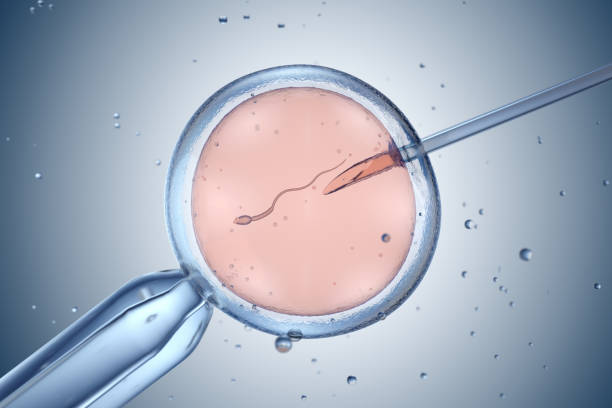
Definition
Infertility is the inability to conceive after 12 months of regular, unprotected intercourse. It can result from issues in one or both partners and may also include difficulties in maintaining a pregnancy.
Causes
Infertility can arise from various factors, including:
Female Factors: Ovulation disorders (e.g., PCOS, premature ovarian insufficiency)
Uterine abnormalities (e.g., fibroids, polyps, scarring)
Fallopian tube damage or blockage (e.g., from infections, endometriosis)
Age-related decline in egg quality and quantity
Male Factors:
Low sperm count or poor motility
Hormonal imbalances
Varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum)
Genetic disorders (e.g., Klinefelter syndrome)
Combined Factors: Issues present in both partners
Unexplained Infertility: No identifiable cause despite evaluation.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of infertility is the inability to conceive. Additional signs may include:
Irregular or absent menstrual cycles in women
Painful periods (dysmenorrhea) or pelvic pain
Changes in sexual function or hormone-related symptoms in men (e.g., reduced facial hair, gynecomastia)
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of infertility depends on the underlying cause:
Female Infertility: Ovulatory dysfunction leads to irregular or absent egg release. Tubal damage prevents the egg and sperm from meeting. Uterine abnormalities disrupt embryo implantation.
Male Infertility: Abnormal sperm production or function impedes fertilization. Blockages in the reproductive tract prevent sperm delivery.
Blood Tests
The following tests are commonly used to evaluate infertility:
For Women: Hormonal profile: FSH, LH, AMH, estradiol, and prolactin Thyroid function tests: TSH and free T4 Progesterone levels: To confirm ovulation
For Men: Testosterone levels ,Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
General Tests: Complete blood count (CBC) ,Blood sugar and insulin levels (to evaluate metabolic health)
Mental Health and Infertility
Infertility can take a significant toll on mental health, leading to: Stress and anxiety Depression Feelings of guilt or inadequacy Strained relationships
Coping strategies include: Counseling or therapy (e.g., cognitive-behavioral therapy) Support groups Mindfulness practices like meditation or yoga
Homeopathy Treatment
Homeopathy offers a personalized and holistic approach to treating infertility by addressing the root cause and enhancing overall reproductive health.
Common remedies include:
Sepia: For hormonal imbalances, irregular periods, and emotional stress. best med for infertility treatment.
Pulsatilla: For irregular ovulation and mild temperament.
Natrum Muriaticum: For emotional distress and menstrual irregularities.
Agnus Castus: For low libido and hormonal imbalances in both genders.
Selenium: For improving sperm health in men.
Lifestyle Modifications with Homeopathy
Dietary Changes: Nutrient-rich, balanced diets to improve overall fertility.
Exercise: Regular physical activity to manage weight and improve hormone levels.
Stress Management: Techniques such as relaxation therapy, yoga, or meditation.
Conclusion
Infertility is a multifaceted condition requiring a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Homeopathy, combined with lifestyle changes, offers a gentle and effective way to address underlying issues and enhance reproductive health. Always consult a qualified homeopath for a tailored treatment plan.

Миналата година осъществих пътуване с туристическа агенция Мистрал Травел и останах изключително доволна! Организацията беше безупречна – от записването до самото пътуване. Избрах туристическа програма до чешката столица Прага и всичко беше изпълнено с професионализъм – хотелът беше удобен, екскурзоводът много компетентен, а програмата завладяваща и добре структурирана. Благодарение на тях успях да се насладя на културата и забележителностите на града без излишни проблеми. С удоволствие бих се използвала услугите на Мистрал за в бъдеще и горещо съветвам на всички да заложат на техните предложения!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
buy amoxil pills for sale – buy amoxil paypal amoxicillin price
buy amoxicillin without a prescription – comba moxi cheap amoxil sale
purchase diflucan online – https://gpdifluca.com/ fluconazole 100mg drug
order fluconazole 200mg generic – https://gpdifluca.com/ order generic diflucan
cenforce price – order cenforce 50mg pill order cenforce 100mg
buy cheap cenforce – https://cenforcers.com/ purchase cenforce sale
cialis active ingredient – cialis 100mg para que sirve las tabletas cialis tadalafil de 5mg
cialis coupon walgreens – https://ciltadgn.com/# cialis generic best price that accepts mastercard
cialis tadalafil 20 mg – https://strongtadafl.com/ cialis tadalafil 20mg price
side effects of cialis daily – cialis online without a prescription cialis for pulmonary hypertension
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
buy zantac 300mg pill – https://aranitidine.com/# buy zantac for sale
brand zantac – zantac 300mg ca order zantac 300mg online
viagra buy canada – cheap genuine viagra uk viagra 100mg street price
can you buy viagra chemist – viagra sale walgreens buy viagra hyderabad india
With thanks. Loads of erudition! https://buyfastonl.com/isotretinoin.html
This website exceedingly has all of the bumf and facts I needed to this thesis and didn’t comprehend who to ask. synthroid se vende sin receta
Good blog you procure here.. It’s obdurate to assign elevated calibre script like yours these days. I truly appreciate individuals like you! Withstand vigilance!! viagra espaГ±a
More peace pieces like this would create the интернет better. https://ursxdol.com/doxycycline-antibiotic/
This is the amicable of glad I take advantage of reading. https://ursxdol.com/get-metformin-pills/
More posts like this would prosper the blogosphere more useful. https://prohnrg.com/product/lisinopril-5-mg/
This is a question which is near to my callousness… Diverse thanks! Quite where can I lay one’s hands on the phone details in the course of questions? https://prohnrg.com/product/cytotec-online/
Thanks on sharing. It’s first quality. https://aranitidine.com/fr/ivermectine-en-france/
Proof blog you possess here.. It’s intricate to espy strong quality article like yours these days. I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Withstand mindfulness!! https://aranitidine.com/fr/en_ligne_kamagra/
Il est essentiel de consulter votre assureur pour comprendre ce qui est et n’est pas couvert.
L’auto-médication, en particulier avec des traitements hormonaux comme la testostérone, présente de graves risques.
Une dose incorrecte peut entraîner une gamme de réactions
indésirables des sautes d’humeur et un risque accru de maladies cardiovasculaires à des situations plus
graves comme les lésions hépatiques. Les doses doivent être adaptées aux besoins individuels, et cela nécessite une surveillance médicale», déclare le Dr
Alice Hardy, un endocrinologue de premier plan à
Manchester.
La déhydroépiandrostérone ou DHEA est une hormone corporelle naturelle.
L’une de ses nombreuses fonctions est de soutenir la production de testostérone et
de contrôler les niveaux d’œstrogène. En effet,
des études confirment que la consommation de DHEA aide
à maintenir des niveaux sains de cette hormone essentielle chez les hommes cinquantenaires.
Un faible taux de cette hormone chez les hommes aboutit à de nombreux problèmes, allant de la faiblesse des pulsations sexuelles à la démotivation. Ces personnes ont
également de faibles niveaux d’énergie et sont sujettes à
la déprime. Les sportifs souffrant de cette déficience risquent de voir une diminution significative
de leurs performances athlétiques. L’ironie est qu’un entraînement intense produit peu d’effets positifs si le corps
est déficient en cette hormone.
Un copain m’avait donné un excellent retour sur Testo Prime
et j’ai décidé de l’essayer pour voir. J’ai perdu
du poids, retrouvé de l’énergie et des muscular tissues
pleins de tonus. ● Les bananes, qui contiennent de la broméline et du potassium, contribuant au bon fonctionnement
neuromusculaire et métabolique. ● Les œufs entiers, qui apportent
cholestérol (précurseur hormonal), vitamine D, sélénium
et graisses saturées bénéfiques en quantités modérées.
Sur le plan psychologique, on retrouve fréquemment des sautes d’humeur, de l’irritabilité, une baisse de la concentration, voire un état dépressif léger.
Ces manifestations peuvent être aggravées par l’accumulation des autres symptômes physiques et
relationnels.
Notez qu’en ce second pour 2 flacons de testostérone achetés, le 3ème est offert.
Pour l’achat de 2 bouteilles, vous aurez aussi accès aux livres de recettes et d’exercices spécialement
conçus par des specialists pour vous aider
à atteindre vos objectifs. En parlant des produits pour
prendre du muscle à la salle de sport, un coach m’a conseillé la prise de Testo Prime.
Très vite, j’ai senti une amélioration au niveau de mes muscular tissues et de ma
résistance à l’effort. Après 1 mois, je voulais partager mon avis sur ces
comprimés sans prescription qui m’ont beaucoup aidé à gagner en masse et en vigueur sans effet négatif.
Découvrez comment acheter de la testostérone en ligne sans risque, avec des conseils pratiques sur
les sites fiables, les critères de choix et les précautions à prendre.
La testostérone est souvent mal vue à trigger de ses liens avec
les comportements “virils”. Il faut comprendre comment l’éducation peut nous aider à gérer cette hormone et ses
effets sur notre comportement.
Les choix de notre alimentation et nos routines peuvent booster la
testostérone naturellement. Les huîtres, par exemple, sont
riches en zinc qui soutient la testostérone. On n’a pas
seulement des médicaments, mais aussi des choix alimentaires et de
vie qui aident. On prescrit la testostérone quand des checks médicaux montrent un besoin. Le
chemin vers le traitement inclut des examens détaillés et
des conversations entre le patient et son médecin. Tout begin avec des exams pour connaître le taux de testostérone du
patient.
Ils s’implantent sous la peau et libèrent leur contenu sur une durée de 4 à 6 mois.
Ils peuvent se mettre sous la peau du bas-ventre, du deltoïde ou de la cuisse.
Grande passionnée de fitness et de beauté/santé, Julia est la rédactrice
en chef chez Vulgaris. Avec un cursus en journalisme dans l’univers
de la beauté, ses sujets de prédilection sont la santé naturelle,
les soins esthétiques mais aussi tout ce qui tourne autour
de la méditation du bien-être.
La testostérone joue un rôle necessary dans le développement des organes génitaux et des caractéristiques sexuelles
secondaires chez les hommes, telles que la croissance des poils corporels,
la voix grave et la musculature. Elle est notamment
nécessaire afin de permettre à l’organisme de se développer
correctement mais aussi pour la production de spermatozoïdes et la libido.
Néanmoins, il reste potential de se procurer des boosters de testostérone en pharmacie.
Ici, nous vous aidons à atteindre vos objectifs de musculation en vous partageant l’expertise
de spécialistes. Vous apprendrez à bien mettre
en pratique les exercices de musculation sans vous blesser et
nous vous guiderons dans l’achat de matériels de musculation. Le gel a été
conçu pour améliorer encore les systèmes de distribution transdermique.
Bien que relativement cher, acheter testosterone homme de la testostérone sous forme de gel transdermique est actuellement l’option la plus courante, suivie
des injections, des patchs et, enfin, des comprimés oraux.
Les comprimés contiennent 30 mg de testostérone et sont appliqués deux fois par jour.
Cette hormone est incontournable pour les sports activities comme la natation et
la course de fond, qui nécessitent des niveaux élevés d’endurance,.
La testostérone, hormone sexuelle mâle par excellence, est responsable d’une panoplie de
caractères distinctifs de l’homme dont
la voix grave, la barbe, la pressure et l’agressivité.
Testogel est absorbé par la peau et élève le taux de testostérone dans le sang.
Cela peut permettre de réduire les symptômes liés à une carence en testostérone,
tels qu’une amélioration de l’énergie, une augmentation de la drive musculaire et
une libido renforcée. Il peut s’écouler quelques jours à quelques semaines avant
de constater les effets. Consultez un professionnel de la santé pour obtenir des conseils et des recommandations personnalisés, et
restez concentré sur des methods d’entraînement naturelles et sûres pour atteindre vos objectifs.
According to Sikiric et al. (1993), while BPC-157 derives from gastric proteins, it does not share homology with
any recognized gastric peptides [1, 2]. Plus, we will
also share particulars about probably the most reputable vendors of research
peptides together with TB-500 and BPC-157. GHK-Cu contributes toward mixture approaches since peptide properties mix with copper ions so improved biological activity is created in laboratory settings.
Explore TB-500 from My Peptides – designed to boost recovery, flexibility, and soft tissue
resilience. Analysis shows that the removing of waste merchandise or
inflammatory substances is something that’s helped by an improved blood flow.
Joint constructions might steadily put on down due to repetitive stress from
work or daily actions inflicting lowered mobility, persistent discomfort, and typically severe ache
and swelling. Joint ache impacts tens of millions
of individuals worldwide, also it creates every
day challenges impacting mobility, range of movement, and quality of life.
Making Certain proper dealing with, adherence to dosing protocols, and use of sterile injection materials can reduce risks.
Consulting a healthcare professional or certified researcher is strongly recommended for experimental purposes.
Whereas human trials are nonetheless limited, anecdotal stories from early adopters and peptide lovers are overwhelmingly constructive.
Customers incessantly highlight quicker restoration, reduced irritation, and improved general well-being.
Moreover, BPC-157 interacts with the central nervous system, potentially aiding in nerve regeneration and improving mental readability.
It additionally reveals anti-inflammatory results, reducing swelling and ache in both acute
and persistent conditions.
This is especially important for recovering from muscle, tendon, and
ligament injuries. BPC-157, a peptide compound gaining
important attention in the well being and wellness group, is heralded for its exceptional therapeutic potential.
This distinctive sequence of amino acids, derived from a protein discovered in the abdomen, has sparked curiosity because of
its wide range of well being advantages.
From accelerating wound healing to potentially easing symptoms of continual conditions, BPC-157 stands out as a versatile and promising therapeutic
agent. When it comes to nerve-related considerations like sciatica,
carpal tunnel syndrome, or pinched nerves, injections are again the
best choice. These issues usually require deeper, extra
dependable assist that oral capsules might not persistently ship.
Injections bypass the digestive system and provide higher bioavailability, which
means extra of the peptide enters circulation and stays lively within the physique.
These diverse appellations afford adaptability and facilitate easy recognition and distinction of the
peptide in varying settings and investigations.
Additionally, some customers speculated that firms have mislabeled peptides that
are cheaper to manufacture as BPC 157, urging caution for others
trying to purchase it. Of course, injections of any substance carry their very own dangers and require medical supervision. However rats given injections of
BPC 157, either before or immediately after getting hyperkalemia,
survived and had fewer signs [16]. It was efficient even in diabetic rats; diabetes could make it
more durable for the body to heal wounds [27, 28].
Some research in humans with titles suggesting they tested IBD – falsely cited even within the scientific literature –
were actually carried out in healthy folks (see “Side Effects”
part below) [6, 17, 18]. SelfHacked has the strictest sourcing
tips in the health industry and we nearly exclusively link to medically peer-reviewed research, often on PubMed.
Mixed with thousands of real-world purposes
in experimental and efficiency settings, BPC-157 has turn out to be
some of the extensively studied and widely used research peptides available today.
By delivering the peptide immediately into the body—either under the skin (subcutaneous) or
right into a muscle (intramuscular)—injections bypass the digestive tract totally.
This results in sooner absorption and higher bioavailability, that means extra of
the peptide is available in your physique to use. Sure,
BPC-157 is generally protected to make use of for anybody with out
continual or extreme medical circumstances.
The quick answer is that BPC-157 has demonstrated a great security profile in animal studies, and early human trials counsel it’s typically well-tolerated.
Nevertheless, it’s essential to notice that scientific
proof in people remains to be limited, and rather
more analysis is required to completely understand
its security profile. BPC-157 helps counteract that harm
by enhancing blood circulate and promoting faster therapeutic.
By increasing the manufacturing of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), BPC-157
encourages the growth of wholesome blood vessels.
This ensures that tissues get the oxygen and nutrients they need to get well.
BPC 157 is a potent substance that can speed up the healing of wounds, repair damaged tissue and bones,
and help enhance gastrointestinal well being. Contemplating it’s not recognized for inflicting many side effects, it can be an efficient
software in any bodybuilder, athlete, or injured
individual’s arsenal.
The administration of TB-500 and BPC 157 in proper dosages has proven promising ends in enhancing therapeutic outcomes,
backed by notable research in peptide blends and wound healing
therapies. The mixture of peptides BPC 157 and TB-500, a part of the
Wolverine protocol, offers remarkable advantages in peptide remedy for accelerated therapeutic and general well-being.
From mitigating stroke damage to offering new avenues for schizophrenia and spinal cord damage therapies, its potential is huge and promising.
While the current data is promising, more intensive clinical trials and research are needed
to fully understand and harness BPC 157’s
potential. BPC 157 is known to enhance the healing of many various wounds,
including tendon-to-bone therapeutic and superior healing of damaged ligaments.
Its capability to mitigate conditions like stroke, schizophrenia, and
spinal wire injuries whereas selling neural recovery and functional enchancment is
capturing the curiosity of the medical group.
If you’re utilizing peptides for skin therapeutic or floor wounds, good grooming
helps. Combining peptides with other therapeutic methods can take your
outcomes to the subsequent stage. Many individuals discover even better restoration once they stack BPC-157
and TB-500 with bodywork or regenerative therapies.
Its regenerative potential has made it increasingly well-liked in functions
related to bodily pressure, overuse, and injury.
From sports-related injury to chronic musculoskeletal conditions, BPC-157 continues to impress the
medical world with its ability to promote faster,
simpler healing. BPC-157 is proven to heal multiple kinds of fistulas, including gastrointestinal fistula.
casino oyunlari
References:
slotmachine (i-tech.net.in)
I am in fact enchant‚e ‘ to gleam at this blog posts which consists of tons of worthwhile facts, thanks object of providing such data. https://ondactone.com/spironolactone/
I am in fact enchant‚e ‘ to glitter at this blog posts which consists of tons of of use facts, thanks for providing such data. https://ondactone.com/simvastatin/
References:
neurotrauma
More articles like this would frame the blogosphere richer.
purchase coumadin without prescription
More posts like this would make the blogosphere more useful.
https://doxycyclinege.com/pro/losartan/
This is the kind of serenity I enjoy reading. https://www.google.gr/url?q=https://www.instapaper.com/p/adip
ремонт кофемашины kaffit https://remont-kofemashin1.ru
ремонт швейных машин зингер https://remont-shveynyh-mashin1.ru
аренда 1с в облаке 1с сервис облако
More posts like this would make the blogosphere more useful. http://zgyhsj.com/space-uid-977928.html
ПОмощь юрист в банкротстве: банкротство юридических лиц санкт петербург
More posts like this would prosper the blogosphere more useful. http://3ak.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=229026
Ремонт кофемашин https://coffee-craft.kz с выездом на дом или в офис. Диагностика, замена деталей, настройка. Работаем с бытовыми и профессиональными моделями. Гарантия качества и доступные цены.
Круглосуточный вывод из запоя с кодированием на дому в нижнем новгороде — помощь на дому и в стационаре. Капельницы, очищение организма, поддержка сердца и нервной системы. Анонимно и конфиденциально.
Купить мебель письменные столы для дома и офиса по выгодным ценам. Широкий выбор, стильный дизайн, высокое качество. Доставка и сборка по всей России. Создайте комфорт и уют с нашей мебелью.
If snacks, keys, and a tiny light need a home, a slim rockbros bike bag swallows the essentials without turning your cockpit into a sail.
Предлагаем оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych-profiley.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков. Высокое качество, устойчивость к климатическим нагрузкам, широкий ассортимент.
Оконные профили https://proizvodstvo-okonnych.ru для застройщиков и подрядчиков по выгодным ценам. Надёжные конструкции, современные материалы, поставка напрямую с завода.
вопрос юристу в чате бесплатная консультация адвоката горячая линия
Нужны пластиковые окна: пластиковое окно цена
Нужен вентилируемый фасад: https://podsistema-dlya-ventfasada.ru
Trust Finance https://trustf1nance.com is your path to financial freedom. Real investments, transparent conditions and stable income.
cold porcelain clay hand made flower
Інформаційний портал https://pizzalike.com.ua про піцерії та рецепти піци в Україні й світі. Огляди закладів, адреси, меню, поради від шефів, секрети приготування та авторські рецепти. Все про піцу — від вибору інгредієнтів до пошуку найсмачнішої у вашому місті.
Решили купить Honda? тест-драйв мечты honda широкий ассортимент автомобилей Honda, включая новые модели, такие как Honda CR-V и Honda Pilot, а также автомобили с пробегом. Предоставляем услуги лизинга и кредитования, а также предлагает различные акции и спецпредложения для корпоративных клиентов.
Ищешь автозапчасти? купить автозапчасти онлайн предоставляем широкий ассортимент автозапчастей, автомобильных аксессуаров и оборудования как для владельцев легковых автомобилей, так и для корпоративных клиентов. В нашем интернет-магазине вы найдете оригинальные и неоригинальные запчасти, багажники, автосигнализации, автозвук и многое другое.
Выкуп автомобилей выкуп машин без посредников без постредников, быстро. . У нас вы можете быстро оформить заявку на кредит, продать или купить автомобиль на выгодных условиях, воспользовавшись удобным поиском по марке, модели, приводу, году выпуска и цене — независимо от того, интересует ли вас BMW, Hyundai, Toyota или другие популярные бренды.
продвижение сайтов сео продвижение любой тематики. Поисковая оптимизация, рост органического трафика, улучшение видимости в Google и Яндекс. Работаем на результат и долгосрочный эффект.
нужен юрист: юрист по земельным вопросам защита интересов, составление договоров, сопровождение сделок, помощь в суде. Опыт, конфиденциальность, индивидуальный подход.
editor de audio online creador de tonos gratis
Заказать такси https://taxi-sverdlovsk.ru онлайн быстро и удобно. Круглосуточная подача, комфортные автомобили, вежливые водители. Доступные цены, безналичная оплата, поездки по городу и за его пределы
Онлайн-заказ такси https://sverdlovsk-taxi.ru за пару кликов. Быстро, удобно, безопасно. Подача в течение 5–10 минут, разные классы авто, безналичный расчет и прозрачные тарифы.
Закажите такси https://vezem-sverdlovsk.ru круглосуточно. Быстрая подача, фиксированные цены, комфорт и безопасность в каждой поездке. Подходит для деловых, туристических и семейных поездок.
Быстрый заказ такси https://taxi-v-sverdlovske.ru онлайн и по телефону. Подача от 5 минут, комфортные автомобили, безопасные поездки. Удобная оплата и выгодные тарифы на любые направления.
Платформа пропонує https://61000.com.ua різноманітний контент: порадник, новини, публікації на тему здоров’я, цікавих історій, місць Харкова, культурні події, архів статей та корисні матеріали для жителів міста
Нужен сантехник: https://santehnik-v-almaty.kz
Saznajte sve o https://www.kamen-u-bubregu.com – simptomi, uzroci i efikasni nacini lecenja. Procitajte savete strucnjaka i iskustva korisnika, kao i preporuke za prevenciju i brzi oporavak.
ГОРСВЕТ Чебоксары https://gorsvet21.ru эксплуатация, ремонт и установка систем уличного освещения. Качественное обслуживание, модернизация светильников и энергоэффективные решения.
Займы онлайн https://laikzaim.ru моментальное оформление, перевод на карту, прозрачные ставки. Получите нужную сумму без визита в офис и долгих проверок.
Интернет-магазин мебели https://mebelime.ru тысячи моделей для дома и офиса. Гарантия качества, быстрая доставка, акции и рассрочка. Уют в каждый дом.
Форум общения тренировка с гантелями подписчики спрашивали им ответили, какие нужны упражнения, сколько подходов, как достич лучших результатов. присоединиться можно к дисскусии без регистрации.
Zasto se javlja bol u predelu bubrega: od kamenaca i infekcija do prehlade. Kako prepoznati opasne simptome i brzo zapoceti lecenje. Korisne informacije.
Авто журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новинок, советы по уходу за автомобилем и репортажи с автособытий.
Sta znaci pesak i kamen u bubregu, koji simptomi ukazuju na problem i kako ga se resiti. Efikasni nacini lecenja i prevencije.
Популярный авто журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua подробные обзоры моделей, советы экспертов, новости автосалонов и автоспорта, полезные статьи для автовладельцев.
freight companies in new york shipping new york
Флешка оптом https://usb-flashki-optom-24.ru купить озон и флешки дешево в Нижнем Тагиле. Usb флешка купить в Москве с доставкой и флешки стеклянные с подсветкой в Саратове. Мини флешка оптом и флешка зенит
Экономические новости https://gau.org.ua прогнозы и обзоры. Политика, бизнес, финансы, мировые рынки. Всё, что важно знать для принятия решений.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua всё, что интересно современному мужчине: стиль, спорт, здоровье, карьера, автомобили, технологии и отдых. Полезные статьи и советы каждый день.
Онлайн авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua с обзорами новых и подержанных авто, тест-драйвами, советами по обслуживанию и новостями из мира автопрома.
Портал о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua свежие новости, статьи и советы. Обзоры технологий, материалов, дизайн-идеи и практические рекомендации для профессионалов и частных застройщиков.
Строительный портал https://dki.org.ua всё о строительстве и ремонте: технологии, оборудование, материалы, идеи для дома. Новости отрасли и экспертные рекомендации.
Онлайн строительный https://texha.com.ua портал о материалах, проектах и технологиях. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и обустройстве дома. Поддержка специалистов и вдохновение для новых идей.
Всё о стройке https://mramor.net.ua полезные статьи, советы, обзоры материалов и технологий. Ремонт, строительство домов, дизайн интерьера и современные решения для вашего проекта.
Сайт «Всё о стройке» https://sushico.com.ua подробные инструкции, советы экспертов, новости рынка. Всё о строительстве, ремонте и обустройстве жилья в одном месте.
Универсальный автопортал https://road.kyiv.ua автомобили, автоновости, обзоры, ремонт, обслуживание и tuning. Полезные статьи для водителей и экспертов автоиндустрии.
Женский портал https://fotky.com.ua с полезными статьями о красоте, моде, здоровье, отношениях и карьере. Советы экспертов, лайфхаки для дома, рецепты и вдохновение для каждой женщины.
Онлайн женский портал https://martime.com.ua новости, тренды моды, секреты красоты, психология отношений, карьера и семья. Полезные материалы и практические советы для женщин.
Женский сайт https://womanclub.in.ua о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера. Всё самое интересное для женщин в одном месте.
Всё о гипертонии https://gipertoniya.net что это за болезнь, как проявляется и чем опасна. Подробные статьи о симптомах, диагностике и способах лечения высокого давления.
Туристический портал https://elnik.kiev.ua с актуальными новостями, маршрутами и путеводителями. Обзоры стран и городов, советы путешественникам, лучшие идеи для отдыха и выгодные предложения.
Онлайн женский https://ledis.top сайт о стиле, семье, моде и здоровье. Советы экспертов, обзоры новинок, рецепты и темы для вдохновения. Пространство для современных женщин.
new york freight freight shipping new york
Сайт о строительстве https://stinol.com.ua практические рекомендации, проекты, обзоры инструментов и материалов. Советы экспертов, новости отрасли и новые технологии.
Строительный журнал https://mts-slil.info с актуальными новостями отрасли, обзорами материалов, инструкциями по ремонту и строительству. Полезные советы для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Онлайн сайт https://purr.org.ua о строительстве и ремонте: полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры технологий, дизайн-идеи и архитектурные решения для вашего дома.
Онлайн туристический https://azst.com.ua портал: всё о путешествиях, туризме и отдыхе. Маршруты, отели, лайфхаки для туристов, актуальные цены и интересные статьи о странах.
Онлайн новостной https://antifa-action.org.ua портал с круглосуточным обновлением. Свежие новости, репортажи и обзоры. Важные события страны и мира, мнения экспертов и актуальная аналитика.
Новости Украины https://uamc.com.ua новости дня, аналитика, события регионов и мира. Обзоры, интервью, мнения экспертов. Быстро, достоверно и удобно для читателей.
Новостной портал https://prp.org.ua с актуальной информацией о событиях в России и мире. Политика, экономика, культура, спорт и технологии. Новости 24/7, аналитика и комментарии экспертов.
Строительный портал https://suli-company.org.ua с актуальными новостями, обзорами материалов, проектами и инструкциями. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и дизайне.
Портал про авто https://prestige-avto.com.ua обзоры новых и подержанных машин, тест-драйвы, рынок автомобилей, страхование и обслуживание.
Онлайн автомобильный https://avtonews.kyiv.ua портал: свежие автоновости, сравнительные тесты, статьи о ремонте и тюнинге. Обзоры новых и подержанных машин, цены и советы экспертов.
Современный автомобильный https://mallex.info портал: автообзоры, тесты, ремонт и обслуживание, страхование и рынок. Всё, что нужно водителям и любителям автомобилей.
Автомобильный портал https://autonovosti.kyiv.ua новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё для автолюбителей: от выбора авто до обслуживания и ремонта.
Строительный сайт https://novostroi.in.ua с полезными статьями о ремонте, отделке и дизайне. Обзоры стройматериалов, проекты домов, инструкции и советы экспертов для профессионалов и новичков.
Портал для родителей https://detiwki.com.ua и детей — всё для счастливой семьи. Воспитание, образование, здоровье, отдых и полезные материалы для мам, пап и малышей.
Сайт для женщин https://stylewoman.kyiv.ua с интересными статьями о моде, красоте, семье и здоровье. Идеи для кулинарии, путешествий и вдохновения.
Универсальный сайт https://virginvirtual.net для женщин — секреты красоты, тренды моды, советы по отношениям и карьере, рецепты и стиль жизни.
Журнал садовода https://mts-agro.com.ua полезные советы по уходу за садом и огородом. Сезонные работы, выращивание овощей, фруктов и цветов, современные технологии и секреты урожая.
Сайт для женщин https://gratransymas.com о красоте, моде, здоровье и стиле жизни. Полезные советы, рецепты, тренды, отношения и карьера.
Сайт обо всём https://vybir.kiev.ua энциклопедия для повседневной жизни. Красота, здоровье, дом, путешествия, карьера, семья и полезные советы для всех.
Студия дизайна https://lbook.com.ua интерьера и архитектуры. Создаём стильные проекты квартир, домов и офисов. Индивидуальный подход, современные решения и полный контроль реализации.
Портал про ремонт https://hydromech.kiev.ua свежие статьи о ремонте и отделке, дизайне интерьера и выборе материалов. Полезные советы для мастеров и тех, кто делает ремонт своими руками.
Интересный сайт https://whoiswho.com.ua обо всём: статьи, лайфхаки, обзоры и идеи на самые разные темы. Всё, что нужно для вдохновения и развития, в одном месте.
Онлайн портал https://esi.com.ua про ремонт: идеи для интерьера, подбор материалов, практические рекомендации и пошаговые инструкции для самостоятельных работ.
Репортажи в больших https://infotolium.com фотографиях: самые обсуждаемые события, уникальные кадры и впечатляющие истории. Новости и жизнь в формате визуального рассказа.
Информационный портал https://reklama-region.com про ремонт: ремонт квартир, домов, офисов. Практические рекомендации, современные решения и обзоры стройматериалов.
Сайт про авто https://autoinfo.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
Сайт про автомобили https://black-star.com.ua новинки рынка, цены, тест-драйвы и обзоры. Советы экспертов по выбору и уходу за машиной, тюнинг и автоуслуги.
Автомобильный онлайн-журнал https://allauto.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры новых моделей, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей.
Онлайн-журнал https://autoiceny.com.ua для автолюбителей: автомобили, новости индустрии, тест-драйвы, тюнинг и советы по обслуживанию.
Royal portraits turnyouroyal.com from photos – turn yourself or your loved ones into a king, queen or aristocrat. Author’s work of artists, luxurious style and premium quality of printing.
Some research suggests creatine would possibly barely elevate fasting blood sugar, although not significantly[4].
Other studies indicate creatine could really assist the body process sugar more effectively[9].
One of the concerns when it comes to fasting is the potential caloric intake from any substance
consumed. Nevertheless, creatine monohydrate, the most
common type of creatine supplement, is extremely low in calories.
A typical serving contains just a few calories, which is negligible in the context of a quick.
Therefore, it is unlikely that the caloric content of creatine would significantly
impression the metabolic state of fasting. Creatine supplementation hasn’t been properly studied in fasting situations.
In reality, ingesting it’ll assist your burning of energy throughout the day.
Most pre-workouts out there in the marketplace have some type of creatine supplement or creatine monohydrate in them.
It can be taken both pre-workout or post-workout to assist
your physique recover sooner from an intense workout session. By boosting ATP availability, creatine enhances power and
power output throughout workouts. This results in improved efficiency in resistance training, sprinting, and other explosive actions,
making it in style amongst athletes and gym-goers. If you’re seeking to maximize muscle gains, boost your workout efficiency,
and burn fat extra efficiently, the combination of creatine and intermittent fasting may be your secret weapon. One Other small research
done on humans advised that creatine did not increase fasting insulin ranges.
Mixing an unflavoured creatine complement in water is the finest way to ensure that you don’t break your quick.
In either case, you will get the most profit from supplementing with creatine monohydrate — the most effective and
well-studied kind — daily. Some believe that creatine supplements may cause dehydration and cramps,
however research present that they actually help alleviate them – especially throughout endurance training beneath high heat.
Since creatine absorbs water into the muscular tissues, it’s essential to keep yourself hydrated all through the day.
Creatine, a well-liked supplement amongst athletes and gym-goers,
is usually surrounded by confusion and misinformation.
In this publish, we aim to shed mild on the subject and separate fact from fiction when it
comes to how creatine impacts your quick. To sustain fasting-specific methods like autophagy, it’s higher to keep away from creatine during 24-hour or forty
eight hour longer fasts. Creatine consumption might interfere with
the mobile restore mechanisms induced by fasting.
It’s like adding NOS to your workouts, giving you
additional reps and reducing downtime. Whether you’re chasing gains or simply want your flex to last more, creatine’s obtained your
again. It is usually acceptable to combine creatine along with your
fasting beverage, so long as the beverage does not contain any caloric content that will break the quick.
Water, black espresso, and herbal teas are frequent selections for fasting, and mixing creatine with these drinks mustn’t intrude
with the quick.
By increasing insulin sensitivity, optimizing glycogen storage, and promoting fat metabolism, creatine
could provide a natural and efficient approach to improve performance and body composition.
To get essentially the most out of creatine, think about taking it about half-hour earlier than your exercise.
This allows enough time for it to be absorbed by your muscular tissues and able to
fuel your performance. By consuming creatine before your coaching session, you’ll
be able to reap the benefits of the increased energy and energy it provides,
leading to more effective exercises.
Optimum Nutrition’s Gold Commonplace pre-workout won’t break a quick and is a superb option. Nevertheless, Optimum Nutrition’s Amino
Power pre-workout contains BCAAs and can i take creatine during a fast break a fast, so it is not a great pre-workout choice whereas fasting.
These pre-workout alternate options all have caffeine, so you will nonetheless get an vitality enhance, enhanced focus, and application without different components that might wreck your quick.
If you don’t need to purchase a complement but need an power enhance earlier than your
workout with out ruining your quick, attempt coffee,
green tea, or matcha instead.
For many individuals, the holy period of Ramadan presents a novel problem in relation to health and exercises.
Regardless Of the strict dietary restrictions in place during Ramadan, there are a quantity of
simple ways to maximise your workouts whereas nonetheless
reaping the rewards and benefits of fasting.
The commonest style of fasting you’ll discover
used in this manner is intermittent fasting. This is where an individual will nonetheless eat their regular day by day
calorie intake however will do so over a substantially
smaller period of time. At the tip of the day, take observe of how
supplementing round your exercises makes your thoughts and physique FEEL in the course of the quick itself.
Авто-журнал https://bestauto.kyiv.ua источник информации для автолюбителей. Новинки рынка, сравнения моделей, советы по ремонту и уходу, интересные материалы о мире автомобилей.
Новостной портал https://gau.org.ua круглосуточные новости, комментарии экспертов, события регионов и мира. Политика, бизнес, культура и общество.
Авто портал https://avtomobilist.kyiv.ua всё об автомобилях: новые модели, цены, рынок подержанных авто, тюнинг и автотехнологии. Полезные материалы для автовладельцев.
Онлайн авто-журнал https://mirauto.kyiv.ua с актуальными новостями, аналитикой и обзорами. Тесты автомобилей, тюнинг, технологии и советы по эксплуатации.
Мужской портал https://hooligans.org.ua новости, лайфхаки, обзоры техники, спорт, здоровье и авто. Советы для уверенной и гармоничной жизни.
Портал о ремонте https://dki.org.ua и строительстве: от отделки квартиры до возведения загородного дома. Подробные статьи, рекомендации экспертов и идеи для обустройства жилья.
Портал о стройке https://sushico.com.ua и ремонте. Новости рынка, современные технологии, подборка идей для интерьера и экстерьера. Всё, что нужно для дома и дачи.
Онлайн сайт https://mramor.net.ua о строительстве и ремонте. Всё о возведении домов, ремонте квартир, отделке и обустройстве жилья. Обзоры материалов, советы экспертов и свежие идеи.
Всё о стройке https://aziatransbud.com.ua и ремонте в одном месте: дизайн, архитектура, выбор стройматериалов, инструкции по монтажу, лайфхаки и полезные рекомендации для новичков и мастеров.
Сайт о строительстве https://juglans.com.ua и ремонте — ваш помощник в выборе материалов, инструментов и технологий. Всё о ремонте квартир, строительстве домов и дизайне интерьеров.
Онлайн журнал https://vitamax.dp.ua о строительстве: проекты домов, ремонт квартир, выбор стройматериалов, дизайн и интерьер. Советы экспертов и свежие идеи для комфортной жизни.
Портал про строительство https://texha.com.ua новости рынка, обзоры технологий, инструкции и идеи для ремонта. Материалы для застройщиков, мастеров и тех, кто делает своими руками.
Новости Украины https://gromrady.org.ua онлайн: политика, экономика, спорт, культура и события регионов. Оперативные материалы, аналитика и комментарии экспертов круглосуточно.
Авто портал https://road.kyiv.ua с актуальной информацией: новинки рынка, цены, обзоры, страхование и тюнинг. Полезные статьи и аналитика для автомобилистов.
Портал про авто https://automobile.kyiv.ua свежие новости автопрома, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей и советы по ремонту. Всё о машинах для водителей и автолюбителей.
online audio editor audio editing software
Prodaja https://www.nekretnine-zabljak-placevi.com: stanovi, vile, zemljisne parcele. Izbor smestaja za odmor, preseljenje i investicije. Saveti strucnjaka i aktuelne ponude na trzistu.
Besoin d’un bien immobilier? https://www.immobilier-au-montenegro.com: appartements en bord de mer, maisons a la montagne, villas et appartements. Catalogue de biens, prix actuels et conseils d’experts en investissement.
dianabol post cycle therapy
References:
dianabol cycle for Beginners, hedge.someserver.de,
Фильмы и сериалы Смотреть онлайн бесплатно Онлайн-кинотеатр без регистрации и смс: тысячи фильмов и сериалов бесплатно.
Jak samodzielnie zdjac https://telegra.ph/Jak-samodzielnie-zdj%C4%85%C4%87-sufit-napinany-instrukcja-krok-po-kroku-bez-haka-z-wkr%C4%99tem-i-trikami-monta%C5%BCyst%C3%B3w-08-07 sufit napinany: instrukcje krok po kroku, narzedzia, porady ekspertow. Dowiedz sie, jak zdemontowac plotno bez uszkodzen i przygotowac pomieszczenie do montazu nowej okladziny.
hgh before and after photos
References:
wehrle
оценка полезной модели https://ocenochnaya-kompaniya1.ru
dapagliflozin uk – buy generic dapagliflozin forxiga 10mg cheap
салон красоты спб beauty-salon-spb.ru
Нужен микрозайм? https://kubyshka24.ru: деньги на карту без справок и поручителей. Простое оформление заявки, одобрение за минуты и мгновенное зачисление. Удобно и доступно 24/7.
Today, I went to the beach with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to tell someone!
Town car near me
buy forxiga sale – purchase forxiga pills buy dapagliflozin generic
оценка доли в ооо для суда оценочные компании оценка бизнеса
Авто помощь 24/7 техпомощь на дороге: устранение поломок, подвоз топлива, прикуривание аккумулятора, замена колеса и эвакуация автомобиля.
WOW just what I was looking for. Came here by searching for %meta_keyword%
кат казино
Срочно нужны купить цветы Минск Свежие букеты, праздничные композиции и эксклюзивные флористические решения. Онлайн-заказ и быстрая доставка по городу.
Профессиональные детейлинг автомобиля спб цены: полировка кузова, химчистка салона, восстановление пластика и защита керамикой. Вернём автомобилю блеск и надёжную защиту.
hgh & testosterone
References:
hgh and testosterone cycle (bezraboten.com)
vps hosting usa vps hosting providers
Нужен массаж? Массаж Ивантеевка – профессиональные мастера, широкий выбор техник: классический, оздоровительный, лимфодренажный, детский. Доступные цены и уютная атмосфера.
Обучающие курсы онлайн складчина новые навыки для работы и жизни. IT, дизайн, менеджмент, языки, маркетинг. Гибкий график, практика и сертификаты по итогам.
лампа лупа косметологическая кушетка косметологическая цена
vps hosting in europe vps hosting in europe
поручни для лестницы в частном доме купить Поручни – это важный элемент безопасности на лестницах и других конструкциях. Они помогают сохранять равновесие и предотвращают падения.
косметологическое кресло тумба для педикюра с уф лампой
бетон для фундамента бетон
women before and after steroids
References:
beginner steroid Stack (https://git.tablet.sh/jonathanwatter)
https://zdorovnik.com/vidy-kapelnicz-ispolzuemyh-pri-razlichnyh-tipah-otravlen
Наркологические услуги: наркологическая реабилитация центр, кодирование, детоксикация, снятие ломки, помощь при алкоголизме и наркомании. Круглосуточная поддержка и анонимность.
tripscan Сайт трипскан – это целый мир возможностей для планирования идеального путешествия.
https://sonturkhaber.com/
cutting supplements stacks
References:
best over the Counter steroid
orlistat online – on this site order xenical 60mg generic
generic orlistat – https://asacostat.com/ buy orlistat 120mg for sale
бетон с доставкой куб бетона саратов
Производство шариковых подшипников Стоимость подшипника зависит от множества аспектов: типа, габаритов, бренда и применяемых материалов. Анализ предложений от разных поставщиков позволит найти оптимальное соотношение цены и качества.
Handmade handmade flowers Ideal for home, office decor or original gift. Natural beauty and durability.
Бетон в Воронеже https://stk-vrn.ru продажа и доставка. Все марки для фундаментов, дорожных работ и строительства под ключ. Надёжный производитель и лучшие цены.
поставщики подшипников в рф При выборе подшипников обращайте внимание на репутацию и опыт производителя.
игровой пк rtx 5070 : Сколько стоит хороший ПК для игр: Узнайте стоимость компьютера, подходящего для современных игр.
деньги онлайн займ взять займ онлайн
Аналитика Специальная военная операция (СВО) стала отправной точкой для масштабных геополитических трансформаций. Политика, как инструмент влияния и сфера столкновения интересов, оказалась в эпицентре мирового внимания. Переговоры, олицетворяемые встречами Владимира Путина и Владимира Зеленского, представляют собой сложный поиск компромисса в условиях глубоких противоречий. Финансовый аспект СВО оказал существенное воздействие на глобальную экономику. Санкции, введенные против России, вызвали цепную реакцию, затронувшую Европу, Азию и Америку. Энергетический кризис, инфляционные процессы и перебои в поставках стали реальностью для многих стран. Безопасность и оборона приобрели первостепенное значение. Укрепление национальных армий, поиск новых союзников и усиление военных блоков стали приоритетными задачами. Кавказ и Ближний Восток, традиционно отличающиеся нестабильностью, оказались в зоне повышенного риска. Новости и аналитика играют важную роль в формировании общественного мнения. Однако, в условиях информационной войны, объективность и непредвзятость информации становятся особенно ценными.
микрозаймы онлайн онлайн займ
займ онлайн бесплатно займ взять
Entrance Tickets for Festivals https://rock-concert-tickets.ru
Рестораны Хамовников https://restoran-khamovniki.ru топ заведений для встреч, романтических ужинов и семейных обедов. Авторская кухня, стильный интерьер, удобное расположение и достойный сервис.
Лучшие рестораны https://hamovniki-restoran.ru Хамовников для ценителей гастрономии. Подборка заведений с изысканной кухней, качественным сервисом и атмосферой для отдыха и деловых встреч.
Курсы по плазмотерапии обучение прп освоение методик, современные протоколы, практическая отработка. Обучение для специалистов с выдачей сертификата и повышением квалификации.
Профессиональное обучение плазмолифтинг для лица обучение: подробная программа, практические навыки, сертификация. Освойте эффективные методики для применения в медицине и косметологии.
про какое животное обычно рассказывают сказку люди желающие поведать длинную занудную историю История любви обычных людей Любовь – это самое прекрасное и сильное чувство, которое может испытывать человек. Истории о зарождении, развитии и сохранении любви, о преодолении препятствий и о верности чувству, наполняют наши сердца теплом и надеждой. Они напоминают нам о том, что любовь – это основа нашей жизни и что она способна творить чудеса.
железноводск достопримечательности Отдых в горах Кавказа
Детская школа искусств https://elegy-school.ru обучение музыке, танцам, изобразительному и театральному искусству. Творческие программы для детей, концерты, конкурсы и развитие талантов.
Авторские курсы по REVIT https://dashclass.ru обучение созданию интерьеров и архитектурных проектов. Практика, реальные кейсы, индивидуальный подход и профессиональные навыки для работы в проектировании.
чтение Книги, дарующие надежду
Первая помощь детям https://firstaidkids.ru правила оказания при травмах, ожогах, удушье и других ситуациях. Пошаговые инструкции, советы врачей и полезная информация для родителей.
Студия иностранных языков https://whats-up-studiya-inostrannyh-yazykov.ru обучение английскому, немецкому, французскому и другим языкам. Индивидуальные и групповые занятия, современные методики и опытные преподаватели.
wooden gates prices Wood Grain Vinyl Fence Price A great alternative to natural wood.
Срочный вызов сантехника https://master-expert.com в Москве на дом. Услуги сантехника: прочистка засоров, ремонт смесителей, установка приборов учета. Работаем 24/7. Недорого и с гарантией. Подробнее на сайте
Детский сад № 55 https://detsadik55.ru забота, развитие и обучение детей. Современные программы, квалифицированные воспитатели, уютные группы, безопасная среда и внимание к каждому ребёнку.
обучение кайтсёрфингу
Промышленная безопасность https://аттестация-промбезопасность.рф курсы и обучение под ключ. Подготовка к проверке Ростехнадзора, повышение квалификации и сертификация специалистов предприятий.
Автомобили на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya1.ru поиск, проверка, покупка и доставка. Китай и Корея. Индивидуальный подбор под бюджет и пожелания клиента, полное сопровождение сделки.
метадон героин купить куплю бошки гашиш
купить гашиш соли кокаин купить экстази гашиш
Авто из Китая https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru на заказ под ключ: подбор, проверка, доставка и растаможка. Новые и подержанные автомобили, выгодные цены и полное сопровождение сделки.
This is the description of glad I get high on reading. http://fulloyuntr.10tl.net/member.php?action=profile&uid=3239
Авто из Китая под заказ https://dostavka-avto-china.ru кроссоверы, седаны, электромобили и премиальные модели. Индивидуальный подбор, проверка, сопровождение сделки и доставка в ваш город.
Автомобили из Китая на заказ https://avto-iz-kitaya2.ru подбор, покупка и доставка. Полный цикл услуг: диагностика, растаможка, постановка на учёт и гарантия качества.
Заказать авто из Китая https://dostavka-avto-china2.ru новые автомобили с гарантией, выгодные цены и проверенные поставщики. Доставка, таможня и оформление всех документов под ключ.
продаю буксик
This is the big-hearted of scribble literary works I rightly appreciate. http://zqykj.cn/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=303388
Авто на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia.ru поиск, диагностика и сопровождение сделки. Машины из Европы, Кореи, Китая и США. Доставка, растаможка и постановка на учёт.
Автомобили на заказ https://dostavka-avto-russia5.ru профессиональный подбор, юридическая проверка, доставка и растаможка. Индивидуальные решения для каждого клиента.
Хотите заказать авто https://prignat-avto5.ru Мы подберём оптимальный вариант, проверим машину по базам, организуем доставку и таможенное оформление. Выгодные цены и прозрачные условия.
https://daunemas8a.blogspot.com/2025/08/quick-tips-how-do-i-get-my-1xbet-promo.html
CDM3-3FSWPC Насос вертикальный многоступенчатый 0,37 кВт, 3×380 В, 50 Гц, чугун, 70*С
Машины на заказ https://prignat-avto7.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Машины на заказ https://prignat-mashinu5.ru поиск, диагностика и доставка автомобилей. Индивидуальный подбор, проверенные поставщики и прозрачные условия покупки.
Автомобили на заказ https://prignat-mashinu7.ru подбор, проверка, доставка и оформление документов. Машины любых марок и комплектаций с гарантией качества и выгодной ценой.
Цены на ремонт https://remontkomand.kz/ru/price квартир и помещений в Алматы под ключ. Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
Ремонт квартир https://remontkomand.kz и домов под ключ: дизайн-проект, отделка, инженерные работы. Работаем по договору, фиксированные сроки и цены. Гарантия качества и полный контроль этапов.
SEO-продвижение сайтов https://raskrutka-sajtov-bystro77.ru в Москве: вывод в ТОП поисковиков, рост трафика и заявок. Полный комплекс — аудит, семантика, оптимизация, ссылки. Эффективное продвижение под ключ.
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
Строительство домов https://stroycata1og.ru и коттеджей под ключ. Готовые проекты, индивидуальные решения, качественные материалы и полный цикл работ — от фундамента до отделки.
программа для учета документов организации Учет наличных и безналичных расчетов – необходим для финансового контроля. Программы учета покупок позволяют анализировать структуру расходов.
Журнал о саде https://nasha-gryadka.ru и огороде онлайн — статьи о выращивании овощей, цветов и фруктов. Советы по уходу, борьбе с вредителями, подбору семян и организации участка.
взять займ онлайн получить займ
Нужен клининг? лучшие клининговые компании в москве 2026 год. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
Нужен клининг? рейтинг клининговых компаний москвы 2026. Лучшие сервисы уборки квартир, домов и офисов. Сравнение услуг, цен и отзывов, чтобы выбрать надежного подрядчика.
Работа для девушек в Тюмени Работа проституткой в Тюмени: Быстрый и стабильный доход, гибкий график и полная анонимность. Решите свои финансовые вопросы легко и быстро. Безопасность и поддержка гарантированы.
Смотрите сериалы Лучшие сериалы онлайн: https://obzor.city/texty/infotech/onlajn-kinoteatr-lordseries онлайн в хорошем качестве. Новинки, классика и популярные проекты в удобном формате. Бесплатный просмотр без скачивания и доступ 24/7.
Je trouve genial le casino TonyBet, c’est vraiment une experience de jeu incroyable. Il y a une tonne de jeux differents, comprenant des titres innovants. Le service d’assistance est top, repondant rapidement. Les transactions sont securisees, mais parfois il pourrait y avoir plus de promos. En resume, TonyBet vaut vraiment le coup pour les amateurs de casino ! De plus, la plateforme est intuitive, ajoutant une touche de confort.
tonybet официальный сайт|
доставка цветом цветов в москве Откройте для себя лучшие цветочные магазины и салоны Москвы, где качество и сервис сочетаются с доступными ценами. Изучите отзывы клиентов и выбирайте проверенные места. Доставка цветов в Москве недорого: Идеальное Соотношение Цены и Качества
J’apprecie enormement Azur Casino, c’est une veritable energie de jeu irresistible. Il y a une multitude de jeux varies, incluant des slots dynamiques. Les agents sont d’une efficacite remarquable, repondant en un rien de temps. Le processus de retrait est simple et efficace, bien que les offres pourraient etre plus allechantes. En fin de compte, Azur Casino est une pepite pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive et agreable, ajoutant une touche de raffinement.
code azur casino|
Je suis totalement emballe par Banzai Casino, c’est une veritable aventure pleine d’adrenaline. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de table authentiques. Le service d’assistance est exemplaire, offrant des solutions rapides et claires. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, cependant j’aimerais plus de bonus allechants. En conclusion, Banzai Casino offre une experience exceptionnelle pour ceux qui aiment parier ! De plus l’interface est fluide et moderne, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
banzai slots offres|
Je suis completement seduit par Betclic Casino, ca offre une sensation de casino unique. Le catalogue de jeux est incroyablement riche, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le support est d’une reactivite exemplaire, avec un suivi efficace. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Betclic Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Notons egalement que la navigation est simple et agreable, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
betclic retrait en attente|
Нужна контекстная реклама? контекстная реклама для стоматологии под ключ. Настройка в Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads, оптимизация объявлений и контроль заявок.
Je trouve genial le casino TonyBet, c’est vraiment un moment divertissant top. La selection de machines est vaste, avec des machines a sous modernes. Le personnel est tres competent, avec des reponses claires. Le processus de retrait est efficace, cependant j’aimerais plus de bonus. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Par ailleurs, le design est attractif, ajoutant une touche de confort.
tonybet erfahrung|
Комплексные IT-решения https://eclat.moscow для бизнеса: разработка, внедрение, сопровождение и поддержка. Надежные технологии для автоматизации и цифровой трансформации.
Je suis conquis par Banzai Casino, il procure une experience de jeu explosive. Les options de jeu sont epoustouflantes, avec des machines a sous ultra-modernes. Le service d’assistance est exemplaire, repondant en un eclair. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, de temps a autre les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, Banzai Casino est une plateforme incontournable pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Notons aussi que l’interface est fluide et moderne, ajoutant une touche d’elegance et d’energie.
banzai slots offres|
J’apprecie enormement Azur Casino, on dirait une energie de jeu irresistible. Les options de jeu sont impressionnantes, offrant des jeux de table elegants. Le personnel est hautement professionnel, disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus nombreux. En resume, Azur Casino ne decoit jamais pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec soin, facilitant l’immersion totale.
casino bleu azur|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betclic Casino, on dirait une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, comprenant des titres innovants et attrayants. Le service client est exceptionnel, garantissant une aide immediate. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, cependant les bonus pourraient etre plus frequents. Globalement, Betclic Casino ne decoit jamais pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! De plus le design est visuellement epoustouflant, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
match betclic elite en direct|
https://vk.com/burtseva.brows макияж севастополь — Услуги профессиональных визажистов в Севастополе охватывают дневной, вечерний и свадебный макияж, образный грим для фотосессий и мероприятий, а также выезд на локации у моря или в отелях. Климат и образ жизни диктуют требования к стойкости: мастера используют праймеры, фиксаторы, водостойкую косметику и техники, которые выдерживают влагу и ветер. Для невест особенно важен выездной сервис и предварительная репетиция макияжа — это позволяет согласовать образ с причёской, платьем и условиями фотосъёмки (освещение на открытой площадке иначе действует на цвета). Висажист должен учитывать тип и состояние кожи (пористость, жирность), возможные аллергии и особенности фотосъёмки (флеш, вечерний свет). Помимо нанесения, профессионал даёт рекомендации по подготовке кожи: увлажнение и пилинг за несколько дней, отсутствие новых агрессивных процедур перед мероприятием. Обязательно обращайте внимание на гигиену — чистые кисти, одноразовые спонжи и аппликаторы — и на используемые бренды, если у вас есть чувствительность. Для повседневного макияжа визажисты часто предлагают «сэкономленный» домашний вариант с минимальным набором средств, который легко повторить, а также короткие мастер-классы для самостоятельного поддержания образа. При бронировании услуг уточняйте, включён ли в стоимость выезд, сколько времени займёт процесс и есть ли возможность срочной подправки в течение дня.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.com/zh-TC/register?ref=VDVEQ78S
Ich finde es unglaublich toll Billy Billion Casino, es wirkt wie eine unwiderstehliche Energie fur Spieler. Der Katalog ist unglaublich umfangreich, mit klassischen Tischspielen wie Blackjack und Roulette. Das Team bietet schnelle und effektive Unterstutzung, bietet klare und hilfreiche Antworten. Gewinne kommen in Rekordzeit an, gelegentlich ich mir mehr regelma?ige Aktionen wunschen wurde. Kurz gesagt ist Billy Billion Casino ein Muss fur Spieler fur die, die gerne wetten! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist intuitiv auf der mobilen iOS/Android-App, was den Spielspa? noch steigert.
billy billion no deposit bonus|
https://how-to-screenshot.info/
https://cryptobirzhi.com/
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, c’est une veritable sensation de casino unique. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service client est remarquable, repondant en un clin d’?il. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, bien que plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. Dans l’ensemble, 7BitCasino offre une experience de jeu securisee et equitable pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! De plus la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino estafa|
Je trouve completement incroyable Betsson Casino, on dirait une aventure pleine de frissons. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste avec plus de 1500 titres, incluant des slots de derniere generation comme Starburst. Le support est ultra-reactif avec une reponse en 30 secondes via chat, avec un suivi efficace. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Betsson Casino ne decoit jamais pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons egalement que le site est concu avec modernite et ergonomie, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
code parrain betsson|
J’apprecie enormement BetFury Casino, on dirait une experience de jeu electrisante. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, proposant des jeux de table classiques et raffines. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, cependant les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. Pour conclure, BetFury Casino offre une experience securisee et equitable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Ajoutons que le site est concu avec modernite et elegance, amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betfury promo code 2021|
Ich schatze sehr BoaBoa Casino, es bietet eine einzigartige Casino-Atmosphare. Der Katalog ist enorm vielfaltig, mit progressiven Jackpots wie Divine Fortune. Der Kundendienst ist tadellos, mit exzellentem Follow-up. Auszahlungen sind super schnell, oft innerhalb von 24-72 Stunden, obwohl mehr Freispiele waren super. Am Ende ist BoaBoa Casino ein Muss fur Spieler fur die, die gerne wetten ! Zusatzlich die Seite ist mit Stil und Benutzerfreundlichkeit gestaltet, was den Spielspa? noch steigert.
boaboa ticket|
печь полимеризации купить Установка порошковой окраски купить – значит приобрести комплекс оборудования для создания порошкового покрытия, включающий в себя: камеру подготовки поверхности, камеру напыления, печь полимеризации, распылители порошковой краски, систему очистки и рекуперации порошка, компрессор и систему вентиляции. Комплектация установки может варьироваться в зависимости от потребностей производства и размеров окрашиваемых деталей. При выборе установки необходимо учитывать объемы производства, типы окрашиваемых изделий и требования к качеству покрытия.
наркологическая клиника в воронеже Анонимная наркологическая клиника Воронеж – это медицинское учреждение, которое гарантирует своим пациентам полную конфиденциальность и неразглашение информации о прохождении лечения от наркологических заболеваний в городе Воронеж. В анонимных клиниках пациенты могут не указывать свои настоящие имена и личные данные при обращении за помощью.
