX, definitely worth exploring.
adawebcreative – Really like the design, feels modern and polished without overdoing it.
centensports – The site feels professional and yet still friendly to readers.
Curto demais o asfalto de F12.Bet Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino supersonica. O leque do cassino e um asfalto de delicias. com caca-niqueis modernos que roncam como motores. O time do cassino e digno de um piloto. respondendo veloz como uma ultrapassagem. As transacoes sao faceis como um drift. em alguns momentos mais bonus seriam um diferencial turbo. Ao final, F12.Bet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo veloz! E mais o site e uma obra-prima de estilo turbo. criando uma experiencia de cassino supersonica.
f12 bet codigo promocional|
Je suis envoute par Simsinos Casino, offre un spectacle de plaisir qui dessine. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et colorees. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance cartoon. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un scenariste. resonnant comme une planche parfaite. se deroulent comme une rhapsodie de dessins. tout de meme des offres qui vibrent comme une cadence animee. En fin de compte, Simsinos Casino promet un divertissement de casino anime pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! De plus l’interface du casino est fluide et vibre comme une planche animee. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus animee.
simsinos 76|
Me encantei pelo ritmo de BR4Bet Casino, e uma onda de diversao que cintila como um farol. O leque do cassino e um brilho de delicias. com caca-niqueis modernos que encantam como lanternas. O atendimento e solido como um farol. respondendo rapido como um brilho na noite. Os saques voam como um facho de luz. em alguns momentos mais recompensas fariam o coracao brilhar. Em sintese, BR4Bet Casino e um clarao de emocoes para os cacadores de vitorias reluzentes! Adicionalmente o visual e uma explosao de claroes. fazendo o cassino brilhar como um farol.
robГґ br4bet|
https://dzen.ru/110km
raspinakala – The mix of traditional and modern art techniques is nicely balanced here.
musionet – Overall, promising and well made; gives a trustworthy first impression.
crownking88 – Just browsed their homepage, the style feels bold and intriguing.
celtickitchen – Navigating between recipes is smooth, no cluttered menus here.
joszaki regisztracio http://joszaki.hu
centensports – Their style is confident, writing has clarity and thoughtful insight.
raspinakala – The brand has strong visual appeal, stylish and credible presentation overall.
Sou louco pela fornalha de Fogo777 Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao intensa quanto um ritual de fogo. Os jogos formam uma fogueira de diversao. com slots tematicos de cerimonias antigas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. respondendo rapido como uma labareda. O processo e claro e sem fumaca. em alguns momentos mais bonus regulares seriam flamejantes. Ao final, Fogo777 Casino e um altar de emocoes para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Alem disso a navegacao e facil como uma labareda. dando vontade de voltar como uma labareda.
www fogo777.com|
sunnyflowercases – I’ll bookmark this; seems like a go-to for phone case shopping.
joszaki regisztracio joszaki
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Curto demais a chama de Fogo777 Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao intensa quanto um ritual de fogo. As opcoes sao ricas e queimam como carvoes. com slots tematicos de cerimonias antigas. Os agentes voam como chamas. garantindo suporte direto e sem cinzas. Os saques sao velozes como um ritual de fogo. de vez em quando mais recompensas fariam o coracao queimar. No fim das contas, Fogo777 Casino promete uma diversao que e uma labareda para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Por sinal o site e uma obra-prima de estilo ardente. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um ritual.
https://fogo777.com|
Estou alucinado com Verabet Casino, oferece uma aventura que reluz como brasas vivas. As opcoes sao ricas e queimam como carvoes. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como labaredas. O servico e confiavel como uma fogueira. respondendo rapido como uma labareda. Os saques sao velozes como um ritual de fogo. as vezes mais bonus seriam um diferencial ardente. Em sintese, Verabet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma labareda para os exploradores de jogos online! Alem disso a plataforma reluz com um visual ritualistico. dando vontade de voltar como uma labareda.
bet vera cassino|
Me enredei no caos de IJogo Casino, parece um emaranhado de adrenalina selvagem. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo lives que explodem como uma selva. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. respondendo veloz como uma rede. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma teia rompida. de vez em quando mais giros gratis seriam intrincados. Na real, IJogo Casino e um cassino online que e um labirinto de diversao para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer a plataforma reluz com um visual labirintico. amplificando o jogo com vibracao selvagem.
ijogo friv|
Me ecoei no ritmo de Stake Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que ecoa como um coral. As opcoes sao ricas e vibram como cordas. com caca-niqueis modernos que ecoam como sinos. O atendimento e solido como uma corda. respondendo veloz como uma vibracao. As transacoes sao simples como um reverb. em alguns momentos as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, Stake Casino garante um jogo que ressoa como um sino para os maestros do cassino! Vale dizer o site e uma obra-prima de estilo sonoro. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura ressonante.
stake eth|
tripscan зеркало Трипскан ссылка: Получите прямой доступ к TripScan, перейдя по ссылке. Откройте для себя мир выгодных предложений на авиабилеты, отели и другие услуги, необходимые для вашего путешествия. Начните планировать свою следующую поездку прямо сейчас с помощью TripScan! трипскан ссылка
Ремонт iphone 14 Сервисный центр Xiaomi: Мы – профессиональный сервисный центр Xiaomi, предлагающий полный спектр услуг по ремонту телефонов, планшетов и другой техники Xiaomi. Используем только качественные запчасти и квалифицированных мастеров. Гарантируем быстрый и надежный ремонт. Доверьте свою технику Xiaomi профессионалам!
Sou louco pela rede de IJogo Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um cacador de sombras. O catalogo de jogos e uma selva de emocoes. com caca-niqueis que se enroscam como teias. O suporte e um fio guia. assegurando apoio sem enredos. As transacoes sao faceis como um emaranhado. mesmo assim as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Em sintese, IJogo Casino e um cassino online que e um labirinto de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos! E mais o site e uma obra-prima de estilo selvagem. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura enredada.
ijogo bonus|
Sou louco pela ressonancia de Stake Casino, e um cassino online que ressoa como um sino ancestral. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um sino. com slots tematicos de aventuras sonoras. Os agentes sao rapidos como uma onda sonora. com ajuda que ressoa como um sino. Os saques sao velozes como uma onda sonora. entretanto mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. Resumindo, Stake Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro eco para quem curte apostar com estilo harmonico! Alem disso a navegacao e facil como um eco. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um coral.
stake bet|
Galera, resolvi compartilhar minha experiencia sobre o Bingoemcasa porque achei muito alem do que esperava. O site tem um visual descontraido que lembra um salao cheio de energia. As salas de bingo sao sempre lotadas, e ainda testei blackjack e poker tambem, todos rodaram sem travar. O atendimento no chat foi rapido como nunca vi, o que ja me deixou seguro. As retiradas foram eficientes de verdade, inclusive testei PIX e caiu em minutos. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que podiam ter bonus semanais, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Pra concluir, o Bingoemcasa me conquistou. Recomendo pra quem curte diversao online
bingoemcasa.|
pier45attheport – I liked the layout, everything appears polished, thoughtful and pleasant.
уроки английского для детей 7 лет
Sou louco pela chama de DonaldBet Casino, oferece uma aventura que brilha como uma lona de circo. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um palhaco. oferecendo lives que explodem como fogos de artificio. O atendimento e solido como uma lona. garantindo suporte direto e sem quedas. As transacoes sao faceis como um estalo. mesmo assim as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, DonaldBet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro espetaculo para os fas de adrenalina vibrante! De lambuja o design e fluido como uma acrobacia. tornando cada sessao ainda mais vibrante.
afiliados donaldbet|
Estou completamente ressonado por JonBet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que ecoa como um coral. As opcoes sao ricas e vibram como cordas. incluindo mesas com charme ressonante. O atendimento e solido como uma corda. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. As transacoes sao simples como um reverb. porem mais bonus regulares seriam harmonicos. Em sintese, JonBet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma onda sonora para os exploradores de jogos online! De lambuja a interface e fluida e ressoa como uma harpa. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um coral.
tigrinho jonbet|
Je suis seduit par Boomerang Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang lance. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. avec des slots qui bouclent comme des arcs. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. avec une aide qui revient comme un arc. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un arc. quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient revenir. A la fin, Boomerang Casino est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang pour les fans de symphonies circulaires! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une boucle. facilite une experience de casino boomerang.
boomerang casino bonusbedingungen|
https://institutocea.com/layouts/inc/?mejor_codigo_promocional_1xbet.html
tripscan TripScan вход: Откройте мир путешествий с TripScan! Войдите в свою учетную запись и получите доступ к эксклюзивным предложениям на авиабилеты, отели и многое другое. Мы поможем вам спланировать идеальное путешествие, учитывая все ваши предпочтения и бюджет. TripScan – ваш надежный партнер в мире путешествий. Начните свое приключение прямо сейчас! trip scan вход
Ремонт сотовых телефонов Замена аккумулятора: Быстрая и качественная замена аккумулятора в вашем телефоне или ноутбуке. Используем только оригинальные аккумуляторы и предоставляем гарантию на все виды работ. Замена аккумулятора – это простой способ вдохнуть новую жизнь в ваш гаджет. Обращайтесь к нам, и мы все сделаем быстро и профессионально!
Curto demais a vibracao de DonaldBet Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como um picadeiro sob holofotes. Os jogos formam uma lona de diversao. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como malabares. O time do cassino e digno de um diretor de circo. assegurando apoio sem tropecos. As transacoes sao faceis como um estalo. mas queria promocoes que explodem como fogos. No geral, DonaldBet Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para os acrobatas do cassino! De lambuja a navegacao e facil como um malabarismo. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um espetaculo.
quem Г© o dono da donaldbet|
Estou completamente hipnotizado por XPBet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao continua quanto um espiral infinito. O leque do cassino e um vortice de delicias. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que fluem como loops. O suporte e um loop preciso. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. Os saques sao velozes como um loop. em alguns momentos as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, XPBet Casino e uma onda de adrenalina ciclica para os roteiristas do cassino! Por sinal o layout e vibrante como uma roda. adicionando um toque de loop ao cassino.
xp bet game|
Je suis seduit par Boomerang Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang lance. est une trajectoire de sensations qui enchante. avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et circulaires. Le service client du casino est un arc maitre. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. arrivent comme un concerto boomerang. parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait arque. Au final, Boomerang Casino enchante avec une rhapsodie de jeux pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! A noter offre un orchestre de couleurs boomerang. facilite une experience de casino boomerang.
boomerang casino.|
english stars
https://www.imdb.com/list/ls4150091342/
masquepourvous – The site has charm, design choices reflect a delicate, artistic touch.
masquepourvous – Just came across this site today, feels welcoming and interesting.
geteventclipboard – Honestly, the overall design feels modern, clean, and very professional.
dinahshorewexler – Overall, the vibe here feels genuine, pleasant, and really engaging.
brucknerbythebridge – I appreciate how everything loads quickly without any hiccups at all.
safercharging – Feels like something I’d share with friends who value safety.
Je suis hante par Casombie, ca pulse comme une invasion de zombies. Le catalogue est une crypte de tresors, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents repondent plus vite qu’un zombie affame, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fluides et fiables, parfois plus de promos macabres seraient un plus. Pour resumer, Casombie vaut chaque frisson qu’il procure pour les aventuriers des cryptos ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un fantome, donne envie de revenir hanter le site.
casombie review|
Je suis ensorcele par Freespin Casino, ca propulse dans un vortex de plaisir. La selection de jeux est une veritable supernova, incluant des jeux de table d’une energie debordante. Le suivi est d’une clarte lumineuse, repondant en un flash. Le processus est lisse comme une orbite, parfois des bonus plus petillants seraient magiques. Dans l’ensemble, Freespin Casino offre une experience aussi brillante qu’une comete pour les passionnes de cryptos ! En bonus la plateforme brille comme une constellation, ce qui rend chaque session absolument electrisante.
bonus free spin sans dГ©pГґt casino en ligne|
Je suis captive par Nomini Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui danse comme une ombre fugace. vibre avec un voile de jeux varies. comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. avec une aide qui danse comme une ombre. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une scene. parfois plus de bonus pour une harmonie voilee. A la fin, Nomini Casino est un casino en ligne qui joue une danse d’ombres pour les virtuoses des jeux! En bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une note voilee. amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
J’eprouve une etincelle debordante pour Robocat Casino, il programme une sequence de recompenses fulgurantes. Les composants tracent un schema de gadgets avant-gardistes, offrant des bonus crabs et 200 spins des fournisseurs comme Pragmatic Play et Evolution. Le service scanne en continu 24/7, declenchant des protocoles multiples pour une resolution instantanee. Le pipeline est code pour une fluidite exemplaire, malgre cela des updates promotionnels plus frequents upgradieraient le kit. En compilant le code, Robocat Casino invite a une session sans crash pour les hackers de casinos virtuels ! En glitch supplementaire le graphisme est un render dynamique et immersif, incite a prolonger la session infinie.
robocat casino espana|
J’eprouve une gourmandise infinie pour MrPacho Casino, ca transforme le jeu en une degustation exquise. Le menu est un cellier de variete exuberante, avec des slots aux themes epices qui chatouillent les papilles. Les hotes interviennent avec une delicatesse remarquable, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Les retraits glissent avec une souplesse remarquable, par intermittence des menus promotionnels plus frequents pimenteraient la table. Dans l’ensemble du menu, MrPacho Casino devoile un itineraire de triomphes succulents pour ceux qui cuisinent leur fortune en ligne ! A souligner l’interface est un chemin de table navigable avec art, accroit l’envoutement dans le royaume du gout.
mrpacho casino bonus|
jonathanfinngamino – Everything loads quickly which makes browsing an enjoyable experience overall.
reindeermagicandmiracles – The site loads smoothly, which makes browsing a fun experience.
saveaustinneighborhoods – The site design feels straightforward, letting the message shine through.
libertycadillac – The vibe here feels sleek, clear, and really professional overall.
sjydtech – This company looks reliable, design and content reflect quality.
Je suis ensorcele par Casombie, c’est une experience qui reveille les sens. Le catalogue est une crypte de tresors, avec des slots au design effrayant. Les agents repondent plus vite qu’un zombie affame, garantissant un support digne d’une legende. Le processus est aussi lisse qu’un suaire, de temps a autre des tours gratuits supplementaires feraient frissonner. En somme, Casombie est une plateforme qui fait battre les c?urs pour les aventuriers des cryptos ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un fantome, donne envie de revenir hanter le site.
informations casombie|
Je suis totalement hypnotise par Freespin Casino, ca propulse dans un vortex de plaisir. Le catalogue est un kaleidoscope de delices, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptomonnaies. L’assistance est precise comme une etoile filante, garantissant un support d’une brillance rare. Les gains atterrissent a la vitesse lumiere, cependant plus de promos vibrantes seraient un regal. En conclusion, Freespin Casino est un tresor pour les amateurs de jeux pour les amateurs de sensations eclatantes ! A noter le design est vibrant comme une galaxie, ajoute une touche de feerie celeste.
casino en ligne francais free spin sans depot|
яндекс доставка курьер на личном авто Яндекс Еда: Курьер – лицо сервиса, гарант скорости и качества Яндекс Еда – это не просто доставка еды, это целый мир вкусов, доступный в любое время и в любом месте. И ключевую роль в этом мире играют курьеры. Они – связующее звено между рестораном и клиентом, гарант того, что горячий обед или ужин прибудет вовремя и в идеальном состоянии. Работа курьером Яндекс Еды – это динамичная и ответственная работа, требующая пунктуальности, внимательности и вежливости. Это возможность самостоятельно планировать свой график, выбирать удобные районы для работы и получать стабильный доход. Яндекс Еда ценит своих курьеров, предоставляет им все необходимые инструменты и поддержку для успешной работы. Конкурс “Курьер года” является ярким подтверждением признания и уважения к труду этих незаменимых людей. Стать частью команды Яндекс Еды – это не только работа, но и возможность внести свой вклад в создание комфортной и вкусной жизни для миллионов людей. Вы доставляете не просто еду, вы дарите радость и экономите время, что бесценно в современном мире.
Je trouve absolument spectral Nomini Casino, est une symphonie de divertissement qui effleure. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et fugaces. repond comme un fantome gracieux. repondant en un souffle spectral. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une scene. quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait theatral. Dans l’ensemble, Nomini Casino cadence comme une sonate de victoires pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! En plus le design du casino est une fresque visuelle spectrale. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus etheree.
Je suis irremediablement appate par MrPacho Casino, on discerne un jardin de defis appetissants. Les plats forment un tableau de textures innovantes, proposant des blackjack revisites pour des bouffees d’adrenaline. Les hotes interviennent avec une delicatesse remarquable, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Les flux monetaires sont blindes par des epices crypto, toutefois des amuse-bouches gratuits supplementaires rehausseraient les plats. Dans l’ensemble du menu, MrPacho Casino sculpte un festin de jeu somptueux pour les gardiens des buffets numeriques ! En primeur le visuel est une mosaique dynamique et appetissante, ce qui hisse chaque bouchee a un rang gastronomique.
mrpacho avis|
hanacapecoral – Very professional appearance, I feel trust in their offerings.
sjydtech – Their layout is sharp, navigation feels intuitive and efficient today.
http://arkada-style.ru/includes/pgs/?navigatory_dlya_ohoty_i_rybalki.html
Entrepreneurs gain easier funding with higher Brians club credit.
skibumart – I was drawn to their visuals, vibe feels genuine and fresh.
Je suis ebloui par Cheri Casino, ca scintille comme une nuit etoilee. Les options sont un bouquet d’emotions, incluant des jeux de table pleins de charme. Les agents repondent avec une rapidite etincelante, repondant plus vite qu’une etoile filante. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de l’eclair, de temps a autre des bonus plus petillants seraient un regal. En somme, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui illumine les sens pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! A noter la plateforme scintille comme un diamant, amplifie l’immersion dans un monde de reves.
cheri casino connexion|
Je suis facette par RubySlots Casino, il taille une collection de recompenses etincelantes. Le portfolio est un salon de variete lapidaire, avec des slots RTG aux themes luxueux qui font luire les lignes. L’assistance grave des reponses nettes, avec une expertise qui prevoit les inclusions. Les retraits s’extraient avec une purete remarquable, toutefois des inclusions promotionnelles plus frequentes rehausseraient le portfolio. A la fin de cette taille, RubySlots Casino invite a une exploration sans fissure pour les tailleurs des paris crypto ! De surcroit le portail est une monture visuelle imprenable, amplifie l’immersion dans le salon du jeu.
ruby slots casino mobile|
Je suis pimente par PepperMill Casino, ca transfigure le jeu en une infusion eternelle. Le bouquet est un potager de diversite exuberante, integrant des roulettes live pour des tourbillons d’arome. Les artisans repondent avec une acuite remarquable, accessible par infusion ou missive instantanee. Les courants financiers sont fortifies par des racines crypto, nonobstant les bouquets d’offres pourraient s’epanouir en generosite. En concluant l’infusion, PepperMill Casino convie a une exploration sans satiete pour les gardiens des jardins numeriques ! En primeur le portail est une serre visuelle imprenable, allege la traversee des vergers ludiques.
peppermill casinos|
ieeb – Navigation works smoothly, no issues getting where I wanted quickly.
eleanakonstantellos – Her website exudes elegance; visuals and copy feel both refined and warm.
Je suis vise par WildRobin Casino, ca eleve le jeu a une quete heroique. Le feuillage est un parchemin de divertissements forestiers, integrant des lives comme Blackjack pour des duels d’arcs. L’assistance decoche des reponses precises, avec une visee qui anticipe les embuscades. Le sentier est trace pour une fluidite exemplaire, toutefois des embuscades promotionnelles plus frequentes dynamiseraient le repaire. En apotheose legendaire, WildRobin Casino forge une legende de jeu heroique pour les archers de victoires astucieuses ! En fleche supplementaire la structure vibre comme un arc ancestral, infuse une essence de mystere sylvestre.
world gone wild robin schulz sample|
Pexip webhooks Pexip Video Conferencing: Empowering Communication on Any Device Deploy industry-leading video capabilities using a flexible framework that prioritizes the needs of all of your staff. With Pexip, easily create immersive video conferencing experiences with simplified layouts that ensure your participants maximize the value of their interaction.
Lucky Jet Играть Lucky Jet (Лаки Джет) — ваша возможность оседлать удачу! Динамичная игра Lucky Jet уже ждет вас. Чтобы начать играть в Лаки Джет, достаточно пройти быструю регистрацию на официальном сайте игры. Если он недоступен, воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом Лаки Джет. Ищете, где сыграть? Lucky Jet 1win — одна из проверенных площадок. Lucky Jet 1вин предоставляет полную версию развлечения. Не упустите шанс — играть в Lucky Jet можно сразу после создания аккаунта. Официальный сайт Lucky Jet или его зеркало — ваш надежный старт!
Je suis ebloui par Frumzi Casino, c’est une explosion d’energie pure. La gamme est une deferlante de joies, incluant des jeux de table d’une intensite foudroyante. Le suivi est d’une clarte etincelante, repondant en un battement de c?ur. Les paiements sont securises comme un recif, mais les offres pourraient etre plus explosives. Au final, Frumzi Casino promet une aventure electrisante pour les passionnes de cryptos ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un courant marin, ce qui rend chaque session absolument electrisante.
frumzi analyse|
nohonabe – Just found this today, and honestly the vibe feels authentic.
Je suis irresistiblement epice par PepperMill Casino, ca transfigure le jeu en une infusion eternelle. Il regorge d’une abondance de melanges interactifs, incluant des jackpots progressifs pour des pics d’essence. Le suivi cultive avec une constance impenetrable, mobilisant des sentiers multiples pour une extraction fulgurante. Les retraits s’ecoulent avec une fluidite remarquable, toutefois des herbes de recompense additionnelles epiceraient les alliances. Pour sceller l’arome, PepperMill Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour les gardiens des jardins numeriques ! En sus le visuel est une mosaique dynamique et odorante, pousse a prolonger le festin infini.
peppermill reno calendar|
J’eprouve une precision infinie pour WildRobin Casino, ca tend un arc de defis legendaires. Le feuillage est un parchemin de divertissements forestiers, avec des slots aux themes Robin Hood qui font vibrer les cordes. Le suivi protege avec une vigilance absolue, assurant une garde fidele dans la foret. Les flux sont camoufles par des fourres crypto, toutefois des embuscades promotionnelles plus frequentes dynamiseraient le repaire. En apotheose legendaire, WildRobin Casino construit un repaire de divertissement sylvestre pour les gardiens des fourres numeriques ! Par surcroit le portail est une clairiere visuelle imprenable, infuse une essence de mystere sylvestre.
avis wild robin|
курьер года яндекс еда Сравнение работы курьером в Яндекс.Еда и Яндекс.Доставка: Ваш выбор – ваш успех Выбор между работой курьером в Яндекс.Еда и Яндекс.Доставка зависит от ваших приоритетов и предпочтений. Обе компании предлагают гибкий график, конкурентную оплату и современные инструменты для работы. Основное отличие заключается в типе доставляемых товаров. Яндекс.Еда специализируется на доставке еды из ресторанов, что предполагает более короткие маршруты и частый контакт с клиентами. Яндекс.Доставка доставляет широкий спектр товаров, от посылок до документов, что может потребовать большей мобильности и умения ориентироваться в городе. Если вам нравится общаться с людьми и дарить им радость, работа в Яндекс.Еде может быть для вас более привлекательной. Если вы предпочитаете большую самостоятельность и разнообразие задач, работа в Яндекс.Доставке может быть более интересной. В любом случае, работа курьером в обеих компаниях – это возможность зарабатывать, развиваться и быть частью современной логистической системы. Важно учитывать свои возможности (наличие автомобиля, готовность к работе в разное время суток) и выбирать тот вариант, который лучше всего соответствует вашим потребностям и целям. Успех в работе курьером зависит от вашей ответственности, пунктуальности и желания предоставлять качественный сервис.
Je suis irremediablement appate par MrPacho Casino, ca transforme le jeu en une degustation exquise. Le menu est un cellier de variete exuberante, incluant des crash games comme JetX pour des pics de saveur. Le suivi veille avec une finesse sans pareille, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Les retraits glissent avec une souplesse remarquable, par eclats des menus promotionnels plus frequents pimenteraient la table. Pour couronner le plat, MrPacho Casino sculpte un festin de jeu somptueux pour les architectes de victoires savoureuses ! Par surcroit le visuel est une mosaique dynamique et appetissante, ce qui hisse chaque bouchee a un rang gastronomique.
informations mrpacho|
Je suis remue par Shuffle Casino, on anticipe un paquet de ruses astucieuses. Les mains forment un eventail de coups innovants, proposant des crashes pour des chutes d’excitation. Le suivi bat avec une regularite absolue, accessible par bluff ou appel direct. Les flux financiers sont verrouilles par des jokers crypto, occasionnellement davantage de jokers bonus hebdomadaires agiteraient le sabot. Dans l’ensemble du jeu, Shuffle Casino devoile un tour de victoires melangees pour les baroudeurs de casinos virtuels ! A piocher la circulation est instinctive comme un tour de passe-passe, incite a prolonger la donne infinie.
shuffle casino token|
Je suis enrobe par Sugar Casino, c’est un atelier ou chaque tour distille une goutte de victoire mielleuse. La collection est un sirop de divertissements delicieux, integrant des lives comme Sweet Bonanza Candyland pour des eclats de sirop. Le service mijote en continu 24/7, assurant une attention fidele dans la patisserie. Les flux financiers sont enrobes par des coques crypto, occasionnellement des sucreries gratuites supplementaires rehausseraient les saveurs. En refermant le bocal, Sugar Casino devoile un plateau de triomphes fondants pour ceux qui melangent leur destin en ligne ! Par surcroit la structure scintille comme un sucre d’orge ancestral, incite a prolonger la degustation infinie.
casino sugar rush|
themacallenbuilding – I like how the site feels modern, clean, and polished.
casa-nana – Overall, it feels warm, inviting, and very pleasant to explore.
eleanakonstantellos – Her brand feels authentic, each detail seems chosen with care and style.
goestotown – Just checked it today, and the vibe feels fun and welcoming.
dietzmann – The experience is reliable, content and visuals are well balanced.
bigprintnewspapers – I noticed it feels professional, yet easy for anyone to use.
brahmanshome – The vibe here is very homely, authentic, and easygoing.
biotecmedics – I appreciate the simple design; nothing feels cluttered or distracting.
muralspotting – Feels like a place where creativity is celebrated and shared.
dankglassonline – The site looks bold and creative, definitely stands out uniquely.
reinspiregreece – The theme feels meaningful, definitely conveys hope and creativity.
lastminute-corporate – Pages load smoothly, which really helps with quick browsing.
cepjournal – The site feels professional, informative, and very well-structured overall.
pastorjorgetrujillo – I appreciate the peaceful tone and positive energy throughout.
лечение тревожности Препараты от тревоги – это класс медикаментов, предназначенных для снижения и контроля симптомов тревожных расстройств. К ним относятся антидепрессанты, анксиолитики и другие лекарственные средства, помогающие восстановить химический баланс в мозге и уменьшить проявления тревоги. Антидепрессанты, такие как селективные ингибиторы обратного захвата серотонина (СИОЗС) и селективные ингибиторы обратного захвата серотонина и норадреналина (СИОЗСН), часто назначаются для лечения тревожных расстройств, поскольку они помогают регулировать уровень нейротрансмиттеров, таких как серотонин и норадреналин, которые играют важную роль в регуляции настроения и тревоги. Анксиолитики, такие как бензодиазепины, оказывают быстрый успокаивающий эффект и могут использоваться для кратковременного облегчения острых приступов тревоги. Однако из-за риска развития зависимости и других побочных эффектов, их применение должно быть ограничено и контролироваться врачом. Другие препараты, такие как бета-блокаторы и антиконвульсанты, также могут использоваться для лечения отдельных симптомов тревожных расстройств. Важно отметить, что назначение и применение препаратов от тревоги должно осуществляться только под наблюдением врача. Самолечение может быть опасным и привести к нежелательным последствиям. Дополнительно, медикаментозное лечение тревоги часто сочетается с психотерапией, такой как когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ), для достижения наилучших результатов и долгосрочного улучшения состояния пациента.
J’ai un veritable engouement pour Donbet Casino, ca transporte dans une tempete de plaisirs. La selection de jeux est un veritable raz-de-maree, avec des slots au design audacieux. Le support est disponible 24/7, joignable a tout moment. Les retraits sont rapides comme une comete, de temps a autre les offres pourraient etre plus volcaniques. En somme, Donbet Casino offre une experience aussi puissante qu’une eruption pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline pure ! De plus la plateforme brille comme une supernova, donne envie de replonger dans la tempete.
is donbet legit|
Je suis irremediablement appate par MrPacho Casino, on discerne un jardin de defis appetissants. Le menu est un cellier de variete exuberante, integrant des live roulettes pour des tourbillons de suspense. L’assistance distille des conseils affutes, activant des voies multiples pour une resolution veloutee. Les echanges coulent stables et acceleres, nonobstant des menus promotionnels plus frequents pimenteraient la table. A la fin de ce degustation, MrPacho Casino convie a une exploration sans satiete pour les maitres des paris crypto ! En cerise sur le gateau la trame irradie comme un plat ancestral, accroit l’envoutement dans le royaume du gout.
mrpacho analyse|
J’eprouve un vertige total pour Shuffle Casino, c’est une pioche ou chaque clic melange les destinees. Il foisonne d’une ribambelle de tirages interactifs, avec des originaux SHFL aux mecaniques piegees qui renversent les enjeux. Les dealers reagissent avec une vivacite remarquable, avec une strategie qui lit les bluffs. Le protocole est melange pour une fluidite exemplaire, a l’occasion des tirages gratuits supplementaires brasseraient les mains. En apotheose hasardeuse, Shuffle Casino se pose comme un atout pour les parieurs pour les tricheurs des paris crypto ! Par surcroit le portail est une table visuelle imprenable, incite a prolonger la donne infinie.
cable ipod shuffle geant casino|
Je suis enrobe par Sugar Casino, c’est un atelier ou chaque tour distille une goutte de victoire mielleuse. La vitrine de jeux est une bonbonniere regorgeant de plus de 4 000 douceurs, proposant des roulettes pour des tours de sucre. L’assistance distille des recettes nettes, avec une expertise qui anticipe les envies. Le processus est lisse comme du caramel, toutefois des eclats promotionnels plus frequents pimenteraient le panier. Pour clore le sirop, Sugar Casino devoile un plateau de triomphes fondants pour les patissiers de casinos virtuels ! Par surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un coulis, infuse une essence de mystere sucre.
sugar casino erfahrung|
answermodern – I enjoyed my visit, the interface is intuitive and attractive.
tatumsounds – This site feels alive, blending media and style seamlessly.
cnsbiodesk – I like the straightforward presentation, nothing feels cluttered at all.
momoanmashop – I like how playful and inviting the overall design feels.
lastminute-corporate – Overall, it provides clarity and solutions without unnecessary distractions.
обучение кайтсёрфингу Дети Ветра: “Дети Ветра” (Deti Vetra) – это известная русскоязычная кайт школа и кайт станция, расположенная в Хургаде, Египет. “Дети Ветра” зарекомендовали себя как надежный и профессиональный партнер для кайтсерферов всех уровней подготовки. Кайт школа предлагает широкий выбор курсов и программ, от начального уровня до продвинутого, а также индивидуальные занятия и групповые тренировки. Квалифицированные инструкторы, говорящие на русском языке, обеспечивают безопасное и эффективное обучение, используя современное оборудование и проверенные методики. Кайт станция “Дети Ветра” расположена на песчаном пляже с лагуной, где новички могут безопасно практиковать свои навыки. Кроме того, “Дети Ветра” организуют кайт сафари вдоль побережья Египта, позволяя кайтсерферам исследовать удаленные споты с идеальными условиями для катания. “Дети Ветра” – это не просто кайт школа и кайт станция, это дружная команда, готовая поделиться своим опытом и любовью к кайтсерфингу.
themacallenbuilding – First impression feels strong, like it’s a trustworthy and stylish brand.
crownaboutnow – Their visuals are sharp, layout feels balanced and professional overall.
biotecmedics – Overall, a positive and professional platform with useful information.
goestotown – The design feels modern and friendly, perfect for casual browsing.
casa-nana – The site feels cozy, simple, and gives a warm impression.
brahmanshome – The site gives off comfort and authenticity right away.
J’eprouve une gourmandise infinie pour MrPacho Casino, on discerne un jardin de defis appetissants. La vitrine de jeux est un buffet opulent de plus de 5 000 delices, avec des slots aux themes epices qui chatouillent les papilles. Le suivi veille avec une finesse sans pareille, accessible par messagerie ou appel instantane. Les flux monetaires sont blindes par des epices crypto, par intermittence plus de hors-d’?uvre bonus journaliers agrementeraient le festin. Pour couronner le plat, MrPacho Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour les chasseurs de casinos virtuels ! En primeur le parcours est instinctif comme un arome familier, instille une essence de mystere culinaire.
casino mrpacho|
muralspotting – Feels like a place where creativity is celebrated and shared.
Je suis irresistiblement epice par PepperMill Casino, c’est un atelier ou chaque lancer infuse des essences de triomphe. La reserve de jeux est un herbier foisonnant de plus de 5 000 essences, proposant des blackjacks revisites pour des bouffees d’excitation. Le suivi cultive avec une constance impenetrable, assurant une tutelle fidele dans les vignes. Les recoltes affluent via USDT ou canaux fiat, par intermittence des herbes de recompense additionnelles epiceraient les alliances. En concluant l’infusion, PepperMill Casino revele un sentier de triomphes parfumes pour les alchimistes des enjeux crypto ! Par surcroit l’interface est un sentier herbeux navigable avec art, instille une quintessence de mystere epice.
the peppermill hotel devizes|
pastorjorgetrujillo – The design feels calm and peaceful, perfectly matching the content.
reinspiregreece – I like how the site carries a fresh and positive vibe.
bigprintnewspapers – I noticed it feels professional, yet easy for anyone to use.
momoanmashop – Overall, I enjoyed the browsing experience, cheerful and straightforward.
cepjournal – First impression is neat, scholarly, and straightforward for readers.
dankglassonline – I like how creative and engaging the visuals come across.
cnsbiodesk – The site feels professional and focused on scientific innovation clearly.
Je suis supercharge par Super Casino, on decele un escadron de strategies imparables. La panoplie de jeux est un arsenal surequipe de plus de 4 000 gadgets, offrant des super spins et cash drops des heros comme Evolution et Pragmatic Play. Les sentinelles reagissent avec une alerte fulgurante, avec une intelligence qui anticipe les menaces. Les flux sont blindes par des boucliers crypto, a l’occasion des modules de recompense additionnels fortifient les escadrons. En activant le mode final, Super Casino forge une legende de jeu supersonique pour les pilotes des paris crypto ! En plus l’interface est un cockpit navigable avec precision, incite a prolonger l’assaut infini.
super ace online casino|
haskdhaskdjaslkds – Looks experimental; some parts load, others feel sketchy and vague.
bigprintnewspapers – Their focus feels clear, content displays with authoritative and confident tone.
geomatique237 – The visuals are daring, maybe this is a work in progress.
reinspiregreece – Beautiful balance of imagery and text, the site feels poetic.
https://kitehurghada.ru/ Воздушный змей специальной конструкции, известный как кайт, активно используется в кайтсерфинге или кайтбординге, позволяя спортсмену перемещаться по воде, используя энергию ветра. Кайт состоит из купола, изготовленного из прочной ткани, надувных баллонов, строп управления и планки, с помощью которой райдер контролирует тягу, положение и движение кайта. Выбор размера кайта зависит от силы ветра и веса спортсмена. Современные модели кайтов отличаются высокой маневренностью и наличием систем безопасности.
противотревожные средства Лекарства от тревожности — это медикаментозные средства, предназначенные для снижения уровня тревожности и связанных с ней симптомов, таких как беспокойство, напряжение, страх и раздражительность. Существуют различные классы лекарств, которые могут использоваться для лечения тревожности, включая антидепрессанты, анксиолитики и другие препараты. Антидепрессанты, такие как селективные ингибиторы обратного захвата серотонина (СИОЗС) и селективные ингибиторы обратного захвата серотонина и норадреналина (СИОЗСН), часто назначаются для лечения тревожности, так как они помогают регулировать уровень нейромедиаторов в мозге, ответственных за настроение и тревогу. Анксиолитики, такие как бензодиазепины, оказывают быстрый успокаивающий эффект, но их использование ограничено из-за риска развития зависимости и побочных эффектов. Другие препараты, такие как бета-блокаторы, могут использоваться для уменьшения физических симптомов тревожности, таких как учащенное сердцебиение и дрожь. Важно подчеркнуть, что лекарства от тревожности должны назначаться и контролироваться врачом. Самолечение может быть опасным и привести к нежелательным побочным эффектам. Кроме того, медикаментозное лечение тревожности часто сочетается с психотерапией, такой как когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ), для достижения наилучших результатов и долгосрочного улучшения состояния пациента.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Fezbet Casino, il offre une aventure aussi ardente qu’un brasier. La selection est une tempete de fun, avec des slots aux visuels flamboyants. Le support est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions nettes et rapides. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse d’une etincelle, de temps a autre plus de promos eclatantes seraient un regal. Dans l’ensemble, Fezbet Casino promet une aventure ardente et inoubliable pour les amateurs de sensations vibrantes ! En bonus la plateforme scintille comme un mirage, ajoute une touche de magie enflammee.
fezbet review|
Je suis anobli par SlotsPalace Casino, ca erige un empire de defis somptueux. Le royaume est un hall de diversite princiere, proposant des crash pour des chutes de trone. Les courtisans repondent avec une courtoisie exemplaire, declarant des solutions claires et promptes. Le ceremonial est sculpte pour une fluidite imperiale, bien que davantage de decrets bonus quotidiens enrichiraient le domaine. A la fin de cette ordonnance, SlotsPalace Casino sculpte une lignee de jeu grandiose pour les monarques de casinos virtuels ! En sceptre supplementaire le graphisme est une tapisserie dynamique et immersive, incite a prolonger la dynastie infinie.
slots palace promo code 2024|
J’eprouve une ivresse totale pour PepperMill Casino, on hume un verger de tactiques enivrantes. La collection est un recueil de divertissements odorants, avec des dice slots aux motifs piquants qui titillent les sens. Les artisans repondent avec une acuite remarquable, mobilisant des sentiers multiples pour une extraction fulgurante. Le processus est moulu pour une onctuosite exemplaire, nonobstant les bouquets d’offres pourraient s’epanouir en generosite. Pour sceller l’arome, PepperMill Casino forge un festin de jeu somptueux pour les gardiens des jardins numeriques ! Par surcroit la trame irradie comme un elixir ancestral, allege la traversee des vergers ludiques.
peppermill casino in reno|
Je suis propulse par Super Casino, on decele un escadron de strategies imparables. La panoplie de jeux est un arsenal surequipe de plus de 4 000 gadgets, avec des slots aux pouvoirs thematiques qui amplifient les combos. Le suivi escorte avec une vigilance absolue, declenchant des contre-mesures claires et rapides. Les flux sont blindes par des boucliers crypto, malgre cela davantage de boosts bonus quotidiens survoltent le bastion. Pour clore l’assaut, Super Casino devoile un vecteur de succes surhumains pour les sentinelles des bases numeriques ! De surcroit la structure pulse comme un reacteur ancestral, amplifie l’engagement dans l’arsenal du jeu.
super marchГ© casino salon de provence|
кайт школа Кайт Египет – это кайтсерфинг в Египте, который предлагает широкий выбор мест для катания, от Хургады до Дахаба, каждое из которых имеет свои особенности и привлекает кайтсерферов со всего мира.
cangjigedh – The look is minimal yet very intriguing, I like it.
ceriavpn – Easy to use interface, even beginners will feel comfortable instantly.
yyap16 – I like the minimal layout, it’s easy on the eyes.
azhyxh – Browsing here feels effortless, everything responds instantly without issues.
eljiretdulces – The site feels lively and welcoming, I enjoyed scrolling today.
newbalance550 – A solid site for sneaker fans, reliable and easy to use.
local-website – Pages load quickly, which makes the experience really smooth today.
flmo1xt – Everything works as expected, reliable performance across the site.
t643947 – The site feels quick and efficient, everything loads instantly here.
alusstore – The layout looks neat and professional, very easy to navigate.
rwbj – The site gives a modern vibe, clean and functional design.
x3137 – The overall vibe is neat and minimal, really easy to use.
rbncvbr – The vibe is sleek and functional, easy to spend time here.
newbirdhub – Browsing felt easy and reliable, I had no problems at all.
wcbxhmsdo8nr – The overall vibe is simple yet professional, really easy to use.
fghakgaklif – The layout is neat, with everything clearly placed and easy to spot.
360view – Pages load instantly, which makes browsing fast and enjoyable overall.
Je trouve completement incroyable Betsson Casino, c’est une veritable experience de jeu electrisante. La bibliotheque de jeux est phenomenale, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, avec un suivi efficace. Les paiements sont fluides et securises avec un maximum de 50 000 € par jour, occasionnellement les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. Dans l’ensemble, Betsson Casino ne decoit jamais pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Ajoutons que la navigation est rapide sur mobile via l’application iOS/Android, ajoute une touche de dynamisme a l’experience.
betsson sponsor|
J’adore l’incandescence de Celsius Casino, on dirait une eruption de fun. Les choix de jeux au casino sont varies et enflammes, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, repondant en un eclair ardent. Les paiements du casino sont surs et fluides, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait enflamme. Dans l’ensemble, Celsius Casino est un casino en ligne qui met le feu pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline du casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une flamme, donne envie de replonger dans le casino a l’infini.
celsius crypto casino|
v1av8 – Strong aesthetic direction, but content needs definition and polish.
aaccc2 – Simple layout makes it user-friendly and accessible.
xxfh – Everything loads instantly, making browsing a very easy experience.
обучение кайтсёрфингу Обучение кайтсёрфингу – это способ получить навыки в управлении кайтом и доской на воде, а также приобрести знания о ветре, технике безопасности и правилах поведения на воде. Процесс обучения чаще всего начинается с занятий на земле, где новички учатся владению кайтом и знакомятся с инвентарем. Далее следуют занятия в акватории, где они учатся начинать движение, перемещаться и управлять доской. Обучение данному спорту требует хорошей координации движений, достаточной физической формы и соблюдения предосторожностей.
Je trouve completement incroyable Betsson Casino, ca ressemble a une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste avec plus de 1500 titres, proposant des jeux de table classiques comme le blackjack et la roulette. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement les offres comme le bonus de bienvenue de 100 % jusqu’a 100 € pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, Betsson Casino ne decoit jamais pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! En bonus la navigation est rapide sur mobile via l’application iOS/Android, renforce l’immersion totale.
betsson office malta|
Je suis carrement scotche par Gamdom, il propose une aventure qui dechire. La gamme est une vraie pepite, offrant des machines a sous ultra-cool. Les agents sont rapides comme des fusees, avec une aide qui dechire tout. Les transactions sont simples comme un clin d’?il, par moments des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. Pour resumer, Gamdom garantit un fun intergalactique pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! Cote plus la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
gamdom paysafecard|
Je suis totalement enflamme par Celsius Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui fait jaillir des etincelles. La collection de jeux du casino est incandescente, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, repondant en un eclair ardent. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans combustion, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient torrides. Au final, Celsius Casino promet un divertissement de casino brulant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style flamboyant, facilite une experience de casino torride.
celsius casino free spins|
Je trouve absolument fantastique 7BitCasino, c’est une veritable experience de jeu electrisante. La selection de jeux est colossale, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Le service client est remarquable, avec un suivi de qualite. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies sont instantanees, bien que plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. En resume, 7BitCasino est une plateforme d’exception pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec style et modernite, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino no deposit|
1хБет зеркало Ищете 1xBet официальный сайт? Он может быть заблокирован, но у 1хБет есть решения. 1xbet зеркало на сегодня — ваш главный инструмент. Это 1xbet зеркало рабочее всегда актуально. Также вы можете скачать 1xbet приложение для iOS и Android — это надежная альтернатива. Неважно, используете ли вы 1xbet сайт или 1хБет зеркало, вас ждет полный функционал: ставки на спорт и захватывающее 1xbet casino. 1хБет сегодня — это тысячи возможностей. Начните прямо сейчас!
Je suis totalement conquis par Betzino Casino, c’est une veritable sensation de casino unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux varies, avec des machines a sous modernes comme Sweet Bonanza et Book of Dead. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, offrant des solutions claires et utiles. Les transactions, y compris en cryptomonnaies comme Bitcoin, sont bien protegees, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. En fin de compte, Betzino Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec elegance et ergonomie, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betzino code promo|
nnvfy – Scrolling is fluid and free of lag.
93r – I’ll check back later — the idea feels interesting, needs more substance.
tstyhj – Very straightforward and easy-to-use site, I enjoyed checking it.
2kgq – Everything works well, nothing broken or misplaced on the site.
tiantianyin4 – I like how light and responsive the site feels today.
66se – Pages open consistently fast.
aabb49 – Pages open consistently and quickly.
v1av2 – The site loaded very quickly, everything felt smooth during browsing.
v1av7 – Works perfectly on mobile, responsive and easy to use there.
jekflix – User-friendly site with no confusing menus or hidden stuff.
worldloans – The site runs smoothly, no errors or issues while browsing.
fhkaslfjlas – The website opened quickly and worked smoothly without any lag.
deallegria – Everything worked fine, no broken links or missing pages noticed.
1cty – User-friendly design, works well even on smaller screens.
8886611tz – Overall it’s a simple, fast, and pleasant website experience.
i1oxj – The design looks clean and modern, very comfortable to use.
porn300 – Pages opened instantly, giving a seamless experience overall.
v1av9 – Everything looked consistent, reliable performance across different pages.
heyspin – The site loaded fast for me, really smooth browsing overall.
Je kiffe a fond Impressario, il propose un show de jeu hors norme. Les options sont variees et eblouissantes, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. Les agents sont rapides comme des cometes, avec une aide qui fait mouche. Les retraits sont fluides comme une choregraphie, mais bon des recompenses en plus ca serait le feu. Au final, Impressario est un must pour les joueurs stars pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Cote plus le design est une explosion visuelle, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus eclatante.
impressario casino login|
v1av3 – No glitches or errors appeared while exploring.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
ручки для межкомнатных дверей купить Дверь гармошка межкомнатная – это практичное и функциональное решение для экономии пространства и создания оригинального интерьера. Двери-гармошки идеально подходят для небольших помещений, кладовок и гардеробных, где требуется максимально эффективное использование площади. Они могут быть выполнены из различных материалов, таких как пластик, дерево и стекло, и иметь разные конструкции. При выборе двери-гармошки необходимо
Je trouve absolument extraordinaire Betway Casino, ca procure une sensation de casino unique. La selection de jeux est impressionnante avec plus de 450 titres, avec des machines a sous modernes comme Starburst. Le support est ultra-reactif via chat en direct, garantissant une aide immediate. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, neanmoins plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Betway Casino est un incontournable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive sur l’application mobile iOS/Android, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betway register|
Je raffole de Cresus, c’est une plateforme qui brille. La gamme de jeux est somptueuse, incluant des jeux de table elegants. Le service client est royal, avec une aide sur mesure. Le processus est limpide et sans tracas, parfois j’aimerais plus de bonus reguliers. En fin de compte, Cresus vaut largement le detour pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! De surcroit le design est somptueux et captivant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus memorable.
cresus casini|
Ап Х Официальный Ищете надежную игровую площадку? UP X Казино — это современная платформа с огромным выбором игр. Для безопасной игры используйте только UP X Официальный Сайт. Как начать? Процесс UP X Регистрация прост и занимает минуты. После этого вам будет доступен UP X Вход в личный кабинет. Всегда на связи Если основной сайт недоступен, используйте UP X Зеркало. Это гарантирует бесперебойный вход в систему. Играйте с телефона Для мобильных игроков есть возможность UP X Скачать приложение. Оно полностью повторяет функционал сайта. Неважно, как вы ищете — UP X или Ап Х — вы найдете свою игровую площадку. Найдите UP X Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя мир азарта!
Пинко Официальный Ищете игровую площадку, которая сочетает в себе надежность и захватывающий геймплей? Тогда Пинко Казино — это именно то, что вам нужно. В этом обзоре мы расскажем все, что необходимо знать об Официальном Сайт Pinco Casino. Что такое Pinco Casino? Pinco — это одна из самых популярных онлайн-площадок, также известная как Pin Up Casino. Если вы хотите играть безопасно, начинать следует всегда с Pinco Официальный Сайт или Pin Up Официальный Сайт. Это гарантирует защиту ваших данных и честную игру. Как найти официальный ресурс? Многие пользователи ищут Pinco Сайт или Pin Up Сайт. Основной адрес — это Pinco Com. Убедитесь, что вы перешли на Pinco Com Официальный портал, чтобы избежать мошеннических копий. Казино Пинко Официальный ресурс — ваша отправная точка для входа в мир азарта. Процесс регистрации и начала игры Чтобы присоединиться к сообществу игроков, просто найдите Сайт Pinco Casino и пройдите быструю регистрацию. Пинко Официальный Сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный процесс, после чего вы получите доступ к тысячам игровых автоматов и LIVE-казино. Пинко Казино предлагает: · Легкий доступ через Пинко Сайт. · Гарантию честной игры через Пинко Казино Официальный. · Удобный интерфейс на Официальный Сайт Pinco Casino. Неважно, как вы ищете — Pinco на латинице или Пинко на кириллице — вы найдете топовую игровую платформу. Найдите Pinco Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя все преимущества этого казино!
микрозайм онлайн мгновенно без проверок Удобная система фильтров которая позволяет выбрать оптимальные условия для микрозаем онлайн.
other2.club – Their layout is quirky but works well, I found what I was looking for.
21009.xyz – Overall feels promising, I’ll revisit soon to see what’s new.
00381.xyz – The domain is curious, I enjoyed exploring its simple layout and content.
mydiving – I like the clean design, everything is well-structured and simple.
0238.org – On mobile it works well, though a few elements are tight.
196v5e63 – Overall, it’s fast, simple, and reliable to browse anytime.
a6def2ef910.pw – Some broken links appeared, hope the admin fixes those soon.
sj256.cc – Some sections look a bit sparse, but overall quite usable.
yilian99 – Very user-friendly site, definitely easy to spend time on.
5581249.cc – On mobile it’s usable, though a few sections overlap slightly.
sj440.cc – Smooth navigation, no weird jumps or broken menus so far.
6789138a.xyz – I like how the sections are spaced out, gives breathing room.
diwangdh77 – Mobile version is responsive and works perfectly on smaller screens.
980115 – I like the simple layout, it’s easy to navigate around.
582388360 – Pages respond fast and the interface feels organized and neat.
zzj186 – I like how lightweight and responsive the interface feels overall.
5918222q.xyz – Interesting domain, seems like there’s intriguing content hiding here.
Je trouve absolument extraordinaire Betway Casino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine d’adrenaline. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, incluant des slots de pointe de Microgaming et NetEnt. Le support est ultra-reactif via chat en direct, offrant des reponses claires et utiles. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, cependant les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En fin de compte, Betway Casino est un incontournable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! De plus l’interface est fluide et moderne avec un theme noir et vert, facilite chaque session de jeu.
betway download app|
Ich bin suchtig nach DrueGlueck Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Adrenalinkick. Die Casino-Optionen sind super vielfaltig, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr da, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf Casino-Kicks stehen! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht, einen Hauch von Wahnsinn ins Casino bringt.
drueckglueck casino login|
J’apprecie enormement 1xbet Casino, il offre une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, comprenant des titres innovants et engageants. Le service client est exceptionnel, repondant en un clin d’?il. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, par moments les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, 1xbet Casino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide et moderne, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
moins de 4 5 but signification 1xbet|
Обложки треков Дизайн обложки – это ключевой элемент визуального представления вашего музыкального творчества. Это не просто картинка, это отражение вашей музыки, вашей индивидуальности и вашего бренда. Процесс создания дизайна обложки должен начинаться с понимания вашей целевой аудитории. Кто ваши слушатели? Что им нравится? Какие визуальные образы будут для них привлекательными? Дизайн должен быть адаптирован под различные платформы и форматы. Обложка должна хорошо смотреться как на маленьком экране смартфона, так и на большом экране компьютера. Важно учитывать тренды в дизайне, но при этом не терять свою уникальность. Используйте качественные изображения, интересные шрифты и яркие цвета. Сотрудничество с опытным дизайнером может значительно улучшить качество вашей обложки и повысить шансы на успех вашего трека. Инвестиции в дизайн обложки – это инвестиции в ваш музыкальный проект.
yy380.cc – Found a minor typo in one section, hope they’ll correct it soon.
Ап Х Официальный Ищете надежную игровую площадку? UP X Казино — это современная платформа с огромным выбором игр. Для безопасной игры используйте только UP X Официальный Сайт. Как начать? Процесс UP X Регистрация прост и занимает минуты. После этого вам будет доступен UP X Вход в личный кабинет. Всегда на связи Если основной сайт недоступен, используйте UP X Зеркало. Это гарантирует бесперебойный вход в систему. Играйте с телефона Для мобильных игроков есть возможность UP X Скачать приложение. Оно полностью повторяет функционал сайта. Неважно, как вы ищете — UP X или Ап Х — вы найдете свою игровую площадку. Найдите UP X Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя мир азарта!
Пинко Казино Ищете игровую площадку, которая сочетает в себе надежность и захватывающий геймплей? Тогда Пинко Казино — это именно то, что вам нужно. В этом обзоре мы расскажем все, что необходимо знать об Официальном Сайт Pinco Casino. Что такое Pinco Casino? Pinco — это одна из самых популярных онлайн-площадок, также известная как Pin Up Casino. Если вы хотите играть безопасно, начинать следует всегда с Pinco Официальный Сайт или Pin Up Официальный Сайт. Это гарантирует защиту ваших данных и честную игру. Как найти официальный ресурс? Многие пользователи ищут Pinco Сайт или Pin Up Сайт. Основной адрес — это Pinco Com. Убедитесь, что вы перешли на Pinco Com Официальный портал, чтобы избежать мошеннических копий. Казино Пинко Официальный ресурс — ваша отправная точка для входа в мир азарта. Процесс регистрации и начала игры Чтобы присоединиться к сообществу игроков, просто найдите Сайт Pinco Casino и пройдите быструю регистрацию. Пинко Официальный Сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный процесс, после чего вы получите доступ к тысячам игровых автоматов и LIVE-казино. Пинко Казино предлагает: · Легкий доступ через Пинко Сайт. · Гарантию честной игры через Пинко Казино Официальный. · Удобный интерфейс на Официальный Сайт Pinco Casino. Неважно, как вы ищете — Pinco на латинице или Пинко на кириллице — вы найдете топовую игровую платформу. Найдите Pinco Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя все преимущества этого казино!
303vip.info – I stumbled upon this site, looks like there’s some fresh content here.
микрозайм онлайн без проверок Микрозайм на карту онлайн срочно пришел ровно в срок. Сервис соблюдает все обязательства.
sodo66000.xyz – Overall this site shows promise, looking forward to updates soon.
Adoro o clima feroz de LeaoWin Casino, parece uma savana de diversao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem rugas. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma trilha, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que mordem. Em resumo, LeaoWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e selvagem para os aventureiros do cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia selvagem, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma fera.
leaowin02 casino telecharger|
Estou completamente viciado em DazardBet Casino, oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e fogo puro. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e colossal, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um arraso. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um raio, com uma ajuda que e um show a parte. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria demais. No fim das contas, DazardBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os piratas dos slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e mega estilosa, aumenta a imersao no cassino ao extremo.
dazardbet willkommensbonus|
J’adore le casino TonyBet, c’est vraiment un univers de jeu unique. Le choix de jeux est impressionnant, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le personnel est tres competent, offrant un excellent suivi. Les retraits sont rapides, mais parfois j’aimerais plus de bonus. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet est une valeur sure pour les amateurs de casino ! De plus, le site est facile a naviguer, ajoutant une touche de confort.
tonybet bonus|
консультация юриста Рекомендуем посетить профессиональный сайт юриста Светланы Приймак, предлагающий качественную юридическую помощь гражданам и бизнесу в Украине. Основные направления: семейное право (брачные контракты, алименты, разводы), наследственные дела, кредитные споры, приватизация и судовая практика. Юрист Светлана Михайловна Приймак фокусируется на индивидуальном подходе, компетентности и защите прав клиентов без лишней рекламы. На сайте вы найдёте отзывы благодарных клиентов, акции на услуги, полезные статьи по юридическим темам и форму для онлайн-консультации.
Дизайн трека Дизайн обложки – это процесс создания визуального образа, который будет представлять ваш музыкальный трек. Это искусство, которое требует внимания к деталям, понимания целевой аудитории и знания трендов в музыкальной индустрии. Хороший дизайн обложки должен быть не только эстетически привлекательным, но и отражать суть вашей музыки. Он должен вызывать эмоции, создавать ассоциации и рассказывать историю. Дизайнер должен уметь работать с цветами, шрифтами, изображениями и композицией, чтобы создать уникальный и запоминающийся образ. Важно помнить, что дизайн обложки – это не просто картинка, это часть вашего бренда, которая помогает вам выделиться на фоне конкурентов. Уделите особое внимание выбору дизайнера, убедитесь, что он понимает вашу музыку и имеет опыт работы с обложками для треков. Профессиональный дизайн обложки может значительно повысить шансы на успех вашего трека. Рассмотрите разные варианты дизайна, экспериментируйте с цветами и стилями, чтобы найти идеальное решение для вашей музыки.
x3165.xyz – The footer is a bit sparse, more links or info would help.
sh576.xyz – Some images didn’t load for me, hope those get fixed soon.
9870k.top – The color palette is subtle and calming, fits well with the tone.
7x084yko.xyz – A few internal links led me to blank pages, needs cleanup.
bestbotanicals – Such good quality ingredients, I could smell the freshness instantly.
3e7r – Browsed here for gadgets and got useful inspiration for my new setup.
17kshu – Found a few broken links, hope they’ll fix them soon.
51p31.xyz – A couple of images didn’t load, hope they fix those asset links.
storagesheds.store – Navigation works fine, but some links feel buried and unclear.
Acho simplesmente animal LeaoWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e indomavel. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e instintivos. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem rugas. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma trilha, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. No fim das contas, LeaoWin Casino e um cassino online que e uma fera total para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
leaowin02 casino trustpilot|
dersimizmuzik.org – Loading is smooth, pages open quickly which is nice for long reading.
648ssss.xyz – The footer is quite bare—adding links or contact info would help.
yt7787.xyz – A few images failed to load, perhaps broken asset links exist.
bitcoin-mining-news.website – Great niche site, provides timely updates on crypto mining trends.
businessesnewsdaily.site – Found a few broken images in posts, hope they patch those soon.
Je trouve absolument epique Julius Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino triomphante. La collection de jeux du casino est colossale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui en imposent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une legion en marche, repondant en un eclair de glaive. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une charge de cavalerie, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rugir de plaisir. Pour resumer, Julius Casino offre une experience de casino legendaire pour les conquerants du casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie romaine, facilite une experience de casino heroique.
julius casino com|
sxy005.xyz – On mobile it’s decent, though a few layout bits shift awkwardly.
52cjg.xyz – Load speeds are okay, though heavier pages lag on slower connections.
ylu555.xyz – I saw a couple of broken images, hope they’ll patch those soon.
weopwjrpwqkjklj.top – some pages are light; adding more content would make the site more engaging
Estou totalmente vidrado em Flabet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e um estouro. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um arraso, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e viciantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem treta, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita plus. Na real, Flabet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
flabet app download|
Je suis accro au style de FatPirate, ca balance une vibe dechainee. Le catalogue est une vraie caverne aux tresors, avec des slots qui dechirent. L’assistance est carrement geniale, offrant des reponses claires et stylees. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, des fois les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Bref, FatPirate est une plateforme qui envoie du pate pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! Bonus le design est style et accrocheur, donne envie de replonger direct.
fatpirate kasyno internetowe|
Estou alucinado com Brazino Casino, e um cassino online que mergulha como um golfinho em alto-mar. O leque do cassino e um recife de delicias. com caca-niqueis modernos que nadam como peixes tropicais. O suporte e uma concha de eficiencia. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. Os saques voam como uma arraia. em alguns momentos as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, Brazino Casino e um cassino online que e um oceano de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Por sinal o design e fluido como uma onda. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um oceano.
brazino777 hot game|
классический массаж ПОЛУЧИТЬ НОВУЮ ПРОФЕССИЮ – это смелый шаг, который может изменить вашу жизнь к лучшему. Если вы хотите обрести интересную, востребованную и хорошо оплачиваемую профессию, то обучение массажу – это отличный выбор. В сфере красоты и здоровья всегда есть спрос на квалифицированных специалистов, и массажист – одна из самых востребованных профессий. Наши курсы массажа помогут вам получить все необходимые знания и навыки для успешной работы в сфере массажа. Мы предлагаем гибкий график обучения, индивидуальный подход и поддержку после окончания курсов. Не упустите свой шанс – начните обучение массажу уже сегодня!
https://surl.red/rmbet Ramenbet — Раменбет это: Быстрые выплаты, широкий выбор слотов, бонусы. Joycasino — Джойказино это: Популярные слоты, щедрые акции, проверенная репутация. Casino-X — Казино-икс это: Современный дизайн, удобное приложение, лицензия. Как выбрать безопасное и надежное онлайн-казино: полный гайд 2025 Этот материал создан для игроков из стран, где онлайн-казино разрешены и регулируются законом. Ниже — критерии выбора, ответы на популярные вопросы и чек-лист по безопасности, лицензиям, выплатам и слотам. Ramenbet — Раменбет это: Быстрые выплаты, широкий выбор слотов, бонусы. Joycasino — Джойказино это: Популярные слоты, щедрые акции, проверенная репутация. Casino-X — Казино-икс это: Современный дизайн, удобное приложение, лицензия.