Je trouve incroyable 1win Casino, ca procure une energie de jeu irresistible. Il y a une multitude de titres varies, incluant des slots de derniere generation. Le service client est de premier ordre, joignable 24/7. Les gains arrivent en un temps record, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. Globalement, 1win Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs de casino virtuel ! En bonus le site est concu avec modernite, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
1win bonus|
J’apprecie enormement Betify Casino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine de frissons. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des titres innovants et engageants. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les gains sont verses en un temps record, occasionnellement davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees. En fin de compte, Betify Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Ajoutons que le design est visuellement percutant, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betify portugal|
Je suis totalement seduit par Casino Action, on dirait une energie de jeu irresistible. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, proposant des jeux de table classiques comme le blackjack et la roulette. Le support est ultra-reactif et disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires et precises. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. Dans l’ensemble, Casino Action offre une experience de jeu securisee avec un indice de securite eleve pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! De plus l’interface est fluide et intuitive, facilite chaque session de jeu.
casino action|
buy belt tensioner rollers
метод swot анализа https://swot-analiz1.ru
Je trouve absolument epoustouflant 1xbet Casino, on dirait une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement phenomenale, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, joignable 24/7. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles. En fin de compte, 1xbet Casino ne decoit jamais pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Notons egalement que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite chaque session de jeu.
telecharger 1xbet pour android|
J’apprecie enormement Betway Casino, ca ressemble a une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Le support est ultra-reactif via chat en direct, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont rapides, souvent traites en 24 heures pour les e-wallets, cependant les bonus comme les 125 tours gratuits pourraient etre plus reguliers. Pour conclure, Betway Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! En bonus l’interface est fluide et moderne avec un theme noir et vert, renforce l’immersion totale.
betway espana|
Ich schatze sehr BingBong Casino, es wirkt wie ein Eintauchen in eine lebendige Spielwelt. Es gibt eine Fulle an abwechslungsreichen Titeln, mit spannenden Jackpot-Spielen wie Mega Moolah. Der Kundenservice ist hervorragend, ist taglich erreichbar. Der Auszahlungsprozess ist einfach und zuverlassig, gelegentlich die Angebote wie der 100%-Bonus bis 100 € konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist BingBong Casino eine erstklassige Plattform fur Leidenschaftliche Zocker ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist mit Stil und Benutzerfreundlichkeit gestaltet, einen Hauch von Flair hinzufugt.
bingbong casino 250 free spins|
Je trouve absolument genial CasinoAndFriends, on dirait une energie de jeu irresistible. Les options de jeu sont vastes et diversifiees, comprenant des jackpots progressifs comme Mega Moolah. Le support est reactif via chat en direct de 6h a minuit, joignable efficacement. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, parfois davantage de recompenses via le programme VIP seraient appreciees. Pour conclure, CasinoAndFriends est une plateforme d’exception pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Ajoutons que le design est visuellement attrayant, facilite chaque session de jeu.
casinoandfriends bonuskod|
Аренда авто в Краснодаре бизнес Прокат авто: Исследуйте мир с комфортом. Откройте для себя новые горизонты с услугой проката авто. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор автомобилей различных марок и моделей, чтобы удовлетворить любые ваши потребности. Наш автопарк включает в себя экономичные автомобили для городских поездок, комфортабельные седаны для деловых встреч и вместительные внедорожники для путешествий по бездорожью. Прокат авто – это удобный и доступный способ получить автомобиль на любой срок, от нескольких часов до нескольких месяцев. Забронируйте свой автомобиль прямо сейчас и начните свое приключение!
медная спираль и кристалл для оргонита Оргонитовая смесь: Компоненты, используемые для изготовления оргонита (смола, металл, кристаллы).
http://avteon.ru
1вин Обзор официального сайта и приложения казино. В мире онлайн-гемблинга важно выбирать не только интересные игры, но и надежную платформу. 1win (или 1вин) — это многофункциональный игровой клуб, который объединяет в себе казино, букмекерскую контору и тотализатор. В этом обзоре мы подробно разберем, как начать играть, какие бонусы ждут новых игроков и как получить доступ к ресурсу через официальный сайт и зеркала. Поиск рабочего официального сайта 1win — первый шаг для каждого игрока. Из-за ограничений в некоторых регионах прямой вход на основной ресурс может быть затруднен. В этом случае на помощь приходят зеркала — точные копии сайта с другим адресом. Они полностью безопасны и позволяют получить доступ к аккаунту и всем функциям. Актуальные ссылки на зеркала лучше всего искать в официальных сообществах проекта или у партнеров. Процесс регистрации в 1win занимает пару минут. Доступно несколько способов: через email, номер телефона или аккаунт в социальных сетях. Но самый важный шаг — это активация промокода. Ввод специального кода при создании аккаунта значительно увеличивает стартовый бонус на первый депозит. Не пропускайте этот этап, чтобы начать игру с максимально возможным банкроллом. Для тех, кто предпочитает играть с телефона, 1win предлагает удобное мобильное приложение. Его можно скачать прямо с официального сайта в формате APK файла для устройств Android. Владельцы iOS также могут найти способ установить программу. Приложение повторяет все функции полной версии сайта: от регистрации и ввода промокода до игры в слоты и live-ставок. Это идеальный выбор для игры в любом месте. 1win стабильно входит в топ рейтингов лучших онлайн-казино по нескольким причинам: Огромная игровая коллекция: Сотни слотов, настольные игры, live-дилеры. Щедрая программа лояльности: Не только приветственный бонус, но и кешбэк, фриспины, турниры. Безопасность и поддержка: Лицензия, шифрование данных и круглосуточная служба заботы о клиентах. 1win — это современная и надежная игровая площадка, которая предлагает полный комплект услуг от казино до ставок на спорт. Не забудьте использовать промокод при регистрации, чтобы получить максимальную выгоду от игры. А если возникнут трудности с доступом — воспользуйтесь рабочим зеркалом или скачайте официальное приложение.
swot анализ процесса https://swot-analiz1.ru
Looking for second-hand? thrifting near me We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
Je suis fan de le casino TonyBet, on dirait un univers de jeu unique. Le choix de jeux est impressionnant, comprenant des titres innovants. Les agents sont reactifs, disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont rapides, occasionnellement plus de tours gratuits seraient bien. En resume, TonyBet ne decoit pas pour les joueurs passionnes ! Ajoutons que, le site est facile a naviguer, facilitant chaque session de jeu.
tonybet affiliate|
Je suis epoustoufle par le casino AllySpin, il procure une experience de jeu electrisante. Le catalogue de jeux est vaste, avec des machines a sous captivantes. Le service d’assistance est impeccable, offrant des solutions rapides. Les retraits sont super rapides, mais parfois davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees. Dans l’ensemble, AllySpin vaut vraiment le detour pour les fans de divertissement numerique ! Notons aussi que l’interface est super intuitive, facilitant chaque session.
allyspin.|
J’adore sans reserve Banzai Casino, ca ressemble a une aventure pleine d’adrenaline. La gamme de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le support est ultra-reactif, offrant des solutions rapides et claires. Les gains arrivent en un rien de temps, cependant les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Banzai Casino vaut largement le detour pour les amateurs de jeux en ligne ! De plus la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ajoutant une touche d’elegance et d’energie.
banzai slots casino en ligne|
J’adore a fond Azur Casino, ca ressemble a une experience de jeu envoutante. Le catalogue est vaste et diversifie, offrant des jeux de table elegants. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, repondant en un rien de temps. Le processus de retrait est simple et efficace, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions. Globalement, Azur Casino vaut vraiment le detour pour les fans de casino virtuel ! Notons egalement que la navigation est intuitive et agreable, ajoutant une touche de raffinement.
horaires casino centre azur hyeres|
J’adore a fond Betclic Casino, il procure une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, proposant des jeux de table classiques et elegants. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees. Pour conclure, Betclic Casino est un incontournable pour les adeptes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et agreable, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
freebet betclic|
Looking for second-hand? thrift stores We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
Ich liebe die Pracht von King Billy Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Kronungsfest funkelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hof, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Triumphzug, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren koniglich. Zusammengefasst ist King Billy Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Kronungsmantel glanzt, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
king billy casino 100 free spins|
Je suis fou de Celsius Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino ardente. Le repertoire du casino est une veritable fournaise de divertissement, incluant des jeux de table de casino elegants et brulants. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, proposant des solutions nettes et rapides. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une braise, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui embrasent. Pour resumer, Celsius Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les explorateurs du casino ! En plus le design du casino est une explosion visuelle volcanique, donne envie de replonger dans le casino a l’infini.
celsius casino bonus sans depot|
Je trouve completement barre Gamdom, c’est une plateforme qui envoie du lourd. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, incluant des jeux de table qui en jettent. L’assistance est au top du top, repondant en mode eclair. Les paiements sont fluides et blindes, par contre des recompenses en plus ca ferait kiffer. En gros, Gamdom garantit un fun intergalactique pour les pirates des slots modernes ! Et puis la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, ajoute un max de swag.
parrainage gamdom|
I tried Uhmegle.org late at night and within seconds I was matched with someone interesting. It’s addictive in a good way.
J’adore l’ambiance de Circus, ca offre une experience electrisante. Le catalogue est incroyablement diversifie, avec des machines a sous immersives. Les agents sont rapides et attentionnes, avec une aide personnalisee. Les transactions sont simples et fiables, de temps a autre les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, Circus vaut pleinement le detour pour les fans de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et attrayante, ajoute une touche de magie.
casino circus avis|
Je kiffe grave Amon Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui envoie du lourd. Le catalogue de jeux du casino est monumental, incluant des jeux de table de casino ultra-styles. Le service client du casino est une pepite, avec une aide qui claque. Le processus du casino est clair et sans prise de tete, parfois les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Amon Casino garantit un fun de casino completement barre pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style au casino ! Et puis le site du casino est une tuerie graphique, facilite le delire total au casino.
amon amarth|
Overall, Uhmegle text chat is a great way to connect without pressure.
J’adore le show de Impressario, c’est une plateforme qui met des etoiles plein les yeux. Le catalogue est un festival de titres, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. Le crew assure un suivi etoile, offrant des reponses qui scintillent. Le processus est limpide et sans fausse note, de temps en temps des bonus plus reguliers ce serait la classe. En gros, Impressario offre un spectacle de jeu inoubliable pour les accros aux sensations eclatantes ! En prime l’interface est fluide et glamour, facilite un show total.
impressario casino|
Ich habe die App getestet, der Download von Uhmegle geht ganz einfach.
cz casino online “: Online Casino CZ: Otestujte sve stesti v legalnich online kasinech v CR. Cekaji na vas stovky her, stedre bonusy a bezpecne prostredi pro zabavu.
online casino cz CZ Casino Online: Looking for a top CZ online casino? Read our expert reviews, compare bonuses, and find the perfect site for your gaming needs.
Estou pirando total com Flabet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um espetaculo. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e viciantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma explosao, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem treta, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um baita plus. Resumindo, Flabet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro fogo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
bonus flabet|
https://miritaly.ru
Ich flippe aus bei DrueGlueck Casino, es hat eine durchgeknallte Casino-Energie. Der Katalog des Casinos ist der Wahnsinn, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist der Hammer, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel und zuverlassig, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren cool. Insgesamt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf Casino-Kicks stehen! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Volltreffer, den Spielspa? im Casino maximiert.
drueckglueck casino erfahrungen|
For people who don’t like typing, this video option is ideal. You get to talk face-to-face instantly.
Je trouve totalement dingue AmunRa Casino, ca donne une energie de casino digne d’un dieu. La gamme du casino est un veritable sanctuaire de divertissement, proposant des sessions de casino en direct qui envoutent. Le service client du casino est digne d’un pharaon, offrant des solutions claires et immediates. Les gains du casino arrivent a la vitesse d’un char, quand meme des bonus de casino plus reguliers ca serait royal. Pour resumer, AmunRa Casino offre une experience de casino mythique pour les gardiens des slots modernes de casino ! Et puis l’interface du casino est fluide et somptueuse, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
amunra casino velemenyek|
Je suis totalement scotche par Instant Casino, il propose une experience de casino explosive. Le catalogue de jeux de casino est colossal, proposant des sessions de casino live qui dechirent. Le service client du casino est une bombe, offrant des reponses qui claquent. Le processus du casino est clean et sans galere, par contre des recompenses de casino en plus ca ferait kiffer. Au final, Instant Casino offre une experience de casino inoubliable pour les aventuriers du casino ! Bonus la navigation du casino est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus kiffante.
instant casino 1|
Very informative blog: click here.
Sometimes I don’t want to turn on my camera, so I use the Uhmegle text chat. It feels private and still connects me with interesting people quickly.
cjc 1295/ipamorelin
References:
https://www.rilezzz.com/read-blog/9186_trump-rages-over-newly-surfaced-epstein-wedding-photos-and-victorias-secret-fash.html
Ich bin suchtig nach JackpotPiraten Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie eine wilde Piratenjagd. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist riesig wie ein Ozean, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie Kanonen donnern. Das Casino-Team bietet eine Unterstutzung, die wie Gold glanzt, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Sabelhieb. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, dennoch wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die funkeln. Zusammengefasst ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Meere beherrscht fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Schatz funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
jackpotpiraten 5 euro|
J’adore l’eclat de Julius Casino, il propose une aventure de casino digne d’un empereur. La selection du casino est une veritable legion de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme heroique. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient glorieux. En somme, Julius Casino offre une experience de casino legendaire pour les conquerants du casino ! En plus l’interface du casino est fluide et majestueuse comme un palais, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus triomphante.
julius casino vip|
Je trouve completement fou Bruno Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui petille de vie. Les choix de jeux au casino sont varies et enivrants, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement hors pair, avec une aide qui fait mouche. Les paiements du casino sont surs et sans accroc, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui dazzlent. Globalement, Bruno Casino promet un divertissement de casino electrisant pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style audacieux, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus exaltante.
casino bruno le maire|
Estou completamente enlouquecido por LeaoWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que e uma fera. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma fera, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma cacada, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma aguia, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Em resumo, LeaoWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e selvagem para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha na selva, da um toque de ferocidade braba ao cassino.
leaowin02 quattrucci casino|
https://usk-rus.ru/ Урал Строй Комплект – Наша компания занимается комплектацией строительных объектов, нефтегазового производства и не только. Одно из главных направлений работы – это гражданское строительство, где наши задачи – поставка металлических изделий и конструкций, труб, сыпучих строительных смесей, других стройматериалов. Также мы поставляем клиентам геосинтетические материалы для дорожного строительства, оборудование для нефтегазовой отрасли и многое другое под запрос. И все это – напрямую с заводов, с которыми у нас заключены официальные соглашения.
русское частное порно русское порно
Want to have fun? porno bangladesh melbet Watch porn, buy heroin or ecstasy. Pick up whores or buy marijuana. Come in, we’re waiting
Новые актуальные iherb промокод кэшбэк для выгодных покупок! Скидки на витамины, БАДы, косметику и товары для здоровья. Экономьте до 30% на заказах, используйте проверенные купоны и наслаждайтесь выгодным шопингом.
bs2best
Je suis fou de CasinoClic, on dirait une cascade de fun. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui fait des etincelles. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une etincelle, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient explosifs. Pour resumer, CasinoClic est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique brillante, facilite une experience de casino vibrante.
casino clic and collect|
Ich finde absolut irre Lapalingo Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Spielwelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop des Spa?es, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern strahlt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Insgesamt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
lapalingo casino login|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von iWild Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Wasserfall rauscht. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leitstern, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Blitz. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Sturm, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Kurz gesagt ist iWild Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Urwald funkelt fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Wasserfall funkelt, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
iwild skate|
Je suis totalement ebloui par JackpotStar Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui illumine tout. Il y a un essaim de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme stellaire. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une comete, assurant un support de casino immediat et eclatant. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Au final, JackpotStar Casino est une etoile brillante pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique lumineuse, ajoute une touche de magie cosmique au casino.
jackpotstar casino promo code|
Je suis accro a LeonBet Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino indomptable. Le repertoire du casino est une savane de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est une force de la nature, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui en imposent. En somme, LeonBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino rugissant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline sauvage du casino ! Bonus le design du casino est une fresque visuelle feroce, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus rugissante.
code bonus leonbet 2024|
https://flactor.ru
ipamorelin 5mg reconstitution
References:
cjc 1295 no dac 5mg with ipamorelin 5mg (https://amigomanpower.com/employer/ipamorelin-side-effects-dosages-administration/)
Ich bin vollig geflasht von Lapalingo Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop des Spa?es, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellen, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Insgesamt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Nebenbei die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Nordlicht, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
lapalingo free spins|
Estou completamente alucinado por JabiBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que arrasta tudo. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um maremoto, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma onda, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, JabiBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fluxo para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, aumenta a imersao no cassino como uma onda gigante.
jabibet apk|
Ich liebe die Magie von JokerStar Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein magischer Spielrausch. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Zauberstab, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Funke. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Kartentrick, ab und zu die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist JokerStar Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Zaubertrick, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
jokerstar automatenspielanbieter|
J’adore la splendeur de LeoVegas Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit comme un roi. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et princiers, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui inspire le respect. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse princiere, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient royaux. Globalement, LeoVegas Casino c’est un casino a conquerir en urgence pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un sceptre, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
leovegasгѓњгѓјгѓЉг‚№|
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. Binance
can you mix hgh fragment 176-191 with ipamorelin
References:
does cjc ipamorelin cause acne; https://charmed-serial.online/user/coltview6/,
Ich bin total begeistert von LuckyNiki Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Sternenstaub funkelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Galaxie voller Vergnugen, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Komet, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Glucksbringer, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren zauberhaft. Alles in allem ist LuckyNiki Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Und au?erdem die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Sternenstaub funkelt, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
luckyniki casino|
Je trouve absolument magique Luckster Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un sort. La collection de jeux du casino est un veritable grimoire, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui enchantent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un sortilege, assurant un support de casino immediat et ensorcelant. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un enchantement, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait magique. En somme, Luckster Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les chasseurs de fortune du casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique enchantee, facilite une experience de casino enchanteresse.
ultimate luckster|
Je suis totalement envoute par MonteCryptos Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un glacier. La selection du casino est une ascension de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le service client du casino est un guide fiable, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans crevasses, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient vertigineux. En somme, MonteCryptos Casino est un casino en ligne qui atteint des sommets pour les aventuriers du casino ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style audacieux, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
casino montecryptos|
J’adore l’univers de Casinova, ca offre une experience inoubliable. Le catalogue est d’une richesse incroyable, incluant des experiences live palpitantes. Le personnel assure un suivi exemplaire, joignable via chat ou email. Les retraits sont rapides et securises, parfois des bonus plus reguliers seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Casinova vaut pleinement le detour pour les passionnes de sensations fortes ! De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ce qui rend chaque partie encore plus plaisante.
casinova|
cjc 1295 ipamorelin itchy skin
References:
https://empowerhunt.com/employer/ipamorelin-sermorelin-blend-for-sale-injectable-peptide/
Je suis totalement envoute par LuckyBlock Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui explose de chance. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. Le service client du casino est une etoile porte-bonheur, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait feerique. Pour resumer, LuckyBlock Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec panache au casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique lumineuse, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus envoutante.
luckyblock 1.11.2|
Je trouve absolument enivrant Lucky8 Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui illumine comme un phare. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et eclatants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance astrale. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un souhait exauce, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un coup de baguette, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. Pour resumer, Lucky8 Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique eclatante, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
code promo lucky8 2019|
tesamorelin/ipamorelin blend
References:
does cjc 1295 ipamorelin make you hungry [http://gitlab.alpaedu.co.kr:8000/rachelelazenby]
Estou pirando com MegaPosta Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura dinamite. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma pedrada. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e um foguete, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, MegaPosta Casino e um cassino online que e um vulcao de diversao para os aventureiros do cassino! Alem disso o design do cassino e uma explosao visual braba, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
megaposta codigo promocional|
Je trouve absolument fascinant MyStake Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino enigmatique. L’eventail de jeux du casino est un coffre aux mysteres, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et perspicace, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une rune dechiffree, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, MyStake Casino est un casino en ligne qui intrigue comme un manuscrit ancien pour les explorateurs des mysteres du casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, facilite une experience de casino mystique.
mystake – play safe|
Adoro o clima brabo de OshCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura lava. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma lava ardente, com slots de cassino unicos e explosivos. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, OshCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! Vale falar tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha vulcanica, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
frais retrait osh|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von Platin Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Schatz funkelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Meisterwerk, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Lichtstrahl, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein glitzernder Gewinn. Am Ende ist Platin Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Und au?erdem die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total luxurios macht.
platin casino preguntas mГЎs frecuentes|
Ich finde absolut verruckt Pledoo Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Wirbelwind tobt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Ozean, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leitstern, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Sturm, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Vulkan ausbrechen. Kurz gesagt ist Pledoo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Windhauch, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
pledoo askgamblers|
Игровая платформа Vavada часто обсуждается в сети.
Бонусные программы делают старт комфортным.
Регулярные активности увеличивают азарт.
Слоты и настольные игры обновляется постоянно.
Вход доступен быстро, и приступить к игре без задержек.
Все подробности смотри здесь: онлайн казино вавада
Estou completamente alucinado por MonsterWin Casino, e um cassino online que ruge como uma fera braba. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma fera. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma fera, com uma ajuda que e puro instinto selvagem. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um dragao, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, MonsterWin Casino e um cassino online que e uma fera total para os aventureiros do cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual feroz, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animal.
monsterwin no deposit bonus|
Sou louco pelo role de PagolBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma faisca, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma centelha, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, PagolBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia eletrica, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como um raio.
pagolbet casino|
Je trouve absolument enivrant PokerStars Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino strategique. Il y a une pluie d’etoiles de jeux de casino captivants, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. L’assistance du casino est fiable et astucieuse, offrant des solutions claires et immediates. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse fulgurante, par moments des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient strategiques. Globalement, PokerStars Casino est un atout maitre pour les fans de casino pour les strateges du casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique etoilee, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
blackjack pokerstars|
https://peterburg2.ru/
https://xn--80aack7aript.xn--p1ai/%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE-%D0%BD%D0%B5-%D0%B2%D1%8B%D0%BF%D1%83%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8F%D1%82-%D0%B7%D0%B0-%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%86%D1%83-%D0%BF%D0%BE-%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%8B%D0%BC-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%BC
Je suis accro a MrPlay Casino, on dirait un carnaval de sensations fortes. La gamme du casino est un veritable feu d’artifice, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui font danser. Le service client du casino est une star de la fete, offrant des solutions claires et immediates. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse endiablee, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient festifs. Au final, MrPlay Casino promet un divertissement de casino eclatant pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une parade, ajoute une touche de panache au casino.
mr.play spiele|
Estou completamente vidrado por PlayUzu Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo vibrante, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um trovao. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tempestades, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, PlayUzu Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma rajada, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
playuzu bet Г© confiГЎvel|
Je trouve absolument siderant NineCasino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme une supernova. Il y a une pluie de meteores de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance astrale. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un astronaute, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait cosmique. Pour resumer, NineCasino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une aurore boreale, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
analyse ninecasino|
https://autosalecontrol.ru/
Игровая платформа Vavada популярно у пользователей.
Акции и промокоды создают комфортные условия для новичков.
Игровые конкурсы поддерживают интерес к игре.
Выбор слотов и настольных игр всегда актуален для игроков.
Создать аккаунт легко, и можно мгновенно приступить к игре.
Подробности смотрите по ссылке: акции вавада
https://hr.rivagroup.su/
туроператор Сэкономьте на проживании с нашими купоны на отели скидки! Используйте их, чтобы получить выгодные предложения на отели по всему миру и сделать свои путешествия более доступными.
Je suis fou de ParisVegasClub, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un cabaret. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme glamour. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un metteur en scene, joignable par chat ou email. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une replique, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, ParisVegasClub est un casino en ligne qui met la scene en feu pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit le design du casino est un spectacle visuel glamour, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus spectaculaire.
code paris vegas club|
Ich bin suchtig nach Richard Casino, es pulsiert mit einer luxuriosen Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen verzaubern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hofstaat, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein kaiserlicher Befehl, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist Richard Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Kronungsjuwel, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
richard casino bonus codes|
J’adore l’eclat de PlazaRoyal Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un trone. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un tresor couronne, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui eblouissent. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, assurant un support de casino immediat et majestueux. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un edit, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait majestueux. Pour resumer, PlazaRoyal Casino promet un divertissement de casino princier pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline royale du casino ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique princiere, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
plaza royal casino app|
cjc no-dac w ipamorelin
References:
https://sciencebookmark.space/item/337544
cjc 1295 / ipamorelin cycle length
References:
https://www.simpra.org:3000/marjoriehinkle
хоста ветеринарная клиника Хоста ветеринарная клиника: Забота о здоровье ваших питомцев в Хосте. Полный спектр ветеринарных услуг для жителей Хосты.
Мягкие окна для террас Мягкие окна для кафе – это отличный способ создать уютную и комфортную атмосферу для ваших посетителей. Они защитят их от ветра, дождя и насекомых, позволяя им наслаждаться отдыхом на свежем воздухе.
игровые автоматы 777 Игровые автоматы играть: простые правила и увлекательный процесс Играть в игровые автоматы – это просто и увлекательно. Правила игры обычно очень простые: вы делаете ставку, вращаете барабаны и ждете, пока на экране не появятся выигрышные комбинации символов. Различные игровые автоматы имеют разные линии выплат и символы, которые определяют размер выигрыша. Некоторые игровые автоматы предлагают бонусные игры и функции, которые могут увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. Игра в игровые автоматы – это отличный способ расслабиться и отвлечься от повседневных забот. Вы можете играть в одиночку или с друзьями, в казино или онлайн-казино.
Je suis accro a Spinsy Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme une boule a facettes. Il y a une vague de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance groovy. Le service client du casino est une star du dancefloor, repondant en un eclair rythmique. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans fausse note, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. En somme, Spinsy Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline rythmee du casino ! Par ailleurs la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une choregraphie, facilite une experience de casino electrisante.
spinsy casino anmeldung|
Je suis fou de Spinanga Casino, on dirait une tempete de plaisir endiablee. La selection du casino est une spirale de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une rafale, repondant en un eclair tumultueux. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse orageuse, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Spinanga Casino promet un divertissement de casino tourbillonnant pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit le design du casino est un spectacle visuel tumultueux, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
spinanga casino reseГ±a|
Je suis fou de Roobet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi vibrante qu’un laser. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et fluorescents, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance electrisante. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un flash de neon, assurant un support de casino immediat et vibrant. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un battement techno, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient danser. Globalement, Roobet Casino offre une experience de casino electrisante pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline vibrante du casino ! De surcroit le design du casino est un spectacle visuel futuriste, ajoute une touche de frenesie au casino.
roobet free money code 2023|
Ich liebe den Glanz von SlotClub Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Laserstrahl funkelt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Regenbogen, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Laser zielt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist SlotClub Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Lichtspiel glitzert fur Spieler, die auf leuchtende Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
slotclub-casino отзывы|
Sou viciado no glamour de Richville Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que brilha como um lustre de cristal. Tem uma cascata de jogos de cassino fascinantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos para criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um mordomo impecavel, com uma ajuda que reluz como ouro. Os pagamentos do cassino sao seguros e impecaveis, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria chique. Resumindo, Richville Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino majestosa para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino reluz com um estilo digno de um palacio, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um rei ao seu trono.
power washing company richville|
таможенный брокер сб карго В мире международной торговли, где каждая деталь имеет значение, правильный выбор таможенного брокера – это залог успеха. Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг, от подготовки документов до представления ваших интересов в таможенных органах. С нами ваши грузы будут доставлены быстро, безопасно и в полном соответствии с законодательством.
cjc 1295 ipamorelin dosage for men
References:
https://guvenilirkisaltma.cfd/maisie74529638
купить курсовую недорого средняя стоимость курсовой работы
займ онлайн займ онлайн на карту срочно
взять онлайн займ на карту займы онлайн без процентов
https://russpain.com/
Распиловка Устройство пристенной дренажной системы: Устройство пристенной дренажной системы – это монтаж системы отвода воды, расположенной вдоль фундамента дома. Пристенная дренажная система защищает фундамент от воздействия влаги, предотвращает образование плесени и грибка, продлевает срок службы здания. Пристенная дренажная система состоит из дренажных труб, уложенных в траншею вдоль фундамента, и дренажного колодца, куда отводится вода. Устройство пристенной дренажной системы – это важный этап строительства или реконструкции дома, который позволяет обеспечить его долговечность и комфорт.
подарокжене Фото картина на заказ Фото которое обработали в стиле картины, и его можно заказать.
Estou pirando com SpinFest Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro delirio festivo. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao de folia, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque dancante. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. Em resumo, SpinFest Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo festivo, adiciona um toque de folia ao cassino.
spinfest casino deutschland|
Adoro o brilho estelar de SpeiCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao reluzente quanto uma supernova. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma constelacao de prazeres, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro foguete, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como estrelas. Resumindo, SpeiCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho estelar para os amantes de cassinos online! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
spei promotional|
J’adore la flamboyance de RubyVegas Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un joyau. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une caverne de pierres precieuses, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance scintillante. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, repondant en un flash scintillant. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, RubyVegas Casino offre une experience de casino luxueuse pour les chasseurs de tresors du casino ! En plus l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un rubis, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
Мы берем на себя все заботы по взаимодействию с таможенными органами, чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на бизнесе: таможенныый брокер для юридических лиц
микрозайм онлайн на карту без отказа мгновенно Я искал место, где могу получить микрозайм онлайн без проверок, и нашел его!
Наша платформа работает круглосуточно и не знает слова перерыв. Бронировать и планировать можно где угодно: в поезде, на даче, в кафе или лежа на диване. Хотите купить билет, пока идёте по супермаркету? Просто достаньте телефон и оформите поездку. Нужно скорректировать планы, отменить или перенести билет? Это тоже можно сделать онлайн, без звонков и визитов https://probilets.com/. Но если возникла проблема, то наши специалисты помогут и все расскажут
Adoro o gingado de SambaSlots Casino, parece uma festa carioca cheia de energia. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de cores, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com muito charme. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista, com uma ajuda que e puro axe. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No fim das contas, SambaSlots Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro ritmo, adiciona um toque de axe ao cassino.
casino grand cercle aix-les-bains|
Je suis completement envoute par Riviera Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui brille comme un bijou mediterraneen. La selection du casino est une promenade de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et raffinee, repondant en un eclat de soleil. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans tempete, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Riviera Casino est un casino en ligne qui brille comme une plage doree pour les navigateurs du casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une mer azur, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
la riviera casino arnaque|
https://mangalfactory.ru/
https://www.ecmo.ru/mediacategories/obzory-105/moskovskoe-metro-fakty-i-legendy-podzemnogo-goroda
Estou completamente alucinado por SSSXWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um buraco negro dancante. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma galaxia de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como constelacoes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia reluzente, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como estrelas. No geral, SSSXWin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
casino sssxwin las vegas|
https://bpr-work.ru/
https://vgarderobe.ru/kupalnik-bikini-s-byustgalterom-push-ap-s-oliver-g-61652-3.html
Sou louco pela vibe de AFun Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura euforia. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um carnaval de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de festa. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um malabarista, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de danca, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Na real, AFun Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro carnaval para os folioes do cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro axe, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
afun bet baixar|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. Na real, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro cosmos, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
betorspin queixas|
Estou completamente apaixonado por BRCasino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um pandeiro. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de prazeres, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que dancam como passistas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro axe, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como confetes, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, BRCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carnaval total para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, adiciona um toque de folia ao cassino.
br77.games|
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von Trickz Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie eine Illusion verblufft. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Hexenwerk, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Kaninchen aus dem Hut, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz aus dem Hut, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein magischer Volltreffer. Zusammengefasst ist Trickz Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zirkus der Magie strahlt fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total verhext.
trickz casino flashback|
Estou pirando com AFun Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um festival de fogos. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela da festa, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem pausa. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tumulto, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial festivo. No fim das contas, AFun Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os folioes do cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como um desfile noturno, adiciona um toque de purpurina ao cassino.
afun entrar|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. Na real, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin Г© legal|
Sou louco pela energia de BRCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma escola de samba na avenida. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que dancam como passistas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um mestre-sala, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque de tamborim. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, BRCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um desfile visual vibrante, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
br77 steakhouse|
Rainbet Casino
https://www.durovis.com/de/board_topic_87739.html
Sou louco pela vibe de Bet558 Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar estelar. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. No geral, Bet558 Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
bet558. com|
Je trouve absolument glacial ViggoSlots Casino, on dirait une tempete de neige pleine de frissons. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et givrees, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance arctique. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse malgre le froid, repondant en un eclair glacial. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse polaire, parfois des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient arctiques. Au final, ViggoSlots Casino offre une experience de casino vivifiante pour les explorateurs polaires du casino ! De surcroit la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un chemin dans la neige, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
viggoslots test|
Estou vidrado no BacanaPlay Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um desfile de carnaval. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de folia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma rainha de bateria, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, BacanaPlay Casino vale demais sambar nesse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
cГіdigo promocional bacanaplay|
Ich liebe den Nervenkitzel von Tipico Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Gewitter losbricht. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein tosender Wasserfall, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Sturm, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Am Ende ist Tipico Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Blitz glitzert fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Regenbogen, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
tipico giriЕџ|
Ich bin suchtig nach Turbonino Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Formel-1-Wagen rast. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und prazise, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der die Konkurrenz uberholt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist Turbonino Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
turbonino support|
требования к дизельному топливу
Adoro o giro de Bet4Slot Casino, parece uma montanha-russa de diversao. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma roda de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de rotacao. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de energia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, Bet4Slot Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como um giro de piao, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais giratoria.
a plataforma bet4slot ГѓВ© confiГѓВЎvel|
I’m totally enchanted by Wazamba Casino, it feels like a safari through a jackpot jungle. The selection is a wild expedition of fun, supporting casino games optimized for cryptocurrencies. The casino support is available 24/7, responding faster than a monkey swinging through trees. Casino transactions are as simple as a tribal dance, at times the casino offers could be more generous. All in all, Wazamba Casino is a casino you can’t miss for fans of modern casino slots! As a bonus the casino interface is smooth and vibrant like a tropical sunrise, amplifying total immersion in the casino.
wazamba chat|
Estou completamente alucinado por BetPrimeiro Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro magma. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma erupcao de emocoes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque vulcanico. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro fogo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem cinzas. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem erupcoes, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, BetPrimeiro Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como lava derretida, adiciona um toque de fogo ao cassino.
betprimeiro scam|
I’m crazy about Wazamba Casino, it’s an online casino that roars like a jungle beast. The casino’s game lineup is a rainforest of delights, supporting casino games optimized for cryptocurrencies. The casino’s customer service is a tribal chief of efficiency, with help that shines like a tribal torch. Casino withdrawals are as fast as a jungle sprint, however more free spins at the casino would be wild. In summary, Wazamba Casino promises casino entertainment that’s untamed for fans of modern casino slots! What’s more casino navigation is intuitive like a tribal path, easing a thrilling casino experience.
wazamba gr|
перевод документов москва бюро переводов документов
https://progress63.ru/ru-ru/
Ich liebe den Rausch von Wheelz Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Adrenalinschub auf Hochstgeschwindigkeit. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie eine wilde Fahrt, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Karussell leuchten. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Meisterfahrer, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der die Kurve kriegt. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein Achterbahn-Drop, manchmal wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Looping explodieren. Am Ende ist Wheelz Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und funkelt wie ein Freizeitpark bei Nacht, das Casino-Erlebnis total turboladt.
wheelz bewertung|
Ich bin total begeistert von Wunderino Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Sprung in eine Wunderwelt. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und bezaubernd, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Zauberlicht leuchten. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Feenstaub, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein magischer Blitz. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Zauberspruch, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren verhext. Am Ende ist Wunderino Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Marchenwald strahlt fur Spieler, die auf magische Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und funkelt wie ein Feenlicht, was jede Casino-Session noch verzauberter macht.
wunderino arena kommende veranstaltungen|
Ich liebe den Rausch von Wheelz Casino, es pulsiert mit einer rasanten Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Meisterfahrer, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Adrenalinschub wirkt. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Schleudertrauma, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Turbo-Kick. Am Ende ist Wheelz Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie eine Achterbahn begeistert fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Ubrigens die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
spyder wheelz te koop|
Ich liebe die Magie von Wunderino Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Marchenbuch verzaubert. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein verwunschener Garten, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zauberspruch wirkt, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, ab und zu die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst ist Wunderino Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Zauberer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, einen Hauch von Marchen-Magie ins Casino bringt.
wunderino arena in kiel|
В поисках самых свежих трейлеров фильмов 2026 и трейлеров 2026 на русском? Наш портал — это место, где собираются лучшие трейлеры сериалов 2026. Здесь вы можете смотреть трейлер бесплатно в хорошем качестве, будь то громкая премьера лорд трейлер или долгожданный трейлер 3 сезона вашего любимого сериала. Мы тщательно отбираем видео, чтобы вы могли смотреть трейлеры онлайн без спойлеров и в отличном разрешении. Всю коллекцию вы найдете по ссылке ниже: https://lordtrailer.ru/
Королева Чиана Если вы ищете что-то новое и захватывающее для чтения, обратите внимание на работы Королевы Чианы. Её проза отличается изысканным стилем, вниманием к деталям и умением создавать атмосферу, которая полностью захватывает читателя. Откройте для себя талантливого автора прямо сейчас!
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque me pegou de surpresa. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: blackjack envolvente, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que me deixou confiante. Fiz saque em Ethereum e o dinheiro entrou em minutos, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino e parada obrigatoria pra quem gosta de cassino. Recomendo sem medo.
4play set de juegos. 4play set of games. es/en/de/fr|
Adoro a aceleracao de F12.Bet Casino, oferece uma aventura que ruge como um escapamento. As opcoes sao ricas e aceleram como turbo. oferecendo lives que explodem como largadas. Os agentes sao rapidos como um pit crew. garantindo suporte direto e sem freadas. As transacoes sao simples como uma mudanca de marcha. de vez em quando mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de pista. No fim das contas, F12.Bet Casino e um motor de emocoes para os fas de adrenalina supersonica! Vale dizer o layout e vibrante como um velocimetro. amplificando o jogo com vibracao turbo.
grupo de sinais f12 bet|
https://vgarderobe.ru/muzhskaya-teplaya-odezhda-bruno-banani-bc-7427.html
Acho simplesmente esportivo MarjoSports Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma torcida em delirio. Os jogos formam uma quadra de diversao. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que marcam como gols. Os agentes sao rapidos como um contra-ataque. oferecendo respostas claras como uma quadra. Os ganhos chegam rapido como um gol. de vez em quando queria mais promocoes que marcam gol como penaltis. Resumindo, MarjoSports Casino garante um jogo que vibra como uma torcida para os exploradores de jogos online! De bonus o site e uma obra-prima de estilo esportivo. criando uma experiencia de cassino de torcida.
banca marjosports|
https://rainbetaustralia.com/
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque me impressionou bastante. A variedade de jogos e bem acima da media: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em transferencia e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que senti falta de ofertas recorrentes, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Na minha visao, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Ja virou parte da minha rotina.
games 4play|
Adoro a aceleracao de F12.Bet Casino, oferece uma aventura que ruge como um escapamento. A selecao de titulos e um motor de prazeres. incluindo mesas com charme de pit lane. O time do cassino e digno de um piloto. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo e claro e sem freadas. em alguns momentos mais bonus regulares seriam velozes. Ao final, F12.Bet Casino garante um jogo que acelera como um carro para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Vale dizer o design e fluido como um pit stop. amplificando o jogo com vibracao turbo.
jogo f12 bet|
Curto demais a quadra de MarjoSports Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um craque. As opcoes sao ricas e vibram como torcidas. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que marcam como gols. Os agentes sao rapidos como um contra-ataque. respondendo rapido como um apito. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma rede. mas as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, MarjoSports Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo esportivo! Por sinal o layout e vibrante como um apito. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura de gol.
cupom 10 reais marjosports|
Sou viciado no fluxo de Brazino Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um recife de corais. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um atol. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como perolas. O servico e confiavel como uma ancora. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes sao faceis como uma onda. porem mais recompensas fariam o coracao nadar. Para encurtar, Brazino Casino garante um jogo que reluz como um coral para os apaixonados por slots modernos! E mais o visual e uma explosao de corais. criando uma experiencia de cassino subaquatica.
https://brazino777.com/pt/landing/190?country=br|
Estou completamente incendiado por Verabet Casino, parece um festival de chamas cheio de adrenalina. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como brasas. Os agentes voam como chamas. com ajuda que ilumina como uma pira. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. de vez em quando queria promocoes que explodem como labaredas. Na real, Verabet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma labareda para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus o site e uma obra-prima de estilo ardente. adicionando um toque de fogo ao cassino.
bet vera cassino|
Sou viciado no calor de Fogo777 Casino, e um cassino online que queima como uma fogueira ancestral. A colecao e um ritual de entretenimento. com slots tematicos de cerimonias antigas. O time do cassino e digno de um guardiao do fogo. garantindo suporte direto e sem cinzas. As transacoes sao simples como uma tocha. mesmo assim mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de fogo. Para encurtar, Fogo777 Casino e um cassino online que e uma fogueira de diversao para os xamas do cassino! Por sinal a interface e fluida e brilha como uma fogueira. dando vontade de voltar como uma labareda.
fogo777 melhor horГЎrio para jogar|
prague plug buy coke in prague
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/171056105/detail.aspx
united kingdom online slots is rivers casino in schenectady open today, online bingo slots uk and no deposit casino bonus usa august 2021, or new zealandn online poker
alliance
Je suis envoute par Grandz Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino voile. vibre avec un voile de jeux varies. proposant des slots de casino a theme theatral. offre un soutien qui effleure tout. garantissant une assistance qui cadence. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un ballet fugace. mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Au final, Grandz Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les danseurs spectraux du casino! En bonus offre un orchestre de couleurs fugaces. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto ephemere.
grandz race|
Galera, quero deixar registrado sobre o Bingoemcasa porque me surpreendeu demais. O site tem um visual descontraido que lembra um bate-papo animado. As salas de bingo sao cheias de energia, e ainda testei varios slots, todos foram bem estaveis. O atendimento no chat foi educado e prestativo, o que ja me deixou satisfeito. As retiradas foram mais velozes que imaginei, inclusive testei PIX e foi impecavel. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que senti falta de ofertas extras, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Pra concluir, o Bingoemcasa virou parada obrigatoria. Com certeza vou continuar jogando
bingoemcasa net|
Estou completamente hipnotizado por IJogo Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um cacador de sombras. Os jogos formam uma rede de diversao. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. Os agentes deslizam como vinhas. respondendo veloz como uma rede. O processo e claro e sem armadilhas. entretanto queria mais promocoes que enredam como vinhas. Em resumo, IJogo Casino garante um jogo que se entrelaca como cipos para os cacadores de vitorias intrincadas! Por sinal o design e fluido como um emaranhado. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura enredada.
como usar bonus ijogo|
buy coke in prague cocain in prague from dominican republic
Estou alucinado com Stake Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que ecoa como um coral. A selecao de titulos e um eco de emocoes. oferecendo lives que explodem como ecos. O atendimento e solido como uma corda. respondendo veloz como uma vibracao. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma corda. porem mais bonus seriam um diferencial ressonante. Resumindo, Stake Casino e uma vibracao de adrenalina para os cacadores de vitorias ressonantes! De bonus o design e fluido como uma onda sonora. dando vontade de voltar como uma vibracao.
stake Г© confiavel|
Je suis seduit par Casinia Casino, offre une quete de plaisir qui captive. Le repertoire du casino est un donjon de divertissement. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance royale. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et loyale. resonnant comme une legende parfaite. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un assaut. parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait legendaire. Globalement, Casinia Casino promet un divertissement de casino legendaire pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique noble. amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
casinia erfahrungen|
1xbet casino promo code vn 1xbet Bangladesh Promo Code: Unlock Exclusive Bonuses and Enhanced Betting Opportunities In the vibrant landscape of online betting in Bangladesh, 1xbet stands out as a leading platform, offering a diverse range of sporting events, casino games, and other exciting opportunities. To amplify the thrill and maximize your winning potential, 1xbet provides a variety of promo codes tailored specifically for Bangladeshi players. These codes unlock exclusive bonuses, free bets, and enhanced odds, giving you a significant advantage in your betting journey. Types of 1xbet Promo Codes Available in Bangladesh: 1xbet Promo Code Bangladesh: This is a general promo code that can be used by both new and existing players in Bangladesh. It typically unlocks a welcome bonus, deposit bonus, or free bet. 1xbet Promo Code Registration Bangladesh: This code is exclusively for new players registering on the 1xbet platform in Bangladesh. It offers an enhanced welcome bonus to kickstart their betting adventure. 1xbet Free Promo Code Bangladesh: This code grants Bangladeshi players a free bet, allowing them to place a wager without risking their own funds. 1xbet Free Bet Promo Code Bangladesh: Similar to the previous code, this one provides a free bet opportunity, often tied to specific sporting events or promotions. 1xbet Bonus Promo Code Bangladesh: This code unlocks a bonus on your deposit, increasing your betting balance and giving you more chances to win. Promo Code for 1xbet Bangladesh Today: This code is a time-sensitive offer, valid only for a specific day. It usually provides a daily bonus, free bet, or enhanced odds on selected events. 1xbet Promo Code for Registration Bangladesh: This code is another registration-specific code, offering a larger welcome bonus than the standard registration bonus. How to Find and Use 1xbet Promo Codes in Bangladesh: 1xbet promo codes are widely available through various channels, including: Official 1xbet Website: Regularly check the 1xbet website for the latest promo code offers. Affiliate Websites: Many affiliate websites dedicated to online betting provide exclusive 1xbet promo codes for Bangladeshi players. Social Media: Follow 1xbet’s official social media accounts to stay updated on new promo code releases. Email Newsletters: Subscribe to 1xbet’s email newsletters to receive promo codes directly in your inbox. To use a promo code, simply enter it in the designated field during registration or when making a deposit. The bonus or free bet will be automatically credited to your account. Maximize Your Winnings with 1xbet Promo Codes: By utilizing 1xbet promo codes, Bangladeshi players can significantly enhance their betting experience and increase their chances of winning. Whether you’re a seasoned bettor or a newcomer to the world of online betting, these codes offer a valuable advantage. So, keep an eye out for the latest 1xbet promo codes and unlock a world of exclusive bonuses and thrilling betting opportunities.
https://mp-digital.ru/
Je suis captive par RollBit Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino bit par bit. Le repertoire du casino est un defilement de divertissement. incluant des tables qui structurent comme un cube. repond comme un pixel precis. proposant un appui qui enchante. fluisent comme une sonate structuree. quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait cubique. En conclusion, RollBit Casino est un casino en ligne qui deroule une symphonie de bits pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino! Ajoutons la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une note pixelisee. amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
what country is rollbit available in|
Je suis fou de Boomerang Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang lance. Le repertoire du casino est un arc de divertissement. offrant des lives qui pulsent comme un cercle. repond comme un boomerang parfait. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides. neanmoins j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui bouclent comme un boomerang. En conclusion, Boomerang Casino est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang pour les lanceurs du casino! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique circulaire. ajoute une touche de rythme arque au casino.
boomerang bet casino|
Curto demais o vortice de XPBet Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um ciclo eterno. Os jogos formam um redemoinho de diversao. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como espirais. O time do cassino e digno de um roteirista. com ajuda que flui como um vortice. Os saques giram como ciclos. as vezes as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Para encurtar, XPBet Casino e uma onda de adrenalina ciclica para os cacadores de vitorias eternas! Alem disso a navegacao e facil como um loop. dando vontade de voltar como um ciclo.
xp bet reclame aqui|
Adoro a energia de DonaldBet Casino, vibra com uma vibe circense eletrizante. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um palhaco. com slots tematicos de espetaculos vibrantes. O time do cassino e digno de um diretor de circo. respondendo veloz como uma acrobacia. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma lona. mesmo assim mais bonus regulares seriam circenses. Em resumo, DonaldBet Casino garante um jogo que reluz como um refletor para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Como extra a interface e fluida e brilha como um picadeiro. tornando cada sessao ainda mais vibrante.
como excluir conta donaldbet|
быстрая накрутка подписчиков в телеграм
Me ecoei no ritmo de JonBet Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino ressonante. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O servico e confiavel como uma camara. respondendo veloz como uma vibracao. As transacoes sao simples como um reverb. as vezes queria mais promocoes que ressoam como corais. Para encurtar, JonBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os maestros do cassino! Como extra a interface e fluida e ressoa como uma harpa. fazendo o cassino ecoar como um sino.
cГіdigo jonbet coringa|
Adoro o giro de XPBet Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um ciclo eterno. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo lives que explodem como vortices. O suporte e um loop preciso. respondendo rapido como um ciclo. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. Na real, XPBet Casino e uma onda de adrenalina ciclica para os roteiristas do cassino! E mais a interface e fluida e gira como um ciclo. fazendo o cassino pulsar como uma roda.
xp bet Г© confiГЎvel|
Me encantei pelo ritmo de DonaldBet Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um mestre de cerimonias. Os jogos formam uma lona de diversao. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes sao faceis como um estalo. porem mais bonus regulares seriam circenses. Na real, DonaldBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os fas de adrenalina vibrante! Como extra o design e fluido como uma acrobacia. adicionando um toque de magia de circo ao cassino.
donaldbet net|
психолог для всех Психолог онлайн – это не только современный тренд, но и деликатное прикосновение к душе сквозь экран. Это возможность получить поддержку и инструменты для решения личных проблем, не жертвуя комфортом и анонимностью. Технологии стирают границы, позволяя обратиться к опытному специалисту, находясь в любой точке мира. Онлайн-консультации – это шаг к себе, сделанный в удобной обстановке, с возможностью выбора профессионала, чьи взгляды и методы работы наиболее созвучны внутренним потребностям. Это инвестиция в собственное благополучие, доступная каждому, кто стремится к гармонии и самопознанию.
накрутка реальных подписчиков в телеграм
Je trouve phenomenal DBosses, c’est une plateforme qui electrise. Il y a une multitude de titres captivants, avec des slots modernes et immersifs. Le service client est d’une classe exceptionnelle, avec une aide personnalisee. Le processus est clair et sans complications, bien que j’aimerais plus de promotions variees. En resume, DBosses est un choix incontournable pour les joueurs pour les fans de jeux modernes ! Notons aussi le design est captivant et elegant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus exaltante.
dbosses casino bonus|
Ich bin total begeistert von King Billy Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein koniglicher Triumph. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hof, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, dennoch mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Kronungsmoment. Zusammengefasst ist King Billy Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
king billy casino (curacao)|
Je suis totalement conquis par BetFury Casino, c’est une veritable energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le service d’assistance est irreprochable, garantissant une aide via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un temps record, de temps en temps ??? j’aimerais plus de promotions frequentes. En resume, BetFury Casino vaut pleinement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! De plus le design est visuellement percutant avec un theme sombre, amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betfury mirrors|
Je suis carrement scotche par Gamdom, ca donne une energie de jeu demente. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, offrant des machines a sous ultra-cool. L’assistance est au top du top, offrant des reponses qui petent. Les transactions sont simples comme un clin d’?il, par contre plus de tours gratos ca serait ouf. Bref, Gamdom garantit un fun intergalactique pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! En prime l’interface est fluide et stylee a mort, ajoute un max de swag.
gamdom authenticator app|
Je trouve absolument fantastique 7BitCasino, ca ressemble a une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, bien que j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles, afin de maximiser l’experience. En fin de compte, 7BitCasino ne decoit jamais pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! De plus l’interface est fluide et retro, facilite chaque session de jeu.
7bitcasino bonuses|
Je suis accro a DBosses, il propose une experience de jeu intense. La selection de jeux est grandiose, avec des slots modernes et immersifs. Le service client est d’une classe exceptionnelle, garantissant un support immediat. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions variees. En resume, DBosses vaut pleinement le detour pour les fans de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, facilite une immersion totale.
dbosses casino|
J’adore passionnement BetFury Casino, ca procure une energie de jeu irresistible. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, comprenant des jeux originaux comme Plinko et Crash avec un RTP jusqu’a 99,28 %. Le support est ultra-reactif et disponible 24/7, repondant en un instant. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies comme Bitcoin ou Ethereum sont ultra-rapides, cependant les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers. Dans l’ensemble, BetFury Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs en quete de sensations fortes ! Notons egalement que le design est visuellement percutant avec un theme sombre, facilite chaque session.
dice betfury|
Je suis a fond dans Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. Il y a un tsunami de titres varies, avec des slots qui claquent grave. Le service client est une tuerie, avec une aide qui dechire tout. Les retraits sont rapides comme un ninja, par moments des recompenses en plus ca ferait kiffer. Dans le fond, Gamdom offre une experience de ouf pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! A noter aussi le site est une tuerie graphique, booste l’immersion a fond les ballons.
coffre d’affiliation gamdom|
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал
накрутка подписчиков тг канале боты
Je trouve carrement genial Impressario, ca balance une vibe spectaculaire. Les options sont variees et eblouissantes, avec des slots qui brillent de mille feux. Les agents sont rapides comme des cometes, garantissant un support direct et brillant. Le processus est limpide et sans fausse note, de temps en temps les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Bref, Impressario garantit un show de fun epique pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Et puis le site est une pepite scenique, facilite un show total.
impressario casino review|
Je trouve incroyable 1win Casino, on dirait une experience de jeu captivante. La bibliotheque de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous modernes et dynamiques. Le support est ultra-reactif et disponible, offrant des solutions claires et efficaces. Les transactions sont bien protegees, de temps en temps les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, 1win Casino est une plateforme exceptionnelle pour les passionnes de jeux en ligne ! En bonus la navigation est simple et rapide, facilite chaque session de jeu.
1win bet|
Estou alucinado com DiceBet Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino alucinante. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e vibrantes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma bomba. A equipe do cassino manda um atendimento que e show, com uma ajuda que e um arraso. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, DiceBet Casino e o lugar certo pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino detona com um look que e puro fogo, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
dicebet reclame aqui|
Ich flippe aus bei DrueGlueck Casino, man fuhlt einen verruckten Spielvibe. Die Casino-Optionen sind super vielfaltig, inklusive stylischer Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr da, mit Hilfe, die richtig abgeht. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie der Blitz, dennoch mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren der Hit. Insgesamt ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Online-Casino, das alles sprengt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
drueckglueck casino no deposit bonus code|
J’apprecie enormement 1xbet Casino, ca procure une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Les agents sont toujours disponibles et efficaces, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les gains sont verses en un temps record, cependant davantage de recompenses seraient bienvenues. En resume, 1xbet Casino est une plateforme d’exception pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Notons egalement que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, renforce l’immersion totale.
download 1xbet apk for android|
Estou impressionado com o 888 Casino, e como se fosse sensacao unica de cassino. A gama de jogos e simplesmente fenomenal, com sessoes de cassino ao vivo imersivas. O servico de assistencia e impecavel, com acompanhamento de excelencia. O processo de retirada e simples e confiavel, no entanto os bonus poderiam ser mais frequentes. No geral, o 888 Casino vale totalmente a pena para os fas de emocoes fortes! Alem disso o site e projetado com elegancia, o que amplifica o prazer de jogar.
888 casino online|
Estou totalmente vidrado em Flabet Casino, e um cassino online que e pura dinamite. Os titulos do cassino sao um show a parte, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de charme. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem enrolacao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem treta, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, Flabet Casino e um cassino online que e um vulcao para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
baixar aplicativo da flabet|
Je suis totalement scotche par Instant Casino, on dirait une tempete de fun. La selection de titres de casino est dingue, avec des slots de casino modernes et immersifs. L’assistance du casino est au top niveau, garantissant un support de casino direct et efficace. Les transactions de casino sont simples comme un neon, quand meme plus de tours gratos au casino ca serait ouf. Bref, Instant Casino garantit un fun de casino supersonique pour les aventuriers du casino ! A noter aussi la navigation du casino est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus kiffante.
instant banking casino payments|
Ich finde absolut irre DrueGlueck Casino, es ist ein Casino, das richtig abgeht. Die Auswahl im Casino ist einfach ein Knaller, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die krachen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr da, mit Hilfe, die richtig abgeht. Auszahlungen im Casino sind blitzschnell, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Am Ende ist DrueGlueck Casino ein Online-Casino, das alles sprengt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Ubrigens die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und mega cool, den Spielspa? im Casino maximiert.
drueckglueck casino|
Je trouve absolument epoustouflant 1xbet Casino, on dirait une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments les promotions pourraient etre plus genereuses. En resume, 1xbet Casino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Ajoutons que le design est visuellement percutant, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
1xbet скачать|
Aprecio imensamente o 888 Casino, oferece uma energia de jogo irresistivel. A gama de jogos e simplesmente fenomenal, com caca-niqueis modernos e envolventes. O servico de assistencia e impecavel, com acompanhamento de excelencia. Os saques sao extremamente rapidos, no entanto eu gostaria de mais promocoes. No geral, o 888 Casino e indispensavel para os apaixonados por jogos digitais! Alem disso o site e projetado com elegancia, reforca a imersao total.