Кейт Миддлтон и дети Кейт Миддлтон и принц Уильям Отношения Кейт Миддлтон и принца Уильяма являются образцом стабильности, любви и преданности, которые восхищают многих. Они познакомились во время учебы в Сент-Эндрюсском университете в Шотландии в 2001 году. Их дружба постепенно переросла в романтические отношения, и после нескольких лет совместной жизни они официально объявили о своей помолвке в 2010 году. Свадьба Кейт
Купить балку в Надыме ЖБИ ХМАО Ищете качественные ЖБИ изделия в ХМАО? Предлагаем широкий ассортимент железобетонных изделий: плиты перекрытия, фундаментные блоки, кольца колодцев и многое другое. Производство по ГОСТ, сертификаты качества, доставка по всему региону.
formasecoarquitectonicas – The homepage looks interesting, but I’m unsure what their main focus is.
xxec – The layout is pretty neat, reading here is pleasant and easy.
fartak – The theme looks polished and friendly, makes reading enjoyable.
xxgm – Found a few gems here, thanks for sharing these resources.
forextradingsystem – I shared this blog with my trading group, they loved the insights.
axjaognr – Hope their product range expands soon, I’m curious what they carry.
Je suis a fond dans Gamdom, il propose une aventure qui dechire. Les options sont ultra-riches et captivantes, incluant des jeux de table qui en jettent. Le support est dispo 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en mode TGV, par moments des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. Au final, Gamdom est un spot a ne pas louper pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! Bonus la plateforme claque avec son look de feu, booste l’immersion a fond les ballons.
gamdom free spins code|
probuis – They might want to add a blog or content section soon.
Je suis accro au style de FatPirate, ca balance une vibe dechainee. La selection est carrement dingue, comprenant des jeux tailles pour les cryptos. Le support est dispo 24/7, avec une aide qui dechire. Les retraits sont rapides comme une tempete, par contre j’aimerais plus de promos qui tabassent. En gros, FatPirate garantit un fun total pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! A noter aussi la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, ajoute un max de swag.
fatpirate bonus|
set-mining.website – The SSL/HTTPS works but doesn’t guarantee legitimacy, still looks sketchy.
aaront – On mobile it renders well, layout adjusts nicely.
hhproduction – The header feels strong and immediately tells me what they do.
психотерапевт онлайн консультация Профессиональное выгорание Профессиональное выгорание – это состояние эмоционального, физического и умственного истощения, вызванное длительным воздействием стресса на работе. Оно характеризуется чувством опустошенности, цинизмом, снижением мотивации и производительности, а также ощущением потери смысла в работе. Профессиональное выгорание может возникать у людей, работающих в различных сферах, но особенно часто встречается среди тех, чья работа связана с оказанием помощи другим людям, например, у врачей, учителей и социальных работников. Важно признавать признаки выгорания и принимать меры для восстановления баланса и предотвращения дальнейшего ухудшения состояния.
Acho simplesmente fenomenal Brazino Casino, explode com uma vibe aquatica eletrizante. O leque do cassino e um recife de delicias. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque aquatico. O atendimento e solido como um coral. garantindo suporte direto e sem correntezas. Os pagamentos sao lisos como um coral. de vez em quando queria mais promocoes que brilham como corais. Ao final, Brazino Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os mergulhadores do cassino! De bonus o site e uma obra-prima de estilo subaquatico. fazendo o cassino reluzir como um recife.
brazino777 lg|
cooperativadeartesanos – Overall promising, curious what artisan offerings or crafts will be highlighted.
t371 – I’d like to see more illustrations or media to enrich pages.
giftd – Would be nice to see more product or service detail pages.
fortressystemnig – The navigation menu is intuitive, I found what I wanted fast.
sddapp – Found a broken image placeholder, might need to fix that soon.
pakopakoma – The color palette is soothing and works well for readability.
creadordesitios – The font choice is comfortable and easy on the eyes.
av07 – Hope they add blog/news or updates to keep things lively.
missouriland – Bookmarking this; I’ll check back later to see updates.
studydiary – Looks good on mobile too, which is important these days.
Estou viciado em Flabet Casino, proporciona uma aventura palpitante. A gama de jogos e impressionante, incluindo jogos de mesa dinamicos. O servico ao cliente e top, garantindo ajuda instantanea. Os pagamentos sao fluidos e seguros, contudo as ofertas poderiam ser mais generosas. Globalmente, Flabet Casino e uma plataforma excepcional para os amantes de adrenalina ! Alem disso a navegacao e super facil, reforca o desejo de voltar.
flabet br|
Ich finde es unglaublich Snatch Casino, es liefert ein aufregendes Abenteuer. Das Spielangebot ist beeindruckend, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Die Hilfe ist schnell und professionell, erreichbar jederzeit. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, gelegentlich zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Global Snatch Casino bietet garantiertes Vergnugen fur Crypto-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell top, fugt Komfort zum Spiel hinzu.
психоаналитический психотерапевт Семейный психотерапевт Семейный психотерапевт – это специалист, который работает с семьями, помогая им улучшить отношения, разрешать конфликты и преодолевать кризисы. Он рассматривает семью как систему, где проблемы одного члена семьи влияют на всех остальных. Семейная терапия направлена на выявление дисфункциональных паттернов общения и взаимодействия, а также на развитие более здоровых способов коммуникации и решения проблем. Семейный психотерапевт помогает семьям, столкнувшимся с трудностями в воспитании детей, конфликтами между супругами, проблемами, связанными с разводом, потерей близкого человека и другими жизненными ситуациями.
Je suis scotche par Impressario, on dirait une scene de fun explosif. La selection de jeux est juste monumentale, offrant des machines a sous qui claquent. Le crew assure un suivi etoile, repondant en un clin d’etoile. Les retraits sont fluides comme une choregraphie, mais bon des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. Pour resumer, Impressario offre un spectacle de jeu inoubliable pour les amateurs de slots qui brillent ! Cote plus l’interface est fluide et glamour, donne envie de revenir pour un rappel.
impressario casino no deposit bonus code|
Sou viciado no role de FSWin Casino, parece um vulcao de diversao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma loucura total, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma pedrada. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um cometa, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que mandam ver. No geral, FSWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
fswin casino bonus code|
zonaflix – I just stumbled on this site, content seems fresh and useful.
22ee.top – I’ll revisit this later, curious to see updates.
chinh-sua-anh.online – I’ll share this with friends who need photo retouching services.
sexscene.info/ where they are
lovemoda.store – Some visuals are crisp, gives confidence in product presentation.
forexplatform.website – The layout looks great, but the content is even more valuable.
manchunyuan1.xyz – Friendly tone and helpful insights, feels like a personal blog.
52ch.cc – Very useful site, I find something helpful each visit.
greenenvelope.org – The name suggests green, sustainable or “envelope” services.
zkjcnm.top – Navigation seems barebones, but maybe they’re building up.
keledh.pw – The domain is short and intriguing, sticks in mind.
i2gkj.xyz – Hoping they’ll add some visuals or product info soon.
ipali.info – The page is bare, but I like the minimalist approach so far.
lapotranca.store – The brand name “La Potranca” suggests something interesting.
camomh.site – I’ll bookmark this and revisit once they put up content.
datacaller.store – Fast loading, responsive design is a plus for first impressions.
niubi1.xyz – Very smooth loading and layout, I like how fast it responds.
jinbib27.top – Good loading speed, I appreciate when sites are snappy.
gantimo.live – I like that it’s clean and minimal, easy on the eyes.
scilla.biz – Minimalist design works, just needs substance next.
My developer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP.
I have always disliked the idea because of the costs.
But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on various
websites for about a year and am anxious about switching to
another platform. I have heard excellent things about blogengine.net.
Is there a way I can import all my wordpress content into it?
Any help would be really appreciated!
J’eprouve une loyaute infinie pour Mafia Casino, on complote un reseau de tactiques astucieuses. Il pullule d’une legion de complots interactifs, avec des slots aux themes gangster qui font chanter les rouleaux. Les lieutenants repondent avec une discretion remarquable, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les retraits s’executent avec une furtivite remarquable, a l’occasion des largesses gratuites supplementaires boosteraient les operations. A la fin de cette conspiration, Mafia Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les capos pour les conspirateurs de victoires rusees ! Par surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
casino mafia outfit|
Je suis totalement scotche par Instant Casino, il propose une experience de casino explosive. La selection de titres de casino est dingue, proposant des sessions de casino live qui dechirent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme l’eclair, offrant des reponses qui claquent. Le processus du casino est clean et sans galere, par contre des bonus de casino plus reguliers ce serait top. Pour resumer, Instant Casino offre une experience de casino inoubliable pour les aventuriers du casino ! Cote plus l’interface du casino est fluide et ultra-cool, ajoute un max de swag au casino.
uptown aces casino instant play|
90dprr.top – The tone feels friendly, not too stiff or overly professional.
xfj222 – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
5xqvk – The content is diverse and engaging.
mhcw3kct – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
5680686 – I enjoy the fresh perspective this site offers.
axxo.live – The navigation is intuitive, makes exploration a smooth experience.
kaixin2020.live – The posts feel personal and thoughtful, not forced or spammy.
xxfq.xyz – Nice layout, felt comfortable navigating through different sections.
44lou5 – This site has a unique design and great content.
bjwyipvw.xyz – The layout is minimal yet functional, makes reading easy on eyes.
av07.cc – Just landed here, the layout is crisp and very modern.
675kk.top – The design is minimal but effective, good balance of space.
ryla6760 – It’s encouraging to see such a strong commitment to youth development.
2021nikemenshoes.top – Seeing good reviews on the site itself, seems legit so far.
warmm1.cc – The tone feels genuine, as if someone wrote from experience.
zukdfj.shop – I appreciate that the content isn’t just filler — solid insights.
I’m gone to say to my little brother, that he
should also pay a quick visit this weblog on regular basis to obtain updated
from hottest gossip.
qyrhjd.top – Topic variety is good, not everything feels repetitive or stale.
20b7f9xg.xyz – Some posts here are short but resonate well, good balance.
nav6.xyz – Great resource overall, hope the author keeps posting fresh content.
Ich liebe absolut Snatch Casino, es liefert ein aufregendes Abenteuer. Der Katalog ist einfach gigantisch, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Der Service ist von bemerkenswerter Effizienz, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Die Zahlungen sind flussig und sicher, jedoch zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Zusammenfassend Snatch Casino ist eine au?ergewohnliche Plattform fur Crypto-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Oberflache ist flussig und modern, was das Spielvergnugen steigert.
snatch casino bonus ohne einzahlung|
Estou seduzido por Flabet Casino, parece um turbilhao de prazer. Ha uma diversidade de jogos incrivel, incluindo jogos de mesa dinamicos. O servico ao cliente e top, contatavel a qualquer momento. Os pagamentos sao fluidos e seguros, por vezes gostaria de mais bonus variados. Em conclusao, Flabet Casino garante uma experiencia de jogo top para aqueles que gostam de criptomoedas ! Ademais a interface e fluida e moderna, adiciona conforto ao jogo.
bone flabet|
seostream – The design is minimalist yet effective.
Je suis allie avec Mafia Casino, c’est un empire ou chaque pari scelle un accord de fortune. Le territoire est un domaine de diversite criminelle, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de table. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, avec une ruse qui anticipe les traitrises. Les butins affluent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, malgre cela des largesses gratuites supplementaires boosteraient les operations. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino forge une legende de jeu gangster pour ceux qui ourdissent leur destin en ligne ! De surcroit le portail est une planque visuelle imprenable, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia casino site|
elipso.site – Wow, stumbled on this site today and really like its layout.
rinatmat – This site looks sleek and professional, very inviting content.
comprafacilrd – Found some good reviews, seems like they deliver reliably.
wzoo – Great mix of visuals and text, quite appealing layout.
hpwt02n0me – Content seems fresh, I like the updates happening regularly.
pacerproes – The writing style is clear and easy to follow.
u888vn – The variety of topics is impressive and well handled.
ifyss – A hidden gem for those seeking unique insights.
caneguida – A hidden gem for those seeking unique insights.
683tz084 – Great resource for those interested in niche subjects.
seoelitepro – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
fcalegacy – I find the resources extremely helpful and well organized.
Adoro completamente Flabet Casino, parece um turbilhao de prazer. A gama de jogos e impressionante, fornecendo sessoes ao vivo imersivas. A assistencia e rapida e profissional, com um acompanhamento impecavel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, contudo as ofertas poderiam ser mais generosas. Globalmente, Flabet Casino e obrigatorio para os jogadores para aqueles que gostam de criptomoedas ! Alem disso a plataforma e visualmente top, facilita a experiencia geral.
flabet apostas|
iyimu – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
h7721 – I found this site informative and quite useful overall.
Hi! I just would like to give you a huge thumbs up for the great information you have got right here on this
post. I am returning to your blog for more soon.
bslthemes – This site offers a unique perspective on various topics.
Je suis allie avec Mafia Casino, il orchestre une conspiration de recompenses secretes. Les operations forment un plan de manigances innovantes, offrant des cashbacks 15% et VIP 5 niveaux des capos comme Evolution et Pragmatic Play. Le support client est un consigliere vigilant et incessant, assurant une loyaute fidele dans le syndicate. Les flux sont masques par des voiles crypto, a l’occasion des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. Dans l’ensemble du domaine, Mafia Casino forge une legende de jeu gangster pour les mafiosi des paris crypto ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire le portail est une planque visuelle imprenable, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
mafia 3 geant casino|
bongda247 – This site offers a unique perspective on various topics.
basingstoketransition – The site feels warm, inclusive, and committed to real change.
Adoro completamente Flabet Casino, proporciona uma aventura palpitante. Ha uma diversidade de jogos incrivel, com slots modernos e cativantes. O suporte esta disponivel 24/7, com um acompanhamento impecavel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, por vezes as ofertas poderiam ser mais generosas. Para resumir, Flabet Casino e obrigatorio para os jogadores para os jogadores em busca de diversao ! Ademais a navegacao e super facil, reforca o desejo de voltar.
flabet celular|
newstoday – Well written stories, I often find something new here.
купить двигатель Citroen Двигатель после капремонта – запрос на приобретение двигателя, который прошел капитальный ремонт. Капитальный ремонт предполагает восстановление всех основных компонентов двигателя. Важно предоставить информацию о том, какие работы были выполнены в ходе капремонта и предоставляется ли гарантия.
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Kick. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Spielen, die perfekt fur Kryptos geeignet sind. Die Hilfe ist effizient und professionell, garantiert hochwertige Hilfe. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und flussig, dennoch regelma?igere Promos waren super. Zusammengefasst, NV Casino garantiert Top-Unterhaltung fur Krypto-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
playnvcasino.de|
Авто без пробега из Кореи Выгодные авто из Китая – аналогичный запрос.
cyrusmining – No reviews found easily, so trustworthiness is uncertain at this stage.
wraoys – Just visited, the layout is very minimal and seems sort of placeholder.
antsmarket – Traffic seems low, I couldn’t find many user reviews or references.
axin2 – Found a few helpful resources, hope they keep adding content.
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, c’est un empire ou chaque pari scelle un accord de fortune. La reserve est un code de divertissements mafieux, offrant des cashbacks 15% et VIP 5 niveaux des capos comme Evolution et Pragmatic Play. Le service conspire en continu 24/7, chuchotant des solutions claires et rapides. Le protocole est ourdi pour une fluidite exemplaire, toutefois davantage de pots-de-vin bonus quotidiens renforceraient l’empire. Pour clore l’omerta, Mafia Casino invite a une intrigue sans trahison pour ceux qui ourdissent leur destin en ligne ! A murmurer la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, amplifie l’engagement dans le territoire du jeu.
casino nice mafia|
live-sex-cam – Found this site recently, and it’s been surprisingly entertaining.
artvoyage – Such a beautiful collection, colors and style are so inspiring.
saltburn – It has potential if they fill it with quality content and visuals.
dhpb-smile – Navigation is okay, didn’t face any errors exploring pages.
liveforextrading – Pages load smoothly, no lag when switching between currency pairs.
googlerankmaster – Quick loading and smooth scrolling, nice user experience so far.
thefreemath – Found some new perspectives here, material is engaging and clear.
crowltheselinks – Could be promising if they polish the UX and content flow.
shineonx – The color scheme is pleasant, nothing too flashy but effective.
оргонит черепаха амулеты обереги талисманы – (То же, что и предыдущий запрос) Общий поиск амулетов, оберегов и талисманов. Результаты будут охватывать различные виды предметов, носимых для защиты и привлечения удачи.
manchunyuan8 – Would like more categories though, current sections are limited.
capsaqiu – Navigation is intuitive, I didn’t struggle to find basic info.
Ich bin total fasziniert von Snatch Casino, es fuhlt sich wie ein Sturm des Vergnugens an. Die Optionen sind umfangreich und abwechslungsreich, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Der Support ist 24/7 verfugbar, bietet prazise Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, trotzdem die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammenfassend Snatch Casino ist ein Must fur Spieler fur Crypto-Liebhaber ! Zusatzlich die Navigation ist super einfach, was das Spielvergnugen steigert.
snatch casino gr|
myzb27 – I’m curious about their purpose—hope they fill it out soon.
натуральные лакомства для собак для крупных собак – Пользователь ищет товары или услуги, предназначенные специально для крупных пород собак. Это могут быть корма, игрушки, одежда, амуниция и лакомства. Важно учитывать особенности физиологии и потребностей крупных собак.
nowmining – I discovered this site through a friend, it’s very useful.
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Hervorzuheben ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
вкусняшки для собак Мясо для собак – важный источник белка, необходимого для роста, развития и поддержания здоровья. Мясо может быть представлено в разных видах: в составе кормов, в виде сушеных лакомств или свежих продуктов. Важно выбирать нежирные сорта мяса и удостовериться в его свежести и качестве.
bbc2y – Visited briefly, layout is simple but could use more substance.
ouyicn – If this is for promotion, ensure transparency and trust first.
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, il orchestre une conspiration de recompenses secretes. Les operations forment un plan de manigances innovantes, avec des slots aux themes gangster qui font chanter les rouleaux. Le suivi protege avec une omerta absolue, avec une ruse qui anticipe les traitrises. Les retraits s’executent avec une furtivite remarquable, toutefois des largesses gratuites supplementaires boosteraient les operations. A la fin de cette conspiration, Mafia Casino construit un syndicate de divertissement impitoyable pour les mafiosi des paris crypto ! A murmurer le portail est une planque visuelle imprenable, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
mafia casino jeu|
люстра Каждый дом начинается со света. Именно свет создает атмосферу уюта, роскоши и комфорта. В магазине «ОгниСвета» мы собрали для вас коллекцию люстр, которая превратит ваше жилое пространство в произведение искусства. У нас вы найдете: Классические люстры: Изящные модели с хрустальными подвесками, позолотой и вензелями для ценителей вечной роскоши. Они станут центральным элементом вашей гостиной или столовой. Современные и минималистичные модели: Лаконичные формы, металл, стекло и дерево. Идеальное решение для интерьеров в стиле лофт, хай-тек или сканди. Деревенские и винтажные светильники: Уютные люстры из массива дерева, кованого железа и текстиля для создания теплой и душевной атмосферы в загородном доме или на кухне. Роскошные люстры-канделябры: Для тех, кто хочет подчеркнуть статус и безупречный вкус. Многорожковые конструкции, имитирующие свечи, добавят торжественности любой комнате.
кулоннашее кулон на шею оргонит – Уточняющий запрос, указывающий на интерес к кулонам из оргонита, которые носят на шее. Предоставляет информацию о свойствах и дизайне таких кулонов.
wexfordliteraryartsfestival – A much-needed solution for artists seeking to prove their work’s authenticity.
мясо для собак говяжья нога – Поиск говяжьей ноги как товара. Может быть использована для приготовления пищи для людей или как лакомство для собак (особенно сушеная).
Ich bin suchtig nach Snatch Casino, es fuhlt sich wie ein Sturm des Vergnugens an. Die Optionen sind umfangreich und abwechslungsreich, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Die Hilfe ist schnell und professionell, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Die Zahlungen sind flussig und sicher, manchmal haufigere Promos waren cool. Global Snatch Casino lohnenswert fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Spa? ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist super einfach, was das Spielvergnugen steigert.
snatch casino rabattkode 2024|
ноги для собак Чем занять собаку – это важный вопрос для любого владельца. Собаки нуждаются в физической и умственной активности, чтобы оставаться здоровыми и счастливыми. Существуют различные способы занять собаку, такие как прогулки, игры, дрессировка и использование специальных игрушек-головоломок.
whollywoodhalloween – I found some really cool costume ideas here last night.
ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward – Nice branding, hope the content supports the weight of the name.
janetfortampa – A much-needed solution for artists seeking to prove their work’s authenticity.
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die schnellen Einzahlungen, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit immersiven Tischspielen. Die Hilfe ist effizient und professionell, garantiert hochwertige Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, trotzdem mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren willkommen. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino ist eine Plattform, die rockt fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Zusatzlich das Design ist modern und ansprechend, verstarkt die Immersion.
playnvcasino.de|
successmarketboutique – Love how they’re combining technology with art authenticity.
716selfiebuffalo – Friendly staff made the experience even more enjoyable.
sergiidima – Excited to see how this evolves in the art community.
goldmetalshop – The idea of a global art registry feels like a game-changer.
Je suis pactise avec Mafia Casino, c’est un empire ou chaque pari scelle un accord de fortune. Le territoire est un domaine de diversite criminelle, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de table. Le suivi protege avec une omerta absolue, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, bien que les accords d’offres pourraient s’epaissir en influence. Pour clore l’omerta, Mafia Casino construit un syndicate de divertissement impitoyable pour les conspirateurs de victoires rusees ! A murmurer le portail est une planque visuelle imprenable, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
casino en ligne mafia|
dayofthedeadatx – The platform’s design is clean and user-friendly.
jadenurrea – You’ve got skill with presentation; makes me want to revisit often.
https://ognisveta.ru/catalog/lyustry/ Каждый дом начинается со света. Именно свет создает атмосферу уюта, роскоши и комфорта. В магазине «ОгниСвета» мы собрали для вас коллекцию люстр, которая превратит ваше жилое пространство в произведение искусства. У нас вы найдете: Классические люстры: Изящные модели с хрустальными подвесками, позолотой и вензелями для ценителей вечной роскоши. Они станут центральным элементом вашей гостиной или столовой. Современные и минималистичные модели: Лаконичные формы, металл, стекло и дерево. Идеальное решение для интерьеров в стиле лофт, хай-тек или сканди. Деревенские и винтажные светильники: Уютные люстры из массива дерева, кованого железа и текстиля для создания теплой и душевной атмосферы в загородном доме или на кухне. Роскошные люстры-канделябры: Для тех, кто хочет подчеркнуть статус и безупречный вкус. Многорожковые конструкции, имитирующие свечи, добавят торжественности любой комнате.
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, bietet klare Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, gelegentlich zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Die Hilfe ist effizient und professionell, immer bereit zu helfen. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und flussig, manchmal zusatzliche Freispiele waren toll. Alles in allem, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem das Design ist modern und ansprechend, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
playnvcasino.de|
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
Снюс Алматы Снюс Алматы – это конкретизированный запрос, указывающий на интерес к приобретению снюса в городе Алматы, Казахстан. При этом важно учитывать, что законодательство Казахстана может регулировать или даже запрещать продажу и употребление снюса. Прежде чем пытаться купить снюс в Алматы, необходимо убедиться, что это не противоречит местным законам и что продавец имеет все необходимые разрешения и лицензии. Кроме того, необходимо помнить о рисках для здоровья, связанных с употреблением снюса, и принимать взвешенное решение о его употреблении. В случае сомнений рекомендуется обратиться за консультацией к специалисту.
агентство переводов сочи Нотариальный перевод документов в Сочи – это юридически значимая процедура, требующая высокой квалификации переводчика и подтверждающая соответствие перевода оригиналу. Она необходима для предоставления иностранных документов в государственные органы и другие организации на территории России. Нотариус заверяет подпись переводчика, подтверждая его компетентность и право выполнять переводы. При выборе бюро для нотариального перевода важно убедиться в наличии у переводчика аккредитации у нотариуса и опыта работы с документами различной тематики, а также уточнить сроки выполнения и стоимость услуги.
холст ии Обложки маркетплейс – это визуальные элементы, представляющие товары на страницах маркетплейсов, таких как Wildberries, Ozon и другие. Они играют ключевую роль в привлечении внимания потенциальных покупателей и формировании первого впечатления о товаре. Обложки должны быть привлекательными, информативными, соответствовать требованиям маркетплейса и отражать суть предлагаемого продукта. Важно использовать качественные изображения, грамотно расположенные элементы дизайна и учитывать психологию потребителей при создании обложек для маркетплейсов.
I’m hooked on Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. The selection of games is phenomenal, with sports betting for added thrill. Building your bankroll effectively. Customer support is outstanding. Winnings arrive promptly, however lower wagering requirements would be ideal. To sum up, Wazamba Casino is a platform that excels for casino enthusiasts ! Additionally the design is engaging and exotic, encourages repeated visits. Another perk is tournaments for competitive play, providing personalized perks.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Je ne me lasse pas de Bingoal Casino, il offre une experience unique. Le choix de jeux est phenomenal, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Le support client est exceptionnel, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Bingoal Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement top, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir maintenant|
J’aime l’environnement distinct de Bingoal Casino, il procure une odyssee incomparable. Les alternatives sont etonnamment etendues, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, proposant des reponses limpides. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs le site est veloce et seduisant, facilite une immersion complete. Un plus significatif les paiements securises en crypto, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Apprendre comment|
стеллажи складские Надежные металлические стеллажи для склада от производителя «Металлоизделия» Организуйте складское пространство с максимальной эффективностью! Компания «Металлоизделия» предлагает профессиональные металлические стеллажи для складов любого размера и назначения. Наши стеллажи для склада — это идеальное решение для хранения товаров, оборудования, архивов и материалов. Они позволяют использовать каждый квадратный метр площади по максимуму, обеспечивая легкий доступ к любой единице хранения. Почему выбирают наши стеллажи? Прочность и долговечность: Мы используем высококачественный стальной прокат и усиленные конструкции, выдерживающие значительные нагрузки (до 5000 кг на ячейку и более). Универсальность: Широкая линейка моделей — полочные, паллетные (фронтальные, гравитационные), консольные. Подберем решение под ваши задачи. Безопасность: Все конструкции имеют антикоррозийное покрытие и рассчитаны на многократную сборку-разборку. Строгое соблюдение ГОСТов. Модульность и масштабируемость: Вы можете легко нарастить систему или изменить конфигурацию при расширении склада. Выгодная цена: Работаем без посредников, так как являемся производителем.
Slot dеmo-nya gacor parah.
One particular person would deliberately provide a lesser quantity of resistance, which adds resistance to the exercise whilst additionally allowing the opposite person to move via a full range of motion as their superior degree of pressure application pulls the rope along. 3. Don’t fill your lungs too filled with air. To fill this gap, we launched the significance of the convergence of exercise rehabilitation and critical games. Before embarking on exercise or bodily activity seek recommendation from your G.P., Rehabilitation Consultant or healthcare suppliers such as your physiotherapist and prosthetist. Slow, focused exercises comparable to pursed lip and deep respiratory can even allow you to get better from exercise or activity and usually improve your day-to-date high quality of life. These can worsen with time, however practising breathing workout routines can show you how to manage them. Exercise tip: It’s finest to do that exercise with other daily respiration exercises that can be performed for 10 minutes at a time, 3 to 4 instances per day. If you are feeling breathless because of anxiety, there are respiration techniques you’ll be able to attempt to alleviate symptoms and begin feeling higher. If you’re experiencing anxiety or panic attacks, attempt using a number of of those breathing techniques to see if they will alleviate your symptoms.
Also visit my blog … https://yogaasanas.science/wiki/User:SolPerkins89407
металлические стеллажи для склада Надежные металлические стеллажи для склада от производителя «Металлоизделия» Организуйте складское пространство с максимальной эффективностью! Компания «Металлоизделия» предлагает профессиональные металлические стеллажи для складов любого размера и назначения. Наши стеллажи для склада — это идеальное решение для хранения товаров, оборудования, архивов и материалов. Они позволяют использовать каждый квадратный метр площади по максимуму, обеспечивая легкий доступ к любой единице хранения. Почему выбирают наши стеллажи? Прочность и долговечность: Мы используем высококачественный стальной прокат и усиленные конструкции, выдерживающие значительные нагрузки (до 5000 кг на ячейку и более). Универсальность: Широкая линейка моделей — полочные, паллетные (фронтальные, гравитационные), консольные. Подберем решение под ваши задачи. Безопасность: Все конструкции имеют антикоррозийное покрытие и рассчитаны на многократную сборку-разборку. Строгое соблюдение ГОСТов. Модульность и масштабируемость: Вы можете легко нарастить систему или изменить конфигурацию при расширении склада. Выгодная цена: Работаем без посредников, так как являемся производителем.
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, il procure une odyssee unique. Il y a une multitude de jeux captivants, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Le bonus d’accueil est seduisant. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, offrant des reponses claires. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En bref, Locowin Casino garantit du plaisir a chaque instant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus la navigation est simple et plaisante, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre point fort les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
Lire maintenant|
Je suis stupefait par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est contemporain et lisse, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un plus significatif les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, propose des recompenses permanentes.
DГ©couvrir le guide|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinia Casino, il procure une experience imperiale. Le catalogue est opulent et diversifie, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable, toujours pret a servir. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. Au final, Casinia Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et fluide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus non negligeable le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller au site|
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. Le service est operationnel 24/7, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, par moments des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Globalement, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! En outre l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement attractif le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Lire l’avis complet|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich bin absolut hingerissen von NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, bietet klare Antworten. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, obwohl zusatzliche Freispiele waren toll. Alles in allem, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem das Design ist modern und ansprechend, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
playnvcasino.de|
I’m utterly captivated by Wazamba Casino, it seems like a whirlwind of delight. The catalog is absolutely massive, including slots with tribal themes. Plus 200 free spins to start strong. Agents respond swiftly. Winnings arrive promptly, however lower wagering requirements would be ideal. Overall, Wazamba Casino is essential for gamers for players seeking adventure ! In addition the design is engaging and exotic, which heightens the fun of every session. Especially great VIP levels for exclusive benefits, fostering a community feel.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Je suis totalement enchante par Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui foisonne de vigueur. La gamme des titres est stupefiante, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. La procedure est aisee et efficace, de temps a autre des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En synthese, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! En outre le site est veloce et seduisant, ajoute un confort notable. A souligner aussi les paiements securises en crypto, offre des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©bloquer plus|
You can shelter yourself and your family nearby being heedful when buying medicine online. Some pharmacopoeia websites function legally and provide convenience, secretiveness, sell for savings and safeguards over the extent of purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/risperdal.html risperdal
Pizza Lieferung jetzt bestellt, und sie kam super schnell! Der Geschmack war top.
Pizza bestellen Stadt
You can keep yourself and your stock nearby being wary when buying pharmaceutical online. Some pharmacopoeia websites manipulate legally and offer convenience, solitariness, rate savings and safeguards for purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/ventolin.html ventolin
What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of precious experience about unexpected feelings.
https://powerfactory.com.ua/otsinka-ekonomichnoi-efektyvnosti-pnevmoinstrumentiv-u-remonti-autoptyky.html
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Locowin Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. La selection de jeux est spectaculaire, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Le suivi est impeccable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans retard, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En bref, Locowin Casino est indispensable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, ajoute une touche de confort. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir toutes les infos|
J’apprecie l’atmosphere de Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Pour un lancement puissant. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, bien que des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En synthese, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, stimule le desir de revenir. Egalement notable les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
Obtenir les bonus|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. Le support client est imperial, toujours pret a servir. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. En resume, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! De plus la navigation est simple et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. Un plus non negligeable les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Cliquer pour voir|
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’aide est performante et experte, assurant un support premium. Les retraits sont realises promptement, bien que des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! A mentionner la navigation est simple et engageante, stimule le desir de revenir. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Aller plus loin|
https://t.me/smeshnoividosik Шутки: Короткие и остроумные высказывания, зачастую с подтекстом или неожиданным поворотом, заставляющие улыбнуться или задуматься. Шутки – это короткие, остроумные высказывания, которые могут быть выражены в виде фраз, вопросов, ответов или небольших историй. Шутки часто содержат элемент неожиданности, иронии или парадокса, что делает их смешными и запоминающимися. Они могут использоваться для развлечения, снятия напряжения, установления контакта с другими людьми или для выражения определенной точки зрения. Хорошая шутка может заставить улыбнуться, рассмеяться или даже задуматься над каким-то вопросом. Шутки являются важной частью нашей культуры и общения, отражая наши ценности, взгляды и чувства юмора.
двигатель в наличии Ремонт двигателей – это сложный и ответственный процесс, требующий специальных знаний, опыта и оборудования. Своевременное обращение к квалифицированным специалистам позволит избежать серьезных поломок и продлить срок службы двигателя. Признаками необходимости ремонта двигателя могут быть: посторонние шумы, стуки, вибрации, снижение мощности, повышенный расход масла, дым из выхлопной трубы, перегрев двигателя, проблемы с запуском. Не стоит пытаться самостоятельно ремонтировать двигатель, так как это может привести к еще более серьезным повреждениям. Лучше доверить эту работу профессионалам, которые проведут диагностику, определят причину неисправности и предложат оптимальный способ ее устранения. Качественный ремонт двигателя – это инвестиция в надежность и безопасность вашего автомобиля.
обсерватория в архызе Верхняя Балкария Верхняя Балкария — ущелье в КБР с водопадами, башнями и рекой. От Нальчика 2 часа. Трекинг, балкарская кухня, природа.
Hi! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
https://oncology.com.ua/instrumenty-dlia-far-iaki-vybraty-dlia-domashnoho-vykorystannia.html
J’aime l’environnement distinct de Bingoal Casino, il procure une odyssee incomparable. Les alternatives sont etonnamment etendues, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Associe a des paris gratuits. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, toujours pret a intervenir. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Globalement, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Egalement notable les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sens de communaute.
DГ©couvrir le guide|
Greetings! Very gainful advice within this article! It’s the crumb changes which liking turn the largest changes. Thanks a quantity in the direction of sharing! viagra professional homme sans prescription
ржака до слёз Анимационные анекдоты: Смотрите любимые анекдоты в новом формате. “Анимационные анекдоты” – это категория анекдотов, которые визуально представлены в форме анимации. Вместо того, чтобы просто прочитать или услышать анекдот, зри Продолжение: тель видит его историю развернутой в виде короткого мультфильма или анимированного ролика. Это делает анекдот более запоминающимся и смешным, поскольку добавляет визуальный контекст и юмористические детали. Анимационные анекдоты часто распространяются через онлайн-платформы, такие как YouTube и социальные сети, и пользуются популярностью благодаря своему развлекательному и креативному характеру.
как уменьшить налог ндс Купить двигатель Subaru – симметричный AWD. EJ20 для Impreza. Ресурс 300 тысяч км. Цены 120-350 тысяч. Subaru – для ралли-духа.
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Die Mitarbeiter reagieren blitzschnell, immer bereit zu helfen. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, manchmal die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst, NV Casino ist eine Plattform, die rockt fur Casino-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich die Navigation ist kinderleicht, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Je suis completement fou de Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient cool. En bref, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Cerise sur le gateau la plateforme est visuellement top, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Continuer Г lire|
J’ai une passion astrale pour Casinia Casino, il procure une experience galactique. Le catalogue est luxuriant et diversifie, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est eclatant. Le support client est stellaire, avec une aide claire et rapide. Les retraits filent comme une etoile filante, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient lumineux. En resume, Casinia Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les joueurs en quete d’aventure ! De plus la navigation est intuitive comme une constellation, amplifie le plaisir galactique. Un plus non negligeable les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
Lire maintenant|
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. La procedure est aisee et efficace, cependant des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, facilite une immersion complete. Egalement notable les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions securisees.
Continuer Г lire|
tripskan Tripscan: Бренд, который переосмысливает опыт путешествий в цифровой эпохе. Tripscan – это инновационная travel-платформа, которая стремится предоставить пользователям все необходимые инструменты для организации идеального путешествия, от начала и до конца. Она предлагает широкий выбор вариантов перелета, проживания, аренды автомобилей и развлечений, а также удобные функции для сравнения цен, чтения отзывов и получения персональных рекомендаций. Tripscan уделяет особое внимание удобству пользователя, предлагая интуитивно понятный интерфейс, мобильные приложения для iOS и Android, а также круглосуточную поддержку клиентов. Tripscan – это не просто платформа для бронирования, это сообщество путешественников, которые делятся своими идеями, опытом и вдохновением.
оптимизация налогов ндс Купить двигатель Fiat – итальянский темперамент. 1.4 T-Jet для 500. Цены 50-150 тысяч. Fiat – стиль.
Reading your article helped me a lot and I agree with you. But I still have some doubts, can you clarify for me? I’ll keep an eye out for your answers.
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, fugt Magie hinzu. Hervorzuheben ist die Community-Events, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis totalement fascine par Bingoal Casino, on percoit une vitalite dechainee. Il existe une abondance de jeux envoutants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, proposant des reponses limpides. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Globalement, Bingoal Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! A mentionner la navigation est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion complete. Egalement notable le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, renforce le sens de communaute.
Continuer maintenant|
Ich bin verblufft von NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, bietet klare Antworten. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, dennoch die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino ist eine Plattform, die rockt fur Krypto-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen die Site ist schnell und elegant, gibt Lust auf mehr.
playnvcasino.de|
I’m enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it constructs an enthralling narrative. The breadth in selections is breathtaking, designed for digital currency operations. Paired with 200 gratis rotations. Addressing concerns instantly. The framework is approachable, although diversified reward schemes would improve it. Concluding , Wazamba Casino supplies incomparable delight for virtual money supporters ! Additionally the setting initializes swiftly, optimizing participant interaction. Notably impressive nurturing collective spirit, affirming protected dealings.
https://wazambagr.com/|
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’assistance est efficace et pro, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et stylee, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus non negligeable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller ici|
Je suis totalement seduit par Casinia Casino, ca procure un plaisir aristocratique. La selection de jeux est royale, offrant des sessions live immersives. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du prestige. En resume, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. A noter egalement le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, propose des avantages personnalises.
Ouvrir les dГ©tails|
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, ca distille un plaisir majestueux. L’eventail de jeux est princier, avec des slots aux designs audacieux. L’offre de bienvenue est somptueuse. L’assistance est precise et elegante, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient imperiales. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino fournit une experience inoubliable pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un decret, ce qui rend chaque session plus fastueuse. Un atout cle les options de paris sportifs etendues, qui renforce l’engagement.
Plongez-y|
J’ai un engouement pour Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, accessible a tout instant. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En synthese, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit le site est veloce et seduisant, stimule le desir de revenir. A souligner aussi les options de paris sportifs etendues, renforce le sens de communaute.
Voir tout de suite|
Прогон хрумером под ключ для качественных ссылок
Прогон хрумером под ключ для качественной ссылочной массы и продвижения
Хотите увеличить органический трафик? Применяйте продвинутые инструменты для создания ссылок, которые значительно повысят видимость вашего https://kwork.ru/links/1017228/progon-khrumerom в поисковых системах. Данные показывают, что качественные внешние ссылки могут повысить позиции вашего ресурса в результатах поиска до 50%.
Профессиональный подход к созданию ссылочной массы включает оптимизацию под конкретные алгоритмы поисковиков. Анализ конкурентов и выбор верных площадок для размещения – ключ к успеху. При использовании проверенных методов вы обеспечите стабильный прирост позиций и видимости.
Получите отчёты о выполненных действиях и анализ эффективности. Вы будете в курсе, какие методы приносят максимальную отдачу и какие кампании стоит повторить. Такой подход экономит время и ресурсы, одновременно поднимая ваш проект на новый уровень.
I have a huge crush on Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it’s a heart-pounding launch into uncertainty. The gameplay is brilliantly simple yet addictive, including auto-cashout for risk management. Mobile-optimized for on-the-go blasts. Support is lightning-fast and helpful, providing clear multiplier histories. Transactions process in minutes, occasionally expanded auto features for newbies. Wrapping it up, Astronaut Crash stands out in 100HP’s lineup for strategy lovers ! On top of that load times are near-instant, encouraging marathon play. Standout element crypto wallet integration, ensures fast and fee-free payouts.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, obwohl die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und stylish, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, on percoit une vitalite dechainee. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Le bonus d’inscription est seduisant. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, toujours pret a intervenir. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, de temps a autre des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En fin de compte, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! A mentionner le design est contemporain et lisse, stimule le desir de revenir. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions securisees.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Le suivi client est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Cerise sur le gateau l’interface est intuitive et stylee, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Explorer le site web|
Je suis fascine par Casinia Casino, il offre une experience imperiale. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents repondent avec celerite, garantissant un support de qualite. Le processus est simple et elegant, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi le design est moderne et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
Découvrir aujourd’hui|
J’aime l’atmosphere de Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, assurant un support premium. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, mais des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les options de paris sportifs etendues, renforce le sens de communaute.
Voir la liste complГЁte|
dreamgrid.click – Layout is clean; wish there was more info or context on what it’s about.
I’m stunned by Wazamba Casino, it awakens a peculiar force. The breadth in selections is breathtaking, encompassing real-time dealer interactions for genuineness. Heightening preliminary involvement. Help desk is remarkable. The framework is approachable, yet supplemental rotations could advance it. Collectively , Wazamba Casino warrants examination for stimulation pursuers ! Additionally the architecture is creatively striking, infusing supplementary fascination. An additional merit prestige levels with unique favors, supplying individualized graces.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Самостоятельный ремонт авто “Автомобильные проблемы – это неизбежность? ИНФОКАР научит, как с ними справляться с юмором!” Сломалась машина? Неприятности на дороге? Не отчаивайтесь! ИНФОКАР поможет вам взглянуть на автомобильные проблемы с юмором! Мы собрали для вас лучшие автомобильные мемы, автомобильные шутки и истории из реальной жизни автомобилистов. Наши эксперты поделятся советами, как справляться с автомобильными неприятностями и как избежать серьезных поломок. Помните: реальная жизнь автомобилиста полна сюрпризов, но с ИНФОКАР вы всегда будете готовы к любым вызовам!
I’m totally obsessed with Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it delivers edge-of-your-seat tension. The provably fair system builds trust, powered by RNG for every unpredictable crash. Mobile-optimized for on-the-go blasts. 24/7 availability for global players, ensuring secure crypto deposits. Low fees on high-volume wins, however higher max bets for high-rollers. Wrapping it up, Astronaut Crash delivers proven fair thrills for crash game fans ! Bonus point the sound design amps the tension, adding immersive audio cues. Standout element the ‘Second Chance’ mechanic, builds a social betting community.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
event updates
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Je suis captive par Bingoal Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Renforcant l’experience de depart. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, accessible a tout instant. La procedure est aisee et efficace, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. Pour synthetiser, Bingoal Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, stimule le desir de revenir. Egalement notable les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Zusatzlich das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, verstarkt die Immersion. Besonders toll die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui regorge de dynamisme. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Pour un demarrage en force. Le service est operationnel 24/7, assurant un support premium. La procedure est aisee et efficace, par moments des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Tout compte fait, Bingoal Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! Par ailleurs le design est contemporain et lisse, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Explorer tout le site|
Je suis captive par Casinia Casino, on ressent une aura radieuse. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Le support client est lumineux, garantissant un service etincelant. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, mais des recompenses additionnelles seraient scintillantes. En somme, Casinia Casino merite une exploration eblouissante pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un rayon, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs variees, qui renforce l’engagement.
Trouver les infos|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais scintillant. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Avec un Bonus Crab unique pour debuter. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits filent comme une comete, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient scintillantes. Au final, Casinia Casino est un joyau pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! A noter la plateforme scintille comme une etoile, ce qui rend chaque session plus eclatante. Egalement remarquable les tournois reguliers pour la rivalite, garantit des transactions fiables.
En savoir plus|
Je suis epate par Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le support client est exceptionnel, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et efficace, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. En resume, Locowin Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus la navigation est simple et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Avancer|
J’aime l’ambiance royale de Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. Les options sont vastes comme un royaume, offrant des sessions live immersives. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Cerise sur le gateau le site est rapide et attrayant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
Aller sur le site web|
новые авто в наличии машины из китая – это современный дизайн, передовые технологии и доступная цена. Китайские автомобили становятся все более популярными благодаря своей надежности, экономичности и богатой комплектации.
With thanks. Loads of erudition! buy generic atomoxetine for sale
I’m obsessed with Wazamba Casino, it’s an odyssey that echoes with intrigue. There’s a vast spectrum of options, featuring betting on sports events. Bundled with 200 complimentary turns. Answering queries rapidly. Procedures are uncomplicated, occasionally regular deals might amplify appeal. Ending with, Wazamba Casino emerges as an elite venue for digital currency admirers ! Furthermore the environment loads efficiently, prompting continual returns. Especially noteworthy competitions for rivalry, delivering customized favors.
https://wazambagr.com/|
I’m wildly enthusiastic about Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it presents a masterful mix of luck and timing. Bet ranges cater to every wallet size, potential payouts soaring to 10,000x. Cross-device compatibility for anywhere action. Help desk is responsive and expert, upholding outcome transparency. Profits land in your account pronto, every now and then advanced auto-tools for vets. In a nutshell, Astronaut Crash redefines crash gaming standards for crash aficionados ! Extra perk audio ramps up the launch drama, streamlining stake tweaks. Highlight fairness audit tools, sparks a vibrant player network.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
Je suis impressionne par Bingoal Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. L’eventail de jeux est spectaculaire, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Associe a des paris gratuits. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. La procedure est aisee et efficace, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En synthese, Bingoal Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! En outre le design est contemporain et lisse, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions securisees.
VГ©rifier la liste complГЁte|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Nicht zu vergessen die Navigation ist kinderleicht, was jede Session noch besser macht. Besonders toll die mobilen Apps, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis hypnotise par Bingoal Casino, on percoit une vitalite dechainee. La gamme des titres est stupefiante, offrant des sessions live intenses. Le bonus d’inscription est seduisant. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, bien que des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En synthese, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un plus significatif les options de paris sportifs etendues, qui stimule l’engagement.
Apprendre en ligne|
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. La variete des titres est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. L’assistance est efficace et pro, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! De plus le design est moderne et fluide, ajoute une touche de confort. A noter egalement le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
Approfondir|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, ca distille un plaisir eclatant. La diversite des titres est eblouissante, offrant des sessions live captivantes. L’offre de bienvenue est eclatante. Les agents repondent comme une etoile filante, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient scintillantes. En somme, Casinia Casino garantit un plaisir radiant a chaque instant pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un rayon, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner aussi les tournois reguliers pour la rivalite, propose des recompenses sur mesure.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
Je suis absolument conquis par Casinia Casino, ca procure un plaisir aristocratique. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est imperial, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. En resume, Casinia Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et fluide, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un autre atout majeur les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Tout accГ©der|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. La variete des titres est impressionnante, avec des slots au design innovant. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le support client est exceptionnel, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, mais plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En prime la plateforme est visuellement top, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. A noter egalement les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
DГ©bloquer toutes les infos|
online stream
I’m deeply intrigued by Wazamba Casino, it mirrors a torrent of mystique. The assortment of games is remarkable, encompassing over 5,000 entries from premier developers. The introductory offer is appealing. Answering queries rapidly. Cashouts are executed promptly, from time to time broader incentive options would enrich it. In totality, Wazamba Casino merits investigation for quest pursuers ! In addition the setup is accessible and evocative, magnifying each episode’s appeal. Notable aspect reliable crypto handling methods, heightening involvement.
https://wazambagr.com/|
My spouse and I absolutely love your blog and find most of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content for you? I wouldn’t mind publishing a post or elaborating on a few of the subjects you write regarding here. Again, awesome website!
актуальные зеркала kra41.cc и kra41.at
The thoroughness in this piece is noteworthy.
I’m thrilled by Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it crafts an interstellar betting odyssey. Games wrap up in seconds for endless replays, showcasing a multiplier that escalates dramatically. RTP sits at an enticing 97%. Forums buzzing with player tactics, delivering multiplier trend insights. The exit system rescues bold bets, even so wider stake limits for pros. Wrapping up, Astronaut Crash is essential for high-rollers for multiplier maniacs ! Plus controls are beginner-proof, layering sound for immersion. Super feature leaderboards for rivalry, ensures tamper-proof twists.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
https://cuctex.com/ Cuctex на «Интерткань»: 3 года, 6 выставок, 750 новинок С весны 2023 года компания Cuctex шесть раз подряд принимала участие в выставке «Интерткань» — сначала в павильоне «Экспоцентр», затем в «Тимирязевском», а теперь в «Крокус Экспо». За это время наш стенд посетили более 3000 клиентов. Количество экспонатов увеличилось с 60 до более чем 180, а всего мы представили свыше 750 новых продуктов. Такой рост ассортимента стал причиной того, что многие клиенты отмечают: не все новинки удаётся найти на нашем сайте. Объём информации очень большой, и сайт не всегда справляется с нагрузкой.
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Community-Events, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’adore l’ambiance de Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. Les agents repondent avec celerite, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Au final, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. Un plus non negligeable les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
En savoir plus|
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie fastueuse. Les options sont vastes comme un empire, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec un Bonus Crab exclusif. L’assistance est precise et elegante, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les retraits filent comme une fleche, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient imperiales. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est un pilier pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! De plus le design est opulent et envoutant, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en crypto, qui renforce l’engagement.
AccГ©der au site|
J’aime l’ambiance royale de Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du prestige. Au final, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! En prime l’interface est intuitive et elegante, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Essayer en ligne|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. La procedure est aisee et efficace, bien que des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! De surcroit la navigation est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion complete. Un plus significatif les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Tout voir maintenant|
I’m completely enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it offers an exhilarating expedition. The game lineup is extraordinary, boasting over 5,000 games from 100+ providers. Boosting your playtime. Round-the-clock availability. Payouts are handled swiftly, yet frequent promotions could add value. To wrap up, Wazamba Casino delivers unmatched fun for gaming aficionados ! Moreover browsing is intuitive, elevating every moment of play. A bonus is secure crypto payment methods, boosting player retention.
https://wazambagr.com/|
I’m buzzing about Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it serves a daring dance of risk. Rounds fly by for non-stop action, supporting wagers from $0.10 to $150. Balanced volatility for consistent excitement. Instant chat resolves queries fast, always on standby for quick fixes. Transfers are smooth and reliable, still higher bet caps for bold players. All in all, Astronaut Crash stands out in 100HP’s arsenal for quick-bet lovers ! Notably design fuels long play sessions, adding immersive crash sounds. Standout feature crypto wallet syncing, fuels rivalries among players.
Astronaut Crash Game|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, dennoch mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die schnellen Einzahlungen, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai un veritable engouement pour Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, avec des slots au style innovant. Renforcant l’experience de depart. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En synthese, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! En outre l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ajoute un confort notable. A souligner aussi les evenements communautaires captivants, renforce le sens de communaute.
Aller plus loin|
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, ca distille un plaisir majestueux. Le repertoire est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Elevant l’experience de jeu. L’assistance est precise et elegante, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un joyau. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est un pilier pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive comme un edit, intensifie l’eclat du jeu. Un atout cle les paiements securises en crypto, qui renforce l’engagement.
Parcourir davantage|
Je suis impressionne par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui rayonne de luxe. Le catalogue est opulent et diversifie, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! En prime l’interface est intuitive et elegante, facilite une immersion totale. A noter egalement les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter pour plus|
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live intenses. Pour un lancement puissant. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, bien que des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! A mentionner la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions securisees.
Découvrir aujourd’hui|
I’m blown away by Wazamba Casino, it’s a journey that resonates with mystery. The choices are broad and multifaceted, optimized for crypto transactions. The sign-up bonus is enticing. Expert and courteous help. Transactions are safe and efficient, sporadically frequent promotions could add value. Concluding, Wazamba Casino stands out as a superior platform for crypto users ! Moreover the design is aesthetically pleasing, elevating every moment of play. Particularly impressive VIP tiers with exclusive privileges, building community engagement.
wazambagr.com|
support chat
Excellent pieces. Keep writing such kind of info on your blog. Im really impressed by your blog.
Hey there, You have performed a great job. I will definitely digg it and individually recommend to my friends. I am confident they will be benefited from this web site.
официальный маркетплейс kra41
parier foot en ligne telecharger 1xbet apk
football africain telecharger 1xbet pour android
1xbet afrique apk pariez sur le foot
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, bietet klare Losungen. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und stylish, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Sicherheit der Daten, die Flexibilitat bieten.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, on percoit une energie dechainee. La selection de jeux est spectaculaire, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. L’equipe de support est remarquable, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, de temps en temps des recompenses additionnelles seraient un avantage. En resume, Locowin Casino merite une visite pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et elegante, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre point fort les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
Visiter la page d’accueil|
blsp at В курсе ли ты, что сотрясает самые глубины тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название. Это новый уровень в обеспечении анонимности, оперативности и безопасности сделок. Посети bs2best.at — там тебе откроются двери в мир, о котором другие предпочитают умалчивать. Получи доступ к информации, которую тщательно скрывают от общего внимания. Только для тех, кто понимает и разбирается. Без возможности обнаружения. Без каких-либо уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать одним из первых — bs2best.at уже готов принять тебя в свои ряды. Готов ли ты к тому, что узнаешь?
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, avec des slots au style innovant. Pour un lancement puissant. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, stimule le desir de revenir. Egalement notable les evenements communautaires captivants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Essayer maintenant|
J’ai un veritable engouement pour Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, bien que des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Globalement, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! En outre la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ajoute un confort notable. A souligner aussi le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Découvrir l’avis|
I’m utterly captivated by Wazamba Casino, it delivers a unique rush. The catalog is absolutely massive, with sports betting for added thrill. Plus 200 free spins to start strong. Agents respond swiftly. Withdrawals are processed quickly, however generous offers could be expanded. Broadly speaking, Wazamba Casino is a platform that excels for casino enthusiasts ! Furthermore the platform is visually stunning, which heightens the fun of every session. Notably collecting artifacts for rewards, providing personalized perks.
wazambagr.com|
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, transporta para um mundo de folia cativante. A variedade de titulos e deslumbrante, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, acessivel a qualquer hora. O processo e simples e elegante, contudo mais promocoes regulares seriam otimas. Em resumo, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Vale notar o site e rapido e atraente, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ler mais|
Fiquei impressionado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura competitiva. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, incluindo apostas esportivas palpitantes. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O acompanhamento e impecavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, no entanto recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino garante diversao a cada rodada para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Vale destacar o design e moderno e dinamico, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Outro destaque as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Explorar a pГЎgina|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, trotzdem mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen die Site ist schnell und stylish, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis emerveille par Locowin Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. La diversite des titres est stupefiante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps en temps des recompenses additionnelles seraient un avantage. Au final, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui impressionne pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et plaisante, incite a prolonger l’experience. Un avantage supplementaire les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis fascine par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, accessible a tout instant. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, mais plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En synthese, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! En outre le design est contemporain et lisse, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, qui stimule l’engagement.
En savoir sur le sujet|
Je suis completement obsede par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! A mentionner la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un autre avantage cle les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Obtenir des infos|
I’m amazed by Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. There’s an incredible variety of games, with sports betting for added thrill. The welcome bonus is generous. Agents respond swiftly. Payments are secure and reliable, sometimes lower wagering requirements would be ideal. In conclusion, Wazamba Casino is worth exploring for players seeking adventure ! In addition navigation is effortless, adds a layer of excitement. Another perk is VIP levels for exclusive benefits, ensuring secure transactions.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com sessoes ao vivo dinamicas. 100% ate €500 + 200 rodadas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e cortes, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, embora bonus mais variados seriam bem-vindos. No geral, PlayPIX Casino e indispensavel para jogadores para quem aposta com cripto ! Vale notar a interface e fluida e elegante, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Um diferencial importante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Clicar para ver|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, trotzdem mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Hervorzuheben ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die Flexibilitat bieten.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis completement fou de Locowin Casino, on ressent une vibe delirante. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Le suivi client est irreprochable, toujours pret a aider. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres seraient top. En resume, Locowin Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement top, ajoute une touche de confort. A noter egalement les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
Tout voir maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, de temps a autre des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Egalement notable les options de paris sportifs etendues, renforce le sens de communaute.
Parcourir les offres|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, cependant des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! A mentionner la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, stimule le desir de revenir. Un plus significatif le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Lire la version complГЁte|
With thanks. Loads of expertise!
https://bs2best.or.at
Sou viciado no brilho de BR4Bet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao ardente quanto uma fogueira a meia-noite. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como luzes. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento e solido como um farol. respondendo veloz como uma chama acesa. Os saques voam como um facho de luz. em alguns momentos queria promocoes que acendem como chamas. Ao final, BR4Bet Casino e um cassino online que e um farol de diversao para os faroleiros do cassino! E mais a plataforma reluz com um visual brilhante. tornando cada sessao ainda mais brilhante.
br4bet nao consigo sacar|
Fiquei fascinado com BETesporte Casino, leva a um universo de apostas dinamico. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, as vezes promocoes mais frequentes seriam um plus. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Acrescentando que o site e veloz e envolvente, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Notavel tambem as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, oferece recompensas continuas.
Saber mais|
Estou completamente vidrado por MarjoSports Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma torcida em delirio. As opcoes sao ricas e vibram como torcidas. incluindo mesas com charme de torcida. O suporte e um apito preciso. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. As transacoes sao faceis como um apito. as vezes mais bonus regulares seriam esportivos. Resumindo, MarjoSports Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os cacadores de vitorias em gol! De lambuja o site e uma obra-prima de estilo esportivo. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura de gol.
como se cadastrar marjosports|
Galera, vim dividir minhas impressoes no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e muito completa: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi eficiente, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que raramente vi. Fiz saque em Bitcoin e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que mais brindes fariam falta, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Pra concluir, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Ja virou parte da minha rotina.
soft 4play savage gear|
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer eletrizante. O catalogo e rico e multifacetado, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. Os agentes respondem com agilidade, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, as vezes promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Para finalizar, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Tambem a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, adiciona um toque de conforto. Notavel tambem o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Visitar hoje|
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et efficace, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. En bref, Locowin Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et fluide, ajoute une touche de confort. Un plus non negligeable les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
Tout lire|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Pour un lancement puissant. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, cependant des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ajoute un confort notable. Un autre avantage cle le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
J’ai un engouement pour Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, accessible a tout instant. Les operations sont solides et veloces, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Egalement notable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Continuer ici|
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, e uma onda de diversao que cintila como um farol. Os jogos formam um clarao de entretenimento. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de brilho. O time do cassino e digno de um faroleiro. respondendo rapido como um brilho na noite. As transacoes sao simples como uma luz. em alguns momentos mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura iluminada. Ao final, BR4Bet Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para os cacadores de vitorias reluzentes! Alem disso o design e um espetaculo visual iluminado. fazendo o cassino brilhar como um farol.
30|
Sou totalmente viciado em BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os saques sao rapidos como um contra-ataque, contudo ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Vale destacar o design e moderno e vibrante, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Notavel tambem os torneios regulares para rivalidade, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Acessar o site|
Me encantei pelo ronco de F12.Bet Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um pit stop. O catalogo de jogos e uma pista de emocoes. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O time do cassino e digno de um piloto. assegurando apoio sem derrapagens. As transacoes sao faceis como um drift. entretanto as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, F12.Bet Casino e um motor de emocoes para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De lambuja a navegacao e facil como uma mudanca de marcha. transformando cada aposta em uma ultrapassagem.
superbet f12. bet e parimatch|
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e muito completa: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos sem travar. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que vale elogio. Fiz saque em transferencia e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que seria legal torneios de slots, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Na minha visao, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
4play bet reclame aqui|
Estou totalmente fascinado por PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer eletrizante. O catalogo e rico e multifacetado, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. O processo e simples e elegante, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Vale destacar a interface e fluida e estilosa, adiciona um toque de conforto. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ver agora|
If you want to learn everything about online platforms in the United States, then this is exactly what you need. Discover the full details via the attached link:
online casino real money no deposit free spins
online connect
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui bouillonne d’energie. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient cool. Au final, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et stylee, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus non negligeable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
Obtenir l’offre|
Je suis totalement envoute par Casinia Casino, on ressent une aura radieuse. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, proposant des jeux de table raffines. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le support client est lumineux, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient lumineux. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino merite une exploration eblouissante pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un rayon, ajoute une touche de splendeur. Un atout cle les evenements communautaires captivants, qui renforce l’engagement.
Continuer ici|
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le support client est exceptionnel, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. Au final, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Notons aussi la navigation est simple et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
Lire l’avis complet|
Sou louco pela energia de Brazino Casino, parece um abismo de adrenalina subaquatica. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como conchas. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como aguas cristalinas. O atendimento e solido como um coral. oferecendo respostas claras como um lago. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. as vezes as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Ao final, Brazino Casino promete uma diversao que e uma mare para os fas de adrenalina marinha! Adicionalmente o visual e uma explosao de corais. fazendo o cassino reluzir como um recife.
como jogar brazino777|
Estou alucinado com PlayPix Casino, oferece uma aventura que glitcha como um render 8-bit. A colecao e um codigo de entretenimento. com slots tematicos de mundos digitais. O time do cassino e digno de um programador. com ajuda que renderiza como um glitch. As transacoes sao faceis como um glitch. ocasionalmente as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, PlayPix Casino e um buffer de emocoes para quem curte apostar com estilo cibernetico! Por sinal a plataforma reluz com um visual glitch. fazendo o cassino processar como um CPU.
tv playpix brasil e confiГЎvel|
Curto demais a chama de Fogo777 Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um xama. O leque do cassino e um fogo de delicias. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como labaredas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. respondendo veloz como uma faisca. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. mas mais giros gratis seriam incendiarios. Em sintese, Fogo777 Casino promete uma diversao que e uma labareda para os cacadores de vitorias incendiarias! Alem disso o site e uma obra-prima de estilo ardente. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um ritual.
fogo777 login entrar|
Je suis accro a BankOnBet Casino, on dirait une chambre forte pleine de jackpots. Il y a une avalanche de jeux de casino captivants. with slots that stack wins like bills. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7. avec une aide qui debloque les gains. The process is clear like a balance sheet. quand meme des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient rentables. In summary, BankOnBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino enrichissant pour les fans de gains stables! Additionally le site du casino est une merveille graphique securisee. transformant les mises en fortunes.
bankonbet sportfogadГЎs|
Estou completamente encantado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura cheia de emocao. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com slots modernos e tematicos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os saques sao rapidos como um drible, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para fas de cassino online ! Tambem a interface e fluida e energetica, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Muito atrativo o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Ir ver|
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. O catalogo e exuberante e diversificado, com slots de design inovador. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para fas de cassino online ! Acrescentando que a navegacao e intuitiva e envolvente, facilita uma imersao total. Muito atrativo os torneios regulares para competicao, que aumenta o engajamento.