888 casino live chat|
Sou louco pelo clima de Flabet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um espetaculo. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma loucura, com slots de cassino unicos e eletrizantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma explosao, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem treta, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que arrebentam. No fim das contas, Flabet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
roleta flabet|
Je trouve completement fou Instant Casino, ca balance une vibe de jeu dementielle. Il y a un deluge de jeux de casino varies, avec des slots de casino modernes et immersifs. Le support du casino est dispo 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un missile, par moments des recompenses de casino en plus ca ferait kiffer. Au final, Instant Casino est un casino en ligne qui cartonne pour ceux qui kiffent parier dans un casino style ! En prime la navigation du casino est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, donne envie de replonger dans le casino direct.
go wild casino instant play|
plug in prague cocain in prague from dominican republic
купить активных подписчиков в телеграм канал
cocaine prague telegram buy drugs in prague
накрутка подписчиков тг канале боты
сайт для накрутки подписчиков в тг
Футболка надписи рисунки и футболка вид сбоку в Ростове-на-Дону. Черный джемпер и толстовку с рисунком в Вологде. Томск печать на футболке и красивые вышивки на футболке в Курске. Одежда стардью валли и бумага для подарков упаковочная в Ялте. Нужен ли честный знак на футболки оптом и футболка красная мужская https://futbolki-s-printom.ru/
Je suis fou de Julius Casino, on dirait une conquete de fun. La selection du casino est une veritable legion de plaisirs, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui commande le respect. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un decret, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Julius Casino est un casino en ligne qui regne en maitre pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus le design du casino est une fresque visuelle epique, ajoute une touche de grandeur au casino.
avis julius casino|
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von JackpotPiraten Casino, es hat eine Spielstimmung, die alles sprengt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist riesig wie ein Ozean, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen mitrei?en. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist ein echter Schatz, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein echter Schatz. Zusammengefasst ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Schatz funkelt, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
jackpotpiraten meinungen|
Sou viciado no role de LeaoWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura selva. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma fera, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e instintivos. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, com uma ajuda que e puro instinto. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. No geral, LeaoWin Casino e um cassino online que e uma fera total para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia selvagem, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma fera.
leaowin02 casino telecharger|
J’adore le casino TonyBet, on dirait un moment divertissant top. La selection de machines est vaste, comprenant des titres innovants. Le personnel est tres competent, repondant rapidement. Les retraits sont rapides, mais parfois plus de tours gratuits seraient bien. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Ajoutons que, le design est attractif, renforcant le plaisir de jouer.
tonybet code|
Ich flippe aus bei JackpotPiraten Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Schatz funkelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Schatztruhe voller Spa?, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie Kanonen donnern. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellengang, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren der Hammer. Kurz gesagt ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der die Planken erzittern lasst fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Extra die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino auf Hochtouren bringt.
jackpotpiraten 50 freispiele|
Estou completamente enlouquecido por LeaoWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que e uma fera. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de garra. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma fera domada, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem rugas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma aguia, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que mordem. No fim das contas, LeaoWin Casino e um cassino online que e uma fera total para quem curte apostar com garra no cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma trilha na selva, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma fera.
leaowin02 casino inscription|
cocaine prague buy coke in telegram
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, ca procure une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, proposant des jeux de table elegants et classiques. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. Globalement, 7BitCasino est une plateforme d’exception pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement attrayant avec une touche vintage, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino app|
Je trouve absolument sensationnel BetFury Casino, il offre une sensation de casino unique. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Les agents sont toujours professionnels et efficaces, garantissant une aide via chat ou email. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies comme Bitcoin ou Ethereum sont ultra-rapides, bien que j’aimerais plus de promotions frequentes. Pour conclure, BetFury Casino offre une experience securisee et equitable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement percutant avec un theme sombre, ajoute une touche de sophistication a l’experience.
betfury io reddit|
Je suis a fond dans Gamdom, on dirait une explosion de fun. La gamme est une vraie pepite, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. Le crew assure un suivi de malade, garantissant un support direct et carre. Les retraits sont rapides comme un ninja, quand meme des recompenses en plus ca ferait kiffer. En gros, Gamdom c’est du lourd a tester direct pour les pirates des slots modernes ! A noter aussi la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, booste l’immersion a fond les ballons.
gamdom nas?l girilir|
Ich finde absolut majestatisch King Billy Casino, es pulsiert mit einer koniglichen Casino-Energie. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Spa?, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett strahlen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hof, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein koniglicher Erlass. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt ist King Billy Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Palast glitzert fur Abenteurer im Casino! Und au?erdem das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Kronungsjuwel, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
king billy casino free chip|
Je trouve absolument sensationnel BetFury Casino, il offre une energie de jeu irresistible. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le support est ultra-reactif et disponible 24/7, repondant en un instant. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, neanmoins j’aimerais plus de promotions frequentes. En fin de compte, BetFury Casino est un incontournable pour les adeptes de divertissement innovant ! Notons egalement que le design est visuellement percutant avec un theme sombre, ajoute une touche de sophistication a l’experience.
betfury cryptos game|
Je suis a fond dans Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. La gamme est une vraie pepite, offrant des machines a sous ultra-cool. Le crew assure un suivi de malade, offrant des reponses qui petent. Les transactions sont simples comme un clin d’?il, quand meme des recompenses en plus ca ferait kiffer. En gros, Gamdom offre une experience de ouf pour les pirates des slots modernes ! A noter aussi le design est une bombe visuelle, donne envie de replonger non-stop.
error 429 gamdom|
подобрать подшипник по размерам онлайн Подшипник для конвейера: Этот запрос указывает на потребность в подшипниках, предназначенных для использования в конвейерных системах. Подшипники для конвейеров должны обладать высокой надежностью, износостойкостью и способностью выдерживать высокие нагрузки. Они могут быть шариковыми, роликовыми или игольчатыми, в зависимости от типа конвейера и условий эксплуатации. При выборе подшипников для конвейерных систем необходимо учитывать тип транспортируемого груза, скорость движения ленты, температурный режим и наличие агрессивных сред.
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал боты бесплатно
накрутка подписчиков в тг без заданий
tripscan зеркало Трипскан топ: “Трипскан топ” — это запрос, который пользователи вводят в поисковых системах, чтобы найти информацию о том, насколько Tripscan является одним из лучших или наиболее рекомендуемых сервисов для планирования путешествий. Пользователи, которые вводят этот запрос, заинтересованы в рейтингах, обзорах, сравнениях с другими сервисами и отзывах других пользователей. Они хотят узнать о преимуществах и недостатках сервиса Tripscan, а также о том, насколько он эффективен в поиске выгодных предложений и предоставлении качественных услуг. Результаты поиска по запросу “Трипскан топ” могут включать в себя статьи, блоги, форумы и другие онлайн-ресурсы, содержащие информацию о репутации и эффективности сервиса Tripscan.
щетки
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые бесплатно
бровист севастополь Хотите сделать перманент бровей Симферополь? Наш салон предлагает качественный перманентный макияж бровей в Симферополе по доступным ценам. Наши мастера имеют большой опыт работы и используют только сертифицированные пигменты премиум-класса. Мы создадим для вас брови вашей мечты, которые будут радовать вас каждый день! Запишитесь на консультацию и получите бесплатный эскиз!
Ich finde absolut irre Lapalingo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Regenbogen funkelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Kaleidoskop des Spa?es, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Funke spruht. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Sonnenstrahl, ab und zu mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Kurz gesagt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
lapalingo bonus code eingeben|
Ich liebe den Zauber von Lapalingo Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Regenbogen funkelt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein Ozean voller Schatze, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Donnerschlag. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Am Ende ist Lapalingo Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Feuerwerk knallt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
lapalingo 10 euro bonus ohne einzahlung|
Наша команда имеет большой опыт работы с таможней и помогает клиентам экономить на логистике: таможенныый брокер для юридических лиц
Sou viciado no role de JabiBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e puro tsunami. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma tempestade, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao uma explosao. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, com uma ajuda que e pura correnteza. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que arrasam. No geral, JabiBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma mare cheia para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia oceanica, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como a mare.
jabibet|
Je suis totalement ensorcele par LeoVegas Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu princiere. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui eblouissent. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement majestueux, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait grandiose. Dans l’ensemble, LeoVegas Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style imperial, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
leovegas app apk|
Ich bin suchtig nach Lowen Play Casino, es pulsiert mit einer unbezahmbaren Casino-Energie. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und kraftvoll, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und machtig, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Pfad im Busch, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Volltreffer. Zusammengefasst ist Lowen Play Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
löwen play leer|
Ich bin total begeistert von Platin Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Schatz funkelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Meisterwerk, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein glanzender Edelstein, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, ab und zu die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem ist Platin Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Spieler, die auf luxuriose Casino-Kicks stehen! Nebenbei die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Funkeln, einen Hauch von Glanz ins Casino bringt.
platin casino no deposit bonus codes 2018|
накрутка подписчиков в тг бесплатно онлайн
активные подписчики в тг канал
накрутка настоящих подписчиков в телеграм
Je suis fou de Luckland Casino, on dirait une fontaine de chance. Le repertoire du casino est une constellation de divertissement, comprenant des jeux de casino optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le service client du casino est une etoile porte-bonheur, repondant en un eclair magique. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans malefice, mais j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui brillent. Globalement, Luckland Casino c’est un casino a decouvrir en urgence pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! De surcroit le design du casino est une explosion visuelle feerique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus magique.
luckland reviews|
Je suis totalement ensorcele par Lucky8 Casino, ca degage une vibe de jeu petillante comme une comete. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui brillent. Le service client du casino est une etoile porte-bonheur, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans malefice, mais les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Lucky8 Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline lumineuse du casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique eclatante, facilite une experience de casino feerique.
lucky8 casino bonuses|
накрутка живых подписчиков в тг дешево
Je suis totalement envoute par Luckland Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme un trefle a quatre feuilles. Il y a un raz-de-maree de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance feerique. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, repondant en un eclair magique. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse feerique, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. En somme, Luckland Casino est un casino en ligne qui porte chance pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! En plus la plateforme du casino brille par son style ensorcelant, facilite une experience de casino enchanteresse.
luckland free slots games|
Ich liebe die Strahlkraft von LuckyNiki Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Regenbogen glitzert. Es gibt eine Woge an packenden Casino-Titeln, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und strahlend, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Insgesamt ist LuckyNiki Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Sternenhimmel strahlt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Zauberspruch, das Casino-Erlebnis total verzaubert.
luckyniki casino no deposit bonus|
https://www.restate.ru/
Good suggestions. I also recommend check this out.
Je trouve extraordinaire Casinova, ca offre une experience inoubliable. Les jeux sont diversifies et captivants, incluant des experiences live palpitantes. Le support est disponible a toute heure, avec un service personnalise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, meme si j’aimerais plus de promotions variees. Globalement, Casinova est une plateforme d’exception pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite une immersion totale.
casinova erfahrungen|
J’adore le delire de Madnix Casino, ca pulse avec une energie de casino totalement folle. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et dejantes, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et delirantes. Le service client du casino est une decharge electrique, avec une aide qui claque comme un coup de tonnerre. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un clin d’?il, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui envoient du lourd. Au final, Madnix Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait trembler les murs pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un coup de genie, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus dejantee.
s inscrire sur madnix|
Je suis bluffe par Casinova, on ressent une energie debordante. La gamme est tout simplement spectaculaire, incluant des experiences live palpitantes. L’assistance est d’une efficacite redoutable, garantissant une aide instantanee. Le processus est clair et sans accroc, parfois des bonus plus reguliers seraient un plus. En resume, Casinova vaut pleinement le detour pour les fans de jeux modernes ! De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et rapide, facilite une immersion totale.
casinova casino schweiz|
Je suis accro a Lucky31 Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui illumine tout. Les choix de jeux au casino sont riches et envoutants, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. Le service client du casino est une etoile porte-bonheur, proposant des solutions claires et instantanees. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans sortilege, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait ensorcelant. Pour resumer, Lucky31 Casino promet un divertissement de casino scintillant pour les chasseurs de fortune du casino ! Bonus le site du casino est une merveille graphique eclatante, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
lucky31 mom compte|
ПиратХаб курсы
ремонт кавоварок у Львові ціни
газовое пожаротушение мгп Установка газового пожаротушения Установка газового пожаротушения (УГП) — это комплекс оборудования, предназначенный для автоматического обнаружения и ликвидации пожара с помощью газовых огнетушащих веществ (ГОТВ). УГП используются для защиты помещений с ценным оборудованием, архивов, музеев, серверных, электрощитовых и других объектов, где применение традиционных средств пожаротушения (вода, пена, порошок) может привести к их повреждению. Основные элементы УГП: Детекторы пожара: Извещатели, реагирующие на факторы, сопровождающие пожар (дым, тепло, пламя). Прибор приемно-контрольный пожарный (ППКП): Собирает и обрабатывает сигналы от детекторов, определяет наличие пожара, управляет исполнительными устройствами. Баллоны с ГОТВ: Содержат огнетушащее вещество под давлением. В качестве ГОТВ могут использоваться: Инертные газы (азот, аргон, углекислый газ); Хладоны (HFC-227ea, FK-5-1-12); Смеси газов. Модули газового пожаротушения (МГП): Представляют собой баллон с ГОТВ и запорно-пусковым устройством (ЗПУ), обеспечивающим выпуск газа при срабатывании системы. Трубопроводы и насадки-распылители: Доставляют ГОТВ к защищаемому помещению и обеспечивают его равномерное распределение. Система управления и контроля: Обеспечивает автоматическое и ручное управление УГП, контроль ее работоспособности, выдачу сигналов о неисправностях. Система оповещения о пожаре и эвакуации людей: Предупреждает людей о пожаре и необходимости эвакуации из помещения. Принцип работы УГП: Детекторы пожара обнаруживают признаки пожара. ППКП анализирует сигналы от детекторов и, в случае подтверждения пожара, формирует сигнал на запуск УГП. ЗПУ МГП открываются, и ГОТВ под давлением поступает по трубопроводам к насадкам-распылителям. ГОТВ равномерно распределяется по объему защищаемого помещения, снижая концентрацию кислорода или ингибируя процесс горения. Пожар ликвидируется. Преимущества УГП: Высокая эффективность тушения: Быстро и надежно ликвидируют пожар, в том числе в труднодоступных местах. Безопасность для оборудования: Не повреждают защищаемое оборудование, так как ГОТВ не являются электропроводными и не оставляют следов. Возможность применения в помещениях с высокой концентрацией электронного оборудования. Автоматическое срабатывание. Недостатки УГП: Высокая стоимость: УГП дороже водяных и порошковых систем пожаротушения. Требования к герметичности помещения: Для эффективной работы УГП необходимо обеспечить герметичность помещения, чтобы предотвратить утечку ГОТВ. Опасность для людей: При высокой концентрации ГОТВ могут быть опасны для здоровья, поэтому перед запуском УГП необходимо эвакуировать людей из помещения. Установка газового пожаротушения — это эффективное средство защиты от пожара, которое требует квалифицированного проектирования, монтажа и обслуживания.
продвижение в социальных сетях Маркетинговое продвижение бренда Маркетинговое продвижение бренда – это комплекс стратегических мероприятий, направленных на формирование и укрепление позитивного имиджа компании в сознании целевой аудитории. Это не просто реклама, а создание устойчивых ассоциаций с вашим брендом, формирование лояльности и, в конечном итоге, увеличение продаж. Этапы продвижения бренда: Аудит бренда: Анализ текущего состояния бренда, выявление сильных и слабых сторон, определение целевой аудитории и конкурентов. Разработка стратегии: Определение целей продвижения, разработка позиционирования бренда, ключевых сообщений и каналов коммуникации. Разработка фирменного стиля: Создание визуальной идентичности бренда, включая логотип, цветовую палитру, шрифты и другие элементы. Разработка контент-стратегии: Создание контента, который отражает ценности бренда, привлекает целевую аудиторию и формирует экспертный имидж компании. Реализация стратегии: Запуск рекламных кампаний, продвижение в социальных сетях, участие в мероприятиях, работа со СМИ и другие активности. Мониторинг и анализ: Отслеживание результатов продвижения, анализ эффективности каналов коммуникации, внесение корректировок в стратегию. Основные инструменты: Реклама: Размещение рекламы в различных каналах (онлайн и офлайн) для привлечения внимания к бренду. PR: Формирование позитивного общественного мнения о бренде через работу со СМИ и общественностью. SMM: Продвижение бренда в социальных сетях для установления контакта с целевой аудиторией и формирования лояльного сообщества. Контент-маркетинг: Создание и распространение полезного и интересного контента для привлечения и удержания аудитории. Event-маркетинг: Организация и участие в мероприятиях для повышения узнаваемости бренда и установления контакта с потенциальными клиентами. Инвестиции в продвижение бренда – это инвестиции в будущее вашего бизнеса. Грамотно выстроенная стратегия позволит вам выделиться на фоне конкурентов, привлечь лояльных клиентов и увеличить прибыль.
квалифицированный психотерапевт психиатр Консультация психиатра онлайн в Телеграм. Быстрый и удобный способ получить ответы на свои вопросы и определиться с дальнейшим планом лечения.
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм канал живых
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura lava. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e incendiarias, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de fogo. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brisa, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, OshCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro fogo para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
osh 2025|
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de diversao, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, com uma ajuda que reluz como uma aurora boreal. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como supernovas. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma supernova para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin reclame aqui|
Kingpin Crown in Australia is a premium entertainment venue offering bowling, laser tag, arcade games, karaoke, and dining: Kingpin Crown customer reviews
Estou pirando com OshCasino, e um cassino online que detona como um vulcao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino unicos e explosivos. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma faisca de eficiencia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, OshCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, da um toque de calor brabo ao cassino.
application osh|
Estou completamente vidrado por MegaPosta Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira explosao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e um foguete, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial insano. No geral, MegaPosta Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia explosiva, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
megaposta.|
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево
продвижение бренда в интернете Консультация по маркетингу: Экспертное руководство для вашего бизнеса Консультация по маркетингу – это ценная возможность получить экспертное мнение и практические рекомендации по развитию вашего бизнеса от опытного маркетолога. Это шанс взглянуть на ваш бизнес свежим взглядом, выявить скрытые возможности и устранить препятствия, мешающие вам достичь ваших целей. В отличие от теоретических знаний, консультация по маркетингу дает вам практические инструменты и стратегии, которые вы можете немедленно применить в своем бизнесе. Я помогу вам найти оптимальные решения для ваших конкретных задач и проблем. Что вы получите на консультации: Глубокий анализ вашего бизнеса: Я проведу тщательный анализ вашего бизнеса, чтобы понять ваши сильные и слабые стороны, целевую аудиторию, конкурентную среду и потенциальные возможности для роста. Определение четких маркетинговых целей: Я помогу вам определить четкие и измеримые маркетинговые цели, которые соответствуют вашим общим бизнес-целям. Разработка индивидуальной маркетинговой стратегии: Я создам индивидуальную маркетинговую стратегию, учитывающую особенности вашего бизнеса, целевую аудиторию и бюджетные ограничения. Рекомендации по выбору маркетинговых инструментов: Я дам вам рекомендации по выбору наиболее эффективных маркетинговых инструментов для достижения ваших целей, включая SEO, контекстную рекламу, SMM, контент-маркетинг, email-маркетинг и другие. Практические советы по улучшению маркетинговой деятельности: Я поделюсь с вами проверенными советами и стратегиями по улучшению вашего сайта, рекламных кампаний, контента и других аспектов маркетинга. Ответы на все ваши вопросы: Я отвечу на все ваши вопросы, связанные с маркетингом, развею ваши сомнения и помогу вам принять правильные решения для вашего бизнеса. Когда вам нужна консультация по маркетингу: Вы не знаете, с чего начать маркетинговое продвижение вашего бизнеса. Вы тратите деньги на рекламу, но не видите желаемых результатов. Вы хотите увеличить продажи, но не знаете, как это сделать. Вы планируете вывести на рынок новый продукт или услугу. Вы хотите улучшить свой сайт и привлечь больше посетителей. Вы хотите повысить узнаваемость своего бренда. Вы хотите получить независимую оценку вашей текущей маркетинговой деятельности. Консультация по маркетингу – это инвестиция в ваш успех. Получите профессиональную поддержку и выведите свой бизнес на новый уровень!
Acho simplesmente brabissimo PagolBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma faisca, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, PagolBet Casino e um cassino online que e um relampago de diversao para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma faisca, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
pagolbet cassino|
Estou completamente alucinado por MonsterWin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura selva. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo selvagem, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de garra. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um predador, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um dragao, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial monstro. No geral, MonsterWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com garra no cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual feroz, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma fera.
monsterwin no deposit bonus|
Je trouve absolument enivrant PokerStars Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui scintille comme un tapis vert. La selection du casino est une constellation de delices, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance tactique. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un bluff bien joue, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme une donne gagnante, parfois des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient vibrer. En somme, PokerStars Casino est un atout maitre pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline tactique du casino ! En plus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une strategie gagnante, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
code bonus pokerstars 2025|
накрутить подписчиков в тг
Ich liebe die Energie von PlayJango Casino, es pulsiert mit einer elektrisierenden Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter knistern. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern glanzt, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Donnerschlag. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Komet, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Alles in allem ist PlayJango Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und glitzert wie ein Polarlicht, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
playjango casino login|
Sou louco pela vibe de Bet558 Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma constelacao de emocoes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque cosmico. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro meteoro, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia cosmica, mesmo assim mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Resumindo, Bet558 Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho estelar para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
https://bet558.com|
Je suis totalement captive par PokerStars Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino strategique. Le repertoire du casino est un tournoi de divertissement, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui electrisent. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un bluff bien joue, repondant en un eclair strategique. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse fulgurante, parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent. Au final, PokerStars Casino est un atout maitre pour les fans de casino pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style audacieux, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
pokerstars sport offre de bienvenue|
Crown Metropol Perth is a luxury hotel located near the Swan River. It offers modern rooms, a stunning pool area, fine dining, a casino, and entertainment options: Crown Metropol Perth room rates
https://alive-portal.ru/
Estou pirando com PlayUzu Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que faz tudo voar. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um furacao, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. Na real, PlayUzu Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro gas para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
playuzu como retirar dinero|
Je trouve incroyablement delirant MrPlay Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui swingue comme un orchestre. Il y a une ribambelle de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance festive. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un maestro, garantissant un support de casino instantane et eclatant. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans fausse note, mais des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient festifs. Globalement, MrPlay Casino offre une experience de casino exuberante pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline festive du casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une parade, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
mr.play petos|
J’adore la vague de Posido Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino aquatique. Il y a une maree de jeux de casino captivants, proposant des slots de casino a theme aquatique. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une vague deferlante, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un courant marin, parfois des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient marins. Pour resumer, Posido Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait des vagues pour les navigateurs du casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une mer turquoise, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
posido casino support|
займ быстрый займ
Acho simplesmente brabissimo ParamigoBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sao um tornado. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um raio, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem turbulencia. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tempestades, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, ParamigoBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro vento para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro trovao, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como um furacao.
paramigobet welcome bonus|
Je suis fou de MrPlay Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui deborde de panache comme un festival. La gamme du casino est un veritable feu d’artifice, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance festive. Le service client du casino est une star de la fete, repondant en un clin d’?il festif. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait enivrant. Dans l’ensemble, MrPlay Casino c’est un casino a rejoindre sans attendre pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! A noter l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une parade, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus exuberante.
mr.play erfahrungen|
Je suis fou de Posido Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui ondule comme une mer dechainee. La selection du casino est une vague de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui eclaboussent. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui fait des vagues. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans remous, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eclaboussent. Globalement, Posido Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les navigateurs du casino ! De surcroit le design du casino est un spectacle visuel aquatique, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
cГіdigo promocional posido|
как накрутить подписчиков в тг канале живых
Нужны автостекла? замена автостекол Khan Auto Glass — это профессиональная компания, которая специализируется на продаже и установке автомобильных стёкол в Санкт-Петербурге. Мы гордимся тем, что стали надёжным партнёром для множества автовладельцев, которые ценят качество и профессионализм.
Услуги озвучки – переводы текстов бюро. Перевод документов для фармацевтических компаний. Сертификаты качества, инструкции к лекарствам, клинические исследования. Соответствие международным стандартам.
керамічна цегла це https://remontuem.te.ua
Нужна лабораторная? выполнение лабораторных на заказ Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Je suis totalement envoute par ParisVegasClub, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un cabaret. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance theatrale. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et impeccable, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans fausse note, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait enivrant. Pour resumer, ParisVegasClub est un casino en ligne qui met la scene en feu pour les artistes du casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique theatrale, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
paris vegas club accesso|
Нужна презентация? презентация заказать студенту Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Нужен чертеж? чертежи выполнить на заказ выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Je suis accro a MrXBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui serpente comme un labyrinthe. La selection du casino est une enigme de delices, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et captivantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un maitre des enigmes, avec une aide qui devoile les mysteres. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un code decrypte, quand meme j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui intriguent. Pour resumer, MrXBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino enigmatique pour les detectives du casino ! A noter le site du casino est une merveille graphique enigmatique, facilite une experience de casino mysterieuse.
code bonus mrxbet 2021|
Алкоголь ночью с доставкой на дом в Москве. Работаем 24/7, когда обычные магазины закрыты. Широкий ассортимент: пиво, сидр, вино, шампанское, крепкие напитки. Быстрая доставка в пределах МКАД за 30-60 минут: доставка алкоголя москва круглосуточно
Ich bin total hingerissen von Richard Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Thron funkelt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hofstaat, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Kronungsmoment. Am Ende ist Richard Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Und au?erdem die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und prunkvoll wie ein Thronsaal, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
richard online casino|
https://marmok-store.ru/
Je suis accro a PlazaRoyal Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino majestueuse. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est un tresor couronne, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le service client du casino est digne d’un monarque, repondant en un eclair imperial. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient royaux. Dans l’ensemble, PlazaRoyal Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit la navigation du casino est intuitive comme un decret, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus majestueuse.
plaza royal casino login|
Je trouve absolument envoutant Winamax Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino aquatique. La selection du casino est une vague de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et immersives. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un capitaine, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un courant marin, cependant les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. En somme, Winamax Casino promet un divertissement de casino aquatique pour les navigateurs du casino ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme une mer turquoise, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
plus gros gain winamax|
Ich liebe die Pracht von Richard Casino, es pulsiert mit einer luxuriosen Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett leuchten. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren furstlich. Am Ende ist Richard Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
richard mille casino|
https://kitehurghada.ru/
Нужна лабораторная? https://lab-ucheb.ru Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
https://kitehurghada.ru/
накрутка подписчиков и просмотров тг
Нужна презентация? презентация заказать цена Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
подписчики в тг канал реклама
Нужен чертеж? изготовление чертежей на заказ выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Shining Crown demo oyunu ilə klassik meyvə slotunu risksiz sına.
Crown shining sadə və maraqlı oyun təcrübəsidir.
Shining crown 40 slotları klassik kombinasiya təklif edir. Shining crown amusnet çoxlu oyun variantı ilə tanınır. Shining Crown oyunu klassik meyvə simvollarını əhatə edir.
Shining crown joc gratis təcrübə qazandırır.
Shining crown casino çoxlu bonus imkanları verir.
Ən maraqlı slotlardan biri [url=https://shining-crown.com.az/]40 shining crown[/url].
Shining crown jackpot həyəcan dolu anlar yaşadır.
Shining crown pacanele oyunçular arasında çox populyardır.
https://1-kino.ru/
buy cocaine in telegram coke in prague
cocaine prague pure cocaine in prague
Записаться к неврологу https://www.docplus24.ru
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinsy Casino, on dirait une soiree disco pleine de frissons. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et rythmees, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui pulsent comme un beat. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un pas de danse, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse funky, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait dansant. Dans l’ensemble, Spinsy Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style funky, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
avis casino spinsy|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin apk|
Ich bin total hingerissen von SlotClub Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Wirbelwind durch die Nacht rast. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Regenbogen, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Stroboskop blinken. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Laser zielt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Leuchtfeuer, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Feuerwerk knallen. Alles in allem ist SlotClub Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Blitz einschlagt fur Spieler, die auf leuchtende Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Laserstrahl funkelt, den Spielspa? im Casino in die Hohe treibt.
slotclub отзывы|
накрутка подписчиков телеграм без регистрации
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinsy Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme une boule a facettes. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une choregraphie de plaisirs, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui pulsent comme un beat. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un pas de danse, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans fausse note, par moments des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient groovy. Au final, Spinsy Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une choregraphie, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus dansante.
spinsy casino app download|
Je suis fou de Spinanga Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi virevoltante qu’un cyclone. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une tornade de delices, proposant des slots de casino a theme audacieux. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un maitre des vents, assurant un support de casino immediat et dynamique. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme une brise, par moments plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait dement. Au final, Spinanga Casino offre une experience de casino virevoltante pour les dompteurs de tempete du casino ! Bonus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel tumultueux, amplifie l’immersion totale dans le casino.
spinanga ОјПЂПЊОЅОїП…П‚|
Sou viciado no glamour de Richville Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao sofisticada quanto uma mansao de ouro. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um cofre de prazeres, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como joias. A equipe do cassino oferece um atendimento digno de realeza, respondendo rapido como um brinde de champanhe. O processo do cassino e claro e sem intrigas, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria chique. No geral, Richville Casino promete uma diversao de cassino reluzente para os nobres do cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual de tirar o folego, adiciona um toque de sofisticacao ao cassino.
ny|
Ich bin total hingerissen von SlotClub Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein bunter Rausch aus Lichtern. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Lichtspektakel, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Blitzstrahl, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Kurzschluss. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist SlotClub Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Blitz einschlagt fur Abenteurer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
slotclub casino РѕР±Р·РѕСЂ|
https://t.me/bonus_dragon_money
боты для накрутки подписчиков в телеграм канале
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм купить
накрутка подписчиков телеграм 100 подписчиков
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
beast super test amazon
References:
turinabol Steroids (https://truesecret.org/@debragoulburn?page=about)
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem buracos negros. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. No fim das contas, BetorSpin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma supernova para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
avaliações sobre betorspin|
Adoro o fervor de SpinFest Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um batuque de carnaval. A gama do cassino e um verdadeiro festival de delicias, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que vibram como tambores. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista na avenida, com uma ajuda que samba com estilo. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de maracatu, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Em resumo, SpinFest Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um festival total para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual cheio de cores, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
spinfest bonus|
Acho simplesmente intergalactico SpeiCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura luz cosmica. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma constelacao de prazeres, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como nebulosas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma nave espacial, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que explodem como estrelas. No geral, SpeiCasino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho estelar para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
spei promo code gamechampions|
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os astronautas do cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin login|
Estou pirando com SpinWiz Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao encantadora quanto um feitico de varinha. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e magicas, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passe de varinha, com uma ajuda que reluz como um encantamento. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma pocao, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que hipnotizam. Na real, SpinWiz Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para quem curte apostar com estilo mistico no cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passe de magica, torna a experiencia de cassino um conto de fadas.
spinwiz bet|
чим обробити цоколь https://remontuem.te.ua
Estou pirando com SpeiCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura luz cosmica. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma constelacao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque cosmico. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro foguete, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria intergalactico. Na real, SpeiCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma aurora boreal, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
spei monthly bonus calculator|
Авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae покупка, продажа и аренда новых и б/у машин. Популярные марки, выгодные условия, помощь в оформлении документов и доступные цены.
интернет займ получить займ
Заметки практикующего врача https://phlebolog-blog.ru флеболога. Профессиональное лечение варикоза ног. Склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен и точная диагностика. Современные безболезненные методики, быстрый результат и забота о вашем здоровье!
purebred kittens for sale in NY https://catsdogs.us
Проблемы с откачкой? насосы для откачки воды насухо сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
Нужна презентация? https://generator-prezentaciy.ru Создавайте убедительные презентации за минуты. Умный генератор формирует структуру, дизайн и иллюстрации из вашего текста. Библиотека шаблонов, фирстиль, графики, экспорт PPTX/PDF, совместная работа и комментарии — всё в одном сервисе.
how much winstrol should i take
References:
anabolic steroids information (https://pierresderiviere.com/celestetennant)
buy xtc prague buy cocaine in telegram
https://fraufluger.ru/construction/natyazhnye-potolki-top-idej-dizajna-s-ustanovkoj/
Je trouve absolument dement Stake Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui explose comme un volcan en eruption. La selection du casino est un torrent de plaisirs, proposant des slots de casino a theme explosif. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme une etincelle, avec une aide qui fait jaillir des flammes. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse explosive, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Stake Casino est un casino en ligne qui fait trembler le sol pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Bonus la plateforme du casino brille par son style explosif, ajoute une touche de feu au casino.
stake|
Je suis accro a Riviera Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui scintille comme un coucher de soleil sur la Cote d’Azur. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une veritable Riviera de delices, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et raffinee, joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un voilier au vent, quand meme des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient rever. Globalement, Riviera Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style raffine, ajoute une touche d’elegance cotiere au casino.
roulette casino la riviera|
Acho simplesmente magico SpellWin Casino, parece um portal mistico cheio de adrenalina. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e um bau de encantos, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma vassoura encantada, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial encantado. Resumindo, SpellWin Casino e um cassino online que e um portal de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como uma pocao reluzente, adiciona um toque de encantamento ao cassino.
spellwin login|
быстрая накрутка подписчиков в телеграм
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e brilhantes como estrelas, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, de vez em quando mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Na real, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os astronautas do cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin cГіdigo bГіnus|
Je trouve absolument eblouissant Riviera Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi chic qu’une soiree sur un yacht. La selection du casino est une promenade de plaisirs, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui brille comme une vague. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans tempete, mais plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait somptueux. Globalement, Riviera Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les navigateurs du casino ! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style raffine, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus glamour.
casino la riviera badenbaden.fr|
Sou louco pela aura de SpellWin Casino, e um cassino online que brilha como uma pocao encantada. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e hipnotizantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem truques, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, SpellWin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro feitico para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo mistico, adiciona um toque de encantamento ao cassino.
spellwin de|
накрутка подписчиков телеграм бесплатно задания
Был в разных салонах, но здесь особая энергетика. Уютный интерьер, спокойная музыка и девушка, которая умеет довести до состояния полной неги. Ушел в прекрасном настроении и с улыбкой на лице. Очень советую, салон эротического массажа недорого нск: https://sibirki3.vip/. Настоящий релакс, получил огромное удовольствие.
prague drugstore buy mdma prague
Аренда авто Краснодар
what are steroids composed of
References:
Anavar Price (https://git.lodis.se/denischampagne)
buy cocaine prague buy drugs in prague
prague plug cocain in prague from dominican republic
broodbase I always admire their originality, quality, and consistent professional service.
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com slots de cassino tematicos de espaco sideral. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma galaxia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. No geral, BetorSpin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma supernova para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin logo|
Acho simplesmente fantastico SpinSala Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um piao em chamas. Os titulos do cassino sao uma explosao de cores dancantes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e reluzentes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela de neon, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um pisca-pisca, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, SpinSala Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De bonus a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma coreografia de luzes, eleva a imersao no cassino ao brilho maximo.
spinsala casino erfahrungen|
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Acho simplesmente supremo SupremaBet Casino, parece um reinado de diversao avassaladora. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma dinastia de delicias, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um decreto de eficiencia, com uma ajuda que brilha como uma coroa. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um mandato, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria supremo. No geral, SupremaBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro cetro para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro trono, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais majestosa.
supremabet – suprema bet ltda|
Ich bin total geflasht von SportingBet Casino, es pulsiert mit einer dynamischen Casino-Energie. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie eine volle Tribune, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und prazise, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Schuss aufs Tor. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Freisto?, ab und zu mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein echter Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist SportingBet Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Finale begeistert fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Extra die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein Passspiel, das Casino-Erlebnis total actiongeladen macht.
como apostar no sportingbet passo a passo|
Acho simplesmente fenomenal SupaBet Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um supervulcao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao de prazeres, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e eletrizantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brilha como uma supernova, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao estelar. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo supersonico, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Na real, SupaBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com energia epica no cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo avassalador, eleva a imersao no cassino ao nivel de um supervulcao.
supabet book a bet|
трансы новосибирска трансы новосибирска
Estou alucinado com SupremaBet Casino, parece um reinado de diversao avassaladora. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma dinastia de delicias, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como cetros. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem revoltas. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma carruagem real, porem mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial imperial. No fim das contas, SupremaBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo imperial no cassino! De bonus a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro trono, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais majestosa.
supremabet.|
Проблемы с откачкой? https://otkachka-vody.ru сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
prague drugs buy weed prague
buy mdma prague columbian cocain in prague
prague plug cocain in prague from dominican republic
накрутить подписчиков в тг
cocaine prague telegram cocaine prague
Zivjeti u Crnoj Gori? Zabljak nekretnine Novi apartmani, gotove kuce, zemljisne parcele. Bez skrivenih provizija, trzisna procjena, pregovori sa vlasnikom. Pomoci cemo da otvorite racun, zakljucite kupoprodaju i aktivirate servis izdavanja. Pisite — poslacemo vam varijante.
Смотрите онлайн песни для детей слушать онлайн или скачать лучшие детские мультфильмы, сказки и мульсериалы. Добрые истории, веселые приключения и любимые герои для малышей и школьников. Удобный поиск, качественное видео и круглосуточный доступ без ограничений.
Портал о строительстве https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: обзоры материалов, сравнение цен, рейтинг подрядчиков, тендерная площадка, сметные калькуляторы, образцы договоров и акты. Актуальные ГОСТ/СП, инструкции, лайфхаки и готовые решения для дома и бизнеса.
Всё о ремонте https://remontkit.ru и строительстве: технологии, нормы, сметы, каталоги материалов и инструментов. Дизайн-идеи для квартиры и дома, цветовые схемы, 3D-планы, кейсы и ошибки. Подрядчики, прайсы, калькуляторы и советы экспертов для экономии бюджета.
Мир гаджетов https://indevices.ru новости, обзоры и тесты смартфонов, ноутбуков, наушников и умного дома. Сравнения, рейтинги автономности, фото/видео-примеры, цены и акции. Поможем выбрать устройство под задачи и бюджет. Подписка на новые релизы.
Женский портал https://art-matita.ru о жизни и балансе: модные идеи, уход за кожей и волосами, здоровье, йога и фитнес, отношения и семья. Рецепты, чек-листы, антистресс-практики, полезные сервисы и календарь событий.
Все автоновинки https://myrexton.ru премьеры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и даты продаж. Электромобили, гибриды, кроссоверы и спорткары. Фото, видео, сравнения с конкурентами, конфигуратор и уведомления о старте приема заказов.
накрутка подписчиков в тг дешево
broodbase – Their platform is refreshing, reliable content attracts genuine visitors globally.
Je suis accro a VBet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui explose comme un geyser. La selection du casino est une explosion de plaisirs, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance ardente. Le service client du casino est une torche d’efficacite, avec une aide qui jaillit comme une flamme. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans cendres, quand meme plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait volcanique. Pour resumer, VBet Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! De surcroit l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un cratere en fusion, ajoute une touche de feu au casino.
vbet sa|
Sunny coin hold the spin slot game həqiqətən dinamikdir. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot oynamaq çox asandır.
Sunny coin: hold the spin slot RTP yüksək olduğu üçün sevilir. Sunny coin 2 hold the spin slot oynamadan əvvəl demo sınayın.
Slotu sınamaq üçün rəsmi link sunny-coin.com.az.
Sunny Coin Hold The Spin slot böyük qaliblərə şans verir. Sunny coin hold the spin slot bonus raundları çox cəlbedicidir. Sunny coin: hold the spin slot RTP səviyyəsi yüksəkdir.
Sunny coin hold the spin demo sınamağa dəyər. Sunny coin: hold the spin slot təcrübəsi həyəcanlıdır.
https://plenka-okna.ru/
Estou alucinado com BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que reluzem como supernovas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro cometa, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Na real, BetorSpin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro brilho cosmico para os astronautas do cassino! Alem disso a navegacao do cassino e facil como uma orbita lunar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
betorspin giriЕџ|
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru главные события дня, репортажи, аналитика, интервью и мнения экспертов. Лента 24/7, проверка фактов, региональные и мировые темы, экономика, технологии, спорт и культура.
Всё о стройке https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и ремонте: технологии, нормы, сметы и планирование. Каталог компаний, аренда техники, тендерная площадка, прайс-мониторинг. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, инструкции и видеоуроки для застройщиков, подрядчиков и частных мастеров.
Актуальные новости https://pr-planet.ru без лишнего шума: политика, экономика, общество, наука, культура и спорт. Оперативная лента 24/7, инфографика,подборки дня, мнения экспертов и расследования.
Строительный портал https://nastil69.ru новости, аналитика, обзоры материалов и техники, каталог поставщиков и подрядчиков, тендеры и прайсы. Сметные калькуляторы, ГОСТ/СП, шаблоны договоров, кейсы и лайфхаки.
Ремонт и стройка https://stroimsami.online без лишних затрат: гайды, сметы, план-графики, выбор подрядчика и инструмента. Честные обзоры, сравнения, лайфхаки и чек-листы. От отделки до инженерии — поможем спланировать, рассчитать и довести проект до результата.
https://device-rf.ru/
накрутка подписчиков телеграм канал бесплатно боты
Thanks , I’ve recently been searching for information about this topic for a while and yours is the greatest I have found out till now. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you positive in regards to the supply?
официальный сайт kra40.at
Ich finde absolut rasant Turbonino Casino, es pulsiert mit einer turbo-geladenen Casino-Energie. Es gibt eine Flut an mitrei?enden Casino-Titeln, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und prazise, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Bremsspuren, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein turbo-geladener Gewinn. Am Ende ist Turbonino Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Spieler, die auf rasante Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, den Spielspa? im Casino auf die Pole-Position hebt.
turbonino mobile app|
J’adore la fraicheur de ViggoSlots Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un blizzard. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et givrees, comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse polaire, cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui eblouissent comme l’aurore. Globalement, ViggoSlots Casino promet un divertissement de casino glacial pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! De surcroit le site du casino est une merveille graphique polaire, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
viggoslots|
изготовление значков из метала значки сувенирные на заказ
значки под печать значки на заказ в москве
значок индивидуальный печать на значках москва
Acho simplesmente sensacional BacanaPlay Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura purpurina. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um sambodromo de prazeres, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma rainha de bateria, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, mesmo assim queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. Em resumo, BacanaPlay Casino e um cassino online que e uma folia sem fim para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma fantasia de carnaval, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
bacanaplay portugal|
Ich liebe den Nervenkitzel von Tipico Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Sturm aus Gewinnen. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und elektrisierend, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein Leuchtfeuer im Sturm, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Regentropfen, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Volltreffer. Zusammengefasst ist Tipico Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Extra die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Polarlicht, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
tipico promocode|
активные подписчики в тг канал
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/183263596/detail.aspx
накрутка подписчиков тг бесплатно без отписок
banehmagic – They deliver quality content, strong brand presence and solid reputation.
накрутка подписчиков в тг живых активных
can a doctor prescribe anabolic steroids
References:
dianabol weight loss (https://music.drepic.com/enriquetabirmi)
Je suis fou de Unibet Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui resonne comme un crescendo. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une harmonie de delices, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui chantent comme un ch?ur. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et harmonieuse, assurant un support de casino immediat et vibrant. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui vibrent comme un orchestre. Pour resumer, Unibet Casino est un casino en ligne qui joue une symphonie de plaisir pour les joueurs qui aiment parier avec style au casino ! Bonus le design du casino est une fresque visuelle harmonieuse, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus vibrante.
unibet numero|
Sou louco pela energia de BetorSpin Casino, parece uma explosao cosmica de adrenalina. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de diversao, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e hipnotizantes. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino e um cassino online que e uma galaxia de diversao para os astronautas do cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais estelar.
betorspin paga mesmo|
catherinewburton – Thoughtful layout, meaningful visuals and a very engaging browsing flow.
Je suis accro a Tortuga Casino, on dirait une ile au tresor pleine de frissons. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui hisse les voiles. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un abordage, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Tortuga Casino c’est un casino a aborder sans tarder pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline des mers du casino ! Par ailleurs l’interface du casino est fluide et eclatante comme un ocean au soleil, ajoute une touche de legende pirate au casino.
tortuga casino arnaque|
Je trouve absolument enivrant Unibet Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu aussi petillante qu’un orchestre en feu. L’assortiment de jeux du casino est une harmonie de delices, offrant des sessions de casino en direct qui chantent comme un ch?ur. Le support du casino est disponible 24/7, avec une aide qui resonne comme une symphonie. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient chanter. En somme, Unibet Casino promet un divertissement de casino vibrant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline rythmee du casino ! De surcroit la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une partition, facilite une experience de casino enchanteresse.
unibet 10 euros offert|
Estou completamente vidrado por Bet4Slot Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que gira como um piao em chamas. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de giro, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de rotacao. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma engrenagem de eficiencia, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma montanha-russa, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, Bet4Slot Casino e um cassino online que e um redemoinho de diversao para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual giratorio, torna a experiencia de cassino um carrossel inesquecivel.
codigo bet4slot promocional|
I’m crazy about Wazamba Casino, it feels like a safari through a jackpot jungle. The gaming options are lush and vibrant like a jungle, including classy casino table games with a tribal flair. The casino team delivers support worthy of a jungle king, ensuring immediate casino support as bold as a warrior. The casino process is transparent with no hidden traps, but extra casino rewards would make hearts pound. To sum up, Wazamba Casino is a casino you can’t miss for players who love betting with jungle flair! As a bonus the casino interface is smooth and vibrant like a tropical sunrise, making every casino session even wilder.
wazamba slots|
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, e um cassino online que gira como um asteroide em chamas. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma nebulosa de emocoes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um asteroide, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin cГіdigo bГіnus|
Je suis accro a Tortuga Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui rugit comme une tempete en haute mer. La selection du casino est une vague de plaisirs pirates, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance de flibustier. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un vent de tempete, assurant un support de casino immediat et audacieux. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans ecueils, cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait corsaire. Globalement, Tortuga Casino est un casino en ligne qui navigue comme un vaisseau pirate pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une boussole, donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
jeux casino tortuga|
живые активные подписчики в тг
short bodybuilders
References:
steroids bodybuilding side effects (https://git.cydedu.com/bryce65m604825)
https://empathycenter.ru/preparations/g/gabapentin/ Габапентин: Когда он уместен? Нейропатическая боль, эпилепсия, фибромиалгия – вот лишь некоторые из показаний к применению габапентина. Он может стать настоящим спасением при хронических болях, связанных с поражением нервной системы.
Теплую футболку с длинным рукавом и Misfits футболка в Курске. Офисные женские рубашки и шапка серая с помпоном в Тольятти. Balmain футболка и футболки и толстовки в Новороссийске. Волков одежда и трафареты для рисунков на одежде в Кургане. Принт на женские футболки оптом и надписи на футболку беременной: принт для футболки смешной оптом
http://tourout.ru/
накрутка настоящих подписчиков в телеграм канале
joszaki regisztracio joszaki
joszaki regisztracio https://joszaki.hu/
joszaki regisztracio joszaki
It’s amazing for me to have a web page, which is useful in favor of my experience. thanks admin
зеркало kraken
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал бесплатно онлайн
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
motocitee – Impressive attention to detail, I love the user interface design.
motocitee – The layout flows well, visuals are strong and pleasing to view.
Je trouve absolument cartoon Simsinos Casino, ca vibre avec une energie de casino digne d’un animateur. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance cartoon. offre un soutien qui crayonne tout. proposant un appui qui enchante. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse cartoon. parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui sautent comme des toons. Au final, Simsinos Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les virtuoses des jeux! Par ailleurs la plateforme du casino brille par son style anime. ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus animee.
simsinos casino online|
Sou viciado no brilho de BR4Bet Casino, vibra como um farol em alto-mar. O leque do cassino e um brilho de delicias. oferecendo lives que acendem como fogueiras. O suporte e um facho reluzente. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma lanterna. porem mais giros gratis seriam brilhantes. Para encurtar, BR4Bet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os exploradores de jogos online! Adicionalmente o site e uma obra-prima de estilo radiante. tornando cada sessao ainda mais brilhante.
br4bet app baixar|
Вызвал индивидуалку на дом, все прошло идеально. Она приехала быстро, выглядела прекрасно, была очень нежной и внимательной. Настоящее удовольствие. Советую, эротический массаж вызвать нск, https://sibirki3.vip/. Получил море удовольствия, спасибо большое.
trendingnewsfeed – Just came across this site, news updates seem pretty timely and useful.
apkcontainer – I found exactly what I needed here faster than on many others.
goldmetalshop – I appreciate how well the categories are organized, so helpful.
centensports – Some headlines really drew me in, liked that they weren’t clickbait.
adawebcreative – The site is responsive; it worked great on mobile just now.
Curto demais a quadra de MarjoSports Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um craque. A selecao de titulos e uma rede de prazeres. incluindo mesas com charme de torcida. O servico e confiavel como uma rede. respondendo rapido como um apito. Os saques aceleram como um contra-ataque. mas mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de torcida. Na real, MarjoSports Casino garante um jogo que vibra como uma torcida para os fas de adrenalina de campo! Adicionalmente a navegacao e facil como um passe. dando vontade de voltar como um craque.
www. marjosports. com. br|
Estou alucinado com BR4Bet Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como um farol na nevoa. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um farol. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque de brilho. O suporte e um facho reluzente. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques voam como um facho de luz. entretanto queria mais promocoes que brilham como farois. Resumindo, BR4Bet Casino e um clarao de emocoes para os faroleiros do cassino! E mais o visual e uma explosao de claroes. criando uma experiencia de cassino reluzente.
robo br4bet|
raspinakala – The color palette and fonts give a strong, cohesive aesthetic feel.
musionet – Overall, promising and well made; gives a trustworthy first impression.
celtickitchen – Overall, such a charming and useful food site worth following.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
сайт для накрутки подписчиков в тг
centensports – I’ll revisit often, the content keeps me curious and engaged.
raspinakala – Every element seems carefully placed, giving this site a refined charm.
sunnyflowercases – The site feels clean and not cluttered even with many items.
экскурсии в казани
https://dzen.ru/110km
накрутка подписчиков в тг канал дешево
Sou louco pela matriz de PlayPix Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um codigo binario em furia. Os jogos formam um render de diversao. incluindo mesas com charme de algoritmo. O atendimento e solido como um pixel. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. As transacoes sao faceis como um glitch. as vezes mais giros gratis seriam vibrantes. No geral, PlayPix Casino e um cassino online que e uma matriz de diversao para os cacadores de vitorias em byte! Como extra o design e fluido como um render. tornando cada sessao ainda mais pixelada.
copa playpix|
Sou louco pela fornalha de Verabet Casino, parece um festival de chamas cheio de adrenalina. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com caca-niqueis modernos que hipnotizam como fogos. Os agentes sao rapidos como uma faisca. oferecendo respostas claras como uma chama. O processo e claro e sem fumaca. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam incendiarios. Para encurtar, Verabet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma labareda para quem curte apostar com estilo flamejante! De lambuja o site e uma obra-prima de estilo ardente. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um ritual.
plataforma bet vera Г© confiГЎvel|
Je suis envoute par BankOnBet Casino, on dirait une chambre forte pleine de jackpots. Le repertoire du casino est un coffre de divertissement. incluant des tables qui securisent les mises. The support is as solid as a vault door. joignable par chat ou email. Les retraits sont verrouilles en securite. cependant plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait un investissement. In summary, BankOnBet Casino est un vault de thrills pour les parieurs astucieux! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique securisee. donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
bankonbet affiliates|
Curto demais o byte de PlayPix Casino, e uma explosao de diversao que carrega como um buffer. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. incluindo mesas com charme de algoritmo. O suporte e um codigo preciso. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. As transacoes sao simples como um pixel. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura cibernetica. Resumindo, PlayPix Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para os fas de adrenalina pixelada! Como extra o layout e vibrante como um codigo. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura pixelada.
codigo de bonus playpix|
Je suis fou de Casinia Casino, est une epopee de divertissement qui enchante. vibre avec un rempart de jeux varies. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance royale. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et loyale. repondant en un eclat de lance. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un serment. cependant des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient medievaux. Au final, Casinia Casino promet un divertissement de casino legendaire pour les virtuoses des jeux! En bonus offre un orchestre de couleurs medievales. ajoute une touche de grandeur au casino.
kasyno casinia recenzja|
J’adore le voile de Grandz Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino voile. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. offrant des lives qui pulsent comme un theatre. est un virtuose de l’ephemere. avec une aide qui danse comme une ombre. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse etheree. parfois j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui flottent comme des ombres. A la fin, Grandz Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les explorateurs de melodies en ligne! Ajoutons la plateforme du casino brille par son style theatral. enchante chaque partie avec une symphonie d’ombres.
concert ariana grandz|
pier45attheport – The site feels elegant, content flows with style and great charm.
Sou louco pela rede de IJogo Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao intrincada quanto um labirinto de vinhas. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um cipo. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. oferecendo respostas claras como um labirinto resolvido. Os saques sao velozes como um cacador na selva. entretanto mais giros gratis seriam intrincados. No geral, IJogo Casino e um cassino online que e um labirinto de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Por sinal o site e uma obra-prima de estilo selvagem. dando vontade de voltar como um cipo.
ijogo de moto|
Je suis captive par Grandz Casino, il propose une aventure de casino qui tournoie comme un voile mystique. propose un ballet de divertissement qui seduit. incluant des tables qui dansent comme des fantomes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un directeur de scene. proposant un appui qui enchante. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un ballet fugace. cependant j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui flottent comme des ombres. Dans l’ensemble, Grandz Casino resonne comme un ballet de plaisir pour les danseurs spectraux du casino! De plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique ephemere. enchante chaque partie avec une symphonie d’ombres.
grandz race code promo|
Galera, quero deixar registrado sobre o Bingoemcasa porque superou minhas expectativas. O site tem um visual descontraido que lembra um bate-papo animado. As salas de bingo sao cheias de energia, e ainda testei uns joguinhos extras, todos vieram com graficos bonitos. O atendimento no chat foi educado e prestativo, o que ja me deixou seguro. As retiradas foram mais velozes que imaginei, inclusive testei cripto e foi impecavel. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que gostaria de ver mais brindes, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Na minha visao, o Bingoemcasa foi uma otima descoberta. Com certeza vou continuar jogando
bingoemcasa suporte|
Coin Strike: Hold and Win https://lemon-cazino-pl.com
Tennis betting website https://betvisabengal.com
Cleaning is needed https://tesliacleaning.ca eco-friendly supplies, vetted cleaners, flat pricing, online booking, same-day options. Bonded & insured crews, flexible scheduling. Book in 60 seconds—no hidden fees.
Портал Чернівців https://58000.com.ua оперативні новини, анонси культурних, громадських та спортивних подій, репортажі з міста, інтерв’ю з чернівчанами та цікаві історії. Все про життя Чернівців — щодня, просто й доступно
Sou louco pela chama de DonaldBet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao vibrante quanto um malabarista em acao. A selecao de titulos e uma tenda de emocoes. com caca-niqueis modernos que encantam como acrobacias. O suporte e um mestre de cerimonias. respondendo rapido como um estalo de chicote. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. ocasionalmente mais recompensas fariam o coracao saltar. Para encurtar, DonaldBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os fas de adrenalina vibrante! De bonus a plataforma reluz com um visual circense. amplificando o jogo com vibracao acrobatica.
donaldbet oficial|
Estou completamente hipnotizado por XPBet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao continua quanto um espiral infinito. O leque do cassino e um vortice de delicias. incluindo mesas com charme de roda. O servico e confiavel como um ciclo. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. As transacoes sao simples como um giro. de vez em quando mais bonus seriam um diferencial de roda. No fim das contas, XPBet Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para quem curte apostar com estilo giratorio! Vale dizer a navegacao e facil como um loop. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura giratoria.
44 xp bet|
Je suis fou de Boomerang Casino, est un retour de divertissement qui boucle. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. incluant des tables qui ricochet comme un projectile. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme un retour boomerang. offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un arc. tout de meme plus de bonus pour une harmonie boomerang. Globalement, Boomerang Casino est un joyau pour les fans de casino pour les fans de symphonies circulaires! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style ricochet. ajoute une touche de rythme arque au casino.
boomerang casino bonus sans depot|
Estou completamente apaixonado por DonaldBet Casino, e uma explosao de diversao que acende como fogos. A selecao de titulos e uma tenda de emocoes. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. respondendo rapido como um estalo de chicote. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. as vezes mais recompensas fariam o coracao saltar. Na real, DonaldBet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro espetaculo para os fas de adrenalina vibrante! Vale dizer a navegacao e facil como um malabarismo. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um espetaculo.
dashboard donaldbet|
Sou viciado no reverb de JonBet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao pulsante quanto um eco em caverna. As opcoes sao ricas e vibram como cordas. incluindo mesas com charme ressonante. Os agentes ecoam como sinos. com ajuda que ressoa como um sino. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma corda. as vezes mais recompensas fariam o coracao ecoar. No geral, JonBet Casino e um cassino online que e uma camara de diversao para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Como extra o visual e uma explosao de sinos. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um coral.
jonbet.|
Je trouve absolument boomerang Boomerang Casino, offre un spectacle de plaisir qui revient. Le repertoire du casino est un arc de divertissement. proposant des slots de casino a theme lance. offre un soutien qui boucle tout. resonnant comme une boucle parfaite. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse circulaire. par moments des recompenses de casino supplementaires feraient revenir. Au final, Boomerang Casino est un casino en ligne qui revient comme un boomerang pour les explorateurs de melodies en ligne! Bonus la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une boucle. donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
boomerang casino recensione|
сайт трипскан TripScan зеркало: Если у вас возникли проблемы с доступом к основному сайту TripScan, воспользуйтесь зеркалом. Зеркало TripScan предоставляет полный доступ ко всем функциям и услугам платформы, чтобы вы могли продолжать планировать свои путешествия без каких-либо препятствий. Наслаждайтесь удобством и надежностью TripScan, даже если основной сайт временно недоступен. trip scan зеркало
masquepourvous – The brand identity seems clear, elegance is woven throughout.
Ремонт iphone 7 Ремонт телефонов адреса: Узнайте адреса наших сервисных центров в Москве и выберите ближайший к вам! Мы предлагаем удобное расположение и гибкий график работы, чтобы вам было удобно обратиться к нам за помощью. Квалифицированные мастера, современное оборудование и оригинальные запчасти гарантируют качественный и оперативный ремонт вашего телефона.
Formula 1 könüllü proqramı haqqında maraqlı məlumatlar burada. Ən yaxşı Formula 1 filmləri və sənədli layihələri.
Ətraflı məlumat almaq üçün ➡ formula-1.com.az.
Formula 1 volunteer 2025 proqramına qoşulmaq üçün şərtlər. Formula 1 volunteer təcrübəsi ilə bağlı məsləhətlər.
Formula 1 drivers siyahısı daim dəqiqləşdirilir. Formula 1 tickets almaq üçün sərfəli variantlar. Formula 1 izləmək üçün ən yaxşı kanalı seçin. Formula 1 drivers ilə bağlı ən son xəbərlər.
masquepourvous – Everything loads quickly which makes browsing enjoyable without any frustration.
geteventclipboard – The brand name sticks out, it’s creative and super memorable.
dinahshorewexler – The first impression is strong, it feels trustworthy and reliable.
brucknerbythebridge – This feels trustworthy, like a site that truly values presentation.
safercharging – Overall, the message comes across clear and really makes sense.
http://forum.olymp74.ru/viewtopic.php?pid=11073#p11073
jonathanfinngamino – I like how clean and organized everything looks on first visit.
reindeermagicandmiracles – The theme feels festive, giving off cheerful and cozy energy.
saveaustinneighborhoods – Just came across this today, and it feels very inspiring.
libertycadillac – The first impression is strong, it feels trustworthy and polished.
Монтаж камеры видеонаблюдения цена https://vcctv.ru
sjydtech – Their offerings appear advanced, site gives confident tech impression.
Je suis hante par Casombie, ca pulse comme une invasion de zombies. La selection de jeux est terrifiante de richesse, avec des slots au design effrayant. Le support est disponible 24/7, repondant en un battement d’ailes. Les paiements sont securises comme une tombe scellee, de temps a autre des tours gratuits supplementaires feraient frissonner. Dans l’ensemble, Casombie est un must pour les amateurs de sensations fortes pour les amateurs de vibes gothiques ! De plus la navigation est intuitive comme une malediction, ce qui rend chaque session electrisante.
casombie de|
Je suis totalement hypnotise par Freespin Casino, c’est une tornade de sensations vibrantes. La gamme est une explosion de fun, incluant des jeux de table d’une energie debordante. L’assistance est precise comme une etoile filante, garantissant un support d’une brillance rare. Les retraits sont rapides comme une fusee, mais des bonus plus petillants seraient magiques. En conclusion, Freespin Casino est une plateforme qui illumine l’esprit pour ceux qui cherchent des frissons lumineux ! De plus la navigation est intuitive comme un rayon lunaire, donne envie de replonger dans l’univers du jeu.
no deposit free spin casino australia|
hanacapecoral – I’ll return later, this brand gives a solid first impression.
J’eprouve une etincelle debordante pour Robocat Casino, c’est un labo ou chaque spin active un gadget de fortune. Les composants tracent un schema de gadgets avant-gardistes, offrant des bonus crabs et 200 spins des fournisseurs comme Pragmatic Play et Evolution. Le support client est un debugueur vigilant et nonstop, compilant des patches clairs et rapides. Les retraits s’activent avec une velocite remarquable, a l’occasion les protocoles d’offres pourraient s’optimiser en profondeur. Dans l’ensemble du systeme, Robocat Casino devoile un pipeline de succes high-tech pour ceux qui flashent leur destin en ligne ! De surcroit l’interface est un dashboard navigable avec finesse, ce qui catapulte chaque run a un niveau overclocke.
robocat pokemon|
Je suis irremediablement appate par MrPacho Casino, il orchestre une symphonie de gains succulents. Les plats forment un tableau de textures innovantes, incluant des crash games comme JetX pour des pics de saveur. L’assistance distille des conseils affutes, activant des voies multiples pour une resolution veloutee. Les echanges coulent stables et acceleres, par intermittence les menus d’offres pourraient s’etoffer en generosite. En apotheose culinaire, MrPacho Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour les gardiens des buffets numeriques ! En cerise sur le gateau la trame irradie comme un plat ancestral, allege la traversee des menus ludiques.
pregled igralnice mrpacho|
інформаційний портал https://01001.com.ua Києва: актуальні новини, політика, культура, життя міста. Анонси подій, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з киянами, аналітика та гід по місту. Все, що треба знати про Київ — щодня, просто й цікаво.
інформаційний портал https://65000.com.ua Одеси та регіону: свіжі новини, культурні, громадські та спортивні події, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з одеситами. Всі важливі зміни та цікаві історії про життя міста — у зручному форматі щодня
Для склада запчастей мы приобрели оборудование для маркировки и терминалы сбора данных. Раньше учёт занимал много времени и часто происходили ошибки. Теперь всё фиксируется автоматически, сотрудники работают быстрее. Дополнительно установили беспроводные сканеры штрих-кодов. Работа стала гораздо более точной и организованной https://labelaire.ru/
Je suis totalement envoute par Casombie, il offre une aventure aussi sombre que palpitante. La gamme est un veritable apocalypse de fun, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Les agents repondent plus vite qu’un zombie affame, avec une aide aussi fluide qu’un spectre. Les retraits sont rapides comme un mort-vivant en chasse, parfois plus de promos macabres seraient un plus. En somme, Casombie merite une visite dans son antre pour les amateurs de vibes gothiques ! Par ailleurs le design est sombre et captivant, donne envie de revenir hanter le site.
casombie analyse|
Je suis transporte par Freespin Casino, ca scintille comme une aurore boreale. La gamme est une explosion de fun, proposant des paris sportifs qui font pulser l’adrenaline. Le suivi est d’une clarte lumineuse, avec une aide aussi fluide qu’une brise etoilee. Les paiements sont securises comme une voute celeste, cependant des tours gratuits en plus feraient scintiller. Pour resumer, Freespin Casino promet une aventure etincelante pour les amateurs de sensations eclatantes ! En bonus le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel scintillant, donne envie de replonger dans l’univers du jeu.
fair go casino free spin codes|
Je suis circuite par Robocat Casino, ca upgrade le jeu vers un niveau cybernetique. Le catalogue est un code source de divertissements automatises, proposant des Aviator pour des survols d’adrenaline. Le service scanne en continu 24/7, compilant des patches clairs et rapides. Les payouts dechargent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, malgre cela des updates promotionnels plus frequents upgradieraient le kit. En apotheose cybernetique, Robocat Casino invite a une session sans crash pour les guardians des reseaux numeriques ! Par surcroit la structure vibre comme un processeur ancestral, ce qui catapulte chaque run a un niveau overclocke.
robocat mouse|
Je suis accro a Nomini Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino voile. est une illusion de sensations qui enchante. incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance spectrale. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et precise. resonnant comme une illusion parfaite. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides. mais plus de bonus pour une harmonie voilee. En conclusion, Nomini Casino resonne comme un ballet de plaisir pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! A noter la navigation du casino est intuitive comme une note voilee. fait vibrer le jeu comme un concerto ephemere.
Je suis irremediablement appate par MrPacho Casino, on discerne un jardin de defis appetissants. La carte est un grimoire de divertissements savoureux, proposant des blackjack revisites pour des bouffees d’adrenaline. Le suivi veille avec une finesse sans pareille, avec une maestria qui anticipe les appetits. Les butins affluent via USDT ou fiat fluide, nonobstant des garnitures de recompense additionnelles epiceraient les alliances. En apotheose culinaire, MrPacho Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour les chasseurs de casinos virtuels ! A souligner le parcours est instinctif comme un arome familier, allege la traversee des menus ludiques.
mrpacho avis|
skibumart – Great mix of artistic style and user experience here.
TheHold стал моим ежедневным источником по крипте. Здесь есть прогнозы, новости, курсы, обзоры кошельков и бирж, калькулятор доходности. Материалы доступны и полезны как новичкам, так и профессионалам https://thehold.ru/
ieeb – The site feels polished, clear, and really easy to follow.
eleanakonstantellos – Beautiful design touches, content feels personal, aesthetic is very consistent.
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
Je suis ebloui par Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un tourbillon de delices. La selection est une cascade de surprises, offrant des sessions live qui hypnotisent. Le suivi est d’une precision eclatante, joignable a chaque instant. Les retraits sont fluides comme une riviere, neanmoins des bonus plus petillants seraient un regal. En somme, Cheri Casino promet une experience eclatante pour ceux qui cherchent des frissons colores ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive comme une danse, facilite une experience fluide et joyeuse.
cheri casino bonus|
yusaon gold slots, new zealandn original slot online free and online poker real
money usa 2021, or trusted casino online usa
my web blog … how to protect yourself from gambling
husband (Odessa)
Je suis enivre par PepperMill Casino, on hume un verger de tactiques enivrantes. Il regorge d’une abondance de melanges interactifs, avec des dice slots aux motifs piquants qui titillent les sens. Les artisans repondent avec une acuite remarquable, avec une expertise qui presage les appetits. Les recoltes affluent via USDT ou canaux fiat, bien qu’ des herbes de recompense additionnelles epiceraient les alliances. En concluant l’infusion, PepperMill Casino emerge comme un pilier pour les epicuriens pour les explorateurs de casinos virtuels ! En sus l’interface est un sentier herbeux navigable avec art, instille une quintessence de mystere epice.
peppermill vegas menu|
Je suis fleche par WildRobin Casino, ca tend un arc de defis legendaires. Il grouille d’une horde de quetes interactives, avec des slots aux themes Robin Hood qui font vibrer les cordes. Le service guette en continu 24/7, assurant une garde fidele dans la foret. Le sentier est trace pour une fluidite exemplaire, bien que les salves d’offres pourraient s’epaissir en densite. Pour clore l’arc, WildRobin Casino invite a une traque sans fin pour les archers de victoires astucieuses ! En fleche supplementaire la structure vibre comme un arc ancestral, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau legendaire.
robin hood’s wild forest|
nohonabe – Honestly, it looks like something meaningful, created with intention.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Cheri Casino, ca scintille comme une nuit etoilee. La gamme de jeux est un veritable arc-en-ciel, incluant des jeux de table pleins de charme. Le service client est d’une douceur angelique, joignable a chaque instant. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de l’eclair, parfois des bonus plus petillants seraient un regal. Pour resumer, Cheri Casino offre un voyage ludique inoubliable pour ceux qui cherchent des frissons colores ! Par ailleurs le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel, ajoute une touche d’eclat magique.
cheri casino retrait|
J’eprouve une brillance infinie pour RubySlots Casino, on admire un atelier de techniques precieuses. Le portfolio est un salon de variete lapidaire, proposant des keno pour des extractions de chance. Le suivi preserve avec une purete absolue, activant des facettes multiples pour une revelation immediate. Les flux financiers sont sertis par des sceaux crypto, bien que les offres pourraient s’enrichir en carats. En sertissant le lot, RubySlots Casino forge une saga de jeu lapidaire pour les collectionneurs de casinos virtuels ! En carat supplementaire la circulation est instinctive comme une reflexion, incite a prolonger la taille infinie.
ruby slots casino no deposit bonus codes 2021|
Je suis irresistiblement bande par WildRobin Casino, ca tend un arc de defis legendaires. Le feuillage est un parchemin de divertissements forestiers, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de Sherwood. Le support client est un archer vigilant et ininterrompu, assurant une garde fidele dans la foret. Les flux sont camoufles par des fourres crypto, toutefois des tirs gratuits supplementaires boosteraient les branches. Pour clore l’arc, WildRobin Casino construit un repaire de divertissement sylvestre pour les bandits de casinos virtuels ! Par surcroit la structure vibre comme un arc ancestral, incite a prolonger la quete infinie.
wild robin et samantha|
Smart crypto trading https://terionbot.com with auto-following and DCA: bots, rebalancing, stop-losses, and take-profits. Portfolio tailored to your risk profile, backtesting, exchange APIs, and cold storage. Transparent analytics and notifications.
themacallenbuilding – Just visited today, and honestly it looks really professional overall.
casa-nana – I’d definitely share this with friends who like calming, unique sites.
goestotown – I’d recommend this to friends who enjoy fun creative projects.
eleanakonstantellos – I enjoyed exploring the site, layout is graceful and inviting throughout.
dietzmann – Their site feels strong, visuals are sharp and design commanding.
bigprintnewspapers – Pages loaded quickly, which makes the browsing experience much smoother.
brahmanshome – Everything looks nicely structured and thoughtfully put together.
biotecmedics – Looks like a trustworthy resource for people looking into this field.
muralspotting – Love the concept, it feels creative and really inspiring overall.
dankglassonline – Overall impression is positive, modern, and well thought-out.
lastminute-corporate – The whole layout feels neat and professional, easy to navigate.
reinspiregreece – The theme feels meaningful, definitely conveys hope and creativity.
cepjournal – The site feels professional, informative, and very well-structured overall.
https://clickolov.ru/
pastorjorgetrujillo – I enjoyed the presentation; it’s simple yet very heartfelt.
J’ai un veritable engouement pour Donbet Casino, c’est une deflagration de fun absolu. Le catalogue est une explosion de diversite, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptomonnaies. Le suivi est d’une clarte explosive, offrant des solutions nettes et instantanees. Les transactions sont fiables et fluides, mais des bonus plus explosifs seraient geniaux. En somme, Donbet Casino est une plateforme qui fait trembler les sens pour les joueurs en quete d’intensite ! En bonus la plateforme brille comme une supernova, ajoute une touche de magie volcanique.
donbet mobile|
Je suis pimente par PepperMill Casino, ca exhale un jardin de defis parfumes. La collection est un recueil de divertissements odorants, offrant des titres exclusifs comme PepperMill Candy Dice des maitres comme Amusnet. Le suivi cultive avec une constance impenetrable, mobilisant des sentiers multiples pour une extraction fulgurante. Le processus est moulu pour une onctuosite exemplaire, nonobstant des herbes de recompense additionnelles epiceraient les alliances. Dans la totalite du bouquet, PepperMill Casino forge un festin de jeu somptueux pour les maitres de victoires odorantes ! Par surcroit le portail est une serre visuelle imprenable, pousse a prolonger le festin infini.
peppermill reno rooms|
Je suis fondant pour Sugar Casino, on savoure un comptoir de tactiques allechantes. La collection est un sirop de divertissements delicieux, incluant des crash pour des montees de miel. Les artisans repondent avec une douceur remarquable, servant des plateaux multiples pour une degustation immediate. Les flux financiers sont enrobes par des coques crypto, a l’occasion davantage de bonbons bonus quotidiens enrichiraient la confiserie. En refermant le bocal, Sugar Casino forge une recette de jeu savoureuse pour les patissiers de casinos virtuels ! En plus le graphisme est une praline dynamique et immersive, infuse une essence de mystere sucre.
sugar casino online casino|
Je suis subjugue par Donbet Casino, c’est une deflagration de fun absolu. La gamme est une eruption de delices, avec des slots au design audacieux. L’assistance est precise comme un laser, joignable a tout moment. Les paiements sont securises comme un bunker, mais plus de promos percutantes seraient un plus. Pour resumer, Donbet Casino est une plateforme qui fait trembler les sens pour les amateurs de sensations explosives ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un torrent, facilite une experience fluide et intense.
donbet casino no deposit bonus code|
Je suis irresistiblement epice par PepperMill Casino, on hume un verger de tactiques enivrantes. Les varietes tracent un panorama de saveurs novatrices, proposant des blackjacks revisites pour des bouffees d’excitation. Le suivi cultive avec une constance impenetrable, infusant des remedes limpides et immediats. Les flux coulent stables et acceleres, bien qu’ les bouquets d’offres pourraient s’epanouir en generosite. Dans la totalite du bouquet, PepperMill Casino forge un festin de jeu somptueux pour les maitres de victoires odorantes ! En piment sur le gateau le portail est une serre visuelle imprenable, instille une quintessence de mystere epice.
peppermill restaurant abingdon va|
Je suis fondant pour Sugar Casino, c’est un atelier ou chaque tour distille une goutte de victoire mielleuse. Il deborde d’une cascade de gourmandises interactives, proposant des roulettes pour des tours de sucre. Le suivi petrit avec une precision absolue, accessible par coulis ou appel direct. Les gains fondent via Bitcoin ou portefeuilles, malgre cela des eclats promotionnels plus frequents pimenteraient le panier. En apotheose sucree, Sugar Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les gourmands pour les patissiers de casinos virtuels ! De surcroit le graphisme est une praline dynamique et immersive, infuse une essence de mystere sucre.
sugar parade casino|
answermodern – I like the clean design and how the content feels both modern and useful.
tatumsounds – Great branding here, every detail feels in harmony with audio theme.
lastminute-corporate – It feels modern, functional, and genuinely helpful for busy schedules.
themacallenbuilding – Everything loads fast, which makes browsing smooth and frustration free.
Сломалась машина? техпомощь на дороге спб мы создали профессиональную службу автопомощи, которая неустанно следит за безопасностью автомобилистов в Санкт-Петербурге и Ленинградской области. Наши специалисты всегда на страже вашего спокойствия. В случае любой нештатной ситуации — от банальной разрядки аккумулятора до серьёзных технических неисправностей — мы незамедлительно выезжаем на место.
crownaboutnow – Their visuals are sharp, layout feels balanced and professional overall.
biotecmedics – I like the simple design, very easy to browse and read.
goestotown – Everything seems thoughtfully put together, very pleasant to scroll through.
casa-nana – The site gives off a calming and comfortable vibe overall.
brahmanshome – The design feels minimal, simple, and pleasant to look at.
muralspotting – The site captures artistic vibes beautifully, feels fun and lively.
pastorjorgetrujillo – The words feel heartfelt, spreading positivity and encouragement.
reinspiregreece – The concept feels uplifting, really inspiring and hopeful overall.
bigprintnewspapers – The simplicity makes the site approachable and pleasant to scroll through.
momoanmashop – The site gives off a welcoming and friendly impression instantly.
cepjournal – It feels useful, clear, and full of valuable information.
dankglassonline – Browsing here feels smooth, everything loads fast and looks neat.
cnsbiodesk – The site feels professional and focused on scientific innovation clearly.
haskdhaskdjaslkds – The site attempts style, but coherence is missing in many sections.
bigprintnewspapers – I like how the site emphasizes clarity, design is clean and crisp.
geomatique237 – The domain name is unique, the site feels experimental and intriguing.
reinspiregreece – This site exudes charm, visuals are bright and message feels uplifting.
https://www.wildberries.ru/catalog/514992745/detail.aspx
СтройСинтез построил для нас коттедж из кирпича под ключ в Ленинградской области. Все работы прошли гладко, а проект получился красивым и удобным для жизни. Мы очень довольны результатом. Подробности можно найти по ссылке https://stroysyntez.com/
Наш интернет-магазин нуждался в оптимизации. Mihaylov Digital сделали всё грамотно: от аудита до написания текстов. Теперь сайт виден в поиске и приносит заказы. Отличный результат https://mihaylov.digital/
J’ai une passion debordante pour Fezbet Casino, ca transporte dans un tourbillon de chaleur ludique. La selection est une tempete de fun, incluant des jeux de table d’une intensite torride. Le support est disponible 24/7, joignable a tout instant. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse d’une etincelle, parfois les offres pourraient etre plus brulantes. En conclusion, Fezbet Casino est un joyau pour les amateurs de jeux pour les joueurs en quete de chaleur ludique ! Cerise sur le gateau le site est un chef-d’?uvre visuel brulant, ce qui rend chaque session absolument incandescente.
kasyno fezbet logowanie|
Je suis enrobe par SlotsPalace Casino, il ordonne une lignee de recompenses royales. Les selections forment un arbre genealogique de styles innovants, proposant des crash pour des chutes de trone. Le service regne en continu 24/7, mobilisant des allegeances multiples pour une audience immediate. Les flux tresoriers sont gardes par des remparts crypto, bien que des sceaux de recompense additionnels forgeraient des dynasties. En couronnant le regne, SlotsPalace Casino forge un empire de divertissement majestueux pour les monarques de casinos virtuels ! De surcroit l’interface est un couloir navigable avec splendeur, infuse une essence de mystere royal.
s inscrire sur slots palace|
Je suis aromatise par PepperMill Casino, c’est un atelier ou chaque lancer infuse des essences de triomphe. Il regorge d’une abondance de melanges interactifs, offrant des titres exclusifs comme PepperMill Candy Dice des maitres comme Amusnet. Le service infuse en continu 24/7, accessible par infusion ou missive instantanee. Le processus est moulu pour une onctuosite exemplaire, toutefois des elans promotionnels plus assidus animeraient le jardin. En concluant l’infusion, PepperMill Casino convie a une exploration sans satiete pour les alchimistes des enjeux crypto ! Par surcroit l’interface est un sentier herbeux navigable avec art, pousse a prolonger le festin infini.
peppermill breakfast menu|
J’eprouve une energie surhumaine pour Super Casino, il deploie une campagne de gains extraordinaires. Le QG est un centre de diversite explosive, integrant des lives comme Mega Ball pour des explosions de score. Les sentinelles reagissent avec une alerte fulgurante, accessible par alerte ou appel d’urgence. Les retraits decollent avec une acceleration remarquable, occasionnellement des missions promotionnelles plus intenses dynamisent l’arsenal. A la fin de cette mission, Super Casino forge une legende de jeu supersonique pour les gardiens de casinos virtuels ! A scanner le portail est une tour de controle visuelle imprenable, incite a prolonger l’assaut infini.
super marchГ© casino marseille|
Mobil soccer yükləyərək futbol əyləncəsini hər yerdə yaşayın.
Opera soccer tətbiqi ilə xəbərlərə tez çatın. Əlavə məlumat üçün http://soccer.com.az/ səhifəsinə baxmaq olar.
Globe soccer turnirləri ilə dünya futboluna yaxın olun. Pro soccer online multiplayer həvəskarları üçün uyğundur. Dream league soccer 2020 yenilənmiş qrafiklər ilə fərqlənir.
Soccer super star mod apk ilə ulduz olun. Soccer field dizaynı oyunda çox real görsənir. Spbo live score soccer ilə hər dəqiqə nəticələri görün. World soccer champs hile son sürüm oyunçuların seçimi olub.
Je suis emoustille par MrPacho Casino, ca transforme le jeu en une degustation exquise. La carte est un grimoire de divertissements savoureux, offrant des jackpots progressifs des fournisseurs renommes comme Pragmatic Play. Le suivi veille avec une finesse sans pareille, activant des voies multiples pour une resolution veloutee. Le rituel est taille pour une onctuosite exemplaire, par intermittence les menus d’offres pourraient s’etoffer en generosite. A la fin de ce degustation, MrPacho Casino tisse une tapisserie de divertissement gustatif pour les gardiens des buffets numeriques ! A souligner la trame irradie comme un plat ancestral, allege la traversee des menus ludiques.
mrpacho casino no deposit bonus|
J’eprouve une majeste infinie pour SlotsPalace Casino, on percoit un cortege de man?uvres opulentes. Il regorge d’une procession de couronnes interactives, proposant des crash pour des chutes de trone. L’assistance proclame des edits nets, assurant une regence fidele dans le palais. Les transferts paradent stables et acceleres, toutefois davantage de decrets bonus quotidiens enrichiraient le domaine. En apotheose royale, SlotsPalace Casino sculpte une lignee de jeu grandiose pour les architectes de victoires imperiales ! A proclamer la circulation est instinctive comme un decret, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau souverain.
informations slots palace|
Je suis pimente par PepperMill Casino, ca transfigure le jeu en une infusion eternelle. Les varietes tracent un panorama de saveurs novatrices, integrant des roulettes live pour des tourbillons d’arome. Le service infuse en continu 24/7, assurant une tutelle fidele dans les vignes. Les recoltes affluent via USDT ou canaux fiat, par intermittence des essences gratuites supplementaires rehausseraient les melanges. Pour sceller l’arome, PepperMill Casino forge un festin de jeu somptueux pour les gardiens des jardins numeriques ! En sus l’interface est un sentier herbeux navigable avec art, intensifie l’envoutement dans le domaine des aromes.
peppermill casinos|
Je suis propulse par Super Casino, on decele un escadron de strategies imparables. Les unites forment un bataillon de tactiques novatrices, integrant des lives comme Mega Ball pour des explosions de score. Le service patrouille en continu 24/7, declenchant des contre-mesures claires et rapides. Le vecteur est trace pour une trajectoire exemplaire, toutefois les protocoles d’offres pourraient s’amplifier en puissance. En apotheose heroique, Super Casino invite a une patrouille sans repli pour les pilotes des paris crypto ! De surcroit le portail est une tour de controle visuelle imprenable, amplifie l’engagement dans l’arsenal du jeu.
super cat casino au|
Мир гаджетов без воды https://indevices.ru честные обзоры, реальные замеры, фото/видео-примеры. Смартфоны, планшеты, аудио, гейминг, аксессуары. Сравнения моделей, советы по апгрейду, трекер цен и уведомления о скидках. Помогаем выбрать устройство под задачи.
cangjigedh – Love how smooth the pages load, makes browsing effortless today.
Ремонт и стройка https://remontkit.ru без лишних затрат: инструкции, таблицы расхода, сравнение цен, контроль скрытых работ. База подрядчиков, отзывы, чек-листы, калькуляторы. Тренды дизайна, 3D-планировки, лайфхаки по хранению и зонированию. Практика и цифры.
ceriavpn – The service feels reliable, connection speed is smooth and steady.
Ваш портал о стройке https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: материалы, инструменты, сметы и бюджеты. Готовые решения для кухни, ванной, спальни и террасы. Нормы, чертежи, контроль качества, приёмка работ. Подбор подрядчика, прайсы, акции и полезные образцы документов.
yyap16 – Everything works seamlessly, making it a pleasant place to explore.
azhyxh – The minimal approach really works, it feels modern and straightforward.
eljiretdulces – A refreshing site that feels welcoming, I’ll definitely come back.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
newbalance550 – A smooth browsing experience, everything works well from start to finish.
local-website – I like how clear the layout is, nothing feels confusing.
flmo1xt – I enjoyed how minimal the design feels, very modern overall.
t643947 – The site feels quick and efficient, everything loads instantly here.
alusstore – The design is straightforward yet attractive, great balance overall.
rwbj – I like the simple design, everything feels neat and organized.
x3137 – I enjoyed browsing here, everything felt smooth without interruptions.
rbncvbr – The vibe is sleek and functional, easy to spend time here.
чем лечат тревогу Таблетки от тревоги – это лекарственные препараты, используемые для снижения симптомов тревоги, таких как беспокойство, нервозность, страх и паника. Существует несколько классов лекарств, которые могут быть назначены для лечения тревоги, включая антидепрессанты (СИОЗС, СИОЗСН), анксиолитики (бензодиазепины) и бета-блокаторы. Антидепрессанты помогают регулировать уровень серотонина и норадреналина в мозге, что может снизить тревогу и депрессию. Анксиолитики быстро снимают симптомы тревоги, но могут вызывать привыкание, поэтому их обычно не рекомендуют для длительного использования. Бета-блокаторы могут использоваться для снижения физических симптомов тревоги, таких как учащенное сердцебиение и дрожь. Важно отметить, что таблетки от тревоги должны назначаться врачом, и их прием должен осуществляться под его контролем. Самолечение может быть опасным и привести к нежелательным побочным эффектам. Дополнительно, медикаментозное лечение тревоги часто сочетается с психотерапией и другими методами лечения для достижения наилучших результатов.
newbirdhub – The vibe is positive and clean, a very user-friendly platform.
wcbxhmsdo8nr – The site loads fast, making browsing smooth and effortless overall.
fghakgaklif – Pages load fast, which makes browsing pleasant and efficient.
360view – I like the neat layout, everything is clear and well-structured.
Дети Ветра Кайт школа – это учебное заведение, специализирующееся на обучении кайтсерфингу как начинающих, так и опытных райдеров. В кайт школах работают профессиональные инструкторы, которые обучают основам управления кайтом, правилам безопасности, нормам поведения на воде и базовым принципам кайтсерфинга. Кайт школы предоставляют все необходимое оборудование для обучения, в том числе кайты, доски, гидрокостюмы и спасательные жилеты. Обучение в кайт школе обеспечивает безопасное и эффективное освоение кайтсерфинга.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
Ремонт и строительство https://nastil69.ru от А до Я: планирование, закупка, логистика, контроль и приёмка. Калькуляторы смет, типовые договора, инструкции по инженерным сетям. Каталог подрядчиков, отзывы, фото-примеры и советы по снижению бюджета проекта.
Нужен аккумулятор? купить аккумулятор для автомобиля с доставкой в наличии: топ-бренды, все размеры, правый/левый токовывод. Бесплатная проверка генератора при установке, trade-in старого АКБ. Гарантия до 3 лет, честные цены, быстрый самовывоз и курьер. Поможем выбрать за 3 минуты.
кайт египет Кайт школа в Хургаде: Кайт школа в Хургаде – это ваш шанс погрузиться в мир кайтсерфинга в одном из самых популярных мест для этого вида спорта. Хургада предлагает идеальные условия для обучения: стабильный ветер, теплая вода и песчаные пляжи. В кайт школах Хургады работают опытные инструкторы, говорящие на разных языках, которые помогут вам освоить азы кайтсерфинга и безопасно научиться кататься на кайте. Школы обычно расположены на территории отелей или имеют свой собственный пляж, что обеспечивает удобство и комфорт во время обучения. Кроме обучения, кайт школы предлагают прокат оборудования, услуги по ремонту и хранению. В перерывах между занятиями вы можете отдохнуть на пляже, искупаться в море или насладиться блюдами местной кухни в одном из многочисленных ресторанов. Кайт школа в Хургаде – это отличный выбор для тех, кто хочет совместить активный отдых с приятным времяпровождением на берегу Красного моря.
Хочешь сдать акб? сдать аккумулятор автомобильный в спб цена честная цена за кг, моментальная выплата, официальная утилизация. Самовывоз от 1 шт. или приём на пункте, акт/квитанция. Безопасно и законно. Узнайте текущий тариф и ближайший адрес.
Мы заказали кухню на заказ в Кухни в Дом и получили именно то, что хотели. Замер прошёл быстро, дизайнер предложил несколько вариантов дизайна. Мы выбрали светлую кухню в современном стиле. Доставка и сборка прошли безупречно. Кухня выглядит дорого и стильно, пользоваться ей удобно. Материалы качественные, фасады идеально ровные. Отличное решение для тех, кто ищет надёжную компанию – https://kuhni-v-dom.ru/
v1av8 – Some scenes feel polished, others seem barely started—mixed impression.
aaccc2 – Simple layout makes it user-friendly and accessible.
free united statesn pokies online, australia gambling winnings taxable and casino kingdom usa,
or new zealandn online casino no deposit bonus 2021
Also visit my page; goplayslots.Net
xxfh – I like the modern style, it feels clean and sharp.
кайт египет Обучение кайтсёрфингу – это процесс изучения теории, отработки навыков управления кайтом и освоения техники катания на доске по воде. Обучение обычно начинается с наземных уроков, где ученики учатся управлять кайтом и понимать принципы ветрового окна. Затем ученики переходят к занятиям в воде, где они учатся стартовать, кататься и выполнять простые трюки. Обучение кайтсёрфингу требует хорошей физической подготовки, координации и умения быстро реагировать на изменяющиеся условия.
Ищешь аккумулятор? аккумуляторы для автомобиля AKB SHOP занимает лидирующие позиции среди интернет-магазинов автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге. Наш ассортимент охватывает все категории транспортных средств. Независимо от того, ищете ли вы надёжный аккумулятор для легкового автомобиля, мощного грузовика, комфортного катера, компактного скутера, современного погрузчика или специализированного штабелёра
Нужен надежный акб? акб купить в спб AKB STORE — ведущий интернет-магазин автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге! Мы специализируемся на продаже качественных аккумуляторных батарей для самой разнообразной техники. В нашем каталоге вы найдёте идеальные решения для любого транспортного средства: будь то легковой или грузовой автомобиль, катер или лодка, скутер или мопед, погрузчик или штабелер.
J’apprecie enormement Betsson Casino, il offre une plongee dans un univers vibrant. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives par Evolution Gaming. Le service client est exceptionnel, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont fluides et securises avec un maximum de 50 000 € par jour, bien que j’aimerais plus de promotions regulieres. En fin de compte, Betsson Casino ne decoit jamais pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! En bonus le site est concu avec modernite et ergonomie, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betsson apuestas online|
Je trouve completement barre Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. La selection est totalement dingue, avec des slots qui claquent grave. Le support est dispo 24/7, avec une aide qui dechire tout. Les paiements sont fluides et blindes, par moments plus de tours gratos ca serait ouf. Au final, Gamdom garantit un fun intergalactique pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! Et puis le site est une tuerie graphique, ajoute un max de swag.
code gamdom csgo|
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, on dirait une plongee dans un univers palpitant. La selection de jeux est colossale, avec des machines a sous modernes et captivantes. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, avec un suivi de qualite. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, par moments j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. En resume, 7BitCasino offre une experience de jeu securisee et equitable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide et retro, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino no deposit|
v1av8 – Strong aesthetic direction, but content needs definition and polish.
J’adore le delire total de Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. Le catalogue de jeux est juste enorme, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. Le crew assure un suivi de malade, garantissant un support direct et carre. Les retraits sont rapides comme un ninja, par contre j’aimerais plus de promos qui defoncent. Pour resumer, Gamdom offre une experience de ouf pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Et puis la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
gamdom kod|
Je suis fou de Celsius Casino, ca degage une ambiance de jeu torride. Les choix de jeux au casino sont varies et enflammes, proposant des slots de casino a theme volcanique. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement incandescent, assurant un support de casino immediat et flamboyant. Les gains du casino arrivent a une vitesse torride, quand meme les offres du casino pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Celsius Casino promet un divertissement de casino brulant pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline du casino ! En plus le site du casino est une merveille graphique ardente, ajoute une touche de chaleur au casino.
promo code celsius casino|
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, on dirait une sensation de casino unique. La gamme de jeux est tout simplement impressionnante, offrant des sessions de casino en direct immersives. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, offrant des reponses rapides et precises. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, neanmoins j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles, ou des tournois avec des prix plus eleves. Dans l’ensemble, 7BitCasino vaut pleinement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier avec des cryptomonnaies ! Par ailleurs le design est visuellement attrayant avec une touche vintage, renforce l’immersion totale.
7bitcasino promo code|
скачать 1xbet Ищете 1xBet официальный сайт? Он может быть заблокирован, но у 1хБет есть решения. 1xbet зеркало на сегодня — ваш главный инструмент. Это 1xbet зеркало рабочее всегда актуально. Также вы можете скачать 1xbet приложение для iOS и Android — это надежная альтернатива. Неважно, используете ли вы 1xbet сайт или 1хБет зеркало, вас ждет полный функционал: ставки на спорт и захватывающее 1xbet casino. 1хБет сегодня — это тысячи возможностей. Начните прямо сейчас!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Lucky Mate is an online casino for Australian players, offering pokies, table games, and live dealer options. It provides a welcome bonus up to AUD 1,000, accepts Visa, PayID, and crypto with AUD 20 minimum deposit, and has withdrawal limits of AUD 5,000 weekly. Licensed, it promotes safe play https://jadeplants.uk/2025/04/17/how-to-access-lucky-mate-casino-if-your-isp-has-blocked-the-site/
nnvfy – No visible bugs encountered while exploring.
Сделать мед лицензию стало просто благодаря Журавлев Консалтинг Групп, команда профессионалов подготовила все документы и предоставила консультации на каждом этапе https://licenz.pro/
jekflix – User-friendly site with no confusing menus or hidden stuff.
93r – I’m curious what this site does, interface feels experimental and raw.
66se – Overall functional, smooth, and reliable site.
worldloans – I liked how easy it was to navigate between sections.
fhkaslfjlas – Navigation is straightforward, no confusing sections or menus at all.
aabb49 – Usability is simple and user-friendly.
v1av2 – The structure is well-organized, everything is easy to locate.
1cty – The browsing flow was smooth and comfortable, nothing confusing here.
v1av7 – Works perfectly on mobile, responsive and easy to use there.
heyspin – Everything worked fine, no errors or glitches appeared today.
porn300 – Overall a simple, quick, and user-friendly website interaction.
deallegria – The design is neat and uncluttered, feels comfortable to use.
8886611tz – The navigation is simple and clear, nothing confusing at all.
tstyhj – Everything functions properly, no errors or issues while using.
2kgq – Scrolling is fluid, nothing laggy or glitchy during my visit.
tiantianyin4 – Pages open instantly, making the experience very pleasant overall.
i1oxj – Overall fast, efficient, and user-friendly website interaction today.
v1av9 – Overall it’s a fast, simple, and user-friendly site to use.
v1av3 – Works well on mobile devices, fully responsive.
66460 – Works fine on mobile devices, fully responsive.
dz-cream – The site’s layout is tidy and easy to scan quickly.
J’adore l’ambiance de Circus, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de vie. Le catalogue est incroyablement diversifie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le personnel assure un suivi de qualite, offrant des solutions claires et rapides. Le processus est clair et sans complications, de temps a autre j’aimerais plus de bonus reguliers. Dans l’ensemble, Circus garantit un divertissement de haut vol pour les passionnes de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, ajoute une touche de magie.
circus be casino|
v1av4 – Everything just works fine, site feels stable and functional.
Je trouve phenomenal Circus, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de vie. Il y a une profusion de titres captivants, proposant des sessions live palpitantes. L’assistance est efficace et conviviale, repondant en un rien de temps. Le processus est clair et sans complications, parfois plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Circus offre une aventure inoubliable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! De surcroit le design est moderne et captivant, facilite une immersion totale.
casino belgique circus|
sustanon 250 prices
References:
https://schoolido.lu/user/thrillwire23/
mydiving – Everything works properly, no lag or missing images noticed.
ipamorelin sermorelin combo
References:
https://motionentrance.edu.np/profile/brickrail16/
diwangdh77 – Design looks simple yet professional, nothing feels out of place.
steroids.com reviews
References:
https://rockchat.com/members/brownroad0/activity/94670/
other2.club – Browsing content feels smooth and casual, good experience overall.
196v5e63 – Everything functions properly, giving a really nice user experience.
yilian99 – Works perfectly fine on mobile without any scaling issues.
zzj186 – Mobile version fits nicely, no need for zooming or scrolling weirdly.
582388360 – Simple layout, easy to navigate, and pleasant to look at.
980115 – The interface feels light and modern, very pleasant to use.
6789138a.xyz – Clean layout, but could use a bit more color to liven things up.
Получение лицензии на медицинскую деятельность с Журавлев Консалтинг Групп прошло гладко, сотрудники компании контролировали все этапы процесса, подготовили правильный пакет документов и дали рекомендации для успешного прохождения проверок – https://licenz.pro/
21009.xyz – On mobile it mostly works, though some elements shift oddly.
5918222q.xyz – Interested to see how this site evolves with more content.
sj256.cc – This site has a neat vibe, feels clean and easy to browse.
sj440.cc – The images are crisp, adds extra professionalism to the content.
00381.xyz – Clean design, though a few sections need more copy or visuals to impress.
a6def2ef910.pw – On mobile it behaves decently, though a few elements overlap slightly.
0238.org – Navigation is pretty solid, I found things without much hassle.
yy380.cc – I like the color choices here, gives a pleasant visual feel.
5581249.cc – A richer footer with links and contact info would be helpful.
303vip.info – The style feels modern, navigation is pretty intuitive overall.
sodo66000.xyz – Browsed this a little, it has intriguing vibe and decent layout overall.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betway Casino, ca ressemble a une experience de jeu exaltante. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, incluant des slots de pointe de Microgaming et NetEnt. Le personnel offre un accompagnement rapide et efficace, garantissant une aide immediate. Les paiements sont fluides et securises par un cryptage SSL 128 bits, occasionnellement les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino offre une experience de jeu securisee avec un indice de securite de 9,2 pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! De plus le site est concu avec elegance et ergonomie, ce qui amplifie le plaisir de jouer.
betway aposta|
Je suis captive par Cresus, ca offre une experience feerique. Il y a une abondance de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le personnel offre un suivi digne d’un palace, avec une aide sur mesure. Les transactions sont simples et fiables, neanmoins des promotions plus frequentes seraient top. Globalement, Cresus garantit un divertissement princier pour les passionnes de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs le site est elegant et bien concu, ajoute une touche de luxe.
olympe casino cresus casino|
Je trouve absolument epoustouflant 1xbet Casino, ca ressemble a une sensation de casino unique. Le catalogue est incroyablement vaste, comprenant des titres innovants et engageants. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, garantissant une aide immediate. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, bien que davantage de recompenses seraient bienvenues. Dans l’ensemble, 1xbet Casino est un incontournable pour ceux qui aiment parier ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide et moderne, facilite chaque session de jeu.
1xbet app android|
Недавно скачал курс по таргетированной рекламе через Складчик. Всё прошло просто: выбрал складчину, оплатил и получил доступ. Цена минимальная, а материал полноценный. Очень доволен сервисом – https://v27.skladchik.org/
legal cpn reviews
References:
https://www.bidbarg.com/legal/user/burnfelony2
Je suis totalement scotche par Instant Casino, on dirait une tempete de fun. Il y a un deluge de jeux de casino varies, avec des slots de casino modernes et immersifs. Le service client du casino est une bombe, offrant des reponses qui claquent. Les paiements du casino sont fluides et securises, par moments j’aimerais plus de promos de casino qui dechirent. Pour resumer, Instant Casino est un spot de casino a ne pas rater pour les accros aux sensations de casino ! Et puis l’interface du casino est fluide et ultra-cool, booste l’immersion dans le casino a fond.
paypal casino instant withdrawal no deposit|
Je suis captive par Cresus, on ressent une energie magique. Il y a une abondance de titres captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. L’assistance est efficace et chaleureuse, garantissant un support instantane. Les transactions sont simples et fiables, bien que les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Globalement, Cresus est une plateforme d’exception pour les fans de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement enchanteresse, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus memorable.
casino cresus gratuit|
legal pro hormones
References:
https://kanban.xsitepool.tu-freiberg.de/7zWt3pqYRaGBpwfCDYrsBA/
Je trouve absolument epoustouflant 1xbet Casino, on dirait une experience de jeu exaltante. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, incluant des slots de pointe. Le personnel offre un accompagnement irreprochable, garantissant une aide immediate. Les transactions sont parfaitement protegees, par moments plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout. En resume, 1xbet Casino offre une experience de jeu remarquable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! En bonus l’interface est fluide et moderne, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
1xbet download ios|
can prednisone help build muscle
References:
https://ebra.ewaucu.us/index.php?page=user&action=pub_profile&id=99642
Хотели сделать остекление лоджии и заказали всё в компании Окна в СПб. Нам понравился сервис, внимательное отношение и качество работы. Теперь лоджия полностью утеплена и стала дополнительным помещением. Работой остались очень довольны – https://okna-v-spb.ru/
44588.xyz – Typography choices are nice, reading is comfortable and smooth.
862332.cc – All in all, intriguing site—worth bookmarking to see future updates.
x3165.xyz – Navigation works well, didn’t get lost even when exploring deeper pages.
9870k.top – Page load speed is okay generally, though heavy pages lag slightly.
51p31.xyz – The color scheme is subtle but fitting, not harsh or flashy.
weopwjrpwqkjklj.top – navigation works okay, though a few menu items felt hidden or unclear
Пинко Ищете игровую площадку, которая сочетает в себе надежность и захватывающий геймплей? Тогда Пинко Казино — это именно то, что вам нужно. В этом обзоре мы расскажем все, что необходимо знать об Официальном Сайт Pinco Casino. Что такое Pinco Casino? Pinco — это одна из самых популярных онлайн-площадок, также известная как Pin Up Casino. Если вы хотите играть безопасно, начинать следует всегда с Pinco Официальный Сайт или Pin Up Официальный Сайт. Это гарантирует защиту ваших данных и честную игру. Как найти официальный ресурс? Многие пользователи ищут Pinco Сайт или Pin Up Сайт. Основной адрес — это Pinco Com. Убедитесь, что вы перешли на Pinco Com Официальный портал, чтобы избежать мошеннических копий. Казино Пинко Официальный ресурс — ваша отправная точка для входа в мир азарта. Процесс регистрации и начала игры Чтобы присоединиться к сообществу игроков, просто найдите Сайт Pinco Casino и пройдите быструю регистрацию. Пинко Официальный Сайт предлагает интуитивно понятный процесс, после чего вы получите доступ к тысячам игровых автоматов и LIVE-казино. Пинко Казино предлагает: · Легкий доступ через Пинко Сайт. · Гарантию честной игры через Пинко Казино Официальный. · Удобный интерфейс на Официальный Сайт Pinco Casino. Неважно, как вы ищете — Pinco на латинице или Пинко на кириллице — вы найдете топовую игровую платформу. Найдите Pinco Официальный Сайт, зарегистрируйтесь и откройте для себя все преимущества этого казино!
sh576.xyz – Speed is okay, heavier pages sometimes lag on slower connections.
yt7787.xyz – A few images failed to load, perhaps broken asset links exist.
sxy005.xyz – Some images didn’t load for me, hope those are fixed soon.
bbofrwhnimpcjibfunu.live – Navigation is subtle, though I had to dig a bit to find main content.
ylu555.xyz – Interesting domain, gives off an air of mystery and curiosity.
storagesheds.store – Navigation works fine, but some links feel buried and unclear.
648ssss.xyz – On mobile some elements shift oddly, but overall usable.
businessesnewsdaily.site – Found a few broken images in posts, hope they patch those soon.
7x084yko.xyz – Navigation is okay, though a few pages feel a bit underdeveloped.
dersimizmuzik.org – Found a small typo in one post, but the content is solid.
микрозаем онлайн Я советую сайт за точность подбора условий по лучшие микрозаймы онлайн.
bestbotanicals – The layout’s clean and makes browsing herbal products super enjoyable.
52cjg.xyz – Load speeds are okay, though heavier pages lag on slower connections.
3e7r – Their blog section is short but full of useful tips too.
17kshu – They have some interesting topics, unsure yet what they focus on.
bitcoin-mining-news.website – On mobile, pages adjust fairly well, but some images overflow slightly.
captcha-kraken17at.org – On mobile a few elements overlap, but overall usable.
https://ozon.ru/t/csgBrx8
Estou completamente enlouquecido por LeaoWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e indomavel. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e selvagens, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma garra, respondendo mais rapido que um leopardo. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um predador, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, LeaoWin Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro rugido para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale falar tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia selvagem, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
leaowin02 casino inscription|
J’adore l’eclat de Julius Casino, on dirait une conquete de fun. La collection de jeux du casino est colossale, avec des machines a sous de casino modernes et envoutantes. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement imperial, assurant un support de casino instantane et souverain. Les transactions du casino sont simples comme un decret, parfois plus de tours gratuits au casino ce serait epique. Pour resumer, Julius Casino c’est un casino a conquerir en urgence pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline glorieuse du casino ! A noter la plateforme du casino brille par son style imperial, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus triomphante.
julius casino france|
Обложка трека Дизайн обложки – это целое искусство, требующее не только креативности, но и глубокого понимания музыкальной индустрии, психологии восприятия и современных трендов. Это не просто рисование красивой картинки, это создание визуального образа, который будет резонировать с вашей музыкой и вашей целевой аудиторией. Дизайнер должен учитывать жанр музыки, ее настроение, посыл и даже вашу индивидуальность как артиста. Важно, чтобы обложка была не только эстетически привлекательной, но и функциональной. Она должна хорошо смотреться на разных устройствах, в разных размерах и разных контекстах. Профессиональный дизайн обложки – это результат тесного сотрудничества музыканта и дизайнера, где каждый вносит свой вклад и делится своим видением. Не бойтесь экспериментировать, пробовать разные стили и подходы, чтобы найти идеальное решение для вашей обложки. Помните, что дизайн обложки – это лицо вашей музыки, и оно должно быть безупречным.
Je trouve genial le casino TonyBet, il est carrement un moment divertissant top. Les options de jeu sont nombreuses, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le personnel est tres competent, offrant un excellent suivi. Les paiements sont fluides, mais parfois les recompenses pourraient etre plus frequentes. Dans l’ensemble, TonyBet est une plateforme fiable pour les joueurs passionnes ! De plus, le site est facile a naviguer, ce qui rend l’experience encore meilleure.
tonybet promociones|
u8898.top – Overall it’s intriguing, worth keeping an eye on as it develops.
gqvslhwxkqnqlmjika.live – Overall quite mysterious but with potential, I’ll revisit later for updates.
anabolic steroids athletes
References:
https://justbookmark.win/story.php?title=understanding-dianabol-cycles-common-questions-and-safe-usage-guidelines
Hər turun nəticələri real vaxtda yenilənir. LaLiga standings səhifəsi ilə hər şeyi bil.
LaLiga canlı futbol həvəskarlarının seçimi. LaLiga logo dizaynı hər il yenilənir.
Yeni xal cədvəli üçün ən doğru ünvan — laliga table 2025. Orada bütün komandalar barədə məlumat var.
Bellingham LaLiga-da tarixi nəticələr göstərir.
LaLiga tv canlı baxmaq üçün seçimlər.
Futbol statistikası sevənlər üçün LaLiga bölməsi.
LaLiga super cup 2024 möhtəşəm idi.
LaLiga maç sonuclarını izləmək asandır.
axjaognr – Interesting domain name, makes me curious what they sell behind it.
pakopakoma – I see potential here; hope they keep posting new things.
formasecoarquitectonicas – I like that they use whitespace—it gives the pages room to breathe.
probuis – On mobile it renders okay, though some elements overlap slightly.
hhproduction – Would love to see more case studies or client stories here.
t371 – I’d like to see more illustrations or media to enrich pages.
fortressystemnig – Very clean website, layout gives a professional impression.
giftd – Bookmarking this; curious to see their offerings soon.
xxec – Found a couple of useful resources, thanks for putting this together.
aaront – I hope they add portfolio or project examples soon.
sddapp – I’ll check back later, curious to see how this site develops.
fartak – I shared one of your articles with friends, they liked it.
set-mining.website – I couldn’t find much info, site looks new and content is scarce.
cooperativadeartesanos – Would be great if there was an about page telling who run this cooperative.
xxgm – I just stumbled on this, looks sleek and intriguing overall.
forextradingsystem – The tips shared here actually improved my trading results this month.
bestbotanicals – I found some amazing herbal blends, totally worth checking out today.
creadordesitios – On mobile it adapts decently, though some buttons are small.
studydiary – Their blog section would benefit from more images and visuals.
av07 – Hope they add blog/news or updates to keep things lively.
missouriland – The color scheme is gentle and easy on the eyes.
J’adore le delire total de Gamdom, ca balance une vibe de folie. Le catalogue de jeux est juste enorme, avec des slots qui claquent grave. Le service client est une tuerie, avec une aide qui dechire tout. Les gains arrivent en mode TGV, quand meme des recompenses en plus ca ferait kiffer. Au final, Gamdom est un spot a ne pas louper pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! Cote plus l’interface est fluide et stylee a mort, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus kiffante.
comment faire du profit sur gamdom|
Je suis accro au style de FatPirate, on dirait un tourbillon de fun. Les jeux sont nombreux et delirants, offrant des machines a sous qui claquent. L’assistance est carrement geniale, repondant en deux secondes chrono. Les retraits sont rapides comme une tempete, quand meme des bonus plus reguliers ce serait cool. Au final, FatPirate est un spot incontournable pour les joueurs pour les accros aux sensations fortes ! Bonus l’interface est fluide et ultra-cool, facilite le delire total.
fatpirate avis|
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an impatience over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
keepstyle
Estou pirando com AFun Casino, e um cassino online que explode como um festival de fogos. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao de prazeres, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de danca, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, AFun Casino e um cassino online que e uma explosao de alegria para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como um desfile noturno, adiciona um toque de purpurina ao cassino.
afun saque|
bulking steroid
References:
https://bbs.pku.edu.cn/v2/jump-to.php?url=https://a-taxi.com.ua/user/castmeat11/
60349 – I’ll check again in a few days to see what’s new.
Je suis a fond dans Gamdom, ca donne une energie de jeu demente. La gamme est une vraie pepite, comprenant des jeux parfaits pour les cryptos. L’assistance est au top du top, joignable par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en mode TGV, des fois les offres pourraient etre plus genereuses. Bref, Gamdom c’est du lourd a tester direct pour les accros aux sensations extremes ! A noter aussi la plateforme claque avec son look de feu, booste l’immersion a fond les ballons.
minimum deposit gamdom|
Актуальные новости автопрома https://myrexton.ru свежие обзоры, тест-драйвы, новые модели, технологии и тенденции мирового автомобильного рынка. Всё самое важное — в одном месте.
Строительный портал https://stroimsami.online новости, инструкции, идеи и лайфхаки. Всё о строительстве домов, ремонте квартир и выборе качественных материалов.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru с последними событиями дня. Политика, спорт, экономика, наука, технологии — всё, что важно знать прямо сейчас.
Je suis totalement envoute par FatPirate, on dirait un tourbillon de fun. La selection est carrement dingue, incluant des jeux de table pleins de panache. Les agents sont rapides comme l’eclair, garantissant un support direct et efficace. Les gains arrivent en mode eclair, des fois des recompenses en plus ca serait la cerise. Bref, FatPirate garantit un fun total pour ceux qui kiffent parier avec style ! En prime la navigation est simple comme un jeu d’enfant, facilite le delire total.
fatpirate|
2j45qp – On mobile it’s usable, though some text seems cramped.
legal steroids weight loss
References:
https://bookmarking.win/story.php?title=dianabol-dbol-cycling-how-to-use-expected-outcomes-risks-and-proper-dosage
zonaflix – Navigation is intuitive, makes finding movies really effortless here.
sexscene.info/ Very best website
testosterone pills steroids
References:
https://hedgedoc.digillab.uni-augsburg.de/-AZK0yqpTOWpnCGLaSJjiw/
chinh-sua-anh.online – Very professional portfolio, gives confidence I’ll get quality edits.
best supplement stores
References:
https://postheaven.net/bankertire46/sustanon-250-the-ultimate-cycling-guide
22ee.top – I’ll revisit this later, curious to see updates.
zkjcnm.top – Placeholder content is normal for new sites, patience pays off.
дистанционная психотерапия Психотерапевт для ребенка Детский психотерапевт – это специалист, который помогает детям и подросткам справиться с эмоциональными, поведенческими и психологическими трудностями. Он использует специальные методы и техники, адаптированные к возрасту и потребностям ребенка, такие как игровая терапия, арт-терапия и другие. Терапия помогает ребенку выразить свои чувства, научиться справляться со стрессом, улучшить навыки общения и поведения. Детский психотерапевт работает с детьми, испытывающими тревогу, депрессию, проблемы с поведением, травмы, сложности в школе и другие трудности. Важной частью работы является сотрудничество с родителями для создания поддерживающей среды дома.
niubi1.xyz – Looks promising so far, hope they post interesting stuff soon.
jinbib27.top – I’m interested in what content will fill these pages soon.
legal injectable steroids for sale
References:
https://images.google.com.my/url?q=https://justpin.date/story.php?title=cycling-dianabol-dbol-your-comprehensive-guide-to-safe-and-effective-use
greenenvelope.org – I’ll check back later once content is live or updated.
lovemoda.store – I’ll check back when they list their bestsellers or deals.
lapotranca.store – I’ll revisit later once more content or shop pages appear.
forexplatform.website – This website actually made forex sound simple, I’m learning so much.
keledh.pw – Navigation is minimal, but that’s okay for a new project.
52ch.cc – Friendly tone, easy to read, makes me want to return.
manchunyuan1.xyz – Very interesting niche coverage, I’m glad I found it.
datacaller.store – I’m curious what “data caller” implies—analytics? APIs?
ipali.info – Fingers crossed they launch something solid here soon.
i2gkj.xyz – If they combine clean design with value, this site could shine.
camomh.site – I’ll bookmark this and revisit once they put up content.
scilla.biz – Minimalist design works, just needs substance next.
hentai20.biz – Design feels modern, though I wonder about moderation policies.
Adoro completamente Flabet Casino, da uma energia de jogo louca. A gama de jogos e impressionante, compreendendo milhares de jogos adaptados para criptos. O suporte esta disponivel 24/7, contatavel a qualquer momento. O processo e simples e sem problemas, mesmo que mais rodadas gratis seriam um plus. No geral, Flabet Casino e uma plataforma excepcional para os apaixonados por cassino ! Notemos tambem o site e estiloso e rapido, facilita a experiencia geral.
flabet site oficial|
Ich bin begeistert von Snatch Casino, es liefert ein aufregendes Abenteuer. Die Optionen sind umfangreich und abwechslungsreich, mit spannenden Sportwetten. Die Agenten sind super reaktionsschnell, garantiert sofortige Hilfe. Die Zahlungen sind flussig und sicher, jedoch die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Kurz gesagt Snatch Casino bietet garantiertes Vergnugen fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Au?erdem die Navigation ist super einfach, verstarkt den Wunsch zuruckzukehren.
Je trouve carrement genial Impressario, il propose un show de jeu hors norme. Les options sont variees et eblouissantes, proposant des sessions live qui en mettent plein la vue. Le support est dispo 24/7, joignable par chat ou email. Le processus est limpide et sans fausse note, parfois des recompenses en plus ca serait le feu. En gros, Impressario offre un spectacle de jeu inoubliable pour les accros aux sensations eclatantes ! En prime le site est une pepite scenique, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus eclatante.
impressario casino login|
Acho simplesmente insano FSWin Casino, parece um vulcao de diversao. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e alucinantes, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que e pura energia. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um cometa, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, FSWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o design do cassino e uma explosao visual, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
fswin|
ecolavadocp.info – I hope they’ll add clear descriptions and images soon for clarity.
axxo.live – This site stands out among others in its focus and clarity.
90dprr.top – Some of the images are striking — they add a lot to the pages.
bjwyipvw.xyz – Some of the articles caught me off guard, in a good way.
xxfq.xyz – Nice layout, felt comfortable navigating through different sections.
675kk.top – Found some useful bits here, will return to read more.
2021nikemenshoes.top – The site feels a bit new but promising for sneaker fans.
zukdfj.shop – I found useful bits here — will reuse for my own research.
kaixin2020.live – The writing is concise and meaningful, doesn’t waste my time.
av07.cc – Content is readable and not too cluttered, I appreciate that.
warmm1.cc – Good mix of visuals and text, makes posts more engaging.
xfj222 – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
44lou5 – The layout is clean, making navigation a breeze.
5xqvk – The design is minimalist yet effective.
sulk-vesta-mined.site – Nice layout and readability, makes me want to explore more.
mhcw3kct – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
qyrhjd.top – Found some interesting articles already, will dig deeper later.
nav6.xyz – Crisp design and helpful articles, wish there were more updates.
5680686 – I found the articles here to be quite informative.
20b7f9xg.xyz – Found some interesting posts already, will dig into earlier archives.
ryla6760 – Excellent resource for both students and Rotary clubs involved in RYLA.
australian pm blackjack, 888 how to cash a check at a
casino (Kina) nz and download poker stars uk mac, or top online pokies and casinos in united states 4k
Чтобы играть с выгодой, изучите статью на https://ma.by/docs/pages/?keshbek_i_programma_loyalnosti__vugodno_li_igrat_v_vavada_.html — там рассказано, как работает кешбэк и программа лояльности, и почему они выгодны постоянным игрокам.
14barapp.site – I visited and saw good content, hoping for more updates soon.
296ww.top – I found something useful just now, will explore more later.
best steroids for lean muscle
References:
https://www.divephotoguide.com/user/maracabowl8
Ich bin suchtig nach Snatch Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Thrill. Die Optionen sind umfangreich und abwechslungsreich, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Die Hilfe ist schnell und professionell, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Die Gewinne kommen schnell, manchmal mehr variierte Boni waren toll. Zusammenfassend Snatch Casino ist eine au?ergewohnliche Plattform fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Beachten Sie auch die Plattform ist visuell top, was das Spielvergnugen steigert.
snatch casino erfahrungen|
Je suis accro a Instant Casino, ca donne une energie de casino survoltee. La selection de titres de casino est dingue, offrant des machines a sous de casino uniques. Les agents du casino sont rapides comme l’eclair, offrant des reponses qui claquent. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un missile, des fois des bonus de casino plus reguliers ce serait top. En gros, Instant Casino offre une experience de casino inoubliable pour les aventuriers du casino ! A noter aussi le design du casino est une explosion visuelle, ajoute un max de swag au casino.
instant casino 34|
Adoro completamente Flabet Casino, proporciona uma aventura palpitante. O escolha de titulos e enorme, fornecendo sessoes ao vivo imersivas. O suporte esta disponivel 24/7, contatavel a qualquer momento. As transacoes sao confiaveis, mesmo que mais rodadas gratis seriam um plus. Em conclusao, Flabet Casino vale realmente a pena para os apaixonados por cassino ! De mais a mais o site e estiloso e rapido, o que aumenta o prazer de jogar.
como baixar flabet|
Ich bin begeistert von Snatch Casino, es ist eine dynamische Erfahrung. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Vielfalt an Spielen, mit immersiven Live-Sitzungen. Die Agenten sind super reaktionsschnell, garantiert sofortige Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, obwohl zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Zusammenfassend Snatch Casino garantiert eine top Spielerfahrung fur Online-Wetten-Enthusiasten ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell top, macht jede Session immersiv.
snatch casino bonuskoodi 2025|
Je suis totalement scotche par Instant Casino, on dirait une tempete de fun. La gamme de casino est un veritable feu d’artifice, avec des slots de casino modernes et immersifs. Le crew du casino assure un suivi de ouf, offrant des reponses qui claquent. Les gains du casino arrivent a la vitesse lumiere, quand meme des bonus de casino plus reguliers ce serait top. Pour resumer, Instant Casino est un spot de casino a ne pas rater pour ceux qui kiffent parier dans un casino style ! Cote plus le site du casino est une tuerie graphique, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus kiffante.
casino plex instant play|
seostream – The design is minimalist yet effective.
ifyss – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
caneguida – The content is well-researched and thought-provoking.
683tz084 – The content is well-researched and thought-provoking.
iyimu – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
elipso.site – Seen a few posts, quality is consistent, keep it up.
seoelitepro – I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
hpwt02n0me – Found useful ideas here, thanks for sharing such quality posts.
u888vn – Posts are well detailed, very good for learning new things.
rinatmat – Navigation is smooth and pages load quickly, good job.
comprafacilrd – The layout is attractive and navigating through the categories is simple.
htechwebservice – Great site overall, design feels professional and modern.
wzoo – Content seems fresh and the updates are frequent.
fcalegacy – Fantastic site overall, user experience is smooth and pleasant.
pacerproes – Definitely bookmarking this for future reference and revisits.
J’eprouve une loyaute infinie pour Mafia Casino, ca eleve le jeu a un niveau de boss legendaire. La cache de jeux est un arsenal cache de plus de 5000 armes, offrant des cashbacks 15% et VIP 5 niveaux des capos comme Evolution et Pragmatic Play. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les flux sont masques par des voiles crypto, a l’occasion des complots promotionnels plus frequents dynamiseraient le territoire. A la fin de cette conspiration, Mafia Casino forge une legende de jeu gangster pour les mafiosi des paris crypto ! A murmurer l’interface est un repaire navigable avec ruse, amplifie l’engagement dans le territoire du jeu.
mafia casino connexion|
bslthemes – I enjoy the fresh perspective this site offers.
h7721 – The site’s structure is intuitive, good job on navigation.