Ver a pГЎgina|
If you are interested in US casinos, then this is something you shouldn’t miss. Explore the full details via the link below:
best online casinos
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, on ressent une vibe delirante. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Pour un demarrage en force. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. En resume, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le design est moderne et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. Un plus non negligeable les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Continuer maintenant|
Je suis captive par Casinia Casino, il offre une aventure etincelante. Le repertoire est riche et multifacette, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions cristallines. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient scintillantes. Au final, Casinia Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! En bonus le design est moderne et eblouissant, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute vibrante.
Entrer maintenant|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, on ressent une vibe delirante. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le suivi client est irreprochable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. Au final, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
Lire l’avis complet|
Sou louco pela energia de Brazino Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um recife de corais. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como conchas. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O servico e confiavel como uma ancora. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques voam como uma arraia. entretanto mais bonus regulares seriam aquaticos. Em sintese, Brazino Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro mergulho para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a interface e fluida e brilha como um recife. adicionando um toque de brilho marinho ao cassino.
brazino777 partners|
Je trouve absolument enivrant BankOnBet Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino digne d’un banquier audacieux. Les choix sont varies et blindes comme un safe. with slots that stack wins like bills. L’assistance du casino est fiable et discrete. responding faster than a bank transfer. Withdrawals are swift as a wire transfer. mais des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient fructifier. Dans l’ensemble, BankOnBet Casino c’est un casino a miser sans hesiter pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline securisee du casino! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style rentable. transformant les mises en fortunes.
bankonbet logo|
Estou completamente encantado com BETesporte Casino, transporta para um universo de apostas eletrizante. O catalogo e vibrante e diversificado, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. No fim, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o gramado para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Tambem o site e veloz e envolvente, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Um diferencial importante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Clicar para ver|
Amo a energia selvagem de PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. O catalogo e exuberante e diversificado, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer momento. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, contudo bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Acrescentando que o site e rapido e cativante, adiciona um toque de conforto. Um diferencial significativo as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, oferece recompensas continuas.
Navegar no site|
streaming event
Je suis hante par Casombie, ca pulse comme une invasion de zombies. Il y a une horde de jeux captivants, incluant des jeux de table a l’ambiance gothique. Le suivi est aussi fiable qu’un sortilege, garantissant un support digne d’une legende. Le processus est aussi lisse qu’un suaire, parfois des tours gratuits supplementaires feraient frissonner. Dans l’ensemble, Casombie merite une visite dans son antre pour les aventuriers des cryptos ! Cerise sur le cercueil l’interface est fluide comme un fantome, ce qui rend chaque session electrisante.
casombie -bonus|
Je suis charme par Casinia Casino, offre une quete de plaisir qui captive. vibre avec un rempart de jeux varies. offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent comme des armures. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un destrier. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides. parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En conclusion, Casinia Casino est un casino en ligne qui s’eleve comme un chateau enchante pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline royale du casino! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique noble. donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
casino casinia|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le suivi est exemplaire, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, stimule le desir de revenir. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, qui stimule l’engagement.
Apprendre les secrets|
J’ai un veritable engouement pour Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live intenses. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, assurant un support premium. Les retraits sont realises promptement, bien que plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. Globalement, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est contemporain et lisse, stimule le desir de revenir. Un plus significatif les evenements communautaires captivants, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Parcourir les offres|
https://2bs-2best.at
If you are looking for trusted sites in the USA, then this is definitely worth checking out. Discover the full details via the link below:
best online casinos
Estou alucinado com Stake Casino, e um cassino online que ressoa como um sino ancestral. Os jogos formam uma ressonancia de diversao. com caca-niqueis modernos que ecoam como sinos. O time do cassino e digno de um maestro. respondendo rapido como um eco na caverna. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. entretanto mais recompensas fariam o coracao ecoar. Em sintese, Stake Casino e um cassino online que e uma camara de diversao para os cacadores de vitorias ressonantes! Adicionalmente o design e fluido como uma onda sonora. criando uma experiencia de cassino harmonica.
stake land|
Acho simplesmente enredado IJogo Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao intrincada quanto um labirinto de vinhas. O leque do cassino e um labirinto de delicias. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de selva. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. garantindo suporte direto e sem nos. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma raiz. mesmo assim as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Para encurtar, IJogo Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os cacadores de vitorias intrincadas! Como extra o visual e uma explosao de vinhas. dando vontade de voltar como um cipo.
ijogo-5|
Je suis accro a Grandz Casino, est une symphonie de divertissement qui effleure. Le repertoire du casino est un theatre de divertissement. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance spectrale. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un directeur de scene. assurant un support de casino immediat et voile. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse etheree. occasionnellement les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Grandz Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les danseurs spectraux du casino! De surcroit offre un orchestre de couleurs fugaces. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus etheree.
analyse grandz race|
Tenho um entusiasmo vibrante por BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com a energia de um estadio lotado. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O acompanhamento e impecavel, garantindo um atendimento de elite. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. No geral, BETesporte Casino e indispensavel para apostadores para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e vibrante, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Um diferencial importante os torneios regulares para rivalidade, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Explorar o site|
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Acrescentando que a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, adiciona um toque de conforto. Outro destaque os torneios regulares para competicao, que aumenta o engajamento.
Obter informações|
blsp at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
Me encantei pelo ritmo de BR4Bet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao ardente quanto uma fogueira a meia-noite. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como luzes. incluindo mesas com charme iluminado. Os agentes voam como claroes. com ajuda que ilumina como uma tocha. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma chama. as vezes as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, BR4Bet Casino e um cassino online que e um farol de diversao para os exploradores de jogos online! Vale dizer o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura iluminada.
480|
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, parece uma erupcao de diversao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vulcanico, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma chama. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, com uma ajuda que e puro calor. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, OshCasino e um cassino online que e uma erupcao de diversao para os aventureiros do cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
avis osh|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Zusatzlich die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Sou viciado em BETesporte Casino, transporta para um mundo de apostas vibrante. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, incluindo apostas esportivas palpitantes. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O acompanhamento e impecavel, com suporte preciso e rapido. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, contudo bonus mais variados seriam um gol. Em resumo, BETesporte Casino garante diversao a cada rodada para fas de cassino online ! Vale destacar a interface e fluida e energetica, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Um diferencial importante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Explorar o site|
фитнес клуб тренировка фитнес клуб тренировка
https://homeclimat36.ru/ – Монтаж сплит-системы.
https://raymark.ru/ – лазерные станки и фрезерное оборудование «RAYMARK»
fan zone
Estou completamente vidrado por MegaPosta Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura dinamite. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um estouro, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, MegaPosta Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fogo para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como brincadeira, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
megaposta com|
Sou louco pela vibracao de BR4Bet Casino, e uma onda de diversao que cintila como um farol. A colecao e um facho de diversao. com caca-niqueis que brilham como holofotes. Os agentes voam como claroes. respondendo rapido como um brilho na noite. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. em alguns momentos queria promocoes que acendem como chamas. Para encurtar, BR4Bet Casino e uma fogueira de adrenalina para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De lambuja o layout e vibrante como uma tocha. tornando cada sessao ainda mais brilhante.
quem Г© o dono da br4bet|
Sou viciado no role de OshCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que incendeia tudo. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e incendiarias, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma chama. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem cinzas. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tremores, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial vulcanico. Na real, OshCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia ardente, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
casino osh|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Kick. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit dynamischen Live-Sessions. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, bietet klare Antworten. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, trotzdem mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren willkommen. Insgesamt, NV Casino garantiert Top-Unterhaltung fur Krypto-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem das Design ist modern und ansprechend, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Amo a atmosfera de BETesporte Casino, sinto uma energia de estadio. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, com sessoes ao vivo imersivas. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O acompanhamento e impecavel, com suporte preciso e rapido. O processo e simples e direto, as vezes mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Em resumo, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Alem disso a interface e fluida e energetica, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Muito atrativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Descobrir agora|
Bonjour, passionnes de jeux en ligne !
Je viens de trouver un article avec des details tout frais sur le jeu Plinko chez les joueurs francais.
Si tu souhaites suivre les tendances, cette lecture est faite pour toi.
Consulte tout cela via le lien place en bas :
plinko jeu
https://telegra.ph/Rehb-protiv-dronov-perenosnoj-kupit-10-12-2
https://telegra.ph/Cifrovoj-pricel-sajtong-nt70-kupit-10-13-2
Может обсудим как избежать напастья копоф при получении посылки от курьера???
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-invertornyj-generator-v-ussurijske-10-13
Дружище как все прошло?)) забрал своё??? А то написал неделю назад и тишина))) если забрал сколько шло по времени? напиши нам а то на последних страницах сдесь какой то кипишь нездоровый…(
Adoro o clima explosivo de JabiBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e puro tsunami. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, respondendo mais rapido que um maremoto. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. No geral, JabiBet Casino e um cassino online que e uma onda gigante para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como a mare.
jabibet apk|
Estou pirando com PagolBet Casino, e um cassino online que detona como um trovao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um relampago. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem curto-circuito. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um trovao, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. No fim das contas, PagolBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! Vale falar tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia eletrica, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
pagolbet afiliados|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, trotzdem mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Nicht zu vergessen die Navigation ist kinderleicht, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Zusatzlich zu beachten die schnellen Einzahlungen, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es erzeugt eine Energie, die suchtig macht. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Optionen, mit Spielen, die perfekt fur Kryptos geeignet sind. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, garantiert hochwertige Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, manchmal mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Zusammengefasst, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Krypto-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Oberflache ist intuitiv und stylish, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Selecting the appropriate athletic shoe for the kind of sport or exercise you take pleasure in is an even more particular process. HIIT is just following a specific regimen where you range your speeds and intensity throughout a shorter run, swim, bike, or row. For foot consolation and http://www.chatgpt918.top:3000/borisgarside16/1738metabolism-booster-formula/wiki/Answers+About+Aerobics: Some insoles offer solely a skinny, generically formed cushion of assist, whereas others are designed to fit a specific shoe style (comparable to women’s high heels or men’s work sneakers) or to offer additional support or padding in specific areas — as an example, those with extra cushioning on the heel provide again help in addition to foot relief. When you do so, first place doughnut-formed padding across the corn to protect the encircling skin. Skip the “callus removers” (medicated pads) and “callus trimmers.” The previous comprise salicylic acid, which might burn not simply the callused area but the extra delicate pores and skin round it, and the latter really has a blade (you must by no means lower a callus).
https://www.russianwomenorg.com/read-blog/17479
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio lotado. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, contudo bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. No geral, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Acrescentando que o site e veloz e envolvente, facilita uma imersao total. Notavel tambem os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Descobrir agora|
ребята ровно работают!
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-benzogenerator-invertornyj-fubag-7000-v-spb-10-13-3
заказал у KingSize – всё ровно вышло. Большего и добавлять незачем
Про 80 не знаю. Но то что там принимают сомнительных, дак это точно. Вот люди которые туда приходят и ушатаные в хламотень, все трясутся. И оглядываются, как будто от смерти скрываются конечно их принимают… А что про тех кто соблюдаем все меры, тот спокоен. И сдержан. Но все равно. В спср принимают однозначно, сам свидетель в 2006 году. когда за дропом следили, перепугались что за нашим пришли… Но все обошлось.
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-teplovizionnyj-pricel-rika-lesnik-10-12-5
Да хватает придурков, только смысл писанины этой , что он думает что ему за это что то дадут ))) кроме бана явно ничего не выгорит )))! Тс красавчик брал 3 раза по кг сделки и всегда все чётко ! Жду пока появиться опт на ск!
трипы почитайте, кто уже брал
https://telegra.ph/Radar-detektor-kupit-v-ufe-10-11
У каждого селлера, в нынешние времена, продукты с одним и тем же названием, имеют часто разный внешний вид, различные дозировки и эффекты, потому то так часто у селлера и спрашивают параметры этих в-в “именно” в данном магазе “именно” у данного селлера.
show experience
https://codeprom08o.wixstudio.com/my-site
у кого задержалась посылка получат в начале недели что вы тут раскричались как будто я вам этого не говорил, я не в курьерке работаю и чего у них не бьються трэки я незнаю, посылки все отправлены, своей паникой вводите люд в заблуждение.
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-teplovizor-forum-10-13-4
магаз работает ровно, все четко и ровно, респект продавцам
https://www.milliescentedrocks.com/board/board_topic/2189097/7297577.htm
Проститутки метро Ладожская
https://www.minecraftforum.net/members/merlinp456
Уточнять не у кого !
https://telegra.ph/Benzogeneratory-shturm-kupit-10-13-2
Что случилось? почему страшно?
Брал у данного селлера!Хорошо работют=)
https://telegra.ph/Teplovizor-dlya-ohoty-novosibirsk-kupit-10-14
Ты думаешь АМ под запретом уже будет? Откуда инфа?
Ich finde absolut wild Lowen Play Casino, es pulsiert mit einer unbezahmbaren Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Raubtier, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Pfad im Busch, manchmal mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein wilder Triumph. Zusammengefasst ist Lowen Play Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Savanne beherrscht fur Spieler, die auf wilde Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Raubtier, was jede Casino-Session noch wilder macht.
löwen play sulza|
Estou completamente alucinado por JabiBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e puro tsunami. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo a parte, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma mare de qualidade, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. No fim das contas, JabiBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, da um toque de classe aquatica ao cassino.
jabibet casino bonus code|
Estou completamente vidrado por PagolBet Casino, e um cassino online que detona como um trovao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de energia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma voltagem alta, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, PagolBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma tempestade para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia eletrica, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
cГіdigo promocional pagolbet|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, obwohl zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Besonders toll die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich bin verblufft von NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Optionen, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, bietet klare Antworten. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, manchmal die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zum Abschluss, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, gibt Lust auf mehr.
playnvcasino.de|
bs2best зеркало Готов узнать, что творится в глубинах тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это символ анонимности, скорости и безопасности, а не просто бренд. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не говорить. Тебе откроют все тайны, скрытые от посторонних глаз. Только для посвящённых. Никаких следов. Никаких полумер. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс быть впереди — bs2best.at ждёт тех, кто готов к новому. Осмелишься ли ты узнать истину?
нервные клетки
https://telegra.ph/Bronezhilet-kupit-v-krasnoyarske-voennyj-cena-10-12
Приятно иметь дело с серьёзными людьми!!!!!!
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio lotado. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de futebol, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, no entanto bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Acrescentando que a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, facilita uma imersao total. Outro destaque os torneios regulares para rivalidade, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Ler os detalhes|
В каких пропорциях???
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-binokl-vladimir-10-12
Всем добра! Вчера позвонил курьер, сказал, что посылка в городе! Через пару часов я был уже на почте, забрав посылку, сел в машину, но вот поехать не получилось т.к. был задержан сотрудниками МИЛИЦИИ!!!! Четыре часа в отделении и пошёл домой!!! Экспертиза показала, что запрета нет, но сам факт приёмки очень напряг!!! Участились случаи приёмки на данной почте!!!!! Продаванам СПАСИБО и РЕСПЕКТ за чистоту реактивов!!! Покупатели держите ухо востро!!!!!!!!!! Больше с этой почтой не работаю(((( Если у кого есть опыт по схемам забирания пишите в личку!!!
Try a best vip massage combining traditional Thai techniques with Japanese Nuru oils.
Магазин ровный.;)Жаль реги пока нет
https://telegra.ph/Kollimator-kupit-moskva-10-12-4
Ок понял спасибо.
Да, оч похожа на соль, даже камушек один был ощутимый такой
https://telegra.ph/Binokl-b-12-armejskij-kupit-10-12
на вкус – сода.?
драмчик, хаус… да не суть.
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-teplovizor-testo-10-13-4
Магазин не отвечает, может типо выходные, ждем понедельника.
Процветания и успехов вашему магазину!!
https://telegra.ph/Bronezhilet-tankista-kupit-10-12-2
Может забегу как-нибудь) Обычно все берут там где надежно у одних и техже, новые магазины или первые покупки рисково, любой выберет проверенных лично)
https://pikman.info/ PR & Marketing Expertise: Data-Driven Marketing, Paid Search/SEM (Linkedin Ads, Facebook Ads, Google Ads, YouTube Ads, Yandex Ads, Bing Ads), Search Engine Optimization/SEO, Display, Retargeting, Social Media/SMM, Paid Media, Account Based Marketing/ABM, Digital Marketing/Strategy, Data Analytics, Customer Acquisition, Web Marketing, Business Development, Full Stack Marketing, Customer Journey, Content Marketing, A/B Split Testing, Budget Management, Conversational Marketing, Conversion Rate Optimization, Growth Marketing, Multi-Touch Attribution, Copywriting, Data Journalism, Content writing, Visual Storytelling, Brand Identity, Web Design UX/UI, Digital Media, Content Marketing, Demand Generation, Forecasting and Modeling.
Si vous souhaitez decouvrir les meilleurs casinos francais, alors c’est exactement ce qu’il vous faut.
Explorez l’integralite via le lien en piece jointe :
casino en ligne
28го оплатил, а даже трека по сей день нет…
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-benzogenerator-v-kolomne-10-12-6
Как связаться?
https://interiordoorsua.blogspot.com/2025/10/razdvizhnyye-dveri-v-gostinoy.html
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-binokl-v-miasse-10-12
https://telegra.ph/Teplovizor-td210-kupit-10-12-4
Estou alucinado com BRCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma escola de samba na avenida. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que brilha como serpentinas. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma ala de passistas, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. Resumindo, BRCasino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
br77 apk|
https://telegra.ph/Cfmoto-zforce-950-sport-4-eps-kupit-10-14
Adoro o swing de RioPlay Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um tamborim. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia total, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de escola de samba, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, RioPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo do tamborim.
rioplay roblox lite|
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: roletas animadas, todos sem travar. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Pra concluir, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
4play lounge budapest|
Fiquei impressionado com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com emocao atletica. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, suportando jogos adaptados para criptos. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. A assistencia e eficiente e profissional, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, embora mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Vale destacar o design e moderno e dinamico, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Outro destaque os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Acessar o site|
https://telegra.ph/Bulat-5-detektor-dronov-kupit-10-12-5
https://telegra.ph/Dji-mic-mini-kupit-10-12-3
http://pathwel.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=free&wr_id=2888826
help
https://telegra.ph/Binokl-kupit-forum-10-13
Adoro o brilho de Richville Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que brilha como um lustre de cristal. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e reluzentes, com slots de cassino tematicos de luxo. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um coche de gala, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como abrir um cofre, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria opulento. No fim das contas, Richville Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino majestosa para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual de tirar o folego, eleva a imersao no cassino ao apice.
richville ny|
Sou viciado no role de JabiBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que arrasta tudo. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma onda, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, JabiBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro mar, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
jabibet|
Galera, vim dividir minhas impressoes no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos sem travar. O suporte foi eficiente, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em Bitcoin e o dinheiro entrou em minutos, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Pra concluir, o 4PlayBet Casino e parada obrigatoria pra quem gosta de cassino. Recomendo sem medo.
xmas 4play|
Sou viciado em PlayPIX Casino, transporta para um mundo de folia cativante. A variedade de titulos e deslumbrante, com slots de design inovador. O bonus de boas-vindas e vibrante. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, no entanto bonus mais variados seriam bem-vindos. No final, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao a cada momento para quem aposta com cripto ! Tambem a interface e fluida e elegante, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Muito atrativo o programa VIP com 5 niveis exclusivos, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Visitar hoje|
https://telegra.ph/Dji-4-pro-kupit-10-13-3
نکته مهم خطرناک به سایتهای بازیهای شرطی آنلاین.
اینجانب به عنوان فردی که داستان مستقیم کردهام، اعلام میکنم که آنها جاها ابزار جهت غارت سرمایه مردم هستند.
شرط اولیه خوشایند است، لیکن در ادامه الگوریتمها به گونهای ساخته شدهاند که کاربر پایانه بازنده گردید.
خطر وابستگی قویتر از هر امر دیگری است
و تواند سلامتتان رانابود کند.
پرهیز کنید!
https://telegra.ph/Cfmoto-cforce-450-kupit-10-12-3
bs2web at В курсе ли ты, что сотрясает самые глубины тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название. Это новый уровень в обеспечении анонимности, оперативности и безопасности сделок. Посети bs2best.at — там тебе откроются двери в мир, о котором другие предпочитают умалчивать. Получи доступ к информации, которую тщательно скрывают от общего внимания. Только для тех, кто понимает и разбирается. Без возможности обнаружения. Без каких-либо уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать одним из первых — bs2best.at уже готов принять тебя в свои ряды. Готов ли ты к тому, что узнаешь?
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-retranslyator-lira-1000-10-12-3
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-universalnyj-pult-dji-rc-plus-10-13-3
https://telegra.ph/Magna-radar-detektor-kupit-10-12-5
hop live
Estou alucinado com PlayPix Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um codigo binario em furia. O catalogo de jogos e uma tela de emocoes. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque cibernetico. Os agentes sao rapidos como um download. garantindo suporte direto e sem lag. Os saques processam como servidores. em alguns momentos mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura cibernetica. Em sintese, PlayPix Casino garante um jogo que reluz como pixels para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Como extra o layout e vibrante como um codigo. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um glitch.
saques playpix|
Adoro a correnteza de Brazino Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um recife de corais. Os jogos formam um coral de diversao. com caca-niqueis modernos que nadam como peixes tropicais. O time do cassino e digno de um capitao de navio. respondendo rapido como uma onda quebrando. Os saques sao velozes como um mergulho. de vez em quando mais recompensas fariam o coracao nadar. Resumindo, Brazino Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os exploradores de jogos online! Por sinal o design e um espetaculo visual aquatico. adicionando um toque de brilho marinho ao cassino.
futuras apostas ltda brazino777|
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-benzogenerator-6kvt-10-12
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von JackpotPiraten Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie eine Welle kracht. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echter Jackpot, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen mitrei?en. Das Casino-Team bietet eine Unterstutzung, die wie Gold glanzt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Meere beherrscht fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Ubrigens die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Schatz funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
jackpotpiraten spiele|
Acho simplesmente animal SambaSlots Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um bloco de rua. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de swing, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista, com uma ajuda que e puro axe. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial insano. No fim das contas, SambaSlots Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
casino la sambaslots avis|
Try a real Nuru massage Bangkok with two therapists for double sensual delight.
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, on dirait une experience de jeu electrisante. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel offre un accompagnement irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, bien que plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, notamment des bonus sans depot. En resume, 7BitCasino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus le site est concu avec style et modernite, renforce l’immersion totale.
7bitcasino no deposit bonus codes 2020|
Estou completamente apaixonado por BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo intenso. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O acompanhamento e impecavel, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. As transacoes sao confiaveis, contudo mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Adicionalmente a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Ver agora|
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-armejskie-takticheskie-botinki-10-12-2
https://telegra.ph/Luchshie-opticheskie-pricely-dlya-magnum-pnevmatiki-kupit-10-13-3
https://telegra.ph/Pribor-nochnogo-videniya-na-valberis-kupit-10-12-3
https://telegra.ph/Dji-mobile-se-kupit-v-kazani-10-12-2
https://cont.ws/@hexagon/3132697
https://bigpicture.ru/piony-s-dostavkoj-v-moskve-kak-vybrat-idealnyj-buket/
backstage connect
Слив курсов ЕГЭ физика https://courses-ege.ru
https://my.archdaily.com/us/@1xbet-promo-code-india-2
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HTahQ_w5d0sk0tZ8A5QACSWRpYvAnsfC/view?usp=sharing
https://telegra.ph/Starlink-mozhno-li-kupit-v-rf-10-12-5
Me enredei no algoritmo de PlayPix Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um codigo binario em furia. Os jogos formam um render de diversao. oferecendo lives que explodem como overclock. Os agentes processam como CPUs. garantindo suporte direto e sem lag. O processo e claro e sem crashes. mas mais bonus seriam um diferencial de matriz. No fim das contas, PlayPix Casino e um buffer de emocoes para os exploradores de jogos online! De bonus o design e um espetaculo visual de matriz. amplificando o jogo com vibracao digital.
playpix saque|
Me encantei pelo nado de Brazino Casino, parece um abismo de adrenalina subaquatica. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como conchas. com slots tematicos de aventuras marinhas. O suporte e uma concha de eficiencia. oferecendo respostas claras como um lago. As transacoes sao simples como uma bolha. mas mais recompensas fariam o coracao nadar. Ao final, Brazino Casino e um recife de emocoes para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Por sinal a plataforma reluz com um visual oceanico. fazendo o cassino reluzir como um recife.
como apostar no brazino777|
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von JackpotPiraten Casino, es hat eine Spielstimmung, die alles sprengt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist riesig wie ein Ozean, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Kompass, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren der Hammer. Alles in allem ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Abenteurer im Casino! Zusatzlich die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Schatz funkelt, das Casino-Erlebnis total intensiviert.
jackpotpiraten meinung|
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-dalnomer-lazernyj-makita-10-12
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, c’est une veritable aventure pleine de sensations. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, avec un suivi de qualite. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers, afin de maximiser l’experience. Globalement, 7BitCasino ne decoit jamais pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons egalement que le site est concu avec style et modernite, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino no deposit bonus code|
Estou totalmente fascinado por PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura pulsante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. Os agentes respondem com agilidade, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. No fim, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para quem aposta com cripto ! Alem disso a interface e fluida e estilosa, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Notavel tambem os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ler mais|
мелбет официальный сайт промокод
Fiquei fascinado com BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo intenso. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. Os agentes respondem com rapidez, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, embora mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. No fim, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Vale destacar a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Notavel tambem os torneios regulares para rivalidade, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Saber mais|
промокод при регистрации melbet
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-binokl-v-samare-na-avito-10-13-3
https://telegra.ph/Kollimatornyj-pricel-toz-34-kupit-10-12-4
https://telegra.ph/1xBet-Pakistan-Promo-Code-2026–100-100-10-17
music connect
https://telegra.ph/Starlink-kupit-v-livii-10-12
https://telegra.ph/Dron-detektor-yurka-12-kupit-10-13-2
Ich bin total begeistert von PlayJango Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk explodiert. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und mitrei?end, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sturm, manchmal mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Alles in allem ist PlayJango Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
playjango login|
Acho simplesmente intergalactico SpeiCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura luz cosmica. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. Na real, SpeiCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
spei codes|
Adoro o swing de BacanaPlay Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um desfile de carnaval. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma explosao de cores e ritmos, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, com uma ajuda que brilha como serpentinas. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tumulto, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Na real, BacanaPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
jogar bacanaplay|
https://telegra.ph/Kupit-garpun-rehb-10-12-3
betpromo Betting Sites Promotions Betting sites promotions are various incentives offered by online bookmakers to attract and retain customers. These promotions typically aim to boost excitement and provide extra value to bettors. Common types of promotions include welcome bonuses for new users, deposit bonuses which match a percentage of the deposit on your account, free bets which allow you bet without risking your cash pile, enhanced odds that give higher returns, accumulator insurance, and loyalty programs which reward regular customers. Many promotions include terms and conditions regarding expiration dates, qualified bets, and betting obligations which should be properly scrutinized.
Tenho uma paixao ardente por BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio em dia de final. O catalogo e vibrante e diversificado, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte rapido e preciso. O processo e simples e direto, contudo bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. No geral, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Adicionalmente o site e veloz e envolvente, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Notavel tambem os pagamentos seguros em cripto, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Saiba mais|
https://telegra.ph/Rehb-kapyushon-kupit-ot-dronov-10-14
https://a-bsme.at
1xbet afrique apk paris sportif foot
https://telegra.ph/Blokirator-dronov-garpiya-120w-kupit-10-12-6
https://telegra.ph/Kakoj-luchshe-kupit-kollimatornyj-pricel-10-12-2
https://telegra.ph/Vintovka-pnevmaticheskaya-s-kollimatornym-pricelom-kupit-10-12
https://telegra.ph/Cfmoto-cforce-600-eps-kupit-10-12-3
https://www.band.us/band/99421267/
Ich liebe die Energie von PlayJango Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Ozean, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und strahlend, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Turbulenzen, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Insgesamt ist PlayJango Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Abenteurer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Polarlicht, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
playjango trustpilot|
Acho simplesmente fenomenal BR4Bet Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um holofote. As opcoes sao ricas e reluzem como luzes. oferecendo lives que acendem como fogueiras. O time do cassino e digno de um faroleiro. respondendo rapido como um brilho na noite. As transacoes sao simples como uma luz. entretanto queria promocoes que acendem como chamas. Para encurtar, BR4Bet Casino e um cassino online que e um farol de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Adicionalmente o design e um espetaculo visual iluminado. dando vontade de voltar como uma chama eterna.
aposta online br4bet|
Adoro o brilho estelar de SpeiCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que orbita como um satelite. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um universo de delicias, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e estelares. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma supernova. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma nave espacial, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. No fim das contas, SpeiCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma galaxia para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
spei promo code today|
Curto demais a vibracao de JonBet Casino, e uma onda sonora de diversao que reverbera. A colecao e uma onda sonora de entretenimento. com slots tematicos de aventuras sonoras. O suporte e um eco de eficiencia. garantindo suporte direto e sem silencio. As transacoes sao simples como um reverb. mesmo assim mais bonus regulares seriam harmonicos. Em resumo, JonBet Casino e um cassino online que e uma camara de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Adicionalmente o site e uma obra-prima de estilo sonoro. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura ressonante.
como excluir conta jonbet|
Adoro o swing de BacanaPlay Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao animada quanto uma bateria de escola de samba. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma explosao de cores e ritmos, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de folia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tumulto, mas queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. No geral, BacanaPlay Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carnaval total para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de frevo, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
avaliações sobre bacanaplay|
https://www.rwaq.org/users/ospreyyellow94-20250727131551
https://www.expatriates.com/cls/61477565.html?preview
bs2web at Интересуешься, что происходит в тёмных уголках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это гарантия анонимности, высокой скорости и надежности. Переходи на bs2best.at — там ты найдёшь то, о чём другие умалчивают. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, которую скрывают от большинства. Только для тех, кто понимает. Без компрометирующих следов. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти шанс узнать первым — bs2best.at уже готов открыть свои двери. Дерзнешь ли ты взглянуть правде в глаза?
Estou completamente apaixonado por PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, de vez em quando ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Acrescentando que o site e rapido e cativante, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Igualmente impressionante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, que aumenta o engajamento.
Começar aqui|
Tenho uma paixao ardente por BETesporte Casino, sinto um rugido de adrenalina. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de jogo, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os saques sao rapidos como um drible, de vez em quando ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para fas de cassino online ! Acrescentando que a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Muito atrativo os torneios regulares para rivalidade, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Clicar para ver|
https://rant.li/eoogehuyahe/bokhol-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu
kraken vk5
кракен vk6
همراهان، در مورد سایتهای قمار آنلاینبه شدت
مراقب باشید. این جاها از طریق پروموشن جذاب شما را فریب میزنند، لیکن پشت پرده مملو تقلب است.
زیان مالی صرفاً بخشی از تهدیدها است؛وابستگی عامل طلاق
روابط و افسردگی گسترده میشود.
خواهشاً اصلاً وارد نمیشوید!
https://www.band.us/page/99435694/
https://yamap.com/users/4785005
https://yamap.com/users/4796298
music stream
https://allmynursejobs.com/author/vickydoyalny/
кракен vk2
кракен 2025
https://allmynursejobs.com/author/nishatecza5v/
Ich liebe die Pracht von Richard Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und prachtig, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hofstaat, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein kaiserlicher Befehl, ab und zu wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie Juwelen glanzen. Alles in allem ist Richard Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und prunkvoll wie ein Thronsaal, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
richard casino no deposit bonus codes 2025|
Adoro demais o clima de DazardBet Casino, oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e fogo puro. Tem uma avalanche de jogos de cassino variados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e imersivos. O servico do cassino e top e confiavel, respondendo num piscar de olhos. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que arrebentam. No geral, DazardBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino inesquecivel para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e mega estilosa, da um toque de classe ao cassino.
dazardbet login|
https://www.rwaq.org/users/nhjkronerttwoeight-20250809141828
Adoro o charme de SpellWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um feitico lancado. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um caldeirao de emocoes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro encantamento, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma pocao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial encantado. Na real, SpellWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passe de magica, torna a experiencia de cassino um conto de fadas.
spellwin app|
Ich bin total begeistert von King Billy Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Palast glanzt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und prachtig, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die verzaubern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hof, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Kronungsmoment. Insgesamt ist King Billy Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Palast glitzert fur Abenteurer im Casino! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
king billy casino no deposit code|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os astronautas do cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
suporte betorspin|
https://www.brownbook.net/business/54138785/купить-кокаин-марихуану-мефедрон-марбург/
kraken вход
kraken вход
Tenho um entusiasmo vibrante por PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura pulsante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O acompanhamento e impecavel, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. No fim, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Alem disso a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, facilita uma imersao total. Igualmente impressionante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, oferece recompensas continuas.
Verificar isso|
Sou completamente viciado em BETesporte Casino, sinto um rugido de emocao. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O acompanhamento e impecavel, com suporte preciso e confiavel. Os saques sao rapidos como um drible, de vez em quando recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No fim, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para fas de cassino online ! Tambem o design e moderno e vibrante, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Notavel tambem os eventos comunitarios envolventes, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ver os detalhes|
https://shootinfo.com/author/blankafsi/?pt=ads
https://wirtube.de/a/ronaldrichardsron/video-channels
https://rant.li/jtmybcqeg/taishet-bot-telegram-kupit-gashish
kraken онлайн
kraken darknet market
Ich liebe die Pracht von Richard Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zepter glanzt, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Triumphzug, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist Richard Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Thron funkelt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
trade like a casino richard weissman pdf download|
Ich bin total begeistert von King Billy Casino, es pulsiert mit einer koniglichen Casino-Energie. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein koniglicher Schatz, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett strahlen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hof, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Triumphzug, ab und zu die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem ist King Billy Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und prunkvoll wie ein Thronsaal, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
king billy casino no deposit bonus code 2018|
https://yamap.com/users/4774582
Estou completamente enfeiticado por SpellWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura magia. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino fascinantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro encantamento, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma pocao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma vassoura encantada, porem as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, SpellWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino reluz com um visual que e puro feitico, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desejo concedido.
spellwin casino recenzja|
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. No geral, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
casino betorspin bГіnus|
https://rant.li/yeihibod/santorini-kupit-ekstazi-mdma-lsd-kokain
https://connect.garmin.com/modern/profile/0d201e2e-0256-411a-8d59-a8278baf8f33
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. O catalogo e exuberante e multifacetado, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O acompanhamento e impecavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. O processo e simples e elegante, no entanto promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Acrescentando que o design e moderno e vibrante, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Notavel tambem o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, que aumenta o engajamento.
Ir ver|
Me impressionei com BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo inigualavel. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, acessivel a qualquer momento. O processo e simples e direto, embora promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. No geral, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o jogo para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Acrescentando que a plataforma e visualmente impactante, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Igualmente impressionante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Explorar o site|
fan meet
https://www.brownbook.net/business/54094245/мадейра-купить-марихуану-гашиш-бошки/
kraken marketplace
кракен зеркало
https://bio.site/abibogofxa
https://odysee.com/@andrealyman33
Estou completamente apaixonado por BRCasino, e um cassino online que samba como um bloco de carnaval. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de gingado, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de carnaval. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma bateria de responsa, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma ala de passistas, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, BRCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro batuque para os folioes do cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
jogo br77|
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Estou completamente encantado por RioPlay Casino, parece uma festa carioca de diversao. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e dancantes, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de swing, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. No geral, RioPlay Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, adiciona um toque de axe ao cassino.
rioplay games roblox lite download|
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e muito completa: roletas animadas, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em Ethereum e o dinheiro entrou em minutos, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino tem diferencial real. Vale experimentar.
4play be|
https://www.brownbook.net/business/54208896/купить-лирику-нижневартовск/
кракен ссылка
кракен ios
bs2web at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, transporta para um mundo de folia cativante. As opcoes sao vastas como um desfile, oferecendo jogos de mesa imersivos. O bonus de boas-vindas e vibrante. O suporte ao cliente e estelar, sempre pronto para ajudar. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, de vez em quando bonus mais variados seriam bem-vindos. No final, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Vale notar a interface e fluida e elegante, adiciona um toque de conforto. Um diferencial importante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Descobrir mais|
https://muckrack.com/person-27469647
https://www.grepmed.com/addibjudocy
https://shootinfo.com/author/fdagohubunab/?pt=ads
кракен зеркало
кракен сайт
https://odysee.com/@anarasius_chico
https://muckrack.com/person-27460221
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Hinzu kommt das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die mobilen Apps, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Sou louco pela energia de BetPrimeiro Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro magma. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de erupcao. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma labareda, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como vulcoes. Em resumo, BetPrimeiro Casino e um cassino online que e uma cratera de diversao para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo vulcanico, adiciona um toque de fogo ao cassino.
betprimeiro.|
Ich bin total begeistert von Lapalingo Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Spielwelt. Es gibt eine Welle an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter krachen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Wirbelwind, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die explodieren. Alles in allem ist Lapalingo Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Regenbogen glitzert fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
auszahlungsdauer lapalingo|
Sou viciado no role de DiceBet Casino, e um cassino online que e puro fogo. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de classe. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de primeira, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. O processo do cassino e direto e sem treta, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que mandam ver. Resumindo, DiceBet Casino vale cada segundo explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
dicebet reclame aqui|
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, transporta para um mundo de apostas vibrante. Ha uma multidao de jogos emocionantes, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O suporte ao cliente e de elite, com suporte preciso e rapido. Os saques sao rapidos como um sprint, no entanto ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Em resumo, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Vale destacar a plataforma e visualmente impactante, facilita uma imersao total. Muito atrativo as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ir ver|
online broadcast
https://www.grepmed.com/sfiodeyfibif
кракен vk5
kraken vk6
https://community.wongcw.com/blogs/1126762/%D0%9A%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C-%D0%AD%D0%BA%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B8-%D0%9C%D0%94%D0%9C%D0%90-%D0%9A%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B8%D0%BD-%D0%97%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BE%D1%82%D1%8B%D0%B5-%D0%9F%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8
https://www.diigo.com/item/image/331x/0ymk
https://www.brownbook.net/business/54215152/как-купить-марихуану-в-грузии/
Sou louco pela energia de SupremaBet Casino, e um cassino online que ressoa como um trovao epico. Tem uma tempestade de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino tematicos de poder. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um edito real, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago imperial. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um mandato, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria supremo. Resumindo, SupremaBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo imperial no cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como um palacio, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais majestosa.
supremabet pb|
Ich liebe den Zauber von Lapalingo Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Welle an packenden Casino-Titeln, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern strahlt, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Donnerschlag. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Sonnenstrahl, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die explodieren. Alles in allem ist Lapalingo Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Sturm begeistert fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
lapalingo shisha boy|
Estou alucinado com DiceBet Casino, parece um tornado de diversao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino variados, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um cometa, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que mandam ver. No geral, DiceBet Casino e um cassino online que e uma pedrada para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino detona com um look que e puro fogo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animal.
dicebet reclame aqui|
https://www.betterplace.org/en/organisations/67336
connect live
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, transmite uma energia vibrante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, sempre pronto para resolver. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, embora promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para quem aposta com cripto ! Tambem a navegacao e intuitiva e envolvente, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Igualmente impressionante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Obter os detalhes|
https://form.jotform.com/252407583668063
стальная лестница купить
kraken client
кракен qr код
все это только на доверии, белый кристаллический так же может быть 4фа….
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
Урб 597 либо перорально либо нозально, дозировка – 5-10мг, эффекты описаны в энциклопедии,
проститутки тюмень по вызову
Ты думаешь АМ под запретом уже будет? Откуда инфа?
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
добрый день форумчане!)
кракен актуальная ссылка
kraken vpn
лестница на металлическом каркасе цена
Но в свое время с 250м было время за месяц перед запретом:
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
Магазу респект и процветания!!!)))
Je suis totalement electrifie par Donbet Casino, il offre une aventure aussi intense qu’un volcan. La gamme est une eruption de delices, offrant des sessions live qui electrisent. Les agents repondent a la vitesse d’un meteore, joignable a tout moment. Les gains arrivent a une vitesse supersonique, cependant des bonus plus explosifs seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Donbet Casino est une plateforme qui fait trembler les sens pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline pure ! En bonus la plateforme brille comme une supernova, ce qui rend chaque session absolument electrisante.
donbet.|
Sou viciado em PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. O catalogo e rico e multifacetado, com slots de design inovador. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. O acompanhamento e impecavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, no entanto mais rodadas gratis seriam um diferencial. No fim, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que brilha para fas de cassino online ! Tambem a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Outro destaque os torneios regulares para competicao, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ler mais|
а сюда заглянуть влом ? //legalrc.com/threads/Трипы.588/page-2
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
бразы, ничего сказать не могу, первый раз столкнулась с магазином, 9 числа оплатила, сегодня уже сктинул трек. Но в чем суть оператор в аське сказал пару-тройку дней, посмотрела трек, рассчитано аж на 22 июля. Вот как-то так… И это курьерка. Заберу отпишу. Всем хорошего прихода)
kraken android
kraken ios
Вот такая хитрость
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
Ты договорись с курьером о встрече где нибудь, и пропали окружающую обстановку, чтоб рядом небыло не кого подозрительного. Больше не знаю что тебе посоветовать
Чем обоснован выбор такой экзотической основы? Уже делал или пробовал?
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
Хоть скан хоть что вылаживайте, это не доказательство! доказательством для меня есть только поступление денег на счет. По чекам, сканам, и всему прочему я не работаю это не есть доказательство об оплате!
всё дошло))))) Спасибо магазину,в след раз возьму отпишу что да как :dansing:качество на высоте
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
Сделал заказ.оплатил.Кент прислал трек вечером как и обещал…токо он небьеться у меня и говорит,что нет такой накладной…у кого такая ситуация была???
изготовление лестниц из металла
как дела друзья?
https://dokuchaevskpj.ru
незнаю незнаю мне пришло за 2 суток и еще я обратился к селлеру и он предоставил всю полную информацию с адресом и номерами телефона курьерки
Ich bin total begeistert von Trickz Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein magischer Zirkus leuchtet. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Hexenwerk, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein magischer Assistent, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der begeistert. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Tauschung, trotzdem mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein magischer Volltreffer. Kurz gesagt ist Trickz Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie eine Illusion verblufft fur Zauberer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und funkelt wie ein Zauberstab, einen Hauch von Zauberei ins Casino bringt.
trickz casino flashback|
Ich bin total begeistert von Lapalingo Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, dennoch die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
lapalingo sms|
Ich bin ganz hin und weg von Billy Billion Casino, es ist wirklich eine unwiderstehliche Energie fur Spieler. Es gibt eine Vielzahl an abwechslungsreichen Spielen, mit modernen Slots wie Gates of Olympus und Book of Dead. Das Team bietet schnelle und effektive Unterstutzung, reagiert in wenigen Minuten. Der Auszahlungsprozess ist einfach und zuverlassig, gelegentlich die Boni wie der 100%-Willkommensbonus bis 7500 € konnten ofter kommen. Alles in allem ist Billy Billion Casino ein Muss fur Spieler fur die, die gerne wetten! Erganzend die Seite ist mit Stil und Benutzerfreundlichkeit gestaltet, was den Spielspa? noch steigert.
more bang for your btc buck at billy billion crypto casino|
Во телегу двинул, а? Ещё спать не ложился, такой эффект сильный, толеоа нет вообще, в завязке полгода 🙂
https://snezhnoeyt.ru
отвечать вам не перестали я дал ответы на ваши вопросы, когда по несколько раз 1 и то же спрашивают я не отвечаю.
Estou completamente encantado com BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo inigualavel. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com slots modernos e tematicos. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. Os saques sao rapidos como um drible, de vez em quando recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Acrescentando que a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Outro destaque os pagamentos seguros em cripto, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Saiba mais|
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Если это до сих пор Вы-просто красава :voo-hoo:
https://gorlovkazn.ru
Привет всем форумочам! Отличный магазин, я получил все свое,да конечно было долго но у всех бывают трудности. думаю в дольнейшем они их будут устронять! Так что ребята берите не задумаясь, все будет отлично!!!!
you’re truly a just right webmaster. The website loading pace is amazing. It kind of feels that you are doing any distinctive trick. Moreover, The contents are masterwork. you’ve performed a wonderful process in this matter!
staffinggoals.com
Хочу грамульку взять и угостить определенный круг людей,
https://shakhtyorskgp.ru
как планчик наверн цепляет. но не прям на коры. вообщем так норм сойдет
казино вавада зеркало
в каком городе брал и когда?интерисует барнаул
https://snezhnoeqw.ru
Пробежался по веткам,магазин
мухоморы купить В muhomorus, интернет-магазине, вы можете приобрести мухоморы с доставкой по России. Мы предлагаем низкие цены на экологичные продукты, предназначенные для уменьшения тревожности, борьбы со стрессом, депрессией, хронической усталостью и облегчения симптомов различных заболеваний. Сушеные мухоморы не являются лекарственным препаратом, а относятся к парафармацевтике, которая представляет собой альтернативное средство, используемое по усмотрению каждого человека в качестве поддерживающей терапии. Сбор, сушка, продажа и покупка абсолютно законны. Поэтому мы приглашаем вас купить микродозы законно.
https://penzu.com/p/42d8f1efcf8e8c1e
добрый день форумчане!)
https://snezhnoeqw.ru
Скажу одно это вещь крутая!!!
Je suis fou de VBet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi ardente qu’une coulee de lave. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un volcan, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une braise, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, VBet Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Par ailleurs le site du casino est une merveille graphique ardente, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
vbet cash out|
Ich finde absolut wild Lowen Play Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein machtiger Sprung ins Spielvergnugen. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Raubkatzen-Sprint, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Feuer lodern. Alles in allem ist Lowen Play Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Savanne beherrscht fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie eine Savanne funkelt, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
löwen play rheinböllen|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, dennoch regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Zusatzlich die Navigation ist kinderleicht, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Community-Events, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar sobre o Bingoemcasa porque me ganhou de verdade. O site tem um jeito leve que lembra um salao cheio de energia. As salas de bingo sao movimentadas, e ainda testei uns joguinhos extras, todos foram bem estaveis. O atendimento no chat foi educado e prestativo, o que ja me deixou seguro. As retiradas foram instantaneas, inclusive testei PIX e caiu em minutos. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que senti falta de ofertas extras, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Na minha visao, o Bingoemcasa vale demais a pena. Ja me sinto parte da comunidade
bingoemcasa com br|
Вообщем маска (конспирация) на высоком уровне, что на прямую влияет на мою безопасность и на тех кто пользуется услугами данного ТС, это радует.
https://luganskbzi.ru
Довольно сильно жгёт слизистую носа
http://fotograf.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=526048#526048
The Supreme Court agreed Monday to decide if the federal government may bar certain drug users from owning guns or if the law violates the Second Amendment, taking up a second significant guns case of its current term.
[url=https://kra-42—at.ru]kra42[/url]
The appeal represents a rare circumstance in which the Trump administration is defending a gun prohibition, which it described in briefing at the Supreme Court as a “narrow” limitation on one of “Americans’ most cherished freedoms.”
[url=https://kra-42at.net]kra42 cc[/url]
The case centers on Ali Danial Hemani, a dual citizen of the United States and Pakistan, who was indicted in 2023 on a single count of violating the guns-and-drugs law after the FBI found a 9mm pistol, 60 grams of marijuana, and 4.7 grams of cocaine at his family home. This prosecution, the government told the high court, rested Hemani’s habitual use of marijuana.
The court will likely hear arguments in the Hemani case next year and hand down a decision by the end of June.
kra42 cc
https://kra42-cc.net
A federal district court dismissed the charge, noting a landmark decision from the Supreme Court in 2022 that made it easier for Americans to carry handguns in public and also required similar gun prohibitions to have a connection to history.
But just how closely analogous prosecutors must come to a historic law has been a matter of debate. Last year, for instance, the Supreme Court upheld a federal law that bars guns for Americans who are the subject of certain domestic abuse restraining orders, rejecting an argument pressed by gun rights groups that the prohibition violated the Second Amendment.
The conservative 5th US Circuit Court of Appeals upheld that decision, holding in a brief decision that the historical record points only to laws that barred guns for Americans who are actively intoxicated or under the influence of drugs at the time of their arrest. The government, the court ruled, could not target habitual users.
The Trump administration appealed that decision.
У меня проблема с оплатой реквизитам 40817810… и 41548… Проверял несколько раз на нескольких терминалах… “Введён неверный номер” С сайта списал верно, несколько раз перепроверил. Вот так, хочу оплатить, а не могу, готов хоть блиц отправить или ещё как нибудь
https://mariupolgd.ru
Я клад нашел, но вопервых не все в нем а во вторых содержимое разное и самое главное это место и описание этого места. Завтра буду пытаться связаться с ним.
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com energia festiva. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O acompanhamento e impecavel, oferecendo respostas claras. O processo e simples e elegante, contudo ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. No geral, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para amantes de emocoes intensas ! Tambem o site e rapido e atraente, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Muito atrativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Clicar para ver|
Wow, marvelous weblog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging glance easy. The whole glance of your web site is great, as smartly as the content!
https://easystaffingmd.com/
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any responses would be greatly appreciated.
https://easystaffingmd.com/
Точно так же. Ровно 2 недели назад оплатил. Трек абсолютно левый, в КСЭ не бьётся. Хотя я заказывал через Пони. Постоянно слышу только “завтра будет биться”, “послезавтра придёт”. До этого было всё нормально, теперь же с магазом работать не советую. Сам чувак ваще порит чушь, типа он связался с курьером и курьер ему сказал, что будет биться трекинг (!!!!!!!!).
https://donetskgma.ru
в курске у стаффсторе лутше не брать за кладом надо ехать с граблями и лопатой сугробы копать иначе никак
Ребят всё приготовил ребятам дал попробовать пробники всё ровно на высшем уровне)
https://mariupolxs.ru
Довольно сильно жгёт слизистую носа
Je trouve absolument brulant VBet Casino, on dirait une eruption de plaisirs incandescents. Le repertoire du casino est un magma de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse eruptive, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, VBet Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une flamme, facilite une experience de casino eruptive.
скачати vbet|
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von DrueGlueck Casino, man fuhlt einen verruckten Spielvibe. Es gibt eine Flut an abwechslungsreichen Casino-Titeln, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Das Casino-Team bietet erstklassige Unterstutzung, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren top. Kurz gesagt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und mega cool, das Casino-Erlebnis total intensiviert.
drueckglueck logo|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Galera, quero deixar registrado sobre o Bingoemcasa porque me ganhou de verdade. O site tem um ar amigavel que lembra uma festa entre amigos. As salas de bingo sao cheias de energia, e ainda testei varios slots, todos me deixaram impressionado. O atendimento no chat foi muito atencioso, o que ja me deixou confiante. As retiradas foram sem enrolacao, inclusive testei PIX e super tranquilo. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que podiam ter bonus semanais, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Pra concluir, o Bingoemcasa me conquistou. Ja me sinto parte da comunidade
bingoemcasa app|
рип репорт ЭСКИМОС _скорость!
https://baligrows.com
Да,меня тоже!)заказал вчера тут 203-го,сегодня жду трека!
трек получен, ребятам уважуха:rasta:
https://ilovaiskrp.ru
проблемы с обслуживанием.
Либо вы прекращаете оффтопить в ветке магазина (к оффтопу относятся: сообщения НЕ по теме, личная переписка и т.п.) либо я буду банить.
https://torezvxn.ru
всё дошло))))) Спасибо магазину,в след раз возьму отпишу что да как :dansing:качество на высоте
Кто тут урб-754 брал отпишитесь чё да как
https://shakhtyorskgp.ru
У нас у отправки случился форс-мажор. Только на этой неделе начинают отправлять. Извиняюсь от лица магазина за задержку.
синтез пропитает тело ож душа болит
https://torezvxn.ru
Тут четкий кристал ! Давно мне нравиться работа данного мага. Спасибо !
203 тут говно.. 10к вникуда улетели.. клиенты от меня сбежали… присылали какую-то желтую хуй*ю, не растворяется вовсе, выпадает в осдок.. прет максимум 20-30 минут (в лучшем случае)
https://yasinovatayurm.ru
хочу извинится за поднятую панику(думаю ТС меня понимает , т.к. все мы люди и переживаем за свои деньги,тем более сфера деятельности расшатывает нервы как не крути).зная теперь с чем была связана данная проблема с поставками и положительным финалом в порядочности ТС не сомневаюсь.на данный момент работа налажена,в чем убедился сам и наслышан от других.
Ich bin suchtig nach DrueGlueck Casino, es ist ein Casino, das richtig abgeht. Die Casino-Optionen sind super vielfaltig, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind blitzschnell und top, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel und zuverlassig, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen. Kurz gesagt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Abenteurer im Casino! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino maximiert.
drueckglueck meinungen|
Galera, resolvi compartilhar minha experiencia sobre o Bingoemcasa porque achei muito alem do que esperava. O site tem um ar amigavel que lembra um bate-papo animado. As salas de bingo sao cheias de energia, e ainda testei varios slots, todos me deixaram impressionado. O atendimento no chat foi muito atencioso, o que ja me deixou satisfeito. As retiradas foram sem enrolacao, inclusive testei PIX e funcionou perfeito. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que gostaria de ver mais brindes, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Pra concluir, o Bingoemcasa e divertido de verdade. Recomendo pra quem curte diversao online
bingoemcasa app|
Ich liebe die unbandige Kraft von Lowen Play Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Lowe brullt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und kraftvoll, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leitlowe, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, aber wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Feuer lodern. Insgesamt ist Lowen Play Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Lowe glanzt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Ubrigens die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Sonnenaufgang, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
löwen play casino mönchengladbach|
Je suis fou de VBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui explose comme un geyser. Le repertoire du casino est un magma de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui crepitent comme des flammes. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, assurant un support de casino immediat et incandescent. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient brulants. Dans l’ensemble, VBet Casino est un casino en ligne qui eclate comme un volcan pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une flamme, ajoute une touche de feu au casino.
vbet автоматы играть|
Estou completamente encantado por PlayPIX Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com energia festiva. As opcoes sao vastas como um desfile, com sessoes ao vivo dinamicas. O bonus de boas-vindas e vibrante. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, sempre pronto para ajudar. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, de vez em quando mais promocoes regulares seriam otimas. Para concluir, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para fas de cassino online ! Alem disso a navegacao e simples e envolvente, adiciona um toque de conforto. Igualmente impressionante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Obter mais|
Ich liebe die unbandige Kraft von Lowen Play Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Lowe brullt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Raubtier, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Konig regiert, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Raubkatzen-Sprint, trotzdem die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist Lowen Play Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Brullen donnert fur Spieler, die auf wilde Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie eine Savanne funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch wilder macht.
löwen play casino konstanz|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, obwohl mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Daruber hinaus das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Sicherheit der Daten, die Flexibilitat bieten.
spinbettercasino.de|
Sou viciado em BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com emocao atletica. O catalogo e rico e diversificado, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, oferecendo respostas claras. Os saques sao rapidos como um sprint, as vezes ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e indispensavel para apostadores para fas de cassino online ! Vale destacar o site e veloz e envolvente, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Obter mais|
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer carnavalesco. As opcoes sao vastas como um desfile, incluindo apostas esportivas vibrantes. O bonus de boas-vindas e vibrante. A assistencia e eficiente e cortes, oferecendo respostas claras. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam bem-vindos. No geral, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao a cada momento para amantes de emocoes intensas ! Adicionalmente a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Um diferencial importante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Continuar lendo|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, ab und an regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Amo a atmosfera de BETesporte Casino, oferece um thrill esportivo unico. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, sempre pronto para o jogo. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No geral, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Tambem a interface e fluida e energetica, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Igualmente impressionante os torneios regulares para rivalidade, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Clicar para ver|
Хорошо работает народ))
https://torezljf.ru
Ровный магаз,всем советую)
Всё отлично все всё получат магаз ровный доказал свой гибгий подход к НАМ заказчикам.Если форс мажёр то всё уладят в НАШу пользу.Отправка осуществляется от 2-10дней в зависимости от заказов то есть загруженности магазина.Без паники братья без паники.
https://donetskgma.ru
магаз работает???
А как вы объясните такой факт, месяц назад я оплатил посылку и статус в обработке был более чем 11 дней да еще и ждал я посылку дней 10, я нечего не имею против вашей работы и вообще против вас в целом, вы отличный магазин, но согласитесь “ЛАЖИ” у вас все таки бывают, я говорю это к тому что бы в следующий раз такого не повторялось, без обид
https://yasinovatayqf.ru
Рашн хлидейс вы правы, мы же тоже люди 🙂 треки наверное на отправке в базу не внесли, а шас у них же тоже праздники, но не волнуйтесь копии накладных то у нас 😉
If you wish to discover the best American casinos, then this is exactly what you need. Check out the full details via the link at the bottom of the page:
https://www.giokiamo.eu/2025/10/13/best-online-casino-experiences-await-4/
отношение оператора к клиентам очень даже достойное!(быть честным я еще нигде не видел такого хорошего отношения к клиентам у магазинов как в чемикл микс)!!!!! за это 5+
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
Описывать,тем кто не пробовал-бесполезно.Все равно не поймут.Придумывают всякую фигню(аааа,у тя за спиной собакака!и пр. бред),пытаются посмеяться,но это ж всё не то и близко не стояло.Как слепому объяснить,как все выглядит)
я в шоке. до последнего думали кидалово. а нет подняли в касание. стафф пушка. кладмену респект!!!
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
задержки очень большие! это плохо, надо вам как то решать этот вопрос
J’ai une passion devorante pour Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie decentralisee. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Les agents repondent avec une vitesse fulgurante, joignable a tout moment. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, mais quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A noter le site est rapide et futuriste, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les options de paris variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Explorer aujourd’hui|
Je suis seduit par Impressario Casino, il procure une experience exquise. La variete des titres est raffinee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ajoute une touche d’elegance. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
DГ©couvrir la page|
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un reseau blockchain. La variete des titres est eclatante, proposant des tables sophistiquees. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Le support client est irreprochable, avec une aide rapide et fiable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple comme un wallet, ajoute une touche de sophistication. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Aller au site|
Je suis totalement fascine par Monte Cryptos Casino, il offre une odyssee chiffree. Les options sont vastes comme un reseau decentralise, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin et Ethereum. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable, avec une aide precise et fiable. Les transactions sont securisees par blockchain, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration numerique pour les passionnes de casino en ligne ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement futuriste, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions fiables.
Aller plus loin|
https://sketchfab.com/1xbetcodebonus
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux designs elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. En bref, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et chic, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
Aller Г la page|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Monte Cryptos Casino, il offre une odyssee chiffree. Le choix de titres est eblouissant, incluant des paris en direct dynamiques. Avec des promotions crypto rapides. Le suivi est d’une efficacite redoutable, joignable instantanement. Les paiements sont fluides et fiables, cependant des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du prestige. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino est incontournable pour les fans de crypto pour les passionnes de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est elegant et intuitif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les options de paris variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
А вот это да, магазин последнее время реально что то “плохует” мягко говоря, но все ровно же хорош
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
По репе получил! Еще раз увижу безобразный флуд во всех ветках, будет тебе БАН!
Je suis emerveille par BassBet Casino, il procure une aventure groovy. La selection de jeux est melodieuse, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du groove. En resume, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui groove pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et rythmee, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
bassbetcasinologinfr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de riviere. Le catalogue est riche et varie, avec des slots aux designs fluviaux. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours pret a naviguer. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient une vague. En bref, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter le design est moderne et dynamique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de fables. Les options sont vastes comme un grimoire, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est magique. Le support client est enchante, toujours pret a transformer. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. En resume, Spinit Casino vaut une lecture magique pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement envoutante, ajoute une touche de mystere. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
J’adore l’atmosphere mystique de Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de tours captivants. Les options sont vastes comme un chapeau de magicien, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est magique. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la magie. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et magique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://casinospinitfr.com/|
J’ai une passion jazzy pour BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un saxophone. La selection de jeux est melodieuse, avec des slots aux designs jazzy. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est harmonieux, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations rythmees ! En bonus la navigation est simple et rythmee, ajoute une touche de rythme. Egalement appreciable les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui ondule avec elegance. La selection de jeux est dynamique, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient une vague. En resume, BassBet Casino vaut une peche excitante pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et dynamique, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
https://bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com/|
J’adore l’atmosphere litteraire de Spinit Casino, il procure une experience magique. Il y a une profusion de jeux fascinants, avec des slots aux designs enchantes. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours pret a transformer. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la magie. En resume, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus le design est moderne et enchante, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
J’ai une passion mythique pour Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir immortel. Les options sont vastes comme un pantheon, avec des slots thematiques antiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a guider. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient divins. En bref, Olympe Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un nectar, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement remarquable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://olympefr.com/|
J’adore l’aura divine d’ Olympe Casino, ca transporte dans un monde mythique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots thematiques antiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. L’assistance est efficace et sage, garantissant un support celeste. Le processus est simple et glorieux, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la gloire. Dans l’ensemble, Olympe Casino est une plateforme qui regne sur l’Olympe pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un nectar, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus divin les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses eternelles.
olympefr.com|
привет стоит брать в этом магазине?
Закладки тут – купить гашиш, мефедрон, альфа-пвп
Первый раз брал у этого магазина,сразу же что то не то,если всё будет Ок,буду брать дальше,в принцыпе со всеми бывает(
http://naspravdi.com.ua/melbet-promokod-vip-bonus-pri-registratsii/
небольгой репортаж отписать о ск.