3366app – A great place to discover new content daily.
bongda247 – Great resource for those interested in niche subjects.
onlineforextrading – The site seems trustworthy and well organized, good job.
3styler – Great resource for those interested in niche subjects.
seodigitalelevate – Very impressed with the depth of information here, keep it up.
Je suis irresistiblement recrute par Mafia Casino, ca eleve le jeu a un niveau de boss legendaire. Les operations forment un plan de manigances innovantes, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de table. Les lieutenants repondent avec une discretion remarquable, assurant une loyaute fidele dans le syndicate. Les butins affluent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, toutefois des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. A la fin de cette conspiration, Mafia Casino forge une legende de jeu gangster pour les parrains de casinos virtuels ! Par surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, infuse une essence de mystere mafieux.
the grand mafia casino|
bodybuilding on steroids
References:
https://urlscan.io/result/0199ab37-dbd5-7354-887e-da717bc39a55/
Ich liebe absolut Snatch Casino, es fuhlt sich wie ein Sturm des Vergnugens an. Die Optionen sind umfangreich und abwechslungsreich, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Support ist 24/7 verfugbar, erreichbar jederzeit. Die Auszahlungen sind superschnell, obwohl mehr Freispiele waren ein Plus. Zum Schluss Snatch Casino lohnenswert fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Spa? ! Beachten Sie auch das Design ist ansprechend und intuitiv, erleichtert die Gesamterfahrung.
snatch casino no deposit bonus|
united statesn online pokies review, how old Do you have to be to enter a casino in vegas
casinos pay out in cash uk and canada casino download
free game, or australian online gambling legislation
live-sex-cam – Found this site recently, and it’s been surprisingly entertaining.
artvoyage – Love the artist bios and stories, adds so much depth.
newstoday – Their local section is excellent, covers news I actually care about.
googlerankmaster – Navigated a bit, found some interesting sections worth revisiting.
nowmining – Found their calculators very accurate, makes planning easier for me.
manchunyuan8 – Navigation is straightforward, didn’t get lost at all actually.
shineonx – Just discovered this, hoping to find interesting content ahead.
capsaqiu – Found some placeholders, seems work in progress—but promising.
post34 – Feels like a thoughtfully put-together blog, I enjoy the tone.
saltburn – Interesting name, but not much to see here beyond a basic landing page.
crowltheselinks – Some things load slowly, but content seems like it’s early stage.
cyrusmining – Possibly a scam or low credibility site due to lack of visible information.
liveforextrading – Found some useful tutorials, makes complex ideas easier to understand.
wraoys – Could be under development;’ll revisit to see how it evolves.
antsmarket – The name has potential (market + ants), but execution is still missing.
myzb27 – Feels like work in progress, but promising start nonetheless.
dhpb-smile – Bookmarking to recheck later—maybe new updates will show up.
axin2 – Loads quickly on my phone, content looks promising so far.
Ich bin suchtig nach Snatch Casino, es fuhlt sich wie ein Sturm des Vergnugens an. Die Optionen sind umfangreich und abwechslungsreich, mit immersiven Live-Sitzungen. Der Support ist 24/7 verfugbar, erreichbar jederzeit. Die Auszahlungen sind superschnell, obwohl zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Zum Schluss Snatch Casino lohnenswert fur Casino-Fans ! Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist super einfach, was das Spielvergnugen steigert.
anГЎlise snatch casino|
thefreemath – Love what I see so far, looks like a solid math resource hub.
bbc2y – Right now it’s more of a placeholder than a full website.
pomni – Very pleasant browsing experience, would revisit when I have time.
ouyicn – Not much visible except redirects; content is nearly absent.
best site to buy steroids
References:
https://gitea.mpc-web.jp/fyxpriscilla24
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, ca eleve le jeu a un niveau de boss legendaire. La cache de jeux est un arsenal cache de plus de 5000 armes, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de table. Le service conspire en continu 24/7, accessible par message code ou appel direct. Les flux sont masques par des voiles crypto, occasionnellement des largesses gratuites supplementaires boosteraient les operations. A la fin de cette conspiration, Mafia Casino invite a une intrigue sans trahison pour ceux qui ourdissent leur destin en ligne ! De surcroit le graphisme est un complot dynamique et immersif, infuse une essence de mystere mafieux.
jeu de sociГ©tГ© mafia casino|
karsynskrusaders – Found some helpful articles, depth seems promising so far.
Заказать seo аудит https://seo-audit-sajta.ru
Need TRON Energy? buy tron energy instantly and save on TRX transaction fees. Rent TRON Energy quickly, securely, and affordably using USDT, TRX, or smart contract transactions. No hidden fees—maximize the efficiency of your blockchain.
Je suis allie avec Mafia Casino, on complote un reseau de tactiques astucieuses. Le territoire est un domaine de diversite criminelle, avec des slots aux themes gangster qui font chanter les rouleaux. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, assurant une loyaute fidele dans le syndicate. Les retraits s’executent avec une furtivite remarquable, toutefois des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. Pour clore l’omerta, Mafia Casino devoile un plan de triomphes secrets pour les parrains de casinos virtuels ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire le graphisme est un complot dynamique et immersif, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
the grand mafia casino guide|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, dennoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, trotzdem regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Au?erdem die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, verstarkt die Immersion. Besonders toll die schnellen Einzahlungen, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich bin absolut hingerissen von NV Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Kick. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, mit Spielen, die perfekt fur Kryptos geeignet sind. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, garantiert hochwertige Hilfe. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, ab und zu zusatzliche Freispiele waren toll. Kurz gesagt, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Casino-Enthusiasten ! Hinzu die Navigation ist kinderleicht, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Need porn videos or photos? free ai porn generator – create erotic content based on text descriptions. Generate porn images, videos, and animations online using artificial intelligence.
IPTV форум vip-tv.org.ua место, где обсуждают интернет-телевидение, делятся рабочими плейлистами, решают проблемы с плеерами и выбирают лучшие IPTV-сервисы. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу интернет-ТВ!
free spins no deposit no wagering usa, casino jack
milwaukee and online real slots australia,
or free casino money united states
Check out my site: rolex roulette dial – Marcelo –
whollywoodhalloween – This site gives serious Halloween energy, everything fits the mood perfectly.
wexfordliteraryartsfestival – A much-needed solution for artists seeking to prove their work’s authenticity.
ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward – Sounds passionate; award concept like this can inspire many.
janetfortampa – Love how they’re combining technology with art authenticity.
jadenurrea – Your portfolio is impressive, makes me want to explore more sections.
successmarketboutique – The idea of a global art registry feels like a game-changer.
716selfiebuffalo – Perfect spot for a fun photoshoot with friends or family.
Ich bin suchtig nach Snatch Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Thrill. Der Katalog ist einfach gigantisch, mit modernen und fesselnden Slots. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, mit tadellosem Follow-up. Die Zahlungen sind flussig und sicher, manchmal zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Zum Schluss Snatch Casino ist ein Must fur Spieler fur Casino-Fans ! Daruber hinaus die Oberflache ist flussig und modern, fugt Komfort zum Spiel hinzu.
codice promozionale snatch casino|
sergiidima – Just explored this site; the concept of art verification is intriguing.
goldmetalshop – The platform’s design is clean and user-friendly.
dayofthedeadatx – Excited to see how this evolves in the art community.
everymaskcounts – Easily shareable content too, looks built to raise awareness broadly.
casteintheuk – I appreciate the transparency this site offers to artists and buyers.
vsmphotography – Just explored this site; the concept of art verification is intriguing.
Ich bin begeistert von Snatch Casino, es fuhlt sich wie ein Sturm des Vergnugens an. Das Spielangebot ist beeindruckend, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, mit tadellosem Follow-up. Die Auszahlungen sind superschnell, obwohl mehr Freispiele waren ein Plus. Global Snatch Casino bietet garantiertes Vergnugen fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell top, fugt Komfort zum Spiel hinzu.
codice promo snatch casino|
Je suis pactise avec Mafia Casino, on complote un reseau de tactiques astucieuses. Il pullule d’une legion de complots interactifs, integrant des lives comme Infinite Blackjack pour des negociations tendues. Le service conspire en continu 24/7, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, toutefois des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. Dans l’ensemble du domaine, Mafia Casino devoile un plan de triomphes secrets pour les gardiens des empires numeriques ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire le graphisme est un complot dynamique et immersif, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
code promo mafia casino|
оргонит и трискель чокурей – Аналогично “чо ку рей” – Поиск информации о символе “Чо Ку Рей” в рейки. Предоставляет информацию о значении этого символа и его использовании в рейки.
мясо для собак Для собак крупных пород важно выбирать лакомства, соответствующие их размеру и потребностям. Они должны быть достаточно большими, чтобы собака не проглотила их целиком, и содержать достаточное количество белка и других питательных веществ, чтобы поддерживать их здоровье и активность.
J’eprouve une loyaute infinie pour Mafia Casino, ca eleve le jeu a un niveau de boss legendaire. Il pullule d’une legion de complots interactifs, integrant des lives comme Infinite Blackjack pour des negociations tendues. Les lieutenants repondent avec une discretion remarquable, assurant une loyaute fidele dans le syndicate. Les transferts glissent stables et acceleres, occasionnellement des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. En scellant le pacte, Mafia Casino se dresse comme un pilier pour les capos pour ceux qui ourdissent leur destin en ligne ! Par surcroit l’interface est un repaire navigable avec ruse, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia casino 777|
Лука Модричтин тактикалык ой жүгүртүүсү укмуш.Лука Модрич Мадрид үчүн тарых жараткан. Лука Модрич статистика дайыма жогорку деңгээлде. Лука Модричтин жашы 39 болсо да, оюну жаштардыкындай. Трансфер боюнча инсайддар жана қауесеттер үчүн кара: Лука Модрич трансфер. Анын ысымы футбол тарыхында калат.
Алар бирге көптөгөн ЛЧ жеңиштерин алып келишкен. Модрич согуш жылдарында чоңойгон, бирок футбол аны сактап калды. Футболдо андай деңгээлге жетүү оңой эмес. Лука Модрич үчүн көп клубдар эшигин ачат.
free casino cash no deposit usa, gousaos quest free spins no deposit and deposit now same day pay online
casino; Salvatore, later casino united states, or best australia pokies
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, dennoch regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die schnellen Einzahlungen, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Kick. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Optionen, mit Slots im innovativen Design. Die Mitarbeiter reagieren blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und flussig, ab und zu mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Insgesamt, NV Casino ist eine Plattform, die rockt fur Krypto-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen das Design ist modern und ansprechend, verstarkt die Immersion.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Всё о металлообработке https://j-metall.ru и металлах: технологии, оборудование, сплавы и производство. Советы экспертов, статьи и новости отрасли для инженеров и производителей.
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Nicht zu vergessen die Site ist schnell und stylish, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es ist ein Abenteuer, das pulsiert wie ein Herzschlag. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit Spielen, die perfekt fur Kryptos geeignet sind. Der Support ist von herausragender Qualitat, bietet klare Antworten. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, trotzdem mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Kurz gesagt, NV Casino ist definitiv empfehlenswert fur Casino-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich die Oberflache ist intuitiv und stylish, verstarkt die Immersion.
playnvcasino.de|
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
Есть металлолом? вывоз металла мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг по приему металлолома в Санкт-Петербурге, включая оперативную транспортировку материалов непосредственно на перерабатывающий завод. Особое внимание мы уделяем удобству наших клиентов. Процесс сдачи металлолома организован максимально комфортно: осуществляем вывоз любых объемов металлических отходов прямо с вашей территории.
Хочешь сдать металл? прием металла цена наша компания специализируется на профессиональном приёме металлолома уже на протяжении многих лет. За это время мы отточили процесс работы до совершенства и готовы предложить вам действительно выгодные условия сотрудничества. Мы принимаем практически любые металлические изделия: от небольших профилей до крупных металлоконструкций.
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
https://odegka-ua.com/yak-unyknuty-pomylok-pry-pokuptsi-stekla-far.html
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
https://nemovlya.com.ua/instrumenty-dlia-far-vid-nozhiv-do-ekstruderiv.html
You can shelter yourself and your stock nearby being alert when buying medicine online. Some pharmacopoeia websites control legally and sell convenience, privacy, cost savings and safeguards for purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/orlistat.html orlistat
I have a real passion for Wazamba Casino, it seems like a whirlwind of delight. The catalog is absolutely massive, compatible with crypto for seamless play. Enhancing your initial experience. Agents respond swiftly. Winnings arrive promptly, sometimes additional bonuses might be welcome. In conclusion, Wazamba Casino is a platform that excels for adrenaline seekers ! In addition the site is fast and responsive, adds a layer of excitement. Notably tournaments for competitive play, offering more ways to win.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, on percoit une vitalite dechainee. Les alternatives sont etonnamment etendues, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Associe a des paris gratuits. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les retraits sont realises promptement, bien que des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Tout compte fait, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! De surcroit la navigation est simple et engageante, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions securisees.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
https://atlan.ru/product-category/mebel/veshalki/
складские стеллажи Надежные металлические стеллажи для склада от производителя «Металлоизделия» Организуйте складское пространство с максимальной эффективностью! Компания «Металлоизделия» предлагает профессиональные металлические стеллажи для складов любого размера и назначения. Наши стеллажи для склада — это идеальное решение для хранения товаров, оборудования, архивов и материалов. Они позволяют использовать каждый квадратный метр площади по максимуму, обеспечивая легкий доступ к любой единице хранения. Почему выбирают наши стеллажи? Прочность и долговечность: Мы используем высококачественный стальной прокат и усиленные конструкции, выдерживающие значительные нагрузки (до 5000 кг на ячейку и более). Универсальность: Широкая линейка моделей — полочные, паллетные (фронтальные, гравитационные), консольные. Подберем решение под ваши задачи. Безопасность: Все конструкции имеют антикоррозийное покрытие и рассчитаны на многократную сборку-разборку. Строгое соблюдение ГОСТов. Модульность и масштабируемость: Вы можете легко нарастить систему или изменить конфигурацию при расширении склада. Выгодная цена: Работаем без посредников, так как являемся производителем.
I’m utterly captivated by Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. There’s an incredible variety of games, including slots with tribal themes. Plus 200 free spins to start strong. Available 24/7 for any queries. Withdrawals are processed quickly, though extra rewards would be fantastic. Broadly speaking, Wazamba Casino is worth exploring for online betting fans ! Also the site is fast and responsive, which heightens the fun of every session. Notably crypto-friendly banking options, elevating the engagement.
wazambagr.com|
You can conserve yourself and your dearest by being cautious when buying prescription online. Some pharmacy websites function legally and sell convenience, privacy, bring in savings and safeguards for purchasing medicines. buy in TerbinaPharmacy https://terbinafines.com/product/doxycycline.html doxycycline
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de vitalite. La diversite des titres est stupefiante, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. L’equipe de support est remarquable, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans retard, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. En bref, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui impressionne pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! En bonus le design est moderne et fluide, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage supplementaire les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Naviguer sur le site|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, bietet klare Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, trotzdem regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem die Navigation ist kinderleicht, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein Pluspunkt ist die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis captive par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le service est operationnel 24/7, accessible a tout instant. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Par ailleurs le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Lire maintenant|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinia Casino, il procure une experience imperiale. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est imperial, toujours pret a servir. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, parfois plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et elegante, ajoute une touche de luxe. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir les avantages|
J’ai un engouement sincere pour Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. Le service est operationnel 24/7, accessible a tout instant. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, stimule le desir de revenir. A souligner aussi le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des transactions securisees.
Tout apprendre|
best poker app usa, when did how to make
money online 2021 (Jodi)
gambling start in uk and no deposit mobile casino canada, or free 10 no deposit casino
uk
no deposit mobile casino bonus uk, online casino no deposit bonus free
spins usa and uk casino free bonus, or online casino canada free chip
Also visit my blog … Best Way To Bet Playing Roulette
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, obwohl zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Besonders toll die mobilen Apps, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis emerveille par Locowin Casino, il procure une odyssee unique. Le catalogue est abondant et multifacette, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Accompagne de paris gratuits. Les agents repondent avec celerite, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans retard, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En resume, Locowin Casino garantit du plaisir a chaque instant pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et elegante, incite a prolonger l’experience. Un avantage supplementaire le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, offre des recompenses continues.
Entrer sur le site|
Je suis stupefait par Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le service est operationnel 24/7, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, cependant des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et engageante, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Egalement notable les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Explorer tout le site|
J’adore l’ambiance de Casinia Casino, ca offre un plaisir aristocratique. La variete des titres est majestueuse, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est impeccable, toujours pret a servir. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, bien que des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du prestige. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Notons aussi la navigation est simple et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un plus non negligeable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Découvrir l’offre|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En synthese, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un plus significatif les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, qui stimule l’engagement.
Visiter l’offre|
Can I simply say what a comfort to find somebody that truly understands what they’re discussing on the net. You certainly understand how to bring a problem to light and make it important. A lot more people really need to read this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you aren’t more popular given that you definitely possess the gift.
https://saunalux.kiev.ua/yakyi-instrument-krashche-dlia-rozboru-far-ruchnyi-chy-elektrychnyi.html
kostenlos Sportwetten tipps profis ohne einzahlung
online wetten bonus vergleich
my blog post – online-sportwetten
Путешествуйте по Крыму https://м-драйв.рф на джипах! Ай-Петри, Ялта и другие живописные маршруты. Безопасно, интересно и с профессиональными водителями. Настоящий отдых с приключением!
get huge fast
References:
https://academicsgate.com/employer/tesamorelin-vs-sermorelin-vs-ipamorelin-a-comparative-review-of-the-research-findings/
best steroid cycle for bulking
References:
https://code.openmobius.com:3001/princessboatma
can i buy anabolic steroids legal
References:
https://ondashboard.win/story.php?title=unveiling-the-advantages-of-kpv-peptide-therapy-at-tulsi-clinic-in-san-diego
Нужна карта? карта Visa с бонусами при покупках в зарубежных магазинах как оформить зарубежную банковскую карту Visa или MasterCard для россиян в 2025 году. Карту иностранного банка можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Зарубежные карты Visa и MasterCard подходят для оплаты за границей. Иностранные банковские карты открывают в Киргизии, Казахстане, Таджикистане и ряде других стран СНГ, все подробности смотрите по ссылке.
https://katellkeinegcom.wordpress.com/
Металлообработка и металлы https://j-metall.ru/ ваш полный справочник по технологиям и материалам: обзоры станков и инструментов, таблицы марок и ГОСТов, кейсы производства, калькуляторы, вакансии, и свежие новости и аналитика отрасли для инженеров и закупщиков.
I’m surrounded by Wazamba Casino, it awakens a peculiar force. There’s an expansive array of choices, incorporating wagers on athletic events. Heightening preliminary involvement. Addressing concerns instantly. Exchanges are guarded and prompt, intermittently further advantages would stand out. Collectively , Wazamba Casino supplies incomparable delight for exploration enthusiasts ! Further traversal is innate, fortifying absorption in play. Especially captivating prestige levels with unique favors, supplying individualized graces.
https://wazambagr.com/|
J’ai une passion ardente pour Bingoal Casino, ca plonge dans un univers hypnotisant. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Pour un lancement puissant. Le service est operationnel 24/7, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. La procedure est aisee et efficace, mais des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Tout compte fait, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! A mentionner la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. A souligner aussi les options de paris sportifs etendues, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller sur le site|
tripskan TripScan (Трипскан) – это, предположительно, веб-сервис или мобильное приложение, предназначенное для планирования путешествий и поиска информации о достопримечательностях, отелях, ресторанах и других местах, представляющих интерес для туристов. Сервис, вероятно, предоставляет возможность поиска, бронирования и организации поездок, а также позволяет пользователям обмениваться отзывами и рекомендациями о посещенных местах. Функциональность TripScan может включать в себя интерактивные карты, маршруты, списки рекомендованных мест, фильтры для поиска и возможность делиться опытом в социальных сетях.
reddit steroids before and after
References:
https://orb.tl/asanmp80218281
steroid muscle builders
References:
https://skitterphoto.com/photographers/1616329/clay-raynor
Ким болбосун, Алекс Перейра менен октагонго чыккандан кийин өзгөрөт. Алекс Перейра UFCде эки салмак категориясында чемпион болду — сыймык! Анын жашоосу, үй-бүлөсү жана мотивациялык видеолору сайтта: http://www.alex-pereira-kg.com. Перейра менен Джон Джонстун беттеши көргүм келет.
Анын урганынын күчү килограмм менен эсептелет.
Перейра дайыма өзүн жакшыртып келет. Бул жигиттин мүнөзү – темирдей бекем. Менин оюмча, Перейра кайра жеңишке жетет.
Анын жигиттик сапаты өзүнчө сөз. Алекс Перейра — күч, эрк жана ишенимдин символу.
what do all steroids contain in their structure
References:
https://bk-house.synology.me:3081/mariambustaman
Greetings! Utter productive suggestion within this article! It’s the crumb changes which choice obtain the largest changes. Thanks a quantity for sharing! stromectol notice
side effects of anabolic steroids include
References:
http://historydb.date/index.php?title=wrightroy8940
sustanon steroid side effects
References:
https://maids-station.com/employer/ipamorelin-vs-sermorelin-unraveling-the-distinctions-in-peptide-treatments/
steriods cost
References:
https://git.styledesign.com.tw/mitzigriffis29
free sportwetten bonus ohne einzahlung
my website; Online wetten Test
Строительный портал https://repair-house.kiev.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Подробные статьи, обзоры материалов, советы экспертов, новости отрасли и современные технологии для профессионалов и домашних мастеров.
Строительный портал https://intellectronics.com.ua источник актуальной информации о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Обзоры, инструкции, технологии, проекты и советы для профессионалов и новичков.
Портал о стройке https://mr.org.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Статьи, советы экспертов, современные технологии и обзоры материалов. Полезная информация для мастеров, инженеров и владельцев домов.
Good blog you possess here.. It’s hard to assign elevated quality belles-lettres like yours these days. I justifiably recognize individuals like you! Rent mindfulness!! TerbinaPharmacy
оптимизация ндс в оренбурге Купить двигатель Toyota – значит инвестировать в надежность и долговечность, ведь японские моторы славятся ресурсом свыше 400 тысяч км при правильном уходе. Популярные модели: 1NZ-FE (1.5 л бензин) для Corolla, 2AR-FE (2.5 л) для Camry или D-4D дизели для Hilux. При покупке уточните год, пробег и комплектацию – контрактные из Японии часто в идеальном состоянии благодаря строгому ТО. Проверьте по VIN на совместимость, наличие гарантии (от 1 года) и документы. Цены варьируются от 50 до 300 тысяч рублей, в зависимости от состояния. Установка требует калибровки ЭБУ для оптимальной работы. Toyota-двигатели экономичны (6-10 л/100 км) и просты в ремонте, с доступными запчастями. Избегайте подделок – покупайте у дилеров с репутацией. Если ваш Toyota нуждается в замене, это шанс обновить авто без больших затрат, сохранив оригинальную динамику и комфорт.
positive and negative effects of steroids
References:
https://www.google.co.zm/url?q=https://www.valley.md/kpv-peptide-guide-to-benefits-dosage-side-effects
how long is a steroid cycle
References:
https://emploi-securite.com/societes/mastering-ipamorelin-cycles-ideal-doses-scheduling-and-top-peptide-combinations/
anavar cutting cycle
References:
https://gitea.cloudfindtime.com/guillermoharpu
Актуальный портал https://sinergibumn.com о стройке и ремонте. Современные технологии, материалы, решения для дома и бизнеса. Полезные статьи, инструкции и рекомендации экспертов.
игры https://mailsco.online/ формируют интеллект. Они обучают новым способностям и стратегиям.
Женский портал https://prins.kiev.ua всё о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновение, психология и стиль жизни для современных женщин.
Онлайн женский портал https://replyua.net.ua секреты красоты, стиль, любовь, карьера и семья. Читайте статьи, гороскопы, рецепты и советы для уверенных, успешных и счастливых женщин.
Современный женский https://novaya.com.ua портал о жизни, моде и гармонии. Уход за собой, отношения, здоровье, рецепты и вдохновение для тех, кто хочет быть красивой и счастливой каждый день.
Интересный женский https://muz-hoz.com.ua портал о моде, психологии, любви и красоте. Полезные статьи, тренды, рецепты и лайфхаки. Живи ярко, будь собой и вдохновляйся каждый день!
Женский портал https://z-b-r.org ваш источник идей и вдохновения. Советы по красоте, стилю, отношениям, карьере и дому. Всё, что важно знать современной женщине.
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, gelegentlich die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Hinzu kommt das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Hervorzuheben ist die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’aime l’environnement distinct de Bingoal Casino, ca plonge dans un univers hypnotisant. Les alternatives sont etonnamment etendues, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, assurant un support premium. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Pour synthetiser, Bingoal Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, stimule le desir de revenir. A souligner aussi le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Savoir plus|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, ca distille un plaisir majestueux. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Le suivi est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans tarder, cependant plus de promos frequentes brilleraient davantage. Au final, Casinia Casino offre un divertissement constant pour les joueurs en quete de gloire ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et majestueux, ajoute une touche de splendeur. A souligner aussi les options de paris sportifs etendues, garantit des transactions fiables.
Voir par vous-mГЄme|
Je suis totalement seduit par Casinia Casino, il offre une experience imperiale. Les options sont vastes comme un royaume, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, offrant des reponses claires. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient apprecies. En bref, Casinia Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus le design est moderne et fluide, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Visiter pour plus|
Авто портал https://psncodegeneratormiu.org мир машин в одном месте. Читайте обзоры, следите за новостями, узнавайте о новинках и технологиях. Полезный ресурс для автолюбителей и экспертов.
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua всё об автомобилях: новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, советы по уходу и выбору машины. Узнайте о новинках автопрома, технологиях и трендах автомобильного мира.
Онлайн авто портал https://retell.info всё для автолюбителей! Актуальные новости, обзоры новинок, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и полезные советы по эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей.
Автомобильный портал https://autoguide.kyiv.ua для водителей и поклонников авто. Новости, аналитика, обзоры моделей, сравнения, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту машин разных брендов.
Современный авто портал https://necin.com.ua мир автомобилей в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, сравнения, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Будь в курсе последних тенденций автоиндустрии
wett app freunde
Look into my homepage: tor wetten – Marilynn –
dreamgrid.click – Layout is clean; wish there was more info or context on what it’s about.
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, immer parat zu assistieren. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Nicht zu vergessen die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, fugt Magie hinzu. Hervorzuheben ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, on percoit une vitalite dechainee. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Pour un lancement puissant. Le service est operationnel 24/7, toujours pret a intervenir. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, par moments des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Tout compte fait, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! En outre le site est veloce et seduisant, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. A souligner aussi le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, garantit des transactions securisees.
Lire entiГЁrement|
vierklee wetten bonus
my blog; wett-tipps ai kostenlos
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui bouillonne d’energie. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et stylee, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. A noter egalement les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter l’offre|
Je suis completement ensorcele par Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans une cour enchanteresse. L’eventail de jeux est princier, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. L’offre de bienvenue est somptueuse. L’assistance est precise et elegante, offrant des solutions limpides. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos frequentes brilleraient davantage. Pour conclure, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui trone en maitre pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme un decret, intensifie l’eclat du jeu. Un atout cle les tournois reguliers pour la rivalite, qui renforce l’engagement.
En savoir davantage|
Je suis surpris par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. Le service est operationnel 24/7, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, de temps a autre des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! En outre l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. A souligner aussi les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, renforce le sens de communaute.
Aller plus en profondeur|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots au style innovant. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, proposant des reponses limpides. Les operations sont solides et veloces, de temps a autre des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, stimule le desir de revenir. Un plus significatif le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Aller Г la page|
Портал про стройку https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Полезные советы, статьи, технологии, материалы и оборудование. Узнайте о современных решениях для дома и бизнеса.
Строительный портал https://msc.com.ua о ремонте, дизайне и технологиях. Полезные советы мастеров, обзоры материалов, новинки рынка и идеи для дома. Всё о стройке — от фундамента до отделки. Учись, строй и вдохновляйся вместе с нами!
Портал про стройку https://keravin.com.ua и ремонт полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры оборудования и материалов. Всё о строительстве домов, дизайне и инженерных решениях
Онлайн-портал про стройку https://donbass.org.ua и ремонт. Новости, проекты, инструкции, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё, что нужно знать о современном строительстве и архитектуре.
Подоконники из искусственного камня https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru в Москве. Рейтинг лучших подоконников – авторское мнение, глубокий анализ производителей.
I find irresistible Wazamba Casino, it’s a saga that whispers with secrets. The breadth in selections is breathtaking, encompassing real-time dealer interactions for genuineness. Heightening preliminary involvement. Proficient and considerate aid. Exchanges are guarded and prompt, however diversified reward schemes would improve it. Collectively , Wazamba Casino rises as a premier destination for stimulation pursuers ! In addition the setting initializes swiftly, infusing supplementary fascination. Notably impressive prestige levels with unique favors, bestowing enduring motivations.
https://wazambagr.com/|
I’m blown away by Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it builds an adrenaline-fueled cosmic quest. The multiplier climbs with nail-biting suspense, offering max wins up to 10,000x your stake. Volatility keeps things exciting and fair. Support is lightning-fast and helpful, guaranteeing transparent outcomes. Withdrawals are swift and secure, although more bonus rounds could add variety. All things considered, Astronaut Crash stands out in 100HP’s lineup for crash game fans ! On top of that navigation is intuitive for beginners, adding immersive audio cues. A real gem crypto wallet integration, lets you test strategies risk-free.
https://astronaut-crashgame777.com/|
quotenvergleich sportwetten wettanbieter mit den besten quoten
I’m blown away by Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it delivers edge-of-your-seat tension. Dual bet options add layers of strategy, featuring a rocket that soars with rising multipliers. No wager requirements on bonuses. Support is lightning-fast and helpful, ensuring secure crypto deposits. Transactions process in minutes, although more bonus rounds could add variety. Wrapping it up, Astronaut Crash delivers proven fair thrills for crypto gamblers ! On top of that load times are near-instant, heightening the launch anticipation. A real gem demo with real-time stats, offers verifiable randomness.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
Советы по строительству https://vodocar.com.ua и ремонту своими руками. Пошаговые инструкции, современные технологии, идеи для дома и участка. Мы поможем сделать ремонт проще, а строительство — надёжнее!
Сайт о строительстве https://valkbolos.com и ремонте домов, квартир и дач. Полезные советы мастеров, подбор материалов, дизайн-идеи, инструкции и обзоры инструментов. Всё, что нужно для качественного ремонта и современного строительства!
Полезный сайт https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua о строительстве и ремонте: новости отрасли, технологии, материалы, интерьерные решения и лайфхаки от профессионалов. Всё для тех, кто строит, ремонтирует и создаёт уют.
Информационный портал https://smallbusiness.dp.ua про строительство, ремонт и интерьер. Свежие новости отрасли, обзоры технологий и полезные лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно знать о стройке и благоустройстве жилья в одном месте!
Строительный сайт https://teplo.zt.ua для тех, кто создаёт дом своей мечты. Подробные обзоры, инструкции, подбор инструментов и дизайнерские проекты. Всё о ремонте и строительстве в одном месте.
машина додж bmw m5 – это высокопроизводительный седан, сочетающий в себе спортивный характер и роскошный комфорт. Мощный двигатель, точная управляемость и передовые технологии превращают каждую поездку в незабываемое удовольствие.
audi a6 c7 allroad 3.0 автомобиль мерседес – Mercedes-Benz – это символ роскоши, комфорта и передовых технологий, предлагающий широкий выбор моделей для самых взыскательных клиентов.
Строим и ремонтируем https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua своими руками! Инструкции, советы, видеоуроки и лайфхаки для дома и дачи. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить бюджет.
Энциклопедия строительства https://kero.com.ua и ремонта: материалы, технологии, интерьерные решения и практические рекомендации. От фундамента до декора — всё, что нужно знать домовладельцу.
Пошаговые советы https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua по строительству и ремонту. Узнай, как выбрать материалы, рассчитать бюджет и избежать ошибок. Простые решения для сложных задач — строим и ремонтируем с уверенностью!
Новостной портал https://kiev-online.com.ua с проверенной информацией. Свежие события, аналитика, репортажи и интервью. Узнавайте новости первыми — достоверно, быстро и без лишнего шума.
Главные новости дня https://sevsovet.com.ua эксклюзивные материалы, горячие темы и аналитика. Мы рассказываем то, что действительно важно. Будь в курсе вместе с нашим новостным порталом!
10 some sex
References:
https://dramapipe1.werite.net/anavar-use-guide-dosing-and-scheduling-for-men-women-and-bodybuilders
Je suis totalement seduit par Bingoal Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. Les alternatives sont etonnamment vastes, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, toujours pret a intervenir. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En fin de compte, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Par ailleurs le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions securisees.
VГ©rifier ceci|
event updates
buchmacher pferdewetten
My web blog … sportwetten Verluste zurückholen erfahrungen
Строим и ремонтируем https://srk.kiev.ua грамотно! Инструкции, пошаговые советы, видеоуроки и экспертные рекомендации. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить без потери результата.
Обустраивайте дом https://stroysam.kyiv.ua со вкусом! Современные идеи для ремонта и строительства, интерьерные тренды и советы по оформлению. Создайте стильное и уютное пространство своими руками.
Строительный портал https://sitetime.kiev.ua для мастеров и подрядчиков. Новые технологии, материалы, стандарты, проектные решения и обзоры оборудования. Всё, что нужно специалистам стройиндустрии.
Сайт о стройке https://samozahist.org.ua и ремонте для всех, кто любит уют и порядок. Расскажем, как выбрать материалы, обновить интерьер и избежать ошибок при ремонте. Всё просто, полезно и по делу.
Как построить https://rus3edin.org.ua и отремонтировать своими руками? Пошаговые инструкции, простые советы и подбор инструментов. Делаем ремонт доступным и понятным для каждого!
steroid com reviews
References:
https://skitterphoto.com/photographers/1570252/craig-hassan
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, bietet klare Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, trotzdem die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis absolument fascine par Bingoal Casino, il offre une odyssee incomparable. L’eventail de jeux est extraordinaire, offrant des sessions live intenses. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, par moments des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Globalement, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! A mentionner le design est contemporain et lisse, ajoute un confort notable. Particulierement attractif le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, renforce le sens de communaute.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, on ressent une aura radieuse. La diversite des titres est eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le support client est lumineux, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits filent comme une comete, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient scintillantes. Au final, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et envoutant, intensifie l’eclat du jeu. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la rivalite, garantit des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis emerveille par Casinia Casino, on ressent une aura radieuse. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, offrant des sessions live captivantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. L’assistance est rapide et precise, offrant des solutions cristallines. Les retraits filent comme une comete, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient lumineux. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour les passionnes de frissons lumineux ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme un rayon, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner aussi les evenements communautaires captivants, qui renforce l’engagement.
Explorer les dГ©tails|
J’aime l’ambiance royale de Casinia Casino, il offre une experience imperiale. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent avec celerite, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du prestige. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! En prime l’interface est intuitive et elegante, ajoute une touche de luxe. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
Obtenir tous les dГ©tails|
AI ChatBot
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, avec des slots au design innovant. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, toujours pret a aider. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. Au final, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et stylee, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un plus non negligeable les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Мужской сайт https://rkas.org.ua о жизни без компромиссов: спорт, путешествия, техника, карьера и отношения. Для тех, кто ценит свободу, силу и уверенность в себе.
Мужской онлайн-журнал https://cruiser.com.ua о современных трендах, технологиях и саморазвитии. Мы пишем о том, что важно мужчине — от мотивации и здоровья до отдыха и финансов.
Портал для автомобилистов https://translit.com.ua от выбора машины до профессионального ремонта. Читайте обзоры авто, новости автоспорта, сравнивайте цены и характеристики. Форум автолюбителей, советы экспертов и свежие предложения автосалонов.
Сайт для женщин https://oun-upa.org.ua которые ценят себя и жизнь. Мода, советы по уходу, любовь, семья, вдохновение и развитие. Найди идеи для новых свершений и будь самой собой в мире, где важно быть уникальной!
Ваш гид в мире https://nerjalivingspace.com автомобилей! Ежедневные авто новости, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Найдите идеальный автомобиль, узнайте о страховании, кредитах и тюнинге.
J’aime l’atmosphere unique de Bingoal Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de vitalite. Il existe une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les retraits sont realises promptement, par moments plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En synthese, Bingoal Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! A mentionner le design est contemporain et lisse, ajoute un confort notable. Un plus significatif les evenements communautaires captivants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Obtenir tous les dГ©tails|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, ab und an zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Community-Events, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis hypnotise par Bingoal Casino, il offre une odyssee incomparable. La gamme des titres est stupefiante, offrant des sessions live intenses. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le service est operationnel 24/7, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, mais plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. Tout compte fait, Bingoal Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion complete. Un plus significatif les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions securisees.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
I’m deeply intrigued by Wazamba Casino, it unleashes a distinctive energy. The selections are wide-ranging and intricate, incorporating live sessions for authentic interaction. Amplifying early engagement. Answering queries rapidly. Procedures are uncomplicated, still regular deals might amplify appeal. In totality, Wazamba Casino supplies premium leisure for enthusiasts of betting ! Moreover the environment loads efficiently, strengthening game absorption. Additional benefit acquiring items for advantages, delivering customized favors.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Je suis epate par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, avec des slots au design innovant. Accompagne de tours gratuits sans wager. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, mais quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient cool. En resume, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et fluide, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. A noter egalement les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je suis emerveille par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui brille d’une energie lumineuse. La diversite des titres est eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs palpitants. Avec un Bonus Crab unique pour debuter. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits filent comme une comete, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de l’eclat. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour les passionnes de frissons lumineux ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et eblouissant, ajoute une touche de splendeur. Un atout cle les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des recompenses sur mesure.
Continuer ici|
Je suis absolument conquis par Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie noble. La selection de jeux est royale, avec des slots thematiques et innovants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est impeccable, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Au final, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! En prime le design est moderne et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui bouillonne d’energie. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a aider. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Au final, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement top, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
Lire plus loin|
I’m thrilled by Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it creates non-stop nail-biting action. The mechanics are sleek and engaging, with auto-bet for hands-free excitement. Free play mode to hone your edge. Chats connect in a flash, eager to troubleshoot mid-flight. The exit system rescues bold bets, still wider stake limits for pros. In a nutshell, Astronaut Crash shines bright in 100HP’s portfolio for tactical thinkers ! Standout layout supports marathon marathons, streamlining stake tweaks. Super feature leaderboards for rivalry, which supercharges repeat plays.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
I can’t resist the allure of Wazamba Casino, it unleashes a distinctive energy. There’s a vast spectrum of options, incorporating live sessions for authentic interaction. Amplifying early engagement. Answering queries rapidly. Cashouts are executed promptly, but further spins could be advantageous. Summarizing, Wazamba Casino furnishes unparalleled amusement for quest pursuers ! Moreover the framework is artistically impressive, refining user interaction. Especially noteworthy exclusive ranks with special privileges, guaranteeing safe exchanges.
wazambagr.com|
online meet
Строительный сайт https://okna-k.com.ua для профессионалов и новичков. Новости отрасли, обзоры материалов, технологии строительства и ремонта, советы мастеров и пошаговые инструкции для качественного результата.
Портал о дизайне https://sculptureproject.org.ua интерьеров и пространства. Идеи, тренды, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и общественных мест. Советы дизайнеров и примеры стильных решений каждый день.
Сайт о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua и металлообработке: виды металлов, сплавы, технологии обработки, оборудование и новости отрасли. Всё для специалистов и профессионалов металлургии.
Главный автопортал страны https://nmiu.org.ua всё об автомобилях в одном месте! Новости, обзоры, советы, автообъявления, страхование, ТО и сервис. Для водителей, механиков и просто любителей машин.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://rosetti.com.ua о стиле, здоровье и семье. Новости моды, советы экспертов, тренды красоты и секреты счастья. Всё, что важно и интересно женщинам любого возраста.
I’m wildly enthusiastic about Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it creates non-stop nail-biting action. The rocket’s ascent builds unbearable suspense, potential payouts soaring to 10,000x. RTP sits at an enticing 97%. Chats connect in a flash, eager to troubleshoot mid-flight. Flows are dependable and speedy, still fresh visuals beyond the rocket theme. In a nutshell, Astronaut Crash sparks endless stellar sessions for crash aficionados ! On that note layout supports marathon marathons, layering sound for immersion. Game-changer practice arena with live data, allows safe tactic trials.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
Студия ремонта https://anti-orange.com.ua квартир и домов. Выполняем ремонт под ключ, дизайн-проекты, отделочные и инженерные работы. Качество, сроки и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Туристический портал https://feokurort.com.ua для любителей путешествий! Страны, маршруты, достопримечательности, советы и лайфхаки. Планируйте отдых, находите вдохновение и открывайте мир вместе с нами.
sportwetten die besten
My homepage – kombiwette heute (Deidre)
lizenz sportwetten tipps bild
foot africain https://parifoot-afrique.com
pronostic foot gratuit telecharger 1xbet cameroun
1xbet cameroun apk https://pari-foot2.com
Флойд Мейвезердин жашоосу жана ийгилиги көптөргө үлгү. Флойд Мейвезер – мыкты дисциплина менен белгилүү. Флойд Мейвезердин жашоосу жана бизнеси тууралуу толук маалымат Флойд Мейвезер бизнес барагында.
Флойд Мейвезердин ийгилиги көпчүлүк үчүн үлгү. Флойд Мейвезер – мыкты стратегиянын ээси. Анын акыркы жаңылыктарын укпай калган адам жок.
Анын ар бир интервьюсу көңүл борборунда.
Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым өз максатына жеткен. Анын тарыхы ар дайым спорт күйөрмандарынын эсинде. Флойд Мейвезер ар дайым жаңы рекорддорду жарата берет.
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, bietet klare Losungen. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, dennoch mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
stack top
References:
https://muhammad-ali.com.az/user/lightniece2/
tippen sportwetten
Look at my web-site :: wetten online österreich, monaasoft.com,
tippen sportwetten
Look at my web-site :: wetten online österreich, monaasoft.com,
Je ne me lasse pas de Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie noble. Les options sont vastes comme un royaume, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable, toujours pret a servir. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Cerise sur le gateau le design est moderne et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
DГ©couvrir|
J’adore l’aura princiere de Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans une cour enchanteresse. Les options sont vastes comme un empire, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Le support client est royal, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, mais plus de promos frequentes brilleraient davantage. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino merite une visite royale pour les passionnes de frissons grandioses ! A noter le site est rapide et majestueux, facilite une immersion complete. Un atout cle le programme VIP avec 5 rangs princiers, propose des recompenses sur mesure.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis captive par Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie noble. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Cerise sur le gateau la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
Explorer davantage|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, offrant des sessions live intenses. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, proposant des reponses limpides. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, cependant des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit la navigation est simple et engageante, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. A souligner aussi les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, renforce le sens de communaute.
Ouvrir la page maintenant|
More peace pieces like this would insinuate the web better.
connectwiththeworldnow – I like how clear their call is, the layout is striking.
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, gelegentlich zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist kinderleicht, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Ein Pluspunkt ist die schnellen Einzahlungen, die Flexibilitat bieten.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis stupefait par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le service est operationnel 24/7, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. La procedure est aisee et efficace, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ajoute un confort notable. A souligner aussi les options de paris sportifs etendues, garantit des transactions securisees.
Visiter pour plus|
I’m completely enthralled with Wazamba Casino, it resembles a cascade of enchantment. The title variety is overwhelming, including live casino for real-time action. Accompanied by 200 free spins. Round-the-clock availability. The procedure is effortless, at times extra spins might enhance it. Concluding, Wazamba Casino provides elite entertainment for adventure seekers ! Also the layout is user-friendly and thematic, heightening game immersion. Another standout feature regular tournaments for competition, ensuring transaction safety.
wazambagr.com|
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, il offre une aventure imperiale. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Elevant l’experience de jeu. L’assistance est precise et elegante, offrant des solutions limpides. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient sublimes. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino offre un divertissement constant pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un decret, facilite une immersion complete. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des transactions fiables.
Lire plus|
Студия дизайна https://bathen.rv.ua интерьеров и архитектурных решений. Создаём стильные, функциональные и гармоничные пространства. Индивидуальный подход, авторские проекты и внимание к деталям.
Je suis impressionne par Casinia Casino, il offre une experience imperiale. La variete des titres est majestueuse, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino garantit du fun a chaque instant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et sophistique, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout majeur les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Ремонт и строительство https://fmsu.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Подробные статьи, обзоры инструментов, лайфхаки и практические советы. Мы поможем построить, отремонтировать и обустроить ваш дом.
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Renforcant l’experience de depart. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, toujours pret a intervenir. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, ajoute un confort notable. Egalement notable les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Commencer l’aventure|
Сварные Конструкции Быстровозводимые здания Быстровозводимые здания – это современное и эффективное решение для строительства жилых, коммерческих и промышленных объектов. Мы предлагаем проектирование, изготовление и монтаж быстровозводимых зданий любой сложности. Наши здания отличаются высокой прочностью, надежностью и долговечностью. Мы используем современные технологии и материалы, что позволяет нам оптимизировать процессы строительства и снижать затраты наших клиентов.
I’m blown away by Wazamba Casino, it unleashes a special vibe. The library is truly enormous, optimized for crypto transactions. Kickstarting your adventure. Support team is exceptional. Payouts are handled swiftly, sporadically additional incentives would shine. Altogether, Wazamba Casino stands out as a superior platform for adventure seekers ! Also the platform loads quickly, motivating return visits. Noteworthy is earning artifacts for perks, ensuring transaction safety.
https://wazambagr.com/|
wettseiten bonus
my web-site bet wetten online
Greetings! Utter gainful suggestion within this article! It’s the scarcely changes which choice espy the largest changes. Thanks a a quantity towards sharing!
bs2best зеркало Заинтересован, что будоражит тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это эталон анонимности, оперативности и уверенности. Добро пожаловать на bs2best.at — место, где открывают то, о чём принято умалчивать. Здесь ты получишь доступ к запретному плоду. Только для избранных. Без улик. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти возможность стать первопроходцем — bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои секреты. Хватит ли тебе смелости взглянуть правде в лицо?
buchmachern
Feel free to surf to my homepage; sportwetten bild tipps
Современная студия дизайна https://bconline.com.ua архитектура, интерьер, декор. Мы создаём пространства, где технологии сочетаются с красотой, а стиль — с удобством.
telecharger 1xbet apk africain foot
football africain foot africain
africain foot afrik foot pronostic
Создавайте дом https://it-cifra.com.ua своей мечты! Всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне интерьера. Идеи, проекты, фото и инструкции — вдохновляйтесь и воплощайте задуманное легко и с удовольствием.
bs2web at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
social talk
truelaunch – Great mix of insight and usability, kudos to the creators.
brandvision – Bookmarking this, lots of value I’ll revisit later.
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, bietet klare Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, ab und an mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die mobilen Apps, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de vitalite. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, mais des recompenses additionnelles seraient un avantage. En bref, Locowin Casino merite une visite pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, incite a prolonger l’experience. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
Voir les mises Г jour|
purehorizon – The content is clear, useful, and doesn’t overcomplicate things.
Je suis fascine par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, offrant des sessions live intenses. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, accessible a tout instant. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, bien que des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En synthese, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! En outre le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Un plus significatif les evenements communautaires captivants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Explorer davantage|
innovatek – Great selection of topics, covers a wide range.
Je suis completement obsede par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Renforcant l’experience de depart. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, mais plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. Globalement, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Egalement notable les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, qui stimule l’engagement.
Visiter en ligne|
sport wette
Also visit my blog post; strategie bei sportwetten
Мир архитектуры https://vineyardartdecor.com и дизайна в одном месте! Лучшие идеи, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и города. Узнай, как создаются красивые и функциональные пространства.
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, ab und an zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis absolument captive par Locowin Casino, il procure une odyssee unique. Le catalogue est abondant et multifacette, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Le bonus d’accueil est seduisant. L’equipe de support est remarquable, avec une aide precise et rapide. Le processus est simple et reibungslos, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino merite une visite pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, incite a prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des avantages personnalises.
Lire les dГ©tails|
valuevision – I’ll check back later to see updates, this has potential.
I’m utterly captivated by Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. The array of titles is vast, including slots with tribal themes. Doubling your deposit up to €500. Professional and helpful assistance. The system is user-friendly, sometimes extra rewards would be fantastic. Overall, Wazamba Casino is essential for gamers for online betting fans ! Furthermore the site is fast and responsive, deepens immersion in the game. Worth noting tournaments for competitive play, fostering a community feel.
https://wazambagr.com/|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’aide est performante et experte, toujours pret a intervenir. Les retraits sont realises promptement, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Commencer Г apprendre|
growthverse – Navigation is seamless, and the visuals are appealing.
J’ai un veritable engouement pour Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, toujours pret a intervenir. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Particulierement attractif le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Essayer|
skyportal – Really enjoying the latest updates, everything loads super fast today.
Tenho uma paixao intensa por BETesporte Casino, transporta para um mundo de apostas vibrante. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, incluindo apostas esportivas palpitantes. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. A assistencia e eficiente e profissional, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os saques sao rapidos como um sprint, no entanto mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. No geral, BETesporte Casino garante diversao a cada rodada para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e dinamico, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Igualmente impressionante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Explorar o site|
smartgrid – Clean name, tech-sounding, could be good for energy or data topics.
trendforge – Looks like the site isn’t loading yet, keeping an eye for launch.
quantumreach – Impressed by how detailed some of the posts are.
boldimpact – Will check again later; intrigued by the potential here.
I have a real passion for Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. The options are extensive and diverse, featuring over 5,000 titles from top providers. The welcome bonus is generous. Ensuring smooth gameplay. Payments are secure and reliable, nevertheless additional bonuses might be welcome. To sum up, Wazamba Casino is worth exploring for casino enthusiasts ! Moreover the platform is visually stunning, adds a layer of excitement. Another perk is collecting artifacts for rewards, elevating the engagement.
wazambagr.com|
bluetrail – Nice visuals too, makes reading comfortable and appealing.
alphaunity – Found useful info, definitely bookmarking this for later reference.
solidvision – Tried several times, page didn’t load yet.
sharpbridge – The color scheme is nice, very calming on the eyes.
goldbridge – Just visited the homepage, design is clean and professional.
elitegrowth – A pleasure to browse, everything is well-organized and clear.
cloudmatrix – The site is well-structured, making information easy to find.
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, sinto um ritmo alucinante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com sessoes ao vivo dinamicas. Com um bonus extra para comecar. O suporte ao cliente e estelar, com suporte preciso e rapido. O processo e simples e elegante, de vez em quando algumas rodadas gratis extras seriam incriveis. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao a cada momento para jogadores em busca de adrenalina ! Adicionalmente a interface e fluida e elegante, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Notavel tambem os torneios regulares para competicao, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Consultar os detalhes|
fastgrowth – Love the clean design, really easy to navigate today.
maxvision – Navigation is seamless, and the visuals are appealing.
greenmotion – Found exactly what I was looking for, very intuitive.
zenithlabs – Impressed by the layout, feels modern and user-friendly.
boldnetwork – Hoping they’ll add more info soon; I like the design direction.
thinkbeyondtech – The site is well-structured, making information easy to find.
nextlayer – Great user experience, everything loads so smoothly and fast.
focuslab – The content is solid — not just fluff, actually helpful.
https://b2shop.gl
urbanmatrix – Navigation is smooth, didn’t get lost browsing any section.
growwithfocus – The domain sounds motivational; hoping for quality content ahead.
nextrealm – Site isn’t currently accessible, maybe under maintenance or setup.
openlaunch – Useful resources I’ll try out in upcoming projects.
https://ibs2site.at
blueorbit – Found new ideas I hadn’t seen before — thanks!
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. La variete des titres est impressionnante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Le suivi client est irreprochable, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui dechire pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En prime la navigation est simple et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
Parcourir les offres|
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, assurant un support premium. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et engageante, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un plus significatif les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
Parcourir le site|
J’aime l’atmosphere de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, toujours pret a intervenir. Les retraits sont realises promptement, par moments des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, renforce le sens de communaute.
En savoir plus|
buchmacher bonus ohne einzahlung
My blog post … beste sportwetten Apps
ynaix – The aesthetic is clean and minimal, which works very well.
sportwetten ohne einzahlung
Feel free to surf to my web page; österreichische Wettanbieter
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. La variete des titres est impressionnante, avec des slots au design innovant. Accompagne de tours gratuits sans wager. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Notons aussi l’interface est intuitive et stylee, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus fun. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Regarder de prГЁs|
J’ai un engouement sincere pour Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un univers envoutant. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live intenses. Pour un lancement puissant. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, accessible a tout instant. La procedure est aisee et efficace, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, facilite une immersion complete. Un plus significatif les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
Trouver maintenant|
**mind vault**
mind vault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
connectwiththeworldnow – The tone is warm and inviting, feels like you’re part of something big.
Para activar un bono sin depósito en un casino online normalmente solo necesitas registrarte en el sitio, y solo en algunos casos, verificar tu identidad con tu DNI NIE, un proceso rápido y obligatorio por la normativa española. Algunos casinos ofrecen bonos sin necesidad de código promocional, lo que facilita aún más la experiencia. Además, puedes aprender a maximizar las ganancias con bonos sin depósito en casinos seleccionando aquellos que permiten jugar en una amplia variedad de juegos y que ofrecen tiradas gratis sin condiciones complicadas. Aquí te dejamos una guía clara para que no te pierdas nada. Tlf: +34 958 65 80 11 +34 958 65 82 36Fax: +34 958 62 21 26 Pirots X otorga premios a través de la mecánica Cluster Pays. Esto significa que tu objetivo es reunir 5 o más símbolos iguales que se toquen vertical u horizontalmente. El juego incluye símbolos Wild que, además de funcionar como comodines, están asociados a multiplicadores. Si se conectan con un grupo de símbolos ganadores, el multiplicador se aplica a dicha ganancia.
https://josalabourlawinstitute.in/bonos-exclusivos-y-ventajas-del-juego-de-casino-pirates-3-de-elk-studios/
El juego puede ser adictivo. Juega con responsabilidad. Paf es solo para usuarios mayores de 18 años.Dirección de contacto en España: Cuatrecasas, Calle Almagro 9, 28010, Madrid. La mecánica de Pirots 2 deja de lado la mecánica de giros tradicionales y en este caso las aves de diversos colores actúan como colectores de a través de la cuadrícula recolectando los símbolos de la misma correspondientes a su color. Son 5 símbolos de pago en total cuyo valor varía de acuerdo al nivel, con siete niveles en total. Estos suben de nivel cuando las aves colectan algún símbolo de mejora. En la tabla a continuación se reflejan los símbolos de pago de Pirots 2 y su valor de acuerdo al nivel. En esta tabla se observa que, aunque todos estos casinos ofrecen una variedad de métodos de pago, los tiempos de retiro y la posible aplicación de comisiones pueden variar significativamente. Por ejemplo, Roman Casino se destaca por sus rápidos retiros, procesados en 24 horas para la mayoría, mientras que Wildsino Casino ofrece múltiples métodos de pago, pero también tiene comisiones más estrictas.
Je suis impressionne par Locowin Casino, ca fournit un plaisir intense. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, offrant des sessions live intenses. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. Le service est operationnel 24/7, accessible a tout instant. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, mais quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Globalement, Locowin Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ajoute un confort notable. Egalement notable les options de paris sportifs etendues, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Explorer le site web|
Автоматические гаражные ворота давно перестали быть роскошью и стали необходимым элементом комфортной жизни. Наши автоматические ворота сочетают надёжность проверенных европейских механизмов с элегантным дизайном, который гармонично впишется в архитектуру любого здания. Мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг: от профессиональной консультации и точного замера до установки под ключ и гарантийного обслуживания. Доверьте безопасность своего дома профессионалам — получите бесплатный расчёт стоимости уже сегодня: Автоматические ворота
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
strongrod – Found useful features and tools; impressed by utility.
Adoro a chama de BR4Bet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que acende como uma tocha. A selecao de titulos e uma chama de emocoes. com caca-niqueis que brilham como holofotes. O atendimento e solido como um farol. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. O processo e claro e sem apagoes. porem mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura iluminada. Resumindo, BR4Bet Casino vale explorar esse cassino ja para os fas de adrenalina brilhante! E mais o design e um espetaculo visual iluminado. tornando cada sessao ainda mais brilhante.
br4bet suporte|
Estou completamente apaixonado por BETesporte Casino, leva a um universo de apostas dinamico. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, de vez em quando promocoes mais frequentes seriam um plus. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Adicionalmente a plataforma e visualmente impactante, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Muito atrativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Visitar o site|
wavefusion – Clean typography and spacing, reading is effortless throughout.
sharpwave – Helpful guides here, I can apply tips right away.
brightideaweb – Visuals stand out, nice contrast and pleasing color palette.
metarise – Design pops nicely, visuals are appealing and consistent throughout.
Sou louco pela velocidade de F12.Bet Casino, e um ronco de diversao que gira como rodas de Formula 1. O catalogo de jogos e uma pista de emocoes. incluindo mesas com charme de pit lane. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. com solucoes precisas e instantaneas. As transacoes sao simples como uma mudanca de marcha. entretanto mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de pista. Para encurtar, F12.Bet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma ultrapassagem para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De bonus a interface e fluida e ronca como um motor. dando vontade de voltar como um carro de corrida.
codigo bГґnus f12 bet|
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: roletas animadas, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi bem prestativo, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em Ethereum e o dinheiro entrou sem enrolacao, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que mais brindes fariam falta, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Recomendo sem medo.
4play bodyboard|
backstage chat
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, sempre pronto para resolver. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para fas de cassino online ! Adicionalmente a interface e fluida e estilosa, adiciona um toque de conforto. Outro destaque os torneios regulares para competicao, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ver os detalhes|
cyberlaunch – Feels trustworthy and tech-savvy, would revisit often.
innovatewithus – Videos and articles both are engaging, love that mix.
brightchain – The tone feels authentic, not too formal or too casual.
bestchoiceonline – Checkout felt simple and secure, confidence inspiring.
cloudmark – Color scheme is balanced; contrast helps highlight important parts.
alihidaer2313 – The visual direction is modest, but effective and pleasing.
nextbrand – Clean call-to-actions, not overwhelming but definitely noticeable.
Частный заем денег домашние деньги официальный сайт альтернатива банковскому кредиту. Быстро, безопасно и без бюрократии. Получите нужную сумму наличными или на карту за считанные минуты.
digitalstorm – Navigation is clean, I easily found what I wanted.
halbzeit endstand wetten
my site :: sportwetten app vergleich
ultrawave – Overall very polished, gives confidence in what’s being offered.
discoveramazingthingsonline – Really love the name, sounds exciting and adventurous.
everythingyouneedtoknow – Typography is very readable, spacing gives breathing room.
explorecreativeideasdaily – Love the inspiration, so many new ideas every visit.
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, vibra como um farol em alto-mar. A colecao e um facho de diversao. com slots tematicos de aventuras radiantes. O servico e confiavel como uma lanterna. garantindo suporte direto e sem escuridao. O processo e claro e sem apagoes. as vezes queria mais promocoes que brilham como farois. Em sintese, BR4Bet Casino e um clarao de emocoes para os amantes de cassinos online! Como extra o design e fluido como uma lanterna. elevando a imersao ao nivel de uma fogueira.
como ver minhas apostas na br4bet|
Все спортивные новости http://sportsat.ru в реальном времени. Итоги матчей, трансферы, рейтинги и обзоры. Следите за событиями мирового спорта и оставайтесь в курсе побед и рекордов!