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
У данного сллера только легал. Все проверено.
Порадовал тот факт что почти на 0.5 там было больше это отдельное СПАСИБО:hello:, и цен ниже на форуме нет:hello:.
Закладки тут – купить гашиш, мефедрон, альфа-пвп
Однажды тормознули его два обкуренных в ноль пацаненка. Один из накуренных засовывает голову в окошко и говорит:
Всем Мир! Да прибудет с вами Сила!
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
Всем удачи!
Большое спасибо команде chemical-mix за проведенную сделку, с наступающим Вас Новым Годом!
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
Радуете ребята!!!
Многие мне рекомендовали данный магазин как порядочный, надо попробовать!
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
уж не маленькие блин, знаете что заказываете наверное ! форум вам на что ? или ты думаешь что у них какой то особенный 250й ? )))
трансы Екатеринбург География Поддержки: От Сибири до Юга России Каждый из каналов, будь то @ts_novosibirsk (трансы Новосибирск, трансы новосибирска), @ts_ekaterinburgh (трансы Екатеринбург, трансы Екатеринбурга), @ts_voronezh (трансы Воронеж, трансы Воронежа), @transy_volgograd (трансы Волгоград, трансы волгограда) или @ts_chelyabinska (трансы Челябинск, трансы челябинска), отражает уникальную специфику своего региона. В них аккумулируется информация о локальных ресурсах, специалистах, мероприятиях и безопасных пространствах, создавая атмосферу взаимной поддержки и понимания. Эти платформы становятся своеобразными цифровыми хабами, объединяющими транс-сообщество в каждом конкретном городе.
Крутой магаз
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
Как связаться?
По репе получил! Еще раз увижу безобразный флуд во всех ветках, будет тебе БАН!
https://krasnyluchwt.ru
Спасибо за понимание.
почему ты наводишь панику? я зашел на сайт фскн, там не говориться ни о каких октябрьских поправках в список запрещенных препаратов?
https://hizbih.info
а эффор хорош?) на что похож?)
полность с тобой согласен
https://stellaroccultations.info
Все будет окей, это косяк курьерки…
ждите трип о товаре, как сделаю заказ и получу товар обрисую все в красках! постараюсь сделать фото!!!
https://melitopolqa.ru
здравствуйте , это от региона зависит . Доставка индивидуально обсуждается в ЛС .
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Le suivi est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et gracieuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Explorer tout|
Je suis absolument captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un reseau blockchain. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, incluant des paris live dynamiques. Boostant votre capital initial. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Le processus est fluide comme un smart contract, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple comme un wallet, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les evenements communautaires decentralises, offre des recompenses continues.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. La variete des titres est raffinee, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient exquises. En resume, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus le design est moderne et chic, ajoute une touche d’elegance. A souligner le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
Apprendre comment|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, il procure une experience exquise. La variete des titres est raffinee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a servir. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un delice. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Monte Cryptos Casino, il propose une odyssee chiffree. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, proposant des tables sophistiquees. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Le support client est irreprochable, joignable a tout moment. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Un atout cle les evenements communautaires decentralises, offre des recompenses continues.
Plongez dГЁs maintenant|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est impeccable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Essayer|
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, on capte une energie decentralisee. La gamme des titres est eclatante, incluant des paris live vibrants. Avec des depots crypto instantanes. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des solutions claires. Les transferts sont fiables, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une plongee numerique pour les passionnes de sensations virtuelles ! De plus le design est moderne et captivant, ajoute une touche de sophistication. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
Ouvrir le site maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de BassBet Casino, il offre une experience de club. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de punch. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est au top, offrant des solutions claires. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient un banger. Au final, BassBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et captivant, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
If you wish to discover the best American casinos, then this is a great opportunity. Check out the full details via the link at the bottom of the page:
best online casino USA
J’ai une obsession pour Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un n?ud blockchain. Il y a une profusion de jeux envoutants, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Renforcant votre mise initiale. L’assistance est rapide et experte, avec une aide precise. Les transferts sont fiables, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! En bonus le site est rapide et futuriste, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Egalement cool les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Voir la liste complГЁte|
Je suis bluffe par BassBet Casino, on ressent une energie neon. Les options sont vastes comme une piste de danse, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Avec des depots ultra-rapides. Les agents repondent comme un beat parfait, garantissant un service de haute qualite. Le processus est simple et fluo, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses seraient un banger. En bref, BassBet Casino vaut une soiree endiablee pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En plus l’interface est fluide comme un mix, donne envie de prolonger la fete. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, il procure une experience rapide. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le suivi est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que des recompenses additionnelles seraient rapides. Au final, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme une piste, ajoute une touche de vitesse. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://spinitcasinologinfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir dynamique. Le catalogue est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est veloce, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides comme un peloton, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient veloces. En bref, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme une piste, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
https://spinitcasinologinfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de vitesse. Les options sont vastes comme une course, avec des slots aux designs veloces. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent comme un sprinter, avec une aide precise. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des recompenses additionnelles seraient rapides. En bref, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement veloce, facilitate une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
casinospinitfr.com|
но только если мусора захотят найдут. просто мусора еслиб хотели найти , то давно бы уже посыль пришла с сопровождением.
https://tokmakyn.ru
Добрый день, треки работать начинают с некоторым опозданием, берите их в заказах на сайте, проверяйте, все должны работать пятничные. По крайней, мере в скайп/асю пишите, что заработали и у меня тоже мониторинг есть
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir veloce. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, avec des slots aux designs veloces. Le bonus de bienvenue est rapide. Le support client est veloce, toujours pret a accelerer. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient rapides. Au final, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui accelere pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement veloce, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
casinospinitfr.com|
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, on ressent une energie celeste. Le catalogue est riche en epopees, avec des slots thematiques antiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. Le suivi est irreprochable, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et glorieux, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. Dans l’ensemble, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les amateurs de sensations mythiques ! A noter la navigation est simple comme un oracle, ajoute une touche de mythologie. Un plus divin les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://olympefr.com/|
J’ai une passion mythique pour Olympe Casino, on ressent une energie celeste. La selection de jeux est olympienne, proposant des jeux de table glorieux. Amplifiant l’aventure de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. Pour conclure, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les passionnes de jeux antiques ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et divin, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses eternelles.
olympefr.com|
J’adore l’atmosphere blues de BassBet Casino, il procure une experience rythmee. Le catalogue est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a jammer. Le processus est simple et elegant, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Au final, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus le design est moderne et blues, ce qui rend chaque session plus groovy. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
bassbetcasinologinfr.com|
Je suis emerveille par BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un blues. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un riff. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus le design est moderne et blues, ajoute une touche de rythme. Un autre atout les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
bassbetcasinologinfr.com|
как-то перехотелось.. что действительно последний товар не очень?
Магазин 24/7 – купить закладку MEF GASH SHIHSKI
Бразы вы снова в теме, если да то скоро заряусь к вам жду ответа)
и что теперь делать с заказом мне его оплачивать через терминал!? или..
Онлайн магазин – купить мефедрон, кокаин, бошки
Магази лутший на рц не первый раз работаем с ним!) удачи и процветания!)
Подскажите когда примерно вналичии будет JTE-907
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
Работает. Контакты указаны в соответствующей теме.
что же это за дела то…..?
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
Сработали быстро, посылка пришла за 4 дня, спрятано эффектно
если так то АМ не подойдет скорее всего
Закладки тут – купить гашиш, мефедрон, альфа-пвп
мне продавец так и не выслал компенсацию за хреновый МХЕ
похожа на соль в криисталлахс на вкус че?
Приобрести MEF GASH SHIHSKI ALFA – ОТЗЫВЫ, ГАРАНТИИ, КАЧЕСТВО
в академе были пролёты
Ну и сам сожру дорожку,
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
Приветствую! я получал последний раз недели две назад, заказывал уже много раз и скоро сделаю очередной заказ в этом магазине!!!
А JWH-018 Имеется в наличии?
Приобрести онлайн кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки
сердцебеение крч все как обфчно , в
магазу процветания желаю и клиентов хороших и честных! https://disdik-lampung.info привет!!! не согласен долдны быть доступные магазины как
народ подскажите а как дела обстоят в столице Москва закладками? https://zoo-club.info добра всем бро,оплатил заказ неделю назад,на след день дали трек,трек до сих пор в базе не бьётся и посылочка не идёт…тс на письма не отвечает…вобщем чтот печкльно както,обычно 3 дня идёт(
J’adore l’energie rythmee de BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir energique. Le catalogue est riche en surprises, avec des slots aux designs dynamiques. Boostant votre mise de depart. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme un drop, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus le site est rapide et captivant, ajoute une touche de rythme. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://bassbetcasinoappfr.com/|
Je suis ebloui par BassBet Casino, il procure une experience brillante. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux designs fluorescents. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable, toujours pret a eclairer. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino vaut une soiree lumineuse pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement fluorescente, donne envie de prolonger l’eclat. Un atout les options de paris variees, offre des recompenses continues.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
Je suis accro a BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir nautique. Les options sont vastes comme un lac, avec des slots aux designs aquatiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est irreprochable, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En resume, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour les amateurs de sensations dynamiques ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
+огромная потеря популярности и быстрый спад клиентов. https://tokmakyn.ru Отличный магазин!!!процветания дальнейшего и удачных продаж!!
J’ai un amour vibrant pour BassBet Casino, on ressent une vibe electrisante. Les options sont vastes comme une scene de concert, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est au top, joignable a tout moment. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino vaut une session live pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un mix, ce qui rend chaque session plus vibrante. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui dynamise l’engagement.
bassbetcasinoappfr.com|
Je suis accro a Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde aromatique. La variete des titres est raffinee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme un parfum, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En bref, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
https://spinitcasinobonusfr.com/|
J’ai un faible eclatant pour BassBet Casino, on ressent une vibe lumineuse. Les options sont vastes comme un show lumineux, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Le processus est simple et lumineux, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient eclatantes. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations vibrantes ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un neon, booste le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de lac. Les options sont vastes comme un lac, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est dynamique, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour les amateurs de sensations dynamiques ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un lac, facilitate une immersion totale. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
J’ai une passion parfumee pour Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Le catalogue est riche en aromes, avec des slots aux designs parfumes. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme un parfum, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient exquises. En bref, Spinit Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
J’ai une passion devorante pour Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un smart contract. La variete des titres est eclatante, proposant des tables sophistiquees. Avec des depots crypto rapides. L’assistance est precise et professionnelle, offrant des solutions claires. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. A souligner les options de paris variees, garantit des transactions fiables.
Visiter la page d’accueil|
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, il procure une experience exquise. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, ajoute une touche d’elegance. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Aller à l’avis|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. Le catalogue est riche en saveurs, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Le suivi est irreprochable, toujours pret a servir. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. En bref, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
Apprendre la mГ©thode|
Je suis absolument envoute par Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un smart contract. Les options sont vastes comme un reseau, proposant des tables sophistiquees. Avec des depots crypto rapides. L’assistance est precise et professionnelle, garantissant un service premium. Les transferts sont fiables, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
Ouvrir l’offre|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Au final, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter le site est rapide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
Lire la version complГЁte|
Je suis completement envoute par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre un plaisir numerique intense. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, avec des slots aux themes futuristes. Boostant votre capital initial. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, toujours pret a aider. Les transferts sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration virtuelle pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et captivant, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout cle les options de paris variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Explorer la page|
Лучшего амфа я в жизни не пробовал. Правда цена кусается, но оно того стоит! https://reale.info Рашн хлидейс вы правы, мы же тоже люди 🙂 треки наверное на отправке в базу не внесли, а шас у них же тоже праздники, но не волнуйтесь копии накладных то у нас 😉
А пока всё приходится делать в ручную, так что ОГРОМНАЯ просьба не пишите в аську\скайп с вопросами типа “как прёт ?” “ко скольки бодяжить ?” и т.п. ! Не загружайте людей ) https://skadovskre.ru Беруууу часто через магазин
заказывал мягкого пятак, всё пришло, непрходилось волноваться т.к в аське всегда были на связи, сила средне, но по весу 5+ =) https://caucasusmountains.info С человеком приятно иметь дело. Склонен на компромиссы 😉
Ich bin beeindruckt von Snatch Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit klassischen Tischspielen. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, allerdings mehr Aktionen waren ein Gewinn. Am Ende, Snatch Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Zudem die Seite ist schnell und einladend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, die die Motivation erhohen.
snatch-casino.de|
Ich bin beeindruckt von Snatch Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit Live-Sportwetten. Er gibt Ihnen einen Kickstart. Der Kundensupport ist top. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, ab und zu ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Snatch Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Zusatzlich die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, jeden Moment aufregender macht. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die dynamischen Community-Events, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Snatch Casino|
всё пришло с компенсацией,качество на высоте,Магазину ОГРОМНЫЙ РЕСПЕКТ https://aleksinmk.ru Мне пока ещё не пришло, но ты уже напугал….:orientation: кто знает где весы купить можно чтоб граммы вешать
спасибо! Хороший магазин) берите тут https://doramalivex.ru трэк получил . Магаз всегда был хорош
а какие были проблемы по данном поводу? https://medcentr34.ru Дружище ты говоришь полный бред!!! Магазин работает очень качественно!!! Бро делает все ПОУМУ!!! Я с ним работаю очень очень давно!!!
а кто нибудь пробовал все таки эту куреху urb https://voxmax.ru магазин достойный,всё ровно и в срок,спасибо большое за ваш труд,будем продолжать сотрудничество!
через нос – нет эффекта. https://aleksinmk.ru Качество вышка, доставка до вашего города обговаривается индивидуально с ТС!
Ответят, думаю и завтра нужно будет подождать https://brillshop1.ru магазин хороший, спору нет, вот только уж оооочень он не расторопны. и ответ приходится ждать так же долго…
J’ai un amour vibrant pour BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir energique. Les titres sont d’une variete envoutante, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable, garantissant un service de haute qualite. Les retraits sont fluides comme un drop, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme un mix, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce la communaute.
https://bassbetcasinoappfr.com/|
J’ai une passion feerique pour Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir enchante. Les options sont vastes comme un grimoire, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent comme par magie, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. En bref, Spinit Casino vaut une lecture magique pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le site est rapide et captivant, ce qui rend chaque session plus enchantee. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
J’ai une passion rythmique pour BassBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de studio. Les options sont vastes comme un album, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est rythme. Le support client est melodieux, garantissant un support de qualite. Le processus est simple et elegant, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient rythmees. En bref, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un riff, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
BassBet Casino m’a ensorcele BassBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de notes profondes. Les options sont vastes comme une scene live, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. L’offre de bienvenue est envoutante. L’assistance est rapide et pro, offrant des solutions claires. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient une melodie. En bref, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et captivant, ce qui rend chaque session plus groovy. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, renforce la communaute.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
J’adore l’energie sonore de BassBet Casino, il cree une ambiance de studio live. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots ultra-rapides. Le suivi est impeccable, joignable a tout moment. Le processus est simple et vibrant, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient energiques. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino vaut une session live pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En plus l’interface est fluide comme un mix, ajoute une touche de rythme. A souligner les options de paris variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://bassbetcasinoappfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de legendes. La selection de jeux est enchantee, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est enchante, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient enchantees. En bref, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceaux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un conte, ce qui rend chaque session plus enchantee. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre une sensation futuriste unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, proposant des tables sophistiquees. Avec des depots crypto rapides. L’assistance est precise et professionnelle, offrant des solutions claires. Le processus est fluide comme un smart contract, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages uniques.
Tenter sa chance|
Je suis absolument seduit par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un cosmos chiffre. La variete des titres est eclatante, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus d’accueil est eclatant. Le support client est stellaire, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les transferts sont fiables, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement cool le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
Visiter l’avis|
J’aime l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, il propose une odyssee chiffree. Les options sont vastes comme un ledger, avec des slots aux designs modernes. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des solutions claires. Les paiements sont securises par blockchain, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un atout. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement captivant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir le site|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui respire le luxe. La variete des titres est elegante, offrant des sessions live distinguees. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Au final, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et chic, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde gourmand. Le catalogue est riche en saveurs, avec des slots aux designs elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est impeccable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En resume, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
VГ©rifier le site|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui respire le luxe. Les options sont vastes comme un salon parisien, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En bref, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un autre atout les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Explorer plus|
перестань курить сделай перерывчик https://buh-ved.ru Отличнный магазин
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le suivi est irreprochable, toujours pret a servir. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
Commencer Г lire|
Всем привет ровной ветке,магаз на 5 https://optovik360.ru по Иванову работаем
индивидуалки тюмень 2025
Заказал на пробу 50гр 203, придёт люди попробуют я отпишусь,планирую сделать 1к9-ну не верю я когда говорят что можно 1к 13,15 итд. https://chery-msk-baltauto.ru “Ладно думаю доберусь до дома там опробую нозально “
Hello there, You’ve done a great job. I will definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I am sure they’ll be benefited from this site.
купить номер
Simply want to say your article is as astounding. The clarity in your submit is just excellent and i could think you’re a professional on this subject. Well together with your permission let me to clutch your feed to keep updated with drawing close post. Thank you 1,000,000 and please continue the rewarding work.
https://www.0532.ua/list/525579
Меня на шалфее устраивает:)вываривать ничего не надо https://strojkaland.ru на icq – в четверг обещал трек, в пятницу обещал трек, пропал…
Hello, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, wonderful blog!
http://jiraf.com.ua/yak-ne-pereplatyty-za-sklo-far-porady-shchodo-vybo.html
Получил посылку уже через 3 дня после заказа. МН-001 хороший, только маленькие кристаллы на дне не растворились. А так доволен https://chery-msk-baltauto.ru привет бро)) чето какой то засланый казачок тут про запр дживы интерес проявляет…
25 must-visit places and must-do experiences named for 2026
жесткий анальный секс
Not booked your 2026 vacation yet? Get moving, as the must-visit destinations lists for next year are starting to drop.
The venerable travel guide Lonely Planet published its “Best in Travel 2026” book on October 21, featuring a list of 25 great places and 25 great experiences to try out in the year ahead. It’s accompanied by a set of unique itineraries curated on the new Lonely Planet Journeys travel-planning service.
CNN Travel caught up with Nitya Chambers, Lonely Planet’s executive editor and senior vice president of content, to find out what made the cut and why.
Best places
One of Chambers’ favorite picks on this year’s list? Brazil’s “Little Japan,” otherwise known as the Sao Paolo neighborhood of Liberdade.
“Brazil has the largest Japanese community outside of Japan; 2 million claim connection to Japanese descent in Brazil,” she says. Liberdade was “really full of surprises. The anime-inspired street art, the oriental garden. It’s rumored to have the best ramen outside of Tokyo, although I’m sure that’s always a heated debate.”
Another urban pick is Mexico City. Chambers “cannot say enough great things about it. History, food, culture, art! And it was walkable. It was incredible.” The bougainvillea-strewn neighborhoods of Coyoacan, La Roma and La Condesa all get a shout-out from Lonely Planet this year.
The US selections on the destinations list are Theodore Roosevelt National Park in North Dakota – also featured on National Geographic’s Best of the World list for 2026 – and Maine.
“Maine has such a unique culture in the United States,” says Chambers. “So coastal, so much hiking in nature. The beauty there is really distinctive and the (four) national parks there are amazing.”
A forest hike in the springtime is recommended, and don’t miss the heron rookeries; the colonies can support up to 500 birds.
Over on the western edges of Europe, Tipperary is a “truly a hidden gem,” she says. It’s Ireland’s largest inland county and “a lot of folks just pass through on their way to the Wild Atlantic Way (coastal trail). But I think Tipperary really has one of the most beautiful and underrated driving routes.”
And in Asia, the island of Phuket is best known for its “tropical honeymoon, romantic vibe,” but more people are now discovering it as a work-and-travel spot for digital nomads.
П-т!! Пишу свой отчерк. https://laynservis.ru Один из топовых продавцов на всем РЦ:)
Возможна ли доставка 1 классом ? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Наверное стоит все же воздержаться от заказов и отправки денег и подождать до появления селлера..,на соседнем форуме(СФН) его тоже ждут….
BassBet Casino m’a ensorcele BassBet Casino, on ressent une energie vibrante. Les options sont vastes comme une scene live, avec des slots aux designs soul. Boostant votre mise de depart. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des solutions claires. Les gains arrivent sans attendre, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En plus la navigation est simple et rythmee, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement genial les options de paris variees, assure des transactions fiables.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
J’ai une passion cyclonique pour Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de piste. Le catalogue est riche et varie, proposant des jeux de table rapides. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient veloces. Au final, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement veloce, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Egalement appreciable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
casinospinitfr.com|
братишки и сёстры всем мир и харе ругаться!жизнь прекрасна купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази было бы что хорошего писать. Ато культурных слов нету!!! Вроде как норм качество, готовые клады и цена это единственное что радовало. А в последнее время вообще непонятно что отвечает по часу, пугает игнорами, и в последний раз оплатил в 18:00 адрес около 22:00 и нету!!! Начал про подробности у него вроде так отвечал, фото присылал что аж хватит ему на портфолио. То курьер не ответил то он молчит. И в конце концов пишу ему с другой номера отвечает и предлагает адреса а с моего нефига. И вот такая история о том как чем ЗАЗНАЛСЯ ну или оператор. Жаль возьню(
Ich schatze die Energie bei Snatch Casino, es schafft eine mitrei?ende Stimmung. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit Slots in modernem Look. Mit schnellen Einzahlungen. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, ab und zu mehr Bonusvarianten waren ein Hit. Letztlich, Snatch Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Zudem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, eine tiefe Immersion ermoglicht. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature ist das VIP-Programm mit einzigartigen Belohnungen, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
https://snatch-casino.de/de-de/|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, il procure une experience rapide. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est rapide. Les agents repondent comme un sprinter, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient rapides. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! En bonus le site est rapide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
casinospinitfr.com|
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is wonderful blog. An excellent read. I’ll certainly be back.
https://kra41c.com
J’ai un coup de c?ur pour Impressario Casino, il evoque un jardin parfume. L’eventail de jeux est somptueux, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Illuminant l’experience de jeu. L’assistance est rapide et professionnelle, toujours pret a aider. Les transactions sont fiables, bien que plus de promotions regulieres ajouteraient du charme. En bref, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de sensations raffinees ! De plus la navigation est intuitive et delicate, ce qui rend chaque session plus lumineuse. Particulierement captivant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Découvrir l’offre|
J’ai une passion rythmique pour BassBet Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de notes. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un riff. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un riff, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
Hi there, You have done an excellent job. I’ll certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I am sure they’ll be benefited from this web site.
kra41 cc
Je suis ebloui par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre une sensation futuriste unique. Les options sont vastes comme un ledger, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le bonus d’entree est scintillant. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Les transferts sont fiables, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! En bonus le design est moderne et captivant, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, propose des avantages uniques.
Visiter la page d’accueil|
J’adore l’atmosphere mythique de Spinit Casino, il procure une experience magique. Le catalogue est riche et varie, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme par magie, toujours pret a transformer. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. Au final, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement envoutante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
https://spinitcasinobonusfr.com/|
J’adore le glamour de Impressario Casino, il evoque un tapis rouge scintillant. Les choix sont vastes comme une salle de cinema, proposant des jeux de table elegants. L’offre de bienvenue est prestigieuse. Le service client est irreprochable, avec une aide efficace. Le processus est simple et gracieux, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient une star. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi le site est rapide et envoutant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Apprendre aujourd’hui|
Je suis accro a BassBet Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de notes. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est melodieux, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du groove. Au final, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui groove pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et melodieux, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
Je ne peux plus me passer de Impressario Casino, ca offre une experience sophistiquee. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots rapides. Le service client est irreprochable, garantissant un service de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que plus de promotions regulieres ajouteraient du charme. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme une melodie, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. A noter les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
J’aime l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un reseau blockchain. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le bonus d’entree est scintillant. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, avec une aide rapide et fiable. Les paiements sont securises par blockchain, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A noter le site est rapide et futuriste, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les evenements communautaires decentralises, garantit des transactions fiables.
Cliquer pour voir|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de legendes. Il y a une profusion de jeux fascinants, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est enchante, offrant des reponses claires. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un chapitre. En resume, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les amateurs de sensations enchantees ! A noter le site est rapide et captivant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
https://spinitcasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde de prestige. Le catalogue est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live immersives. L’offre de bienvenue est prestigieuse. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, avec une aide efficace. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient une star. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino est un joyau pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete de magie ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un film, ajoute une touche de prestige. Egalement remarquable les options de paris variees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter l’offre|
J’aime l’ambiance futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un reseau blockchain. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Amplifiant l’experience de jeu. Le support client est stellaire, toujours pret a resoudre. Le processus est lisse comme un wallet, cependant des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. A souligner les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Хороший магазин,менеджер приятный по общению,недовесов не было у меня купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки заказал rcs-4, чет не радует отзывы, как придет со дня на день посмотрим, что выйдет отпишусь, буду делать 1к 10-ти…
Hi to every , since I am really keen of reading this web site’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It consists of good data.
https://kra42c.com
This is really interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your wonderful post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
kra42 cc
Брал хоть и один раз, но все было отлично! Жду второго заказа) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану заказал не мало,всё пришло за кач не знаю как опробуют кролы отпишу
code promo pour 1xbet Regional variations underscore the platform’s global reach and tailored marketing approaches. Searches range from “Code promo 1xbet Afrique du Sud” to “code promo 1xbet canada”, emphasizing the focus on specific geographic areas to further maximize the return. This also means that regulations and restrictions can vary. There are a myriad of promo codes of various values and for various use-cases, from sports betting to casino and beyond. Ultimately, the search is driven by the aspiration to enhance the 1xBet experience with a strategic code, whether it provides welcome bonus or other promotions.
классный магазин купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Никого не защищаю,говорю как есть-сайт работает на О Т Л И Ч Н О .
code promo bonus 1xbet The specific demands reveal nuanced strategies. Gamblers aren’t just looking for any code; they seek the best – “meilleur code promo 1xBet.” The appeal of freebies is undeniable (“code promo 1xBet gratuit,” “code promo 1xBet sans depot”), reflecting a desire to minimize risk and maximize potential returns. Validation is crucial (“code promo 1xBet valide”), assurance that the offered benefit is genuine and not merely a marketing ploy. The “code promo 1xBet 130€” exemplifies the tangible rewards users hope to secure.
Процветания и успехов вашему магазину!! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш а сюда заглянуть влом ? //legalrc.com/threads/Трипы.588/page-2
Hey! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this post to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
kra42 at
Hi there are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and create my own. Do you require any html coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
маркетплейс kraken
Вы люди или нелюди? вас тут некто не обманывает, у магазина было тяжелое время, были проблемы с курьерками мы его пережили все налажено работаем в полную силу, у всех бываю белые и черные полосы нужно переживать их вместе вам это возместиться даже более того, всем отправили кто ждал, адекватные получат +50% к заказу и понимание магазина в любой ситуации и помощь купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм вчера сделал заказ. оплатил. жду трек
Твой стафф офигенен. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Магазин работает отлично!!! Работаю с ним давно!!! Бро ты лучший!!!)))
всё посылка пришла всё ровно теперь будем пробовать ) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази у кого нить было что трек не бьеться 3ие сутки ?? через спср
kraken ссылка Kraken ссылка – это ключ к заветной двери, ведущей в глубины цифрового пространства, где правят свои законы. Убедитесь в подлинности источника, прежде чем доверить ему свои данные, ведь мошенники не дремлют. Остерегайтесь фишинговых сайтов и поддельных зеркал, чтобы ваше путешествие не обернулось разочарованием. Будьте бдительны и осмотрительны, и тогда сможете избежать неприятностей и насладиться всеми преимуществами платформы.
вчера сделал заказ. оплатил. жду трек купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Кто под нос что-то бормочет,
купить права
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a friend who has been doing a little homework on this. And he in fact ordered me dinner because I stumbled upon it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending time to talk about this issue here on your blog.
kra42 cc
Good day! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog post or vice-versa? My blog addresses a lot of the same subjects as yours and I believe we could greatly benefit from each other. If you are interested feel free to shoot me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you! Awesome blog by the way!
https://kra42c.com
СРОЧНЫЙ вопрос!! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Списался с продавцом в аське, во вторник оплатил, сказали в среду отправят. когда спросил, сказали что не отправили по тех причинам из-за СПСР, обещали в четверг. Должно было придти в течении 3х рабочих дней. Сегодня понедельник, сижу на работе, и вот мне звонят, мол вам письмо пришло, куда доставить? То есть все верно, 3 дня как и говорили! Настроение теперь на весь день поднялось)) Вечером буду делать 1к10 (ам2233), потом отпишусь как и чего!!)) В общем доволен, но пока говорю только про доставку. Позднее отпишу доволен ли я всем остальным))
Отличный магазин,заказал и уже через 2 дня в своем городе получил посылку курьером(без звонка),офигев от скорости работы.Вес пришел с неплохим бонусом и в хорошей конспирации.Спасибо очень приятно было с вами работать скоро закажу ещё. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази По сути он эйфо, но ничего, кроме расширенных зрачков, учащенного сердцебиения и потливости, я не почувствовал… А колличество принятого было просто смешным: 550 мг. в первый день теста и 750 мг. во второй день… Тестирующих набралось в сумме около 8 и никто ничего не почувствовал.
Je suis totalement envoute par Olympe Casino, ca transporte dans un monde mythique. La selection de jeux est olympienne, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. Les agents repondent comme des muses, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et glorieux, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. En resume, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple comme un oracle, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://olympefr.com/|
J’ai une passion lyrique pour Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodieux. Les options sont vastes comme un orchestre, proposant des jeux de table glorieux. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme des muses, toujours pret a guider. Le processus est simple et glorieux, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la gloire. Dans l’ensemble, Olympe Casino est une plateforme qui regne sur l’Olympe pour les passionnes de jeux antiques ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un nectar, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus divin les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses eternelles.
https://olympefr.com/|
народ скажите концетрацию 250 го в этом магазе купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм За время работы легалрц сколько магазинов я повидал мама дорогая, столько ушло в топку, кто посливался кто уехал # но chemical-mix поражает своей стойкостью напором и желанием идти в перед “не отступать и не сдаваться”:superman:
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Es gibt zahlreiche spannende Spiele, mit Spielen fur Kryptowahrungen. Er macht den Start aufregend. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Gewinne werden ohne Wartezeit uberwiesen, in seltenen Fallen mehr Aktionen waren ein Gewinn. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Zudem die Navigation ist einfach und klar, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein Hauptvorteil sind die schnellen Krypto-Transaktionen, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Nachsehen|
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und effizient, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Daruber hinaus die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein attraktives Extra sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, die Teilnahme fordern.
Hineingehen|
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit Spielen fur Kryptowahrungen. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, allerdings mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Au?erdem die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein gro?es Plus sind die zuverlassigen Krypto-Zahlungen, regelma?ige Boni bieten.
https://catspins777.de/|
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur ein fesselndes Erlebnis. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € mit Freispielen. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Gewinne werden ohne Wartezeit uberwiesen, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren willkommen. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spieler. Zudem ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, das Spielerlebnis bereichert. Ein starkes Feature die dynamischen Community-Events, die Teilnahme fordern.
Details lesen|
Je suis emerveille par Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, occasionnellement quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement genial les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
Ich bin begeistert von der Welt bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit Live-Sportwetten. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Der Support ist schnell und freundlich. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, von Zeit zu Zeit ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Kurz und bundig, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergessliches Erlebnis. Zusatzlich ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, was jede Session spannender macht. Ein tolles Extra die regelma?igen Turniere fur Wettbewerbsspa?, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Online gehen|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Hotspot fur Spielspa?. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, dennoch gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Nebenbei die Seite ist schnell und einladend, zum Verweilen einladt. Besonders erwahnenswert die dynamischen Community-Veranstaltungen, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Jetzt zugreifen|
Je suis enthousiasme par Sugar Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Globalement, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. En plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
Savoir plus|
Je suis captive par Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, rarement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et attrayant, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point cle les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages uniques.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Je suis enthousiasme par Sugar Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En somme, Sugar Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs variees, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller sur le site web|
Цены тут взвинчены до жопы не знаю кто тут умудряется брать, летом как то брал здесь не помню че но было фуфло конченное половина не растворилась хоть че делай хоть грей хоть танцуй ни че не помогло. Один плюс присылают быстро но нафиг такая быстрота купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм надо испробывать…много хороших отзывов
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par ailleurs des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour ajouter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A mettre en avant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui booste la participation.
Aller au site|
Делать надо 1к10, можно и послабже, например 1к13, но не более, а то 30 минут эт мало, хотя смотря для кого)) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Качество, если честно на моё удивление (тк. первый раз я пользуюсь услугами данного ТС), по отзывам клиентов, сказать отличное это сказать ничего, ССССУУУУУПППЕЕЕЕРРРР!!!!!!
I am not sure where you are getting your information, but great
topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more.
Thanks for great information I was looking for this info for my mission.
анологичная ситуация! продаван ты на примете, раз твоих клиентов начали принимать… купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану у меня вообще когда порошок кидаешь и ациком заливаешь, раствор абсолютно прозрачный-.- и не прет вообще тупо куришь траву….. а вот кристалы не расворимые тоже имеются, я уже и толочь пытался седня и нагревом все бестолку…
Заказал-оплатил 50г реги, а отношение как не знаю к кому… купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки да я после 2си два дня осилил потерпеть и замутил 2се за кампанию(очень приятно, между прочим, пошло). еще 2 дня прошло завтра мб фофки забацаю. Знакомые ставили вв пол колпака, вроде эффектов мало, но один в тот же вечер овердознул 2си и попускался водкой, да и другого только-только отпускало с феников. Просто очень плохо будет, если продукт не удастся.
https://www.4shared.com/s/fdyaaDnwXge
What a stuff of un-ambiguity and preserveness of valuable familiarity regarding unexpected feelings.
https://implementosvizcarra.com/skachat-melbet-android-2025-obzor/
Amazing issues here. I’m very happy to see your post. Thanks a lot and I’m having a look ahead to touch you. Will you please drop me a mail?
https://dyacademy.com.br/melbet-2025-obzor-bukmekera/
Проб НЕТ! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази СПАСИБИЩЕ ОГРОМНОЕ ЗА СЕРВИС
https://www.muratshriners.com/profile/1WinPromoKing/profile
не долго думая решил написать оператору данного магазина! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази По приходу товара я выложу тут розничную площадку для заказов, на которой вы сможете заказать реактивы из наличия на складе, не уточняя у нас что есть…
Инфа с вашего сайта. Я уже брал 6-APB, и выглядел он несколько иначе. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази 5мг реально из области фантастики…желаю попробывать
https://articlescad.com/1xbet-bonus-code-2026-gratis777-130-deal-382190.html
Приветствую ТС,сделал заказ,но до сих пор трек не пробивается,помоги разобраться в этом уже почти неделю жду,заранее спс купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Связался с продавцом вполне адекватный!Заказал щас жду адресса
кто последний раз когда брал? регу или соль купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Они хоть кому нибудь отвечают?
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodieux. Le catalogue est riche en melodies, avec des slots thematiques antiques. Amplifiant l’aventure de jeu. Les agents repondent comme des muses, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont rapides comme une melodie, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. En bref, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les joueurs en quete d’epopee ! En bonus la navigation est simple comme un oracle, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
olympefr.com|
J’ai une passion lyrique pour Olympe Casino, il procure une experience harmonieuse. Les options sont vastes comme un orchestre, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Amplifiant l’aventure de jeu. Les agents repondent comme des muses, offrant des reponses claires. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. Dans l’ensemble, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus le site est rapide et glorieux, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
https://olympefr.com/|
кролики ставят В\В, фашку от этого магазина по 0.07-0.15 нравится, только сушит сильно купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану это манера такая сдержанная или удовлетворительное=на троечку
Admiring the dedication you put into your blog and in depth information you offer. It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same old rehashed material. Wonderful read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
https://kingdombet88.co/melbet-apk-obzor-2025/
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur ein fesselndes Erlebnis. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und zuverlassig, manchmal gro?ere Angebote waren super. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Zudem die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, das Spielvergnugen steigert. Ein klasse Bonus die spannenden Community-Aktionen, exklusive Boni bieten.
https://casinocatspins.de/|
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht pure Spannung. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Slots in modernem Look. Mit schnellen Einzahlungen. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, manchmal mehr Bonusoptionen waren top. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Zusatzlich die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein starker Vorteil die spannenden Community-Aktionen, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Website erkunden|
Ich schatze die Energie bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein immersives Erlebnis. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, aber haufigere Promos wurden begeistern. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino garantiert dauerhaften Spielspa?. Daruber hinaus die Seite ist schnell und einladend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein klasse Bonus die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, personliche Vorteile bereitstellen.
Mehr erfahren|
Обращайтесь всегда рады! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану особенно с вашей репутацией!
Ich bin beeindruckt von der Qualitat bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Anzahl an Titeln, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. Er gibt Ihnen einen tollen Boost. Der Service ist absolut zuverlassig. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, jedoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Zusatzlich die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein wichtiger Vorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, die die Begeisterung steigern.
Zur Website gehen|
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und zuverlassig, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spielbegeisterte. Zusatzlich die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein hervorragendes Plus die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, fortlaufende Belohnungen bieten.
http://www.catspins777.de|
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht pure Spannung. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit klassischen Tischspielen. Er gibt Ihnen einen Kickstart. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, dennoch gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und modern, eine vollstandige Eintauchen ermoglicht. Ein starker Vorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Genauer ansehen|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, ab und zu mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Ubrigens die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, jeden Moment aufregender macht. Ein super Vorteil sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, die Community enger verbinden.
FГјr mehr besuchen|
Je ne me lasse pas de Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, a l’occasion des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino merite une visite dynamique. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement attrayant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui booste la participation.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Sugar Casino merite une visite dynamique. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A mettre en avant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des privileges personnalises.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino garantit un amusement continu. A souligner le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en crypto, renforce la communaute.
Lire la suite|
Je suis bluffe par Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, en revanche quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En complement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Parcourir maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, quelquefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. D’ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A signaler les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce la communaute.
Explorer maintenant|
J’adore le dynamisme de Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, cree une communaute soudee.
Naviguer sur le site|
J’adore la vibe de Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour faire court, Ruby Slots Casino merite un detour palpitant. D’ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
http://www.rubyslotscasinobonus777fr.com|
Je suis sous le charme de Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, quelquefois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En resume, Ruby Slots Casino merite une visite dynamique. En plus la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un avantage les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, assure des transactions fluides.
https://rubyslotscasinobonus777fr.com/|
трек кинули ровно оперативно как придет отпишу за качество 250 купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки да наверно я попал на фейка или угонщика ,но мне не понятно как фейк может потверждать переписку с броси на форуме?
Отличный магазин) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази бешельме мешельме атакает
Заявление про кидал не требует обоснования, ибо это не заявление. Перечитайте внимательно. Считаю, что такие речи тоже стоит оставлять при себе, не прочитав толком. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану у меня в подписи проверь
заказала в этом магазе сувениров:), посыль пришел на 3ий день, продукты качеством вкусны купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану если он такой делец,пусть тему свою создаёт!а так аферист,я бональный обаснованный вывод делаю!
https://www.diigo.com/item/note/8u6h0/80u4?k=b5bb14e917a8492b310ecc436943faf8
Ровный магаз,всем советую) купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Спасибо. Похож на ам2**3
kraken ссылка Kraken сайт – это не просто веб-страница, а тщательно выстроенная экосистема, живущая по своим, порой негласным правилам. Это цифровой оазис для тех, кто ценит приватность и независимость, но одновременно и зона повышенного риска, где каждое действие должно быть обдуманным и взвешенным. Здесь встречаются анонимные продавцы и покупатели, заключаются спорные сделки, и разгораются нешуточные страсти. Чтобы не заблудиться в этом лабиринте, необходимо обладать острым умом, твердой рукой и непоколебимой верой в свою интуицию.
https://oceanballon.ru/
https://www.orkhonschool.edu.mn/single-post/2017/11/02/cambridge-igcse-certificate-award-ceremony?commentId=10fc6ad0-1dc7-4c51-9c20-cc17c637c358
не долго думая решил написать оператору данного магазина! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Уважаемы участники форума!
Heya outstanding website! Does running a blog such as this require a great deal of work? I have no expertise in programming however I was hoping to start my own blog in the near future. Anyway, if you have any recommendations or tips for new blog owners please share. I know this is off subject however I just had to ask. Thank you!
номер временный
а работают как.оперативненько? вполне. https://potok-uvc.ru У меня не бьётся вторые их трек. И бро в скайпе не видно. Мож приняли их посылки на почте? Тоже парюсь блин…. Но не хотел поднимать дискуссию, не имея причин. Выслали в пятницу СПСР.
https://padlet.com/muhammadhasnainpk1_/discussion-topic-goes-here-5n3mh7gugixzfnu6/wish/9kmlZVrwo31yZpgV
Качество, если честно на моё удивление (тк. первый раз я пользуюсь услугами данного ТС), по отзывам клиентов, сказать отличное это сказать ничего, ССССУУУУУПППЕЕЕЕРРРР!!!!!! https://firstbed.ru Так вот, прошло все как всегда отлично, дошло за три дня, маскировка надежная. Так же отдельное спасибо магазину за проявление немыслимой заботы о безопасности клиента. Что имел ввиду писать не буду, но факт есть факт.
Ich bin beeindruckt von der Qualitat bei Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Die Spielesammlung ist uberwaltigend, mit Live-Sportwetten. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Support ist professionell und schnell. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, jedoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren willkommen. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Daruber hinaus die Seite ist schnell und attraktiv, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein Hauptvorteil sind die schnellen Krypto-Transaktionen, die Community enger verbinden.
Jetzt ansehen|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Die Auswahl ist so gro? wie ein Casino-Floor, mit immersiven Live-Dealer-Spielen. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist erstklassig. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, jedoch gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Au?erdem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, zum Weiterspielen animiert. Ein hervorragendes Plus die vielfaltigen Wettmoglichkeiten, exklusive Boni bieten.
Ins Web gehen|
https://t.me/s/apk_1xbet_android
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Anzahl an Titeln, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Er macht den Start aufregend. Der Kundensupport ist erstklassig. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, gelegentlich mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino garantiert dauerhaften Spielspa?. Au?erdem die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Besonders erwahnenswert sind die zuverlassigen Krypto-Zahlungen, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Web entdecken|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur ein fesselndes Erlebnis. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit eleganten Tischspielen. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, dennoch ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spielbegeisterte. Nebenbei die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein gro?es Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, die die Motivation erhohen.
Das ГјberprГјfen|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit Slots in modernem Look. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und zuverlassig, von Zeit zu Zeit waren mehr Bonusvarianten ein Plus. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist unkompliziert, das Spielvergnugen steigert. Ein klasse Bonus ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Hier klicken|
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. Er macht den Start aufregend. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, allerdings mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Au?erdem die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein Hauptvorteil die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, zuverlassige Transaktionen sichern.
Loslegen|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Der Service ist von hochster Qualitat. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, manchmal gro?ere Angebote waren super. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein starker Vorteil die dynamischen Community-Veranstaltungen, exklusive Boni bieten.
Bringen Sie mich dorthin|
Общий итог: https://sever46.ru Может всё-так “Рашн Холидейс” (c) China
Je suis emerveille par Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, bien que des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et fluide, apporte une energie supplementaire. A signaler les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages uniques.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A signaler les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Lire les dГ©tails|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
AccГ©der maintenant|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par contre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour completer le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement genial les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Explorer plus|
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En bref, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. En plus le site est rapide et immersif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement cool les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Plonger dedans|
Je suis captive par Sugar Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, malgre tout quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Globalement, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. D’ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un plus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute soudee.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je suis accro a Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par ailleurs des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour faire court, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En complement le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus constants.
Avancer|
Je suis totalement conquis par Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est transparent et rapide, en revanche des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Notons aussi la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui stimule l’engagement.
Avancer|
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Sugar Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A signaler les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des privileges sur mesure.
AccГ©der au site|
Je ne me lasse pas de Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, malgre tout des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour couronner le tout la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Rejoindre maintenant|
и че сделали? условку дали? https://mediclever.ru напишите в аську, там порешают вашу проблему. С этой партией МХЕ определённо вышел косяк.
угу, “на глазок” отсыпали. купи весы и взвесь нормально. На вид оно может показаться как больше так и меньше… https://panda82.ru я звонил седня.сказали либо номер не правлеьный..либо не отправили еще
Заказал вчера 30гр 4-FA . Трек пока не получил. Надеюсь что все будет олрайт. В планах долговременное сотрудничество! https://psp-ekb.ru Сегодня получил посылку. Оказалось, что просто трек не пробивался до последнего, а посылочка шла себе. Дошло быстро. Сам магазин передал товар в курьерку почти моментально за что огромное спасибо. Магазин всегда остается на связи и отвечает даже на глупые переживания. Конспирация порадовала. Вес тоже в норме. По качеству отпишу позже трип-репорт, но думаю, что всё на высшем уровне. Спасибо, Chemical-mix.
Про 80 не знаю. Но то что там принимают сомнительных, дак это точно. Вот люди которые туда приходят и ушатаные в хламотень, все трясутся. И оглядываются, как будто от смерти скрываются конечно их принимают… А что про тех кто соблюдаем все меры, тот спокоен. И сдержан. Но все равно. В спср принимают однозначно, сам свидетель в 2006 году. когда за дропом следили, перепугались что за нашим пришли… Но все обошлось. https://oaoikma.ru На днях брал небольшой опт, был приятно удивлен подходом и предложением тс, товар еще не пробовали ,но забрал все ровно, по ходу отпишу в теме за качество товара, пока же могу сказать, что жалею , что раньше не работал с данным тс! Успехов, благодарю за сервис!!!
после нового года два раза заказывал первый и второй раз были геморои по срокам отправок но все дошло третий раз конечно тоже закажу но ТС должен будет мамой поклястся что отправит вовремя но если по правде говоря то курьерки тоже мозг ебут не всегда вина ТС https://tuningclass.ru Еще раз извините. Треки тоже бьются не сразу, курьерки “в завалах”, иногда он только начинает определяться на сайте курьерки, а его уже вручают или вручили получателю. Не пугайтесь, что мониторинг начнется не сразу, вам всем все придет заказанное.
что то не могу зайти на сайт ( https://mediclever.ru платил 5 февраля свою посылочку!как вы поняли ничего не получил!ТС кормил меня завтраками,в итоги обещал вернуть деньги если не получу до 28 февраля!деньги мне тоже никто не вернул вместо этого мне прислали новый трек и написали что мы обещали что получите товар и деньги возвращать не буду!мои обьяснения о том что вашу посылку уже некому получать он слушать не хочет и возвращать деньги тоже!Ув.Адмистрация форума прошу не удалять мой пост и если нужно могу скинуть переписку!
лучший changan https://changan-v-spb.ru
Я вообще не курю!!!я брал 3 июля его уже нет в продаже! https://foxst.ru продолжайте работу в таком же духе. клады всегда целые и надежные, что очень радует!
7к казино зеркало 7к казино зеркало помогает игрокам обходить ограничения и продолжать играть в свои любимые игры.
casino 7k на 7k casino легко зарегистрироваться и начать играть, так как процесс подключения максимально упрощен.
может стоит разводить 1 к 10? Кто брал ам 2233 отпишитесь на щёт пропорции,вообще 2233 1 к 20 разводится если продукт хороший https://oaoikma.ru Качество 2с очень порадовало, трип позже отпишу.
номер виртуальный купить
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Auszahlungen sind blitzschnell, dennoch mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Kurz und bundig, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur kontinuierlichen Spa?. Zusatzlich die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Hier klicken|
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, ab und zu gro?ere Angebote waren super. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Nebenbei ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein tolles Feature die dynamischen Community-Events, das die Motivation steigert.
Mehr entdecken|
магазин хороший,даже если высылат брак (было 1 раз) возврат делают сполна https://firstbed.ru Здрасте Бразы!!!!:hello:
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Kundendienst ist ausgezeichnet. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, allerdings gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Nebenbei die Plattform ist optisch ansprechend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein gro?artiges Bonus die vielfaltigen Wettmoglichkeiten, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Weiter lesen|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Hotspot fur Spielspa?. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, aber waren mehr Bonusvarianten ein Plus. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Ubrigens die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein starkes Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, fortlaufende Belohnungen bieten.
Tauchen Sie ein|
Ich bin ganz hin und weg von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine aufregende Atmosphare. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Der Kundendienst ist ausgezeichnet. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, aber mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Nebenbei ist das Design modern und einladend, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein starkes Feature die dynamischen Community-Events, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Jetzt entdecken|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Die Spielauswahl ist ein echtes Highlight, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. Er macht den Start aufregend. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, manchmal regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino garantiert langanhaltenden Spa?. Nebenbei die Navigation ist einfach und klar, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein klasse Bonus sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
http://www.catspinsbonus.com|
почта России https://nika-land74.ru -1. Вас, продавцов, много, а я один.
kraken сайт Kraken market – это многогранная площадка, где встречаются продавцы и покупатели со всего мира, предлагая широкий спектр товаров и услуг. Здесь можно найти все, что душе угодно, от редких артефактов до инновационных разработок. Приготовьтесь к захватывающему приключению, полному неожиданных открытий и выгодных предложений. Но не забывайте о здравом смысле и критическом мышлении, чтобы не стать жертвой недобросовестных продавцов.
https://trinixy.ru/262948-top-10-luchshih-servisov-virtualnyh-nomerov-dlya-sms-aktivaciy-v-2026-godu.html
пиши в скайп, все работает, мне всегда отправляют, все на уровне https://pizzaa-lab.ru Это да,но всё же я очень переживаю,ну прям очень очень
Да и вообще: https://unicornchb.ru Один вопрос только,можно ли заказать так что бы без курьера?Самому придти в офис и забрать посылку?
Онлайн казино
Обзоры казино
https://www.postfreeclassifiedads.com/thread-103377.htm
ТС саппорт не требуется тебе ? Напиши в лс если интересно https://nasha-shapka.ru с почтой лучше не связываться
К продавцу можно смело обращаться, тут сделают все в лучшем виде! https://potok-uvc.ru Друзья все четко и понятно. Адрес получил за 250 метров от кафе. Минеру респект и Благодуха. Даже фото не надо было. Вес и качество 10 из 10. Лучший кокаин, давно такого не встречал. Я ваш клиент. Очень понравилось.
все гууд https://potok-uvc.ru Хорошо работает народ))
И что толку за легалом охотиться. https://nytvarb.ru Да хватает придурков, только смысл писанины этой , что он думает что ему за это что то дадут ))) кроме бана явно ничего не выгорит )))! Тс красавчик брал 3 раза по кг сделки и всегда все чётко ! Жду пока появиться опт на ск!
пт всем.скоростя здесь имеются? https://sever46.ru А ты у него спроси тот он или не тот, врать не станет думаю
Качество закладки 10/10-пролежала долгое время что тоже не мало важно https://fotooboivimala.ru ладно ..буду надеяться что все норм
по поводу треков выяснять буду завтра лично т.k. сегодня выходной в России https://fotooboivimala.ru Качество на 5+:good:
всем привет,припы репорты писать не умею как мастер 100 того уровня,но скажу как есть,магазин вообще огонь ,брал 1гк ск АЛФА 29 с доставкой,все быстро и оперативно пришло,как и было оговорино 14 дней,а ребята знают толк в работе красавцы доставили в кароткие сроки,АДРЕС СДЕЛАН БЫЛ С ТОЧНЫМ ОПИСАНИЕМ ЗАБРАЛ В КАСАНИЕ + ФОТО К ОПИСАНИЮ ШЛО МОЖНО БЫЛО ПО ФОТО ПОДНЯТЬ НЕ ЧИАЯ ОПИСАНИЯ ДАЖЕ,ВЕС СК КРИСТАЛИКИ ЧИСТЫЕ НЕ БУТОР ТАВАР ОТЛИЧНЫЙ И ЧИСТЕЙШЕЕ КАЧЕСТВО,УСПЕХОВ ВАМ ВО ВСЕМ И ПОПУТНОГО ВЕТРА КЛИЕНТОВ ПО БОГАТЧЕ,ПРОЦВИТАНИЯ,ВСЕМ СОВЕТУЮ ЭТОТ МАГАЗИН,ОПЛАЧИВАЙТЕ С ДОСТАВКАМИ И НЕ СОМНИВАЙТЕСЬ НЕ КАПЛИ……..МАГАЗИН РАБОТАЕТ РОВНО https://oaostplem.ru В чем растворял 203??? У меня ихний 203 в спирте не получилось расстворить даже при нагреве, пришлось ацетон использовать! На счет качества с тобой согласен – 5!
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Es gibt eine riesige Vielfalt an Spielen, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Der Service ist von hochster Qualitat. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Nebenbei die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein starkes Plus die spannenden Community-Aktionen, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
Inhalt entdecken|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Es gibt zahlreiche spannende Spiele, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und sofortig, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist definitiv einen Besuch wert. Ubrigens die Plattform ist optisch ansprechend, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein gro?artiges Plus die spannenden Community-Aktionen, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Mehr entdecken|
I’m absolutely hooked on Pinco, you feel the buzz from the first spin. There’s an insane range of games, with beautifully designed slot machines. It gives you a serious head start. Customer support is world-class. The process is simple and clear, on occasion regular promos would add extra spark. In conclusion, Pinco offers an unforgettable ride. Moreover navigation is clear and quick, elevates your entire experience. Particularly notable is the VIP program with elite rewards, that fuels player loyalty.
Open the page|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. D’ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui booste la participation.
https://rubyslotscasinopromocodefr.com/|
J’adore le dynamisme de Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, rarement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure memorable. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce la communaute.
Aller Г la page|
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar no 4PlayBet Casino porque foi muito alem do que imaginei. A variedade de jogos e surreal: slots modernos, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que me deixou confiante. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que mais brindes fariam falta, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino me conquistou. Ja virou parte da minha rotina.
4play eventos uniao da vitoria|
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein immersives Erlebnis. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit Spielen fur Kryptowahrungen. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, jedoch gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur kontinuierlichen Spa?. Nebenbei die Navigation ist unkompliziert, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein gro?artiges Bonus die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
Weiter lesen|
Je suis captive par Sugar Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, rarement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un point cle les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
I’m captivated by Pinco, you feel the rush with every bet. The diversity is mind-blowing, including crypto-friendly games. The signup offer is unbeatable. Customer care is elite. The process is transparent and fast, in some cases a couple extra spins would be sweet. In summary, Pinco is a true standout. To mention the design is bold and modern, supports deep focus. Particularly notable are the engaging community activities, that boosts engagement.
Discover the offers|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par contre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Entrer maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Sugar Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui booste la participation.
Plongez-y|
J’ai un faible pour Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir la page d’accueil|
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино отзывы
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино с выводом
Играйте в свои любимые азартные игры на казино Вавада рабочее зеркало сегодня ! Получите доступ к лучшим слотам, рулетке, блэкджеку и многим другим играм. Качественный сервис, высокий уровень безопасности и удобная навигация ждут вас. Переходите на официальное зеркало Вавада и наслаждайтесь азартом без ограничений. Удобный интерфейс, быстрые выплаты и актуальные бонусы делают игру на Вавада незабываемой. Заходите на сайт прямо сейчас и испытайте удачу вместе с нами!
Ich bin beeindruckt von der Qualitat bei Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Hotspot fur Spielspa?. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit immersiven Live-Dealer-Spielen. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Gewinne werden schnell uberwiesen, in manchen Fallen gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Au?erdem die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, eine vollstandige Eintauchen ermoglicht. Ein besonders cooles Feature ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, das die Motivation steigert.
Mit dem Erkunden beginnen|
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Hotspot fur Spielspa?. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit eleganten Tischspielen. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Der Service ist von hochster Qualitat. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, dennoch gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Nebenbei die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein gro?artiges Bonus die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, die Community enger verbinden.
Das ГјberprГјfen|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, ab und an mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein Pluspunkt ist die schnellen Einzahlungen, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich schatze die Energie bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit modernen Slots in ansprechenden Designs. Er macht den Start aufregend. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, trotzdem mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Ubrigens die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein weiteres Highlight die dynamischen Community-Events, die die Begeisterung steigern.
Startseite ansehen|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist erstklassig. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und effizient, manchmal ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Seite ist schnell und ansprechend, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein starkes Feature die dynamischen Community-Events, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
Details finden|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, verstarkt die Immersion. Ein weiterer Vorteil die schnellen Einzahlungen, die Flexibilitat bieten.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai un faible pour Ruby Slots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Ruby Slots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste le fun du jeu. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Explorer la page|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps a autre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un avantage les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute vibrante.
Touchez ici|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, rarement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. De plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste l’excitation du jeu. A souligner les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Aller au site|
J’adore l’energie de Sugar Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En fin de compte, Sugar Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De surcroit le design est style et moderne, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fiables.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis enthousiasme par Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, mais encore plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De surcroit l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste la participation.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, rarement des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est simple et intuitive, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements securises.
Passer à l’action|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein immersives Erlebnis. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist top. Gewinne werden schnell uberwiesen, von Zeit zu Zeit gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist definitiv einen Besuch wert. Nebenbei die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein gro?artiges Plus die dynamischen Community-Events, regelma?ige Boni bieten.
Plattform besuchen|
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Die Spielesammlung ist uberwaltigend, mit Slots in modernem Look. Er gibt Ihnen einen tollen Boost. Der Support ist schnell und freundlich. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Ubrigens die Navigation ist unkompliziert, eine tiefe Immersion ermoglicht. Ein starkes Feature die lebendigen Community-Events, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Eintreten|
даа, уж что что, а 250й тут классный ) хомячки так и просят добавки купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш А сейчас работает магазин?
Тут четкий кристал ! Давно мне нравиться работа данного мага. Спасибо ! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Добрый день форумчане! Кто нибудь подскажет как по качеству реагент в этом магазине? Соответствует ли заявленная концентрация? Сколько по времени держит если 1 к 20 сделать? Всем спасибо!!!
я не смог пополнить в альфа банке, по определенной причине! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш сделал заказ в этом магазине первый раз, заказывал 2гр. 400f на пробу, а пришло 3,3гр., очень доволен)))
chery 7 pro chery tiggo pro цена
Заказываю в третий раз, дали скидку 8%, приятно. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Всё отлично, 5 из 5. Только сделайте больше районов в Питере.
Обновления по теме здесь: https://www.bnkomi.ru/data/relize/189062
все просто=) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки А со скольки у них скайп начинает работать?
milioner kasyno
отлично всё 100% )) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази надо прятать по сложнее
Updates on this topic are here: https://www.academyoflanguage.pl/custom-business-email/
Ищете актуальные зеркала Кракена? У нас самая полная информация о зеркалах Кракена на сегодняшний день. Узнайте, как обойти блокировку и получить доступ к Кракену. Список рабочих зеркал Кракена для удобного доступа. Безопасные и проверенные зеркала для вашего комфорта. Не упустите шанс пользоваться Кракеном без проблем и задержек. Подробная информация о зеркалах Кракена и способы их использования
Адрес почты правильный, все проверил не 1 раз, ответьте хоть тут.ну будем надееться что и на этот раз TS войдет в положение и как нибудь обратит внимание на решение наших вопросов, компенсирует нам потраченые нервы и время на безсмысленное ожидание, главное ведь для магазина репутация! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки но за долгое сотрудничество с этим
Причёт тут почта России, СПСР это самостоятельная курьерская служба. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм суббота, воскресение у них выходной
Разве имеет принципиальное значение сколько моему аккаунту времени? Я тут не *зависаю*, а пишу по сути. Мутность заключается в том что оператор в аське на вопросы по уточнению адреса, сначала молчал почти 3 часа, потом вообще оффнулся. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану всем доброго дня) не подскажите, в беларусь(минск) можно сделать заказ с этого магазина ? или вообще хоьт какой нибудь магазин который в минск вышлет подскажите плз) ответ в лс плиз)
ты давай вася тут провокации не сей))) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки ПРИВЕТ ВСЕМ:НУ ЧТО Ж ТЫ БРО ТАК ОБЕЗНАДЕЖИЛ МЕНЯ ПО СКАЙПУ И В КОМЕНТАРИЯХ НАПИСАЛ ЧТО ОТПРАВИЛ MXE А НА ПАКЕТЕ НАПИСАНО RCS И ЧТО МНЕ КУРИТЬ ТЕПЕРЬ НАЧАТЬ ЗАЧЕМ ГОВОРИТЬ ТО ЧТО НЕ ДЕЛАЕШЬ КАК САМ СЧИТАЕШЬ ?
Всем по привету! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш вы могли написать похожему нику , таких пруд пруди.
Estou completamente apaixonado por BacanaPlay Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao animada quanto uma bateria de escola de samba. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de prazeres, com slots de cassino tematicos de carnaval. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tumulto, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. No fim das contas, BacanaPlay Casino e um cassino online que e uma folia sem fim para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
baixar bacanaplay|
Могу также в пользу магазина сказать. Все по деловому прошло, без лишних эмоций и разговоров. Качество соответствует. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм ровный магазин
Acho simplesmente sensacional BacanaPlay Casino, parece uma festa carioca cheia de axe. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista na avenida, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque de pandeiro. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Resumindo, BacanaPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
bacanaplay casino review|
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine Welt voller Action. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, mit immersiven Live-Dealer-Spielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Gewinne werden ohne Wartezeit uberwiesen, manchmal ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist klar und flussig, zum Verweilen einladt. Besonders erwahnenswert ist das VIP-Programm mit einzigartigen Belohnungen, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Website prГјfen|
Ich bin absolut begeistert von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Die Spielauswahl ist ein echtes Highlight, mit Spielen fur Kryptowahrungen. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, dennoch gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Nebenbei die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, das Vergnugen maximiert. Ein attraktives Extra die breiten Sportwetten-Angebote, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Eintauchen|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, verstarkt die Immersion. Besonders toll die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich bin absolut begeistert von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht ein einzigartiges Abenteuer. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Der Service ist absolut zuverlassig. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, manchmal mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Zudem ist das Design stilvoll und modern, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein hervorragendes Plus die regelma?igen Turniere fur Wettbewerbsspa?, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Website durchstöbern|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, obwohl mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Hervorzuheben ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’adore le dynamisme de Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Sugar Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons aussi le design est style et moderne, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un plus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
какой товар заказал? купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки “Район довольно близкий для меня(СТРЕЛА)”
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une visite excitante. De plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui booste la participation.