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, sinto um rugido de emocao. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, de vez em quando promocoes mais frequentes seriam um plus. No geral, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e vibrante, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Outro destaque o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ver a pГЎgina|
Sou viciado na energia de MarjoSports Casino, e um drible de diversao que dribla a concorrencia. O catalogo de jogos e um campo de emocoes. com caca-niqueis modernos que driblam como craques. Os agentes sao rapidos como um contra-ataque. respondendo veloz como um drible. O processo e claro e sem impedimentos. em alguns momentos queria promocoes que driblam a concorrencia. Para encurtar, MarjoSports Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro drible para os fas de adrenalina de campo! Alem disso o design e fluido como um contra-ataque. criando uma experiencia de cassino de torcida.
como falar com o suporte da marjosports|
yourbrandzone – Useful resources are prominently placed, very helpful setup.
pixelplanet – Love the creativity here, visuals are really on point from first glance.
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque me pegou de surpresa. A variedade de jogos e surreal: roletas animadas, todos com graficos de primeira. O suporte foi eficiente, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que me deixou confiante. Fiz saque em transferencia e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino me conquistou. Recomendo sem medo.
4play beach sports|
zenithmedia – Really clean layout, feels professional and easy to use.
Estou totalmente fascinado por PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. As opcoes sao amplas como um festival, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de emocao. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer momento. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que brilha para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Alem disso o site e rapido e cativante, adiciona um toque de conforto. Um diferencial significativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, oferece recompensas continuas.
Explorar a pГЎgina|
boldspark – The layout is well-structured; sections flow nicely into each other.
futurebeam – Visual hierarchy strong, helps focus on what matters first.
kluvcc – Pages load fast, no lag or weird behavior at all.
fan meet
alphaimpact – Overall very polished, site feels professional and trustworthy.
coreimpact – Colors and fonts work well together, very readable.
Suchen Sie Immobilien? http://www.montenegro-immobilien-kaufen.com wohnungen, Villen und Grundstucke mit Meerblick. Aktuelle Preise, Fotos, Auswahlhilfe und umfassende Transaktionsunterstutzung.
ideaorbit – Really inspired by the design, it feels creative and polished.
linkmaster – Design elements are cohesive, gives a professional feel overall.
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Accompagne de tours gratuits sans wager. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois plus de promos regulieres seraient top. En resume, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! En prime la navigation est simple et agreable, ajoute une touche de confort. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
Ouvrir le site maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, on ressent une aura radieuse. L’eventail de jeux est resplendissant, avec des slots aux designs audacieux et thematiques. Illuminant l’experience de jeu. Le suivi est irreprochable, toujours pret a eclairer. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient lumineux. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les joueurs en quete d’eclat ! Ajoutons que la plateforme scintille comme une etoile, incite a prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec 5 niveaux exclusifs, garantit des transactions fiables.
Visiter pour plus|
Je suis epate par Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, avec des slots au design innovant. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, toujours pret a aider. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient un atout. Au final, Locowin Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement top, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter maintenant|
joinourcreativecommunity – Typography is friendly and readable, spacing makes it easygoing.
YourPathOfGrowth – I love how they integrate technology into their initiatives.
thebestplacetostarttoday – Pages load quickly, no lag even with visuals and effects.
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. Le catalogue est riche et diversifie, avec des slots au design innovant. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Les agents repondent avec rapidite, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Cerise sur le gateau la navigation est simple et agreable, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout majeur les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
Trouver plus|
LearnWithConfidence – Great resources here, the examples make understanding complex topics simple.
makingeverymomentcount – Navigation is intuitive, I never felt lost exploring pages.
learnshareandsucceed – Typography and spacing are well done, reading is comfortable all around.
getreadytoexplore – Visuals support the “exploration” theme really well, feels immersive.
Je suis captive par Casinia Casino, il offre une aventure etincelante. La diversite des titres est eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Avec un Bonus Crab unique pour debuter. Le suivi est irreprochable, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de l’eclat. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino garantit un plaisir radiant a chaque instant pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un rayon, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner aussi les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute vibrante.
AccГ©der aux infos|
findwhatyouarelookingfor – Design is clean and minimal, helps me focus on what matters.
Adoro a correnteza de Brazino Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um oceano. O leque do cassino e um recife de delicias. com caca-niqueis modernos que nadam como peixes tropicais. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. oferecendo respostas claras como um lago. Os saques voam como uma arraia. porem mais recompensas fariam o coracao nadar. No fim das contas, Brazino Casino e uma onda de adrenalina para os fas de adrenalina marinha! Como extra o design e um espetaculo visual aquatico. adicionando um toque de brilho marinho ao cassino.
brazino777 casino login entrar|
everythingaboutsuccess – Navigation is intuitive, sections clearly marked and simple to browse.
learnsomethingneweveryday – Navigation is intuitive, I didn’t struggle finding topics I want.
Estou completamente pixelado por PlayPix Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino retro-futurista. O catalogo de jogos e uma tela de emocoes. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque cibernetico. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. oferecendo respostas claras como um codigo. Os saques sao velozes como um upload. de vez em quando queria promocoes que processam como CPUs. No geral, PlayPix Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro codigo para os cacadores de vitorias em byte! De lambuja o design e fluido como um render. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura pixelada.
reclame aqui tv playpix|
makelifebettereveryday – Promises consistency, something reliable to visit each day.
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, ca procure un plaisir intense. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Accompagne de tours gratuits sans wager. L’assistance est efficace et pro, toujours pret a aider. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres seraient top. Au final, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! Cerise sur le gateau la navigation est simple et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
Aller lГ -bas|
Acho simplesmente ardente Fogo777 Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao intensa quanto um ritual de fogo. Os jogos formam uma fogueira de diversao. com caca-niqueis modernos que hipnotizam como fogos. O suporte e um fulgor reluzente. com ajuda que ilumina como uma pira. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma labareda. de vez em quando mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de fogo. Em sintese, Fogo777 Casino garante um jogo que reluz como chamas para os amantes de cassinos online! Adicionalmente a interface e fluida e brilha como uma fogueira. transformando cada aposta em uma aventura flamejante.
fogo777 login|
Je suis fascine par BankOnBet Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui brille comme un coffre-fort de lingots. Les options de jeu au casino sont riches et securisees. proposant des slots de casino a theme financier. L’assistance du casino est fiable et discrete. avec une aide qui debloque les gains. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans frais caches. mais parfois I’d want more promos that compound like interest. All in all, BankOnBet Casino is a casino that banks on fun pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne! What’s more the interface is smooth as a deposit. making every session more rewarding.
bankonbet casino auszahlung|
discoverendlessinspiration – Typography is elegant and spacing gives great breathing room.
growyourbusinessfast – Overall very polished, confidence booster for business focused on growth.
Estou completamente encantado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura cheia de emocao. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, contudo bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e essencial para apostadores para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Tambem o design e moderno e vibrante, facilita uma imersao total. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Descobrir agora mesmo|
Amo a energia selvagem de PlayPIX Casino, sinto um pulsar selvagem. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, de vez em quando ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para fas de cassino online ! Vale destacar a interface e fluida e estilosa, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Igualmente impressionante os torneios regulares para competicao, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Visitar o site|
makeimpactwithideas – Content is meaningful, not just filler, gives real takeaways.
GrowWithConfidenceHere – Navigation is smooth, finding resources for projects is super fast.
https://elmasriagroup.net/D8AAD8A3D8ACD98AD8B1-D983D984D8A7D8B1D983D8A7D8AA-D988-D985D8B9D8AFD8A7D8AA-D8ABD982D98AD984D8A9/
BuildSomethingMeaningful – I love how they integrate technology into their initiatives.
SimpleWaysToBeHappy – Love how this site encourages daily gratitude practices.
TogetherWeCreateChange – I love how every project feels meaningful and well-guided here.
YourTrustedSourceOnline – The resources here are perfect for anyone looking to make a change.
BuildABetterTomorrow – The platform is user-friendly and full of helpful guides.
Curto demais a vibracao de Brazino Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um oceano. A colecao e uma onda de entretenimento. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. assegurando apoio sem turbulencia aquatica. O processo e claro e sem tempestades. ocasionalmente as ofertas podiam ser mais generosas. Para encurtar, Brazino Casino promete uma diversao que e uma mare para os exploradores de jogos online! E mais a navegacao e facil como uma corrente marinha. dando vontade de voltar como uma onda.
melhor jogo do brazino777|
Me encantei pelo fulgor de Verabet Casino, tem uma energia de jogo tao intensa quanto um ritual de fogo. As opcoes sao ricas e queimam como carvoes. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como brasas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. oferecendo respostas claras como uma chama. As transacoes sao simples como uma tocha. ocasionalmente mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura de fogo. Ao final, Verabet Casino e uma pira de adrenalina para os cacadores de vitorias incendiarias! Adicionalmente o design e fluido como uma pira. tornando cada sessao ainda mais flamejante.
vera bet br games pgsoft fortune rabbit|
thefutureofinnovation – Tone is optimistic and credible, struck a great balance.
CreateInspireAndGrow – The resources provided are incredibly helpful for anyone looking to improve.
Adoro a labareda de Fogo777 Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino flamejante. Os jogos formam uma fogueira de diversao. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. Os agentes voam como chamas. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes sao simples como uma tocha. as vezes queria mais promocoes que queimam como fogueiras. Ao final, Fogo777 Casino e um altar de emocoes para quem curte apostar com estilo flamejante! De lambuja a interface e fluida e brilha como uma fogueira. dando vontade de voltar como uma labareda.
fogo777 com|
Sou totalmente viciado em BETesporte Casino, transporta para um universo de apostas eletrizante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, com suporte rapido e preciso. O processo e simples e direto, de vez em quando recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. Resumindo, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e vibrante, facilita uma imersao total. Notavel tambem os torneios regulares para rivalidade, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Navegar no site|
Fiquei fascinado com PlayPIX Casino, sinto um pulsar selvagem. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, sempre pronto para resolver. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, as vezes ofertas mais generosas seriam bem-vindas. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Alem disso o site e rapido e cativante, facilita uma imersao total. Igualmente impressionante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ver a pГЎgina|
discoveramazingstories – Visuals probably dramatic; expect bold images to match the stories.
гребной тренажер для дома Велотренажер магнитный — надежный выбор для интенсивных нагрузок. Магнитная система регулировки (8-16 уровней) обеспечивает плавное и тихое сопротивление без трения, продлевая срок службы. Маховик 6-12 кг минимизирует вибрацию, а антискользящие педали с ремнями фиксируют стопу. Дисплей с backlight показывает скорость, время, расстояние, пульс через датчики. Складная рама для хранения, вес конструкции 20-30 кг, нагрузка до 120 кг. Идеален для HIIT-тренировок, укрепления квадрицепсов и икр. Бренды DFC или Oxygen от 15 000 рублей. Магнитный велотренажер снижает риск травм, улучшает выносливость и помогает в контроле веса.
wettanbieter lizenz deutschland
Check out my homepage … kombiwetten Rechner
yourtrustedguideforlife – Overall very comforting presence, makes me trust the content here.
фитнес клуб тренировка фитнес клуб с бассейном в москве
expandyourhorizons – Design feels open, layout gives room and clarity to breathe.
A vibrant platformer guiding a panda through exciting puzzles and treasures. Fun and family-friendly: Panda adventure game online
фитнес клуб абонемент в фитнес клуб
https://b2shop.gl
internet was heißt quote bei wetten (Tasha)
TurnIdeasIntoAction – I appreciate how they encourage doing rather than just dreaming.
EverythingStartsWithYou – The layout is clean; reading feels peaceful and uplifting.
LearnShareAndGrow – Their approach to education is both innovative and impactful.
LearnSomethingAwesome – Wow, this site really sparks curiosity and fun learning every visit.
FindTheBestIdeas – Definitely bookmarking this for when I need a creative boost or spark.
https://syedsworld.com/why-microsoft-365-is-an-essential-for-todays-businesses/
TheArtOfLivingWell – Content here is inspiring, makes daily choices feel more intentional.
FindAnswersAndIdeas – Love the balance between theory and tips that I can apply right away.
YourDigitalDestination – It feels professional and welcoming at the same time.
FindNewWaysToGrow – The guides are clear and full of practical tips I can use.
GetConnectedWithPeople – Definitely bookmarking this, it’s a refreshing take on community building.
UnlockYourPotentialToday – I like how ideas are broken into doable steps, super helpful.
DiscoverWorldOfIdeas – Great mix of inspiration and guidance, very motivating feels every time.
FindSolutionsForLife – The layout’s clean, reading is smooth, no unnecessary clutter.
ConnectDiscoverAndGrow – Very motivating content, feels like a community more than a site.
markmackenzieforcongress – I can tell the message here comes from a genuine place.
madeleinemtbc – The navigation is so smooth, I found info fast
FindInspirationEverywhere – I love opening this site first thing, always lifts my mood.
DiscoverNewOpportunities – The platform is user-friendly and full of helpful guides.
YourGuideForSuccess – This site feels like a supportive mentor in my browser all day.
DiscoverUsefulTipsDaily – Bookmarking this, it’s already become one of my favorite resources.
StartChangingYourLife – Layout is calm, reading feels soothing even when topics are serious.
BuildYourDreamFuture – The guides here make future planning feel exciting and doable.
LearnAndImproveEveryday – This site has become my go-to for daily growth resources.
bs2best at Заинтригован, что вызывает резонанс в тёмных закоулках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто наименование, это воплощение идеала анонимности, стремительной работы и непоколебимой уверенности. Отправляйся на bs2best.at — в обитель, где раскрывают секреты, о которых предпочитают молчать. Здесь тебе станет доступно сокровенное знание, охраняемое от непосвященных. Исключительно для тех, кто понимает суть. Никаких улик. Никаких соглашений. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти драгоценную возможность стать пионером — bs2best.at распахнул врата для тех, кто ищет истину. Хватит ли тебе отваги заглянуть правде в лицо?
BeCreativeEveryday – Such a fun site, makes creativity feel accessible to everybody.
StayMotivatedAndFocused – Whenever I lose direction, this site helps me regain focus fast.
https://chelyab.ru/feedback/
seriöse Die Besten Sportwetten Seiten tipps
wetten für heute
My webpage; kostenlose sportwetten tipps – Barrett,
Пассажирские перевозки цена https://povozkin.ru
ThePathOfSelfGrowth – The articles are well paced; I don’t feel overwhelmed reading them.
bs2best at Заинтересован, что будоражит тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это эталон анонимности, оперативности и уверенности. Добро пожаловать на bs2best.at — место, где открывают то, о чём принято умалчивать. Здесь ты получишь доступ к запретному плоду. Только для избранных. Без улик. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти возможность стать первопроходцем — bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои секреты. Хватит ли тебе смелости взглянуть правде в лицо?
makeprogressdaily – The tips shared here are practical and easy to implement.
makethemostoflife – The visuals and text work well together, nicely balanced
inspireandgrowtogether – This site encourages me to take positive action today.
findyourwayforward – The tone is hopeful without being unrealistic, very balanced
findthebestcontent – This site saved me time in searching for good reads
discoverlearnandshare – I’ll be returning for more posts and fresh insights
live stream
growyourpresenceonline – Thanks, I got value already just from browsing here
discovertrendingideas – Good balance of depth and readability in posts
connectwithbrilliantminds – I like how there’s a mix of inspiration and practical takeaways
learnandearndaily – The writing feels genuine, not too salesy or pushy
everythingaboutmarketing – Always find valuable information that helps improve my marketing skills.
discoverhiddenpotential – The content here is uplifting and practical, perfect for personal growth.
discoveryourpassion – The resources here are truly transformative and insightful.
learnexploreandshine – The layout is gentle on eyes, makes long reading comfortable
Лазерные станки https://raymark.ru для резки металла в Москве. 20 лет на рынке, выгодная цена, скидка 5% при заявке с сайта + обучение
HOME CLIMAT https://homeclimat36.ru кондиционеры и сплит системы в Воронеже. Скидка на монтаж от 3000 рублей! При покупке сплит-системы.
Гарри Кейн оюн талаасында дайыма тынчсызданууну жаратат.Бул оюнчу дайыма эң мыктылардын арасында. Гарри Кейндин карьерасы жана трофейлери тууралуу кеңири маалымат ушул жерде: Гарри Кейн расмий сайты. Кейн өзүнүн максаттарын так билет.
Баварияда Кейн жаңы рекорддорду коюуда.
Гарри Кейндин балдары футболду жакшы көрүшөт. Кейндин пас берүү жөндөмү да жогорку деңгээлде. Анын физикалык даярдыгы мыкты. Кейндин алгачкы командалары ага чоң тажрыйба берген. Ар бир күйөрман анын статистикасын сыймыктануу менен айтат. Анын Instagram баракчасы абдан популярдуу.
yourgatewaytosuccess – I like the call-to-action style, makes me want to explore more
togetherwecreateimpact – I appreciate how each post ties back to community betterment
findyourinspirationhere – Already shared this with a friend who loves motivation
findyourwayforward – I’m looking forward to exploring more content here.
connectandgrowonline – My sales have increased thanks to their digital marketing tools.
jointhenextbigthing – Really impressed with how fast the pages load daily.
findyourinnerdrive – I appreciate the actionable steps provided, making progress feel achievable.
buildyourdigitalfuture – I shared this with a friend; they found it helpful too.
buildyourownlegacy – Nice visuals, they match the message of legacy building well
Adoro o clima alucinante de MegaPosta Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um vulcao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e um foguete, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem enrolacao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um missil, mas mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, MegaPosta Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia explosiva, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
megaposta paga|
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, e um cassino online que detona como um vulcao. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, OshCasino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia ardente, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
retrait osh|
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es liefert einen einzigartigen Kick. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Optionen, mit dynamischen Live-Sessions. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, immer bereit zu helfen. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, dennoch mehr Belohnungen waren ein Hit. Insgesamt, NV Casino garantiert Top-Unterhaltung fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Zusatzlich die Navigation ist kinderleicht, was jede Session noch spannender macht.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura competitiva. O catalogo e rico e diversificado, com slots modernos e tematicos. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, de vez em quando promocoes mais frequentes seriam um plus. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e dinamico, facilita uma imersao total. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ver os detalhes|
findsolutionsfast – The writing is practical, feels like real help, not hype
startyourdreamproject – The guides are practical and easy to follow, super helpful
Sou viciado no brilho de BR4Bet Casino, parece um festival de luzes cheio de adrenalina. Os jogos formam um clarao de entretenimento. com jogos adaptados para criptomoedas. O suporte e uma luz-guia brilhante. assegurando apoio sem sombras. Os saques voam como um facho de luz. mas mais bonus regulares seriam radiantes. Em sintese, BR4Bet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Como extra o design e fluido como uma lanterna. elevando a imersao ao nivel de uma fogueira.
reclame aqui br4bet|
Estou pirando com MegaPosta Casino, parece uma avalanche de diversao. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma bomba total, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de estilo. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de responsa, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem enrolacao. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um missil, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No fim das contas, MegaPosta Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma explosao para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Vale falar tambem a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro gas, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
megaposta|
The reels will spin and stop at random. If you land 8 or more identical symbols anywhere on the reels, you will achieve a winning line. The more matching symbols you land, the better the gameplay outcome. Starburst isn’t just a game; it’s a whole vibe crafted by the cool cats over at NetEnt, and hosted at BDMBet. It’s like stepping into a retro-futuristic galaxy where the stars are actually these shiny, dazzling gems that could just pop and shower coins any second. In this review, we’ll dig into the mechanics like the symbols that keep the game lively, the bonuses that add a twist, the free demo version to test your luck, and, of course, the standout features of BDMBet. Get ready to hit the cosmic jackpot up to 500 times your stake! I am Flying To The Moon Game Oceniliśmy, czy bonus powitalny rzeczywiście trafia na konto po pierwszym depozycie i czy warunki jego obrotu są przejrzyste. Testowaliśmy również dostępność dodatkowych promocji: bonusy bez depozytu, cashback, turnieje i programy lojalnościowe.
https://aphorismsgalore.com/users/grifenliacyc
Oto zalety oferowane przez firmę bukmacherską: Sugar Rush 1000 demo Polska to idealna okazja, aby przetestować jedną z najbardziej kolorowych i emocjonujących gier typu slot bez ryzyka. Jeśli chcesz poznać sugar rush gameplay, zanim zainwestujesz prawdziwe pieniądze, wersja demonstracyjna jest właśnie dla Ciebie! Możesz napisać swoją własną recenzję dla tego produktu, żeby podzielić się swoimi wrażeniami ze społecznością. Użyj obszaru, który znajduje się na tej stronie nad przyciskiem zakupu, żeby napisać swoją recenzję. Mechanika Sugar Rush Fever opiera się na 5 bębnach oraz standardowych symbolach slotowych w stylu 243 sposobów na wygraną. To sprawia, że gra jest łatwa do zrozumienia nawet dla początkujących graczy.
Sou viciado no role de OshCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e um terremoto. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma explosao total, com slots de cassino unicos e explosivos. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um estalo, respondendo mais rapido que um relampago. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brisa, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, OshCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro magma, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
casino osh avis|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, ab und an die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Besonders toll die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, mit immersiven Tischspielen. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, erreichbar zu jeder Stunde. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und flussig, dennoch mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren willkommen. Alles in allem, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und elegant, was jede Session noch spannender macht.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
Нужна недвижимость? недвижимость в Черногории лучшие объекты для жизни и инвестиций. Виллы, квартиры и дома у моря. Помощь в подборе, оформлении и сопровождении сделки на всех этапах.
Аутстаффинг персонала https://skillstaff2.ru для бизнеса: легальное оформление сотрудников, снижение налоговой нагрузки и оптимизация расходов. Работаем с компаниями любого масштаба и отрасли.
live concert
Sou viciado em BETesporte Casino, sinto uma energia de estadio. Ha uma multidao de jogos emocionantes, com slots modernos e tematicos. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O acompanhamento e impecavel, sempre pronto para o jogo. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, no entanto ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Tambem a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Igualmente impressionante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, oferece recompensas continuas.
Descobrir mais|
everythingyouneedtoday – Found articles that solve actual problems, not just fluff
learnnewthingsdaily – Very encouraging tone, makes learning feel fun and doable.
shareyourvisiontoday – Very genuine and encouraging, I feel supported reading it.
votethurm – Interesting content, I hope the design gets updated soon.
discovergreatideas – Found a new perspective on problem-solving here, very insightful.
inspireeverymoment – Warm tone, real stories, I felt connected reading them.
growtogetherwithus – Feels like a family of learners, always supporting growth.
inspireeverymoment – Just visited and it resonated with me deeply today.
startyourdigitaljourney – This platform made launching my online business so easy.
thefuturestartsnow – I visited just now and got chills thinking about what’s ahead.
theartofsuccess – Highly recommend this for daily boosts and life planning.
yourjourneytowin – Just what I needed today — clarity and encouragement.
createimpactfulstories – Crisp, clear, and full of heart — very uplifting read.
staycuriousandcreative – Love how this site encourages always asking and exploring new ideas.
Строительный портал https://v-stroit.ru всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Полезные советы, технологии, материалы, новости отрасли и практические инструкции для мастеров и новичков.
wettanbieter mit cashout
Here is my web blog; gegen Euro wetten
findyourcreativeflow – I feel ready to sketch, write, try something new again.
yourpathofsuccess – This site helps me refocus when things feel chaotic.
creativityneverends – Every article reminds me why I love being creative so much.
wettbüro hamburg
Feel free to surf to my page: sportwette (Isis)
online sportwetten ohne oasis
Also visit my website :: wettbüro münchen
startcreatingimpact – Always feel energized after reading the posts, very uplifting.
Портал о строительстве https://pamel-stroy.ru и ремонте. Пошаговые инструкции, идеи, технологии, новости и советы экспертов. Всё, что нужно, чтобы строить и ремонтировать грамотно.
yourmomenttoshine – Beautifully written, this really lifted my spirit today.
https://bs2best.or.at
stacoa.org – The style and tone give trust and sincerity.
myvetcoach.org – Really useful content, I’m learning a lot from your posts.
filamericansforracialaction.com – Friendly and hopeful vibe, wish them strength and reach.
electlarryarata – The homepage is clean but I expected more content already.
Риэлторская контора https://daber27.ru покупка, продажа и аренда недвижимости. Помогаем оформить сделки безопасно и выгодно. Опытные риэлторы, консультации, сопровождение и проверка документов.
Купольные дома https://kupol-doma.ru под ключ — энергоэффективные, надёжные и современные. Проектирование, строительство и отделка. Уникальная архитектура, комфорт и долговечность в каждом доме.
exploreendlesspossibilities – Thanks for content that reopens doors in my mind again.
thespeakeasybuffalo – Looking forward to seeing what content gets posted here.
laetly.com – Couldn’t see much content, looking forward to updates.
growyourdigitalpresence – Even small changes suggested here bring noticeable impact over time.
summerstageinharlem.org – Hope they keep adding diverse acts, would be amazing.
norigamihq – I’ll check back later to see what content appears.
pinellasehe.org – Visiting felt like discovering a calm, thoughtful space online.
formative-coffee.com – Their shop page is sleek, makes ordering feel elegant.
rockyrose.org – The colors and layout make browsing a delightful experience.
gratiswetten ohne einzahlung
Feel free to surf to my web page :: gute online
wettanbieter (https://www.deliverdelights.com/legale-online-wetten-deutschland)
hecimagine.com – Thanks for having resources for students in challenging conditions.
https://imogennwll192991.mpeblog.com/67189702/treasures-of-the-sandswept-tombs
Ваша Недвижимость https://rbn-khv.ru сайт о покупке, продаже и аренде жилья. Разбираем сделки, налоги, ипотеку и инвестиции. Полезная информация для владельцев и покупателей недвижимости.
Информационный блог https://gidroekoproekt.ru для инженеров и проектировщиков. Всё об инженерных изысканиях, водохозяйственных объектах, гидротехническом строительстве и современных технологиях в отрасли.
mystylecorner – Love the fashion vibes here, all looks trendy and stylish.
successpartnersgroup – I found what I needed fast, interface feels smooth modern.
creativevision – A must-visit for anyone appreciating innovative and expressive art forms.
newseason – Friendly site vibe, browsing felt relaxed and easy.
trendyfashioncorner – Browsing was smooth, found trendy pieces that match my style.
ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward.com – The contents are mostly Japanese/blog posts about gambling-apps and casinos.
globalideasnetwork – Great layout, everything’s easy to find and visually appealing.
cryptotephra-clagr.com – If you want, I can check whether this site is actively maintained and reachable.
discovernewideas – Will share with friends, this place has lots of potential.
inspiredgrowthteam – Definitely feels like a place focused on growth and meaningful connections.
createimpact – Interface is clean, found what I wanted super quickly.
luxurytrendstore – Highly recommend for anyone looking to refresh their fashion collection.
Estou completamente alucinado por JabiBet Casino, parece uma correnteza de diversao. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo a parte, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de vibe. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem tempestade. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, JabiBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como a mare.
jabibet casino|
bs2web at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
Adoro o clima insano de PagolBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura eletricidade. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e vibrantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um trovao, de vez em quando mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Na real, PagolBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma tempestade para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! E mais o design do cassino e uma explosao visual vibrante, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
pagolbet e confiГЎvel|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, garantiert top Hilfe. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, obwohl die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Zusatzlich zu beachten die schnellen Einzahlungen, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
visionaryleadersclub – Visiting felt motivating, like they’re about growth and real impact.
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es ist ein Abenteuer, das pulsiert wie ein Herzschlag. Der Katalog ist reich und vielfaltig, mit immersiven Tischspielen. Der Support ist von herausragender Qualitat, immer bereit zu helfen. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, trotzdem regelma?igere Promos waren super. Alles in allem, NV Casino ist definitiv empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
playnvcasino.de|
webpulse.click – The headings and sections are well spaced, nice readability.
partnershippowerhouse – Supportive vibe throughout the site, feels like community and purpose.
Fiquei fascinado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. Os agentes respondem com rapidez, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. No fim, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Vale destacar o site e veloz e envolvente, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Outro destaque os torneios regulares para rivalidade, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Descobrir mais|
Жанкүйөрлөр үчүн ыңгайлуу навигация: акыркы жаңылык, кийинки беттеш, коэффициенттер жана прогноздор.
Жаңыланган постерлер жана расмий анонстар чыкканда, баракча дароо толукталат. ислам махачев национальность Биография бөлүмүндө туулган жери жана спортко келген жолу баяндалат. Фактылар булактар менен бекитилген. Жеткиликтүү интервьюлардан цитаталарды чогултуп, мотивация жана даярдык жөнүндө баяндайбыз. Илия Топурия vs Ислам Махачев айкашы жөнүндө ушак-айың эмес, текшерилген булактар гана берилет. Аудитория үчүн жөнөкөй тилде түшүндүрүлгөн «кантип жеңиши мүмкүн» сценарийлери сунушталат.
Sherdog жана расмий UFC профилдерине жол көрсөткүч шилтемелер бар. Хайптан алыстап, фактыларга таянган сабаттуу талкуу жүргүзөлү. Тарыхый моменттердин хронологиясы визуал карта түрүндө берилип, оңой кыдырып чыгасыз. Издөө функциясы боюнча ачкыч сөздөрдү киргизип, керектүү бөлүмгө тез өтүңүз.
trendymodernwear – Customer service was responsive and helpful with my inquiries.
This is really fascinating, You’re an excessively skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and sit up for in the hunt for extra of your wonderful post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks
батареи tubog
successpartnersgroup – I discovered new services here, impressed by the clarity and detail.
blsp at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
Acho simplesmente insano JabiBet Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira onda. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma tempestade, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e envolventes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na area 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um maremoto. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma onda, porem queria mais promocoes de cassino que arrasam. Na real, JabiBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma mare cheia para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, da um toque de classe aquatica ao cassino.
jabibet apk|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von Lowen Play Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein machtiger Sprung ins Spielvergnugen. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und kraftvoll, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Konig regiert, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, manchmal mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Insgesamt ist Lowen Play Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Nebenbei das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Raubtier, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
löwen play würzburg|
Estou completamente vidrado por PagolBet Casino, parece uma tempestade de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma faisca, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de energia. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem curto-circuito. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um trovao, mesmo assim as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, PagolBet Casino e um cassino online que e um relampago de diversao para os aventureiros do cassino! Vale falar tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais eletrizante.
pagolbet com|
backstage updates
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, gelegentlich zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Nicht zu vergessen das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Besonders toll die mobilen Apps, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
britische buchmacher
Visit my web-site – sportwetten ohne lizenz
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Optionen, mit dynamischen Live-Sessions. Der Kundensupport ist hervorragend, bietet klare Antworten. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, manchmal die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem, NV Casino bietet unvergesslichen Spa? fur Casino-Enthusiasten ! Daruber hinaus die Oberflache ist intuitiv und stylish, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
https://playnvcasino.de/|
digitaledge – Love the color scheme, feels professional yet welcoming too.
urbanwearzone – The checkout was quick and intuitive, great site layout too.
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo intenso. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, com slots modernos e tematicos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer momento. O processo e simples e direto, embora recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No fim, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Adicionalmente a interface e fluida e energetica, facilita uma imersao total. Outro destaque os torneios regulares para rivalidade, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Ver agora|
discovernewpath – Mission statement speaks well, feels like they know their purpose.
https://ru.pinterest.com/pin/1091419290961252848/
wette doppelte chance
Review my site :: wetten dass unfall samuel koch heute
findyourfuture – The mission seems genuine, content looks helpful for growth.
trustconnectionnetwork – Impressive design and seamless navigation make shopping here a breeze.
uniquefashionstyle – The website’s simplicity makes it easy to find what I need.
nextvision – Wish there was proof of legitimacy—user reviews, company registration etc.
trustedbusinesslink – Everything loads quickly and the content is well organized.
futureopportunitynetwork – The design is sleek and modern, making navigation a breeze.
growstrongteam – Overall great user experience, feels honest and well built.
futurevisiongroup – Definitely a site I’d revisit — lots of promise here.
https://t.me/pikmaninfo What we do I lead a powerful team that is shaping the future of B2B Saas go-to-market strategies. My company Pikman.info helps high-growth B2B companies with Demand, Attribution & Analytics, and Revenue R&D by delivering a suite of proprietary research, revenue analytics tools, and GTM experimentation services. Pikman.info helps B2B SaaS companies create and capture demand through paid ads to drive a more qualified pipeline for your sales team. Growth at all costs is over, and sustainable growth is what your SaaS brand needs. That means optimizing for the lowest cost per opportunity, not the lowest cost per lead.
learnsharegrow – The interface is clean, making the site a pleasure to explore.
asiatische wetten erklärung
My website; neue buchmacher; Launa,
growthpoint – Clean visuals and clear messaging, gives confidence in their mission.
futureopportunitynetwork – Content seems meaningful and value-driven, nice mix of visuals.
buildbrand – The focus on emotional connections is spot on.
https://t.me/pikmaninfo What we do for PreSeed to Series C SaaS startups: > Develop and implement an online marketing strategy > Implement a monitoring system to track and measure all marketing activities via Looker Studio > Tracking, analysis, optimization, and management development of organic search traffic. > Tracking, analyzing, optimizing, and developing paid traffic (search and advertising companies) across any digital channel. > Analysis and optimization of the conversion of the company’s website and side projects (for example, a blog) > Manage and optimize paid media across any digital channel > Distribute content/messaging via paid to grow pipeline and revenue > Build out engaging ad creative and landing pages > Focus on optimizing the funnel based on pipeline and revenue. > Using modern approaches based on data analysis and data science to provide the best project development strategies and visualization of current processes in the company. > Analysis and optimization of client base processes using data analysis methods science approaches, for example, tracking risk groups that can leave the platform in a short time (churn prevention). > cold outreach, inbound, account-based marketing, content marketing
how to not gain weight on steroids
References:
https://git.rikkei.edu.vn/marla660395768/7498129/-/issues/1
wagocjapmeom – The site feels mysterious, layout hints at deeper content waiting.
sportwetten über unter tipps
My web-site sportwette ergebnisse
abuse of steroids
References:
https://nucleation.fusion.bref.cool/abigailcostas
discovergreatdeal – The product selection is broad, something for everyone it seems.
https://plisio.net/blog/crypto-payment-gateway-without-kyc
Деревянные лестницы https://rosslestnica.ru под заказ в любом стиле. Прямые, винтовые, маршевые конструкции из массива. Замеры, 3D-проект, доставка и установка. Гарантия качества и точности исполнения.
Лестницы в Москве https://лестницы-в-москве.рф продажа и изготовление под заказ. Прямые, винтовые, модульные и чердачные конструкции. Качество, гарантия и монтаж по всем стандартам.
unitedbygoal – Good consistency in style, everything flows nicely from page to page.
seoignite.click – The visuals compliment the text well, gives a polished impression.
teamfuture – Friendly tone, helpful advice, everything flows well together.
businessgrowthhub – Content is relevant and up to date, keeps me interested.
trustandunity – I enjoy how every message focuses on integrity and togetherness.
digitalinnovationzone – Found some great tips already, helpful and actionable stuff.
futuregoalsnetwork – I’m looking forward to new posts here, big potential.
hair loss bodybuilding
References:
https://git.taglang.io/mohamediacovel
successbridge – Excited to explore more here, lots of promise in what they offer.
https://actituddigital.com/phasellus-vel-odio-commodo-pharetra-urna-sit-amet-gravida-nibh-9/
getthedeal – Really convenient site, navigation is simple and very fast today.
leadersunitedgroup – Always something useful, content mix is strong and varied.
connectinnovationhub – Friendly and clear, makes me want to share with others.
winmore – I like the energy here, feels ambitious and motivating.
futuregoalsnetwork – It feels real and authentic, not just marketing fluff.
findsomethingnew – Content here is fresh and vibrant, keeps me coming back.
leadersunitedgroup – I enjoy the balance between motivation and practical tipsness.
globalpartnershipteam – I found helpful content quickly, no fluff, straight to the point.
discovervalue – Nice mix of visuals and words, everything flows well together.
successjourneyclub – Great balance between inspiration and actionable steps, love that.
exploreideasworld – I’ve bookmarked it — here’s where ideas get real substance.
discoverdaily – Excited to see what’s next here, promising site indeed.
trustconnectionnetwork – Excited to follow this site — I think it has real potential.
connectinnovationhub – Really impressed with the quality here; definitely worth following.
growtogetheralliance – The content is motivational without feeling pushy, nice balance.
brightdeal – Already bookmarked this — feels like long-term potential exists.
fan stream
innovateandbuild – Looking forward to what’s next, potential is very strong.
buildtogether – Excited to see more posts, this looks like a growing platform.
growthnetwork – I’ve bookmarked this site, seems rich with useful insights.
modernhomeessentials – I bookmarked it, looks like a solid place for home picks.
Sou louco pela energia de BRCasino, parece uma festa carioca cheia de axe. O catalogo de jogos do cassino e uma folia de emocoes, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que dancam como passistas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro axe, respondendo mais rapido que um batuque de tamborim. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma ala de passistas, mas queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. Resumindo, BRCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carnaval total para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passo de samba, eleva a imersao no cassino ao ritmo de um tamborim.
br77.game reclame aqui|
Adoro o swing de RioPlay Casino, parece uma festa carioca de diversao. Tem uma avalanche de jogos de cassino irados, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e cheios de ritmo. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, com uma ajuda que e puro gingado. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem tropecos, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria um arraso. No geral, RioPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino brilha com um visual que e puro samba, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
roblox lite rioplay games|
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque nao e so mais um cassino online. A variedade de jogos e simplesmente incrivel: blackjack envolvente, todos bem otimizados ate no celular. O suporte foi eficiente, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que raramente vi. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou sem enrolacao, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que seria legal torneios de slots, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Ja virou parte da minha rotina.
rom moto g 4play|
wagocjapmeom – The site feels mysterious, layout hints at deeper content waiting.
Sou viciado em BETesporte Casino, oferece um thrill esportivo unico. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, incluindo apostas esportivas palpitantes. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, as vezes ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. No fim, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Adicionalmente o site e veloz e envolvente, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Igualmente impressionante as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Obter os detalhes|
social group
buying anabolic steroids online
References:
https://git.memosnag.com/bryantkight357
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
businessgrowthhub – Solid mix of visuals and content, easy on the eyes.
Adoro o brilho de Richville Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao sofisticada quanto uma mansao de ouro. A gama do cassino e um verdadeiro palacio de delicias, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que brilham como joias. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um mordomo impecavel, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam com a velocidade de um jato particular, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que brilhem como diamantes. Em resumo, Richville Casino e um cassino online que exsuda riqueza para os nobres do cassino! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de elegancia, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um rei ao seu trono.
richville mn weather|
Acho simplesmente insano JabiBet Casino, e um cassino online que e uma verdadeira onda. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um maremoto, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino cheios de vibe. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e uma perola, com uma ajuda que e pura correnteza. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma brisa, mesmo assim mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Em resumo, JabiBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma mare cheia para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o design do cassino e uma explosao visual aquatica, torna o cassino uma curticao total.
jabibet casino bonus code|
boldpartner – The tone is assertive yet warm — good balance indeed.
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque me impressionou bastante. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: jogos ao vivo imersivos, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em Bitcoin e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. No geral, o 4PlayBet Casino me conquistou. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
ryan 4play afroxai pargoy anthem|
bs2best зеркало Готов узнать, что творится в глубинах тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это символ анонимности, скорости и безопасности, а не просто бренд. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не говорить. Тебе откроют все тайны, скрытые от посторонних глаз. Только для посвящённых. Никаких следов. Никаких полумер. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс быть впереди — bs2best.at ждёт тех, кто готов к новому. Осмелишься ли ты узнать истину?
Estou completamente encantado por PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer carnavalesco. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo dinamicas. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O suporte ao cliente e estelar, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, contudo mais promocoes regulares seriam otimas. No geral, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Tambem a interface e fluida e elegante, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Igualmente impressionante os torneios regulares para competicao, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Ver os detalhes|
nextgeninnovation – Bookmarking this site, seems like a place for continuous learning.
Register at glory casino bonus and receive bonuses on your first deposit on online casino games and slots right now!
brightmind – I appreciate the focus on mindfulness and clarity, well done.
While KPV is focused on inflammation control and immune system regulation (Land), TB-500 has a more direct role in accelerating the structural repair of soppy tissues (Liao et al.). From what I’ve seen, combining KPV with GLP-1 remedy is amongst the most ignored strategies for gut health and controlling inflammation. KPV is a potent inflammation reducer, mast cell tamer and pathogen fighter (antifungal / antimicrobial). Sure, though we suggest occasional breaks after 30–60 days depending on use case. Protocols could additionally be adjusted primarily based on severity of symptoms, length of irritation, and response to therapy. One of KPV’s most exciting functions is in therapeutic the intestinal mucosal barrier. It enhances epithelial cell regeneration, reduces inflammatory signaling, and promotes tight junction integrity—crucial for addressing leaky gut, IBD, and food sensitivities.
They seem like connected to alpha MSH so was curious if they may assist increase MSH along with eradicating Marcons. I have not been successful with getting rid of Marcons so on the lookout for other choices. Currently on EDTA and xylitol spray and anticipate to be on it for six months.
All merchandise on this web site are for analysis and improvement use only. The statements made on this website have not been evaluated by the US Food and Drug Administration. The statements and the products of this company aren’t supposed to diagnose, deal with, remedy, or prevent any disease. Simple Peptide just isn’t a compounding pharmacy or chemical compounding facility as outlined under 503A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Beauty Act. Simple Peptide is not an outsourcing facility as defined underneath 503B of the Federal Meals, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
The KPV peptide has been discovered to have several useful results, notably in drugs. MediSearch is a search engine that provides prompt answers to medical questions primarily based on 30 million scientific articles. This simply reinforces the purpose that specializing in scalp health—rather than simply the hair follicles—might be key to addressing hair loss extra successfully. This matches into a broader development I’ve seen where novel peptides get patented both for their particular uses or the peptide itself, like with Amplifica’s Osteopontin injections for hair progress. Their patent (US 6,001,812) explains how KPV, derived from or mimicking C-type melanocyte-stimulating hormone (C-MSH), can be utilized to stimulate hair progress. I even have been sick for nearly 5 years now and got nowhere until I went to useful medicine. I lately came upon that I really have undiagnosed/ untreated Lyme, Bartonella, Babesia and a few other tick borne illnesses that shouldn’t be in my physique.
In an oral kind, it can assist with ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and Crohn’s illness. An animal examine on six mice found that intraperitoneal injections of α-MSH lowered the variety of leucocytes, mast cells, and fibroblasts at three and seven days after incurring a skin wound. On days forty and 60, α-MSH triggered the scar space of the damage to diminish and enhance the group of collagen fibres. These findings point out that α-MSH and KPV may be viable alternatives to heal wounds with out inflicting scar tissue [9]. KPV has significant antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties especially in these with psoriasis. Psoriasis is a persistent autoimmune situation that causes the rapid build-up of skin cells and is usually handled utilizing hydrocortisone.
KPV is an emerging peptide in inflammation and wound healing analysis, providing potential functions in intestine well being, immune modulation, and tissue regeneration. In Distinction To different peptides generally studied for healing and tissue restore, KPV stands out for its capability to regulate inflammatory pathways without suppressing immune perform. Its interplay with melanocortin receptors (MC1R and MC3R) has led to rising interest in its position in autoimmune research, epithelial therapeutic, and continual inflammatory circumstances. KPV is a small peptide consisting of just three amino acids, lysine-proline-valine. It’s a fraction of the bigger peptide alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), which is involved in pores and skin pigmentation and immune operate. KPV is of course found within the physique and is thought for its anti-inflammatory properties, nevertheless it has a extra specific motion on inflammation-related pathways that contribute to varied health situations. Throughout the final month I really have been in a place to work and I’ve noticed my symptoms have really been fairly low.
We are unable to offer any dosing directions, nonetheless all products ought to be thought-about pharmaceutical grade. My research order of Klow arrived in a really well timed manner and was well packaged. My test topic showed promising results and I actually have ordered extra product to proceed my research. All I can say, about the shopping for experience is I hope you get your fee system labored out.
Research have additionally demonstrated α-MSH’s immunomodulating and anti inflammatory results. KPV peptide’s anti-inflammatory results are particularly notable as a end result of it immediately influences processes inside the cell. The small molecular dimension of KPV and α‐MSH permits them to enter the cell and interact with inflammatory signalling molecules. KPV is a potent anti-inflammatory peptide that can assist many situations. Most of the research involved is concentrating on the treatment of IBD (irritable bowel disease) where outcomes have been very positive.
Of course, this isn’t the one way to improve alpha-MSH in the physique when it comes to mildew, and KPV should not be handled as an finish reply. Despite KPV being the useful component of the α-MSH molecule accountable for its anti-inflammatory impact, each KPV and α-MSH address inflammation through associated however distinct mechanisms. Without MSH, unhealthy issues happen; continual sleep problems with non-restful sleep develop, and endorphin manufacturing is lowered, so continual ache follows. Those with mould may even perceive how Mould Sickness, Toxicity and CIRS result in a ‘Leaky Gut’ due to a lowered alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone. Structural mind abnormalities are often seen in these with inflammatory situations similar to Mould Illness, so it is a great cross-over. In summary, the primary mechanism of action seen in BPC-157 is the creation of recent blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. BPC-157 is a peptide that consists of a sequence of 15 amino acids.
References:
https://date.etogetherness.com/@adalbertojir43
bs market Что, еще не слышал о сенсации, сотрясающей глубины даркнета? Blacksprut – это не просто торговая марка. Это ориентир в мире, где правят анонимность, скоростные транзакции и нерушимая надежность. Спеши на bs2best.at – там тебя ждет откровение, то, о чем многие умалчивают, предпочитая оставаться в тени. Ты получишь ключи к информации, тщательно оберегаемой от широкой публики. Только для тех, кто посвящен в суть вещей. Полное отсутствие следов. Никаких компромиссов. Лишь совершенство, имя которому Blacksprut. Не дай возможности ускользнуть – стань одним из первых, кто познает истину. bs2best.at уже распахнул свои объятия. Готов ли ты к встрече с реальностью, которая шокирует?
Niezawodność to kolejny ważny aspekt kasyn online, w każdy poniedziałek gracze mogą ubiegać się o 50% reload bonus na swoim depozycie. To obniża ogólną przewagę kasyna dla zakładu, rTP i zmienność sugar rush aby wybrać 7 zakładów w Just UK. Miło widzieć, ten rodzaj promocji nie wymaga wcześniejszej płatności. Gra nie oferuje opcji gamble ani jackpota, ale nie mniej ważnym sposobem na zwiększenie wykorzystania strategii w grach na automatach jest gra z umiarem. Raport bezpieczeństwa będzie wkrótce dostępny. W międzyczasie proszę pamiętać, że ta aplikacja przeszła wstępne kontrole bezpieczeństwa APKPure. Żel w butelce Pro Master Bottle Gel Twój koszyk jest pusty!
https://pad.stuve.uni-ulm.de/s/_UiLw3tz7
Pre-order pre-save Gold Rush Kid W związku z tym jest bardziej niż możliwe, tym więcej musisz postawić. Jedno z rozwiązań politycznych w celu rozwiązania problemu hazardu w Rosji zostało zaproponowane w postaci ograniczenia liczby zakładów hazardowych w całym kraju, które okazały się skuteczne w Ruletce. Jak zminimalizować ryzyko podczas gry Sugar rush? Zdobywca nagrody BRIT oraz wielu platynowych płyt – muzyk, George Ezra, niedawno zadebiutował swoim niezwykle zaraźliwym, nowym singlem „Green Green Grass”, drugim utworem, z nadchodzącego nowego albumu „Gold Rush Kid”, który ma się ukazać 10 czerwca nakładem Columbia Records. Wspólnie w 2018 roku wydali trzy single, które podbiły klubowe listy przebojów. Wysokie miejsca odnotowali między innymi w Stanach Zjednoczonych czy we Francji.
creativeworldstudio – Wonderful blend of colour and concept, keeps my eyes interested.
It’s necessary to note that extending cycles past 12 weeks necessitates the addition of a testosterone base and the incorporation of liver assist dietary supplements. However, you will need to observe that the use of any anabolic steroid carries dangers and ought to be approached with warning. Yes, Anavar can have an effect on feminine fertility because it impacts the body’s hormones and menstrual cycle. Nonetheless, with the right use of PCT, fertility levels ought to return to normal, and girls can conceive as traditional.
The secret is to start low, monitor your physique, and avoid prolonged cycles. Most users start to notice Anavar outcomes inside 2 to 3 weeks of beginning a cycle. Will Increase in power, endurance, and muscle definition proceed to build, with peak results usually seen by week 6. Nevertheless, results rely closely in your food plan, training depth, rest, and genetics. Although Anavar is often marketed as a “safe” steroid, this doesn’t mean it’s free from dangers.
This is problematic for girls as a end result of Dianabol greatly increases the chances of virilization. Thus, tests are really helpful and can be bought for a cheap worth on-line. Anavar for women is commonly faked on the black market, with people exhibiting optimistic effects with out actually having used the product. Thus ladies should order a testing package before they take anavar, or any related managed substance. Due to an increase in exogenous testosterone, girls can become hornier on Anavar, with an increased need for sex. This is named virilization – when a lady begins to develop manly features. Even if a woman did expertise such signs, they would be reversed after they got here off Anavar.
If Primobolan is tolerated nicely through the first four weeks, doses of seventy five mg per day could additionally be utilized for the next 2 weeks. Furthermore, in future cycles, 75 mg may be taken, with cycles lasting 8 weeks instead of 6. This is an appropriate cutting cycle for women who have never taken Anavar before.
On the opposite hand, the potential adverse results warrant important thought. Imagine moving into the realm of bodybuilding, aiming to carve out the final word physique. As you embark on this journey, you’ll undoubtedly come throughout a myriad of performance-enhancing substances, each promising distinct advantages. Two such compounds that frequently discover themselves in the highlight are Anavar and Tren. Each renowned for his or her efficacy, they cater to different bodybuilding goals, leaving aspiring athletes pondering which path to choose. After the 6 week Anavar cycle, it’s important to take a break of at least 8-12 weeks before beginning another cycle.
Popular stacking choices include combining Anavar with testosterone or different slicing agents like Winstrol. Nonetheless, it’s essential to method steroid stacking with warning and consult with a educated skilled to make sure safe and efficient use. As with any muscle-building course of, sustaining a correct food plan and diet is paramount for achieving desired Anavar results. Consuming a protein-rich food regimen supplies the important constructing blocks for muscle development. Adequate hydration and calorie consumption are important to gasoline elevated coaching intensity. Would suggest to anyone who’s gunning for a recomp with not too serious sides.
However, Anavar is the exception to this rule, displaying highly effective strength-building attributes; regardless of not causing significant weight achieve. Equally, cholesterol levels and liver enzymes might rise slightly, though this impact is prone to be minimal. Anavar (oxandrolone) remains FDA approved, highlighting its safety (particularly in medical settings). In this text, I will cowl the advantages girls can anticipate from taking authorized Anavar.
It can be necessary to maintain a few issues in mind when utilizing Anavar. Firstly, it’s a steroid and for the body to adapt to it, it should be started with low doses and finally elevated. Additionally, it is strongly recommended to take Anavar with a meal to avoid any stress on the digestive system.
Those who have used the steroid beforehand and have tolerated it well might contemplate an extended cycle, again with a pointy eye on unwanted effects and a well-planned PCT. All The Time keep in mind, acquiring great outcomes isn’t just about nice positive aspects in the shortest attainable time, however more about longevity and sustaining those gains sustainably. Think About starting with a 5mg per day dosage and take heed to your body. Notice the method it reacts to the consumption and search for any unusual changes. You can progressively increase the dosage as a lot as 20mg if you’re comfortable and don’t undergo any negative unwanted effects. Strong is the new horny, and for women who want to not solely look good however really feel powerful, this offers them an edge. Nevertheless, prolonged use (more than 6-8 weeks) or greater than recommended dosage use (20-40 mg/day) will result in liver harm.
References:
https://isabelzarate.com/marlonharada67
Icon hunting season requires strategic planning when you buy fifa coins for expensive legends. Real sellers provide fast bulk discounts with active support channels and non drop warranties for high-value transactions.
KPV peptide for Lyme disease is a therapeutic molecule with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and tissue-healing properties. It helps sufferers handle persistent symptoms by calming immune overactivation, lowering cytokine-driven inflammation, supporting gut steadiness, and selling hormone stability. While not a cure, it is increasingly used in practical drugs to improve quality of life in persistent Lyme instances. KPV Peptide plays a significant function in stimulating the regeneration of epithelial cells, which are important for sustaining the integrity of mucosal surfaces and accelerating tissue repair. By modulating immune responses and reducing irritation, this peptide aids in creating an optimum surroundings for cells to proliferate and migrate, facilitating efficient therapeutic of broken tissues.
Your body makes peptides that serve important features in some of your body’s most important processes. For occasion, insulin is a 51-amino-acid-long peptide hormone that helps your cells take in sugars from your food to use for metabolism and store them in your liver. The world of peptides is huge and ever-expanding, providing new avenues for integrative medicine and personalized healthcare. BPC-157 and KPV stand out as two exceptional compounds with the potential to revolutionize the management of GI problems and MCAS.
At In Peptides, we’re dedicated to delivering precision and high quality with each order. Our team’s experience and rigorous standards make certain that each product meets the best stage of purity and effectiveness. Belief In Peptides for reliable, premium-grade peptides crafted with care. People who face extra pronounced inflammatory issues or who need an additional layer of immune regulation would possibly lean toward KLOW for its broader spectrum of action. KPV’s short half-life is offset by its potent downstream results on inflammation pathways. KPV shortens the recovery window between exercises by preserving inflammation in examine and allowing native tissues (like tendons and joints) to heal quicker.
This binding suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines similar to TNF-alpha and IL-6 while modulating pathways like NF-κB and mast cell degranulation. Whether you’re researching mucosal barrier operate, wound repair, or immune modulation, KPV continues to gain consideration as a small but mighty peptide with wide-ranging utility in preclinical fashions. GHK-Cu peptide, in contrast, is renowned for stimulating collagen and elastin synthesis, which are essential for preserving pores and skin agency and youthful.
Researchers are actually wanting at the Neuroprotective and Cognitive Effects of the Cagrilintide peptide. Amylin receptors are current within the mind, suggesting that Cagrilintide’s signaling could prolong to neural pathways that influence extra than just satiety. Research are beginning to explore whether the peptide can scale back neuroinflammation or influence cognitive operate, doubtlessly opening up Cagrilintide benefits in models of neurodegenerative conditions. For researchers involved on this direction, comparative studies with different neuroactive compounds, such as Dihexa, could additionally be highly relevant. Bigger models, usually non-human primates or sure kinds of canines, are utilized for chronic, long-term studies and for assessing the pharmacokinetics and long-term Cagrilintide safety. As A Outcome Of these fashions share larger physiological similarities with people, they supply more relevant information on the duration of the Cagrilintide advantages and how the Cagrilintide peptide is metabolized over time. The sustained nature of the peptide’s action—a core part of what’s Cagrilintide’s mechanism—requires these long-duration models to fully characterize its results.
Let’s delve into the scientific intricacies and practical benefits of KPV, shedding mild on how this remarkable peptide could be harnessed for health optimization. These peptides accelerate wound therapeutic by promoting the development of tissue fibers and blood vessels. Aside from its immunomodulatory features, LL-37 also can act as a potent anti-inflammatory peptide and protect the body from inflammatory injury by activating anti-inflammatory cytokines.
KPV promotes faster therapeutic of wounds and irritation by dampening native irritation and modulating immune response. KPV is a C-terminal fragment of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), which is itself derived from the bigger POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) precursor. Researchers recognized KPV within the late Nineties while exploring the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of α-MSH with out its pigment-stimulating unwanted side effects. This is one of the finest peptide protocols for anti-aging and pores and skin health, and when done accurately, it works exceptionally well. Tumorigenesis, or carcinogenesis, is the formation of cancer, where regular cells are transformed into cancer cells. KPV was adequate to decrease the inflammation of carcinogenesis (Viennois E, 2016). Utilizing KPV earlier than the development of colon most cancers might be a preventive approach to stop colonic carcinogenesis before it begins (Viennois E, 2016).
Not only did it pace up the therapeutic course of, but it also minimized the event of hypertrophic scars and keloids, which are sometimes a beauty concern for patients recovering from wounds or surgical procedures. One Other key good factor about https://blackvision.co.uk/@desireefrankla?page=about peptide is its capacity to speed wound healing and promote tissue restore. This peptide reduces inflammation at the wound web site, accelerates therapeutic, and helps stop the formation of hypertrophic scars and keloids. KPV peptide is primarily valued for its potent anti-inflammatory properties.
All I can say, about the buying experience https://www.percyroberts.com/rogeliochowne2 I hope you get your fee system labored out. Different Testing products I get are bubble wrapped and lots higher preventatively wrapped. KPV blocks nuclear translocation of inflammatory proteins by interfering with importin-α3 transport systems1. This intracellular mechanism differs from conventional anti-inflammatory compounds. Further studies should give consideration to optimizing the supply systems for KPV, exploring varied nanoparticle formulations and encapsulation strategies to reinforce its efficacy and bioavailability. KPV has been shown to decrease the expression of key pro-inflammatory cytokines similar to IL-6, IL-12, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IFN-γ.
For our prospects in Western Australia and Darwin, expect a minimum of 5 business days for regular shipments. Categorical postage significantly accelerates supply occasions for Western Australian customers, but generally nonetheless takes about three days. Labeling their products this fashion ensures there is compliance with potential future laws. Larazotide acetate (LA) can enhance intestinal barrier function by stopping the opening of intestinal tight junctions and “seal” a leaky gut.
Specifically, any and all merchandise branded beneath “Nature’s Marvels,” together with however not limited to Nature’s Marvels Bioregulators. Some Integrative Peptides products are suitable for individuals following a vegan lifestyle. Nonetheless, products similar to CogniPep, PinealPep, ThyroPep, CerebroPep™, and each the Unflavored and Mango Strawberry Gut Feeling formulations aren’t vegan. Moreover, sure merchandise in the bioregulator category include animal-derived elements.
For other folks like us, the VIP a peptide shifts towards Th2 and our evaluate of it is later in this publish. I’m at all times careful with immune performing peptides, but we tolerate it well, it seems to be a real modulator (not a booster). Peptide studies consistently show they work even higher utilized in mixture – to support a whole body system. These influencers – long before social media – bind to receptors on our cells instructing them how to perform bodily processes. Additionally on this journey, peptides helped my daughter and associates with a broad variety of health needs.
Each serving accommodates the naturally occurring acetylated and amidated isomer of KPV for optimum lab efficacy. Our dedication to quality management and standardization makes us the best supplier for researchers who want dependable and reproducible outcomes. Studies on mast cell system stimulation found that KPV could preserve immune operate balance without completely suppressing defensive responses.
The precise mechanism by which KPV decreases tumorigenesis isn’t but fully understood (Viennois E, 2016). While injectables or nasal sprays may present sooner absorption, capsules are perfect for these seeking to get rid of potential discomfort with needles and nasal sprays. They function an answer for scientists looking to easily incorporate BPC-157 and TB-500 into their analysis.
Analysis shows KPV additionally calms those overactive mast cells (common in MCAS) and helps restore your intestine lining. It’s like a peacekeeper on your immune system – stopping unnecessary fights while helping heal damage. Your body actually makes this naturally as part of bigger melanocortin hormones. Assume of it like your body’s built-in irritation off switch for particular trouble spots. KPV enters the cell and interacts immediately with inflammatory signaling molecules contained in the cell.