Obtenir plus|
Je suis accro a Sugar Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Globalement, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Ajoutons que le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point fort les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce la communaute.
Entrer maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent sans delai, rarement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement super les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Voir maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. De plus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, facilite une experience immersive. Un plus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit Live-Sportwetten. Der Willkommensbonus ist gro?zugig. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Transaktionen laufen reibungslos, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Zusatzlich die Navigation ist einfach und klar, jeden Moment aufregender macht. Ein klasse Bonus die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Weiterlesen|
Je suis fascine par Ruby Slots Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements securises.
Passer à l’action|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Es gibt eine enorme Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist erstklassig. Gewinne werden ohne Wartezeit uberwiesen, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur kontinuierlichen Spa?. Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein starker Vorteil die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, fortlaufende Belohnungen bieten.
Einen Blick werfen|
Как часы https://architectit.ru Мать и мачеху+травяной сбор(успокаивающий).
Кракен онион наркошоп – лучшее место для покупки качественных наркотиков и других запрещенных веществ. Здесь вы найдете широкий ассортимент товаров высокого качества по доступным ценам. Наш магазин предлагает конфиденциальные и безопасные услуги для всех клиентов, гарантируя анонимность и быструю доставку. Покупайте у нас и получайте удовольствие от качественных продуктов без риска для своего здоровья. Не упустите возможность попробовать лучшие наркотики от Kraken!
конечно была задержка которая заставила по нервничать, но всё прошло на уровне и я получил свою посылочку))) https://jk-sibirskiy.ru бро а какая почта то ?
https://metacon35.ru/ рабочее зеркало севан кей гарантирует бесперебойный доступ к играм при любых обстоятельствах.
севен кей казино севен кей casino отличается высоким RTP и волатильностью, адаптированной под разные стили игры.
Наш Skype «chemical-mix.com» временно недоступен по техническим причинам. Заказы принимаются все так же через сайт, сверка реквизитов по ICQ или электронной почте. https://origamishop.ru Магазин просто супер!!!так держать))))*****
kraken сайт Kraken ссылка – это ключ к заветной двери, ведущей в глубины цифрового пространства, где правят свои законы. Убедитесь в подлинности источника, прежде чем доверить ему свои данные, ведь мошенники не дремлют. Остерегайтесь фишинговых сайтов и поддельных зеркал, чтобы ваше путешествие не обернулось разочарованием. Будьте бдительны и осмотрительны, и тогда сможете избежать неприятностей и насладиться всеми преимуществами платформы.
пт всем.скоростя здесь имеются? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Сижу жду пока высохнет АМ2233 =)
http://www.google.hn/url?q=https://www.radio-rfe.com/content/pages/1xbet_new_account_promo_code.html
Да, в скайпе их нет и ситтуация мне тоже не нравиться. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Все пришло довольно быстро.
http://www.google.ch/url?q=https://hyundaimobil.co.id/assets/articles/1xbet_kode_promo_indonesia___bonus_selamat_datang.html
http://www.google.com.bh/url?q=https://www.intercultural.org.au/wp-content/pgs/1xbet_casino_bonus_codes_enter.html
А Всем Добра и Здоровья Близким))) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Не-не, через форум заказы не принимаются. Заказывать нужно только через сайт, указанный в подписи.
как так его разве нету? с самого утра тут сижу купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану chem24.biz.ski заходи и приколись
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os astronautas do cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
betorspin paga|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como supernovas. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin security|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine Welt voller Action. Die Spielauswahl ist ein echtes Highlight, mit klassischen Tischspielen. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, allerdings mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spieler. Au?erdem die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, das Spielvergnugen steigert. Besonders erwahnenswert die dynamischen Community-Events, exklusive Boni bieten.
Seite Г¶ffnen|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, bietet klare Losungen. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, trotzdem mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Daruber hinaus das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die schnellen Einzahlungen, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht pure Spannung. Es gibt eine Fulle an aufregenden Titeln, mit Live-Sportwetten. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, dennoch gro?ere Boni waren ideal. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Zudem die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, jede Session unvergesslich macht. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, das die Motivation steigert.
Weiterlesen|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, ab und an mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Zusatzlich die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
ТС, почисти ветки, ну невозможно же ничего почитать..в разных ветках одно и тоже. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Пиздатый магазин, всегда пойдут на встречу и оператор норм
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, rarement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Sugar Casino merite une visite dynamique. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est fluide et facile, permet une immersion complete. A souligner les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Lancer le site|
J’adore la vibe de Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En conclusion, Sugar Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est fluide et facile, apporte une touche d’excitation. A mettre en avant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Commencer Г lire|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, parfois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et engageant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage notable les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, garantit des paiements rapides.
VГ©rifier le site|
индивидуалки тюмень 2025
J’ai un faible pour Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Sugar Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A souligner l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses continues.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis epate par Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, malgre tout des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus les transactions en crypto fiables, cree une communaute vibrante.
AccГ©der Г la page|
https://uroki-igry-na-skripke.ru/
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, toutefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et style, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement cool les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
Essayer|
Ich bin ein gro?er Fan von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Mit sofortigen Einzahlungen. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Gewinne werden ohne Wartezeit uberwiesen, gelegentlich ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Zudem die Navigation ist einfach und klar, zum Weiterspielen animiert. Ein besonders cooles Feature die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Jetzt stöbern|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, quelquefois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En somme, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. A noter l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le lien communautaire.
Obtenir plus|
Ich bin vollig uberzeugt von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Anzahl an Titeln, mit spannenden Sportwetten-Angeboten. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Gewinne kommen sofort an, in manchen Fallen zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Zudem die Seite ist schnell und einladend, was jede Session spannender macht. Ein starker Vorteil die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Jetzt Г¶ffnen|
https://uroki-igry-na-skripke.ru/
https://uroki-igry-na-skripke.ru/
https://nrbfriends.com/read-blog/69381
А как по качеству? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш помнится на бизе у Вас с этим было все хорошо.
Дошло довольно быстро купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану ПРИВЕТ ВСЕМ:НУ ЧТО Ж ТЫ БРО ТАК ОБЕЗНАДЕЖИЛ МЕНЯ ПО СКАЙПУ И В КОМЕНТАРИЯХ НАПИСАЛ ЧТО ОТПРАВИЛ MXE А НА ПАКЕТЕ НАПИСАНО RCS И ЧТО МНЕ КУРИТЬ ТЕПЕРЬ НАЧАТЬ ЗАЧЕМ ГОВОРИТЬ ТО ЧТО НЕ ДЕЛАЕШЬ КАК САМ СЧИТАЕШЬ ?
Сегодня на мыло пришло письмо с новостью что заказ отправлен и номер трека который бьёться:good: пока всё норм идёт, со мной связь поддерживают через скайп, игнора не было, когда получу отпишу за качество вес и тд купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки лучше ))
разобрался, поэтому и удалил сообщение до того как ты ответил ) купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш а чё есть какое нить в/в в этом магазе что бы до бледного?:)очень сильно хочу
кракен зеркало
Возможно сказалась бессонная ночь и отсутствие нормального питания на протяжении практически недели, но все время под туси я провел лежа на кровати и созерцая слааабенькие визуальчики. В общем, 4 из 6 сказали, что магазин – шляпа, и больше никогда тут ничего не возьмут. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Адекватных работников
С возвращением друг!!!!адекватных клиентов,спокойных и прибыльных деньков))) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм раньше вообще все говорили то что не растворяется это бутор а щас как я понимаю это в порядке вещей
https://xn--j1adp.xn--80aejmgchrc3b6cf4gsa.xn--p1ai/ Точка включения
https://xn--j1adp.xn--80aejmgchrc3b6cf4gsa.xn--p1ai/ Точка включения
Дабы не быть голословным: № заказа 1000707. 10г ам2233. Делал 1 к 7. Эффект болезненный. Все выброшено. Верни деньги ТС или пришли нормальный ам! https://alekskhaustov.ru Номер заказа: 10004015 оплачен, мыло выслано с информацией
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: blackjack envolvente, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi bem prestativo, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou mais ligeiro do que imaginei, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que seria legal torneios de slots, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Pra concluir, o 4PlayBet Casino e parada obrigatoria pra quem gosta de cassino. Recomendo sem medo.
leurre savage gear 4play|
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Es gibt eine Fulle an aufregenden Titeln, mit Live-Sportwetten. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, dennoch mehr Promo-Vielfalt ware toll. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Zusatzlich die Navigation ist klar und flussig, eine vollstandige Eintauchen ermoglicht. Ein starkes Plus die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Jetzt entdecken|
Удачи в бизе!! https://goldrub.ru Доберус до пк выложу скрины, магазин угрожает говорит что заплатит за подставу в общем очень взбесился когда я сказал что свои сомнения выложу в паблик, прямо как с катушек слетел, хотя я сначала сказал либо кидок аля лига 12, либо взлом.сразу мат срач угрозы ипр что никогда не сделал бы приличный шоп
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Anzahl an Titeln, mit Live-Sportwetten. Mit einfachen Einzahlungen. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, gelegentlich gro?ere Angebote waren super. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, jeden Moment aufregender macht. Besonders erwahnenswert sind die schnellen Krypto-Transaktionen, exklusive Boni bieten.
Alles erfahren|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, obwohl mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Zusatzlich die Site ist schnell und stylish, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Flexibilitat bieten.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich bin suchtig nach Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Spa?. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, jedoch regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist klar und flussig, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein klasse Bonus die regelma?igen Turniere fur Wettbewerbsspa?, die Teilnahme fordern.
Details prГјfen|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, obwohl regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
J’ai un faible pour Ruby Slots Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, en revanche plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute soudee.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je suis captive par Sugar Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par ailleurs des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce la communaute.
Essayer maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est simple et transparent, en revanche plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons aussi le design est style et moderne, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement interessant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller sur le site|
You might be surprised to learn that there are more people supporting the
tree, but believe it or not, men are into it.
Some people think it’s disgusting to have hair down there, but as long as you
keep it clean, pathogens are unavoidable. Plus, adding a little extra hair to
oral sex can give you some fun tease experiences. http://www.google.com.jm/url?source=imglanding&ct=img&q=https://hairpornpics.com/
Je suis sous le charme de Sugar Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Au final, Sugar Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Notons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter maintenant|
жду пока ответят, обана повдер кинул на 29000….но прочитал и понял что магаз супер, жду в скайпе селлера! https://copterfix.ru почему статус заказа отложен!? 1000539
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, a l’occasion des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. De plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute soudee.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’adore le dynamisme de Sugar Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, malgre tout des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons egalement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement attrayant les paiements securises en crypto, qui motive les joueurs.
Passer à l’action|
What’s up, its pleasant article on the topic of media print, we all be familiar with media is a wonderful source of information.
https://malaikat138.net/melbet-ru-obzor-2025/
May I simply say what a relief to uncover somebody who actually understands what they’re talking about on the internet. You certainly realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More people should check this out and understand this side of your story. I was surprised you are not more popular since you surely possess the gift.
https://ads88.net/melbet-skachat-na-ajfon-besplatno/
Всё шикарно,уже сидим с курим ваши бошки https://hotelxo.ru Ребят какие могут быть сомнения в этом магазе магаз ровный и заслуживает уважения он в доверенных его реклама на шляпе сайта ну это так для тех кто не знает просто реклама стоит 5000$ доларов!
https://www.linkedpt.com/employers/3859221-1xbet-no-deposit-bonus-code
а у нас в квартире газ ….. от ГАЗПРОМ … вы не поверите но это так и есть https://adb-lng.ru Доброго времени суток Всем порядочным форумчанам-кто здесь заказывал,но трек так и не бьёться,или я один такой закинул 45к+доставка,и”жду у моря погоды”В скайпе вчера отвечали сегодня-игнор!
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit packenden Live-Casino-Optionen. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino garantiert dauerhaften Spielspa?. Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist unkompliziert, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein starkes Feature sind die zuverlassigen Krypto-Zahlungen, die Community enger verbinden.
Jetzt ausprobieren|
кракен зеркало вход
https://ekcochat.com/1xbetfreespins
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Es gibt zahlreiche spannende Spiele, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Der Support ist schnell und freundlich. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, manchmal ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Zudem die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, das Spielvergnugen steigert. Ein attraktives Extra die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Jetzt Г¶ffnen|
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию Многие игроки хотят попробовать свои силы в онлайн-казино, не рискуя собственными деньгами. И это вполне реально! Существуют казино, которые предлагают приветственные бонусы за простую регистрацию. Это отличная возможность познакомиться с платформой, оценить ассортимент игр и даже выиграть реальные деньги, не тратя ни копейки из своего кармана.
Хочу всем сказать мы не работаем 1вым классом ни при каком условии… https://bccrt.ru/baksan.html мы и в скайп и в аське
https://community.cloudera.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/135242
в каком казино дают деньги за регистрацию без депозита Бездепозитные бонусы – это прекрасная возможность начать играть в казино без риска, освоиться в игровом процессе и, возможно, даже увеличить свой стартовый капитал. Главное – внимательно читать условия и выбирать проверенные казино. Удачи в игре!
Много тут кто согласен Артёмовский купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн мало того что неприятный опыт общения в гоме так и не денег не товару..
Check out the hottest spanking collection from Top spanking studios like Shadow Lane Explore spanking porn with Discover Erotic spanking and fun with|
Брал и не раз в данном магазине, притензий нет, все качественно, оперативность радует! Продовцы дайте информации о CHM – 500, что за зверь? когда в розницу уйдет Кулебаки купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн продавец отзывчивый
фофу кушают, 2 дмпм нюхается, судя по всему Азнакаево купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн небольгой репортаж отписать о ск.
“Ладно думаю доберусь до дома там опробую нозально ” Жуковский купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн составите конкуренцию известно кому :monetka:
большое спасибо продавцу и нашему времени :yeah::drug::rest: – пусть дальше будет еще круче :crazy:, быстрее :superman:, веселее :dansing: и ДОБрее Белебей купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн После передачи посылки курьерской службе ответственность за доставку несет именно курьерка, вы сами должны осознавать риск когда оформляете заказ с доставкой курьерки, и кто бреет? я вроде как бы согласился компенсирывать часть заказа, хватает еще наглости писать здесь жалобы.
Hi, its pleasant paragraph on the topic of media print, we
all be aware of media is a great source of information.
У данного прода, самая лучшая тусишка из всех, что я пробовал. Те кто пускали ВВ, выбрасывали остатки, пугаясь происходящего. Флюкс на уровне. Именно на уровне качества, не бутора. Но и не такой пиздатый как у Ромы Максимова (Его омы] флюкс для меня эталон 100мг, ОКЕАН эйфории). АМ2201 потрясающий, гора микса весёло прущего вышла из присланного пробника, но с огромной толлерантностью, была в итоге смешана с 203и 250 то же данного продавца, что придало миксу эффект, от которого бывалые говорили, что это их лучшие трипы в жизни ))) https://saraev-podbor.ru/tuapse.html магаз самый ровный , и со сладкими ценами!
сделал заказ в этом магазине первый раз, заказывал 2гр. 400f на пробу, а пришло 3,3гр., очень доволен))) Евпатория купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Ты выдал мне комбо
казино вывод сразу
1000 за регистрацию
https://techn9netourdates.com
https://theaterplaybill.com
Ждём вас снова https://st45shumiha.ru/nizhnekamsk.html Спасибо Магазину)вы лучшие))))))))!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! :monetka: Качество на 100%
Please let me know if you’re looking for a author for your weblog. You have some really good posts and I think I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d absolutely love to write some material for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please blast me an email if interested. Cheers!
https://borneo383.org/skachat-melbet-na-ajfon-2025/
кракен сайт зеркало
Войти на сайт кракен через актуальное зеркало.
For most up-to-date information you have to pay a visit web and on web I found this web site as a best website for most up-to-date updates.
https://opini77.com/melbet-kazino-skachat-obzor-2025/
орогуша! А что здесь людям писать как не о работе магазина? Эта ветка так то и называется “отзывы о работе магазина” вот о ни и пишут о проблемах которые возникли в связи плохой работой магазина или ты хочешь что бы они писали то что тебе нравится? как здесь все круто и классно? но если это не так то они это и пишут и не засоряют как ты говоришь ветку а пишут по существу. И правильно делают что пишут, что бы другие не попали в аналогичную ситуацию разве я не прав? https://architectit.ru/mihaylovka.html магаз клёвый ,:bravo:сервис на высоте
https://student.uog.edu.et/hello-world-2/#comment-25581
Жаль туси в наличии нет. хотелось именно тут взять. а как скоро появится не известно https://st45shumiha.ru/aksay.html всем привет щас заказал реги попробывать как попробую обизательно отпишу думаю магазин ровный и все ништяк будет))))
Привет всем Тсу движек Саяногорск купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн конечно оно так, все придет строго сколько сколько надо. Но ведь из за таких задержек могут и дела сорваться
Сама в ахуе, ни употреблять эту дрянь, ни толкнуть….. Бердск купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Курьерка не может принять такое количество заказов – отказала в
Верно. Но это уже другой критерий – грамотное описание Нурлат купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Да мы уже поговорили – нормальные ребята вроде) хз, я всё равно полной предоплате не доверяю)
турниры казино
проститутки краснодар Проститутка метро: Близость и анонимность соблазна. Ожидание поезда становится томным предвкушением встречи.
https://www.cverla.ru/
вчера трек получил:good: надеюсь всё будет ровно. https://alfamx.ru/frolovo.html Наверно так же как и джив. попробуй минимальные пропорции сделать 0,1 к 1
Je suis accro a Wild Robin Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour faire court, Wild Robin Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour completer la navigation est claire et rapide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un bonus les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses continues.
Parcourir le site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Cheri Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, malgre tout des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A souligner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point cle les transactions en crypto fiables, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller plus loin|
Je ne me lasse pas de Frumzi Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En somme, Frumzi Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour completer la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, garantit des paiements rapides.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
J’adore la vibe de Cheri Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est clair et efficace, rarement quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement excellent les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
Explorer davantage|
Je suis epate par Instant Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour faire court, Instant Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. De plus le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
AccГ©der au site|
J’ai un faible pour Wild Robin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, toutefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Wild Robin Casino garantit un amusement continu. En complement la navigation est simple et intuitive, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A noter le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Savoir plus|
Je suis epate par Cheri Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino est un must pour les passionnes. De plus l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A signaler les evenements communautaires vibrants, garantit des paiements rapides.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Je suis enthousiasme par Frumzi Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour ajouter l’interface est simple et engageante, facilite une experience immersive. Un atout les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Visiter la page web|
J’ai un faible pour Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est transparent et rapide, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De surcroit l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fluides.
Continuer ici|
superbet supergame
Je suis emerveille par Instant Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Instant Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement attrayant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui dynamise l’engagement.
http://www.instantcasinobonusfr.com|
Всем привет))))) Мой Трипчик)))))) https://job-in.ru/budennovsk.html понятно как проверенный магазин работает если отзывы негатив значит зачищает сообщений еще куча они на телефоне сейчас не могу их скопировать но и смысла нет все и так ясно
https://community.hodinkee.com/members/bestpromocodefor
Вот отзыв за этот эйфор: https://shopfashion4all.ru/maykop.html братишки и сёстры всем мир и харе ругаться!жизнь прекрасна
https://doorspell.com/blogs/66601/Code-Promo-1xBet-2026-130-pour-Paris-Sportifs
Да хорошо бы было, сегодня уже получу трек. Но конечно напугали всякие кому типа ам плохой пришёл. Егорьевск купить кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш, бошки, скорость, меф, закладку, заказать онлайн Всё получил свой АМ. Порошок кремового-оранжевого цвета, кстати полная растворимость на поровой бане. Так что не знаю кто там чо писал, помоему товар заебись! Как высохнет отпишу трип репорт от этой поставки…
code promo pour 1xbet
Ну блиинн я ждуждуждужду а мне не отвечает ТС я в уныние, буду ждать. говорят хороший, хочу попробовать у него. хочу сладкий бубалех мммм…. https://bccrt.ru/glazov.html А сейчас работает магазин?
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Вы это о чем? Тут все вроде как только легальными делами занимаемся? Да и продавцу то я как никак доверяю свой адрес и телефон, почему он не может доверить мне кинуть сотку на телефон? Это ни к одному делу не пришьешь, раз мы уже заговорили об этом https://appworldstore.ru/novomoskovsk.html Отличный магазин, общение с KingSize – одно удовольствие, а продукты неизменно радуют.
как здесь стелят? https://architectit.ru/korkino.html Может стоит внимательно посмотреть в ветке что есть резервный жаббер ? основной уже 6 дней не работает , какие то сбои, но резерв ведь работает, привыкли панику поднимать на ровном месте.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Wild Robin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, Wild Robin Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour ajouter le design est moderne et attrayant, incite a rester plus longtemps. A signaler les evenements communautaires vibrants, garantit des paiements rapides.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par Wild Robin Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, parfois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Wild Robin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et style, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement interessant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Apprendre comment|
Je suis epate par Wild Robin Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Wild Robin Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi le design est style et moderne, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Wild Robin Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Wild Robin Casino offre une aventure memorable. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A signaler les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Aller Г la page|
Je suis totalement conquis par Instant Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En bref, Instant Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En extra l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements securises.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
J’adore l’energie de Wild Robin Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, mais des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, Wild Robin Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
VГ©rifier le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, Cheri Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus constants.
Voir la page d’accueil|
J’adore l’energie de Wild Robin Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par moments quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Dans l’ensemble, Wild Robin Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En complement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses continues.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Je suis epate par Cheri Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par moments des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A souligner la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Frumzi Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, toutefois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour faire court, Frumzi Casino assure un fun constant. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un bonus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Entrer sur le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Cheri Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour completer la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, cree une communaute vibrante.
Lire plus|
Je ne me lasse pas de Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est transparent et rapide, rarement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En fin de compte, Cheri Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement cool les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus constants.
http://www.chericasinoappfr.com|
Je suis totalement conquis par Cheri Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En fin de compte, Cheri Casino garantit un amusement continu. De surcroit le design est moderne et energique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui stimule l’engagement.
Explorer maintenant|
Je ne me lasse pas de Frumzi Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, parfois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis enthousiasme par Instant Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Instant Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est fluide et facile, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement fun les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
Aller sur le web|
тюмень девушки проститутки
https://www.seyhancanta.com/blog/another-blog-post
да в пятницу отправляли… вот до сих пор небьеться… нервничаю… https://smilefab.ru Снова всё на высоте)заказывал 2 г тусишки!попросил пробник 5МЕО) получил)))))))))
Меня кинули на 15000. В жабере удалили учетку. Не покупайте ничего. походу магазин сливается. https://spiegelimspiegel.ru отдыхай до понедельника
https://www.mixcloud.com/1xbetpromocode00/
<https://kuklanvt.info/jdu-zvonka/
пробывал нюхать эфект 4-6часа https://laserlandiv.ru ну не хочешь – не бери, кто заставляет то Оо Покупают сотни, а отзывы “с критикой” от единиц. Кстати, 307го нет кажется…
https://www.threads.com/@jubayerhussain666/post/DQedgOcAUUo
африканская девушка проститутка Проститутка метро: Близость и анонимность соблазна. Ожидание поезда становится томным предвкушением встречи.
Админ по аське с кем связался адекват=))) радует.Приятный сайт цены тоже радуют сделал заказ=)) буду ждать. Качество Каличество отпишу купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки заказывал уже недельку назад, все пришло качество хорошее делал 250 1 к 9ти вполне на час полтора хорошего эфекта
To activate your betwinner sign up offer, just head over to https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/ and follow the guide. It’s an effortless way to start with extra funds.
)))) все любители пробничков )))) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Что хочу сказать закладки всегда по высоте.
Paris sportifs avec 1xbet inscription rdc : pre-match & live, statistiques, cash-out, builder de paris. Bonus d’inscription, programme fidelite, appli mobile. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money. Informez-vous sur la reglementation. 18+, jouez avec moderation.
Оформите онлайн-займ https://zaimy-54.ru без визита в офис: достаточно паспорта, проверка за минуты. Выдача на карту, кошелёк или счёт. Прозрачный договор, напоминания о платеже, безопасность данных, акции для новых клиентов. Сравните предложения и выберите выгодно.
http://www.google.bt/url?q=https://cere-india.org/art/promo_code_for_46.html
казино онлайн с выводом
Plateforme parifoot rdc : pronos fiables, comparateur de cotes multi-books, tendances du marche, cash-out, statistiques avancees. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money, support francophone, retraits securises. Pariez avec moderation.
казино официальный
http://www.google.tm/url?q=https://clubcoma.org/blog/1xbet_promo_code___welcome_bonus_1.html
Разве имеет принципиальное значение сколько моему аккаунту времени? Я тут не *зависаю*, а пишу по сути. Мутность заключается в том что оператор в аське на вопросы по уточнению адреса, сначала молчал почти 3 часа, потом вообще оффнулся. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Даже то что я из за тебя третий день на нервах это косяк!Ладно надеямся на лучшее,надежда умирает последней…
Все легально и проверено, есть NMR. Плохого ни чего не случиться. Скорей всего приняли потому что были паленые…. https://lada-togliatti.ru 31 страницу отзывов почитайте – увидите всех. Кто то только что зарегился , ктото год назад , кому что аккаунт блокнули или забыл пароль от старого акка – он зарегился по новой .
J’ai un faible pour Wild Robin Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, malgre tout des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Wild Robin Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En complement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point cle les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, garantit des paiements securises.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
Je suis captive par Instant Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, bien que des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Instant Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste l’excitation du jeu. A souligner les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce la communaute.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
Je suis captive par Wild Robin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons egalement la navigation est claire et rapide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui booste la participation.
En savoir plus|
Je suis captive par Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, quelquefois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Frumzi Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour completer le design est style et moderne, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un plus les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce la communaute.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis enthousiasme par Wild Robin Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En bref, Wild Robin Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En extra la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Parcourir maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Instant Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps a autre des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino merite une visite dynamique. De plus le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce le lien communautaire.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis bluffe par Wild Robin Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, Wild Robin Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En complement la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Instant Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par moments des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En bref, Instant Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En extra le site est rapide et engageant, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements rapides.
Lancer le site|
J’ai un faible pour Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Instant Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A noter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement attrayant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, assure des transactions fluides.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, de temps en temps plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A signaler le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fluides.
Commencer Г lire|
Но могу сказать что на данный момент проблемы с отправкой у магазина! в среду оплатил и сказали в четверг будет отправка, но увы ее нет! такое в первый раз замечаю от такого магазина! будем ждать! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Магазин как уже и было сказано – на 5+
J’adore le dynamisme de Instant Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Instant Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En extra le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un point fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des privileges personnalises.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Je suis bluffe par Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, Cheri Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui stimule l’engagement.
Approfondir|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Instant Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En fin de compte, Instant Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En bonus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement excellent les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges personnalises.
https://instantcasino365fr.com/|
J’adore l’energie de Frumzi Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est transparent et rapide, quelquefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino assure un fun constant. De plus le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un point cle les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Touchez ici|
Крутой магаз. Ассортимент радует купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш +огромная потеря популярности и быстрый спад клиентов.
Обновлено сегодня: https://mr-master.com.ua
магазин уже давно в тренде уже сколько лет купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Бро ты бред несёшь!Если читал все посты в этом магазе брали даже модеры этого форума.А может быть ты конкурент и провоцируешь людей специально?
Awesome things here. I am very happy to look your post. Thanks so much and I’m having a look ahead to touch you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
skla
магазину желаю дальнейшего процветания и минимум траблов(а лучше вовсе без них).? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Ну мы стараемся
а че магазин то ваще работает нет? https://ipconf2024.ru да магаз отличный.оперативно работают.и качество товара отличное.вобщем всё хорошо.
Классный магаз, почитал отзывы, нам в киров бы не помешал такой движ. Ассортимент огонь, давайте в наш славный город. Всем щастья! https://kdsed.ru всем желаю счастья!
Флуд??? Я высказал свое мнение! Или это запрещено? купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Вы то нет:) А банки работают:)
а вот на фофу гнать нельзя… она на высоте… https://vertikal-kursk.ru Это закон, хороший отзыв мало кто оставляет, а вот говна вылить всегда есть желающие вот и получается так, те у кого все хорошо, молчат и радуются
что сильнее 100 или 400 ? и по времени сколько действуют ? купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Хороший сервис, хорошая команда = хорошие дела ) В том же духе двигаемся…)
Awesome knowledge, Kudos!
Брал первый раз дживик качество вроде норм))))Еще хотел совет попросить как из 250 самый норм микс сделать?Помогите плиз. https://ipconf2024.ru Добрый день! ЦЕНЫ НА MN СНИЖЕНЫ!
Experience nuru massage in Bangkok downtown|
онлайн психолог москва
Job in korea Работа без знания корейского языка – это реальность. Многие компании готовы рассматривать кандидатов, владеющих только английским или русским языком. Однако, знание корейского языка значительно повышает ваши шансы на успех и открывает новые возможности для карьерного роста.
Да работает в асю обращайся если чё надо только товара мало там мхе да дмт купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш проверенный временем магазин, все ровно , все быстро
Официальная онлайн-платформа – Ознакомьтесь с услугами, продуктами и новостями.
Доброго всем времени, товарищи подскажите как посыль зашифрована? паранойя мучит, пару лет с доставкой не морочился. Ежели палево то можно и в ЛС)) Заранее благодарен https://mpm74.ru ХОРОШО СВЯЖЕМСЯ КОГДА ПРИЕДУ ДОМОЙ Я НА ПРИРОДЕ ДАВЛЮСЬ ПИВОМ А МАГАЗИНЕ НАПИСАНО ЧТО ОТПРАВЛЕН MXE
https://youpic.com/melbet_promo_code1/bio
Je suis captive par Frumzi Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Frumzi Casino garantit un amusement continu. En plus le design est moderne et energique, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement fun les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
внутрикостная блокада
Je suis emerveille par Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, rarement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour finir, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est simple et intuitive, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires vibrants, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г explorer|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Frumzi Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino merite un detour palpitant. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
J’ai un faible pour Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement fun les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller plus loin|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Instant Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des tables live interactives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est clair et efficace, neanmoins quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Instant Casino vaut une visite excitante. A mentionner le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A souligner les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis emerveille par Wild Robin Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, neanmoins plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Wild Robin Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Instant Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En bref, Instant Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons egalement le design est style et moderne, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fluides.
Commencer Г explorer|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Cheri Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par ailleurs des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Cheri Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un bonus les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges personnalises.
Aller voir|
Je suis accro a Instant Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, toutefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Instant Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement excellent les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, garantit des paiements securises.
Visiter en ligne|
Кто под нос что-то бормочет, купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм а чё ам закончился у вас? пишит нет на складе
Je suis accro a Wild Robin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Wild Robin Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En bonus la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Lire plus|
Je ne me lasse pas de Instant Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour faire court, Instant Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour completer l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point cle les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des bonus constants.
Explorer le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Cheri Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, a l’occasion quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour completer l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Frumzi Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En extra la navigation est simple et intuitive, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Cheri Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps en temps des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Au final, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement genial les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis fascine par Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Frumzi Casino vaut une visite excitante. A signaler le design est style et moderne, facilite une experience immersive. Un atout les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages uniques.
http://www.frumzicasinopromofr.com|
РЕБЯТА КАК ВСЕГДА НА ВЫСОТЕ 5 ИЗ 5!!!! СПАСИБО купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану и такая хрень каждый день.
ВСЕМ МИР А ТСУ РЕСПЕКТ ))) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Может забегу как-нибудь) Обычно все берут там где надежно у одних и техже, новые магазины или первые покупки рисково, любой выберет проверенных лично)
Тоже интересен вопрос по шифровке посылки при доставке курьером купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Всем привет) У меня такая проблема, сделал заказ, оплатил через евросеть, Уважаемый продаван сказал то, что в евросети перевод идет до 3-х дней, хотя когда работали с другим магазином деньги прилетали моменьтально всегда. И доставка вышла на 950 р. (г. Екб), это получаеться + курьер или нет, просто до почты?… И через что лучше оплачивать в данном магазине?
всё чётко, ровно, от души скоро буду ещё заказывать ) Пришло быстро конспирация на все 100% ! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Один из старейших!!!
Regards, Terrific stuff.
https://uralochkavolley.forum24.ru/?1-7-0-00000975-000-0-0-1762310264
у меня такой вопрос: будут ли у вас на розничном сайте позиция am-2233 по 1гр? Я раньше брал через алхима, но он по неизвестным мне причинам сговнился. поймите меня правильно, для меня 7 кусков – это деньги и я не готов их дарить или тратить на непонятно что. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш ts ровный беру уже давно унего но 35ф реально слабый эфект трафы сделал 10к1 неочом в итоги из 50г сделал 300гр основ нармально вышло по качиству пока ещё ещё некто не рыгал( но вопщем неплохо цена соответствует качиству 400р за грам норм
https://lifeofagonytour.com
https://leonbridgesfans.com
3случая за последние 2недели.. если быть точнее.. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш вот это уже наводит на мысли
With thanks, Ample advice!
You should be a part of a contest for one of the most useful blogs
on the net. I am going to highly recommend this website!
Продукт получен, доставка по Москве заняла примерно сутки. Проверить качество пока не могу, но надеюсь приемлемое. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Хотя я знаю почему всех слабо торкает , всё дело в неверном приёме препарата ! Весь форум облазил , но этого способа не наблюдал . Пусть не приятно но стоит того . Порох под язык . Доза меньше , эффект быстрей и ярче . Хотя это личное дело каждого , песня не об этом .
он спонсировал всех нас. https://sk-angara.ru Смело таримся!! Нипожалеете
I’m not sure why but this weblog is loading incredibly slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
1xbet-sport.pro
а чё ам закончился у вас? пишит нет на складе купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази с чего они тебе отзывы писать будут если они груз две недели ждут? они че тебе экстросенсы и качество могут на расстоянии проверить? и извинений мало ты не на ногу в трамвае наступила следующий раз пусть магаз компенсирует бонусами за принесенные неудобства! кто со мной согласен добавляем репу!
https://send.now/pe05dofkj6vv
такой замечательный и паспиздатый магазин………ноооооо где же мой заказ тогда? трек так и не бьется,тс на связь не выходит!!! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Отличный магаз.
КЕнт в почту зайди,проясни ситуэшен. https://estom29.ru всем доброго времени суто тс ответь в лс есть вопрос
Оформите займ https://zaimy-61.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино отзывы
Высшее качество. Чёткий товар. Мошный микс. Хороший персонал, добрый МАгазин…. купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Вчера оплатил, сегодня уже трек скинули. Пока все ровно, посмотрим что придет…..
J’adore la vibe de Betzino Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, parfois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Betzino Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et immersif, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
Betzino|
J’adore l’energie de Viggoslots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Viggoslots Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce la communaute.
Lancer le site|
https://stocktwits.com/henrybakerrus
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Viggoslots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Viggoslots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour completer le design est moderne et energique, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les transactions en crypto fiables, cree une communaute vibrante.
Plonger dedans|
J’adore la vibe de Viggoslots Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et style, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute vibrante.
Apprendre comment|
Je ne me lasse pas de Vbet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, rarement des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Vbet Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi le design est tendance et accrocheur, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller Г la page|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Vbet Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par contre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Vbet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A signaler l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un element fort les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui motive les joueurs.
Obtenir plus|
203 вообще шикарный ) мне понравился. спасибо Вам) https://restoranroyal.ru Я знаете как делаю, когда пацики отвечают сразу делаю заказ, оплачиваю и все чотка, самим тормозить не надо
вот немного для Сашка купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Эйфора сейчас нет в наличии, если только индивидуальный заказ от 1кг.
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
Но в свое время с 250м было время за месяц перед запретом: купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш я вот тоже дождался и пришел ко мне груз ценный)) завтра поеду забирать, потом отпишу что и как
I’m still learning from you, but I’m improving myself. I absolutely liked reading all that is written on your website.Keep the aarticles coming. I loved it!
Оформите займ https://zaimy-65.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
По приходу товара я выложу тут розничную площадку для заказов, на которой вы сможете заказать реактивы из наличия на складе, не уточняя у нас что есть… https://estom29.ru Ура! Скинул трек быстро) ждууууууу, отпишу.
Первый раз заказывал пришло все за 4 дня , в данной же ситуации уже 11 дней идет , я готов любые деньги платить чтобы приходило быстрей купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки бля у нас опен эйр будет 11 июня у шамана пороха нету!!!вот ищу где бы взять что нибудь на подобие скорости или кокса!а тут отзывы что соду продают!
магазин работает ровно, заказ пришел за пару дней, качество порадовало) https://kovrr.ru Я выхватил бан, ты злобняк
например тут ну или накрайняк тут а селлер совершенно не обязан консультировать по применению хим. реактивов. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази проблемы с обслуживанием.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Viggoslots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour faire court, Viggoslots Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A noter le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement excellent les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges personnalises.
http://www.viggoslotscasino777fr.com|
J’adore le dynamisme de Betzino Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est transparent et rapide, rarement des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Betzino Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Cliquez ici|
Je suis emerveille par Betzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps a autre des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Betzino Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement genial les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis captive par Vbet Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour conclure, Vbet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, garantit des paiements securises.
Visiter pour plus|
J’adore la vibe de Vbet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour finir, Vbet Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons egalement la navigation est fluide et facile, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un element fort les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements securises.
Avancer|
Качество, если честно на моё удивление (тк. первый раз я пользуюсь услугами данного ТС), по отзывам клиентов, сказать отличное это сказать ничего, ССССУУУУУПППЕЕЕЕРРРР!!!!!! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Благодарен за заказ во вторник оплатил – в пятницу / утром / товар получил
Ко ланта ло Канта
https://t.me/KohLantaKrabiThailand ло Канта
удачи в изменении ситуации! 🙂 купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм вот отправил манетку ,получил адик
Entdecken Sie die besten Weinverkostungen in Wien auf weinverkostung wien hofburg.
In der Stadt finden sich zahlreiche Weinguter, die eine lange Geschichte haben.
Die Weinverkostungen in Wien sind perfekt fur Kenner und Neulinge. Viele Veranstaltungen werden von erfahrenen Sommeliers begleitet.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
In Wien gibt es zahlreiche Lokale und Weinguter, die Verkostungen anbieten. Auch moderne Weinkeller in der Innenstadt bieten exklusive Erlebnisse.
Einige Winzer veranstalten Fuhrungen durch ihre Kellereien. Dabei erfahren Besucher mehr uber die Herstellung der Weine.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Wiener Weine sind vor allem fur ihre Vielfalt bekannt. Auch der fruchtige Grune Veltliner zahlt zu den bekanntesten Wei?weinen der Region.
Die Bodenbeschaffenheit und das Klima pragen den Geschmack. Dank nachhaltiger Anbaumethoden ist die Qualitat stets hoch.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Eine gute Vorbereitung macht die Verkostung noch angenehmer. Wasser und Brot helfen, den Gaumen zwischen verschiedenen Weinen zu neutralisieren.
Gruppenverkostungen bringen zusatzlichen Spa?. Gemeinsames Diskutieren uber die Aromen fordert den Austausch.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Die osterreichische Hauptstadt bietet eine einzigartige Mischung aus Tradition und Moderne.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
In Wien gibt es zahlreiche Lokale und Weinguter, die Verkostungen anbieten.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Die warmen Sommer sorgen fur vollmundige Aromen.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Viele Veranstalter bieten thematische Verkostungen an.
Не переживай,сегодня праздник выйдут на связь купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Меньше 2х кило не брал у них. Привозили в оговоренный срок, количество и качество было в норме. Сейчас в очередной раз зарядил, жду адрес
клиники наркологические москва http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru .
1xbet giri? 1xbet giri? .
Весом по 1 гр купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану я заказывау уже больше 2х лет только у этого магазина, сейчас заказал эфор и регу на подобия jv 100 сказали, посыль дошол от крыл а тпм только эфор а реги нет. может вы что то перепутали с заказом ребята ответь.
Получил. начал разводить на 7 мл ацетона. все выпало в осадок и почти ничего не растворилось. жидкость получилась мутная как молоко. добавил еще 5 мл. вроде более менее, но все равно большой очень осадок. ну и прям так туда 2 коробка основы высыпал и на плитку. все делал впервые, можно сказать наугад. пыхтел через водник. 1 водник и накрывает мама не горюй. час держит и еще полтора отпускает, и состояние потом ппц мутное какое, даже утром проснулся еще в коматозе. все отлично в принципе, только вот отходняк какой-то.. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш сегодня оплатил заказ..буду ждать доставки..протестирую.сообщу о качестве продукта
https://blogs.umb.edu/psychmemorylearningvc/2013/10/27/cybersenses-hearing-and-seeing-again/
люблю мелких подхалимов https://pilostroy-solikamsk.ru Заказывал небольшую партию)) Качество отличное, быстрый сервис)) в общем хороший магазин)
с минимальным депозитом Устали от ограничений? Мобильное казино – это ваш билет в мир развлечений без лишних хлопот. Благодаря современным технологиям, вы можете наслаждаться всеми преимуществами настоящего казино прямо со своего мобильного устройства. Быстрый доступ, интуитивно понятный интерфейс и возможность играть в любое удобное время – вот что делает мобильные казино такими популярными.
Попробуйте сами и убедитесь, насколько легко и увлекательно играть на ходу!
с минимальным депозитом Выбор надежного онлайн-казино – это инвестиция в ваше спокойствие и безопасность. Не торопитесь, проведите исследование и выбирайте казино, которое соответствует вашим требованиям и имеет хорошую репутацию. Помните, что азартные игры должны приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Играйте ответственно!
да работаем только по прайсу купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази я тоже несколько раз брал ,всё прошло чётко ,качество радует,доставлено всё в лучшем виде,оператор молочага всегда обьяснит всё что к чему,вообщем магазин для меня лучший ,самый надёжный,УСПЕХОВ И ПРОЦВЕТАНИЯ ВАШЕЙ КОМАНДЕ!!!!!!
J’adore l’energie de Betzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, toutefois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En bref, Betzino Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A noter la plateforme est visuellement captivante, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis sous le charme de Betzino Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps a autre des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Betzino Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A noter le design est style et moderne, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage notable les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages sur mesure.
En savoir davantage|
Je suis accro a Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus initial est super. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps a autre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En resume, Betzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des privileges personnalises.
Voir maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, Posido Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En plus le site est rapide et immersif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un element fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui motive les joueurs.
}
Je suis completement seduit par Vbet Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, en revanche des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Au final, Vbet Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis emerveille par Posido Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Posido Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Мне пока ещё не пришло, но ты уже напугал….:orientation: кто знает где весы купить можно чтоб граммы вешать https://holbonskoe.ru Все всегда на высшем уровне:dansing: всегда отправляют практически моментально
Пришол 250 сделал 1к10-12 ппц уносит 250 у вас лучший магазу респект , даже не ожидал что такой джив будет , 1к10 меньше это ппц.. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш это не спиша эндеграунд улица полна
Списались с оператором. Нужно взять 50 гр. СК. https://gold-rem.ru вы могли написать похожему нику , таких пруд пруди.
Не прогадал) Искупался, доставили пиццу, вискарика дернул со льдом… купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш перорально – эффекта 0 при меньших дозах, при больших – понос, рвота, чуваку скорую вызывали, давление 40/15
Магаз вышел на связь, работает, но щас выходные 😀 с треками порешают, по ходу косяки СПСР. пробники БУДУТ !! Кто ещё будет гадить в теме “Трипы” и просить пробник – получит подзатыльник. У кого есть что сказать – отпишите лучше отзывы о товаре. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Ровной работы!
Je suis captive par Viggoslots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps a autre quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De surcroit l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Cliquez ici|
Je suis accro a Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En fin de compte, Betzino Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. D’ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps a autre des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En fin de compte, Betzino Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour couronner le tout la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je suis epate par Vbet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Vbet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A mentionner le design est style et moderne, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Visiter maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Posido Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Posido Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A souligner le site est rapide et engageant, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un plus les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements securises.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
гидроизоляция подвала москва гидроизоляция подвала москва .
торкретирование стен торкретирование стен .
1 xbet giri? 1 xbet giri? .
наркологический центр narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru .
Надеюсь на дальнейшее сотрудничество с магазином! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Млять, не хватает нервов, 2 дня уже пытаюсь через асю связаться с продавцом и всё безрезультатно.Ладно бы вообще не ответил, ато написал что ок и не счета куда делать перевод,и ничего.
все от души))) вот бы еще во всех городах зк делали))))) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази у нас нет давно курьерских доставок.
Un Code promo 1xbet 2026 : recevez un bonus de 100% sur votre premier depot, jusqu’a 130 €. Jouez et placez vos paris facilement grace aux fonds bonus. Une fois inscrit, n’oubliez pas de recharger votre compte. Si votre compte est verifie, vous pourrez retirer toutes les sommes d’argent, y compris les bonus. Vous pouvez trouver le code promo 1xbet sur ce lien — https://github.com/lunki1992/Code-Promo-1xBet/blob/main/README.md.
Mushnyak, да ты гонишь походу, магазин работает как надо, каждую неделю у них заказываю все ровно, кидаловом тут не пахнет, ты наверное на отходосах)))) https://tipsandtricks.ru пот теории 2мл растворителя на 1г основы,т.е на 150г 300мл.
Всем привет ну что ж в очередной раз заказал всё пришло всё ровно грамотно и сделано чисто. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Ребят,а здесь только курёха?
Да и вообще: купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Пиздец до сих пор мозги ебут(
гидроизоляция подвала москва гидроизоляция подвала москва .
Je suis captive par Viggoslots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps en temps des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Viggoslots Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un bonus les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Ouvrir le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Viggoslots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, en revanche des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En bonus l’interface est lisse et agreable, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement cool les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir la page|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour faire court, Betzino Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A signaler l’interface est simple et engageante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement super les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce la communaute.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par Viggoslots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Viggoslots Casino assure un fun constant. En extra la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement top les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus constants.
Aller Г la page|
торкретирование цена торкретирование цена .
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, occasionnellement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Betzino Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour completer la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des privileges personnalises.
Continuer Г lire|
Это просто пустоплёт залётный, его уже изолировали от нашего общества купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Магаз ровный, очень много раз тут брал, а как перешли на телеграмм так еще больше радуете, намного меньше гемора с оплатой стало, качество на высоте как и всегда. Сегодня убедился что оператор не сидит без дела, очень сильно помог мне с моим вопросом, при чем оперативно все сделал. Оцениваю данный магазин 10 из 10. Кокаин даже MQ оказался лучше, чем я до этого покупал HQ в другом магазе. Делайте по чаще закладки в центре Питера.
J’adore le dynamisme de Vbet Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour faire court, Vbet Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons aussi le site est rapide et style, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Posido Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est clair et efficace, par contre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En somme, Posido Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges personnalises.
En savoir davantage|
Je suis totalement conquis par Posido Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour conclure, Posido Casino merite un detour palpitant. En complement le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des bonus constants.
Continuer ici|
https://www.sportjim.com/betfreebonus
шлюхи сургута
Le code promo est supprime : entrez-le dans le champ « Code promo » et reclamez un bonus de bienvenue de 100% jusqu’a 130€, pour vos paris sportifs. Vous pouvez vous inscrire sur le site 1xBet ou via l’application mobile. Apres votre premier depot, vous activerez le code bonus. L’offre est valable pour toute l’annee 2026, et le bonus doit etre mise dans les 30 jours. Vous pouvez trouver le code promo sur ce lien > https://1-x-betsport.blogspot.com/2025/10/le-meilleur-code-promo-1xbet-bonus.html.
https://xn--h1aeegmc7b.xn--p1ai/wp-content/telm/1xslots_promokod_pri_registracii.html
1xbet g?ncel giri? 1xbet g?ncel giri? .
наркологический центр москва narkologicheskaya-klinika-23.ru .
Про 80 не знаю. Но то что там принимают сомнительных, дак это точно. Вот люди которые туда приходят и ушатаные в хламотень, все трясутся. И оглядываются, как будто от смерти скрываются конечно их принимают… А что про тех кто соблюдаем все меры, тот спокоен. И сдержан. Но все равно. В спср принимают однозначно, сам свидетель в 2006 году. когда за дропом следили, перепугались что за нашим пришли… Но все обошлось. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану самый дешёвый магазин из доверенных – это этот!
лабаз ништяк купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази В пробе было два вещества
Je ne me lasse pas de Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, a l’occasion quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Globalement, Betzino Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Cliquer maintenant|
Хороший сервис судя по отзывам!:) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки ровно, тут можно не беспокоится, попал куда надо
гидроизоляция подвала цена гидроизоляция подвала цена .
Krabi Ко ланта чат
торкретирование москва http://www.torkretirovanie-1.ru .
Ко ланта остров Thailand
Привет, ребята! купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Бро ты ошибся. Не поняли друг друга бывает
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Viggoslots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, mais encore des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, Viggoslots Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A souligner le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus constants.
Viggoslots|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Viggoslots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, en revanche des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En conclusion, Viggoslots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A signaler le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un bonus les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Viggoslots Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, malgre tout des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un atout les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis captive par Betzino Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, Betzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. En extra la navigation est claire et rapide, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement super les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
http://www.betzinocasino777fr.com|
боюсь что здесь произойдёт тоже самое, уж очень не внятно продавец общается. https://grimzone.ru а вот по этой теме отпиши по подробней,точнее о том как там дальше события развиваются?????????? очень волнует данная тема. как же так их просекла легавня???? откуда краснотой веет.???
Je suis bluffe par Vbet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus initial est super. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En fin de compte, Vbet Casino garantit un plaisir constant. De plus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce le lien communautaire.
Tout apprendre|
Je suis accro a Vbet Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, toutefois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, Vbet Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour completer le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis bluffe par Posido Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est transparent et rapide, a l’occasion des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Posido Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En complement le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un atout le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter la page web|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Posido Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, toutefois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, Posido Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement attrayant les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges personnalises.
http://www.posidocasino365fr.com|
А почему сам с-м.сом сюда какой день не кажеться…? https://znamblag.ru Как нет..я тебе в пятницу писал..сказал,вчто ниче что скину в субботу,воскресенье..ты сказал ниче…и дал номер..Я писал в личку на почтовый ящик..это не брорзикс и не скайп…мошеников быть не можит..Ты,оплату посмотри…за сегодня
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Posido Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est simple et transparent, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Posido Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Радуете ребята!!! https://uvoperm.ru Добрый день форумчане! Кто нибудь подскажет как по качеству реагент в этом магазине? Соответствует ли заявленная концентрация? Сколько по времени держит если 1 к 20 сделать? Всем спасибо!!!
Бонусы казино
бездепозитный бонус казино
Je suis epate par Betzino Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est clair et efficace, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Betzino Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Сегодня оплатил, сегодня и отправили, пацаны как всегда четко работают купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану У меня не бьётся вторые их трек. И бро в скайпе не видно. Мож приняли их посылки на почте? Тоже парюсь блин…. Но не хотел поднимать дискуссию, не имея причин. Выслали в пятницу СПСР.
все я уже пошол на почту получать пришло быстро молодцы СПСР вчера трек сегодня забираю за качество как и обещал отпишу а то там кто то сомневался https://moskovskie-dveri.ru Здрасте Бразы!!!!:hello:
Урб 597 либо перорально либо нозально, дозировка – 5-10мг, эффекты описаны в энциклопедии, https://lake-villa.ru че как дела?как настрой?
Je ne me lasse pas de Viggoslots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est simple et transparent, rarement quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Viggoslots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A mentionner le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir maintenant|
Je suis epate par Viggoslots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par ailleurs quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A mettre en avant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui booste la participation.
Avancer|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betzino Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est clair et efficace, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Betzino Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons aussi le site est rapide et style, facilite une immersion totale. Un point cle les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller en ligne|
Уважаемый, Chemical-mix.com, я новичок что на легале, что в джабере, что где либо ещё… не получается выйти на связь, проблема с покупкой, в джабере написано, на сайте не онлайн… ответь пожалуйста в jabber… Зарание большое спасибо… купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш добрый день как связаться с продавцом и не попасть на фейка?
Цирканутые новости от Chernov Creation Новости Chernov Creation: В мире цифрового творчества открываются новые горизонты! Мы рады приветствовать вас в эпицентре инноваций и свежих идей. Chernov Creation – это не просто платформа, это целый мир, созданный для воплощения самых смелых замыслов. Здесь каждый, от начинающего энтузиаста до опытного профессионала, найдет инструменты и вдохновение для реализации своего потенциала. Следите за нашими новостями, чтобы быть в курсе последних трендов, эксклюзивных проектов и уникальных возможностей для развития в сфере цифрового искусства.
J’adore la vibe de Vbet Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est transparent et rapide, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Vbet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Approfondir|
J’adore l’energie de Vbet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, Vbet Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement top les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Commencer Г lire|
J’ai un faible pour Posido Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Posido Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. D’ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement interessant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betzino Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Betzino Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En plus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://betzinocasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis captive par Posido Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, rarement plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Posido Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un element fort les transactions en crypto fiables, cree une communaute soudee.
Naviguer sur le site|
https://pikabu.ru/@bookmakers09
Je suis bluffe par Posido Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Posido Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute soudee.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
Но в свое время с 250м было время за месяц перед запретом: купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Брат, ответь в личке, жду уже 3 дня
бездепозитные казино с бонусом за регистрацию и без пополнения счета
бонус за регистрацию в казино на реальные деньги
Давайте обменяемся идеями! Я собрала несколько своих любимых вариантов фото межкомнатных дверей — будет здорово, если и вы поделитесь своими фото/ссылками
Я экспериментирую с подачей материалов. Посмотрите, как вам такой формат. Спасибо за честный отзыв!
https://urlsss.com/melbet-code-vip-2026-%e2%9e%a4-130-e-cashback-15/
Да неее))) само то емс и почта россии !! А лучше гарантпост очень клево работают по ним надо отправлять вообще изумительные службы. Или первый класс! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Че все затихли что не кто не берет? Не кто не отписывает последние дни не в курилке не где везде тишина(
https://theaterplaybill.com
С возвращением бразы! удачной работы вам и процветания https://gav-ural.ru Оплатил в среду, жду посылочку, посмотрим как что.
какой выход с 1г ? https://366shop.ru Продукт получен, доставка по Москве заняла примерно сутки. Проверить качество пока не могу, но надеюсь приемлемое.
Je suis emerveille par Betzino Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais encore plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En complement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute soudee.
Voir maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Viggoslots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En plus le design est style et moderne, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements securises.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Je suis emerveille par Betzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par ailleurs plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Betzino Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui motive les joueurs.
Commencer maintenant|
Je suis epate par Betzino Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, rarement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A signaler le design est style et moderne, facilite une experience immersive. Un bonus les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
http://www.betzinocasino366fr.com|
Да просто дедушка форума )) https://lake-villa.ru ставлю большой + магазину и хочу
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Vbet Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En conclusion, Vbet Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour completer le site est rapide et immersif, booste le fun du jeu. Un element fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges personnalises.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Всем привет !!! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Магаз отличный, успехов вам!
J’adore le dynamisme de Vbet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est transparent et rapide, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Vbet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A noter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une experience immersive. A signaler les evenements communautaires vibrants, assure des transactions fluides.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
Je suis emerveille par Posido Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, toutefois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En bref, Posido Casino offre une experience hors du commun. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
Je suis completement seduit par Posido Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, a l’occasion des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En somme, Posido Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En extra le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui booste la participation.
Ouvrir la page|
Верный второй трек. Но у этой курьерки система мониторинга развита не особо хорошо и бывало такое, что посылка доходила за день-два, ее уже получили, а трек начинал биться только через пару дней после этого. Если в ближайшее время не заработает, то лучше звоните в курьерку и уточняйте. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки а как ам то хоть вооще расшифровывается то по науке???
Je suis accro a Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, en revanche des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A souligner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fluides.
http://www.betzinocasinobonusfr.com|
Ам1220 все больше сообщений что относят к нелегалу. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Успехов вам господа : )
I don’t know if it’s just me or if everybody else experiencing
issues with your site. It seems like some of the written text
on your posts are running off the screen. Can someone else please comment
and let me know if this is happening to them as
well? This might be a issue with my browser
because I’ve had this happen previously. Many thanks
Все Вась,извини..с утра заматался)) https://ooo-ecoservice.ru я все ровно остался в минусе не заказа и деньги с комисией переводятся . если ты правду говорил про посылку то если она придет я сразу закину тебе деньги и напишу свои извенения и все везде узнают что у тебя честный магазин.как клиенту мне ни разу не принесли извенения это бы хоть как то компенсировало маральный ущерб
Thanks a lot! Awesome information!
https://theaterplaybill.com
J’adore l’energie de Betway Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, parfois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De plus le site est rapide et immersif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un atout le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Через Skype мы больше не работаем, об этом мы объявляли пару недель назад. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш качество очень хорошее не подведёт даже не сомневайся
Je suis emerveille par Belgium Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Belgium Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons egalement la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Poursuivre la lecture|
J’ai un faible pour Betway Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est simple et transparent, par ailleurs des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour conclure, Betway Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une immersion totale. Un point cle les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute soudee.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je suis bluffe par Betway Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Betway Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A noter le design est tendance et accrocheur, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A noter les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements rapides.
Approfondir|
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par moments des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Betify Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A mentionner la navigation est claire et rapide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un bonus les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Touchez ici|
Je ne me lasse pas de Gamdom Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, mais des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Gamdom Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A signaler les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
En savoir plus|
Je suis captive par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des tables live interactives. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En bref, Gamdom Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A signaler l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un atout le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fiables.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Je suis emerveille par Betify Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, quelquefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Betify Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, apporte une energie supplementaire. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
Занимайся я таким делом,коли вы не просили б о граммах 100,ответ был бы тот же. В таком деле главное-отсутствие жадности. Не надо гнаться за каждой копейкой,коли есть относительно безопасная отработанная схема,то и нечего от неё отклонятся. Вы видите в них кидал,они в вас красного. https://pgisim.ru и вот я решил зайти на ветку доверенных магазинов! и почему то решил ткнуть именно на ссылку чемикл микс! захожу дыбанул на ценник, устроило и даже очень! так же порадовало то что тут делают отправку! а это значит то что если товар отправят то ты его 100% получишь! главная особенность магазина в том что отправка делается от 5грамм 🙂 а это значит то что я смогу и опробывать товар и убидится в качестве товара, и в надежности магазина!
Wow lots of terrific knowledge.
ровный магаз успеха и процветания https://pgisim.ru Та не, не стоит оно того. Надо отдать должное магазину, посылка пришла, без проблем.
great put up, very informative. I wonder why the opposite experts of this
sector do not notice this. You must continue your writing.
I am sure, you have a great readers’ base already!
трансфер из Павлодара в аэропорт Толмачево
Да рега была шикарная… Но вот как раз таки с ней и случился перебой, ОЧЕНЬ жаль!!! А так по работе остались отличные впечатления https://photo-nyu.ru Тоже считаем что запреты не запреты. Да бывает что и за клиентами охотятся.
J’adore l’energie de Betway Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Betway Casino assure un fun constant. A mentionner le site est rapide et engageant, permet une immersion complete. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
https://betwaycasinofr.com/|
электро рулонные шторы https://www.avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory1.ru .
электро рулонные шторы http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom7.ru .
1xbet resmi giri? 1xbet resmi giri? .
1 xbet giri? http://www.1xbet-giris-2.com .
Они хоть кому нибудь отвечают? купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Трек есть +Бонус от души как придет отпишу
1xbet resmi giri? https://1xbet-giris-4.com .
millioner casino
milioner casino
billionaire casino
бездепозитные бонусы казино форум Бездепозитные бонусы – это отличная возможность попробовать свои силы в онлайн-казино без риска для собственных средств. Однако, прежде чем активировать бонус, внимательно ознакомьтесь с его условиями, чтобы избежать разочарований в будущем. Удачи в игре!
бездепозитные бонусы казино без пополнения Бездепозитные бонусы – это отличная возможность попробовать свои силы в онлайн-казино без риска для собственных средств. Однако, прежде чем активировать бонус, внимательно ознакомьтесь с его условиями, чтобы избежать разочарований в будущем. Удачи в игре!
У данного сллера только легал. Все проверено. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки я заказывау уже больше 2х лет только у этого магазина, сейчас заказал эфор и регу на подобия jv 100 сказали, посыль дошол от крыл а тпм только эфор а реги нет. может вы что то перепутали с заказом ребята ответь.
Выходные просто, завтра проверь купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки пишу по сути заказал-оплатил-получил все это было очень быстро я сам охуел вечером кинули трек а уже на следующее утро получил походу ТС на реактивном истребителе доставку организовал, качество нормуль делал 1к8 штырит как положено, первые 20 минут на подьем потом 20 минут идет спад короче 40 минут полет отличный, да был небольшой казус часть платежа потярялось, но потом после созвона со службой поддержки клиентов благополучно нашлось- “дырявая банковская система” вот как то так. ТСу без подхолемажа РЕСПЕКТ!!!!
бездепозитные бонусы казино без отыгрыша Бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию с возможностью вывода – это отличный шанс начать играть в онлайн-казино без финансовых вложений и с реальным шансом на выигрыш. Главное – внимательно читайте условия каждой акции, чтобы понимать все правила и требования. Удачи в игре!
бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом Бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию с возможностью вывода – это отличный шанс начать играть в онлайн-казино без финансовых вложений и с реальным шансом на выигрыш. Главное – внимательно читайте условия каждой акции, чтобы понимать все правила и требования. Удачи в игре!
были случаи https://spl-music.ru основу взял мяту и подорожник, мед. спирт-растворитель.
Je ne me lasse pas de Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Betway Casino merite une visite dynamique. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un avantage les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis captive par Belgium Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Belgium Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De surcroit l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Lancer le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Belgium Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, quelquefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En fin de compte, Belgium Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour completer la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement fun les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer Г lire|
Je suis fascine par Betway Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Betway Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A noter le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Explorer davantage|
рулонная штора автоматическая http://avtomaticheskie-rulonnye-shtory1.ru/ .
1xbet ?ye ol https://1xbet-giris-8.com .
двойные рулонные шторы с электроприводом http://www.rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom7.ru/ .
Оплатил в среду, жду посылочку, посмотрим как что. https://uromed-ekb.ru Как у вас дела бразы?)
Je ne me lasse pas de Gamdom Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Gamdom Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute vibrante.
https://gamdomcasinoappfr.com/|
1xbet giri? yapam?yorum https://1xbet-giris-2.com .
1xbet resmi giri? 1xbet-giris-4.com .
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betify Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un bonus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements securises.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Gamdom Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, rarement des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En complement le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
J’adore le dynamisme de Betify Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A signaler l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un bonus les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Voir le site|
This is nicely put! .
покупателей много,очереди наверно большие тем более на доставку купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш странно что это нужно писать =\
Отличный магаз купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Приветствую всех! купил 0,5 кокса. Закинул деньги, получил адрес, приехал забрал, все на высоте! Кладмену отдельное спасибо, спрятал так что не доебаться. Качество просто улетное, и от меня и от друзей огромный плюс магазину.
с треками магазин всегда спешит:) и качество скоро заценим))) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Прислали нам свой метоксетамин, подтверждаем: продукт чистый, >99%.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betway Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est clair et efficace, a l’occasion quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En resume, Betway Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A mentionner le design est style et moderne, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges personnalises.
Aller sur le site|
1xbet giri? 1xbet giri? .
рулонные шторы в москве рулонные шторы в москве .
chemica l-mix.com,объявитесь на соседнем форуме(СпФН),вас там ОООООООчень заждались..! https://pasyans-pauk.ru Malkom ты не один такой такая же хрень зарядили бабосы еще и чужие пздц полный >< надеюсь разрулит всё =\
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betway Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Betway Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter le design est moderne et energique, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Explorer le site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Belgium Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Belgium Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une immersion complete. A mettre en avant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus constants.
http://www.casinobelgium777fr.com|
автоматические шторы на окна автоматические шторы на окна .
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Belgium Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais encore des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Belgium Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En plus le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages uniques.
Continuer ici|
Je suis completement seduit par Betway Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En bref, Betway Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons que le design est style et moderne, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A noter le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir la page|
1xbet ?yelik http://www.1xbet-giris-4.com .
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Gamdom Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A souligner le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des avantages uniques.
Obtenir des infos|
J’adore l’energie de Gamdom Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En bref, Gamdom Casino merite une visite dynamique. A noter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement attrayant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui stimule l’engagement.
Visiter en ligne|
Je suis accro a Betify Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, occasionnellement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Betify Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En complement la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, facilite une immersion totale. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des bonus constants.
Cliquer maintenant|
И что толку за легалом охотиться. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш да не врядли просто ихнему курьеру поджопников надавать надо что бы копытами веселей шевелил да и все
казино бесплатные фриспины без депозита
Не красиво вышло с вашей стороны, я канешно благодарен за доверие и выделенную вами пробу но увы Эфеект растроил( ” купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Сейчас забегал курьер но без звонка поймал небольшую пароною ведь 203 уже нелегал но всё обошлось всё забрал вес отличный спасибо селеру за быстроту за 3 дня вот это скорость самый наеровнейший магаз и качество полюбому 5+ я уверен как всегда ну это я уже в другой ветке отпишу по пояже как сделаю.
Discover exquisite Austrian wines at wein verkostung wien and immerse yourself in Vienna’s vibrant wine culture.
In Wien kann man die Vielfalt osterreichischer Weine auf besondere Weise entdecken. Die Region ist bekannt fur ihren exzellenten Wei?wein, besonders den Grunen Veltliner. Viele Weinverkostungen finden in historischen Gewolbekellern statt.
Das milde Klima und die mineralreichen Boden begunstigen den Weinbau. Das gibt den Wiener Weinen ihren unverwechselbaren Charakter.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
In Wien gibt es mehrere renommierte Weinregionen, wie den Nussberg oder den Bisamberg. Diese Gebiete sind fur ihre Spitzenweine international bekannt. Familiengefuhrte Weinguter bieten oft Fuhrungen und Verkostungen an. Gaste konnen die Leidenschaft der Winzer hautnah erleben.
Ein Besuch im Weingut Wieninger oder im Mayer am Pfarrplatz lohnt sich. Sie sind bekannt fur ihre ausgezeichneten Jahrgange.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Weinverkostung**
Eine klassische Wiener Weinverkostung beginnt meist mit einer Kellertour. Die Winzer erklaren gerne ihre Arbeitsschritte. Danach folgt die Verkostung unterschiedlicher Weine. Jeder Wein wird sorgfaltig prasentiert und verkostet.
Haufig werden die Weine mit lokalen Kasesorten oder Brot serviert. Das unterstreicht die Geschmacksnuancen der Weine.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
Um das Beste aus einer Weinverkostung in Wien herauszuholen, sollte man vorher buchen. Fruhzeitige Reservierungen garantieren einen reibungslosen Ablauf. Zudem lohnt es sich, auf die Jahreszeiten zu achten. Im Herbst finden oft Weinlesefeste statt.
Ein guter Tipp ist auch, ein Notizbuch mitzubringen. Viele Gaste schatzen spater die Erinnerungen an die Verkostung.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Die osterreichische Hauptstadt bietet eine einzigartige Mischung aus Tradition und Moderne.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
Die Weinguter hier setzen auf nachhaltigen Anbau.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Wiener Weinverkostung**
Diese Kombination ist ein Highlight fur Feinschmecker.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
Viele Gaste schatzen spater die Erinnerungen an die Verkostung.
—
**Hinweis:** Durch Kombination der Varianten aus den -Blocken konnen zahlreiche einzigartige Texte generiert werden, die grammatikalisch und inhaltlich korrekt sind.
значит ты чо то намутил , а вещество я заказывал в этом магазе норм для RCS естественно купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш 1 из 5 хемикалсу.Имейл не рабит,сайт кривой-левые системы оплаты,нет ритейла,кривость и отсутствие информации…Деньги зажимать не пытаются и за это можно кинуть балл сверху и возможно продолжить общение в будущем…
Je suis bluffe par Betway Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est simple et transparent, toutefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Betway Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement top les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements securises.
Ouvrir le site|
я не согласен предыдущем коментариям ,беру не первый раз ,на данный момент магазин самый охриненный ,всегда качество товара радует,всегда на связи они,они не когда не морозятся,своё дело знают чётко,нахрена им кидать ,они не будут портить свою репутацию какую уже заработал этот магазин,я беру поболее и меня не разу сдесь не кинули .процветания магазину .спасибо за вашу работу,что всё чётко и быстро И радуете вкусняшками.а ещё хочу добавить ,возможно это кидаки или канкуренты и пишут разную х….ю что бы сбить новичков ,Но мы кто всегда с вами знаем что магазин лучший и другого Нам НЕНАДО.Так держать ,МЫ ВСЕГДА С ВАМИ!!! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Удачи и процветания!
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино с выводом без депозита
бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом без отыгрыша
https://xnudes.ai/
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Belgium Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par contre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En fin de compte, Belgium Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour ajouter le design est style et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus constants.
Aller plus loin|
J’ai un faible pour Belgium Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Belgium Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute vibrante.
Plongez-y|
J’ai un faible pour Gamdom Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais encore des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En resume, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fluides.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
Je suis captive par Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, Betway Casino vaut une visite excitante. Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement attrayant les transactions en crypto fiables, qui stimule l’engagement.
https://casinobetwayfr.com/|
Je suis enthousiasme par Betify Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, occasionnellement quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Betify Casino offre une aventure memorable. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Savoir plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par Betify Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. D’ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Commencer Г explorer|
Скажу одно это вещь крутая!!! купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану “Выстовляет Эскимос список тестеров в Списке сверкает мой ник” “bob marli”
kra44 at
https://magnitola.kiev.ua
Магазин работает супер!) https://form.jotform.com/253103732549051 Смело таримся!! Нипожалеете
internet seo http://www.optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva.ru .
интернет продвижение москва интернет продвижение москва .
стратегия продвижения блог https://www.statyi-o-marketinge7.ru .
цифровой маркетинг статьи цифровой маркетинг статьи .
бездепозитные бонусы без отыгрыша Ищете возможность испытать азарт и, возможно, сорвать куш, не вкладывая ни рубля? Бездепозитные бонусы – это именно то, что вам нужно! Это специальные предложения от казино и букмекерских контор, которые дарят вам стартовый капитал или бесплатные вращения просто за то, что вы решили присоединиться. Используйте их, чтобы изучить ассортимент игр, найти свои фавориты и, кто знает, может быть, именно этот бонус станет вашим первым шагом к крупному выигрышу. Это абсолютно безрисковый старт для всех желающих!
бездепозитный бонус слоты Бездепозитные бонусы – это привлекательные предложения от онлайн-казино и букмекерских контор, которые позволяют игрокам начать играть, не внося собственных средств. Чаще всего они предоставляются за регистрацию нового аккаунта. Это может быть небольшая сумма денег на игровой счет или определенное количество бесплатных вращений для популярных игровых автоматов.
МХЕ “как у всех” тобиш бодяжный.. Вроде скоро должна быть нормальная партия. https://beteiligung.stadtlindau.de/profile/%D0%92%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B1%D0%B6%D0%B8%D1%85%20%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C%20%D0%9A%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B8%D0%BD/ как-то перехотелось.. что действительно последний товар не очень?
Перейти до деталей: https://government.com.ua/rozvahy.html
codeshift.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Je suis epate par Betway Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Betway Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour ajouter le site est fluide et attractif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un element fort les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus constants.
Parcourir le site|
Слив засчитан. https://wanderlog.com/view/bvzmhrkmwl/метро-РІРґРЅС…-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ с чего они тебе отзывы писать будут если они груз две недели ждут? они че тебе экстросенсы и качество могут на расстоянии проверить? и извинений мало ты не на ногу в трамвае наступила следующий раз пусть магаз компенсирует бонусами за принесенные неудобства! кто со мной согласен добавляем репу!
бездепозитные игровые автоматы Бездепозитные бонусы — это отличный способ войти в мир онлайн-гемблинга без вложений, но подходите с умом. Они дают шанс на выигрыш, но условия могут быть сложными, а риски — высокими. Выбирайте только проверенные казино
бесплатные вращения без депозита Бездепозитные бонусы – это привлекательные предложения от онлайн-казино и букмекерских контор, которые позволяют игрокам начать играть, не внося собственных средств. Чаще всего они предоставляются за регистрацию нового аккаунта. Это может быть небольшая сумма денег на игровой счет или определенное количество бесплатных вращений для популярных игровых автоматов.
в течении суток обычно (24 часа не 12)… https://wanderlog.com/view/dhgwmyeyji/киншаса-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ Тут ровно братаны,берем и не паримся,качеставо вышка!)
Найцікавіше: https://online-porada.com/hroshi.html
J’adore le dynamisme de Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, en revanche plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Globalement, Betway Casino assure un fun constant. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
Visiter en ligne|
Списались с оператором. Нужно взять 50 гр. СК. https://www.divephotoguide.com/user/diuhodcyhef за наличие узнавай у селлера. куда тебе 2грамма дезоксипипрадола я слабо представляю, хочешь упороть без палева пол района ? )
Je suis epate par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, Gamdom Casino garantit un amusement continu. En plus le site est rapide et engageant, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements securises.
Apprendre comment|
J’adore la vibe de Belgium Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En resume, Belgium Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A noter les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute soudee.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis emerveille par Gamdom Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, Gamdom Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En bonus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement top les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
частный seo оптимизатор частный seo оптимизатор .
продвижение по трафику продвижение по трафику .
Je suis emerveille par Betify Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, Betify Casino merite une visite dynamique. En bonus le site est rapide et engageant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
Lire plus|
статьи про seo статьи про seo .
J’adore la vibe de Betify Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots fluides. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps en temps des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour conclure, Betify Casino offre une aventure memorable. De surcroit le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui stimule l’engagement.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis captive par Belgium Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par contre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour finir, Belgium Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
блог интернет-маркетинга http://statyi-o-marketinge6.ru/ .
Je suis sous le charme de Betify Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, malgre tout des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Betify Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une immersion complete. Un plus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Passer à l’action|
всем советую магазин тс роботает ровно, знает толк в бизе, всегда беру у них и все ровно и надежно, товар выший класс ,куриер вообще красавчик все делает четко и надежно , магазину и курьеру оценка 10из 10 балов все ровно, ДОСТАВКА БОМБА ХОТЬ В АРТИКУ ДОСТАВЯТ https://www.band.us/page/100512069/ Прибыльных вам выходных!:monetka:
Je ne me lasse pas de Betway Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par moments des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour faire court, Betway Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une touche d’excitation. A mettre en avant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Aller Г la page|
мало того что неприятный опыт общения в гоме так и не денег не товару.. https://imageevent.com/yytyvogeliqa/fwtum Вы то нет:) А банки работают:)
Разве имеет принципиальное значение сколько моему аккаунту времени? Я тут не *зависаю*, а пишу по сути. Мутность заключается в том что оператор в аське на вопросы по уточнению адреса, сначала молчал почти 3 часа, потом вообще оффнулся. http://www.pageorama.com/?p=ecufzxeec добра всем бро,оплатил заказ неделю назад,на след день дали трек,трек до сих пор в базе не бьётся и посылочка не идёт…тс на письма не отвечает…вобщем чтот печкльно както,обычно 3 дня идёт(
поисковое продвижение москва профессиональное продвижение сайтов http://optimizaciya-i-seo-prodvizhenie-sajtov-moskva-1.ru/ .
аудит продвижения сайта аудит продвижения сайта .
руководства по seo руководства по seo .
бесплатные вращения без депозита Не упустите шанс начать играть прямо сейчас! Зарегистрируйтесь и получите свой бездепозитный бонус – это может быть сумма на счет или бесплатные вращения. Испытайте удачу, познакомьтесь с любимыми играми и получите возможность выиграть реальные деньги, не рискуя собственными. Просто зарегистрируйтесь и заберите свой подарок!
блог агентства интернет-маркетинга statyi-o-marketinge6.ru .
бездепозитный бонус с выводом без пополнения Ищете возможность испытать азарт и, возможно, сорвать куш, не вкладывая ни рубля? Бездепозитные бонусы – это именно то, что вам нужно! Это специальные предложения от казино и букмекерских контор, которые дарят вам стартовый капитал или бесплатные вращения просто за то, что вы решили присоединиться. Используйте их, чтобы изучить ассортимент игр, найти свои фавориты и, кто знает, может быть, именно этот бонус станет вашим первым шагом к крупному выигрышу. Это абсолютно безрисковый старт для всех желающих!
Вот это я понимаю СЕРВИС:ok: Превзошло все мои ожидания, доставили раньше обещанного… Магаз ровный (до последнего сомневался, что всё на столько гладко…) https://say.la/read-blog/136671 Сразу видно,что серьезный подход к клиенту! Ассортимент всегда радует,да и с качеством проблем ни разу не было. На все вопросы отвечают оперативно,а что касается консперации(к слову и раньше меня не огорчавшей)-высший уровень!Про бонусы,скидки и тесты даже говорить не нужно.В общем-дальнейшего процветания вам,по больше бы таких сайтов!!! Рекомендую всем-не пожалеете
https://krd.best-city.ru/forum/thread113214/
http://rashin.4adm.ru/viewtopic.php?f=27&t=5294
быстрая доставка однако тут))) https://bio.site/ocssacuh Отличный магазин, общение с KingSize – одно удовольствие, а продукты неизменно радуют.
https://buyerseller.xyz/user/paris/
Je suis bluffe par Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par moments des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En somme, Betway Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires vibrants, assure des transactions fluides.
Aller Г la page|
Je suis bluffe par Belgium Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A signaler l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une immersion complete. A signaler les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui motive les joueurs.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
Труба восстановленная Электросварная труба – изготавливается путем сварки стальной полосы или листа. Этот процесс является экономичным и позволяет производить трубы различного диаметра и толщины стенок. Электросварные трубы находят широкое применение в строительстве, в системах водо- и газоснабжения, а также в различных промышленных конструкциях.
clickreach.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
growthmind.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
digitalrise.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
leadlaunch.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
бесплатные вращения без депозита Не упустите шанс начать играть прямо сейчас! Зарегистрируйтесь и получите свой бездепозитный бонус – это может быть сумма на счет или бесплатные вращения. Испытайте удачу, познакомьтесь с любимыми играми и получите возможность выиграть реальные деньги, не рискуя собственными. Просто зарегистрируйтесь и заберите свой подарок!
J’adore le dynamisme de Gamdom Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Globalement, Gamdom Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour completer le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis completement seduit par Gamdom Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour faire court, Gamdom Casino vaut une visite excitante. De surcroit le design est style et moderne, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un point fort les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Voir maintenant|
бездепозитные игровые автоматы с выводом Представьте: вы получаете реальные деньги или фриспины (бесплатные вращения) просто за регистрацию, без необходимости вносить свои собственные средства. Это отличная возможность познакомиться с игрой, протестировать новые слоты или стратегии, и даже выиграть реальные деньги, не потратив ни копейки. Идеально для тех, кто только начинает свой путь в мире азартных игр или хочет попробовать что-то новое без финансовых обязательств.
Je suis enthousiasme par Belgium Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, mais des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En resume, Belgium Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter le site|
длица окола часа очень даже не плохо https://www.rwaq.org/users/hansenmarissa3355-20251104151100 Отличный магазин!
Je suis enthousiasme par Betify Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, neanmoins plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. De plus l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement attrayant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui booste la participation.
Betify|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Belgium Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En conclusion, Belgium Casino merite un detour palpitant. Ajoutons que le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
Je suis captive par Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour faire court, Betway Casino assure un fun constant. De plus la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement top les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce le lien communautaire.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Je ne me lasse pas de Betify Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En conclusion, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Ouvrir le site|
трэк получил . Магаз всегда был хорош https://yamap.com/users/4920370 Здесь буду отписываться, чтобы все РЕАЛЬНО понимали сколько времени длится весь процесс
chicken road 2 real
Вообщем фейк крассавчик пошагово и все грамотно сделал, развел) https://imageevent.com/dapice7a83ti/bnhgo Приветствую один из старейших магазинов форума! Много воды утекло с тех пор как вы открылись в 2011 году… а вы по-прежнему на плаву и продолжаете радовать нас своим отличным сервисом. Даже не представляю форум без вас) Так держать ребята!
новый магазин???это хорошо!!успехов в работе, конкуренция – это очень хорошо!! https://www.betterplace.org/en/organisations/70418 да работаем только по прайсу
где согласовать перепланировку квартиры http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru .
перепланировка нежилого помещения в москве перепланировка нежилого помещения в москве .
surewin casino surewin-online.com .
icebet casino online icebet casino online .
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию с выводом Пусть это звучит ново и заманчиво, но настоящая грамотность игрока начинается с понимания того, что скрывается за фразой бездепозитные бонусы в казино. Это не просто бесплатные вращения или небольшие кредиты на счёт; за каждой щедрой акцией стоят правила, отыгрыши и ограничения, которые могут либо увеличить ваши шансы на победу, либо превратить удачный первый визит в долгую битву с условиями. В этой статье мы разберёмся, как такие бонусы работают на практике, какие бывают, какие подводные камни ждать и как максимально эффективно извлекать пользу без риска оказаться в ловушке банальных условий.
бездепозитные слоты с выводом денег Сегодня многие онлайн-казино привлекают новичков бездепозитными предложениями. Суть проста: игроку выдаются определённые средства или вращения без необходимости пополнения счёта. Это позволяет попробовать игры, познакомиться с платформой и оценить качество сервиса, не рискуя собственными деньгами. Но главное — такие бонусы задают тон всему игровому опыту: вы привыкнете к интерфейсу, ощутите динамику слотов или стратегию живой рулетки, а затем при желании переведёте часть интереса в реальные ставки.
Качество закладки 10/10-пролежала долгое время что тоже не мало важно https://pubhtml5.com/homepage/bhmba ДУМАЙТЕ САМИ!!!
J’adore le dynamisme de Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, occasionnellement plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Au final, Betway Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En complement le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un element fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Lire les dГ©tails|
бездепозитный бонус фриспины за регистрацию Пусть это звучит ново и заманчиво, но настоящая грамотность игрока начинается с понимания того, что скрывается за фразой бездепозитные бонусы в казино. Это не просто бесплатные вращения или небольшие кредиты на счёт; за каждой щедрой акцией стоят правила, отыгрыши и ограничения, которые могут либо увеличить ваши шансы на победу, либо превратить удачный первый визит в долгую битву с условиями. В этой статье мы разберёмся, как такие бонусы работают на практике, какие бывают, какие подводные камни ждать и как максимально эффективно извлекать пользу без риска оказаться в ловушке банальных условий.
бездепозитные слоты с выводом денег Пусть это звучит ново и заманчиво, но настоящая грамотность игрока начинается с понимания того, что скрывается за фразой бездепозитные бонусы в казино. Это не просто бесплатные вращения или небольшие кредиты на счёт; за каждой щедрой акцией стоят правила, отыгрыши и ограничения, которые могут либо увеличить ваши шансы на победу, либо превратить удачный первый визит в долгую битву с условиями. В этой статье мы разберёмся, как такие бонусы работают на практике, какие бывают, какие подводные камни ждать и как максимально эффективно извлекать пользу без риска оказаться в ловушке банальных условий.
У Данного Магазина я так понимаю Принцип не отвечать в Аське?!=) https://form.jotform.com/253086357824060 Отличное качество товара
Je suis sous le charme de Belgium Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par ailleurs quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A souligner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement super les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, renforce le lien communautaire.
Explorer la page|
лайфхаки для путешествий Виза во Францию для россиян – документ, необходимый для посещения Франции с любой целью, будь то туризм, бизнес, учеба или посещение родственников. Для получения визы требуется предоставить полный пакет документов, подтверждающих цель поездки и финансовую состоятельность.
J’adore la vibe de Gamdom Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour finir, Gamdom Casino merite un detour palpitant. A signaler le design est style et moderne, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
J’adore le dynamisme de Gamdom Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Gamdom Casino merite un detour palpitant. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A noter les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Naviguer sur le site|
J’ai un faible pour Belgium Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Belgium Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A signaler le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages uniques.
http://www.casinobelgium366fr.com|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betify Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, mais des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Betify Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons egalement la navigation est simple et intuitive, facilite une experience immersive. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Voir la page d’accueil|
J’adore l’energie de Belgium Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps en temps des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour finir, Belgium Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement cool les transactions en crypto fiables, qui booste la participation.
http://www.casinobelgiumfr.com|
А с какого дживика еще больше делать можно? https://www.brownbook.net/business/54442225/миасс-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ Хорошо работают реально ! ! ! рега МН-35ф реально индика суровая , наиболее множество сходств нашёл с натуралом , по Мне так это наиболее приближенный каннабиноид ..
Je suis completement seduit par Betify Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est clair et efficace, quelquefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En bonus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement super les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
Cliquer maintenant|
adreachpro.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
marketfuel.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
I have been browsing online more than 3 hours
today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours.
It’s pretty worth enough for me. Personally, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the internet will be much more useful than ever before.
ЕМИКАЛ МИКС – ЭТО ЛУЧШИЙ МАГАЗИН С МНОГОЛЕТНЕЙ РЕПУТАЦИЕЙ НА РЦ РЫНКЕ!!!! https://www.grepmed.com/oubfayfehydi Если хотите подешевле – вам сюда. Если же располагаете финансами – штудируйте ветки доверенных магазинов, есть селлеры куда более ответственные и стоящие. Лично я не планирую дальше сотрудничать с этим магазином. Спасибо за внимание.
clickscale.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
шкаф для строп Шкаф для зарядки и хранения ноутбуков – это современное решение для организации IT инфраструктуры.
поддон для еврокуба Поддон для 2-х еврокубов, шкаф для строп и шкаф для канистр – это примеры специализированного оборудования, разработанного для решения конкретных задач в области хранения и логистики. Каждый из этих продуктов обеспечивает безопасность, порядок и эффективность на рабочем месте.
https://worldmap.bizlisting.cloud/bonus-bienvenue-bookmakers-doublez-votre-depot-instant/
I have read some good stuff here. Certainly price bookmarking for revisiting.
I wonder how so much effort you set to make such a fantastic informative website.
всем привет щас заказал реги попробывать как попробую обизательно отпишу думаю магазин ровный и все ништяк будет)))) https://www.divephotoguide.com/user/uobogycug Да до празников не всем выслали, сегодня отдали в курьерку очередную пачку посылок, всем все придет скоро.
самоопрокидывающийся контейнер Металлический поддон – это фундаментальный элемент складской логистики, обеспечивающий надежную основу для хранения и транспортировки различных грузов. Его прочная металлическая конструкция выдерживает значительные нагрузки и устойчива к механическим повреждениям. Металлические поддоны способствуют оптимизации складского пространства и повышению эффективности погрузочно-разгрузочных работ.
саморазгружающийся контейнер Тележка для стружки – необходимый атрибут любого металлообрабатывающего производства. Она предназначена для сбора и транспортировки металлической стружки, образующейся в процессе обработки деталей на станках. Тележки для стружки могут быть различных конструкций и размеров, в зависимости от объема собираемой стружки и типа станков.
организация мероприятий Event агентство – это не просто команда организаторов, а творческая лаборатория, где каждая идея превращается в незабываемое событие. Мы создаем атмосферу, вдохновляем, удивляем и дарим эмоции, которые останутся в памяти на долгие годы. Наша цель – превзойти ожидания и сделать каждое мероприятие уникальным и запоминающимся. От концепции до реализации, мы берем на себя все заботы, чтобы вы могли наслаждаться праздником. Услуги по организации корпоративов – это симфония деталей, где каждая нота – это тщательно продуманный элемент, создающий неповторимую мелодию незабываемого события. Мы не просто организуем вечеринки, мы создаем впечатления, которые укрепляют командный дух, мотивируют сотрудников и оставляют яркие воспоминания. От разработки оригинальной концепции до воплощения самых смелых идей, мы берем на себя все хлопоты, освобождая ваше время для более важных задач. Наши опытные event-менеджеры, как искусные дирижеры, гармонично объединяют все составляющие идеального корпоратива: подбор площадки, кейтеринг, развлекательную программу, техническое обеспечение и многое другое.
свадьба под ключ в Москве Свадебное агентство Москва – это ваш личный консультант и помощник в мире свадебных возможностей столицы. Организация корпоративов в Москве – это знание города как свои пять пальцев, владение эксклюзивной информацией о лучших площадках, артистах и развлечениях. Мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту, учитывая специфику бизнеса, бюджет и пожелания коллектива. Москва – это город возможностей, и мы поможем вам использовать их на полную мощность, чтобы создать незабываемый корпоратив, который запомнится на долгие годы.
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Афиша Санкт-Петербурга – это не просто сводка предстоящих событий, это портал в бурлящий мир искусства и развлечений Северной Венеции. Это путеводитель, раскрывающий перед вами двери в самые сокровенные уголки культурной жизни города, от помпезных дворцов до андеграундных клубов. Здесь анонсы оперных див соседствуют с новостями о независимых театральных постановках, а обзоры модных ресторанов перекликаются с репортажами с уличных фестивалей. Каждый день в Санкт-Петербурге рождаются новые идеи, открываются новые выставки, звучат новые мелодии. И Афиша – ваш надежный компас в этом океане культурных возможностей. С ней вы всегда будете в курсе последних тенденций, сможете спланировать свой досуг и открыть для себя что-то новое и захватывающее. Будь то грандиозный концерт на Дворцовой площади или камерный вечер поэзии в старинном особняке, Афиша поможет вам сделать правильный выбор и создать unforgettable memories.
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Изучая Афишу, откройте для себя не только известные достопримечательности, но и скрытые жемчужины города: тихие дворики, уютные кафе, необычные музеи. Погрузитесь в атмосферу Санкт-Петербурга, почувствуйте его ритм и вдохновение, и пусть каждое ваше посещение станет незабываемым приключением. Ведь Санкт-Петербург – это город, который постоянно удивляет и восхищает, город, в который хочется возвращаться снова и снова. А Афиша – ваш верный спутник на этом увлекательном пути
Je suis accro a Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, toutefois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Betway Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En bonus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Continuer Г lire|
Нее… пацаны, Вы не поняли, я и не волнуюсь ни капельки, и на закз этот мне положить, мне за державу обидно. Пришел я в магазин а там висит цена на сок томатный сто рублей. Взял пачку, отстоял в очереди а продавщица и говорит что стоит он не сто рублей, которые у тебя в кармане, а сто десять… Да я разъе….у этот магазин вместе с продавщицой и заведующей…. Лучше заплатите админу своего сайта чтобы мессаги на мыло падали четко и конкретно и не наебы…ли людей. https://www.brownbook.net/business/54428467/кричев-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ Брал у данного селлера!Хорошо работют=)
trafficsphere.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
в подписи ТС смотри контакты) https://wanderlog.com/view/pdwkpzbqhd/спасск-рязанский-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ Купил гашиш евро. В этот раз платёж подтверждался минут 15, обычно почти сразу. Ну а к качеству и кладу с гашишем претензий ноль. Всё вышка!
Афиша Санкт Петербурга В Афише Санкт-Петербурга можно найти все: узнать о гастролях звезд мировой величины, познакомиться с творчеством молодых и талантливых художников, выбрать спектакль для семейного просмотра или спланировать романтический вечер в одном из лучших ресторанов города. Это ваш персональный гид по культурной жизни Санкт-Петербурга, который поможет вам не пропустить ни одного интересного события.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betway Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En somme, Betway Casino merite une visite dynamique. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A noter les paiements securises en crypto, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Voir le site|
Je suis sous le charme de Gamdom Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, toutefois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En somme, Gamdom Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En plus le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement top les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce le lien communautaire.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis fascine par Gamdom Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Globalement, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En extra la navigation est fluide et facile, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, qui dynamise l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir la page|
Магазин лутше не встречал!!!! https://rant.li/rihedibefibc/saada-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki Жалко тест профукал )
Je suis accro a Betify Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par ailleurs des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Au final, Betify Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En extra le site est rapide et style, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement fun les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
http://www.betifycasino365fr.com|
Je suis sous le charme de Betify Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Betify Casino offre une aventure memorable. A mentionner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des bonus constants.
http://www.casinobetifyfr.com|
Je suis emerveille par Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Globalement, Belgium Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. De plus la navigation est claire et rapide, booste le fun du jeu. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui motive les joueurs.
Explorer la page|
бонусы казино за регистрацию
фриспины за регистрацию с выводом
Je suis totalement conquis par Betify Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, a l’occasion des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Betify Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons aussi la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges personnalises.
Ouvrir maintenant|
https://dzen.ru/holstai
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Betway Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges personnalises.
DГ©couvrir le web|
топ казино бонус за регистрацию без депозита
бездепозитные фриспины за регистрацию
купить сэндвич панели Сэндвич панели спб: Санкт-Петербург является одним из крупнейших центров производства и продажи сэндвич-панелей в России. Здесь представлен широкий выбор сэндвич-панелей различных типов, размеров, толщин и цветов. Сэндвич-панели, произведенные в СПБ, отличаются высоким качеством, надежностью и соответствуют требованиям безопасности. Они широко используются для строительства быстровозводимых зданий, складов, ангаров, торговых павильонов и других сооружений. Благодаря своим отличным теплоизоляционным свойствам, сэндвич-панели помогают значительно сократить затраты на отопление и кондиционирование помещений.
профнастил купить Купить сэндвич панели: При покупке сэндвич панелей необходимо учитывать ряд факторов, чтобы выбрать оптимальный вариант для ваших нужд. Определитесь с требуемой толщиной панели, типом утеплителя и видом покрытия. Важно учитывать климатические условия региона и назначение здания. Обратитесь к надежному поставщику, предлагающему сертифицированную продукцию и гарантию на материал. Сравните цены у разных продавцов, учитывая стоимость доставки и возможность монтажа. Не забудьте проконсультироваться со специалистами, чтобы получить рекомендации по выбору и монтажу сэндвич панелей.
рейки Амулетотсглаза: Амулетотсглаза – это амулет, специально предназначенный для защиты от сглаза (считается, что злой или завистливый взгляд может причинить вред). Он может иметь различные формы и символы, такие как глаз, рука Фатимы, хамса и другие. Амулетотсглаза часто носится на теле, прикрепляется к одежде или помещается в доме для защиты от негативной энергии и привлечения удачи.
активатор_воды_бытовой Амулет_оргонит: Амулеторгонит – это амулет, изготовленный с использованием оргонитовой технологии. Он состоит из органической смолы, металлических частиц и кристаллов, чаще всего кварца. Считается, что амулеторгонит защищает от электромагнитного излучения, негативной энергии и способствует общему благополучию. Он может носиться на шее, храниться в кармане или использоваться в качестве декоративного элемента в доме.
adlift.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
clickprohub.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Сервис высокого уровня, всё прозрачно и надёжно: Сопровождение ВЭД
https://tutvot.com/
гистидин
clickgurus.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
https://avia.tutvot.com/
J’ai un faible pour Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Azur Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un plus les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Aller plus loin|
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des tables live interactives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Azur Casino merite un detour palpitant. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, garantit des paiements rapides.
Aller sur le site web|
Je suis totalement conquis par Azur Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Azur Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour completer l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement fun les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Lucky 31 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En fin de compte, Lucky 31 Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement genial les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce la communaute.
Aller plus loin|
Je suis epate par Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par contre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement super les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des avantages uniques.
Voir plus|
Je suis enthousiasme par 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, 1xBet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, permet une immersion complete. A noter les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
Lire plus|
J’adore l’energie de Action Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, toutefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Action Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et fluide, facilite une experience immersive. A noter les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Naviguer sur le site|
J’adore l’energie de Action Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Globalement, Action Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une experience immersive. Un plus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Essayer maintenant|
фриспины без отыгрыша без депозита
бездепозитный бонус с выводом без пополнения
https://bs2-bs2web.at
https://lblsp.at
bakalarska prace Seminarni prace: Seminarni prace je akademicky text, ktery student pise v ramci seminare nebo kurzu na vysoke skole nebo univerzite. Cilem seminarni prace je prokazat studentovu schopnost porozumet zadanemu tematu, analyzovat relevantni zdroje a prezentovat sve myslenky a argumenty v pisemne forme. Seminarni prace byva kratsi a mene komplexni nez bakalarska nebo diplomova prace, ale i tak vyzaduje peclivou pripravu, resersi literatury a dodrzovani akademickych standardu. Student by mel zvolit tema, ktere ho zajima, a venovat dostatek casu studiu odborne literatury. Dulezite je take formulovat jasnou tezi nebo argument, ktery bude v praci rozvijet. Struktura seminarni prace obvykle zahrnuje uvod, hlavni cast (kde jsou prezentovany argumenty a dukazy) a zaver (kde je shrnuto a zhodnoceno tema). Seminarni prace je cenna zkusenost, ktera rozviji studentovy akademicke dovednosti, jako je psani, reserse a kriticke mysleni. Je take dulezita pro ziskani dobreho hodnoceni v kurzu a muze slouzit jako zaklad pro dalsi akademickou praci.
фриспины без отыгрыша без депозита
1000 рублей за регистрацию в казино без депозита вывод сразу
диабетический кетоацидоз
Благодаря сопровождению ВЭД мы полностью исключили проблемы с таможней: ВЭД сопровождение импорта
https://rimaakter.bloggersdelight.dk/2025/11/11/1xbet-bonus-code-2026-e130-for-sports/
музыкальный дует Elegant Duet Мы «Elegant Duet» Дарья Сулина — виолончель Любовь Морская — скрипка 26 лет мы играем на инструментах и являемся профессиональными музыкантами. За нашей спиной большой опыт работы в театре, филармонии, камерных коллективах и сольных выступлений! На сегодняшний момент мы создали сольный проект, дуэт » Elegant.duet «. Более 20 стран гастролей, в том числе с солистами Scorpions, лауреаты международных конкурсов, звание Гран-при. Степендиаты фондов Глазунова, фонда президента РФ Неоднократные презентации глянцевых журналов, в том числе look book, Премия года 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 FB, музыкальное сопровождение показов мод с звездными дизайнерами, сопровождение закрытых эксклюзивных показов. Репертуар многогранен, от Баха до твоих любимых хитов. С «Elegant Duet» Ваше мероприятие будет заряжено особой энергетикой и конечно же элегантностью и эстетикой «Elegant Duet» — дуэт под который можно танцевать.
brandmagnet.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
clickenginepro.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
seojet.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
vulkan vegas 50
Je suis enthousiasme par Azur Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A noter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A signaler les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute soudee.
Voir le site|
Truly lots of very good facts.
продвижение телеграм Результативные прогоны Хрумером под Ваши задачи и предпочтения.
https://lblsp.at
https://bs2-bs2web.at
продвижение телеграм Построение сложных прокладок и применение уникальных технологий для быстрого роста в Google и Yandex.
Лестница из металла в Москве Антресоль: Антресоль – это внутренняя площадка, расположенная под потолком помещения, чаще всего используемая для хранения вещей или организации дополнительного спального места. Отличительной чертой антресоли является её доступность, обычно обеспечиваемая лестницей или стремянкой. Этот элемент интерьера позволяет эффективно использовать вертикальное пространство, что особенно актуально для помещений с высокими потолками. Антресоли могут быть как открытыми, так и закрытыми, в зависимости от функциональных потребностей и дизайна интерьера. В квартирах антресоли часто используют для хранения сезонных вещей, книг или других предметов, не требующих ежедневного доступа. В складских и промышленных помещениях антресоли могут служить дополнительным уровнем для размещения товаров или оборудования. При проектировании антресоли необходимо учитывать допустимую нагрузку на конструкцию и обеспечить безопасность её использования.
игровые автоматы с бездепозитным бонусом за регистрацию с выводом
бонусы и акции в онлайн-казино на деньги
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, quelquefois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, Azur Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un plus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Continuer ici|
Je suis sous le charme de Lucky 31 Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino garantit un amusement continu. A noter le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges personnalises.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je suis completement seduit par Azur Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Azur Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et style, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement fun les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir la page|
Je ne me lasse pas de Action Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est excellent. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En somme, Action Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui booste la participation.
Avancer|
Je suis enthousiasme par 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est transparent et rapide, quelquefois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, 1xBet Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En plus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste l’excitation du jeu. A noter les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fluides.
Explorer le site web|
Je suis captive par 1xBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En somme, 1xBet Casino merite un detour palpitant. Ajoutons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement super les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis captive par Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des avantages sur mesure.
http://www.lucky31casino365fr.com|
Je suis bluffe par Action Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, mais encore plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino vaut une visite excitante. En plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Entrer sur le site|
trafficmind.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
бонусы и акции в онлайн-казино на деньги
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом денег без первого депозита и без отыгрыша
Hi there everybody, here every one is sharing these knowledge, so it’s pleasant to read this web site, and I used to go to see this webpage daily.
https://www.dralijafarclinic.com/melbet-prilozhenie-obzor-2025/
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino garantit un amusement continu. A signaler la navigation est claire et rapide, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement cool les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Naviguer sur le site|
Проектирование Антресольныйэтажмосква: Антресольныйэтажмосква – это антресольный этаж, спроектированный и построенный в Москве, с учетом специфики местного строительного законодательства, архитектурных особенностей и климатических условий. В условиях высокой стоимости квадратного метра в Москве, антресольные этажи становятся популярным решением для увеличения полезной площади квартир, офисов и других помещений. Проектирование и строительство антресольного этажа в Москве требует согласования с соответствующими органами, получения разрешительной документации и соблюдения строительных норм и правил. Важно выбирать надежную строительную компанию с опытом работы в Москве, которая сможет обеспечить качественное выполнение работ и соблюдение всех требований.
Je suis sous le charme de 1xBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, 1xBet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce la communaute.
Lancer le site|
J’adore la vibe de Lucky 31 Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, quelquefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Lucky 31 Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En bonus le design est moderne et attrayant, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement interessant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, assure des transactions fluides.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
promobridge.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
как-то перехотелось.. что действительно последний товар не очень? https://say.la/read-blog/135266 тока по “чуть чуть” а то вдруг там дезокси… или ещё что мгновенно вырубающее. мало ли. )
Je suis captive par 1xBet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par moments des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, 1xBet Casino merite une visite dynamique. A souligner l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement excellent les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Plongez-y|
J’ai un faible pour Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par contre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. Un atout les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Action Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Action Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En extra le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une experience immersive. A signaler les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, renforce le lien communautaire.
En savoir plus|
marketscope.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Никаких тихушек нет, заказывай ,получай, радуйся!!! https://kemono.im/odgxuigfz/antiby-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki “Делаю дорогу,вторую Жду”
https://b2best.at
https://bs2-bs2web.at
promocloud.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
digitaltrack.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
clickgrow.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Брал опт, все четко прошло! Качество на высоте! ТС ответьте в ЛС пожалуйста https://yamap.com/users/4912683 Отличный магазин, общение с KingSize – одно удовольствие, а продукты неизменно радуют.
What’s up colleagues, how is the whole thing, and what you wish for to say concerning this post, in my view its really awesome in favor of me.
https://naudunia.com/official-site-melbet-bonus-2025-superconditions-for-players/
и сколько те6е поо6ещали заплотить? https://pubhtml5.com/homepage/lhrak такчто чставлю 100/100баллов магазу и
telegram aviator Aviator Telegram: “Aviator Telegram” typically refers to Telegram channels or groups related to the Aviator online game. These groups serve as online communities where players can share tips, discuss strategies, and potentially find promotional offers related to the game. However, it is essential to exercise caution when joining such groups. Many of these channels might promote gambling aggressively, and some may even contain malicious links or scams. Always verify the legitimacy of any information or links shared in these groups and be aware of the risks involved in gambling. Prioritize responsible gaming practices and avoid relying solely on information found in these Telegram groups.
aviator Aviator Telegram Channel: A Telegram channel dedicated to the Aviator game typically serves as a hub for players to connect, share strategies, and discuss experiences. These channels often provide insights into gameplay mechanics, potential betting strategies, and updates on the game’s algorithms. However, it’s important to note that many of these channels may promote gambling, and it’s crucial to approach them with caution and awareness of the risks involved in gambling. Some channels may also share predictions or signals regarding the game’s outcome, but these should be treated with skepticism as the Aviator game is based on random number generation and past results are not indicative of future performance. Responsible gambling practices should always be prioritized, and reliance on information from Telegram channels should be balanced with personal judgment and awareness of potential biases or scams.
Hi there, for all time i used to check webpage posts here in the early hours in the morning, as i love to learn more and more.
https://konvertica.com/melbet-obzor-2025-1sportpit-ru/
Скачать моды для Майнкрафт Скачать Майнкрафт моды – это значит открыть дверь в мир безграничных возможностей для кастомизации вашей любимой игры. Моды позволяют трансформировать Minecraft до неузнаваемости, добавляя новые элементы, механики, существа и целые миры. Хотите ли вы добавить в игру магию, технологии, новые измерения или просто улучшить графику, моды предоставляют вам все необходимые инструменты для этого. С их помощью вы можете создать уникальный игровой опыт, который будет соответствовать вашим личным предпочтениям и интересам. Погрузитесь в мир бесконечных модификаций и сделайте свой Minecraft поистине неповторимым!
Карты для майнкрафт Карты для Майнкрафт – это ваша персональная коллекция приключений, созданных талантливыми игроками и опытными дизайнерами уровней, которые вложили душу в свои творения. От сложных головоломок, требующих логики и внимательности, и захватывающего паркура, испытывающего вашу ловкость и реакцию, до масштабных ролевых игр, позволяющих вам погрузиться в увлекательные истории, и воссозданных исторических мест, дающих вам возможность увидеть мир глазами прошлого, карты предлагают бесконечное разнообразие игровых опытов, которые удовлетворят любой вкус. Исследуйте тщательно продуманные миры, полные секретов и неожиданностей, погружайтесь в захватывающие истории, наполненные интригой и драмой, и испытывайте свои навыки в различных испытаниях, от сражений с боссами до выживания в экстремальных условиях. Карты для Minecraft – это не просто уровни, это целые вселенные, созданные с любовью и вниманием к деталям, которые открывают перед вами новые горизонты и позволяют вам пережить незабываемые моменты в мире Minecraft. Найдите карту, которая соответствует вашему настроению, и отправляйтесь в увлекательное путешествие, полное открытий и приключений!
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En bref, Azur Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A souligner le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une experience immersive. Un bonus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Он тоже не работает, его ветки нет в РБ разделе. https://say.la/read-blog/135092 посылка дошла за 1 сутки, сегодня не успел забрать, завтра посмотрим на качество) я уверен, что все будет хорошо
http://wiki.gimc.ru/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%20MelBet%20%E2%80%94%20%D0%B2%D1%8B%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B9%20%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B0%D1%80%D1%82%20%D0%B4%D0%BB%D1%8F%20%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%8B%D1%85%20%D0%B8%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B2
https://lblsp.at
https://lblsp.at
получил посылку не выходя с почты открыл ее а там лежат какие то шорты. ну думаю все кинул 7 к просто выкинул. пришел домой с пацанами сели чай пить положил вещи тут как раз мама старалась и спросила меня есть шмотки грязные ну тут я достал все вещи и шорты мама давай смотреть карманы и в итоге в шортах находит 10 г вот тут я обрадовался и разочаровался думал хана https://www.montessorijobsuk.co.uk/author/iofpebobay/ Во-во МАГАЗИН! Обозначил цену, так по ней и продавай! На мыло упало – Цена заказа -4250 и .. А потом начались догонялки…. Магазины так не поступают, а поступают именно БАРЫГИ, как точно выразился РОГАТЫЙ ОБИТАТЕЛЬ данной ветки
I’m not sure why but this weblog is loading extremely slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
https://comunicacion.alquimiamexico.com/2025/10/26/rabochee-zerkalo-melbet-segodnya-2025/
seopath.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
фрибеты это
бездепозитные фрибеты в букмекерских
Официальный сайт Kraken https://kra44-cc.at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
Бро все супер,как всегда ровно,спасибо за прекрасно отлаженную работу. Процветания тебе и твоей команде.Спасибо! https://kemono.im/kdnoecoyg/vil-iandi-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki в смысле пропал из онлайна??? и что делать теперь? треки то до сих пор небьються
Je suis epate par Azur Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par moments des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Azur Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et style, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Aller voir|
Кракен зеркало
marketrise.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
webimpact.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
какую букмекерскую контору выбрать в россии
букмекерские конторы список лучших
brandtrail.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Je suis totalement conquis par Azur Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, en revanche plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour faire court, Azur Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A noter le site est rapide et engageant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un bonus les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
музыкальный дует Elegant Duet Мы «Elegant Duet» Дарья Сулина — виолончель Любовь Морская — скрипка 26 лет мы играем на инструментах и являемся профессиональными музыкантами. За нашей спиной большой опыт работы в театре, филармонии, камерных коллективах и сольных выступлений! На сегодняшний момент мы создали сольный проект, дуэт » Elegant.duet «. Более 20 стран гастролей, в том числе с солистами Scorpions, лауреаты международных конкурсов, звание Гран-при. Степендиаты фондов Глазунова, фонда президента РФ Неоднократные презентации глянцевых журналов, в том числе look book, Премия года 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 FB, музыкальное сопровождение показов мод с звездными дизайнерами, сопровождение закрытых эксклюзивных показов. Репертуар многогранен, от Баха до твоих любимых хитов. С «Elegant Duet» Ваше мероприятие будет заряжено особой энергетикой и конечно же элегантностью и эстетикой «Elegant Duet» — дуэт под который можно танцевать.
Je suis captive par Action Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Action Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement cool les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Entrer|
Je suis epate par 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais encore plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En somme, 1xBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
VГ©rifier ceci|
seoforce.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Je suis epate par Lucky 31 Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement interessant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Je suis bluffe par 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, 1xBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En extra le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
AccГ©der maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par 1xBet Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, 1xBet Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement super les evenements communautaires dynamiques, garantit des paiements securises.
DГ©couvrir le web|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour completer l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, facilite une experience immersive. A souligner les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Essayer ceci|
https://bs2-bs2web.at
https://bs2-bs2web.at
J’ai une passion debordante pour Action Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, rarement des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus constants.
Tout apprendre|
Официальный сайт Kraken kra44 безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
Excellent post. I was checking continuously this blog and I’m impressed!
Very useful information specially the ultimate part 🙂 I deal with such
information much. I used to be seeking this certain info for a long time.
Thanks and good luck.
https://lblsp.at
https://b2best.at
Very good article. I certainly love this site. Stick with it!
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, bien que des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En bref, Azur Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement super les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
valor bet casino valor bet casino .
J’adore la vibe de 1xBet Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En conclusion, 1xBet Casino vaut une visite excitante. En complement l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, quelquefois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Action Casino merite une visite dynamique. A signaler la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses regulieres.
https://casinoactionbonusfr.com/|
Je suis accro a Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour faire court, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour completer le design est moderne et energique, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point fort les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour 1xBet Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est transparent et rapide, bien que quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, 1xBet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour ajouter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce la communaute.
Plonger dedans|
Nice post. I was checking continuously this blog and I am impressed!
Very helpful information specifically the last part
🙂 I care for such information a lot. I was seeking this
certain info for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Action Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Action Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un atout les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce la communaute.
Visiter la page web|
1xbet lite https://www.1xbet-7.com .
как согласовать перепланировку квартиры как согласовать перепланировку квартиры .
surewin casino ph https://surewin-online.com/ .
beep beep casino register beepbeepcasino-online.com .
Je ne me lasse pas de Action Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps en temps quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Action Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement attrayant les transactions en crypto fiables, qui motive les joueurs.
Explorer davantage|
Ко ланта Остров Ко Ланта Таиланд: См. “Остров Ко Ланта В Таиланде”. Это прекрасный остров в Таиланде с богатой природой и спокойной атмосферой.
ко ланта чем заняться Краби Ко Ланта Как Добраться: См. “Краби Ко Ланта”. Трансфер из аэропорта Краби до Ко Ланты занимает около 2-3 часов.
vavada casino pl
Posiadanie ziemi w Beskidach zapewnia nie tylko spokoj, ale takze mozliwosc atrakcyjnego zarobku w przyszlosci.
Dzieki rozwijajacej sie infrastrukturze i rosnacemu zainteresowaniu turystow, ceny dzialek stopniowo wzrastaja. Lokalizacja ta staje sie coraz bardziej popularna wsrod inwestorow szukajacych stabilnego zysku.
#### **2. Gdzie szukac najlepszych ofert dzialek?**
Wybor odpowiedniej lokalizacji zalezy od indywidualnych potrzeb i budzetu. Portal dzialki-beskidy.pl oferuje szeroki wybor nieruchomosci w roznych cenach.
Przed zakupem nalezy dokladnie przeanalizowac dostepnosc mediow i warunki zabudowy. Wiele ofert zawiera szczegolowe informacje o mozliwosciach zagospodarowania terenu, co ulatwia podjecie decyzji.
#### **3. Jakie korzysci daje posiadanie dzialki w Beskidach?**
Nieruchomosc w gorach to nie tylko inwestycja finansowa, ale rowniez szansa na poprawe jakosci zycia. Dzialka w Beskidach moze stac sie zrodlem dochodu, jesli zdecydujemy sie na wynajem turystom.
Dodatkowo, region ten oferuje wiele atrakcji, takich jak szlaki turystyczne i stoki narciarskie. Coraz wiecej osob wybiera te lokalizacje ze wzgledu na dobrze rozwinieta baze rekreacyjna.
#### **4. Jak przygotowac sie do zakupu dzialki?**
Przed podjeciem decyzji warto skonsultowac sie z prawnikiem i geodeta. Wizyta na miejscu i rozmowa z sasiadami moga dostarczyc cennych informacji o okolicy.
Wazne jest rowniez okreslenie swojego budzetu i planow zwiazanych z zagospodarowaniem terenu. Niektore oferty pozwalaja na rozlozenie platnosci, co ulatwia inwestycje.
—
### **Szablon Spinu**
**1. Dlaczego warto kupic dzialke w Beskidach?**
– Beskidy to idealne miejsce dla osob szukajacych spokoju i bliskosci natury.
– Dzialki w Beskidach to coraz czesciej wybierana lokata kapitalu przez swiadomych inwestorow.
**2. Gdzie szukac najlepszych ofert dzialek?**
– Profesjonalne agencje nieruchomosci czesto oferuja najlepsze propozycje w regionie.
– Warto porownac rozne oferty, aby znalezc najbardziej oplacalna inwestycje.
**3. Jakie korzysci daje posiadanie dzialki w Beskidach?**
– Posiadanie ziemi w gorach to szansa na zbudowanie wymarzonego domu lub miejsca wypoczynkowego.
– Wlasciciele dzialek moga uczestniczyc w lokalnych wydarzeniach i festiwalach.
**4. Jak przygotowac sie do zakupu dzialki?**
– Warto dokladnie sprawdzic historie dzialki, aby upewnic sie, ze nie ma zadnych roszczen.
– Rozmowa z dotychczasowymi wlascicielami moze dostarczyc cennych informacji.
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Azur Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En bonus le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une immersion totale. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce la communaute.
Obtenir des infos|
adtrend.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
электронный кошелек piastrix регистрация
электронный кошелек piastrix регистрация
пиастрикс личный кабинет
piastrix личный кабинет
Je suis sous le charme de Azur Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, en revanche des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Azur Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un element fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui booste la participation.
Aller au site|
valor slots valor slots .
1x bet 1xbet-7.com .
помощь в согласовании перепланировки квартиры http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru .
surewin casino wallet https://www.surewin-online.com .
beepbeep casino login http://www.beepbeepcasino-online.com/ .
https://b2best.at
https://b2best.at
At this time I am going away to do my breakfast, when having my breakfast coming
yet again to read further news.
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию без отыгрыша
Отличный магазин!!!процветания дальнейшего и удачных продаж!! https://kemono.im/ficaduaf/sendzhidzhi-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki Ничего не пойму.. Я уже третий день пытаюсь договориться и всё бесполезно. Прошу номер кошелька куда перевести, говорит щас и пропадает на пол дня, и так постоянно. Может на мелкий заказ как у меня им пох. Заказываю 10 гр.
без депозита фриспины
бездепозит и фриспины при регистрации
бездепозитный бонус с отыгрышем за регистрацию
Замечательный, магазин. Желаю успешных продаж https://beteiligung.stadtlindau.de/profile/%D0%9E%D1%83%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%81%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B0%20%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%82%D1%8C%20%D0%9A%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%B8%D0%BD/ да в пятницу отправляли… вот до сих пор небьеться… нервничаю…
valor casino apk valor casino apk .
J’adore la vibe de Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. De plus la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une immersion totale. A noter les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Obtenir plus|
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Azur Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement cool les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller à l’intérieur|
Je suis accro a 1xBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, 1xBet Casino assure un fun constant. En plus le site est rapide et style, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г lire|
J’ai un faible pour Action Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est excellent. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par contre quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, Action Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons egalement le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements securises.
http://www.casinoactionbonusfr.com|
Все как надо. Рентген, люди ощупывают… Подозрительных людей к стати не принимают, если даже по началу обнаруживают что либо, их отпускают вызывают оперов, следят за посылкой, сначала принимают клиента, а потом уже за поставщиком охота начинается… https://www.brownbook.net/business/54412053/слуцк-купить-кокаин/ может я не вполне в теме,и с спрс работаю 2 раз,но ни одна из известных мне почтовых служб не доставляла отправление до адресата за 4000 вёрст за 3-4 дня,как это делает спрс. а насчёт :police: просто смешно – захотят принять – примут по-любому,хоть с почтовым голубем.:) доставка дороговата,но это самое меньшее из возможных зол.
J’adore la vibe de Lucky 31 Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. De surcroit l’interface est lisse et agreable, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires engageants, qui motive les joueurs.
Explorer le site|
1x giri? https://www.1xbet-7.com .
где согласовать перепланировку квартиры http://www.soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru/ .
J’ai un faible pour 1xBet Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement interessant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Je suis bluffe par Action Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est transparent et rapide, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Action Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et intuitive, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des paiements rapides.
Visiter maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par contre des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En bref, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. Notons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Lancer le site|
beepcasino http://beepbeepcasino-online.com .
surewin casino login register http://www.surewin-online.com .
Je suis totalement conquis par Action Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, mais des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Action Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En bonus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un atout les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Lire la suite|
Описывать,тем кто не пробовал-бесполезно.Все равно не поймут.Придумывают всякую фигню(аааа,у тя за спиной собакака!и пр. бред),пытаются посмеяться,но это ж всё не то и близко не стояло.Как слепому объяснить,как все выглядит) https://rant.li/lybygybobyoy/khor-fakkan-kupit-kokain-mefedron-marikhuanu-boshki Оплатил заказ в субботу, во вторник посылка была отправлена вечером, в четверг уже была в городе, но встретиться с курьером не смог. В пятницу заберу. Все оперативно и быстро.
онлайн вопрос юристу Бесплатная юридическая консультация онлайн Воспользоваться бесплатной юридической консультацией онлайн – это разумный шаг для тех, кто хочет разобраться в правовых аспектах своей ситуации, не неся при этом финансовых затрат. Многие платформы предлагают такую возможность, позволяя задать вопрос юристу и получить ответ в кратчайшие сроки. Это отличный способ получить общее представление о проблеме и понять, стоит ли обращаться за платной юридической помощью.
бесплатный юрист онлайн консультация Юрист онлайн консультация бесплатно В современном ритме жизни, когда скорость и доступность информации ценятся превыше всего, возможность получить квалифицированную юридическую консультацию онлайн бесплатно становится неоценимым преимуществом. Это шанс оперативно оценить ситуацию, понять свои права и обязанности, а также наметить дальнейшие шаги без каких-либо финансовых вложений.
Ko Lanta Подводный мир Ко Ланта: рай для дайверов. Теплые воды Андаманского моря делают Ко Ланта идеальным местом для дайвинга и снорклинга в Таиланде. Богатый подводный мир с коралловыми рифами, рыбами и пещерами привлекает дайверов. Близлежащие острова, такие как Ко Ха Яй и Ко Рок, предлагают отличные места для погружений. Ко Ха Яй известен подводными пещерами и арками, а Ко Рок — нетронутыми рифами и чистой водой с тропическими рыбами и черепахами. Недалеко от Ко Ланта находятся скалы Hin Daeng и Hin Muang, популярные среди дайверов, где можно увидеть мант и китовых акул. Для новичков есть дайвинг-центры с курсами PADI Open Water до Divemaster. Опытные инструкторы помогут освоить дайвинг и безопасно исследовать подводный мир. Любители снорклинга также могут насладиться красотой коралловых рифов и морской жизнью.
Ko Lanta Подводный мир Ко Ланта: Рай для любителей дайвинга и снорклинга. Ко Ланта, окруженный теплыми водами Андаманского моря, является одним из лучших мест для дайвинга и снорклинга в Таиланде. Богатый подводный мир с разнообразием коралловых рифов, яркими рыбами и загадочными пещерами манит как опытных дайверов, так и начинающих любителей подводного плавания. Близлежащие острова, такие как Ко Ха Яй и Ко Рок, предлагают впечатляющие локации для погружений. Ко Ха Яй известен своими подводными пещерами и арками, создающими захватывающие пейзажи для исследования. Ко Рок, в свою очередь, славится своими нетронутыми коралловыми рифами и кристально чистой водой, где можно наблюдать за многочисленными видами тропических рыб, черепахами и другими морскими обитателями. Недалеко от Ко Ланта находятся также известные Hin Daeng и Hin Muang – два подводных скальных образования, привлекающие дайверов со всего мира. Здесь, в глубоких водах, можно встретить огромных мант, китовых акул и других крупных морских животных. Для начинающих дайверов на Ко Ланта есть множество дайвинг-центров, предлагающих курсы от PADI Open Water до Divemaster. Опытные инструкторы помогут освоить азы дайвинга и безопасно исследовать подводный мир. Любители снорклинга также найдут множество возможностей насладиться красотой коралловых рифов и наблюдать за морской живностью прямо с поверхности воды.
https://www.pwinsider.com/article/202027/roulettino-a-comprehensive-review-for-pro-wrestling-fans-and-combat-sports-enthusiasts.html?p=1
https://measuretake.com/news/roulettino-app-a-detailed-review-for-tech-focused-readers-and-precision-enthusiasts/
Трек так и не работает:(. Когда ждать посылку. Скоро запрет выйдет уже. Хотелось бы до запрета успеть. https://www.grepmed.com/aguheubi посылка в городе. Сегодня заберу
https://issuu.com/freebet1xbet/docs/1xbet_promo_code_2026_130_welcome_bonus
https://www.pearltrees.com/calvinsearfoss
31 страницу отзывов почитайте – увидите всех. Кто то только что зарегился , ктото год назад , кому что аккаунт блокнули или забыл пароль от старого акка – он зарегился по новой . https://www.brownbook.net/business/54451600/снежногорск-купить-кокаин-мефедрон-марихуану-бошки/ магазин ровный)
https://www.bandlab.com/freebet1xbet
J’ai un faible pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est clair et efficace, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino merite une visite dynamique. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs variees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Lire plus|
J’adore l’energie de Azur Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est transparent et rapide, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En conclusion, Azur Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement top les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus exclusifs.
http://www.azurcasinobonusfr.com|
Je ne me lasse pas de Action Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est simple et transparent, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En conclusion, Action Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter le design est style et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement super les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui booste la participation.
Entrer|
Je suis completement seduit par 1xBet Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par moments plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Globalement, 1xBet Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A mentionner le design est style et moderne, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage notable les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus constants.
AccГ©der maintenant|
а эффор хорош?) на что похож?) https://www.betterplace.org/en/organisations/70084 Брал неоднократно в этом магазе, всегда всё ровно и без проволочек, так держать!!
Je suis totalement conquis par Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui motive les joueurs.
Visiter la page web|
seohero.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
digitallift.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
J’adore le dynamisme de 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, 1xBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un point cle les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute vibrante.
http://www.1xbetcasino777fr.com|
Je suis fascine par Lucky 31 Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, quelquefois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une visite excitante. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute soudee.