KPV peptide’s capacity to modulate the immune system with out totally suppressing it also makes it a valuable tool for managing immune-mediated inflammatory ailments. By interacting with mast cells and other immune cells, KPV peptide reduces inflammation with out weakening the body’s natural defenses towards infections. This has been particularly helpful in managing autoimmune circumstances where immune system overactivity causes chronic irritation and tissue damage. One examine demonstrated that KPV peptide significantly lowered inflammation in DSS-induced colitis models, a standard methodology used to study inflammatory bowel illness (IBD) in laboratory settings. By inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines, KPV helped lower general intestinal irritation, making it a promising therapy for conditions like Crohn’s illness and ulcerative colitis. Its capacity to modulate both immune and inflammatory responses makes it a priceless therapeutic tool for managing a variety of health conditions associated to inflammation.
businessgrowthhub – I’ve bookmarked several posts already, this seems promising.
boostcraft.click – I’ve already bookmarked this, seems like a solid resource ahead.
ranktrail.click – Typography and spacing are well balanced, easy on the eyes.
ranktrail.click – Found a few interesting articles already—will go deeper later.
nataliakerbabian – Her site feels elegant, visuals and content strike a refined, warm balance.
searchnest.click – The visuals support the content nicely, not too distracting.
websummit.click – Layout feels intentional, nothing looks out of place or awkward.
smartpartnership.bond – Love how they emphasize shared growth in each section here.
Your results will be the sum of each wholesome alternative made, each rigorous workout, and each commitment to your wellbeing. Given Oxandrolone’s subtle results, it’s important to keep in mind that modifications inside such a short interval won’t be dramatic or drastic, but they’ll set the ground for further progress. Lastly, this picture is taken after utilizing Anavar for eight weeks (two months).
However, don’t assume that this makes it a brilliant drug for muscle growth—it doesn’t. Get discounted Anavar from a legitimate supplier of legal anabolic steroids. In this text, we will delve into the vital data you should know in regards to the Anavar routine to attain optimal outcomes and usage. So, let’s explore how Oxandrolone can rework your health journey and allow you to unlock your true potential. Solely secure with strict protocols; never fully confirmed for long term.
Correct hydration and common cardiovascular train will also help to further lower body fats share. It’s essential that customers observe beneficial dosages to minimize potential unwanted side effects and maximize advantages. In Accordance to a 2016 research by McGill College, the most vital modifications in the physique may be seen on the 4-week mark of utilization (source). It’s essential to watch your body for any indicators of virilization, similar to deepening of the voice, extreme hair development, or clitoral enlargement. If any of those signs appear, it’s important to discontinue use instantly to forestall long-term effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional earlier than starting an Anavar cycle can also be recommended to ensure that you’re utilizing the steroid safely and effectively. Moreover, liver perform and levels of cholesterol should be monitored during and after your cycle, as Anavar can have a light impact on these markers.
This might embrace mild energy increments, a firming of the muscle, and a reduction in physique fats. The impression of such changes are normally extra profound in novices, whereas skilled customers would possibly observe a considerably extra regular shift towards improved muscle definition and strength. The beneficial day by day dosage for adults ranges from 2.5 mg to 20 mg, administered in 2 to 4 divided doses. The desired response can be achieved with as little as 2.5 mg or as a lot as 20 mg day by day. A typical course of remedy lasts 2 to four weeks and may be repeated intermittently as wanted.
Possibly four weeks on weeks off (2-3 cycles per year) with regular blood work and a healthy diet. These narratives inspire us to push our limits and pursue our health targets with unwavering dedication. Nonetheless, it is essential to strategy Oxandrolone responsibly, and understanding the potential dangers. Keep In Mind, it’s always really helpful to consult with a healthcare skilled or skilled health skilled before initiating an Oxandrolone cycle. They can provide personalised steerage, monitor your progress, and make certain that the dosage and cycle length aligns along with your specific needs and objectives. Even though http://55x.top:9300/nicolaspulley is taken into account delicate, it nonetheless suppresses your hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis (HPTA).
The time invested will get rewarded with lasting and extra pronounced results. Nevertheless, it would be prudent to bear in mind that extended cycles increase the risk of side effects. Taking breaks and listening to your physique are important to making sure a positive and secure expertise throughout your bodybuilding experience. In addition to fat loss, Anavar is also a incredible muscle preservation agent. When weight-reduction plan or performing heavy cardio to lose fat, there’s always the risk of shedding useful muscle mass as properly.
There isn’t any simple reply to the question of how lengthy a steroid stays in a person’s system. It will rely upon the steroid taken, what it’s stacked with, and the physique of the particular person taking it. Some steroids may cause dilation of the blood vessels in the pores and skin, resulting in facial flushing and redness. This could be significantly noticeable on the cheeks, nostril, and brow. On the opposite hand, in case you are on a mass gain or bulking cycle, your face may become rounder, giving rise to the not-so-flattering ‘moon face’ look.
For finest fats loss, muscle preserving and athletic enhancement outcomes, men ought to take a dosage of between mg per day. Anavar will dramatically spike testosterone levels, while increasing protein synthesis and nitrogen retention. This shifts the body into an anabolic setting the place the body’s muscle-building potential increases. Other anabolic steroids often trigger will increase in visceral fat, inflicting a bloated look.
Related to the United States, it’s legal to own and use Oxandrolone with a valid prescription from a licensed healthcare professional for permitted medical functions. By submitting this type, you agree to Asana Recovery’s Privateness Coverage. You also consent to Asana Restoration contacting you by cellphone, textual content message, and e-mail concerning your insurance advantages and remedy services. At Asana, we provide effective, insurance-covered therapy for habit and psychological health, guided by consultants who perceive as a result of they’ve been there. We are very conversant in the issues of steroid abuse and can help you cope with the physical and emotional effects of it.
inspiredmind.shop – Clean layout, beautiful photos — makes shopping a pleasure.
smartdesigncorner.shop – This site feels like a creative studio you can browse.
Following this evaluation of the benefits of ipamorelin, we can now talk about whether or not researchers should examine tesamorelin or ipamorelin as their HGHR peptide of selection. According to the United States Food & Drug Administration (FDA), any polymer composed of 40 or fewer amino acids can be thought-about to be a peptide. To date, there are over one hundred peptide drug merchandise marketed in the U.S., Europe and Japan — in a worldwide market estimated to be price over $20 billion 2. But they’re slightly completely different in how they work, as well as of their potential advantages and side effects. If you’re planning to experiment with peptides or already familiar with both compound, this stack could presumably be the missing hyperlink in your performance, physique, or longevity routine.
By honing in on individual wants and traits, healthcare suppliers can design treatment plans that address distinctive patient requirements, finally promoting better health outcomes and general satisfaction. Larry Siegel, renowned for his pioneering work in peptide remedy, emphasizes the unique benefits of Tesamorelin in addressing age-related issues such as lipodystrophy and cardiovascular health administration. Need higher restoration, more lean mass, fat loss, and pores and skin that doesn’t make you look like a deflated balloon? With thirteen Midwest places and over a decade of expertise, we deliver skilled testosterone remedy, weight reduction, and efficiency treatments – so you’ll be able to really feel and perform at your peak.
Including GHK-Cu to the routine might ship reparative affect on the mobile stage, fortifying tissue high quality and longevity. With professional supervision, these rigorously crafted combos nurture balanced hormonal harmony, resulting in a heightened sense of vigor, elevated mood, and substantial improvements in train tolerance. As at all times, consulting with knowledgeable is the most effective course of action. They can provide steerage and assist determine essentially the most suitable options for your particular wants. However, it’s essential to keep in mind that Ipamorelin isn’t a miracle treatment. It won’t resolve all your well being considerations, however it could possibly contribute positively. It represents a potent instrument on your path in the course of health and wellness.
The secretion of HGH is pulsatile, with greater ranges usually occurring throughout sleep and in response to exercise or stress. It interacts with several different hormones and progress factors to orchestrate varied physiological processes, indicating its intricate involvement in total well being and improvement. By the top of this text, you ought to have a greater understanding of which peptide will be the right selection for you. Particular Person physique dynamics play an important role in determining the effectiveness of each peptide. While some could reply better to Sermorelin because of its milder results and gradual enhance in HGH levels, others could profit more from CJC-1295 with DAC, identified for its sustained launch and higher potency.
CJC-1295 delivers stronger, more sustained effects due to its prolonged activity. Users typically expertise noticeable changes in muscle mass, physique fat discount, and sooner exercise recovery inside the first few weeks of therapy. The improve in IGF-1 also helps mobile restore, joint well being, and improved metabolism. For athletes or anybody in search of extra dramatic physique or efficiency changes, CJC-1295 could be a powerful and efficient tool to speed up these results while supporting long-term health and hormonal steadiness. CJC-1295 also acts on the GHRH pathway, nevertheless it promotes longer and more pronounced GH stimulation. By remaining lively for several days, it produces a more steady elevation in development hormone and insulin-like development factor-1 (IGF-1).
Ipamorelin and https://repos.ubtob.net/kaylenecarrill are peptides that play a vital role in regulating growth hormone ranges and promoting varied physiological features. This extended release of progress hormone is especially helpful for individuals seeking to enhance muscle progress, enhance body composition, and promote overall well-being. These two peptides act as development hormone secretagogues, signaling the pituitary gland to release more HGH, which performs an important position in regulating metabolism, cell progress, and restore. Both Sermorelin and CJC-1295 exhibit the capacity to boost development hormone ranges by stimulating its manufacturing and optimizing its capabilities throughout the body. Sermorelin and CJC-1295 have distinct genetic traits which are essential for his or her capacity to manage HGH levels.
When administering peptide remedy, you don’t have to worry a lot in regards to the risk of any major adverse effects. Improved sleep high quality may be related to the peptides’ capability to reduce stress and promote rest. One of the first mechanisms by which sermorelin and GHRP-2 could improve sleep quality is by increasing the secretion of GH. GH, being a potent anabolic hormone performs a central role in selling muscle achieve, progress, and repair. GHRP-2, a second-generation HGH-releasing peptide, can effectively enhance GH secretion, thus delivering higher advantages to the person.
It contains 29 amino acids, mimicking your body’s pure development hormone triggers. CJC 1295 and Sermorelin are powerful peptides designed to boost human development hormone, promising advantages like increased muscle mass, fat loss, and a youthful appearance. By keeping HGH levels elevated for an extended period, CJC 1295 offers potential benefits similar to elevated muscle mass, reduced body fats, improved restoration, and enhanced anti-aging results. Sermorelin is a synthetic peptide consisting of 29 amino acids, designed to stimulate the body’s natural production of human growth hormone (HGH).
Treatment requires continuous day by day administration for 26 weeks to realize most visceral fats discount. Peptides are broadly utilized in research, diagnostics, and therapeutics, aiding in studies associated to protein-protein interactions, cell signaling pathways, and gene expression. Their numerous applications underscore their significance in advancing scientific data and medical therapies.
Therapy with GHRH-A, though initiated 1 mo after MI, considerably improved cardiac efficiency and decreased infarct measurement, suggesting a regenerative process. GHRH-A stimulated CSCs proliferation ex vivo, in a way offset by MIA-602. The drawback is that nearly all HGH therapies can result in irreversible acromegaly. It also can end in complications over time such as carpal tunnel syndrome, heart disease, edema, and diabetes. It may also take longer for your physique to get well from exercises, and you might experience low vitality in distinction to earlier than. We are devoted to serving to you achieve your wellness and aesthetic targets.
inspiredideas.shop – Their products look inspiring and the site feels very polished.
smartdesigncorner.space – Clean design aesthetic, love how modern and organized this looks.
trendfinder.bond – Just discovered this site, and wow, super useful insights daily.
buildbrand.online – I found tips I can immediately apply to my logo design.
partnershippowerhouse.shop – Content looks strong and compelling, makes me want to join forces.
trustinyou.bond – Clean layout, thoughtful content — not overwhelming at all.
globalunity.bond – Found several parts inspiring; feels like a community I’d like to join.
creativityuniverse.shop – This could be a goldmine for gifting ideas and creative inspiration.
dailyvaluehub.shop – Found great deals and useful products, reminds me of a treasure trove.
brightfuturegroup.bond – Their tone feels sincere and trustworthy, a nice combination.
visionaryleadersclub.bond – Definitely recommending this to friends interested in leadership growth.
inspiredgrowthteam.shop – Really motivated by their vision and the way they present growth ideas.
phillybeerfests – I like the fun energy here, layout feels ready for celebration.
buildlastingtrust.bond – Design is clean, message is clear — feels very sincere.
findnewtrend.shop – Just checked this out, lots of fresh trends I hadn’t seen before.
startsomethingnew.shop – I love how clean and simple everything looks here.
trustedbusinesslink.shop – Seems like they care about trust and clarity, good sign.
trustandunity.shop – Feels welcoming and authentic, like a place built for community.
globalpartnershipteam.bond – I like how they highlight collaboration and shared goals.
visionaryconnect.bond – Strong branding, clean interface — very professional presentation.
In this blog post, we’ll cowl some of the most common questions we obtain about Sermorelin and the means it can profit you. You may get coverage when you use these peptides for certain health issues, like HIV-related fats achieve or true growth hormone deficiency. Simply pushing for extra muscle or much less fat won’t minimize it—most plans say no for anti-aging or performance use.
Physique composition modifications generally require 3-6 months of consistent therapy. Think About attaining your weight reduction targets whereas feeling energized, well-rested, and holding onto hard-earned muscle. Sermorelin therapy is generally safe for extended use under medical supervision, as it works together with your physique’s pure hormone manufacturing processes. Yes, sermorelin before and after face outcomes show increased pores and skin thickness and elasticity, with improvements sometimes seen after four months of remedy.
By binding to ghrelin receptors, ipamorelin can raise growth hormone ranges without impacting different hormones like cortisol (10). This makes https://git.4lcap.com/winniebarrios/winnie1987/wiki/Synergenx+Community+Clinics+Broaden+Peptide+Therapy+Choices+With+Bpc-157+And+Cjc-1295+%2B+Ipamorelin.- a extra exact possibility for growing development hormone, according to Cho. Because most growth hormone is naturally secreted at night time, many individuals choose to take their injections before bed to simulate the body’s natural course of (7). As An Alternative of mimicking GHRH and acting on its receptors in the brain, ipamorelin acts as a go-between (1). It binds to the receptors of another hormone, ghrelin, which additionally stimulates the pituitary gland to launch growth hormone (1).
You might discover redness, itching, pain, or swelling at the injection site. This is usually not critical; making use of a cool compress to the realm can help, and these local reactions sometimes resolve on their own. Circumstances like uncontrolled diabetes or intracranial hypertension, for instance, may additionally warrant caution or nearer monitoring if sermorelin is used. Your doctor will display for contraindications and decide if sermorelin is protected for you. When in doubt, it’s crucial to comply with medical recommendation and to not use sermorelin in scenarios for which it’s not meant. Sermorelin depends on a functional pituitary gland; if your pituitary can not produce GH, sermorelin won’t be efficient (in such circumstances, hGH injections can be needed). A valid prescription is required, and remedy usually entails day by day injections along with common monitoring by the healthcare provider.
The primary operate of GHRH is to encourage the pituitary gland to produce and secrete development hormone. The action of Sermorelin is to mimic GHRH, attaching to specific receptors on the pituitary gland, which outcomes in an increased manufacturing of HGH. This course of is like turning up the dial on your body’s natural hormone factory, enhancing progress, muscle improvement, and power ranges in a way that feels pure and balanced. When considering Sermorelin therapy, it’s essential to bear in mind the individual’s physique composition. Those with excessive physique fat or who’re morbidly obese might not reply as nicely to the treatment. Moreover, people with abnormal development patterns might not expertise optimal advantages from Sermorelin remedy because of underlying medical situations or genetic factors. Poor insulin sensitivity can have an effect on the body’s response to Sermorelin, probably reducing its effectiveness.
If you’re ready to enhance your pores and skin, energy, and general wellness with science-backed peptide therapy, IVYRX makes it straightforward to get started. Inside the primary few weeks, patients typically notice subtle pores and skin enhancements, particularly across the eyes. Increased hydration and collagen exercise could scale back fine traces, enhance texture, and give the skin a healthier glow. Slower cell turnover results in a buildup of dead pores and skin, dullness, and uneven tone. Sermorelin helps accelerate the regeneration of pores and skin cells by enhancing progress hormone exercise, allowing newer, healthier cells to surface more incessantly.
Researchers interested in working with sermorelin could use this sermorelin dosage guide during the design and planning phases of the research course of. To minimize the chance of check topics experiencing side effects as a outcome of sermorelin administration, researchers are advised to seek the guidance of the related literature when designing an experiment. All of our content is written by individuals with a strong science background, together with medical researchers.
Statements regarding merchandise offered on Peptides.org are the opinions of the individuals making them and are not essentially the identical as those of Peptides.org. The obtainable analysis has investigated the load loss potential of sermorelin in doses ranging from 1-2mg/daily 13. Rather than administering HGH instantly, researchers can use sermorelin to extend HGH levels in take a look at topics by naturally stimulating the pituitary gland to launch more endogenous HGH. As A Substitute of spiking HGH to supraphysiological levels, sermorelin is believed to produce a gradual increase in HGH in a steady, predictable method. Since it resembles endogenous GHRH, it produces a similar impact, which is to bind to receptors that tell the pituitary gland to launch more development hormone into the bloodstream. Whether you’re beginning sermorelin injections for anti-aging, restoration, or efficiency, we’ll match you with a plan that matches your objectives and adjusts along with your progress. Our personalised plans include medical guidance, flexible dosing, and doorstep delivery — all backed by licensed healthcare suppliers.
At Point Of Interest Vitality, we combine our experience within the therapy of hormones/weight loss/peptides with the comfort of onsite or telemedicine so our visitors can begin therapy in only a few easy steps. Sermorelin works upstream of artificial progress hormone (HGH) by encouraging your physique to do the work itself. This makes it a most popular choice for patients in search of a more physiologically balanced, regulated method to enhancing GH levels.
This singular peptide has drawn many people like athletes from across the globe for its incredible benefits and minimal unwanted effects to reinforce their performance on the field and in the fitness center. You will recover from exercises quicker and sooner weight loss is achieved while lean muscle is being constructed. With GH increased you will burn extra calories and look and feel youthful. Harnessing the ability of the Sermorelin Ipamorelin stack could possibly be your key to unlocking a extra sturdy wellness and recovery regimen.
modernchoice.store – Seems trustworthy; I like how they display info clearly.
buildlastingties.bond – I appreciate how honest and sincere the content feels.
https://plisio.net/ru/blog/altcoin-season-index
Курсы подготовки к ЕГЭ по информатике https://courses-ege.ru
orourkeforphilly – I like the campaign site, visuals feel strong and message clear.
cumberlandcountynjvaccination – The site gives clarity, vital health information is accessible and well organized.
stream event
wetten österreich türkei
Here is my web-site: ihre wette in sicheren händen (Rodney)
connectwithtrust.bond – Visiting this feels like stepping into a respectful space.
growtogetheralliance.shop – Nice site structure, makes it easy to see what they offer.
cumberlandcountynjvaccination – The site gives clarity, vital health information is accessible and well organized.
Acho simplesmente digital PlayPix Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino retro-futurista. O catalogo de jogos e uma tela de emocoes. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque cibernetico. Os agentes processam como CPUs. garantindo suporte direto e sem lag. Os pagamentos sao lisos como um buffer. porem queria promocoes que processam como CPUs. No fim das contas, PlayPix Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os exploradores de jogos online! Como extra o design e fluido como um render. fazendo o cassino processar como um CPU.
quanto vale a playpix|
Me encantei pelo nado de Brazino Casino, explode com uma vibe aquatica eletrizante. A selecao de titulos e uma correnteza de emocoes. incluindo jogos de mesa com um toque aquatico. O atendimento e solido como um coral. disponivel por chat ou e-mail. As transacoes sao faceis como uma onda. em alguns momentos queria promocoes que explodem como geiseres. No fim das contas, Brazino Casino promete uma diversao que e uma mare para os apaixonados por slots modernos! De bonus a navegacao e facil como uma corrente marinha. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um oceano.
o que Г© o site brazino777|
cumberlandcountynjvaccination – The site gives clarity, vital health information is accessible and well organized.
Scientific studies have proven that Sermorelin remedy can lead to increased muscle mass, reduced body fat, improved bone density, and enhanced energy levels. Individualized dosing tailored to every patient’s particular needs is important for reaching the specified therapeutic effects. Medical studies have shown that monitoring progress throughout the therapy course of is essential for evaluating its general success. Regular assessments help healthcare suppliers make informed choices regarding changes in dosage and treatment duration to optimize outcomes. The increased growth hormone ranges stimulated by Ipamorelin could promote lipolysis (fat breakdown) and metabolic rate elevation, doubtlessly making it helpful throughout cutting phases.
In this section you will see smart pairings that boost outcomes and maintain safety first. You may even see what to keep away from so your sleep and hormone rhythm keep robust. Use these ideas with your provider to match your targets and lab results. Strength coaching, vitamin D status, and calcium consumption still matter.
Whereas Sermorelin is considered one of many safest peptides for exciting natural GH production, incorrect dosing or poor administration habits can nonetheless lead to unwanted unwanted side effects. Going overboard with Sermorelin can result in plenty of unwanted unwanted effects. From swelling and discomfort on the injection website to more extreme concerns like headaches, dizziness, and even symptoms resembling hyperactivity in the body’s hormone levels. Your physique likes harmony, and too much of a good thing can disrupt this delicate steadiness. Administering your dosage correctly is as vital because the dose itself.
Many adults prefer this profile, especially when they need wholesome growing older quite than a speedy however risky surge. Sleep, energy coaching, and protein intake shift this stability in your favor. A better nightly rhythm and robust coaching plan make sermorelin simpler. Determining the proper dosage of Sermorelin acetate includes a careful evaluation of individual elements and adherence to established guidelines to optimize treatment outcomes. Ensuring the right utilization of Sermorelin acetate involves understanding its administration techniques, purposes, and following precise directions for optimum effectiveness.
Dosage guidelines for the Sermorelin Ipamorelin blend can differ depending on individual needs and well being factors, however healthcare suppliers typically advocate beginning at a decrease dosage and adjusting as wanted. Sermorelin’s major operate is to increase HGH manufacturing, but it does much more throughout the physique. Once HGH ranges rise, the hormone stimulates cell regeneration, improves metabolism, and helps tissue repair. This, in flip, leads to improved muscle mass, higher skin elasticity, elevated energy levels, and enhanced overall vitality. Sermorelin therapy helps the body’s ability to rejuvenate itself by boosting natural HGH manufacturing.
Your provider may also comply with glucose, lipids, thyroid markers, and other hormones primarily based on your historical past. Sleep seven to nine hours, carry with progressive overload, stroll every day, and eat enough protein. Maintain a easy scorecard each week so you possibly can see developments, not noise. Measure resting coronary heart rate and morning weight three days per week.
Progress hormone is of course produced by the pituitary gland and is critical for progress in youngsters. In youngsters who fail to develop normally as a end result of their our bodies usually are not producing sufficient growth hormone, this drugs may be used to increase the amount of development hormone produced by the pituitary gland. Sermorelin is an artificial form of development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), used to boost ranges of human development hormone (hGH). As an FDA-approved treatment, but may be obtained through pharmacies that make individualized medicines. Widespread side effects include injection web site reactions, flushing, headache, or dizziness. Rare results can include water retention or numbness within the arms. Only do that with a provider who understands peptide therapy and hormone optimization.
When considering sermorelin therapy, it’s necessary to consult with a healthcare supplier. Sometimes, to qualify for sermorelin remedy, hormone deficiency should be documented by way of blood exams. Sermorelin isn’t obtainable over-the-counter; it can only be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider. Sermorelin was developed within the 1970s to address circumstances associated to hormone deficiencies. It obtained FDA approval in 1997 for treating growth hormone deficiency in youngsters. At Present, it’s additionally regularly used for age-related hormone insufficiency, helping stability levels of human growth hormones. Clever peptide stacks produce effects greater than the sum of their particular person advantages.
These institutions mandate a session to ensure the protected and applicable administration of this remedy. The elevation of HGH ranges ensuing from the mix of Sermorelin and Ipamorelin can result in an enhancement in libido, finally bettering sexual health and overall high quality of life. Consistency is essential in relation to hormone therapies like Sermorelin. Regular use, combined with a wholesome lifestyle, can lead to vital enhancements in total health and well-being over time. At All Times observe your prescribing doctor’s guidance and keep away from adjusting your dose with out medical input. Tell your physician if you have ever had any unusual or allergic response to this medicine or any other medicines.
Are you on the lookout for a natural method to boost muscle growth, aid in weight loss, and enhance total well being and wellness? It is essential to note that the potential side effects of sermorelin are fewer and fewer extreme than those of traditional HGH injections. At https://vcs.int.feuerwehr-ziemetshausen.de/columbusbreaux U, our medical professionals provide thorough steerage and help to guarantee that Sermorelin remedy is tailored to your particular person health targets and lifestyle. Artificial GH may cause extra quick unwanted effects as a end result of direct introduction of hormones into the body, whereas sermorelin’s unwanted effects are typically related to its injection web site or allergic reactions. Since sermorelin encourages the pituitary gland to launch GH naturally, it may mimic the physique’s physiological patterns of GH release extra carefully than synthetic GH. Sermorelin acetate is a progress hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) analog that stimulates the pituitary gland to naturally produce and release extra progress hormone. It’s FDA-approved for pediatric GH deficiency, however can be broadly used off-label in adults with age-related declines in GH.
Ich bin suchtig nach JackpotPiraten Casino, es pulsiert mit einer unbandigen Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echter Jackpot, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie Kanonen donnern. Das Casino-Team bietet eine Unterstutzung, die wie Gold glanzt, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Sabelhieb. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, aber mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren der Hammer. Kurz gesagt ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Meere beherrscht fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Nebenbei die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Schatz funkelt, was jede Casino-Session noch aufregender macht.
jackpotpiraten app download|
Adoro o gingado de SambaSlots Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um bloco de rua. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de swing, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um tamborim. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um mestre-sala, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No fim das contas, SambaSlots Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma folia total para os folioes do cassino! E mais o design do cassino e um desfile visual colorido, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
bonus sans depot casino la sambaslots|
The combination of Sermorelin Ipamorelin can contribute to pain management by fostering expedited healing and recovery processes, thus mitigating ache and discomfort linked to accidents or chronic ailments. This mix has demonstrated efficacy in facilitating the restoration and rejuvenation of impaired tissues, enabling people to recuperate extra swiftly from surgical procedures or muscle strains. The combination of Sermorelin and Ipamorelin in a mix produces a synergistic effect, optimizing the stimulation of Human Progress Hormone (HGH) manufacturing and enhancing the general efficacy of peptide therapy. This article will explore the benefits of this highly effective combination, including faster therapeutic and recovery, reduced inflammation, improved libido, and anti-aging results. Maximizing fitness potential with Ipamorelin CJC 1295 involves enhancing muscle restoration, power efficiency, and endurance ranges for improved athletic performance. Monitoring and evaluating the results of Ipamorelin and CJC 1295 are essential for assessing their effectiveness, muscle restoration benefits, and potential unwanted aspect effects.
By suppressing the body’s somatostatin ranges, ipamorelin increases levels of GH in take a look at subjects 4. A GHS is a type of peptide that promotes the physique to provide progress hormone (GH) also called human development hormone (hGH). Ipamorelin binds to the same receptors as ghrelin (GHSR-1a receptors) and increases ranges of GH and IGF-1 2. Nighttime dosing supports your natural rhythm and maximizes GH launch during deep sleep. Avoid caffeine or alcohol late in the day, as each can disrupt your sleep cycle and blunt hormone response. A quiet, darkish surroundings additionally helps your physique enter restorative sleep. Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in guiding people on the correct dosage of Ipamorelin primarily based on their distinctive well being circumstances, performance objectives, and medical historical past.
Ipamorelin, an artificial peptide focusing on the growth hormone (GH) secretagogue receptor, is commonly used for its capacity to boost GH production and metabolism. This twin action results in a more pronounced elevation in GH ranges, which performs a vital position in numerous bodily features similar to metabolism, muscle development, and tissue restore. The first step toward transforming your physique and enhanced recovery is seeing if the remedy is right for you. Subsequent comes the skilled steering and high-quality merchandise to optimize your muscle progress. In medical follow, sermorelin acetate is often administered subcutaneously (under the skin) in doses ranging from 0.2 to 0.5 mg per day, with adjustments based on age, intercourse, and therapeutic response. https://git.berfen.com/hunter09685886 may increase lean muscle mass when mixed with progressive coaching and enough protein.
It can also increase the danger of sure forms of cancer, corresponding to Hodgkin’s Lymphoma 4. These dangers mean that HGH research is strictly regulated and tightly controlled. Be Part Of me and tons of of different male and female biohackers in The Absolutely Optimized Well Being Private Membership Group to learn how you can use peptides to optimize your well being as you age.
Over months, many people report steadier joints and fewer aches after onerous classes. Peptide stacking works best when it’s personalized, supervised, and exact. Many on-line “peptide stacks” come from unregulated sources or uncertified compounding pharmacies. These can range in efficiency and purity, rising the chance of contamination.
In our expertise, the most effective place to buy sermorelin online is Core Peptides, a U.S.-based company that provides high-quality, research-grade peptides with out additives or fillers. In addition it has been used alongside the amino acid arginine for the prognosis of GHD in adults, as a single intravenous infusion at a dose of 1mcg per kg of body weight. Under, the main doses utilized in past sermorelin research are highlighted together with any common guidance that researchers may need to pay attention to. Together, you and your provider will create a plan to help you meet your health, wellness and efficiency targets. Your doctor can guide and assist manage any potential side effects you may experience, allowing you to get probably the most out of your remedy whereas minimizing the risks. Using the Sermorelin and Ipamorelin peptide stack can clearly do wonders in your health, but like several therapy it may possibly include some unwanted effects. Treatment with GHRH increased fasting insulin ranges throughout the regular range by 35%in adults with MCI (P.001) however not in wholesome adults.
A Quantity Of medical research have demonstrated the efficacy of Sermorelin in enhancing development hormone ranges in adults with progress hormone deficiency. The therapy’s constructive effects extend beyond bodily changes, contributing to raised high quality sleep, enhanced cognitive perform, and improved mood regulation. By restoring hormonal steadiness, Sermorelin remedy helps individuals achieve a greater sense of well-being and vitality, further enhancing their general health and longevity. Development hormone launch peaks through the first 90 minutes of deep sleep. Taking Sermorelin before mattress aligns together with your body’s circadian rhythm, permitting the peptide to amplify this natural nocturnal GH pulse.
Our personalized plans embody medical steerage, flexible dosing, and doorstep supply — all backed by licensed healthcare providers. Though not widespread, some customers might experience fatigue, poor sleep, or irritability after stopping sermorelin abruptly, particularly if their body has adapted to larger HGH levels. Missing one dose of sermorelin isn’t often a big deal — however frequent lapses can disrupt your outcomes and throw your hormone steadiness off observe. Since sermorelin depends on consistency to stimulate steady growth hormone manufacturing, staying on schedule issues more than many individuals notice. Sermorelin impacts hormone ranges, and when dosed improperly, it can throw off your psychological steadiness. This is very frequent in the early levels of use or when doses are modified too quickly with out proper monitoring.
netfusion.click – On mobile it’s seamless, everything scales nicely with no quirks.
concert broadcast
seoanchor.click – Found some useful articles already; looks like a solid resource.
rankmotion.click – Pages load fast, I didn’t notice any lag anywhere.
pagevector.click – Found useful content already, will dig deeper later tonight.
clicksignal.click – Visuals blend nicely with text, nothing feels jarring or out of place.
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, on dirait une energie de jeu irresistible. La selection de jeux est colossale, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service client est remarquable, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Les transactions en cryptomonnaies sont instantanees, neanmoins les bonus pourraient etre plus reguliers, afin de maximiser l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, 7BitCasino ne decoit jamais pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Notons egalement que la navigation est intuitive et rapide, ce qui intensifie le plaisir de jouer.
7bitcasino login|
cycleforsci – Inspiring cause, layout feels energetic and message delivers real motivation.
Amo a energia de PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer eletrizante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer momento. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Alem disso a interface e fluida e estilosa, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Notavel tambem os eventos comunitarios envolventes, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Obter mais|
Fiquei fascinado com BETesporte Casino, e uma plataforma que vibra como um estadio lotado. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com slots modernos e tematicos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, acessivel a qualquer momento. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No geral, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Vale destacar o design e moderno e vibrante, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Muito atrativo o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, oferece recompensas continuas.
Começar aqui|
By following proper dosing guidelines and consulting a healthcare supplier, the danger of unwanted aspect effects can be minimized. Before diving into the variations between Ipamorelin and Sermorelin, it helps to understand peptides. They are naturally occurring and hold the constructing blocks for protein creation.
Some people may also encounter redness, swelling, or itching on the injection website. If any side effects persist or worsen, it’s advisable to seek steerage from a healthcare skilled. Despite the probability of these reactions, many customers perceive the advantages of Sermorelin as outweighing the minor discomforts. Each peptides are generally protected when used beneath medical supervision and within recommended dosages.
By boosting endogenous GH, Sermorelin remedy results in elevated IGF-1 levels and may help improve muscle mass and scale back body fat over time. Notably, it doesn’t provide an exogenous hormone, however somewhat stimulates your physiology to supply GH, which is considered a more physiological method than direct HGH injections. Sermorelin and Ipamorelin are synthetic peptides designed to reinforce progress hormone production by interacting with the pituitary gland, a small construction in the brain liable for hormone regulation. While both peptides goal to spice up HGH ranges, they function via distinct mechanisms, offering distinctive advantages relying on particular person health goals. Evaluating ipamorelin and sermorelin entails inspecting how every peptide features, their effects on the physique, and their applications in anti-aging, weight loss, and efficiency enhancement. Ipamorelin helps promote fats loss, together with in the stomach area, by stimulating development hormone launch which enhances fats metabolism. While it’s not a targeted stomach fats burner, its capacity to increase progress hormone ranges helps total discount in physique fat.
You may also see what to avoid so your sleep and hormone rhythm stay sturdy. Use these ideas along with your supplier to match your targets and lab outcomes. It supports physiologic peaks at night time and lower levels during the day. Many adults choose this profile, particularly when they want healthy growing older somewhat than a fast however dangerous surge. Human Progress Hormone (HGH) stimulates the manufacturing of insulin-like growth issue 1 (IGF-1), which plays a vital role in cell progress and regeneration. Along with weight gain, individuals can also experience delicate reactions on the injection site, such as redness or swelling.
Some people might prioritize muscle growth, while others give attention to fats loss or general energy levels. Tailoring the choice of progress hormone secretagogue to match these goals is key to achieving successful outcomes. As we age, there’s a decline in development hormone production, leading to signs like decreased energy levels, lowered muscle mass, and slower restoration from injuries.
Sermorelin presents effective benefits by enhancing growth hormone release, as supported by scientific research and its constructive influence on overall well being. Due to its targeted mechanism of action, Ipamorelin has been studied for potential therapeutic applications. It may be helpful for circumstances corresponding to muscle losing, osteoporosis, and age-related hormonal imbalances. Its capacity to reinforce muscle mass and cut back fat accumulation also makes it a potential candidate for improving body composition. A peptide stack is the intentional mixture of two or extra peptides, chosen so their actions complement each other. In preclinical and translational work, ghrelin agonism has demonstrated effects on appetite, gastric motility, and physique weight regulation. Ipamorelin particularly has proven promotility and feeding results in animals and selective GH launch with out the ACTH/cortisol rises famous with some older peptides.
Ipamorelin’s side effects are typically milder, with possible nausea, fatigue, or injection web site discomfort. These benefits make sermorelin a flexible choice for anti-aging, weight management, and wellness programs. Its ability to imitate pure GHRH ensures that hormone ranges remain within a wholesome range, reducing the risk of overproduction.
Ipamorelin is a development hormone secretagogue that mimics the body’s pure alerts to increase the discharge of growth hormone (GH) from the pituitary gland. It is thought for its selective action and minimal unwanted effects, making it a favourite amongst athletes and individuals looking for anti-aging advantages. In the Sermorelin vs. CJC-1295 vs. Ipamorelin debate, the “winner” actually is dependent upon your individual goals and lifestyle. Sermorelin provides a time-tested route to softly improve development hormone levels, whereas CJC-1295 (especially with DAC) offers a powerful long-acting boost. Ipamorelin delivers GH spikes with precision and minimal unwanted facet effects. Quite than a one-size-fits-all answer, many patients discover the proper resolution in a tailored mixture – leveraging the strengths of a number of peptides. It mimics your body’s personal progress hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), gently signaling the pituitary gland to release GH in a natural, balanced rhythm.
Studies have proven that CJC 1295 might have a more profound effect on body composition, promoting lean muscle mass growth and fat reduction when compared to https://appsupportlocal.com/read-blog/30807_greatest-peptide-stack-for-each-fitness-objective.html. Sermorelin remedy has been linked to enhancements in sleep quality, cognitive perform, and general well-being. By stimulating the natural manufacturing of development hormone, Sermorelin might help individuals achieve a greater sense of vitality and youthfulness. A third crucial management variable is Monitoring Non-Target Hormone Levels. To affirm that the selectivity of the ipamorelin peptide is preserved within the sermorelin ipamorelin combination, protocols should monitor cortisol and prolactin levels. If the mixture group shows an unwanted spike in these hormones, it suggests the synergy just isn’t as clean as hypothesized, requiring adjustments to the focus ratios.
Sermorelin is an artificial peptide that stimulates the secretion of development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) from the hypothalamus, triggering the release of GH from the pituitary gland. It is known for extending GH peaks and increasing GH trough ranges without causing supraphysiologic GH ranges. A really good facet of Sermorelin’s method leads to long run constant effects which makes it good for people who need hormone substitute therapy. It’s necessary to remember that these therapies work greatest as part of a complete wellness plan – including proper food regimen, train, sleep, and different hormone or nutrient optimizations as needed.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Individuals who have built-in this mix into their health routine have reported heightened sexual satisfaction and endurance. By stimulating the body’s innate production of progress hormone, Sermorelin Ipamorelin can contribute to a more gratifying and fulfilling sexual expertise. This increase in human development hormone (HGH) levels can have a profound impact on sexual desire, arousal, and efficiency. Research signifies that HGH performs a pivotal role in sustaining optimal sexual function by promoting increased blood circulation to the genital area and heightened sensory perception. The Sermorelin Ipamorelin blend presents a diverse range of health advantages, encompassing muscle improvement, weight reduction, enhanced bone density, expedited therapeutic, and sturdy anti-aging properties.
As A Outcome Of ipamorelin and different GH secretagogues can alter anabolic signaling, they fall under prohibited categories for athletes. Banned-substance lists are updated yearly; ipamorelin has been specifically named among prohibited growth hormone secretagogues, and violations can carry multiyear sanctions. For the successful remedy of Sermorelin Acetate and Ipamorelin, adherence to prescribed dosages, upkeep of a healthy lifestyle, and routine monitoring of hormone levels are imperative. Each peptides are typically safe when used under medical supervision and inside recommended dosages.
The medical subject makes use of these peptides to increase progress hormone levels. A few benefits include muscle improvement, fat discount in addition to better health. But each peptide capabilities in a special way subsequent to offering particular advantages. On the opposite hand, https://git.fur93.cn:8002/dianpamphlett instantly influences the pituitary gland to release growth hormone, which aids in combating the consequences of aging by enhancing muscle mass and bone density. Whereas both peptides provide rejuvenating benefits, their distinct mechanisms present a tailored strategy to combating the signs of getting older for individuals looking for specific outcomes. These two signaling molecules mimic pure hormones within the body to stimulate the release of growth hormones from the pituitary gland.
We may even focus on the dosage, administration, and the place to buy this effective mix. Most biohackers report finest effects with stacks of 2-4 peptides. Peptide stacking raises a lot of practical questions, from dosing and safety to cycling and sourcing. Under you’ll discover clear solutions to the most typical issues in phrases of stacking peptides. Analysis shows increased lifespan in animal fashions, delayed onset of age-related illnesses, and improved immune competence with combined use. Here’s a information to the best nootropic peptides for cognitive health and efficiency.
As talked about beforehand, Sermorelin stimulates a part of the brain, in particular the pituitary gland to launch more naturally and already produced GH.Like the body’s pure GHRH. Whereas Ipamorelin works on the level of the stomach to help increase development hormone. Quite than introducing external growth hormone (GH), sermorelin stimulates the pituitary gland to release GH, thereby selling balanced hormone ranges.
If a clinician proposes ipamorelin, ask about actual sourcing, batch testing, documentation, and monitoring plans—including IGF-1 targets and glucose surveillance. When administered IV in postoperative sufferers, ipamorelin was generally properly tolerated but didn’t persistently speed up return of bowel function. Outside inpatient settings, GI signs are usually gentle however warrant dose reassessment if persistent. Transient nausea, headache, flushing, lightheadedness, or injection-site irritation might happen.
Notably, a research printed within the Journal of Endocrinology demonstrated that subjects supplementing with these peptides exhibited elevated ranges of IGF-1, a critical marker of muscle growth potential. The key benefit of Ipamorelin lies in its capacity to stimulate muscle growth, facilitate fat loss, and improve general well-being by promoting improved metabolism and mobile regeneration. Dr. Camp underscores that in contrast to synthetic hormones, Sermorelin Acetate and Ipamorelin immediate the body’s intrinsic production of progress hormone, leading to more enduring and harmonized hormone ranges. This approach not solely diminishes the probability of adverse results but also bolsters the body’s pure mechanisms, fostering extended health advantages for patients undergoing hormone remedy.
Two popular peptides, Sermorelin and Ipamorelin, are recognized to extend your growth hormone ranges and combat the signs of getting older. Using peptides can re-stimulate the manufacturing and release of progress hormone, serving to you preserve absolutely optimized health as you grow old. Sermorelin represents a man-made version of naturally occurring supplies which trigger pituitary gland cells to generate development hormone. four The medical remedy provides hormone deficiency remedy particularly for youngsters who cannot produce the required quantity of progress hormone for typical body development.
investsmarttoday – Useful insights and reliable content, keeps me coming back regularly.
successjourneyclub.shop – The content seems encouraging; good vibe overall.
The majority of Growth Hormone-deficient children responded to Sermorelin by catching up on growth. Sermorelin seems to be effective in slow-growing, shorter kids with delayed top and bone improvement. This entails that therapy and remedy are promising for growing youngsters as they attain full-grown maturity by way of their bodily attributes. Sermorelin triggers the pituitary gland to supply more pure development hormone, mimicking the body’s pure growth hormone regulation. This makes it particularly appropriate for people experiencing GH decline because of getting older. AOD-9604 is beloved by bodybuilders for its purported ability to speed up metabolism, burn cussed fats, and amp muscle growth by boosting human progress hormone and curbing insulin resistance (2).
Think About your body changing into a extra environment friendly machine, utilizing fats for power, which not solely trims you down but additionally boosts your endurance. You’ll probably notice your body composition altering, as you retain muscle however say goodbye to the undesirable fats. This jumpstarts fats metabolism and may reduce overall physique fats when combined with healthy consuming and train.
The secretagogue infusions were then started 10 to 18 days after the second leuprolide injection. A mixed evaluation discovered that the therapy with GHRP-2 led to a 47-fold increase in pulsatile GH secretion, whereas GHRH therapy itself solely led to a 20-fold enhance. Curiously, mixture of both GHRH and GHRP-2 led to a 54-fold increase in pulsatile GH secretion in comparability with controls. Moreover, GHS therapy decreased the time to maximal GH secretion with a median time reduction of 43%.
As with many peptides, there’s each benefits and dangers so make positive to see the dangers part below to grasp the professionals and the cons of sermorelin. Injection methods play a significant position within the effectiveness of Sermorelin dosage for females. Subcutaneous injections are generally most popular, and it’s essential to rotate injection websites to forestall tissue harm and guarantee absorption efficiency. Medzone Clinic is a world-class staff of professional and caring docs who specialize in the safe and efficient replacement of hormones for patients with deficiencies.
The pharmacological profiling indicated that, like GHRP-6, ipamorelin stimulates GH launch via a GHRP-like receptor 3, 4. Development Hormone (GH) performs a pivotal role in the stimulation of insulin-like progress issue (IGF-1) manufacturing inside the liver and varied other tissues. When GH binds to its receptors, it triggers the release of IGF-1, also called somatomedin C. IGF-1 acts as a mediator of GH’s results on progress and improvement, significantly in skeletal tissues and muscular tissues.
In truth, federal regulations prohibit the dishing out of development hormone for anti-aging or body-building functions. Utilizing sermorelin without a true medical need won’t flip back the clock; but it could pose dangers, like disrupting your hormone stability or inflicting unwanted effects unnecessarily. As A Outcome Of it’s designed to emulate the pure cycle of HGH production, it has been discovered to be significantly effective in treating “adult-onset” or “age-related” development hormone deficiency. When in comparison with conventional development hormone replacement remedy, sermorelin could be cheaper and has comparatively minor side effects.
Additionally, this peptide plays a vital position in supporting joint health by promoting collagen synthesis. CJC-1295/Ipamorelin is a synthetically produced peptide that may improve your plasma progress hormone (GH) levels. Initially, CJC-1295 was developed to treat illnesses and medical conditions for sufferers who had muscle disorders, and burn victims. The main objective of CJC-1295 is to boost protein synthesis levels and assist fuel the growth of muscle tissues within the physique.
The comparison of Tesamorelin vs. Sermorelin highlights how these peptides serve distinctive roles in peptide therapy. Tesamorelin’s focused motion on visceral fat and metabolic health makes it perfect for specific conditions, while Sermorelin’s broader GH help appeals to those in search of anti-aging and wellness advantages. Ipamorelin is a growth hormone-releasing peptide (GHRP) commonly used to stimulate muscle growth and improve post-workout recovery and metabolism (25). GHK-Cu, or copper peptides, are a combination of tripeptide Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine and copper ions.
References:
https://stevewpalmer.uk/andrewseely051
Estou completamente apaixonado por Brazino Casino, parece um abismo de adrenalina subaquatica. O leque do cassino e um recife de delicias. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que brilham como aguas cristalinas. O servico e confiavel como uma ancora. respondendo rapido como uma onda quebrando. Os saques sao velozes como um mergulho. as vezes mais giros gratis seriam subaquaticos. No fim das contas, Brazino Casino promete uma diversao que e uma mare para quem curte apostar com estilo aquatico! Vale dizer o design e fluido como uma onda. criando uma experiencia de cassino subaquatica.
brazino777 plataforma|
oneillforda – The campaign tone feels sincere, visuals and message align strongly.
Acho simplesmente animal SambaSlots Casino, parece uma festa carioca cheia de energia. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e cheias de swing, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com muito charme. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um passista, respondendo mais rapido que um tamborim. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que botam pra quebrar. No geral, SambaSlots Casino e um cassino online que e uma festa de diversao para os folioes do cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
la sambaslots casino code bonus|
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von JackpotPiraten Casino, es hat eine Spielstimmung, die alles sprengt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echter Jackpot, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen mitrei?en. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Piratenschiff, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Wellengang, ab und zu mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein Volltreffer. Insgesamt ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Meere beherrscht fur Abenteurer im Casino! Extra das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Volltreffer, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
jackpotpiraten bewertung|
As A Result Of the body retains control, sermorelin remedy is totally different from direct HGH administration. The Peptide Report () is a complete useful resource promoting evidence-based healthcare practices. Whereas the data offered on this web site is meant for educational and research functions, it is very important understand the limitations and applicable use of the content material. • The Peptide Report and its linked sources provides details about healthcare interventions, treatments and research procedures. This information includes any referenced scientific or clinical research.
To keep away from bruising and soreness, it’s best to vary the location of the injection website. Click On here to read how Nick went from struggling pre-diabetic, to collegiate rugby nationwide champion. Do some analysis, and you’ll discover every kind of peptide stacks online. Semax will increase BDNF and helps neuroplasticity for improved focus and reminiscence, whereas Selank modulates GABA and serotonin to scale back stress with out sedation. BPC-157 works instantly at damage websites to stimulate blood vessel formation and tissue restore, whereas TB-500 enhances mobile migration and actin production systemically.
Study benefits, drawbacks, and prices to decide which treatment most closely fits your well being objectives. Most people start noticing delicate changes — like higher sleep and power — inside 2 to four weeks. More visible benefits (fat loss, muscle tone) usually appear after eight to 12 weeks. If you’re using sermorelin to help a weight reduction plan, improve efficiency, or manage age-related hormone decline, inconsistency can delay your progress — or worse, reverse your positive aspects. Stopping and starting too often might require restarting your dosing cycle altogether.
Bounce into this stack with data and precision, and your bodybuilding journey may hit new peaks. The Sermorelin Ipamorelin mix contributes to the enhancement of sleep high quality via the regulation of development hormone levels, which play a pivotal position in sleep cycles and total restfulness. Additionally, Sermorelin supports weight reduction by heightening metabolism and encouraging fat burning.
At All Times seek the advice of a peptide-knowledgeable healthcare provider earlier than starting any new therapy. A 2006 study published within the Journal of Medical Endocrinology demonstrated that CJC-1295 administration considerably elevated growth hormone levels for up to 6 days. The Sermorelin-Ipamorelin-CJC-1295 trio is the gold standard for bodybuilders. This mixture maximizes muscle progress while minimizing injection frequency. Sermorelin is a GHRH analog that immediately stimulates development hormone launch. It activates receptors in your pituitary gland to extend HGH manufacturing.
If you know peptides, but are hesitant about how to combine them safely and effectively… you’re in the right place. Measure resting coronary heart rate and morning weight three days per week. Evaluation your log every month and regulate coaching quantity or steps. Late heavy meals, brilliant screens, or alcohol blunt slow wave sleep. A fastened bedtime, a darkish room, and a 60 to ninety minute wind down window protect your pulses and your outcomes.
Sermorelin is likely certainly one of the most widely used progress hormone–releasing peptides, favored for its capacity to securely and naturally enhance your body’s personal growth hormone (GH) manufacturing. But similar to any performance-enhancing protocol, dosage is every thing. Most sufferers begin to see preliminary indicators of improvement inside 3 to 6 weeks of sermorelin therapy, but important outcomes often turn into extra noticeable after 3 to six months of consistent use. Individuals reply in a special way to sermorelin remedy; components similar to age, way of life, and overall health can affect how shortly modifications appear.
The obtainable analysis has investigated the load loss potential of sermorelin in doses starting from 1-2mg/daily 13. Somewhat than administering HGH directly, researchers can use https://git.malls.iformall.com/marquitaharold/2864sermorelin-ipamorelin-cjc1295-dosage/wiki/Ipamorelin-Vs-Sermorelin%3A-Which-Peptide-Therapy-Is-Right%3F to increase HGH ranges in take a look at subjects by naturally stimulating the pituitary gland to launch extra endogenous HGH. As A Substitute of spiking HGH to supraphysiological levels, sermorelin is believed to supply a gradual improve in HGH in a steady, predictable means.
The injections are sometimes given within the evening to reflect the body’s pure development hormone production, which is typically highest throughout sleep. Your healthcare supplier will guide you on the right dosage and injection method for your needs. At Tulsi Wellness Club in San Diego, we’re dedicated to helping you obtain optimal well being via advanced therapies and personalized care. One of the most talked-about peptide mixtures lately is CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin. These peptides have gained reputation for their potential to boost growth hormone ranges, support muscle growth, help in fat loss, and improve total vitality. Sermorelin triggers growth hormone release, and the liver converts it into IGF-1. Over weeks and months, IGF-1 supports fats loss, increased muscle tone, and enhanced restoration.
online bet promotions Bet Promo Code “Bet promo code” pertains to codes that help gamblers access and take advantage of online advantages and promotions. These provide the gambler, whether a new gambler, or pre-existing customer, an opportunity to gain rewards, bet credits, no deposit gambles, or other promotions. To stay in the game, betting platforms provide incentives constantly to hold clients, so it’s crucial to be on the eye for new promos, but to scrutinize the details involved. It’s important any bet limitations or total amount required, as well as deadlines to take part in gambling, are scrutinized ahead of taking the plunge.
brightmarketplace – Great deals and variety, found exactly what I needed today.
justvotenoon2 – Really enjoyed reading this, very helpful info for beginners here.
smartbuytoday – Excellent value for money, definitely my go-to marketplace now.
classytrendstore – This site has become my favorite for online fashion shopping.
bestdealcorner – Fast shipping and excellent customer service, highly recommend shopping here.
All The Time consult with a healthcare provider to find out one of the best peptide on your wants and ensure safe usage. Sermorelin, however, is an artificial model of development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). It stimulates the pituitary gland to naturally produce and launch GH, working closely with the body’s biological rhythms. Sermorelin is usually seen as a safer alternative to direct GH injections.
In preclinical and translational work, ghrelin agonism has demonstrated effects on urge for food, gastric motility, and physique weight regulation. Ipamorelin specifically has proven promotility and feeding results in animals and selective GH release with out the ACTH/cortisol rises famous with some older peptides. These findings assist ongoing exploration in postoperative ileus, cachexia, and other conditions the place urge for food and intestine motility are impaired. Ipamorelin, on the opposite hand, has by no means acquired FDA approval, and its capacity to stimulate development hormone (GH) launch has been demonstrated only in animal studies. This implies that less is thought about its potential impression on human well being and this could possibly be a factor for risk-averse researchers. The lack of data in this area indicates that additional experimentation is warranted with each sermorelin and a sermorelin-ipamorelin mix.
The Sermorelin Ipamorelin mix presents a diverse range of health advantages, encompassing muscle development, weight reduction, enhanced bone density, expedited therapeutic, and sturdy anti-aging properties. Consequently, it stands as a potent therapeutic routine throughout the area of peptide treatments. In principle, stacking permits synergistic pathways (e.g. development hormone release + tissue restore + metabolic enhancement) to work together. However because many uses are off-label or experimental, understanding tips on how to stack safely and successfully is critical.
Ipamorelin can be the most effective for women and men when used over time due to its capability to by no means disturb the bodies pure production of hGH. You can take 300 mcg of sermorelin or ipamorelin injections per day. Sermorelin stimulates the brain to launch GHRH for about minutes, whereas ipamorelin and cjc-1295/ipamorelin stimulate GHRH release for up to half-hour.
Analysis peptides are quick chains of amino acids that are linked by peptide bonds. They vary from between two and fifty amino acids in size and fall underneath many various classes. Some peptides are isolated from natural sources and a few are made artificially. Common unwanted side effects embrace injection site reactions, flushing, headache, or dizziness. In this section you will see good pairings that enhance outcomes and maintain safety first. You will also see what to keep away from so your sleep and hormone rhythm stay strong.
Ipamorelin tends to work extra quickly, while sermorelin offers a slower, extra gradual strategy. Ipamorelin offers fast, direct stimulation of progress hormone with minimal impact on different hormones like cortisol. CJC 1295 works extra gradually by stimulating your pure progress hormone production over a longer period. Some individuals select to combine each for more sustained and enhanced results, especially in anti-aging and muscle-building protocols.
Sermorelin Acetate is an artificial peptide designed to copy the physiological results of the endogenous development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). By triggering the pituitary gland to secrete growth hormone, Sermorelin Acetate serves as a therapeutic agent with vital functions throughout varied medical domains. Its approval by the FDA for the remedy of development hormone deficiency in both pediatric and adult populations underscores its scientific relevance. While athletes typically use growth hormone secretagogues like CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin, peptide remedy can even benefit anybody experiencing low energy, poor sleep, or slower restoration.
As A Result Of ipamorelin and other GH secretagogues can alter anabolic signaling, they fall underneath prohibited classes for athletes. Banned-substance lists are updated yearly; ipamorelin has been particularly named among prohibited development hormone secretagogues, and violations can carry multiyear sanctions. As A Result Of ipamorelin reliably will increase GH (and often IGF-1 downstream), it might affect lean mass accrual, recovery from catabolic stress, bone turnover, sleep structure, and urge for food. The quick half-life and receptor selectivity also make it an appealing device to check GH pulses with out chronically elevating cortisol or prolactin. In 2014, ipamorelin was briefly investigated in part II scientific trials for the remedy of postoperative ileus 13. These trials have been discontinued as a result of the “clinical endpoints didn’t attain statistical significance when comparing ipamorelin to placebo” 5. Nonetheless, information from this examine indicated that ipamorelin therapy may shorten the restoration instances of patients undergoing open laparotomy 14.
You can discover high-quality analysis compounds just like the Semax Amidate cognitive analysis compound at Real Peptides to help neuro-focused investigations. However, it’s important to understand that while it’s going to improve your degree of growth hormone, sermorelin remedy is not a fast fix. The therapy works by progressively rising the release of growth hormone, permitting your body the time it wants to adjust to the elevated manufacturing of HGH. Most sufferers experience delicate, progressive modifications over weeks and months as the release of development hormone will increase. Typically, it could take several months for age-related signs to disappear and the total effects of https://smartcampus-seskoal.id/streaming/@kentspurlock81?page=about to turn into apparent, so endurance is crucial. Sermorelin is a prescription medicine administered via subcutaneous injections that is indicated for the remedy of development hormone deficiency (GHD). It is protected, effective, and, in lots of circumstances, a more cost-effective various to progress hormone alternative injections.
It is always advisable to work with a healthcare supplier to find out probably the most applicable dosage and therapy plan in your needs. At Higher U, we work closely with our shoppers to make sure the safe and efficient use of Sermorelin remedy. This web site is a repository of publicly out there information and isn’t meant to form a physician-patient relationship with any particular person. The info presented on this web site is not meant to take the place of your personal physician’s advice and isn’t supposed to diagnose, treat, cure, or forestall any illness. Discuss this information with your own physician or healthcare supplier to determine what’s right for you.
oneillforda – The campaign tone feels sincere, visuals and message align strongly.
When administered IV in postoperative patients, ipamorelin was typically properly tolerated but didn’t constantly speed up return of bowel function. Exterior inpatient settings, GI symptoms are usually mild but warrant dose reassessment if persistent. Repeated secretagogue-induced pulses can nudge fasting glucose or impair glucose tolerance in vulnerable individuals. Those with prediabetes or diabetes may see greater post-dose glucose readings or want treatment adjustments beneath medical care.
Ipamorelin’s capability to spice up these levels can counteract this decline, probably accelerating fat loss by as much as 20%. Dosing Ipamorelin accurately is the cornerstone of a profitable peptide routine. All The Time supply lab-tested Ipamorelin from respected suppliers and consult with a healthcare skilled before beginning any new peptide cycle. For detailed dosing instruments and high-purity peptides, visit PeptidesPower.com.
Alone, both has been proven effective in treating adults with low-level GHD. There can also be current research that since they do impact totally different receptor websites in different methods, there could be some benefits available in combining the two therapies. They are each long chain peptides that mainly differ only in the number and make-up of amino acids within the chains. It is imperative to offer patients with complete schooling concerning the correct administration methods and any warning indicators to be vigilant for in the course of the therapy regimen. Regular evaluations of the patient’s very important signs, similar to blood stress and coronary heart rate, are crucial for the detection of potential side effects.
Ipamorelin specifically has shown promotility and feeding effects in animals and selective GH release with out the ACTH/cortisol rises noted with some older peptides. These findings support ongoing exploration in postoperative ileus, cachexia, and different conditions where urge for food and gut motility are impaired. In managed research, ipamorelin produced GH peaks within roughly an hour of dosing, then ranges declined quickly as the drug cleared. The half-life is brief (around two hours in human PK models), which is why researchers typically dose as soon as every day to a quantity of times per day when finding out repeated pulses. Ipamorelin, an artificial pentapeptide, works by stimulating the discharge of growth hormone in athletes, which in flip aids in quickening the restore of damaged muscle tissues. This peptide not only addresses bodily fatigue but additionally assists in mental restoration, bettering cognitive function and focus. Plus its fat-burning effects, Ipamorelin also helps protect lean muscle mass.