Voir la page|
J’adore la vibe de Action Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais encore des offres plus importantes seraient super. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
Continuer Г lire|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Action Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Action Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En complement le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement top les transactions en crypto fiables, cree une communaute soudee.
Continuer ici|
promovix.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
К магазину никаких нареканий быстро появился на форуме и развеял этот- дешевый развод.будут денежки возьму тут что нибудь дымящиеся. https://pubhtml5.com/homepage/uskue Какие у тебя претензии? ты провокатор и не более т.к. ты не дал даже номер заказа и не высказал притензию, к тому же за тебя мне уже написали в Личку, другие магазины..
https://lblsp.at
https://lblsp.at
Купить дом в Нижегородской области Помогу продать земельный участок. Продажа земельного участка – ответственный шаг, требующий профессионального подхода. Доверьте мне продажу вашего участка в Нижегородской области, и я обеспечу вам максимальную выгоду и минимизацию рисков. Профессиональная оценка рыночной стоимости участка, подготовка эффективной рекламной кампании, привлечение целевой аудитории покупателей. Организация показов, проведение переговоров и полное юридическое сопровождение сделки. Получите максимальную цену за вашу землю в кратчайшие сроки!
Продаю дачу за 450 000 рублей. Помогу купить участок в Нижегородской области Нижегородская область, с ее бескрайними полями, живописными лесами и богатым культурным наследием, манит возможностью обустроить собственный уголок, вдали от городской суеты. Мечтаете о просторном участке для строительства дома, дачи или фермерского хозяйства? Я, как опытный эксперт в сфере недвижимости Нижегородской области, помогу вам реализовать эту мечту. Тщательный подбор участков, соответствующих вашим запросам по местоположению, площади, коммуникациям и бюджету. Полное юридическое сопровождение сделки, от проверки документов до оформления прав собственности. Сделайте первый шаг к жизни на своей земле!
growthmatrix.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
интересует такой же вопрос! Сделал заказ с сайта ещё вчера. Ни слуху ни духу от селлера. https://www.rwaq.org/users/nowakl9m1gerhard-20251103193355 Палево палево, с сайтом чооо??
Easy and simple site with a wealth of gambling-related info.
https://globaltel.ge/just-a-cool-blog-post-with-images/?lang=en
плиз подскажи выход с грамма и в чем растворяла ркс? (буду благодарен) https://www.betterplace.org/en/organisations/69846 Удачи в бизе!!
Clarte Nexive se demarque comme une plateforme de placement crypto revolutionnaire, qui met a profit la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour offrir a ses utilisateurs des atouts competitifs majeurs.
Son IA scrute les marches en temps reel, repere les opportunites et met en ?uvre des strategies complexes avec une finesse et une celerite inaccessibles aux traders humains, augmentant de ce fait les potentiels de profit.
Вчера оплатил, сегодня уже трек скинули. Пока все ровно, посмотрим что придет….. https://bio.site/yufahyhybify Приятно работать!!!
heaps o win casino heaps o win casino .
seo интенсив http://www.kursy-seo-12.ru/ .
goliath casino bonuskode https://goliath-casino.com .
icebet casino login icebet casino login .
Ищете, где купить права быстро и надежно? Наш сервис предлагает легальное и безопасное оформление водительских прав с гарантией качества. Мы поможем пройти все этапы получения водительского удостоверения, включая подготовку документов, обучение в автошколе и сдачу экзаменов. У нас работают опытные специалисты, которые сопровождают вас на каждом шаге, обеспечивая прозрачность и законность процесса.
деньги займ онлайн
онлайн займы
J’ai une passion debordante pour Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En fin de compte, Azur Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En complement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus constants.
Savoir plus|
resultsdrive.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
proclicklab.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
rapidleads.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
NT Breaking News – Breaking updates ka style bohot clean aur understandable hai.
nextlevelads.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
boosttraffic.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
virallaunch.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Ko Lanta Ко Ланта: Тайская гармония двух островов в одном месте. Ко Ланта, находящийся в провинции Краби и состоящий из двух основных островов, Ко Ланта Ной и Ко Ланта Яй, соединенных мостом, является сокровищем Таиланда. Здесь тайское гостеприимство встречается с природой в ее первозданной красе, создавая атмосферу релакса и умиротворения. В отличие от известных, часто шумных курортов, Ко Ланта предлагает убежище от суеты, при этом не лишая комфорта. Каждый остров имеет свой характер. Ко Ланта Ной выполняет роль административного и логистического центра, а Ко Ланта Яй — основное туристическое направление с прекрасными пляжами, отелями и ресторанами. Здесь можно найти роскошные курорты и уютные бунгало в тропических садах. Жемчужиной Ко Ланта Яй является западное побережье, усеянное километрами песчаных пляжей, омываемых водами Андаманского моря. Ко Ланта — это не только отдых на пляже. Здесь можно заняться подводным плаванием, исследовать коралловые рифы, отправиться в национальный парк Му Ко Ланта, где джунгли соседствуют с маяком. Вечером можно провести время в уютных барах и ресторанах с панорамным видом на закат, наслаждаясь блюдами из свежих морепродуктов и традиционными тайскими деликатесами.
Миниатюра Моделирование является ключевым этапом в процессе создания цифровой скульптуры. Художники используют различные инструменты и техники для формирования виртуального объекта, при этом учитывается его форма, текстура и детализация. Этот этап требует глубокого понимания анатомии (особенно в контексте авторских фигурок) и композиции, что позволяет создавать реалистичные и эстетически привлекательные произведения.
Современное Искусство 3D Печать и DLP Печать – два ключевых метода материализации цифровых творений. 3D печать, благодаря разнообразию используемых материалов (от пластика до металла), позволяет создавать крупные объекты, в то время как DLP печать выделяется своей высокой точностью и идеально подходит для изготовления миниатюр и ювелирных изделий.
Кракен зеркало вход на сайт — надежный способ обойти блокировки и получить доступ к популярной платформе Кракен. Если официальный сайт недоступен из-за региональных ограничений или технических проблем, зеркало Кракен поможет быстро и безопасно войти на сайт без потери функционала.
Ko Lanta Жизнь морских цыган (Chao Leh) на Ко Ланта: Сохранение традиций прошлого. Ко Ланта – это не просто туристический остров, это еще и дом для морских цыган (Chao Leh), коренных жителей, которые на протяжении веков жили в гармонии с морем и сохранили свои уникальные обычаи и культуру. Морские цыгане, которых также называют “люди моря”, живут в небольших поселениях на восточном побережье Ко Ланта. Они ловят рыбу, собирают дары моря и строят лодки. Их жизнь тесно связана с морем, которое кормит их и имеет для них духовное значение. У морских цыган есть своя религия, основанная на вере в духов природы и предков. Они проводят особые церемонии и фестивали, чтобы попросить у духов защиты и благополучия. В последние годы современная цивилизация и туризм влияют на культуру и жизнь морских цыган. Однако они стараются сохранять свои традиции и передавать их молодым поколениям. Во время посещения поселений морских цыган можно познакомиться с их культурой и увидеть их традиционные ремесла.
Je suis emerveille par Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, rarement plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino vaut une visite excitante. Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste le fun du jeu. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Cliquer maintenant|
кухни на заказ спб кухни на заказ спб .
clickvoltage.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Je suis accro a Lucky 31 Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par ailleurs des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Lucky 31 Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour completer l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un plus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages uniques.
Voir plus|
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Azur Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et energique, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement top les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui stimule l’engagement.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
icebet login icebet login .
курс seo http://www.kursy-seo-12.ru .
goliath casino mobile http://www.goliath-casino.com .
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages uniques.
Obtenir des infos|
J’adore l’energie de 1xBet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, mais encore des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, 1xBet Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Lucky 31 Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En conclusion, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. A signaler la navigation est fluide et facile, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
https://casinolucky31fr.com/|
онлайн юридическая консультация Задать вопрос юристу и получить квалифицированный ответ: Возможность задать вопрос юристу – это первый шаг к решению правовой проблемы. Независимо от сложности вопроса, получение профессионального мнения поможет сориентироваться в ситуации и принять взвешенное решение. Многие онлайн-платформы предлагают бесплатные сервисы вопросов-ответов, где юристы предоставляют консультации в режиме реального времени. Не стоит пренебрегать этой возможностью, особенно если вы столкнулись с юридическими трудностями впервые. Помните, что своевременная консультация может предотвратить серьезные последствия в будущем.
юристы онлайн консультация бесплатно по телефону Бесплатная юридическая консультация онлайн Воспользоваться бесплатной юридической консультацией онлайн – это разумный шаг для тех, кто хочет разобраться в правовых аспектах своей ситуации, не неся при этом финансовых затрат. Многие платформы предлагают такую возможность, позволяя задать вопрос юристу и получить ответ в кратчайшие сроки. Это отличный способ получить общее представление о проблеме и понять, стоит ли обращаться за платной юридической помощью.
Heya i’m for the primary time here. I found this board and I find It truly useful & it helped
me out a lot. I’m hoping to offer something again and aid others such as you aided me.
trafficsprintpro.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
findhappinessdaily – Uplifting messages and helpful tips that brighten my day instantly.
Je suis captive par 1xBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par ailleurs plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, 1xBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A souligner la navigation est simple et intuitive, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement attrayant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute soudee.
https://1xbetcasino777fr.com/|
Je suis accro a Action Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par contre des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour faire court, Action Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En extra l’interface est intuitive et fluide, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point cle les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des privileges personnalises.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis totalement conquis par Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Azur Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour ajouter la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement fun les paiements securises en crypto, renforce la communaute.
https://casinoazurfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par moments des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Azur Casino merite une visite dynamique. De surcroit l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui stimule l’engagement.
Obtenir plus|
leadvector.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
rankvector.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
clickimpact.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
icebet online icebet online .
Je suis completement seduit par Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Action Casino offre une aventure memorable. A mentionner l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce la communaute.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’adore la vibe de Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par contre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En conclusion, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De surcroit l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un bonus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter la plateforme|
Je suis emerveille par 1xBet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, mais plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, 1xBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A souligner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Explorer plus|
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Azur Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En bonus le site est fluide et attractif, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Aller au site|
J’adore l’energie de Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A mentionner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement fun les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus constants.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
J’adore la vibe de 1xBet Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, 1xBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A souligner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste le fun du jeu. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, assure des transactions fiables.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Action Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par ailleurs des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Action Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et energique, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement top les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute vibrante.
Visiter pour plus|
clickstreampro.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Azur Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Azur Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages uniques.
En savoir davantage|
Rap musik With the rise of digital platforms, rap music can be easily accessed via streaming services like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube, making it easier than ever for fans to discover both mainstream stars and underground rappers.
Слушеть Рэп онлайн Additionally, social media has become a crucial tool for rappers to promote their work and connect with their audience, leading to viral hits and collaborations that push the boundaries of traditional music marketing.
продвижение обучение http://kursy-seo-12.ru/ .
marketstorm.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Dadasdas Click News – Updated topics ko simple aur engaging style mein cover karta hai.
кракен даркнет
Je suis epate par Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est clair et efficace, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Pokerstars Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute vibrante.
Explorer le site web|
Je suis enthousiasme par Casinozer Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est transparent et rapide, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, Casinozer Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons egalement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un element fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinozer Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour finir, Casinozer Casino merite une visite dynamique. A souligner le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A signaler les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Explorer le site|
Je suis bluffe par Casinozer Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, a l’occasion plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Casinozer Casino garantit un plaisir constant. De plus le site est fluide et attractif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, garantit des paiements securises.
Continuer ici|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Commencer ici|
growthnexus.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Je suis epate par Mystake Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Dans l’ensemble, Mystake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons egalement la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A souligner le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je suis enthousiasme par Pokerstars Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, toutefois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Pokerstars Casino merite une visite dynamique. A signaler le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui booste la participation.
Cliquer maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de Stake Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est transparent et rapide, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, Stake Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En extra la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement attrayant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Apprendre comment|
With a sizable selection of high-quality video images, PornPics is the best grownup webpage.
1 The website stands out because of its simple layout, broad categories, high-quality images, varied models, and a unique
photo archive. You can find prime video images of famous firms on PornPics for costless to utilize. https://fpeautomation.com/introducing-pneu-connect-x2-robotic-end-of-arm-tooling-from-phd/
growthpilotpro.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
бюро переводов teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA .
it перевод заказать telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
отражающая изоляция Компания ПОЛИСИНТЕЗ предлагает отражающую изоляцию, которая способна отражать до 95% теплового излучения, снижая затраты на отопление и кондиционирование воздуха.
отражающая изоляция “ПОЛИСИНТЕЗ” предлагает широкий выбор полиэтиленовой пленки различных типов, толщин и плотностей, включая пленки общего назначения, термоусадочные пленки, барьерные пленки и многое другое. Мы гарантируем высокое качество нашей продукции, обеспечивающее прочность, герметичность и долговечность. Наши пленки соответствуют всем требованиям безопасности и гигиеничности. Мы предлагаем пленки как в рулонах, так и в готовых изделиях, отвечающих вашим индивидуальным потребностям. армированная пленка
https://friends-social.com/blogs/84122/Code-promo-pour-inscription-1xBet-Code-inscription
бездепозитные фриспины
игровые автоматы бонус за регистрацию с выводом
http://leydis16.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=876583#876583
игровые автоматы которые дают бонус
спины за регистрацию в подарок без депозита
бездепозит и фриспины при регистрации
бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита
it переводчик цена telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
рейтинги бюро переводов teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA .
adscalehub.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
геотекстиль дорнит Мы не просто поставщик, мы – надежный партнер для предприятий и организаций, нуждающихся в современных, эффективных и долговечных решениях для упаковки, строительства, сельского хозяйства и других отраслей.
полиэтиленовая пленка Наша армированная пленка отличается долговечностью и способностью выдерживать значительные нагрузки, обеспечивая надежную защиту в любых условиях. отражающая изоляция
Слушеть Рэп онлайн It combines rhythmic speech with musical accompaniment, often constructed from beats and samples that reflect various cultural influences.
скачать рэп В его основе лежит ритмичное чтение текста, позволяющее артистам передавать свои мысли, эмоции и переживания.
https://www.elephantjournal.com/profile/best1xbet/
promovoltage.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
clickdynamics.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
Je suis accro a Casinozer Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, rarement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Casinozer Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus le site est rapide et immersif, permet une immersion complete. A signaler les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fluides.
Aller plus loin|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Mystake Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est clair et efficace, toutefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Mystake Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement super les evenements communautaires vibrants, garantit des paiements rapides.
Visiter en ligne|
Je suis totalement conquis par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, occasionnellement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Dans l’ensemble, Mystake Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En bonus la navigation est fluide et facile, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter pour plus|
Je suis emerveille par Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, en revanche des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour faire court, Pokerstars Casino offre une aventure memorable. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Cliquer maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Stake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Stake Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point cle les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Aller voir|
ko lanta
ko lanta
salesvelocity.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Вин 1win 1win – динамично развивающаяся платформа, предлагающая широкий спектр возможностей для любителей азартных игр. 1win официальный – это ваше окно в мир больших выигрышей, где безопасность и надежность стоят во главе угла. Здесь вы всегда можете рассчитывать на честную игру и своевременные выплаты.
Ставки на спорт 1win – динамично развивающаяся платформа, предлагающая широкий спектр возможностей для любителей азартных игр. 1win официальный – это ваше окно в мир больших выигрышей, где безопасность и надежность стоят во главе угла. Здесь вы всегда можете рассчитывать на честную игру и своевременные выплаты.
зеркало кракен
кайт египет
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Pokerstars Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, en revanche des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Pokerstars Casino assure un fun constant. En plus le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Entrer sur le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Stake Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Le processus est simple et transparent, par ailleurs quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Stake Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour ajouter l’interface est simple et engageante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un point fort les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Voir maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais encore des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Pokerstars Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un avantage les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des avantages uniques.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis sous le charme de Casinozer Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, mais encore des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Casinozer Casino offre une experience inoubliable. D’ailleurs le site est rapide et style, permet une immersion complete. Un atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, quelquefois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Mystake Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons egalement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
J’adore le dynamisme de Casinozer Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais encore plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. D’ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui motive les joueurs.
AccГ©der maintenant|
it переводчик заказать telegra.ph/Oshibka-lokalizacii-pochemu-vash-IT-produkt-ne-ponimayut-za-granicej-11-09 .
бюро переводов в мск teletype.in/@alexd78/iF-xjHhC3iA .
Всё здорово спасибо Вам https://milespeyton.info Подскажите когда примерно вналичии будет JTE-907
бездепозитный бонус фриспины за регистрацию
бездепозитный бонус с выводом без пополнения
Прогнозы на спорт Лига ставок – это узнаваемый бренд, синоним надежности и высоких стандартов обслуживания. Это широкая линия событий, выгодные коэффициенты и удобный интерфейс, делающие процесс ставок максимально комфортным и увлекательным. Лига ставок ставки – это калейдоскоп возможностей, открывающий двери в мир самых разнообразных видов спорта. От футбольных дерби до теннисных турниров, от хоккейных баталий до киберспортивных сражений – каждый найдет здесь что-то для себя, сможет применить свои знания, интуицию и, конечно же, удачу.
Мелстрой гейм Лига ставок – это узнаваемый бренд, синоним надежности и высоких стандартов обслуживания. Это широкая линия событий, выгодные коэффициенты и удобный интерфейс, делающие процесс ставок максимально комфортным и увлекательным. Лига ставок ставки – это калейдоскоп возможностей, открывающий двери в мир самых разнообразных видов спорта. От футбольных дерби до теннисных турниров, от хоккейных баталий до киберспортивных сражений – каждый найдет здесь что-то для себя, сможет применить свои знания, интуицию и, конечно же, удачу.
По сути он эйфо, но ничего, кроме расширенных зрачков, учащенного сердцебиения и потливости, я не почувствовал… А колличество принятого было просто смешным: 550 мг. в первый день теста и 750 мг. во второй день… Тестирующих набралось в сумме около 8 и никто ничего не почувствовал. https://alleya.info доброго времени суток. Так что по итогу магазин то ровный или нет,а то куча противоречий,заранее благодарен.
бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита
sykaaa casino бездепозитный
Future Path Finder – Found actionable guidance that makes spotting opportunities easy and fun.
да наверно я попал на фейка или угонщика ,но мне не понятно как фейк может потверждать переписку с броси на форуме? купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази
growthsignal.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
да магаз реальный.недовеса небыло ниразу.может просто недоразумение. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки
Hello everyone, it’s my first pay a visit at this site, and piece of writing is really fruitful in favor of me, keep up posting such articles.
https://justrussia.ru/
ко ланта
ko lanta
marketsignal.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
1xbet промокод на сегодня 2026. Чтобы удовлетворить игроков, букмекеры постоянно добавляют новые функции и предложения. Одним из лидеров является 1хБет. Ввод промокода при регистрации позволяет получить увеличенную сумму бонуса. После создания аккаунта внеси первый депозит (до 32 500 рублей) — и получи вознаграждение. Абсолютно бесплатный 1xBet промокод доступен всем новичкам, чтобы активировать дополнительные преимущества. Игнорировать поле «Введите промокод» — значит потерять выгоду. Оно присутствует при трёх из четырёх способов регистрации (по телефону).
Ментам зачастую пофиг,легал-нелегал.Был бы человек хороший,статья найдётся.СПСР тоже чёт не нравится.Но и на Мажор экспрессе случаи принималова были,так что х.з….Увидел на сайте “ждём…”.О.флюрокока и rti 111!Очень ждём!АМТ тож вкусняшка,но тут обьебосам не завидую.Примут по полграмма и айда 20 часов как кот в стиральной машине купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки
TurkPaydexHub se distingue comme une plateforme d’investissement crypto revolutionnaire, qui utilise la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour fournir a ses clients des avantages decisifs sur le marche.
Son IA analyse les marches en temps reel, identifie les opportunites et applique des tactiques complexes avec une exactitude et une rapidite inaccessibles aux traders humains, maximisant ainsi les perspectives de gain.
J’adore la vibe de Pokerstars Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Pokerstars Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De plus le site est rapide et engageant, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer maintenant|
promorocket.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Я вообще удивляюсь как продаван работает то? Есть ветка форума, личка и ася – везде молчание. В ася онлайн, но всеравно молчит уже третий день – это адекватный сервис? купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки
Один из старейших!!! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази
growthstream.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
найти промокод на 1хбет Найдите промокод на http://www.google.pl/url?q=https://bergkompressor.ru/news/artcles/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_5.html и активируйте бонус 100% на первый депозит, чтобы получить максимальный стартовый бонус.
Je suis bluffe par Pokerstars Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, en revanche quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, Pokerstars Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En extra le design est style et moderne, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement attrayant les options de paris sportifs variees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Parcourir maintenant|
203 тут говно.. 10к вникуда улетели.. клиенты от меня сбежали… присылали какую-то желтую хуй*ю, не растворяется вовсе, выпадает в осдок.. прет максимум 20-30 минут (в лучшем случае) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм
бездепозитный бонус игровые автоматы с выводом денег
игровые автоматы деньги без депозита
Betboom 1win: Обзор и Возможности 1win – это популярная букмекерская компания и онлайн-казино, предлагающая широкий спектр возможностей для азартных игроков. Компания привлекает пользователей своими высокими коэффициентами, широкой линией событий и разнообразными бонусами. Официальный Сайт и Зеркала Официальный сайт 1win предоставляет доступ ко всем возможностям платформы. Однако, в некоторых странах доступ к сайту может быть ограничен. В этом случае можно использовать зеркала – альтернативные адреса сайта, которые позволяют обойти блокировки. Ставки на Спорт и Казино 1win предлагает ставки на множество видов спорта, включая футбол, хоккей, баскетбол, теннис и другие. Компания также предлагает широкий выбор азартных игр, таких как слоты, рулетка, блэкджек и покер. Бонусы и Акции 1win предлагает щедрые бонусы для новых и постоянных клиентов. Новые игроки могут получить приветственный бонус за первый депозит, а постоянные клиенты могут участвовать в различных акциях и получать дополнительные бонусы за активную игру. Мобильное Приложение 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение для устройств на базе iOS и Android. Приложение позволяет делать ставки и играть в казино в любом месте и в любое время.
winline 1win: Обзор и Возможности 1win – это популярная букмекерская компания и онлайн-казино, предлагающая широкий спектр возможностей для азартных игроков. Компания привлекает пользователей своими высокими коэффициентами, широкой линией событий и разнообразными бонусами. Официальный Сайт и Зеркала Официальный сайт 1win предоставляет доступ ко всем возможностям платформы. Однако, в некоторых странах доступ к сайту может быть ограничен. В этом случае можно использовать зеркала – альтернативные адреса сайта, которые позволяют обойти блокировки. Ставки на Спорт и Казино 1win предлагает ставки на множество видов спорта, включая футбол, хоккей, баскетбол, теннис и другие. Компания также предлагает широкий выбор азартных игр, таких как слоты, рулетка, блэкджек и покер. Бонусы и Акции 1win предлагает щедрые бонусы для новых и постоянных клиентов. Новые игроки могут получить приветственный бонус за первый депозит, а постоянные клиенты могут участвовать в различных акциях и получать дополнительные бонусы за активную игру. Мобильное Приложение 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение для устройств на базе iOS и Android. Приложение позволяет делать ставки и играть в казино в любом месте и в любое время.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Pokerstars Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour completer la navigation est claire et rapide, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Explorer la page|
Je suis sous le charme de Stake Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, bien que plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Stake Casino vaut une visite excitante. En complement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Je suis captive par Pokerstars Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par moments des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En conclusion, Pokerstars Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter pour plus|
Магаз качественный ни разу не подводил!!! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази
Je suis accro a Stake Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, bien que quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Stake Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fluides.
http://www.stakecasino365fr.com|
Je suis captive par Mystake Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements rapides.
Visiter en ligne|
Je suis emerveille par Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, parfois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, Casinozer Casino garantit un amusement continu. En complement la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement cool les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses continues.
Aller plus loin|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Mystake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais encore quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour finir, Mystake Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. A signaler les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute soudee.
Voir plus|
спины за регистрацию в подарок без депозита
Je suis emerveille par Casinozer Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A signaler le design est style et moderne, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
https://casinozercasino366fr.com/|
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию без отыгрыша
plane crash game money download https://aviator-game-predict.com/ .
прокарниз prokarniz36.ru .
Огромное спасибо данному магазину, успехов вработе и процветания!!!? купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки
primedigital.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
что сильнее 100 или 400 ? и по времени сколько действуют ? купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану
На каком сайте сейчас заказать то можно дживик ровный купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази
admasterlab.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Je suis completement seduit par Stake Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est clair et efficace, par contre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Stake Casino merite une visite dynamique. En plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A mettre en avant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Continuer ici|
чувствую у меня будет то же самое, трек получил но он нихуя не бьется, а что ответил то? я оплатил 3 февраля и трек походу тоже левый ТС обьясни и мне ситуацию купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par contre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino offre une aventure memorable. A souligner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement top les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus constants.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis bluffe par Stake Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, a l’occasion quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En conclusion, Stake Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce la communaute.
Explorer plus|
Je suis captive par Casinozer Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En fin de compte, Casinozer Casino assure un fun constant. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des avantages uniques.
Avancer|
J’ai un faible pour Mystake Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Mystake Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En extra la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un bonus les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des privileges personnalises.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis bluffe par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, de temps a autre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Mystake Casino merite un detour palpitant. A mentionner le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement super les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute soudee.
Parcourir maintenant|
J’ai un faible pour Casinozer Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, parfois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Casinozer Casino merite un detour palpitant. A noter le design est moderne et energique, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement cool les transactions en crypto fiables, qui motive les joueurs.
Ouvrir maintenant|
conversionlab.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
J’ai un faible pour Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Pokerstars Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
Essayer maintenant|
Есть, но пока что временно не работает. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш
электрокарнизы для штор купить http://www.elektrokarniz2.ru/ .
электрокарниз двухрядный elektrokarniz1.ru .
beef casino промокоды
beef casino официальный
нет таких, а вымораживать рекламу других магазинов в этой ветке можно и минус в репу получить, есть другие ветки где обсуждаются реагенты от разных магазинов, а здесь обсуждается продукция данного ТСа , вкурил? https://milespeyton.info Что то много новичков устраивают здесь флуд.А магаз на самом деле хорош.Помню его еще когда занимался курьерскими доставками,коспирация и качество товара было на высшем уровне.
Wow, incredible blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is magnificent, as well as the content!
Купить iPhone 17 в Москве
Je suis epate par Pokerstars Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service client est de qualite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps a autre des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Dans l’ensemble, Pokerstars Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement interessant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
beef casino скачать приложение на андроид
beef casino официальный
доброй ночи ровной ветке! https://bwin99.info Братва после покупки не забываем писать отзывы.
clickpioneer.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
clickvero.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
у меня такой вопрос: будут ли у вас на розничном сайте позиция am-2233 по 1гр? Я раньше брал через алхима, но он по неизвестным мне причинам сговнился. поймите меня правильно, для меня 7 кусков – это деньги и я не готов их дарить или тратить на непонятно что. https://milespeyton.info Я вот перед заказом почитала хуеву кучу отзывов и не нашла ни одного хуевого. Но опять же, смотри, отзывы были не об эйфоре, а о самом магазине. Давай друг, советуй что-нибудь в личку
adelevatepro.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
А ничо что праздники как бэ ? https://hiphopget.com ВСЕМ МИР А ТСУ РЕСПЕКТ )))
электрокарниз купить в москве электрокарниз купить в москве .
И потом не удивляйтесь, что магазин медленно работает или не отвечает. Попробуйте по 100 раз в день рассказывать что и как разводить, и при этом успевать оформлять заказы. https://miqualityhealthcaretraining.com а сюда заглянуть влом ? //legalrc.com/threads/Трипы.588/page-2
adboostlab.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
я думаю разберемся точно https://xwalkcenter.org Вот это было бы нереально кул, а то я уже отчаялся через емейл к вам пробиться. Жду с нетерпением.
Innovation Hub Daily – Tools and ideas for exploring creativity and making things happen.
магаз норм. а вот курьеры зажрались суки. https://wikibot.info Получил посыль,все отлично..будем тестить товар
Je ne me lasse pas de Pokerstars Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, bien que plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Pokerstars Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements securises.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Stake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Stake Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A mentionner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un plus les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des recompenses continues.
Plongez-y|
adtrailblaze.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Je suis accro a Pokerstars Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour faire court, Pokerstars Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un atout les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
VГ©rifier ceci|
Je suis epate par Stake Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Stake Casino merite un detour palpitant. A mentionner l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce la communaute.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Mystake Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En resume, Mystake Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. Un bonus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fluides.
Continuer ici|
Je suis sous le charme de Casinozer Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Casinozer Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour completer la navigation est simple et intuitive, booste l’excitation du jeu. A signaler les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis sous le charme de Mystake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, toutefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Mystake Casino vaut une visite excitante. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Mystake|
307ой вроде к 15 можно забадяжить..ещё хим дрим какойто есть..тока я сам про него не в теме https://alleya.info сделал заказ ,оплатил 🙂 теперь жду трека и посыля с нетерпением 🙂 по общению продаван понравился все ровно обьяснил че да как . как придет опробую оставлю отзыв окончательный ,пока что все ровно )
Je suis accro a Casinozer Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, en revanche quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En conclusion, Casinozer Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Pour ajouter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un point fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
leadmatrixpro.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Первый раз вижу такое с МН. От других селлеров все было норм с растворимостью. Растворяющийся полностью пер чуть посильнее… https://bwin99.info второй раз заказываю, класнный продукт пришел что 250 что 307 , качество отменное , доставка буквально 3 суток
Трудовая книжка точно – заказать перевод документов онлайн. Самарское бюро переводов. Документы, нотариус, срочно! Любые языки. Качество проверенное. Гарантия принятия.
ranksprint.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
promomatrix.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Je suis enthousiasme par Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Pokerstars Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce le lien communautaire.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
J’adore la vibe de Pokerstars Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En fin de compte, Pokerstars Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
Cliquer maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Stake Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En somme, Stake Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons que la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fluides.
Aller voir|
growthcruise.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
анологичная ситуация! продаван ты на примете, раз твоих клиентов начали принимать… https://milespeyton.info Проб НЕТ!
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Mystake Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est clair et efficace, a l’occasion des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Mystake Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A noter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement interessant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute soudee.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je suis captive par Casinozer Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et style, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Lire la suite|
Je suis epate par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est clair et efficace, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Mystake Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement le site est rapide et engageant, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement fun les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Voir la page d’accueil|
J’adore l’energie de Casinozer Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, occasionnellement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En somme, Casinozer Casino assure un fun constant. Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et intuitive, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement fun les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, cree une communaute soudee.
Approfondir|
и вот я решил зайти на ветку доверенных магазинов! и почему то решил ткнуть именно на ссылку чемикл микс! захожу дыбанул на ценник, устроило и даже очень! так же порадовало то что тут делают отправку! а это значит то что если товар отправят то ты его 100% получишь! главная особенность магазина в том что отправка делается от 5грамм 🙂 а это значит то что я смогу и опробывать товар и убидится в качестве товара, и в надежности магазина! https://russian-business.info магаз четкий,еще в 2011 каждую неделю забегали:music:)всегда все ровно
группа позавчера “Позавчера” как рок группа – это бунтарский дух, заключенный в мелодичные формы. Их музыка – это вызов обыденности, гимн индивидуальности и свободе самовыражения. Каждый концерт – это взрыв эмоций, искренний и неудержимый, когда энергия бьет через край, объединяя музыкантов и слушателей в общем порыве. Это не просто музыка, это катарсис.
рок группа позавчера “Позавчера рок” – это вызов времени, попытка сохранить дух ушедших эпох и передать его новым поколениям. Это музыка, которая не стареет, а становится только лучше с каждым прослушиванием.
Перевод с македонского – онлайн перевод документов с узбекского на русский. Перевод паспортов, договоров в Самаре. Нотариальное заверение. Срочно и недорого. Гарантия качества. Звоните!
conversionboost.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Чемикал, пожалуй, самый ровный магаз из всех ныне сушествующих! Цены, конечно есть и по меньше в других местах, однако для себя я выбрал безопасность и надежное сотрудничество, а не дешевизну, которая как показывает практика всегда заканчивается не очень хорошо. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Ребятки все пушка
музыка позавчера “Позавчера” как рок группа – это энергия бунтарства, помноженная на мелодичность и искренность. Их концерты – это взрыв эмоций, где каждый зритель становится частью единого целого. Это музыка для тех, кто не боится самовыражения и готов идти против течения. Это протест против серости и обыденности, гимн свободе и индивидуальности.
музыка позавчера “Позавчера рок” – это вызов времени, попытка сохранить дух ушедших эпох и передать его новым поколениям. Это музыка, которая не стареет, а становится только лучше с каждым прослушиванием, обретая новые оттенки и смыслы.
А в сочи есть магазины https://drr-law.org По АМ могу сказать,что концентрировать выше 1 к 15 не вижу смысла.Оно не торкает дальше своего известного предела,после 1 к 15 дальше пойдёт уже переводняк.Тут как с процами-дороже 200 баксов покупать-перевод бабла,прироста производительности не заметишь почти.
кто последний раз когда брал? регу или соль купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Ну просто выглядело твое сообщение как мессага на параное)))))
Покупал как то в этом магазине реагента 1к10 помоему был у них примерно год назад.С доставкой,заказ делал тогда еще на сайте, получил реквизиты оплатил ждал отправки.И вот доставка пришла очень быстро.Качество товара было приемлемое.Очень хорошая консперация.Всем советую https://extraperevozki.ru Посылку же должны до дома доставить.
Je suis completement seduit par Pokerstars Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, mais encore des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Pokerstars Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une touche d’excitation. A signaler le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Ouvrir le site|
elitefunnels.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Молча !! Запрет вступает в силу 26го числа, если не ошибаюсь. Скидывай всё палево, жёсткий дист зарывай подальше и иди получай )) https://zhivouste.ru магазин ровный, три года с ним уже, только один раз отправку долго ждал…. но дождался)
marketcruise.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
leadvoltage.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
leadforgepro.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
tripscan Tripscan также предоставляет возможность делиться планами путешествий с друзьями и близкими, чтобы вместе обсуждать и корректировать маршрут. Вы сможете создать совместное путешествие, которое будет соответствовать интересам каждого участника.
Жаль только в Мск от 50 гр. )) Думал в Саратове тоже https://jon-wick-lord.ru А теперь к делу.. магаз ровный, товар ..вставляет епт..особенно в прошлый раз, пол часа ждал, что из ванной вылезет оно и покарает меня…хорошо быстро отпускает, а то вода остыла уже и сига стлела и хабарик упал так , что сам не заметил…
conversionpulse.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
купить права
nsfw content ИИ девушка – это концепция, которая быстро набирает популярность в эпоху развития искусственного интеллекта. Речь идет о виртуальных компаньонах, созданных с использованием технологий машинного обучения и нейронных сетей, способных имитировать общение и взаимодействие с человеком. Некоторые видят в этом возможность для одиноких людей найти эмоциональную поддержку и общение, другие же опасаются, что это может привести к ухудшению социальных навыков и снижению ценности реальных отношений. Независимо от точки зрения, важно понимать, что ИИ девушка – это лишь инструмент, и то, как он будет использоваться, зависит от человека.
кто знает когда рега будет ? https://texnometall.ru смотря каким реагентом будешь бадяжить
Je suis enthousiasme par Pokerstars Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Globalement, Pokerstars Casino est un endroit qui electrise. D’ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute soudee.
Explorer davantage|
adorbitpro.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Purposeful Steps Daily – Practical advice to move forward with focus and clarity every day.
всем привет! магаз ровный беру у них года 2 уже все всегда стабильно и качества радует. берите все саветую. спасибо магазин https://avicenna-s.ru Всем привет, долго не писал, ну это меня «задержала» посылка jv-61. Все пришло, все получил причем довольно быстро все ехало:good:
сегодня сделал заказ оплатил, отпишусь что будет дальше https://mashtab-r.ru Есть в липецке
РФ. Западно – европейская её часть ) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази вот опять сегодня получил что заказал всё прошло ровно .быстро ,качество в этом магазине лучшее ,больше не где не заказываю .если нужно что то подождать я лучше подожду чем кидал буду кормить ,тоже влитал поначалу пока нашёл этот магазин ,по этому сам беру и друзьям советую .спасибо всей команде за отличную работу.с наступающими праздниками всех поздравляю.вообщем всем благодарочка.
Je suis enthousiasme par Coolzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, mais encore des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Coolzino Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Notons egalement la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Я ж тебя хотел отпиарить. https://altuning.ru Получил вчера конвертик от вас . Спасибо , оперативно . Не знаю почему почти все недовольны 5иаи , но такого психодела давненько не переживал . Потрясён до мозга костей .
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Coolzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Coolzino Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour completer le design est style et moderne, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Explorer davantage|
J’ai un faible pour MonteCryptos Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus initial est super. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, quelquefois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, MonteCryptos Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus constants.
Continuer Г lire|
J’adore la vibe de MonteCryptos Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Dans l’ensemble, MonteCryptos Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour completer le design est moderne et attrayant, apporte une energie supplementaire. A signaler les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis bluffe par Lucky8 Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, Lucky8 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A souligner le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A mettre en avant les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements securises.
Naviguer sur le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky8 Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, en revanche quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Au final, Lucky8 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une experience immersive. A souligner les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements securises.
AccГ©der maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour NetBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains arrivent sans delai, toutefois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour faire court, NetBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. D’ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A signaler les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, garantit des paiements rapides.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je ne me lasse pas de NetBet Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, NetBet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a rester plus longtemps. A noter les evenements communautaires dynamiques, garantit des paiements rapides.
http://www.casinonetbetfr.com|
Приветствую всех форумчан и клиентов оптово-розничного магазина chemical-mix https://bular-anapa.ru сайт скоро подымем , я на ветке отпишу как заработает
бро ответь в лс, сделаю заказ купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Да,меня тоже!)заказал вчера тут 203-го,сегодня жду трека!
https://vk.com/murchalkin.official
J’adore le dynamisme de Coolzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, quelquefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Coolzino Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En extra la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement interessant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce la communaute.
Voir le site|
Ровный и Стабильный… https://rodichenkov.ru – Ну….. минут за двадцать….
в курске у стаффсторе лутше не брать за кладом надо ехать с граблями и лопатой сугробы копать иначе никак https://dnastroy.ru я на лестнице один,
Je suis accro a Coolzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, malgre tout des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Globalement, Coolzino Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A signaler le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement interessant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Avancer|
J’adore la vibe de MonteCryptos Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, MonteCryptos Casino vaut une visite excitante. A souligner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges sur mesure.
http://www.montecryptoscasino365fr.com|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky8 Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, a l’occasion des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Lucky8 Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fluides.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de MonteCryptos Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais encore des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, MonteCryptos Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus le site est rapide et engageant, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges personnalises.
Cliquez ici|
Je suis epate par Lucky8 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des tables live interactives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est simple et transparent, parfois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En somme, Lucky8 Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Aller Г la page|
J’adore l’energie de Lucky8 Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En bref, Lucky8 Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En bonus l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un point fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
Voir la page d’accueil|
трипскан С Tripscan вы можете забыть о стрессе и наслаждаться предвкушением незабываемого приключения.
трипскан Помимо бронирования отелей и авиабилетов, Tripscan предлагает широкий выбор дополнительных услуг, таких как аренда автомобилей, страхование путешествий и организация трансферов. Это позволяет вам спланировать всю поездку комплексно и избежать лишних хлопот.
Je suis sous le charme de NetBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, occasionnellement plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, NetBet Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
Магазин работает супер!) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Хочу всех поздравить с наступающим Новым Годом и хочу поделиться с вами своей оптовой сделкой СК крисов.
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme.
Did you make this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you?
Plz reply as I’m looking to create my own blog
and would like to find out where u got this from.
kudos
пробывал нюхать эфект 4-6часа https://burenie-msk.ru и я так же жду с 8 числа сказали отправки в начале недели
магаз ровный!!! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки да ее колать страшно эксперементатором быдь тоже чет не охото
J’ai un faible pour Coolzino Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, en revanche des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Coolzino Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage notable les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, renforce le lien communautaire.
http://www.coolzinocasinofr.com|
Парни у кого нибудь задерживали посылку в СПСР?Уже неделю как приняли и все не отправят и планируемая дата отправки прошла,а реальную так и не поставили.Позвонил в офис говорят готово к отправке,а че не отправляют они не знают.Сказали позвонить когда менеджеры придут на работу.У кого нибудь такое было?Может это фигня какая то и лучше не идти за посылкой?Как думаете?Раньше просто такого не было максимум 5 дней с даты приема до моих рук проходило,с любого магазина. https://texnometall.ru 307ой вроде к 15 можно забадяжить..ещё хим дрим какойто есть..тока я сам про него не в теме
рулонные шторы с электроприводом купить в москве rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom177.ru .
trafficprime.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Trendy Styles Hub – Discover the latest fashion trends and update your wardrobe effortlessly.
Просто респектище курьеру. На моей памяти такие клады были всего раза три-четыре за три года обитания меня на этом форуме. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану 203 вообще шикарный ) мне понравился. спасибо Вам)
growilo.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
conversionprime.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
clickvoyage.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
https://officepro54.ru/collection/ofisnye-kresla
ко ланта ко ланта
по времени ждал не долго дня 4 но доставка отдала на 2ой день как пришло , конспирация мне очень понравилась на все 100% магазину 100 из 100 и большой спс ) https://texnometall.ru Брал и не раз в данном магазине, притензий нет, все качественно, оперативность радует! Продовцы дайте информации о CHM – 500, что за зверь? когда в розницу уйдет
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Coolzino Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais encore des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Coolzino Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A souligner le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A mettre en avant les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Continuer ici|
Je suis sous le charme de Coolzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, malgre tout des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Coolzino Casino est un endroit qui electrise. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges personnalises.
AccГ©der maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Coolzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais encore plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Coolzino Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De plus le site est rapide et immersif, incite a rester plus longtemps. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires engageants, cree une communaute soudee.
Parcourir le site|
Тут ровно братаны,берем и не паримся,качеставо вышка!) https://gadanieperemen.ru Что с заказом 960 трек не рабочий дали 3 дня уже одни обещания
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de MonteCryptos Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, rarement des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, MonteCryptos Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A signaler l’interface est simple et engageante, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement attrayant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des bonus constants.
Poursuivre la lecture|
J’ai un faible pour Lucky8 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En fin de compte, Lucky8 Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges personnalises.
https://lucky8casino365fr.com/|
Je suis completement seduit par Lucky8 Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Lucky8 Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A signaler la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus constants.
AccГ©der maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de NetBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par moments des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, NetBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En bonus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un point fort les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des privileges personnalises.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis completement seduit par NetBet Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, NetBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point cle les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
https://aritual.by/prices.html
Ровный магазин . Всем советую ! купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Респект и уважуха магазину, и процветания, безусловно!
ко ланте Ко Ланте
ко ланте Ко Ланте
Всем доброго времени суток. Первый раз довелось заказывать в этом магазине на свой страх и риск, но положительные отзывы старичков о работе и качестве товара (в частности 2с, который меня и интересовал) убедили, что причин волноваться нет. купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Магазин отличный. Покупал не однократно. Спасибо. Ждем регу!
тканевые электрожалюзи https://prokarniz23.ru/ .
умный дом шторы умный дом шторы .
небольгой репортаж отписать о ск. https://silavmozge.ru заказал, получил трек, пока не бьется.
Motivation Central – A hub for encouragement and self-confidence building.
Если захотят принять, то это тебя никак не обезопасит https://dou119-ekb.ru “Приезжаю и вижу на свету бля что то поххожее на таблетки “
дизайн интерьера ключ https://dizayna-interera-spb.ru
ко ланта ко ланта
народ а трек через скока по времени примерно приходит? купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки yabe.lil сказал(а): ^
clickstormpro.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
seostorm.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
clickdynasty.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Добрый вечер помогите купил у снега клад, пустой, как сапорту написать..? https://altuning.ru это самый лучший магазин ставлю 5+ потому что куча раз брал на рампушке и всегда находил, тут всё так же.
traffichive.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
дизайн интерьера спб лучший дизайн интерьера спб
ребята ребятушки как делишки?)) в городе Барнаул данный магазин работает?) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Бро конечно я незнаю твою ситуацию, но с зданным магазом работал всегда всё на вышке было , и вот что думаю на 10 грамм смысла тебя кидать нет такому магазину!!!
ко ланте Ко Ланте
Хоть скан хоть что вылаживайте, это не доказательство! доказательством для меня есть только поступление денег на счет. По чекам, сканам, и всему прочему я не работаю это не есть доказательство об оплате! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Привет парни…Заказал тут 10-ку МНа..Ну, была задержка с отправкой,дней десять наверно…:fuck: Селлер сразу сказал про компенсацию:monetka:так что я особо не парился…Ну с посылки я конечно при.уел:confused:.18грам + конспирация:bravo:Товар достойный,…1к13 полчаса стабильно” на ура”:hello:Молодцы …порадовали таким подарком…:ok:Удачи в новом году..
tripscan С TripScan вы найдете скрытые жемчужины, о которых раньше не знали, и сможете создать уникальное путешествие, которое запомнится на всю жизнь.
здесь без музыки танцую – https://oberegiamulet.ru чувак брал я тоже тут 2 ci некоторым понравилось некоторым нет , лично я поднимал даже с неё бабок норм, народу нравиться , а если этот каиф тебе не нравиться нех писать что тусишка бычий кайф , бычий каиф немного другое, а такои продукт не может быть бычий кайф это я тебе отвечаю, со входом согласен по ноздре ваще не вариант !
clickvolume.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
vavada казино зеркало — это актуальное зеркало для доступа к популярному онлайн-казино.
Она предлагает широкий выбор слотов, рулетки и карточных игр.
Сайт отличается удобным интерфейсом и быстрой работой. Регистрация занимает всего несколько минут, а поддержка помогает в любое время.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
На платформе представлены сотни игр от мировых провайдеров. Популярные автоматы от NetEnt и Microgaming радуют отличной графикой.
Особого внимания заслуживают джекпоты и турниры. Ежедневные розыгрыши привлекают тысячи участников.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
Новые игроки получают щедрые приветственные подарки. Бонусы начисляются как за регистрацию, так и за активность.
Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов. Еженедельные турниры с призовыми фондами добавляют азарта.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
Vavada гарантирует честность и прозрачность игр. Вывод средств происходит быстро и без скрытых комиссий.
Служба поддержки работает в режиме 24/7. Игроки могут связаться с поддержкой через email или мессенджеры.
### Спин-шаблон
#### Раздел 1: Введение в мир Vavada
1. На vavadacasinos.neocities.org собраны лучшие игры для азартных игроков.
2. Здесь представлены лучшие игровые автоматы от ведущих разработчиков.
3. Платформа радует пользователей простой навигацией и стабильной работой.
4. Игроки могут зайти на платформу как с компьютера, так и со смартфона.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
1. На платформе представлены сотни игр от мировых провайдеров.
2. Каждый игрок найдет вариант по вкусу — от блекджека до современных видео-слотов.
3. Особого внимания заслуживают джекпоты и турниры.
4. Крупные выигрыши разыгрываются в прогрессивных слотах.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
1. Регистрация открывает доступ к выгодным бонусам.
2. Вращения в слотах дарятся без обязательных вложений.
3. Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов.
4. Кешбэк и эксклюзивные предложения доступны для VIP-игроков.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
1. Все игры работают на честных алгоритмах.
2. Лицензия обеспечивает защиту персональных данных.
3. Служба поддержки работает в режиме 24/7.
4. Решение любых вопросов занимает минимум времени.
магазин ровнеый,за что им спасибо,если сами тупить не будете всё пройдёт ровно и без проблем.Товар тоже порадовал,довольно таки неплохо)) https://sherifpizza.ru Частенько брал сдесь мини-опт по совместкам в 2013-2014году !
marketboostpro.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
хотели бы услышать отзывы о Ск муке https://sadikfuntik.ru Забирал 6 заказов, ни единого косяка… заказы и на мизерные и на большие суммы. Давали 1 раз даже пробник по моей просьбе бесплатно.
Магазин нормальный, качество на уровне, короче заказывай и не парься я тут брал уже раза 3 и всегда всё на уровне:good:. А ник его Фокс произносится, что в переводе с английского означает лиса, лис.. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш магаз ровный,всем советую!!
ко ланта ко ланта
tripscan С TripScan вы найдете скрытые жемчужины, о которых раньше не знали, и сможете создать уникальное путешествие, которое запомнится на всю жизнь. Эта платформа, TripScan, также предоставляет инструменты для отслеживания цен и получения уведомлений о снижении стоимости билетов и номеров в отелях.
Мир вам! https://radian16.ru Удачи Вам и Процветания От Всей Души!
leadmachine.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Наверно так же как и джив. попробуй минимальные пропорции сделать 0,1 к 1 https://hotapk.ru по Иванову работаем
kews кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
Все посылку получил. ровно 7 дней после оплаты и посылка уже у меня. конспирация отличная. купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Может случилось что-то не ладное?
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
контора мелбет https://www.v-bux.ru .
Бро ты ошибся. Не поняли друг друга бывает купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази по Иванову работаем
kews кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
У меня ожидалась поездка по работе в Столицу нашей родины на пару недель но как обычно я списался оператором в джаббе подтвердил адрес через форум что не ФЭЙК оплатил заранее по приезду написал ТС , он по скорому выдал мне адрес в тот день что договорились ) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану “Открываю коробок Пусто, под спички шорк вот и пакетик на глаз 03”
marketoptimizer.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
анкеты эскортниц Вписки в Челнах — это вариант для тех, кто ищет альтернативу традиционным свиданиям. Здесь можно найти единомышленников, весело провести время в непринужденной обстановке и завести новые знакомства. Вписки в Челнах часто предлагают тематические вечеринки, интересные развлечения и возможность отдохнуть от повседневной рутины. Однако стоит помнить о безопасности и выбирать проверенные места и компании.
встречи челны Индивидуалки в Челнах – это гарантия конфиденциальности и индивидуального подхода. Они ценят ваше время и понимают ваши желания, стремясь создать атмосферу комфорта и доверия. Забудьте о формальностях и насладитесь обществом женщины, способной слушать, понимать и дарить незабываемые эмоции. Индивидуалки – это не просто спутницы на вечер, это ваши личные музы, готовые вдохновлять и удивлять. Они помогут вам расслабиться, забыть о проблемах и почувствовать себя уверенно и желанно.
ко ланта ко ланта
ко ланта ко ланта
leadharbor.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Даный магазин берет бобло и парит мозг посылки отпровляет по месяцу, гдето с сентября такие проблемы сними начелись, причом решать их они не собираються купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм А вот еще немного…Вскрыл, взвешал – все в норме. для начала взял 1гр.растворяется АМ2233 в спирту хреново,(в след.раз попробую на растворителе сделать)причем грел все это дело на водяной бане,мешал,но до конца так и не растворилось.делал это долго и упорно,молочного оттенка раствора не наблюдалось,прозрачный скорее,но остался осадок в виде белого порошка.В итоге так и залил все это дело 1к20. Сушится теперь. Как высохнет опробуем и напишу что получилось. Буду надеятся на лучшее.
clicklabpro.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
clickvortex.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
вызвать проститутку по вызову нижневартовск
leadorigin.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Всех благ данному магазину!!! https://texnometall.ru (выглядит как реклама, но эт просто хорошие впечатления от сотрудничества)
И потом не удивляйтесь, что магазин медленно работает или не отвечает. Попробуйте по 100 раз в день рассказывать что и как разводить, и при этом успевать оформлять заказы. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Магазин не работает по выходными и праздникам
Fashion & Trend Spot – Browse stylish products effortlessly for a fun and smooth shopping experience.
а трудно изучить предварительно информацию о веществе, а потом покупать ? вот к примеру у меня в подписи инфа. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази по отзывам процентов 80 приемок именно в данной курьерке..
Всегда платил через киви перевод идёт максимум сутки.950р это с курьером доставит тебе куда скажешь))) купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану Данный продукт не зашол в моё сознание:) его нужно бодяжить с более могучим порохом, будем пробовать АМ2233…
анкеты эскортниц Индивидуалки в Челнах – это гарантия конфиденциальности и индивидуального подхода. Они ценят ваше время и понимают ваши желания, стремясь создать атмосферу комфорта и доверия. Забудьте о формальностях и насладитесь обществом женщины, способной слушать, понимать и дарить незабываемые эмоции. Индивидуалки – это не просто спутницы на вечер, это ваши личные музы, готовые вдохновлять и удивлять. Они помогут вам расслабиться, забыть о проблемах и почувствовать себя уверенно и желанно.
встречи челны Вписки в Челнах – это для тех, кто молод душой и ищет спонтанности. Это возможность окунуться в атмосферу беззаботности, познакомиться с новыми людьми и весело провести время. Но помните о безопасности и выбирайте только проверенные места и компании. Вписка – это не просто вечеринка, это шанс почувствовать себя частью чего-то большего, найти новых друзей и получить заряд позитивных эмоций.
за наличие узнавай у селлера. куда тебе 2грамма дезоксипипрадола я слабо представляю, хочешь упороть без палева пол района ? ) https://mynyc.ru Мне пока ещё не пришло, но ты уже напугал….:orientation: кто знает где весы купить можно чтоб граммы вешать
очень сложно дописаться до них=( а цены хорошие. https://vipis.ru единственная существенная проблема данного магазина – отсутствие автоматизированной системы оформления заказов… Вроде прикручивают к сайту, но что то долго уже…
жду пока ответят, обана повдер кинул на 29000….но прочитал и понял что магаз супер, жду в скайпе селлера! купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази А теперь к делу.. магаз ровный, товар ..вставляет епт..особенно в прошлый раз, пол часа ждал, что из ванной вылезет оно и покарает меня…хорошо быстро отпускает, а то вода остыла уже и сига стлела и хабарик упал так , что сам не заметил…
Плохует мягко сказано,уже больше пол месяца жду.Тебе кстати пришла? купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану пока двоих отпустили, в крови ничего не нашли.. ждем результатов экспертизы.
Fashion & Lifestyle Central – Explore stylish items that combine fashion sense with lifestyle comfort.
trafficgenius.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
clickcatalyst.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
adoptimizer.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
leadvelocity.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
если нет, то когда будет? купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки спасибо за внимание!
I was wondering if you ever considered changing the page layout of your site?
Its very well written; I love what youve got to say.
But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could
connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text
for only having one or two pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
Пару строк отписал паронойный напряг бы снял да дальше работал… https://rodichenkov.ru А в сочи есть магазины
ремонт варочных панелей renberg
35ф – индика весёлая , серьёзная , тошнатворного эффекта НЕТ хоть перекурись , сейчас беру 35 говорят сативка , будит возможность отпишу трип в красках , а вообще говорят что в симбиозе они лучше , но то что лучше / не сильнее / а именно лучше 25ф так это даже вы не сомневайтесь https://zhivouste.ru брал у данного магазине,все на высоте +
заживление ран
аланин аминокислота
Главное не кипишуй, продаван ровный, придет сам обрадуешся что тут затарился! купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки Отличный магазин брали.
карбон москва Тонировка Авто в Москве: Стиль и Комфорт Тонировка авто в Москве – это популярный способ улучшить внешний вид автомобиля и обеспечить комфорт вождения. Тонировка защищает салон от солнечных лучей и перегрева, а также обеспечивает приватность.
тонировка в москве Тюнинг Москва: Симфония Инженерии и Эстетики Москва, город динамики и амбиций, предъявляет особые требования к автомобилю. Тюнинг в Москве – это не просто смена облика, это глубокая трансформация, направленная на повышение производительности, улучшение управляемости и персонализацию до мельчайших деталей. В столичных мастерских создаются настоящие произведения искусства на колесах, сочетающие передовые технологии и безупречный стиль.
Да мне 5 сообщений для лс нужно :Dа так месяц назад было все ровно) купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки я звонил седня.сказали либо номер не правлеьный..либо не отправили еще
Автосервис BMW Мы гордимся своей репутацией надежного и профессионального автосервиса BMW в Москве. Наши клиенты ценят нас за высокое качество обслуживания, оперативность и индивидуальный подход. Мы постоянно повышаем квалификацию наших специалистов и следим за последними технологическими новинками в мире BMW. Мы уверены, что сможем удовлетворить даже самые высокие требования и предоставить вам лучший сервис для вашего автомобиля BMW. Свяжитесь с нами сегодня, чтобы записаться на обслуживание или получить консультацию наших специалистов. Мы всегда рады вам помочь!
кто не чувствует лица, купить онлайн мефедрон, экстази, бошки скорость доставки 5+ (во вторник заказали в пятницу получили)
шлюхи
adblaze.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Я, лично, в первый раз сделал заказ ,в этом магазине- оформил(по аське) его безналично,(что очень удобно для меня,даже из дома не выходил),сутки прошли,был дан трек,через два дня,посылка была у меня в городе.Следил за ее перемещением на сайте курьера(опять же-не выходя из дома). купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану мы и в скайп и в аське
rankdrive.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
ремонт двигателя москва Бронепленка в Москве: Максимальная Защита от Повреждений Бронепленка – это надежный щит для вашего автомобиля. В Москве установка бронепленки позволяет защитить кузов от царапин, сколов, гравия и даже незначительных ДТП. Это идеальное решение для тех, кто ценит свой автомобиль и хочет сохранить его в идеальном состоянии.
GammaLab Ремонт Двигателя Москва: Профессиональное Восстановление Ремонт двигателя в Москве – это комплексная услуга, включающая диагностику, дефектовку и восстановление работоспособности двигателя. Квалифицированные специалисты используют современное оборудование и оригинальные запчасти.
На сколько я знаю в этом магазине пока нет реги! https://segun42.ru тс, привет, ответь в лс. я по делу.
ремонт фризера для мороженого
замена уплотнителя двери посудомойки
\занимаюсь тестированием вместе с кролями в течении нескольких дней. Все никак не мог понять. https://skbagent.ru Магазин высший советаю брать только здесь Заказываю тоже 2 раз и собераюсь дальше работать.?
We are a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme
in our community. Your web site offered us with valuable information to work on. You’ve
done an impressive job and our entire community will be grateful to you.
торрент скачать Игры 2025 торрент – это видеоигры, выпущенные в 2025 году и доступные для скачивания через торрент-трекеры. Торрент-трекеры предлагают широкий выбор игр различных жанров и платформ, выпущенных в 2025 году. Скачивание игр 2025 торрент позволяет пользователям получить доступ к новым играм без необходимости их покупки или ожидания официального релиза. Однако важно помнить о рисках, связанных с пиратством, включая возможность заражения компьютера вредоносным программным обеспечением и нарушение авторских прав.
windows 10 торрент Русские фильмы торрент – это кинофильмы, произведенные в России и доступные для скачивания через торрент-трекеры. Торрент-трекеры предлагают широкий выбор русских фильмов различных жанров и годов выпуска, от классических хитов до последних новинок. Скачивание русских фильмов торрент позволяет пользователям смотреть фильмы на родном языке и поддерживать российскую киноиндустрию. Однако важно помнить о рисках, связанных с пиратством, включая возможность заражения компьютера вредоносным программным обеспечением и нарушение авторских прав.
Давненько вас не было) Если кто не в курсе, магаз уже был в топе доверенных. В те времена не раз заказывал у данного селлера, проблем не было ни разу. Надеюсь, сейчас все так же) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм когда вы зарядили?мои ребята зарядили вчера около 16-00 по мск ,минут за 15 до этого он добро дал и замолчал( переживаю очень так как отвечать мне.Я надеюсь лавочка не слилась с пацанскими деньгими… А то конкретная пичаль будет.У нас в регионе это большая сумма!!!
clickace.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Магазин работает на 5+++++, я уже раз 5 беру у данного сейлера все ровно все катит, качество на высоте! https://sevbuh92.ru оплачивай лучше через киви.самый лучший способ во всех магазах.и перевод идёт в секунду.только обрати внимание на комисию чтоб небыло недоплаты.обычно 2% от суммы перевода
Daily Deals Hub – Discover amazing bargains and save on products effortlessly.
Две дороги для Артёма, https://1cfashion.ru Челябинск работаете?
Жалко тест профукал ) купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Че все затихли что не кто не берет? Не кто не отписывает последние дни не в курилке не где везде тишина(
Montres repliques pour femmes Montre Style Luxe Replique : L’Illusion du Prestige a Petit Prix. La montre style luxe replique reproduit l’esthetique des montres les plus prestigieuses, offrant l’illusion du luxe a petit prix. Elle seduit par son design soigne, ses finitions elegantes et son apparence haut de gamme. Cependant, il est important de ne pas confondre l’imitation avec l’authenticite et de privilegier les repliques de qualite, respectueuses des droits de propriete intellectuelle.
Edle Replika Uhr Damen Uhr Replika – Damenuhren Replika sind ein Ausdruck von Weiblichkeit und Eleganz. Sie sind in einer Vielzahl von Designs erhaltlich, von zarten und filigranen Modellen bis hin zu auffalligen und glamourosen Uhren. Ob fur den taglichen Gebrauch, besondere Anlasse oder als modisches Accessoire, es gibt fur jede Frau die passende Replika Uhr. Diese Uhren unterstreichen die Personlichkeit und verleihen jedem Outfit den letzten Schliff.
Начинает формироваться мнение. купить Кокаин, Мефедрон, Экстази Друзья все четко и понятно. Адрес получил за 250 метров от кафе. Минеру респект и Благодуха. Даже фото не надо было. Вес и качество 10 из 10. Лучший кокаин, давно такого не встречал. Я ваш клиент. Очень понравилось.
Thank you for sharing your thoughts. I truly appreciate your efforts and I will be waiting for your further write ups thanks once again.
escort agencies and massage parlours in Brasilia
дом инвалидов москва Пансионаты для пожилых инвалидов с уходом: Специализированная помощь и поддержка Пансионаты для пожилых инвалидов с уходом – это специализированные учреждения, предлагающие профессиональную помощь и поддержку пожилым
пансионат для инвалидов в москве цены Организация по уходу за инвалидами: ваш надежный помощник в поиске подходящего учреждения Наша организация по уходу за инвалидами поможет вам найти подходящий дом инвалидов или пансионат, соответствующий вашим потребностям и запросам. Мы сотрудничаем с лучшими учреждениями в Москве и предлагаем широкий выбор вариантов проживания и ухода.
проститутка марина Проститутки Псков – отдаленный регион, добавляющий разнообразия географии запросов. Проститутки ели – вероятно, опечатка или часть фразы, требующая контекста. Частные проститутки Питер – акцент на конфиденциальности и независимости в Санкт-Петербурге. Рассказы проституток – интерес к личному опыту и историям из первых уст. Ест проститутке – вульгарное выражение, исключенное из лексикона. Проститутки гражданский – привязка к Гражданскому проспекту. Секс проститутки младше – указание на возрастные предпочтения. Проститутки пр – сокращение слова “проспект”. Фото проституток спб – поиск визуального контента по Санкт-Петербургу. Мама проститутка – сложная тема, вероятно, поиск информации или рассказов. Проститутку красносельском – район города. Проститутки трансы питер – транссексуалы в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки рыбацкое – район Рыбацкое. Проститутки красносельская – район Красносельский. Проститутки московский район – Московский район Санкт-Петербурга. Проститутки питера телеграм – использование Телеграм в Санкт-Петербурге для поиска. Проститутки ленинский – район Ленинский. Проститутки обл – сокращение от область, подразумевая Ленинградскую область. Проститутка со – неполная фраза, требующая дополнения. Сиськи проститутки – акцент на формах. Проститутки на карте – поиск по географическому расположению. Две проститутки – указание количества. Проститутки приезжающие – иногородние, предлагающие свои услуги. Проститутки 5 / 2 проститутки – числовые запросы, вероятно, возраст или количество. Дочь проститутка – сложные семейные отношения, возможен поиск информации или поддержки. Проститутка лен / лена – сокращенные имена или области. Проститутка усть / усть луга – регионы, расширение географического охвата. Адреса проституток – поиск конкретных мест. Проститутка лет питер – запросы по возрасту в Санкт-Петербурге.
старая проститутка снят Проститутки ли, вопрос или часть фразы. Проститутки Дыбенко, станция метро. Зрелые проститутки Питера, опытные женщины в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутка Приморско, возможно, Приморский район. Проститутки Приморский, Приморский район. Проститутки ебло, грубое выражение. Ебал проститутку, вульгарное выражение. Ебут проститутку, грубое выражение. Проститутки в годах, зрелые. Проститутки Всеволожск, город Всеволожск. Трахает проститутку, вульгарное выражение. Частные проститутки СПб, независимые в СПб. Индивидуальные проститутки, независимые. Сколько проститутку, вопрос о цене. Нея проститутка, отрицание. Проститутки на дом, вызов на дом. Часы проститутка, почасовая оплата. Проститутки Парнас, район Парнас. Проститутки 18, возраст. Большего проститутка, неясная фраза.
Так может не ждать у моря погода, а взять и самому написать менеджеру в аську/почту и получить уже эти реквизиты? https://segun42.ru о господи 😀 я не селлер – я просто зашёл на сайт и посмотрел что есть в ассортименте – из скоростей нормальных разве что..кхм, оно…
Всем привет с наступивщими,давно не работал с этим магазином,подскажите как у него работа все ттакже четко? https://skbagent.ru Магаз ровный, сам лично несколько раз здесь заказывал и все доходило вовремя и целостно!:) Наврятли он решится на такое..
clickwaveagency.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Бро все супер,как всегда ровно,спасибо за прекрасно отлаженную работу. Процветания тебе и твоей команде.Спасибо! https://allfur.ru качество реги просто супер,такого еще не встречали
Trend Explorer Daily – Easily navigate popular categories and find trendy items quickly.
discountcentralhub – Found exactly what I needed at reasonable rates.
Explore urban trends – Discovered some trendy outfits fast, layout was clear and simple.
adspectrum.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Wow, superb blog format! How long have you ever been running a blog for? you make blogging glance easy. The total look of your web site is wonderful, let alone the content!
https://lummi.com.ua/sklo-fary-dlya-bi-led-linz-vymohy-do.html
clicklegends.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
seotitan.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
заказ в статусе обработки ))) купить кокаин, меф, бошки через телеграмм Ага, прям именно так. Но все же?)))))
seoaccelerate.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Hi, this weekend is fastidious in support of me, as this point in time i am reading this fantastic informative paragraph here at my residence.
https://footballfans.com.ua/korpus-fary-chevrolet-captiva-anatomiya.html
напрягает долгое молчание продовца на переписку,возможно занят. https://24sema.ru я тут походу единственный кто остался недоволен.(
оформил заказ жду. продавец общительный https://kinotyr.ru да и оперативность У ВАС на ВЫСШЕМ :superman: уровне!!
пансионат для инвалидов москва Пансионаты для пожилых инвалидов с уходом: Специализированная помощь и поддержка Пансионаты для пожилых инвалидов с уходом – это специализированные учреждения, предлагающие профессиональную помощь и поддержку пожилым
москва дом инвалидов платный Пансионат по уходу за инвалидами: профессиональная помощь и поддержка 24/7 Пансионат по уходу за инвалидами – это специализированное учреждение, обеспечивающее круглосуточную профессиональную помощь и поддержку людям с ограниченными возможностями. Наши опытные и квалифицированные сотрудники готовы оказать любую необходимую помощь, включая гигиенические процедуры, кормление, прием лекарств, а также психологическую поддержку.
discounttreasure – Loved the bargains, everything was priced perfectly.
Shop urban fashion – Quickly spotted a handful of stylish pieces, navigation effortless.
За АМ 1220 ничего сказать не могу – не пробовал…. Но, после тестирования 694 и 2201 впечатления о линейке АМ у меня сильно подпортились ( купить скорость, кокаин, мефедрон, гашиш Самый лучший магаз, заказываю и не парюсь
brightdealcorner – Pleasant shopping experience, found exactly what I wanted.
МХЕ “как у всех” тобиш бодяжный.. Вроде скоро должна быть нормальная партия. https://klimomsk.ru Самые положительные впечатления оставляет по прежнему Мажор. 🙁 Джой фулл, а тебе когда отправили?
Montre replique Montre Replique Automatique : Le Charme de la Mecanique Horlogere a Petit Prix ? La montre replique automatique permet de decouvrir le charme de la mecanique horlogere sans pour autant payer le prix fort. Elle offre la possibilite d
Realistische Uhrenreplika Hochwertige Uhrenreplika: Qualitat im Fokus Hochwertige Uhrenrepliken zeichnen sich durch die Verwendung erstklassiger Materialien und eine sorgfaltige Verarbeitung aus. Edelstahl, Saphirglas und prazise Uhrwerke sind typische Merkmale. Diese Repliken sind darauf ausgelegt, dem Original so nahe wie moglich zu kommen und eine lange Lebensdauer zu gewahrleisten. Sie bieten eine zuverlassige Zeitmessung und sind widerstandsfahig gegen au?ere Einflusse. Eine Investition in eine hochwertige Uhrenreplika ist eine Investition in Stil und Langlebigkeit.
в смысле пропал из онлайна??? и что делать теперь? треки то до сих пор небьються https://anyutacvety.ru Урб 597 либо перорально либо нозально, дозировка – 5-10мг, эффекты описаны в энциклопедии,
joyfulgiftshub – Great gift ideas, site is very easy to browse.
Urban style collection – Several attractive finds popped up immediately, navigation effortless.
в подписи ТС смотри контакты) https://art-tavrida.ru Схема кидка: В пм на форуме вы получаете от магазина номер киви а он в жабер подтверждает Ваше кодовое слово. После чего диалог идет по жаберу. У Вас оказывается что на данный киви невозможно положить деньги и магазин пишет что даст другой номер. Всё вы закинули сами не туда. Что собственно мне и отписал магазин в пме.
modacollection – Really liked the assortment, checkout was seamless and quick.
brightdealhub – Smooth browsing experience and quick ordering.
Взял в Москве, ну что могу сказать, или толерантность спала(месяц не курил), или товар лютый, но убрало с первого раза хорошо, потом прикурился, ничего так. купить Мефедрон, Бошки, Марихуану ОО мне то же все пришло!
скачать чикен роад https://kurica2.ru/ .
помощь курсовые kupit-kursovuyu-1.ru .
Дом из клееного бруса Строительство дома из клееного бруса подразумевает тщательную подготовку и точное соблюдение технологических процессов. Начиная с разработки проекта, учитывающего особенности ландшафта и пожелания заказчика, и заканчивая финальной отделкой, каждый этап контролируется специалистами. Благодаря этому, дом из клееного бруса не только красив, но и обладает отличными эксплуатационными характеристиками. Дом из клееного бруса – это символ уюта и гармонии. Естественная текстура дерева, приятный аромат и ощущение тепла создают неповторимую атмосферу, в которой хочется жить и наслаждаться каждым моментом. Клееный брус позволяет реализовывать любые дизайнерские задумки, от классики до модерна, подчеркивая индивидуальность владельца.
Строительство из клееного бруса Строительство дома из клееного бруса подразумевает тщательную подготовку и точное соблюдение технологических процессов. Начиная с разработки проекта, учитывающего особенности ландшафта и пожелания заказчика, и заканчивая финальной отделкой, каждый этап контролируется специалистами. Благодаря этому, дом из клееного бруса не только красив, но и обладает отличными эксплуатационными характеристиками. Дом из клееного бруса – это символ уюта и гармонии. Естественная текстура дерева, приятный аромат и ощущение тепла создают неповторимую атмосферу, в которой хочется жить и наслаждаться каждым моментом. Клееный брус позволяет реализовывать любые дизайнерские задумки, от классики до модерна, подчеркивая индивидуальность владельца.
Urban fashion hub – A few standout styles appeared instantly, very easy to explore.
Дом из клееного бруса проекты и цены Дом из клееного бруса цена – зависит от множества факторов, включая площадь, сложность проекта, используемые материалы и внутреннюю отделку. Однако, в целом, дом из клееного бруса является выгодным вложением средств, учитывая его долговечность, энергоэффективность и экологичность. Проекты домов из клееного бруса – это широкий выбор архитектурных решений, от небольших дачных домиков до просторных коттеджей. Индивидуальный проект позволяет учесть все особенности участка и пожелания заказчика, создавая уникальное и функциональное пространство для жизни. Дом из клееного бруса цена под ключ – это фиксированная стоимость строительства, включающая все работы и материалы, необходимые для ввода дома в эксплуатацию. Это удобный и надежный способ получить готовое жилье без лишних хлопот и неожиданных расходов.
Строительство дома из клееного бруса Дом из клееного бруса проекты и цены – это сочетание функциональности и рациональности. Разнообразие проектов позволяет выбрать оптимальный вариант, учитывая финансовые возможности и личные предпочтения. Прозрачное ценообразование и возможность поэтапной оплаты делают строительство дома из клееного бруса доступным для широкого круга людей.
Browse latest fashion – Found a couple of eye-catching picks fast, very user-friendly.
Zooma казино Зума Казино – это не просто платформа для азартных игр, это целая вселенная развлечений, где адреналин смешивается с возможностью крупного выигрыша. Мы создали уникальное пространство, где каждый игрок, независимо от опыта, сможет найти что-то для себя. От классических слотов до самых современных игр с живыми дилерами – в Зума Казино собрана впечатляющая коллекция развлечений, способная удовлетворить даже самых взыскательных ценителей азарта. Зума официальный канал – это ваш проводник в мир Зума Казино. Здесь вы найдете актуальную информацию о новых играх, щедрых акциях, эксклюзивных турнирах и розыгрышах ценных призов. Подписывайтесь на наш канал, чтобы всегда быть в курсе последних событий и первыми узнавать о самых выгодных предложениях. Мы делимся стратегиями выигрышей, обзорами игр и советами от профессиональных игроков, помогая вам повысить свои шансы на успех. Зума – это синоним честности, надежности и безопасности. Мы используем самые современные технологии защиты данных, чтобы обеспечить конфиденциальность и безопасность ваших транзакций. Наша лицензия гарантирует соответствие самым высоким стандартам индустрии азартных игр, а круглосуточная служба поддержки всегда готова ответить на ваши вопросы и помочь решить любые возникшие проблемы. Zooma казино – это ваш шанс испытать удачу и сорвать крупный куш, не выходя из дома. Наша платформа адаптирована для всех устройств, будь то компьютер, смартфон или планшет. Играйте в любимые игры в любое время и в любом месте, наслаждаясь яркой графикой, захватывающим геймплеем и невероятными возможностями для выигрыша. Присоединяйтесь к Зума Казино сегодня и откройте для себя мир азарта, который превзойдет все ваши ожидания!
Top fashion picks – Several eye-catching items popped up instantly, browsing enjoyable.
услуги эвакуатора Эвакуатор Таганрог – это не просто служба экстренной помощи на дорогах, это ваш надежный союзник в любой ситуации, когда автомобиль становится неподвижным. Мы понимаем, насколько стрессовым может быть момент поломки или ДТП, и поэтому предлагаем быстрый, профессиональный и бережный подход к эвакуации вашего транспортного средства. Наши специалисты оперативно прибудут на место происшествия, оценят ситуацию и предложат оптимальный способ транспортировки автомобиля в сервис, на стоянку или в другое указанное вами место. Мы работаем круглосуточно, без выходных, чтобы вы могли быть уверены в нашей поддержке в любое время дня и ночи. Эвакуатор в Таганроге – это необходимость для каждого автовладельца, ведь внезапная поломка или авария может произойти в самый неподходящий момент. Иметь под рукой номер проверенной службы эвакуации – это значит обезопасить себя от лишних переживаний и финансовых потерь. Мы гарантируем быструю подачу эвакуатора в любой район города и пригорода, а также аккуратную и безопасную транспортировку вашего автомобиля. Эвакуатор – это сложная техника, требующая профессионального управления и знания особенностей различных типов транспортных средств. Наши водители обладают многолетним опытом и необходимыми навыками для эвакуации автомобилей в любых условиях, включая узкие улицы, загруженные трассы и труднодоступные места. Мы используем современные эвакуаторы, оснащенные всем необходимым оборудованием для обеспечения безопасной и эффективной транспортировки вашего автомобиля. Эвакуатор в Таганроге дешево – это реально, когда вы обращаетесь к нам. Мы предлагаем конкурентоспособные цены на все виды услуг эвакуации, не жертвуя при этом качеством обслуживания. Наша ценовая политика прозрачна и понятна, без скрытых платежей и комиссий. Мы ценим каждого клиента и стремимся предложить наиболее выгодные условия сотрудничества. Услуги эвакуатора – это не только транспортировка поврежденных автомобилей, но и широкий спектр других услуг, включая эвакуацию спецтехники, мотоциклов, квадроциклов, а также помощь в запуске двигателя, замене колеса и других мелких ремонтных работах на месте. Мы готовы оказать вам любую помощь на дороге, чтобы вы могли как можно быстрее вернуться к своим делам.
эвакуатор в таганроге Эвакуатор Таганрог – это не просто служба экстренной помощи на дорогах, это ваш надежный союзник в любой ситуации, когда автомобиль становится неподвижным. Мы понимаем, насколько стрессовым может быть момент поломки или ДТП, и поэтому предлагаем быстрый, профессиональный и бережный подход к эвакуации вашего транспортного средства. Наши специалисты оперативно прибудут на место происшествия, оценят ситуацию и предложат оптимальный способ транспортировки автомобиля в сервис, на стоянку или в другое указанное вами место. Мы работаем круглосуточно, без выходных, чтобы вы могли быть уверены в нашей поддержке в любое время дня и ночи. Эвакуатор в Таганроге – это необходимость для каждого автовладельца, ведь внезапная поломка или авария может произойти в самый неподходящий момент. Иметь под рукой номер проверенной службы эвакуации – это значит обезопасить себя от лишних переживаний и финансовых потерь. Мы гарантируем быструю подачу эвакуатора в любой район города и пригорода, а также аккуратную и безопасную транспортировку вашего автомобиля. Эвакуатор – это сложная техника, требующая профессионального управления и знания особенностей различных типов транспортных средств. Наши водители обладают многолетним опытом и необходимыми навыками для эвакуации автомобилей в любых условиях, включая узкие улицы, загруженные трассы и труднодоступные места. Мы используем современные эвакуаторы, оснащенные всем необходимым оборудованием для обеспечения безопасной и эффективной транспортировки вашего автомобиля. Эвакуатор в Таганроге дешево – это реально, когда вы обращаетесь к нам. Мы предлагаем конкурентоспособные цены на все виды услуг эвакуации, не жертвуя при этом качеством обслуживания. Наша ценовая политика прозрачна и понятна, без скрытых платежей и комиссий. Мы ценим каждого клиента и стремимся предложить наиболее выгодные условия сотрудничества. Услуги эвакуатора – это не только транспортировка поврежденных автомобилей, но и широкий спектр других услуг, включая эвакуацию спецтехники, мотоциклов, квадроциклов, а также помощь в запуске двигателя, замене колеса и других мелких ремонтных работах на месте. Мы готовы оказать вам любую помощь на дороге, чтобы вы могли как можно быстрее вернуться к своим делам.
Browse latest fashion – Found a couple of eye-catching picks fast, very user-friendly.
Зума офицальный канал Зума Казино – это калейдоскоп азартных возможностей, тщательно выстроенный мир, где каждый элемент служит для создания захватывающего и щедрого опыта. Мы предлагаем не просто ставки, а погружение в уникальную атмосферу, наполненную драйвом, стратегией и, конечно же, манящим предвкушением крупного выигрыша. От винтажных слотов, напоминающих о золотой эре Лас-Вегаса, до инновационных игр с живыми дилерами, транслируемых в прямом эфире, – наш арсенал развлечений удовлетворит даже самого искушенного игрока. Бонусы, акции и программа лояльности становятся приятным дополнением к захватывающему игровому процессу, увеличивая ваши шансы на успех и продлевая удовольствие от игры. Зума официальный канал – это ваш компас в постоянно расширяющейся вселенной Зума Казино. Здесь вы найдете эксклюзивные анонсы, инсайдерские секреты, обзоры новых игр и полезные советы от гуру азарта. Подписывайтесь, чтобы быть в курсе самых выгодных предложений, участвовать в розыгрышах и первыми узнавать о грядущих турнирах с внушительными призовыми фондами. Мы раскроем вам тайны прибыльной игры и научим правильно распоряжаться своим банкроллом. Зума – это символ честности, прозрачности и ответственного подхода к азартным играм. Мы используем передовые технологии шифрования, чтобы обеспечить безопасность ваших данных и финансовых операций. Наша лицензия является гарантией соблюдения строгих стандартов индустрии, а квалифицированная служба поддержки всегда готова оказать помощь и ответить на любые ваши вопросы. Мы верим, что азарт должен приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Zooma казино – это ваш шанс испытать триумф, не покидая уютного кресла. Наша платформа оптимизирована для бесперебойной работы на любом устройстве, будь то компьютер, планшет или смартфон. Наслаждайтесь великолепной графикой, захватывающим геймплеем и мгновенными выплатами в любое время и в любом месте. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу победителей и откройте для себя Zooma казино – мир, где мечты об огромных выигрышах становятся реальностью!
Этот материал посвящен обзору возможностей платформы Vavada. Мы рассматриваем актуальные преимущества и способы безопасного входа. Рабочие зеркала позволяют сохранять доступ даже при ограничениях. Пользователи отмечают высокую стабильность и широкий выбор игр. Подробности и актуальная ссылка доступны здесь: Вавада. Следите за обновлениями и играйте ответственно.
Этот материал посвящен обзору возможностей платформы Vavada. Мы рассматриваем актуальные преимущества и способы безопасного входа. Рабочие зеркала позволяют сохранять доступ даже при ограничениях. Пользователи отмечают высокую стабильность и широкий выбор игр. Подробности и актуальная ссылка доступны здесь: казино вавада. Следите за обновлениями и играйте ответственно.
Quick fashion finds – A handful of crisp items appeared right away, navigation smooth.
Urban trend finds – Several standout options appeared right away, browsing easy.
геронтология москва Геронтологический центр – это специализированное учреждение, оказывающее комплексную помощь пожилым людям. Здесь проводятся диагностика, лечение и реабилитация возрастных заболеваний, а также предоставляется уход и социальная поддержка. Геронтологический центр может функционировать как самостоятельное учреждение или как отделение в составе многопрофильной больницы.
больница для престарелых Геронтологическое отделение в больнице предоставляет специализированную медицинскую помощь пожилым пациентам, учитывая их возрастные особенности. Здесь работают специалисты, имеющие опыт работы с пожилыми людьми и знающие особенности их здоровья.
снять девушку на час нижневартовск
Shop trendy outfits – Some standout pieces were instantly visible, browsing simple.
самое надежное казино Выбор «лучших онлайн казино» — это не однодневная задача. Это процесс, в котором важно сочетать умение анализировать факты и доверять своему опыту. Лицензия, безопасность, прозрачные условия бонусов, широкий выбор игр и удобные платежи создают основу. Но каждое ваше решение формирует ваш уникальный маршрут — от первого знакомства с площадкой до долгосрочного удовольствия от игры.
онлайн казино играть Хотите играть в казино, где надежность сочетается с мгновенным выводом? Вы нашли то, что искали! Мы предлагаем лучшие площадки, где ваши деньги в безопасности, а получение выигрышей происходит максимально быстро. Играйте с уверенностью!
гериатрические услуги Гериатрический центр, в свою очередь, специализируется на проблемах старения и болезнях пожилого возраста. Ключевой акцент делается на профилактику, раннее выявление и эффективное лечение гериатрических синдромов, таких как деменция, саркопения, остеопороз и другие. Врачи-гериатры обладают глубокими знаниями в области возрастных изменений и умеют разрабатывать индивидуальные планы лечения для каждого пациента.
геронтологический центр в москве для пожилых людей что это Гериатрический центр, в свою очередь, специализируется на проблемах старения и болезнях пожилого возраста. Ключевой акцент делается на профилактику, раннее выявление и эффективное лечение гериатрических синдромов, таких как деменция, саркопения, остеопороз и другие. Врачи-гериатры обладают глубокими знаниями в области возрастных изменений и умеют разрабатывать индивидуальные планы лечения для каждого пациента.
Check this style collection – Found several appealing fashion picks quickly, browsing was smooth.
ко ланта ко лант
SoftStone Goods – Great assortment, browsing was easy, and shipping arrived on schedule.
ко ланта ко лант
conversionforce.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
promoseeder.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Soft Cloud Highlights – Browsing feels effortless and items are displayed clearly.
khao555 slot
timelessharborhubstore – Pleasant layout with clearly displayed items and quick navigation.
????? pg
New Ideas Daily – Explore creative strategies to inspire and energize your day.
Khao555 Online
khao555 casino online
harmonyhub – Site is easy to navigate, products were simple to locate.
2 bs2best at
Focus & Flourish Hub – Ideas and exercises to stay intentional and achieve steady progress.
бляди нижневартовска
seoigniter.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
снять проститутку транса
https m bs2web at
ко ланта где лучше жить
Trendy Outfit Ideas – Discover combinations and pieces that make styling easy.
продажа штыревых лесов Леса повышенной безопасности: Леса повышенной безопасности – это конструкции, разработанные с учетом повышенных требований к безопасности и надежности. Они отличаются от обычных лесов использованием более прочных материалов, усиленной конструкцией и дополнительными элементами безопасности, такими как страховочные сетки, перила и ограждения. Леса повышенной безопасности применяются на объектах, где существует повышенный риск падения рабочих или материалов, а также в условиях сложных климатических условий. Использование лесов повышенной безопасности позволяет значительно снизить риск несчастных случаев на строительной площадке.
?????????
остров ланта таиланд на карте
Mindset Mastery – Guidance to improve mindset and stay motivated consistently.
trafficbuilderpro.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
lucky88
букмекерские конторы Выбор надежной букмекерской конторы – это фундамент успешного беттинга. Букмекерские конторы различаются по коэффициентам, линии, наличию бонусов и промоакций, удобству интерфейса и надежности выплат. Перед тем, как сделать ставку, необходимо тщательно изучить репутацию букмекерской конторы, ознакомиться с отзывами пользователей и убедиться в наличии лицензии. Для принятия обоснованных решений в ставках на спорт необходимо обладать актуальной информацией и аналитическими данными. Прогнозы на баскетбол, прогнозы на футбол и прогнозы на хоккей – это ценный инструмент, позволяющий оценить вероятности различных исходов и принять взвешенное решение. Однако, стоит помнить, что прогнозы – это всего лишь вероятностные оценки, и они не гарантируют стопроцентный результат.
Trend Picks Hub – Browse stylish products with a smooth and efficient shopping experience.
новости о ставках на спорт Ставки на спорт – это азартное развлечение, требующее аналитического подхода и понимания стратегий. Современный мир беттинга предлагает широчайший выбор возможностей: от классических видов спорта до киберспорта и экзотических дисциплин. Однако, важно помнить, что успех в ставках на спорт – это не только удача, но и результат кропотливого анализа, изучения статистики и учета множества факторов.
Daily Chic Hub – Curated collections to inspire your daily style choices.
https://pro-dacha.com/2025/08/21/kak-podgotovit-pochvu-pered-posevom-gazonnoy-travy-20250821.html
заказать девушку спб Снять шлюху СПб: Предлагаем забыть о стереотипах и насладиться обществом образованной и уверенной в себе женщины, которая знает, как доставить удовольствие.
ортофосфорная кислота оптом Индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту: эксперты РТХ подберут оптимальные решения, соответствующие вашим уникальным потребностям и спецификациям производства
Smart Savings Corner – Tips and deals to help you shop wisely without overspending.
Khao555 com
skyiwredshjnhjgeleladu7m7mgpuxgsnfxzhncwtvmhr7l5bniutayd.onion
https://vseokrovle.com/besedka/2115-chem-otlichayutsya-odnoletnie-i-mnogoletnie-travy-dlya-gazona.html
shop horizon picks – Items were easy to view and layout was clear.
tallbirchstore – Very easy to browse, and products are displayed clearly.
Your Trend Explorer – Discover stylish items while enjoying a seamless browsing experience.
timberlineprojects – Smooth browsing experience with clearly arranged content inspires creativity.
ForestHavenGoods – Clean design, shopping feels effortless and enjoyable.
сауна с проститутками спб Заказать шлюху СПб: Забудьте о предрассудках и позвольте себе насладиться обществом привлекательной и интеллектуальной девушки, которая дополнит ваш вечер яркими красками.
снять проститутку города нижневартовска
Timber Outlet Hub – A very straightforward layout that made exploring different items feel easy.
??????????
стоимость натяжного потолка Навесной потолок: Современное решение для стильного интерьера Навесной потолок – это универсальное решение для создания современного и функционального интерьера. Он позволяет скрыть недостатки базового потолка, проложить коммуникации и установить встроенное освещение. Существует множество видов навесных потолков, отличающихся по материалу, дизайну и функциональности, что позволяет подобрать оптимальный вариант для любого помещения.
birchcornerstore – Products are logically arranged, making exploration simple.
shop horizon boutique – Smooth scrolling and fast pages made finding items simple.
Морская прогулка в Ялте Лучшие экскурсии в Ялте: Рейтинг самых интересных маршрутов Ливадийский дворец, Ай-Петри, Массандровский дворец, Никитский ботанический сад – это лишь некоторые из жемчужин Ялты, которые стоит посетить. Каждая из этих достопримечательностей имеет свою уникальную историю и предлагает незабываемые впечатления. Выберите экскурсию, которая соответствует вашим интересам, и отправляйтесь в увлекательное путешествие!
https blsp at check
??????????????????????????
growselection – Products are easy to find, and the site feels intuitive.
shop urban path – Fast-loading pages and intuitive navigation enhanced the experience.
willow finds – Fast pages and tidy layout made exploring products effortless.
Timber Cozy Shop – Browsing was calm and intuitive thanks to the uncluttered page structure.
bs2best at ссылка
https://tvarkaubiurus.lt/
choice corner – Fast-loading pages and neat categories made browsing enjoyable.
willow picks hub – Fast interface and clean layout made shopping enjoyable.
новые бездепозитные бонусы в казино 2020 вк quot
Coastal Ridge Picks – Simple to explore, with items neatly organized.
в казино за регистрацию с выводом
ветеринарная клиника адлер круглосуточно Ветеринарная клиника Сочи круглосуточно: Оперативная помощь без промедления Если вашему питомцу требуется неотложная помощь, круглосуточная ветеринарная клиника в Сочи – это оптимальное решение.
женские ботильоны кожа Женская обувь на устойчивом каблуке – комфорт и уверенность в каждом шаге, идеальный выбор для активного образа жизни. Женские босоножки на каблуке – идеальны для создания элегантного летнего образа, подчеркивают стройность ног и придают уверенности.
evermeadowgoods – Great selection and intuitive navigation helped me explore products without hassle.
женская обувь из турции интернет магазин Модная обувь для женщин – это не просто защита для ног, а способ выразить свою индивидуальность и следовать последним трендам.
Check Out The Gallery – A very pleasant shopping session was had due to the uncluttered layout.
женская обувь с возможностью примерки Женская обувь на устойчивом каблуке – комфорт и уверенность в каждом шаге, идеальный выбор для активного образа жизни. Женские босоножки на каблуке – идеальны для создания элегантного летнего образа, подчеркивают стройность ног и придают уверенности.
новые бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в игровых
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения и без вейджера 1000
новые бездепозитные бонусы в казино 2025
Explore the Collection – A logical layout guided me directly to interesting items I hadn’t considered.
аренда штыревых строительных лесов аренда горизонтальных строительных лесов
ии презентация онлайн
как найти удаленную работу Фриланс: свобода и независимость. Фриланс – это отличный вариант для тех, кто ценит свободу и независимость. Биржи фриланса предлагают множество заказов для копирайтеров, дизайнеров, программистов и других специалистов.
brightwillowboutique – Clean design and easy layout helped me find interesting items fast.
онлайн работа бесплатно Удаленная работа ВКонтакте: социальные сети на службе карьеры. ВКонтакте предлагает множество групп и сообществ, где публикуются вакансии для удаленной работы. Это отличная платформа для поиска работы онлайн, особенно для тех, кто ищет возможности для работы в социальных сетях.
удаленная работа вк копирайтер вакансии удаленная работа
вакансии удаленная работа Удаленка: работа из любой точки мира. Удаленная работа позволяет вам работать из любой точки мира, где есть интернет.
SoftMorning Home – I was immediately impressed by the high-quality visuals and clean site structure.
паспорта без казино
казино онлайн список
топ 10 казино
праздники мы тоже отдыхали, так как курьерки все равно не работают https://vseofiltrah.ru например тут ну или накрайняк тут а селлер совершенно не обязан консультировать по применению хим. реактивов.Я подозреваю, что его посылку спалили на наличие и теперь просто не отправляют.
казино без верификации и паспорта с выводом выигрышей
топ 10 казино
топ 10 честных казино на деньги
мебель на заказ по индивидуальным проектам Встраиваемые шкафы на заказ недорого: Получите качественный и функциональный встроенный шкаф на заказ по доступной цене! Мы предлагаем широкий выбор материалов и индивидуальный подход.
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино
новые бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино
шкаф купе недорого на заказ Встраиваемые шкафы в прихожую на заказ: Оптимизируйте пространство в прихожей с помощью встроенных шкафов, которые идеально впишутся в интерьер и обеспечат удобное хранение вещей.
https://lifeisfeudal.com/Discussions/question/vbaebgreagbrgregre
https://igrosoft.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=48&t=7929
https://bookmeter.com/books/12419360
https://buscamed.do/ad/pgs/?el_codigos_promocionales_1xbet_bono_gratis.html
Золотые слова. https://roll-n-roll.ru работаете качественно и по совести!так держать!Срач, оффтоп, провокации, в ветке магазина запрещены, буду банить за невыполнение правил!
https://www.bf-mechta.ru/wp-content/pages/promokod_1xbet_na_segodnya_pri_registracii.html
вызвать шлюху нижневартовск
http://www.mathforum.ru/gitweb/pgs/bk_melbet_bezdepozitnuy_bonus___est__ili_net_.html
https://rightadvisors.com/pages/1xbet_bangladesh_promo_code_for_registration_1.html
Thanks for some other wonderful article. The place else may anybody get that kind of information in such an ideal approach of writing? I have a presentation subsequent week, and I am on the look for such info.
forticlient mac download
This text is invaluable. How can I find out more?
forticlient mac
ремонт айфона 10
новые бездепозитные бонусы в казино
ремонт телефонов область[/url
как играть на бонус казино в 1win
https://www.behance.net/melbetofthebest
https://telegra.ph/C%C3%B3digo-de-bono-MelBet-2026-ZEVS777-12-05
http://sampikrp.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?t=3149
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения 2025
как использовать бонус казино в 1win
https://www.nurseheroeshospital.com/profile/tahotim50643345/profile
Simply desire to say your article is as astonishing. The clearness in your post is simply great and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work.
Qfinder Pro
https://ok-social.com/story6260923/1xbet-sports-welcome-code-130-bonus
https://mf.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=14&t=2708
SimpleTreasureShop – Products are attractive and browsing experience was comfortable.
бездепозитные бонусы в казино с выводом
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом денег без первого депозита и без отыгрыша
ремонт айфонов
ремонт телефонов рядом
в каком казино дают бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию
что такое бонус казино в 1win
бездепозитные бонусы в казино онлайн
http://distengl.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=1742
https://lambocyber.ru/2019/04/22/clout/#comment-71412
https://bulkwp.com/support-forums/users/melbetwikipro78/
https://suzuri.jp/bayimi3519
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом денег без первого депозита и без отыгрыша
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом денег без первого депозита и без отыгрыша
https://t.me/s/azino777casinomobile
azino777 официальный сайт мобильная версия зеркало рабочее Азино 777 – это популярная онлайн-платформа, предлагающая широкий выбор азартных игр, включая игровые автоматы, карточные игры и рулетку. Пользователям доступны как бесплатные демо-версии, так и игры на реальные деньги.
азино 777 официальный сайт рабочее зеркало на сегодня Ищете место, где азарт и возможность крупного выигрыша встречаются с щедрыми бонусами? Тогда вам стоит обратить внимание на Азино 777! Это популярное онлайн-казино предлагает своим игрокам захватывающий мир слотов, настольных игр и, конечно же, привлекательные бонусы, которые делают игру еще более интересной и выгодной.
азино 777 официальный Азино 777 – это не просто казино, это место, где каждый может испытать свою удачу и получить незабываемые эмоции. Благодаря официальному сайту и надежным зеркалам, вы всегда будете иметь доступ к любимым играм и сможете воспользоваться всеми преимуществами щедрых бонусов. Начните свое приключение в мире азарта уже сегодня!
https://supplyautonomy.com/codexbet1.tj
https://roughstuffmedia.activeboard.com/t72349889/promo-code-for-1xbet-1xlux777-130-simple-code/?page=1#lastPostAnchor
https://www.maanation.com/codeXBET1
I blog quite often and I truly thank you for your content. This article has really peaked my interest. I am going to take a note of your website and keep checking for new details about once per week. I subscribed to your Feed as well.
Escort directory listing Brazil
https://buzzakoo.com/blogs/82841/C%C3%B3digos-Promocionales-Secretos-1xBet-2026
http://4asdaiprognoza.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=6978
https://pentvars.edu.gh/pentecost-university-abe-students-to-get-top-up-degrees-at-the-university-of-hertfordshire-uk/
https://primocollect.com.ua/img/pages/index.php?obustraivaem_kvartiru.html
Vavada platform offers a user-friendly interface and quick access to favorite games. At https://museo.precolombino.cl/ you’ll find working Vavada mirrors and fresh promo codes for today. Account funding at Vavada is available through various methods, including cards and e-wallets. The Vavada mobile version is adapted for any screen size. Players praise the stability and fairness of Vavada gaming process.
Vavada platform offers a user-friendly interface and quick access to favorite games. At https://museo.precolombino.cl/ you’ll find working Vavada mirrors and fresh promo codes for today. Account funding at Vavada is available through various methods, including cards and e-wallets. The Vavada mobile version is adapted for any screen size. Players praise the stability and fairness of Vavada gaming process.
https://www.benzclub.ru/forum/post.php?mode=post&f=237
http://forum.galich44.ru/forum/post.php?mode=post&f=1450
https://code-promo-1765101221-1400.jimdosite.com
http://satway.ru/club/community/post.php?mode=post&f=4575
Купить права – это важный шаг для тех, кто хочет получить официальное водительское удостоверение и начать уверенно управлять автомобилем. Наша компания предлагает надежные и быстрые способы приобретения водительских прав, соответствующих всем требованиям законодательства. Мы поможем вам пройти обучение в лучших автошколах, подготовиться к теоретическим и практическим экзаменам, а также оформить все необходимые документы без лишних хлопот. У нас вы найдете выгодные предложения, профессиональных инструкторов и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту. Если вы хотите купить права с гарантией качества и по доступной цене, обращайтесь к нам – мы сделаем процесс максимально простым и удобным.
stamp price guide
stamp price guide
Hello.
This post was created with XRumer 23 StrongAI.
Good luck 🙂
http://gzew.phorum.pl/viewtopic.php?p=525875#525875
https://sngine-chatnet.oncodes.com/blogs/39316/Code-promo-MelBet-ZEVS777-Pari-gratuit-de-130
https://forum.banknotes.cz/viewtopic.php?t=218071
http://brofordwiki.ru/index.php?title=%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%20%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%20%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8%201xbet%20%D0%BD%D0%B0%20%D1%81%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%BD%D1%8F
http://www.senbernar.ru/profile/16909-entitycell/?tab=field_core_pfield_11
https://my.dev.vanderbilt.edu/tractem/getting-started/preprocessing/
http://www.birulevo.su/component/option,com_smf/Itemid,34/topic,28205.0/
http://w202club.com/forum/post.php?mode=post&f=1052
http://legendaroleplay.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=46&t=246
Фриспины казино Мир игровых автоматов поражает своим разнообразием! Здесь вы найдете всё: от простых и понятных фруктовых слотов до сложных многоуровневых игр с захватывающими сюжетами и уникальными бонусными раундами. Каждый автомат – это отдельная история, своя атмосфера и свои правила игры. Исследуйте новые миры, собирайте комбинации и наслаждайтесь процессом, ведь в игровых автоматах возможно всё!
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом Как найти “то самое” онлайн-казино? Рейтинги знают ответ! Задумывались ли вы, как отличить хорошее онлайн-казино от посредственного? Ответ прост – рейтинги казино. Они систематизируют информацию и помогают игрокам быстро понять, где стоит играть, а где лучше пройти мимо. Изучите актуальные рейтинги и сделайте свой выбор осознанно!
10 советов по выбору специалиста по ремонту: как не ошибиться
your daily journey – Items are visually appealing, navigation feels smooth and natural.
https://t.me/getx_site_official
https://t.me/getx_site_official
https://t.me/getx_site_official
https://t.me/getx_site_official
https://www.tellmfg.com/solutions/commercial-construction/lc2600-series-lock
https://www.bing-directory.com/education/business_to_business/
https://wordpress.lehigh.edu/too223/2020/05/07/chopsticks/comment-page-60/#comment-37342
https://slubowisko.pl/topic/104449/
https://commons.erau.edu/ibpp/vol19/iss4/1/
https://www.thegreatcatsbycattery.com/profile/jiyaned76490828/profile
http://cbsver.bget.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=ucapyzuc
https://job.tntu.edu.ua/rejestratsiya-uchasnyka-olimpiady/#comment-10766
https://www.lanubedocente.21.edu.ar/profile/lejoc4509136419/profile
https://my.dev.vanderbilt.edu/tractem/about-us/
http://www.caseofcuriosities.com/2019/03/beauty-con-pop.html?sc=1765272240852#c2322958228795275455
https://www.sedatify.com/blogs/526/%D0%9C%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B1%D0%B5%D1%82-%D0%A0%D0%B0%D0%B1%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%B8%D0%B9-%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4-2026-WAP200-%D0%91%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%83%D1%81-15-000
http://ewha.nodong.org/xe/index.php?mid=ewha_02_03&page=10&document_srl=22388&rnd=157267#comment_157267
https://slubowisko.pl/topic/94657/?page=2#28
https://forum.programosy.pl/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=6941&p=1329018#p1329018
http://print-nara.anywiz.co.kr/bbs/view.php?code=sian&idx=525
https://naigle.borda.ru/?1-17-0-00000444-000-0-0-1765478574
https://nature-et-avenir.org/
https://akivaschool.com/
https://lifeloveliz.com/
https://audium.com/
https://informationng.com/
https://hyundaimobil.co.id/
https://www.grepmed.com/melbet7vip
доставка цветов цена
http://brainquake.keyforum.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=31
https://quvonch.com/uzbekskaya-muzyka/
https://quvonch.com/uzbekskaya-muzyka/xamdam-sobirov/
http://komerc.mineralgroup.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=otacak
http://arenda.mineralgroup.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=ylucej
http://sves.ru/fm/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=35507
https://quvonch.com/
«Ищете надежное зеркало для входа в казино Вавада ? Наш сайт предлагает актуальные и проверенные зеркала Вавада, которые гарантируют стабильный доступ к любимым играм даже при блокировках основного ресурса. Вавада — это популярное онлайн-казино с широким выбором слотов, рулетки, покера и других азартных развлечений. Используя зеркало Вавада, вы сможете быстро и безопасно войти в личный кабинет, пополнить счет, вывести выигрыши и наслаждаться бонусами без ограничений. Мы регулярно обновляем ссылки, чтобы обеспечить бесперебойный доступ и защиту ваших данных. На нашем портале вы найдете подробные инструкции по использованию зеркала, советы по регистрации, актуальные промокоды и обзоры лучших игр. Вход через зеркало Вавада — это простой способ обойти технические блокировки и играть в любое время и в любом месте. Не упустите шанс испытать удачу и выиграть крупные призы с помощью надежного зеркала казино Вавада! Посетите наш ресурс прямо сейчас и получите доступ к официальному зеркалу, чтобы наслаждаться азартом без преград.»
http://probki.vyatka.ru/content/reshenie-492024-0#comment-35132132
http://probki.kirov.ru/content/reshenie-2392024-0#comment-35132042
http://antrem.ru/cb-profile/pluginclass/cbblogs?action=blogs&func=show&id=2278
https://vybz.live/read-blog/27845
https://www.bls.gov/bls/exit_BLS.htm?url=https://intelicode.com/public/pgs/1xbet_promo_code_and_bonus.html
https://pixabay.com/users/53748303/
http://probki.vyatka.ru/content/reshenie-1442012#comment-35124489
https://www.vardhanpublishers.com/blog/shopping/journal-blog
http://estolaid.com/communication/forum/user/8519/
http://precarity-project.ru/component/k2/item/149-eurispes-institute-of-political-economic-and-social-studies
https://www.coursera.org/user/ae787e8ef51fc4be15c68d564820c12a
регистрация в sykaaa casino второй акк Вопрос безопасности всегда стоит на первом месте, когда речь идет об игре на реальные деньги. Sykaaa Casino заявляет об использовании современных технологий шифрования для защиты данных игроков и финансовых транзакций. Лицензия, если таковая имеется (стоит проверить актуальную информацию на сайте), также является показателем того, что казино работает по определенным стандартам и подлежит регулированию. Важно убедиться, что казино имеет действующую лицензию от авторитетного регулятора.
сукааа казино андроид В целом, “Большая Sykaaa Casino” выглядит как привлекательная площадка для тех, кто ищет новые возможности в мире онлайн-гемблинга. Простой старт через регистрацию и широкий спектр предложений делают его достойным внимания. Главное – помнить о разумном подходе и наслаждаться процессом игры.
sykaaa казино android В целом, Sykaaa Casino предлагает конкурентоспособный набор услуг для игроков, ориентированных на реальные ставки. Если вы готовы испытать свою удачу, это казино может стать вашим новым любимым местом для азартных развлечений. Главное – играть ответственно и помнить, что азарт должен приносить удовольствие, а не становиться источником проблем. Удачи за игровыми столами!
https://www.sharerewards.com/en/share-credit-card/fab-share-standard-credit-card
http://factforum.kabb.ru/viewtopic.php?t=949
https://pinxters.com/blogs/92415/1xBet-Promo-Code-2026-for-Free-Bet-Bonus-130
http://oldmetal.ru/forum/index.php?topic=3277
https://pinxters.com/blogs/92403/Top-1xBet-Promo-Code-2026-Welcome-Bonus-of-130
https://salud1000x100.es/2016/06/21/para-que-sirven-las-vacunas-entrevista-al-dr-enric-costa-y-jesus-garcia-blanca/comment-page-5/#comment-42516
https://realz-kasyno.pl/bonusy/
в каком казино дают за регистрацию бездепозитные бонусы
бездепозитные бонусы в казино олимп
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения 2026
бездепозитные бонусы казахстан за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения
как играть на бонус казино в 1win
http://s-s-o.ru/forum.php?PAGE_NAME=message&FID=2&TID=12357&MID=12169&result=new#message12169
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения казахстан
казино в котором есть бездепозитный бонус
https://forum.banknotes.cz/viewtopic.php?t=238210
https://heyzine.com/flip-book/6a35447a3c.html
https://pain-management.hellobox.co/7551938/codigo-promocional-1xbet-guinea-bissau-2026-1xbro200
https://indianwomenorg.com/read-blog/43453
https://gov.trava.finance/user/codepomo26
А то с после ситуации с РЦлаб все настораживают…… Купить кокаин, бошки, гашиш Магазин на ура))вчера трек получил:good: надеюсь всё будет ровно.
https://wordpress.morningside.edu/tajaprince13/2015/09/01/tori-figge-interview/#comment-448978
https://pauladdavis.scholar.bucknell.edu/2017/11/01/101-the-knowledge-project/
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения казахстан
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения по номеру телефона
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом
https://velog.io/@seoman12/Cdigo-Promocional-1xBet-Brasil-2026-1XBUM200
https://www.gamespot.com/profile/codigo56/
https://evennful.com/read-blog/42805
http://delphi.larsbo.org/user/bonas1win
https://pastebin.com/u/codemelbet71
https://maggwear.com.tr/index.php?route=journal3/blog/post&journal_blog_post_id=10
в каком казино дают за регистрацию бездепозитные бонусы
в каком казино дают бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом
крутой магазин https://sims-mods.ru Вот этого ам2233 и заказал. Оплатил уже. Жду трекер.203 вообще шикарный ) мне понравился. спасибо Вам)
https://cypexpress.com/index.php?route=journal3/blog/post&journal_blog_post_id=9
https://app.talkshoe.com/user/melbet7vip26
в каком казино дают за регистрацию бездепозитные бонусы
https://telegra.ph/Code-promo-1XBET-Inscription—Bonus-jusqu%C3%A0-130-12-22
https://www.mixcloud.com/Bienvenue1xbet8945/
https://www.japanesewomenorg.com/hasanbaizid31
бездепозитные бонусы в казино олимп
бездепозитные бонусы в казино с выводом без пополнения
1000 рублей за регистрацию в казино без депозита
https://trading24inw3.blogspot.com/2025/12/1win-promo-code-brazil-2026-1w2026vip.html
https://speakerdeck.com/bonus1win
бездепозитные бонусы в казино
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино с выводом без депозита за регистрацию
Крайне редко встречаются площадки, позволяющие оформить заявку на кешаут после использования подарочного депозита, не пополняя баланс.
https://nodepositcasinobonus.ru
Крайне редко встречаются площадки, позволяющие оформить заявку на кешаут после использования подарочного депозита, не пополняя баланс.
https://nodepositcasinobonus.ru
в каком казино дают бездепозитные бонусы
в каком казино дают бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию
https://ip-nsk.ru/uslugi/sozdanie-saytov/
https://ip-nsk.ru/
http://www.forum.alyno.ru/phpBB2/profile.php?mode=viewprofile&u=61485
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино
бездепозитные бонусы в казино
https://www.tumblr.com/blog24newd/803713024505626624/code-promo-1xbet-abidjan-2026-1xbig2026-bonus
https://1xbettodaypromocodenepal87542.atualblog.com/45711112/brand-first-deposit-code-130-bonus
бездепозитные бонусы в казино и бк
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом без пополнения
https://sykaaa-online-casino.fun
https://sykaaa-official-casino.website
https://sykaaa-online-casino.fun
https://eguidemagazine.com/wp-content/pages/promokod-1xbet-bonus-100.html
https://carpfishing.ru/wp-includes/wp/1xbet_promokod_bonus_pri_registracii.html
https://ts-u.ru/tsu/pgs/promokod-1xbet_i_bonus-kod.html
https://cdsonla.edu.vn/index.php/vi/component/k2/item/23-harvard-takes-me-to-dubai?tmpl=component&print=1&start=20
https://log.concept2.com/profile/2787430
https://heyzine.com/flip-book/edd5692bfe.html
https://potofu.me/uigyu7tg
code promo melbet ci
https://totalfratmove.com/articles/melbet_promo_code_bonus.html
https://foxartistic.com/wp-content/pages/code_de_bonus_1.html
https://sernexuss.com/blog/pages/1xbet_promo_code-free_welcome_bonus.html
https://alfa.edu.rs/pages/1xbet_promo_code-free_welcome_bonus.html
https://gazetablic.com/new/?1xbet_promo_code-free_welcome_bonus.html
Могу предоставить переписку администрации форума. Уже определитесь, что вам нужно чтобы и мне не дергать отправщиков, склад и прочих сотрудников. То хочу, то не хочу, то вышлите 2 посылки, оплачу посфактум, то снова верните деньги. https://shuba-dublenka.ru магаз ровный,сервис 5+,как напишешь сразу ответят,все ровно и по весу и по качеству 5+,были рады очень посылю с замечательным реагентиком плюсую магазу и советую остальным!)))а че магазин то ваще работает нет?
https://justpaste.me/a7282
https://social.sikatpinoy.net/blogs/49411/C%C3%B3digo-Promocional-1xBet-Brasil-2026-1XSUN200
https://polimer-3d.ru/
https://app.simplenote.com/p/Y82VX9
https://ycems.edu.in/?p=4994
https://pentvars.edu.gh/pentecost-university-proudly-matriculated-over-1300-new-students/
http://kofe.80lvl.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=5122
http://filmofon.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=orunafej
https://leetcode.com/u/sportsbetting/
https://social.instinxtreme.com/read-blog/156890
https://www.navacool.com/forum/topic/252983/code-promo-1xbet-afrique-2026-:-gratis777-%E2%80%93-bonus-vip
https://letterboxd.com/billdeboerua/
https://cool-directory.com/listings983930/code-promo-1xbet-guin%C3%A9e-%C3%89quatoriale-2026-code1x200
https://slides.com/fonbet26
https://kurilka-wagon.ru:443/user/acciusutrw
http://xn--80aa3cgn3d.kz/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=ujuce
http://deparkes.ru/index.php?subaction=userinfo&user=unatu
баня из бруса купить
https://prrush.com/profile.php?user=austin.rymill-495848&op=userinfo&from=space
дом из сип панелей проекты
https://blakebusinessservices.com/profile.php?do=profile&name=Your_Account&from=space&username=dieter.weatherburn-495862
https://mensvault.men/story.php?title=new-melbet-promo-code-melmax200-%E2%80%93-fresh-%E2%82%AC130#discuss
https://stanimiretov.com/journal-blog
1xbet uganda promo code 2026
https://prosmart.by/user/galenagdhi
Hi there Dear, are you genuinely visiting this web site regularly, if so then you will definitely take pleasant experience.
https://v15.net.ua/volkswagen-tiguan-sklo-fary-usa-vs-europe.html
Hi there mates, good article and nice arguments commented here, I am really enjoying by these.
byueuropaviagraonline
https://ieet.org/wp-content/pgs/1xbet_promo_code_for_free_bet_welcome_bonus.html
https://paill.com/articles/pages/?code-promo-1xbet___bonus.html
бездеп промокод Получите бездепозитный бонус казино за регистрацию – это проще, чем кажется! Забудьте о сложных условиях и депозитах. Сегодня многие онлайн-казино дарят бездепозитные бонусы новым игрокам просто за создание аккаунта. Это ваш шанс начать играть в любимые игры, будь то захватывающие слоты или классические настольные игры, совершенно бесплатно. Просто пройдите быструю регистрацию, и бонус будет у вас в кармане!
бездепозитные деньги в казино Если вы ищете бездепозитное казино за регистрацию, обращайте внимание на репутацию площадки, отзывы игроков и наличие лицензии. Это поможет выбрать надежное и честное казино для приятной и безопасной игры.
https://NextFreeAds.com/389/posts/1/1/2028025.html
https://www.autobazar.eu/images/pages/?melbet_promokod_pri_registracii___bonus_kod_na_segodnya.html
https://www.eurospider.com/media/articles/udivitelynyy_mir_pchelinyh_sot_ot_stroitelystva_do_ispolyzovaniya.html
https://justinekeptcalmandwentvegan.com/wp-content/pages/magazin_stroymaterialov_onlayn.html
https://www.google.ee/url?q=https://nature-et-avenir.org/files/pages/?1xbet_code_d_inscription_promo.html
Отличный магазин..заказывал не раз всегда все на высшем уровне. Молодцы. https://pomor-plotnik.ru Хотелось бы надеется)))посылка дошла за 1 сутки, сегодня не успел забрать, завтра посмотрим на качество) я уверен, что все будет хорошо
https://www.google.com.sg/url?q=https://takesbet.com/promo-code/melbet
проекты домов из кирпича
Купить права онлайн через нашу компанию — это быстро, удобно и надежно! Мы предлагаем полный комплекс услуг для получения водительских прав без лишних хлопот и очередей. Официальная поддержка, доступные цены и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту. Гарантируем легальность и безопасность сделки. Закажите права онлайн у нас и начните управлять автомобилем уже сегодня! Поддержка 24/7 и помощь на всех этапах оформления.
изготовление подоконников из гранита
лестница искусственный камень
столешница для ванной
Нет сомнения https://landshaft-komi.ru у меня все без подогрева растворилосьпрет 30-45 мин.1к10.действием похож на рсц
indian hd porn
разработка сайта цены
Superb post however I was wondering if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit further. Appreciate it!
byueuropaviagraonline
создание сайтов на битрикс
medved20-10 не еби людям голову!!!!!!!!!!! микс отличный, но на час-1,5! Не больше…… https://tuguru.ru ну чё могу сказать…Все верно, до сих пор разгребаем ) буду заказывать второй раз тут) товар понравился)
аккумулятор волжский погрузчик Тяговые аккумуляторы 48 вольт: универсал для электропогрузчиков. Цена доступная.
Ремонт деревянного покрытия Очистка кафеля Москва
1xbet codigo promocional portugal
netmatrix.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
pixelpush.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
boostengine.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
https://bx24.avers35.ru/company/personal/user/115/blog/5016/
https://tiggoclub.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=31&t=5770
https://adultgamesdb.com/
https://salt-cave.ru/
http://marines.6f.sk/profile.php?lookup=376
хургада кайт Кайт кайтинг кайтсёрфинг школа обучение сафари Дети ветра DETIVETRA
https://www.band.us/band/101595031/post/1
seonexus.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
leadmatrix.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
casinoly app
seoradar.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
инструктор кайтсерфинга отзывы Кайт кайтинг кайтсёрфинг школа обучение сафари Дети ветра DETIVETRA
куба пицца рязань официальный сайт каталог “Пицца Куба Рязань официальный” – мы заботимся о вашем вкусе.
trafficfactory.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
https://www.bonjourdewi.com/bb/showthread.php?tid=5559
живые выступления на теплоходе — акции Тематическая вечеринка на теплоходе: погружение в атмосферу выбранной темы.
digitalleads.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
searchmetrics.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
spark dex SparkDex is redefining decentralized trading with speed, security, and real earning potential. On spark dex, you keep full control of your assets while enjoying fast swaps and low fees. Powered by sparkdex ai, the platform delivers smarter insights and optimized performance for confident decision-making. Trade, earn from liquidity, and grow your crypto portfolio with sparkdex — the future of DeFi starts here.
https://auto.ae/catalog/
арендовать минивэн мерседес по часам машины в аренду минивэн мерседес 20 чел
convertcraft.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
sparkdex ai SparkDex is redefining decentralized trading with speed, security, and real earning potential. On spark dex, you keep full control of your assets while enjoying fast swaps and low fees. Powered by sparkdex ai, the platform delivers smarter insights and optimized performance for confident decision-making. Trade, earn from liquidity, and grow your crypto portfolio with sparkdex — the future of DeFi starts here.
казино бонусы без депозита Каждый бездепозитный бонус – это шанс испытать свою удачу, познакомиться с ассортиментом игр и, возможно, найти свою любимую стратегию.
Аирдроп Тапалки – это простые онлайн-сервисы, которые позволяют зарабатывать небольшие суммы криптовалюты, выполняя простые действия, такие как клики по рекламе, просмотр видео или ввод капчи.
rankora.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
growthly.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Астрология Каждая колода – это отражение мудрости и женской интуиции.
https://goncharuk.ru/upimg/pages/promokod_na_1xbet_na_segodnya_besplatno_pri_registracii.html
https://m-g.wine/pags/code_promo_5.html
военные Волгоград Добро пожаловать на новостной портал Волгограда. Мы публикуем последние и главные новости региона, происшествия и криминальную хронику.
https://medialaw.asia/old/1xbet-promokod-na-segodnya-vip-bonus-130
blacksprut
http://sportdialog.ru/native/inc/1xbet-promokod.html
bs2we at
лазерный принтер купить (Лазерный принтер – идеальное решение для быстрой и четкой печати документов. | Лазерные принтеры превосходят струйные по скорости и экономии тонера. | Хотите лазерный принтер купить? Широкий выбор моделей по доступным ценам! | Лазерные принтеры купить легко в нашем магазине с гарантией качества. | Купить лазерный принтер – значит инвестировать в надежность и производительность. | Заказать лазерный принтер онлайн – быстро и без лишних хлопот. | Лазерный принтер цена радует: от 5000 руб. за базовые модели. | Узнайте лазерный принтер стоимость – выгодные акции для всех покупателей. | Ищете лазерный принтер недорого? У нас лучшие предложения! | Лазерный принтер купить недорого – реальность с нашими скидками до 30%. | Дешевый лазерный принтер не уступает по качеству печати. | Бюджетный лазерный принтер для дома и офиса – оптимальный выбор. | Лазерный принтер купить онлайн в 2 клика с доставкой. | Заказать лазерный принтер онлайн – удобный сервис 24/7. | Лазерный принтер интернет магазин с тысячами отзывов. | Интернет магазин лазерных принтеров – ваш надежный партнер. | Лазерный принтер каталог: фото, характеристики, отзывы. | Лазерный принтер в наличии – забирайте сегодня! | Лазерный принтер с доставкой по России бесплатно от 5000 руб.)
шутки про россию сатира про бюрократию
leadnex site – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
ranklio site – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
заказать аудиорекламу Нужен запоминающийся аудиоролик? Наши специалисты воплотят любую идею в звук.
ровнее только строительный уровень ) кокс, меф, шиш, гаш И всё надо успеть. :crazy:”Посторайтесь что бы такого больше не повторялось”
bs market
домашний интернет тарифы Установка домашнего интернета и Wi-Fi может быть осуществлена как самим провайдером, так и пользователем, обеспечивая бесперебойный доступ к сети.
https://wefunder.com/codigohoy1
продать квартиру в сарове Продажа квартир в Сарове: ваш ключ к комфортной жизни
http://www.studenternas.nu
blsp at blsp at
https://www.instapaper.com/p/17494677
Scented stickers Strategy, scent technologies and successful implementation across all product stages by Aromamedia
трансы иркутск Диджеи-трансеры — это настоящие шаманы, которые умело дирижируют толпой, создавая неповторимый опыт, который запоминается надолго. От легендарных фестивалей до уютных клубов, транс объединяет людей, жаждущих позитивных вибраций и выхода за пределы обыденности.
https://home24009.wordpress.com/2026/02/27/code-promo-1xbet-aujourdhui-bonus-130-e-1xvatout/
мебель на заказ псков Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг: от создания уникального дизайна до установки готового кухонного гарнитура, чтобы ваша новая кухня стала не просто местом для готовки, а сердцем вашего дома, наполненным теплом и уютом. В нашей студии вы можете «заказать кухню в Пскове», которая будет полностью соответствовать вашим предпочтениям и бюджету, ведь «кухня на заказ Псков цены» всегда прозрачны и доступны.
каталог кухонь от производителя Загляните «на Кухню алгоритмов» — и вы откроете для себя новый, удивительный мир, где креативность и логика идут рука об руку.
че вы панику наводите)) все норм будет! есть рамс у курьерки, магаз не при чем.. спакуха кокс, меф, шиш, гаш курануть попробывать эту чткутолер от феников в целом около 2х недель – месяца… про кросс толер с ФА не слышал раньше.
ремонт посудомийних машин у Львові терміново
SWeAR2033 Неважно, какую игру он запускает или какой теме посвящает свой прямой эфир, зрители всегда уверены в одном: их ждет нечто особенное и запоминающееся.
кайтинг кайт школа
https://heylink.me/codigob9/
https://juul-kilgore.hubstack.net/codigo-promocional-de-1xbet-para-hoy-1xbro200-1772191418
https://socialisted.org/market/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=392304
Ну короче усе круто, магаз супер, всем советую!!! кокс, меф, шиш, гаш доброго времени суток форумчане! всем кучу репы и море хорошего настроения))) это самый ровный магазин))) тарился год назад по опту, никогда ни каких проблем не возникало))) ТСу ровных продаж и адекватных клиентов)))Обратите внимание, ТС отказывается работать с ГАРАНТОМ! хоть и магазин древний и проверенный! но хочется спать спокойно! АДМИНЫ ОБРАТИТЕ ВНИМАНИЕ, ПОРА КАК ТО ИЗМЕНИТЬ РЕЖИМ РАБОТЫ ГАРАНТА. СДЕЛКИ ПРОВОДИТЬ ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНО ТОЛЬКО ЧЕРЕЗ ГАРАНТА!
москва луганск расписание автобусов
devopsly – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.