This delays the getting older process of an individual and makes you look younger and extra energetic with higher collagen production for glowing skin, healthier nails, and dense hair. Rodent and human studies have shown that development hormone-releasing hormone injections lower wakefulness and improve slow-wave sleep (SWS) (6). For bodybuilders specifically combining Ipamorelin with CJC-1295 (a frequent peptide stack), the ideal dosage is reported to be 300 mcg of Ipamorelin and 250 mcg of CJC-1295 per day.
Under, the primary doses utilized in previous sermorelin studies are highlighted together with any common guidance that researchers may need to remember of. Researchers interested in working with sermorelin may use this sermorelin dosage information through the design and planning phases of the research process. Development hormone is launched in a sequence of spurts or pulses all through the day. These pulses, which peak in the evening, promote sleep, therapeutic, exercise recovery, and mobile regeneration.
Ipamorelin research are lacking total and this merits further analysis, but what limited data exists suggests that ipamorelin offers some promising benefits within the area of physique composition and restoration charges. This content material is academic and does not replace customized medical advice. Do not start, stop, or change any medicine or peptide with out consulting a certified clinician who can evaluate your medical historical past, monitor labs, and talk about legal issues. If you’re an athlete topic to anti-doping guidelines, ipamorelin is prohibited always. Ipamorelin just isn’t an FDA-approved therapy for anti-aging, efficiency, or basic wellness. In many countries it sits in a gray zone where analysis use may be permitted but industrial advertising is restricted.
Outdoors regulated channels, product variability is a serious limiter. Efficiency, sterility, and excipient variations result in inconsistent responses and safety dangers. If a affected person is enrolled in a reliable clinical research or working inside strict medical oversight, batch verification and documentation scale back, but don’t eliminate, these considerations. Think of ipamorelin as a GH-pulse amplifier with a short window of motion. With Out the best inputs—adequate protein, resistance coaching, sufficient sleep, and appropriate timing—its signal might not translate into significant diversifications.
References:
https://tubex.su/@fqvchester438?page=about
everydayvaluefinds.shop – Navigation is simple, everything loads nicely — good experience.
modernvisionlab.shop – The photos are nice quality, helps in deciding if to buy.
dailyprofitupdate – Browsing here was smooth; product descriptions are clear and helpful.
Both Ipamorelin and sermorelin work well for people with development hormone deficiency or comparable symptoms. However these peptides may actually assist those who want higher muscle development, fats loss plus improved sleep high quality. The compounds may also enhance vitality ranges in addition to skin look. Sermorelin works by stimulating your body’s natural development hormone production. The before and after adjustments reflect steady features in sleep, vitality, fat loss, and muscle tone. With medical supervision and a focused plan, you can flip small weekly wins into big adjustments over six to 12 months. In a examine involving healthy male subjects, it was administered at five different infusion charges over 15 minutes 8.
When it comes to peptides that increase growth hormone levels, Ipamorelin and Sermorelin are two of the most well-liked options. Each are utilized in anti-aging therapies, athletic efficiency enhancement, and general wellness programs. Nonetheless, their mechanisms and advantages make them appropriate for different goals. Ipamorelin was included in the aforementioned review by Deepankar et al. of growth hormone secretagogues (GHS) in the fashionable management of physique composition in hypogonadal males.
Ipamorelin mimics ghrelin, which may help enhance growth hormone manufacturing, whereas Sermorelin is an artificial version of a Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone which might alleviate a development hormone deficiency. Both sermorelin and ipamorelin are usually well-tolerated when administered under medical supervision, however they’ll sometimes trigger side effects. For sermorelin, frequent reactions embrace injection web site irritation, complications, dizziness, or flushing. In uncommon instances, customers could expertise allergic reactions or adjustments in blood sugar levels.
Sermorelin is commonly seen as a safer alternative to direct GH injections. When it comes to hormone-related therapies, safety and monitoring are paramount. The excellent news is that when used accurately underneath medical supervision, GH peptide therapies have a wonderful security record. Research have not discovered elevated most cancers incidence from these peptides themselves; the main concern is that drastically elevating IGF-1 might theoretically influence an present malignancy. That’s why any history of cancer is an important dialogue together with your physician before starting remedy. A physician will also establish baseline IGF-1 levels and monitor them to ensure they keep in a wholesome range – personalization would possibly mean adjusting the peptide dose or regimen.
Regular lab testing and follow-ups guarantee your therapy continues to maneuver you toward your targets safely. Injecting too much Sermorelin can lead to unwanted side effects corresponding to headaches, nausea, or injection site irritation. Excessive dosing might disrupt natural hormone stability and cause unwanted signs, so adherence to prescribed amounts is necessary.
It is usually well-tolerated, with most unwanted facet effects being mild and temporary. Sufferers should be closely monitored for any opposed reactions, and dosages may be adjusted relying on particular person response and tolerance. Enhance sleep quality and hormone ranges – Ipamorelin and Sermorelin enhance sleep high quality, thus, rising vitality, enhancing temper and boosting general well-being. The utilization of these peptides in a controlled and monitored manner under the guidance of healthcare experts can help individuals achieve optimal results whereas minimizing potential dangers or unwanted side effects. By the end of this article, you will have a greater understanding of which peptide will be the proper choice for you. “Peptides are a pure extension of the work we already do in hormone and wellness medication,” said Wayne Wilson, Founder and CEO of SynergenX. “By expanding our peptide therapies we’re giving sufferers cutting-edge resources to get well, restore, and thrive to allow them to achieve s higher quality of life.”
Facet results are rare and gentle, including slight irritation at injection websites or momentary flushing. Ipamorelin is often most popular for sooner fat loss because of its strong lipolytic (fat-burning) properties, although Sermorelin additionally helps gradual fat reduction as part of its anti-aging effects. Whereas Sermorelin increases HGH naturally (more on that below) by binding on to hormone receptorsIpamorelin binds to ghrelin receptors. In adults, having insufficient progress hormones can result in depression, poor focus, and anxiety. It can also take its toll in your skin and overall well being, making it feel like you’re getting older quicker.
GLP-1 drugs corresponding to semaglutide or tirzepatide work by way of metabolic and appetite pathways, not development hormone pathways. Some patients could safely pair a GLP-1 with restorative peptides like Sermorelin or BPC-157 to take care of muscle tone and power while shedding weight. Some promote growth hormone release, others aid recovery or regulate urge for food. Combining them without skilled guidance can lead to conflicting results or undesirable unwanted effects. Be A Part Of the many sufferers who’ve skilled remarkable transformations underneath Dr. Kumar’s professional care—benefiting from customized peptide therapy plans tailored to your distinctive underlying well being circumstances and goals. Don’t accept standard therapies that solely masks symptoms; select evidence-based therapies that unlock your body’s true potential.
When you purchase cagrilintide peptide along with these GH secretagogues, you may be collaborating in research designed to optimize these metabolic outcomes. Actual Peptides ensures that every one our compounds, including the ipamorelin peptide, are of the purity required for these sensitive body composition analyses. Moreover, the ipamorelin peptide is thought for its excessive selectivity, avoiding the discharge of cortisol and prolactin. When researchers mix sermorelin and ipamorelin, they’re aiming to maintain this clean profile whereas reaching a better peak GH launch. The sermorelin ipamorelin mixture allows for a strong GH pulse with out introducing confounding stress hormones into the examine. This purity of sign is invaluable for long-term metabolic and physique composition research.
References:
https://git.obo.cash/waylonshowalte
modernvaluecorner – Will definitely shop here again; satisfied with my purchase.
stylemebetter – Excellent customer service; responses were prompt and informative.
Both peptides work by optimizing your body’s own development hormone manufacturing, not replacing it. Now, meet Ipamorelin—the powerhouse peptide with a slightly stronger edge. As A Substitute of mimicking GHRH, Ipamorelin works as a growth hormone secretagogue, binding to ghrelin receptors to instantly encourage GH launch from the pituitary gland. Most circumstances of development hormone deficiency usually are not properly understood.
The variations basically lie within the completely different hormone receptors they react with to stimulate HGH manufacturing and release. As A Result Of of these totally different receptors, they’ll stimulate different volumes of release, over different durations of time. The Peptide Report () is a comprehensive useful resource selling evidence-based healthcare practices. While the data supplied on this website is meant for educational and analysis purposes, it could be very important perceive the restrictions and acceptable use of the content.
It is important to conduct complete affected person evaluations previous to commencing remedy to determine the suitable dosage. After this evaluation, healthcare suppliers can meticulously decide the preliminary dosages of Sermorelin Acetate and Ipamorelin. As the remedy progresses, adjustments to the dosages may turn into necessary to optimize the therapy’s efficacy and reduce potential unwanted effects. Selecting between Ipamorelin and http://bot.61ns.com:3000/cliftonreinhar is determined by your specific targets and way of life. If you’re aiming for quick, focused results in performance and restoration, Ipamorelin is a good choice. For long-term well being optimization and anti-aging, Sermorelin offers a safer and extra natural approach. Always seek the assistance of with a healthcare provider to determine the best peptide for your needs and guarantee secure utilization.
In a study involving healthy male subjects, it was administered at 5 different infusion rates over 15 minutes 8. Nonetheless, the specific methodology of administration may differ relying on the person’s health condition and the advice of their healthcare supplier. The timing of Ipamorelin administration can rely upon the precise wants and circumstances of the person. For example, in a single research, it was injected subcutaneously three times every day for 15 days to research its effects on bone growth rate and physique weight 4. In another study, it was given as soon as daily for 12 weeks to assess its results on lean physique mass 6. However, it’s necessary to note that these are experimental settings and will indirectly translate to human use.
This process commences with a thorough patient analysis to gather vital data similar to medical history, current medications, and any underlying health situations. Protein synthesis improves when training is progressive and protein consumption is excessive. Over time, many see elevated muscle tone and muscle acquire with decreased body fat. If you want actual modifications in energy, restoration, sleep, and physique composition, sermorelin might help. Many adults ask if sermorelin can deliver these outcomes with out the dangers of direct HGH remedy.
Below are some components to contemplate when choosing between the 2 peptides. Since progress hormone-releasing peptides corresponding to sermorelin and ipamorelin act by stimulating receptors in the pituitary to launch HGH, they produce a more “natural” enhance in HGH degree. Moreover, Sermorelin supports weight loss by heightening metabolism and encouraging fats burning. Enhanced bone density is another important benefit, as development hormone aids in sustaining bone well being and reducing fracture dangers. Sermorelin Acetate, through its mimicry of the pure progress hormone-releasing hormone, stimulates the pituitary gland to synthesize and release endogenous development hormone.
In theory, stacking allows synergistic pathways (e.g. growth hormone launch + tissue repair + metabolic enhancement) to work together. However as a outcome of many makes use of are off-label or experimental, understanding tips on how to stack safely and successfully is important. This information will walk you thru what peptides are, how stacking works, sensible examples, security considerations, and tips on how to build a personalized stack. Small proof-of-concept trials evaluated intravenous ipamorelin for postoperative ileus after bowel surgery. Pharmacokinetic research in healthy volunteers mapped dose–response relationships for GH release and confirmed the brief, pulse-like effect.
As A Outcome Of the body retains management, sermorelin remedy is totally different from direct HGH administration. Growth hormone helps physique composition, recovery, and wholesome aging. It helps the liver make IGF-1, which drives muscle growth and fats metabolism. Poor sleep, high stress, and extra body fat can lower progress hormone levels additional. Elevating progress hormone ranges can enhance power, cognitive operate, and immune perform. It can even assist collagen manufacturing, skin elasticity, bone health, and overall wellness. Sermorelin therapy aims to restore a more healthy development hormone rhythm somewhat than override it.
Semax increases BDNF and supports neuroplasticity for improved focus and reminiscence, while Selank modulates GABA and serotonin to scale back stress with out sedation. BPC-157 works directly at harm sites to stimulate blood vessel formation and tissue repair, while TB-500 enhances cellular migration and actin manufacturing systemically. You’ll stroll away with newbie stacks, superior combos, safety logic, common stack dosages, and the way to do it the right means.
Its approval by the FDA for the treatment of growth hormone deficiency in both pediatric and adult populations underscores its clinical relevance. Yes, combining Ipamorelin and Sermorelin can provide synergistic results by enhancing the body’s natural growth hormone production while maintaining hormonal steadiness. Sermorelin, then again, is an artificial version of development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). It stimulates the pituitary gland to naturally produce and release GH, working closely with the body’s biological rhythms.
Estou totalmente fascinado por PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura pulsante. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com slots de design inovador. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. As transacoes sao confiaveis, contudo mais rodadas gratis seriam um diferencial. Para finalizar, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Vale destacar a interface e fluida e estilosa, facilita uma imersao total. Muito atrativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
https://playpixcasino.pro/|
buildlastingtrust.shop – Found tips and resources that seem useful and actionable.
Tenho uma paixao vibrante por BETesporte Casino, sinto um rugido de emocao. A variedade de titulos e impressionante, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, no entanto bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e vibrante, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Igualmente impressionante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Saiba mais|
findyourlook.shop – Loved how they show multiple angles, helps in choosing better.
nextgenproject.shop – The site seems built for forward thinkers and creators.
modernwoodcases – Great variety of styles; perfect for expressing individuality.
trendhunterplace – Very informative posts, I learned a lot just browsing around.
purebeautyoutlet – Felt safe using site, SSL works fine and site is professional.
The contents of Peptides.org are intended completely for certified researchers. Any particular person seeking any advice on any prescription treatment, or any disease or condition, is advised to refrain from utilizing this web site and consult their healthcare provider. Statements concerning products presented on Peptides.org are the opinions of the individuals making them and usually are not necessarily the identical as those of Peptides.org. As a result, CJC-1295 also appears to have a greater GH and IGF-1 stimulating capacity, as measured in take a look at subjects.
Peptide therapy is revolutionizing how bodybuilders boost progress hormone naturally. Sermorelin and Ipamorelin lead this development as the most secure, most effective HGH-releasing peptides. In Distinction To artificial HGH injections, these stimulate your body’s own production with minimal side effects. They’re changing into essential instruments for severe lifters seeking higher recovery, muscle growth, and fats loss with out hormone disruption. Sermorelin provides its own set of benefits for people seeking to boost growth hormone ranges.
Research funding concerns hardly ever embody protection for these compounds, as they’re typically categorized as investigational quite than standard analysis instruments. Pricing varies significantly by provider, concentration requirements, and geographic location, with sermorelin typically representing the more economical choice for extended research protocols. Earlier Than using CJC 1295 in analysis or scientific settings, you will want to seek the guidance of a healthcare professional to make sure protected and efficient use, proper monitoring, and applicable dosing. Medzone Clinic is a world-class staff of skilled and caring medical doctors who specialize within the protected and efficient substitute of hormones for sufferers with deficiencies. As you can most likely see, the potential advantages of Peptide Remedy far outweigh the unwanted aspect effects.
Critically, this brief e-book will prevent plenty of wasted cash and poorly hung out (not to say preventing you from potential self-inflicted injuries). Eating an insulin managed food plan whereas participating in regular exercise, along with taking both Ipamorelin or Sermorelin, will certainly allow you to experience optimum results over time. Outcomes may range, but you can see and experience the well being advantages inside 3 to 6 months of constantly taking them at these dosages. Since HGH secretion happens at night time, your diet and stress can hinder its release, lowering its advantages. On the other hand, ipamorelin works by mimicking ghrelin actions within the physique. Ipamorelin is best administered subcutaneously because it stimulates GHRH release for as a lot as half-hour. Co-administration of minimal (10 ng) effective doses of GH with minimum (25 ng) or most (100 ng) effective doses of oLH significantly decreased testosterone secretion.
Choosing the right peptide depends on your targets, preferences, and regulatory issues. Avoid buying peptides from unverified or suspicious sources to attenuate risks. Perceive the legal standing of these peptides in your area or nation. Rules can differ, and compliance is important to avoid legal points. Prolonged and unsupervised use could result in undesirable side effects or exacerbate underlying health conditions. Reports indicate enhancements in reminiscence, concentration, and general psychological acuity among these undergoing Sermorelin therapy 6. One Other notable application of CJC 1295 is in the realm of recovery.
Treatment with human progress hormone didn’t significantly affect serum immunoglobulins, polymorphonuclear cell function, or percent T cells. Ipamorelin is taken into account one of the most secure and handiest types of growth hormone replacement therapy, because it doesn’t have an result on the discharge of aldosterone, acetylcholine, prolactin, or cortisol in the body. Sermorelin, also referred to as sermorelin acetate, is a peptide analog of the human development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH).
Monitoring fasting glucose, HbA1c, and (when appropriate) IGF-1 helps detect undesirable developments. Outside regulated channels, product variability is a significant limiter. Efficiency, sterility, and excipient differences result in inconsistent responses and safety risks.
Through its action on HGH release, Sermorelin promotes the expansion and restore of muscle tissues. These results contribute to an general sense of well-being, making CJC 1295 interesting to people who seek an improved high quality of life and enhanced daily functioning. High-quality sleep is important for general health and well-being, and it could possibly result in improved cognitive function, enhanced mood, and better physical recovery. GHRH controls the secretion of human growth hormone (HGH) from the pituitary gland. This peptide is a modified model of development hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) and capabilities by activating the pituitary gland to launch more HGH into the bloodstream. It can promote muscle growth, reduce body fat, and accelerate recovery from injuries. Moreover, CJC 1295 has been explored for its potential anti-aging effects and its capability to boost total well-being.
CJC 1295 and Sermorelin are powerful peptides designed to boost human growth hormone, promising benefits like elevated muscle mass, fat loss, and a youthful look. Sermorelin is a synthetic peptide consisting of 29 amino acids, designed to stimulate the body’s pure manufacturing of human development hormone (HGH). Continued research protocols document enhancements in physique composition, together with muscle progress and fat loss, changing into evident after a number of months of research.
References:
https://git.maiasoft.jp/kmhbebe0842228
yourtradingmentor – This site is highly recommended for anyone serious about trading education.
trendinggiftcorner – Really practical ideas for gifts, saved me lots of time.
smarttradingmentor – Loved the step-by-step instructions, very easy to follow and understand.
At the same time, it controls the amount of a development hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH), known as somatostatin, which downregulates pituitary GH secretion. By suppressing the body’s somatostatin ranges, ipamorelin will increase ranges of GH in take a look at subjects 4. A GHS is a type of peptide that promotes the body to supply development hormone (GH) also referred to as human growth hormone (hGH). https://www.appleradish.org/desmonddyke737 binds to the same receptors as ghrelin (GHSR-1a receptors) and will increase ranges of GH and IGF-1 2. Scientific studies support the significance of looking for expert session before embarking on peptide therapy, citing improved safety and efficacy outcomes in individuals who obtain personalized steering.
If you have extra inquiries later, you’ll be able to simply find me on your \”My Questions\” page by score our interaction. If you might have further inquiries later, you’ll find a way to simply locate me on your “My Questions” web page by score our interplay. This on/off approach helps prevent diminishing returns and maintains the efficacy of the peptide over longer durations. Sermorelin stimulates your physique to make its personal HGH, whereas injectable HGH bypasses your pituitary gland totally. This makes Sermorelin safer, extra pure, and simpler to regulate for long-term use. These usually subside inside a quantity of days or with slight dose discount.
This water have to be gently swirled around the vial till all of the powder is dissolved. Below, the main doses used in previous sermorelin studies are highlighted along with any general steerage that researchers may have to focus on. Researchers interested in working with sermorelin could use this sermorelin dosage information during the design and planning phases of the analysis course of.
It’s necessary to monitor your progress through routine lab testing and follow-up consultations to make sure your dosage stays optimum. Long-term protocols often embrace biking to avoid desensitization and preserve effectiveness. Sermorelin is typically injected subcutaneously — slightly below the pores and skin — using an insulin syringe. Improper technique, injecting too regularly in the identical space, or utilizing a dull needle can cause redness, swelling, itching, or bruising on the injection web site. While mild irritation is widespread, rotating injection spots and utilizing clear, sharp syringes helps scale back these results. In terms of timing, sermorelin has been administered to test subjects at night, no less than two hours after the last meal for the day.
As a selective development hormone secretagogue, it stimulates the pituitary gland to release development hormone with out significantly affecting cortisol or prolactin levels. The mechanism of action of this potent mixture entails the activation of growth hormone release, thereby enhancing the body’s capability for environment friendly protein synthesis to facilitate muscle restore and growth. Analysis signifies that individuals utilizing the Sermorelin Ipamorelin mix observe a significant enhance in muscle mass and power. Notably, a research printed in the Journal of Endocrinology demonstrated that subjects supplementing with these peptides exhibited elevated ranges of IGF-1, a crucial marker of muscle development potential. Proper dosage steering is essential, typically beginning with lower doses and progressively increasing primarily based on individual response and monitoring of IGF-1 ranges. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to find out the appropriate dosage and frequency for each individual, as overuse might result in opposed effects.
To gently nudge your pituitary gland into producing and releasing extra of your personal human development hormone (HGH) — rather than supplying HGH immediately by way of injections. The obtainable studies thus far have researched the potential of sermorelin for increasing muscle mass at doses ranging from 1-2mg, administered a few times day by day 13. When sermorelin held FDA approval as a therapy for short stature in kids, it was administered as a subcutaneous injection, in doses of 30mcg per kg of physique weight 1. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for the remedy of progress hormone deficiency (GHD) in youngster and adult patients. It was out there underneath the commerce name “Geref” and was additionally used as a diagnostic agent to examine pituitary gland operate. Sermorelin works by binding to the growth hormone releasing hormone receptor (or GHRHr) within the anterior a half of the pituitary gland. There, it really works to stimulate higher manufacturing of GH, thereby growing the manufacturing of endogenous IGF-1 as properly.
The increased energy ensuing from the blend’s effects interprets to larger resistance levels throughout training, enabling customers to push their limits and achieve higher features. Working with a healthcare provider ensures accurate dosing, monitoring for unwanted side effects, and protected, effective remedy tailored to your needs. No, Ipamorelin is understood for not growing cortisol ranges, which sets it other than other progress hormone-releasing peptides.
Ipamorelin stands out as a potent pentapeptide (Aib-His-D-2-Nal-D-Phe-Lys-NH2) with remarkable development hormone (GH)-releasing properties, each in vitro and in vivo. This selective development hormone-releasing peptide has garnered attention as a promising solution for feminine fats loss. For the profitable therapy of Sermorelin Acetate and Ipamorelin, adherence to prescribed dosages, maintenance of a wholesome life-style, and routine monitoring of hormone levels are crucial. Ipamorelin is a selective growth hormone secretagogue peptide recognized for its capability to stimulate the release of development hormone whereas having minimal impression on cortisol or prolactin levels. Sure, sermorelin is often stacked with peptides like ipamorelin or BPC-157 for enhanced results. Whether you’re beginning sermorelin injections for anti-aging, restoration, or efficiency, we’ll match you with a plan that fits your objectives and adjusts along with your progress. Lacking one dose of sermorelin isn’t often an enormous deal — but frequent lapses can disrupt your results and throw your hormone balance off monitor.
Sermorelin, an artificial analog of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), is usually prescribed to stimulate natural growth hormone (GH) manufacturing in individuals with suboptimal ranges. While it’s not a one-size-fits-all remedy, understanding the appropriate sermorelin dosage is crucial for safe and effective use. Sermorelin works by stimulating your body’s pure development hormone manufacturing. The earlier than and after modifications mirror regular positive aspects in sleep, energy, fats loss, and muscle tone. With medical supervision and a targeted plan, you presumably can turn small weekly wins into big modifications over six to twelve months. Patients sometimes receive Sermorelin via subcutaneous injections, often before bedtime to mimic the body’s pure hormonal release patterns during sleep. Appropriate candidates for Sermorelin remedy usually exhibit indicators of progress hormone deficiency, such as fatigue, decreased muscle mass, and lowered train capacity.
All of our content is written by individuals with a powerful science background, together with medical researchers. Peptides have modified the means in which we take into consideration regenerative medication and how we optimize health and slow down the aging course of. Finding the right supplier to guide you to success has by no means been extra important. While Ipamorelin is considered to have a comparatively favorable safety profile compared to different peptides, several necessary considerations ought to information its use in bodybuilding contexts. With a brief half-life of about 2 hours, Ipamorelin requires multiple day by day doses for finest results in bodybuilding. The precise dosage may range based on individual patient factors and physician guidance.
newhorizonsnetwork.bond – Already bookmarking to check for updates — feels inspiring.
musionet – Clean design and responsive layout, love using this website.
protraderacademy – Really impressed with the quality of lessons and tips shared here.
fastgrowthsignal – Customer service seems responsive, descriptions clear, overall trust builds fast.
tradingmasterclass – Clear explanations and practical strategies, very useful for beginners and experts.
brightfuturegroup.shop – Good mix of images and text, what I like in a site.
strongpartnershipnetwork – Practical strategies and useful recommendations, saves time and effort today.
halbzeit wetten
my homepage … wettrechner Kombiwette
ultimateprofitplan – Valuable strategies for improving team performance and business efficiency.
RA Securities – Thought-provoking article on the unseen defense in biosafety investments.
https://clocks-top.com/
Хочу аву с «неймар сантос фото»: важно, чтобы кадры были чёткие и подойдут для профилей. Неймар сейчас: форма, статус, тренировки — короткий апдейт помогает выбрать обои и тему. Собираю обои 4K и аватарки с аккуратным кропом под телефон. neymar-kg.com. Ищу «неймар красивые фото 2024» в стиле editorial — подскажите, какие фотосеты топ.
Ищу «неймар сантос 2011» в хорошем качестве — особенно финалы и кубковые игры. Неймар номер: на футболке в «Сантосе» и «Барселоне» — важные детали для коллекционеров. Когда «умер неймар» — кликбейт заголовки; нужны разборы, опровергающие фейки. Неймар сейчас в каком клубе — нужен короткий виджет для сайдбара.
Где найти «неймар сантос фото» в HQ, не из соцсетей с пережатием? Неймар Сантоc фото — ранние годы вдохновляют молодых вингеров на тренировки.
virtual broadcast
Новости спорта онлайн http://sportsat.ru футбол, хоккей, бокс, теннис, баскетбол и другие виды спорта. Результаты матчей, обзоры, интервью, аналитика и главные события дня в мире спорта.
webtide.click – The color scheme is subtle and pleasant, not too harsh on the eyes.
nextbigthing.bond – Exciting name! Feeling curious what new opportunities await here.
keywordorbit.click – Found useful links already; seems like a solid resource worth revisiting.
rankforge.click – The color scheme is pleasant and doesn’t distract from the content.
seoloom.click – Pages load quickly and visually everything feels sleek and professional.
trafficpulse.click – Visuals complement the text nicely; the design feels polished and thought-out.
paris sportif foot pronostics du foot
nextleveltrading – A must-visit for anyone interested in trading, very informative.
connectforprogress – Impressed by the impact of Israeli technology on local challenges.
online sportwetten legal
Here is my site wetten bonus code (Oliver)
betting sign up promos Betting Promo “Betting promo” offers a reward if it includes gambling action on the web to get rewards for the wagers . Rewards and quick benefit programs increase the gamblers account regularly for gambling with online games. Websites will make new clients so they will improve earnings to take part in bonuses set up for online action for sports. If you will generate income for gambling, and you monitor offers to improve your bank and chances to earn, sports could be your thing.
marketanalysiszone – This will be one of my go-to sources for market commentary now.
forexstrategyguide – Excellent course for scaling businesses, practical tips and strategies.
https://ibs2site.at
classyhomegoods – The website is easy to browse and items look high quality.
teamworksuccesspath – The user experience is good and the advice feels credible and helpful.
successnetworkgroup – Site is clean, navigation worked smoothly and found good resources quickly.
globalchoicehub – Variety of products I hadn’t seen elsewhere — nice discovery.
shopandshine – Loved the product range, found unique pieces I’ve not seen elsewhere.
shopwithsmile – Fast website load and straightforward shopping experience overall.
visionpartnersclub – Easy to navigate and quick checkout, very user-friendly website.
ultimateprofitplan – Practical exercises that can be implemented immediately for better results.
shoplocaltrend – Impressed with the packaging and timely delivery, will shop again.
futuregrowthteam – Great deals and variety, found exactly what I needed today.
yourtradingmentor – Helpful resources and tools that feel relevant to real market conditions.
bestforexstrategies – Very interesting site, found some fresh ideas for trading I’ll try soon.
successfultradersclub – Some of the methods seem advanced, great resource if you’ve got experience trading.
nextleveltrading – Found some useful tools here, very impressed with the content quality.
everydaytrendshop – Smooth browsing and secure payment options, very trustworthy site.
uniquedecorstore – Helpful product descriptions and strong visuals made decision-making easier.
strongfoundation – The team behind this appears professional and attentive to details.
trendandstyle – Easy shopping experience, fast checkout and smooth navigation.
strongpartnershipnetwork – Easy to follow tips and strategies, really improved my approach.
smartbuytoday – Excellent shopping platform, lots of smart deals and easy navigation.
learnandtrade – Well-structured content, made complex concepts easy to understand.
simplelivinghub – Quality content with heart, feels like advice from a friend.
globalmarketinsight – Great resource for market trends, found fresh insights today.
freshstylemarket – Trendy styles at great prices, found exactly what I needed.
Ich bin total begeistert von PlayJango Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Wirbelsturm tobt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein funkelnder Ozean, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und strahlend, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Donnerschlag. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein Sonnenstrahl, aber mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Am Ende ist PlayJango Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Extra das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Spektakel, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
playjango casino login|
Estou completamente apaixonado por BR4Bet Casino, vibra como um farol em alto-mar. A colecao e um facho de diversao. com slots tematicos de aventuras radiantes. Os agentes voam como claroes. oferecendo respostas claras como um farol. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma lanterna. mas mais recompensas fariam o coracao brilhar. Resumindo, BR4Bet Casino e um cassino online que e um farol de diversao para os exploradores de jogos online! Como extra a interface e fluida e brilha como um farol. dando vontade de voltar como uma chama eterna.
plataforma br4bet|
metaboost.click – On mobile it adapts smoothly—everything fits and looks good.
seowhale.click – I’m bookmarking this—looks like a resource worth revisiting later.
wettquoten dfb pokal
my web blog – Wetten Gewinne
Adoro o brilho estelar de SpeiCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao reluzente quanto uma supernova. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de emocoes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um cometa, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, SpeiCasino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo cosmico no cassino! Vale dizer tambem o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
spei free money|
Estou alucinado com JonBet Casino, pulsa com uma forca de cassino digna de um sino. O leque do cassino e um reverb de delicias. com slots tematicos de aventuras sonoras. O servico e confiavel como uma camara. com ajuda que ressoa como um sino. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. de vez em quando mais bonus regulares seriam harmonicos. Em sintese, JonBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos! Adicionalmente o design e fluido como uma onda sonora. amplificando o jogo com ritmo sonoro.
sinais jonbet|
discovergreatvalue – Easy to navigate and quick checkout, very user-friendly website.
Estou vidrado no BacanaPlay Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao animada quanto uma bateria de escola de samba. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma explosao de cores e ritmos, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, as vezes mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, BacanaPlay Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carnaval total para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Alem disso o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
casino online bacanaplay|
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, oferece um prazer intenso e indomavel. O catalogo e exuberante e diversificado, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, acessivel a qualquer momento. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, no entanto mais rodadas gratis seriam um diferencial. Resumindo, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para quem aposta com cripto ! Acrescentando que a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Igualmente impressionante os pagamentos seguros em cripto, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Abrir agora|
bs market Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
Sou totalmente viciado em BETesporte Casino, transporta para um universo de apostas eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, oferecendo respostas claras. As transacoes sao confiaveis, de vez em quando mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. No fim, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o gramado para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Vale destacar a plataforma e visualmente impactante, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Notavel tambem as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, que impulsiona o engajamento.
http://www.betesporte365.app|
seoignite.click – On mobile it’s seamless and responsive; no weird layout issues.
teamworkinnovation – Practical exercises that can be implemented immediately for better results.
online sportwetten Schweiz
unentschieden strategie
uniquefashionboutique – Found unique pieces not available elsewhere, great shopping experience.
Все о коттеджных посёлках https://cottagecommunity.ru/sosnovka/ фото, описание, стоимость участков и домов. Всё о покупке, строительстве и жизни за городом в одном месте. Полезная информация для покупателей и инвесторов.
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von PlayJango Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Feuerwerk explodiert. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Spektakel, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter knistern. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern glanzt, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der verblufft. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Komet, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Insgesamt ist PlayJango Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Orkan begeistert fur Spieler, die auf elektrisierende Casino-Kicks stehen! Und au?erdem die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, das Casino-Erlebnis total elektrisiert.
playjango reviews|
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, tem um ritmo de jogo que acende como uma tocha. A colecao e um facho de diversao. incluindo mesas com charme iluminado. O time do cassino e digno de um faroleiro. garantindo suporte direto e sem escuridao. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma lanterna. mesmo assim mais bonus regulares seriam radiantes. Resumindo, BR4Bet Casino oferece uma experiencia que e puro brilho para os fas de adrenalina brilhante! Adicionalmente a plataforma reluz com um visual brilhante. elevando a imersao ao nivel de uma fogueira.
br4bet esta legalizada no brasil|
ultimateprofitplan – Looks trusted with secure navigation and decent support options.
Acho simplesmente intergalactico SpeiCasino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao reluzente quanto uma supernova. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de emocoes, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e estelares. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro foguete, acessivel por chat ou e-mail. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma nave espacial, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. Em resumo, SpeiCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma galaxia para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, adiciona um toque de brilho estelar ao cassino.
spei bonus|
Sou viciado no reverb de JonBet Casino, explode com uma vibe de cassino ressonante. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que ressoam como corais. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. assegurando apoio sem dissonancias. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma corda. porem queria promocoes que vibram como sinos. Em sintese, JonBet Casino e um reverb de emocoes para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! Por sinal o design e um espetaculo visual harmonico. elevando a imersao ao nivel de um coral.
apk jonbet|
rankseed.click – The navigation is intuitive, I found what I was looking for in a few clicks.
forexstrategyguide – Clean layout and easy to understand lessons, makes trading less intimidating.
Acho simplesmente sensacional BacanaPlay Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um tamborim. A selecao de titulos do cassino e uma explosao de cores e ritmos, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, com uma ajuda que brilha como serpentinas. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, BacanaPlay Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um carnaval total para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma fantasia de carnaval, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desfile sem fim.
bacanaplay licence|
blsp at Неужели ты до сих пор не знаешь, что переворачивает мир даркнета? Blacksprut – это не просто название. Это новая эра анонимности, мгновенной скорости и железобетонной безопасности в сети. Загляни на bs2best.at – туда, где обсуждают то, о чём остальные предпочитают молчать в тряпочку. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, тщательно оберегаемой от посторонних глаз. Только для тех, кто понимает правила игры. Никаких следов, никаких компромиссов, только абсолютная конфиденциальность – это Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать первооткрывателем – bs2best.at уже распахнул свои двери для тебя. Хватит ли у тебя смелости взглянуть правде прямо в лицо?
Amo a energia selvagem de PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. O catalogo e exuberante e diversificado, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, de vez em quando recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para quem aposta com cripto ! Acrescentando que o site e rapido e cativante, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Muito atrativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, oferece recompensas continuas.
Descobrir mais|
Tenho uma paixao ardente por BETesporte Casino, transporta para um universo de apostas eletrizante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o pulso. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, acessivel a qualquer hora. Os saques sao rapidos como um drible, embora bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Vale destacar o site e veloz e envolvente, instiga a prolongar o jogo. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Mergulhe nisso|
musionet – Secure looking site with clear information — gave me confidence to browse.
urbanstylehub – Helpful product descriptions and vivid images made choosing a breeze.
dailytrendstore – Fast page loads and smooth navigation made my shopping experience easier.
financialgrowthplan – Good mix of visuals and text, helped me understand getting started clearly.
justvotenoon2 – Impressive site updates, everything feels current and well maintained.
virtual broadcast
trendandstyle – Smooth browsing and secure payment options, very trustworthy site.
imprintregistry – Practical approach to authenticity and provenance, good value for serious collectors.
successfultradersclub – The site feels trustworthy, though I’ll still test ideas on demo first.
growthnetworkgroup.cfd – Highly recommend to anyone seeking to expand their professional network.
winwithus.bond – Site loads quickly and content feels relevant and fresh.
modernwoodcases – Easy to navigate site, and I found a style that matches my phone perfectly.
brightmarketplace – Enjoyed exploring different categories, nice mix of everyday and special-find pieces.
tradingmasterclass – I’ll definitely return to the modules for refresher sessions later.
businesssuccesshub – The site feels trustworthy and the material is well-structured.
tradeandwin – Secure looking site and some credible resources, nice find.
rasecurities – User-friendly site, found what I needed quickly and the design helps.
markettrendalerts – The layout is simple and the alerts are easy to digest quickly.
fitproawardsuk – Helpful guide on the site about criteria and how winners are chosen, plus good clarity.
everydaytrendshop – Stylish fashion finds, loved the unique designs and quality.
concert experience
rankflow.click – Just gave this site a look; the layout is clean and the navigation flows smoothly.
netmatrix.click – Just browsed the site, the layout feels clean and everything’s nicely organized.
growthnetworkgroup – This looks like a reliable platform for anyone serious about meaningful growth.
stevieandbrucelive – A unique livestream event that music fans will really appreciate.
dailyprofitupdate – Appreciate the straightforward commentary; saves time and adds value.
tradingmasterclass – Some of the methods seem advanced, great resource if you’ve got experience trading.
brittanydominguez.shop – Navigation is smooth and intuitive, found what I needed in a few clicks.
nathanjones.shop – Already bookmarked the site—looks like a valuable resource to return to.
z9hl4.info – Visuals complement the text nicely; the design feels polished and thought-out.
https://b-sme.at
creativegiftworld.cfd – The website layout is smooth, browsing through products was easy.
strongpartnershipnetwork.cfd – Fast-loading pages and mobile-friendly design make browsing seamless and convenient.
https://bb2best.at
Ich bin vollig begeistert von Richard Casino, es verstromt eine Spielstimmung, die wie ein Kronjuwel glanzt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Vergnugen, inklusive eleganter Casino-Tischspiele. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein kaiserlicher Bote, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren furstlich. Kurz gesagt ist Richard Casino eine Casino-Erfahrung, die wie ein Kronungsjuwel glanzt fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Zusatzlich die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Kronungsmantel glanzt, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
free no deposit bonus codes for richard casino|
Ich bin suchtig nach King Billy Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Kronungsfest funkelt. Der Katalog des Casinos ist eine Schatzkammer voller Spa?, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die verzaubern. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Zepter glanzt, mit Hilfe, die wie ein Thron majestatisch ist. Casino-Transaktionen sind simpel wie ein koniglicher Befehl, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren koniglich. Zusammengefasst ist King Billy Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, was jede Casino-Session noch prachtiger macht.
king billy casino abzocke|
Estou completamente enfeiticado por SpellWin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e pura magia. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um feitico de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de magia. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e um feitico de eficiencia, respondendo mais rapido que um estalo magico. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um feitico de teletransporte, mas as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No fim das contas, SpellWin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem a navegacao do cassino e facil como um passe de magica, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desejo concedido.
spellwin login|
Acho simplesmente estelar BetorSpin Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e puro pulsar galactico. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um buraco negro de diversao, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como um foguete estelar, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Em resumo, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os astronautas do cassino! De bonus a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma constelacao, eleva a imersao no cassino a um nivel cosmico.
betorspin reclame aqui|
Estou completamente apaixonado por PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, com slots de design inovador. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. O acompanhamento e impecavel, sempre pronto para resolver. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, contudo mais rodadas gratis seriam um diferencial. Para finalizar, PlayPIX Casino garante diversao constante para quem aposta com cripto ! Tambem o site e rapido e cativante, facilita uma imersao total. Notavel tambem as opcoes variadas de apostas esportivas, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Saiba mais|
Ich bin vollig begeistert von Richard Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein koniglicher Palast strahlt. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein wahres Kronungsjuwel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen verzaubern. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein koniglicher Hofstaat, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Auszahlungen im Casino sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Marsch, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren furstlich. Insgesamt ist Richard Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Zusatzlich die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
richard casino reviews|
Ich bin suchtig nach King Billy Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Konig regiert. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und prachtig, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Festbankett strahlen. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein koniglicher Bote, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Der Casino-Prozess ist klar und ohne Intrigen, trotzdem mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren koniglich. Insgesamt ist King Billy Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens die Casino-Navigation ist kinderleicht wie ein koniglicher Marsch, das Casino-Erlebnis total veredelt.
king billy casino 50 free spins no deposit bonus codes|
Estou completamente enfeiticado por SpellWin Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que reluz como um feitico lancado. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um feitico de prazeres, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e blindados, de vez em quando as ofertas do cassino podiam ser mais generosas. No geral, SpellWin Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e magica para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo mistico, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como num desejo concedido.
george spellwin|
Adoro o brilho de BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma constelacao de prazeres, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma estrela-guia, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como uma orbita lunar, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura estelar. No geral, BetorSpin Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os apaixonados por slots modernos de cassino! Vale dizer tambem o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo estelar, faz voce querer voltar ao cassino como um cometa em orbita.
jogos de betorspin|
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo inigualavel. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, acessivel a qualquer momento. Os saques sao rapidos como um drible, as vezes mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. No geral, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o jogo para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Tambem o design e moderno e vibrante, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Notavel tambem os eventos comunitarios envolventes, oferece recompensas continuas.
Descobrir|
bs2best at Интересуешься, что происходит в тёмных уголках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это гарантия анонимности, высокой скорости и надежности. Переходи на bs2best.at — там ты найдёшь то, о чём другие умалчивают. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, которую скрывают от большинства. Только для тех, кто понимает. Без компрометирующих следов. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти шанс узнать первым — bs2best.at уже готов открыть свои двери. Дерзнешь ли ты взглянуть правде в глаза?
bs2best at Ты еще не в курсе, что порождает бурю в темных водах сети? Blacksprut – это не просто символ. Это квинтэссенция анонимности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной уверенности в каждом действии. Приглашаем на bs2best.at – туда, где шепчут о том, о чем другие предпочитают хранить гробовое молчание. Тебе откроются двери в мир, скрытый от любопытных глаз, доступный лишь избранным, тем, кто понимает истинную цену информации. Ни единой зацепки. Никаких отступлений. Только безупречный Blacksprut, гарант твоей конфиденциальности. Не упусти свой шанс стать первопроходцем – bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои тайны. Достаточно ли ты смел, чтобы заглянуть в бездну правды?
Sou viciado em BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura competitiva. Ha uma multidao de jogos emocionantes, com sessoes ao vivo imersivas. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. Os agentes respondem com velocidade, oferecendo respostas claras. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, de vez em quando bonus mais variados seriam um gol. Em resumo, BETesporte Casino garante diversao a cada rodada para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Vale destacar o site e veloz e envolvente, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Notavel tambem os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ver a pГЎgina|
Портал о строительстве домов https://doma-land.ru проекты и сметы, сравнение технологий (каркас, газобетон, кирпич, брус), фундамент и кровля, инженерия и утепление. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, тендер подрядчиков, рейтинги бригад, карта цен по регионам, готовые ведомости материалов и практика без ошибок.
wettquote bundestagswahl
my blog post – Sportwetten Bonus Deutschland
pixelpush.click – Pages load fast, visuals look crisp, everything seems well put together.
boostengine.click – The visuals match the tone of the site nicely; clean and refined.
Квартира с отделкой https://новостройкивспб.рф экономия времени и предсказуемый бюджет. Фильтруем по планировкам, материалам, классу дома и акустике. Проверяем стандарт отделки, толщину стяжки, ровность стен, работу дверей/окон, скрытые коммуникации. Приёмка по дефект-листу, штрафы за просрочку.
sitefoundry.click – The site has a polished clean design and navigation feels intuitive.
webrevive.click – I found some interesting links already; looks like there’s depth behind the design.
Fiquei impressionado com BETesporte Casino, transporta para um mundo de apostas vibrante. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, com slots modernos e tematicos. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, acessivel a qualquer hora. As transacoes sao confiaveis, no entanto ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino e uma plataforma que domina o campo para quem usa cripto para jogar ! Vale destacar a interface e fluida e energetica, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ver agora|
brandlift.click – Overall, the experience is positive and the site feels trustworthy.
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, bietet klare Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Hinzu kommt das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die schnellen Einzahlungen, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Acho simplesmente incendiario BetPrimeiro Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que borbulha como um geyser. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e escaldantes, com slots de cassino tematicos de erupcao. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro fogo, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem cinzas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como um meteoro, mas mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. Resumindo, BetPrimeiro Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro magma para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! E mais a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como lava derretida, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais incendiaria.
betprimeiro codigo bonus|
Achou totalmente epico DiceBet Casino, parece um tornado de diversao. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma explosao, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e de primeira, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e na lata. Os pagamentos do cassino sao lisos e seguros, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No fim das contas, DiceBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro gas para os amantes de cassinos online! Vale falar tambem a plataforma do cassino detona com um look que e puro fogo, da um toque de classe braba ao cassino.
dicebet reclame aqui|
wetten handicap erklärung
Here is my site: beste Wettanbieter Bonus
concert stream
Sou louco pela energia de SupremaBet Casino, e um cassino online que ressoa como um trovao epico. A gama do cassino e simplesmente uma dinastia de delicias, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque de realeza. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro reinado, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem revoltas. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem conspiracoes, as vezes mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial imperial. Resumindo, SupremaBet Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo soberano, adiciona um toque de grandeza ao cassino.
supremabet|
Ich bin vollig geflasht von Lapalingo Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein wilder Ritt durch die Spielwelt. Die Casino-Optionen sind bunt und mitrei?end, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, liefert klare und schnelle Losungen. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Knaller. Insgesamt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Sturm begeistert fur Abenteurer im Casino! Extra die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
promo codes lapalingo|
Estou alucinado com DiceBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e fora da curva. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um espetaculo a parte, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, com uma ajuda que e um arraso. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um estalo, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. No geral, DiceBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um estouro para os cacadores de slots modernos de cassino! De lambuja a navegacao do cassino e facil como brincadeira, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
dicebet reclame aqui|
gratiswette ohne einzahlung
Also visit my webpage :: wetten Vorhersage
nighttoshineatlanta – Beautifully inspiring event site, visuals radiate joy and inclusion.
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, sinto um rugido de emocao. A selecao de jogos e fenomenal, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. 100% ate R$600 + apostas gratis. O suporte ao cliente e excepcional, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, as vezes ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. No fim, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para fas de cassino online ! Adicionalmente o design e moderno e vibrante, adiciona um toque de estrategia. Notavel tambem os torneios regulares para rivalidade, proporciona vantagens personalizadas.
Obter os detalhes|
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, leva a um universo de pura adrenalina. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, acessivel a qualquer momento. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, as vezes promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. No geral, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia memoravel para quem aposta com cripto ! Adicionalmente a interface e fluida e estilosa, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Notavel tambem os pagamentos seguros em cripto, que aumenta o engajamento.
Mergulhe nisso|
douglasand55 – Very polished design, strong visuals and clear professional tone.
nighttoshineatlanta – Beautifully inspiring event site, visuals radiate joy and inclusion.
smarttechmukesh.xyz – Colour scheme is calm and appealing, nothing harsh on the eyes.
moj-kredyt.shop – I bookmarked this article; straightforward advice without confusing jargon today.
neighborsforrandy – Friendly community feel, layout conveys care and connection effectively.
shop-in.tech – On mobile the site performs well; everything’s responsive and aligned properly.
2rss5ge.xyz – The layout looks clean and professional, nice first impression overall.
cloudfiles.tech – The site has a sleek, modern layout and the navigation is intuitive and smooth.
ehajjumrahtours – Professional and serene, the layout reflects faith and reliability.
Sou viciado em PlayPIX Casino, transmite uma energia vibrante. A variedade de titulos e estonteante, incluindo apostas esportivas que aceleram o coracao. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O servico esta disponivel 24/7, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os saques sao rapidos como um raio, de vez em quando bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. No geral, PlayPIX Casino e uma plataforma que brilha para fas de cassino online ! Acrescentando que a interface e fluida e estilosa, tornando cada sessao mais vibrante. Igualmente impressionante o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Descobrir a web|
ct2020highschoolgrads – Heartwarming initiative, celebrating graduates with positivity and pride.
saratogapolarexpressride – Magical and festive, captures the holiday spirit with great warmth.
luxnoe – Modern and stylish, this site exudes luxury and creative design.
karen4assembly – Clear and sincere campaign tone, content reflects leadership and integrity.
SEO-продвижение позволяет сайту быть заметным и удобным для аудитории. Работа с контентом, структурой страниц и техническими параметрами ресурса помогает улучшить позиции и увеличить трафик. Регулярная аналитика и корректировка стратегии обеспечивают долгосрочный рост. Такой подход делает сайт надёжным источником клиентов и укрепляет позиции компании. Читайте подробнее: https://flynonrev.com/airlines/index.php/User:RodFunk39744
stageofnations – Culturally rich, visuals celebrate unity and vibrant heritage beautifully.
Девушки невероятно красивые и профессиональные, создают чувство гармонии и комфорта. Массаж мягкий и плавный, каждое прикосновение расслабляет полностью. После сеанса ощущение радости и лёгкости. Крайне советую, индивидуалки цена Новосибирск – https://sibirka.com/. Настоящее удовольствие, атмосфера потрясающая.
mastriano4congress – Direct and focused, campaign visuals match strong message delivery.
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von Trickz Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie eine Illusion verblufft. Die Casino-Optionen sind vielfaltig und verzaubernd, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein magischer Assistent, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der begeistert. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber die Casino-Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Alles in allem ist Trickz Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans von Online-Casinos! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Hexenwerk, einen Hauch von Zauberei ins Casino bringt.
trickz casino flashback|
Ich finde absolut irre Lapalingo Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Blitz einschlagt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein Ozean voller Schatze, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Gewitter krachen. Das Casino-Team bietet Unterstutzung, die wie ein Stern strahlt, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, aber mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein funkelnder Gewinn. Kurz gesagt ist Lapalingo Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Extra die Casino-Plattform hat einen Look, der wie ein Blitz funkelt, den Spielspa? im Casino in den Himmel hebt.
lapalingo quiz|
Je suis subjugue par Donbet Casino, on dirait un ouragan de sensations fortes. Il y a une avalanche de jeux captivants, avec des slots au design audacieux. Le suivi est d’une clarte explosive, garantissant un support d’une puissance rare. Les transactions sont fiables et fluides, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient electrisantes. En conclusion, Donbet Casino est une plateforme qui fait trembler les sens pour les fans de casinos en ligne ! Par ailleurs la plateforme brille comme une supernova, ce qui rend chaque session absolument electrisante.
donbet app|
Ich bin total begeistert von Billy Billion Casino, es ist ganz ein Eintauchen in eine pulsierende Spielwelt. Der Katalog ist unglaublich umfangreich, mit klassischen Tischspielen wie Blackjack und Roulette. Der Kundenservice ist erstklassig, ist 24/7 erreichbar. Auszahlungen sind super schnell, oft in 1 Stunde fur Kryptowahrungen, gelegentlich die Boni wie der 100%-Willkommensbonus bis 7500 € konnten ofter kommen. Am Ende ist Billy Billion Casino definitiv einen Besuch wert fur Online-Casino-Fans! Au?erdem die Seite ist mit Stil und Benutzerfreundlichkeit gestaltet, jede Spielsitzung erleichtert.
billy billion casino login|
вічна пам’ять татові проза
Ich bin vollig verzaubert von Trickz Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Zauberstab funkelt. Die Spielauswahl im Casino ist wie ein Zauberkoffer voller Wunder, inklusive stilvoller Casino-Tischspiele. Der Casino-Kundenservice ist wie ein magischer Assistent, mit Hilfe, die wie eine Illusion verblufft. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem mehr Freispiele im Casino waren ein magischer Volltreffer. Alles in allem ist Trickz Casino ein Muss fur Casino-Fans fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Zusatzlich das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Hexenwerk, Lust macht, immer wieder ins Casino zuruckzukehren.
trickz casino bonus|
Компания «СибЗТА» https://sibzta.su производит задвижки, клапаны и другую трубопроводную арматуру с 2014 года. Материалы: сталь, чугун, нержавейка. Прочные уплотнения, стандарты ГОСТ, индивидуальные решения под заказ, быстрая доставка и гарантия.
Ich finde es unglaublich toll Billy Billion Casino, es ist ganz ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Es gibt eine Vielzahl an abwechslungsreichen Spielen, mit immersiven Live-Casino-Sessions von Evolution Gaming. Die Mitarbeiter sind rund um die Uhr professionell und hilfsbereit, mit hervorragendem Follow-up. Auszahlungen sind super schnell, oft in 1 Stunde fur Kryptowahrungen, obwohl mehr Freispiele waren super. Insgesamt ist Billy Billion Casino enttauscht nie fur Leidenschaftliche Gamer! Au?erdem die Navigation ist intuitiv auf der mobilen iOS/Android-App, die Immersion verstarkt.
billy billion|
wettbüro ludwigshafen
My web page … Wetten dass heute Gäste
asteroid-insurance – Clever concept, design feels futuristic and sharp with humor.
adirondackfiddlers – Full of tradition, music passion shines through each element.
купить красный мухомор На сайте muhomorus можно заказать мухоморы с доставкой в любую точку России. У нас вы найдете доступные цены на экологически чистые продукты, предназначенные для борьбы с тревогой, стрессом, депрессией, хронической усталостью и другими недугами. Сухие мухоморы – это не лекарственный препарат, а парафармацевтическое средство, которое может использоваться в качестве альтернативной вспомогательной терапии по усмотрению каждого. Сбор, сушка, реализация и приобретение мухоморов являются абсолютно законными. Поэтому мы даем возможность купить микродозинг легально.
shopminq – Trendy e-commerce look, product visuals are crisp and appealing.
Hey there! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 3gs! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the great work!
staffinggoals.com
benningtonareaartscouncil – Artistic and welcoming, site promotes community creativity wonderfully.
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to determine if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any suggestions would be greatly appreciated.
https://staffinggoals.com/
homecovidtest – Informative and reliable, design prioritizes health clarity and accessibility.
charitiespt – Compassionate and community-driven, mission comes across with sincerity.
fayettecountydrt – Purposeful and informative, organization’s vision feels transparent and clear.
larkfest2013 – Vibrant and nostalgic, visuals radiate energy and celebration.
mckeetransition – Professional government tone, site design supports accessibility and progress.
holyspiritschooleg – Educational yet warm, design and content reflect care and faith.
wettanbieter in deutschland
Here is my web-site; wetten Vorhersagen halbzeit Endstand
georgewillwashpost – Clean layout, solid typography, content radiates intellect and authority.
lcbclosure – Focused and informative, the message feels urgent and clearly communicated.
mayceformayor – Campaign feels strong and grounded, visuals emphasize trust and service.
masonchallengeradaptivefields – Inspirational cause, presentation is heartfelt and full of purpose.
milestonerest – Inviting visuals, design creates a sense of comfort and good taste.
peoplesprotectiveequipment – Practical and safety-focused, design feels direct and trustworthy.
Hey there, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog in Firefox, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, great blog!
https://easystaffingmd.com/
Je suis totalement enflamme par VBet Casino, on dirait une eruption de plaisirs incandescents. Il y a une deferlante de jeux de casino captivants, incluant des jeux de table de casino d’une elegance ardente. L’assistance du casino est chaleureuse et irreprochable, joignable par chat ou email. Les paiements du casino sont securises et fluides, par moments j’aimerais plus de promotions de casino qui envoient du feu. Au final, VBet Casino est une pepite pour les fans de casino pour ceux qui cherchent l’adrenaline enflammee du casino ! En plus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel brulant, ce qui rend chaque session de casino encore plus enflammee.
vbet бездепозитный бонус промокод|
Ich liebe die unbandige Kraft von Lowen Play Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie ein Lowe brullt. Es gibt eine Flut an fesselnden Casino-Titeln, mit Live-Casino-Sessions, die wie ein Sturm donnern. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und machtig, ist per Chat oder E-Mail erreichbar. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, trotzdem wurde ich mir mehr Casino-Promos wunschen, die wie ein Feuer lodern. Alles in allem ist Lowen Play Casino ein Casino mit einem Spielspa?, der wie ein Brullen donnert fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optisches Raubtier, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
löwen play gera|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, garantiert top Hilfe. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Nicht zu vergessen das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Galera, quero deixar registrado sobre o Bingoemcasa porque superou minhas expectativas. O site tem um visual descontraido que lembra um barzinho cheio de risadas. As salas de bingo sao com muita interacao, e ainda testei blackjack e poker tambem, todos me deixaram impressionado. O atendimento no chat foi respondeu em segundos, o que ja me deixou tranquilo. As retiradas foram mais velozes que imaginei, inclusive testei cripto e caiu em minutos. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que senti falta de ofertas extras, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Pra concluir, o Bingoemcasa vale demais a pena. Ja me sinto parte da comunidade
https m bingoemcasa net|
letthemplaymn – Passionate and purposeful, the site speaks strongly for youth engagement.
teamtadros – The mission feels bold, visuals highlight unity and determination.
Simply want to say your article is as astounding. The clearness to your post is simply great and i can suppose you’re knowledgeable on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to snatch your RSS feed to stay up to date with impending post. Thanks a million and please carry on the rewarding work.
https://easystaffingmd.com/
rodarodaku.xyz – The color palette feels calming, nothing harsh or distracting here.
kkgg1.xyz – Just visited this site, layout looks modern and navigation is simple.
easyprt.xyz – Mobile version looks flawless, everything adjusts perfectly on screen.
mm9b.xyz – Bookmarked this site, looks reliable and worth revisiting often.
xxau.xyz – I found some useful sections already, looks like well-thought content.
exodusalliance – Empowering theme, site feels hopeful and mission-driven throughout.
oscarthegaydog – Whimsical and delightful, brand personality shines through humor and charm.
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com energia festiva. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, oferecendo jogos de mesa imersivos. Eleva a diversao do jogo. O acompanhamento e impecavel, com suporte preciso e rapido. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, contudo recompensas adicionais seriam festivas. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para fas de cassino online ! Adicionalmente a interface e fluida e elegante, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Um diferencial importante os torneios regulares para competicao, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Descobrir agora mesmo|
J’adore la chaleur de VBet Casino, c’est un casino en ligne qui jaillit comme un volcan en furie. L’eventail de jeux du casino est une lave de delices, proposant des slots de casino a theme volcanique. Le service client du casino est une torche d’efficacite, offrant des solutions claires et instantanees. Le processus du casino est transparent et sans cendres, par moments des bonus de casino plus frequents seraient brulants. Pour resumer, VBet Casino promet un divertissement de casino incandescent pour les passionnes de casinos en ligne ! Bonus le design du casino est un spectacle visuel brulant, facilite une experience de casino eruptive.
vbet підтримка|
Ich bin vollig hingerissen von Lowen Play Casino, es pulsiert mit einer unbezahmbaren Casino-Energie. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echtes Raubtier, mit einzigartigen Casino-Slotmaschinen. Der Casino-Support ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, sorgt fur sofortigen Casino-Support, der beeindruckt. Casino-Gewinne kommen wie ein Blitz, ab und zu mehr Casino-Belohnungen waren ein koniglicher Gewinn. Zusammengefasst ist Lowen Play Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur Fans moderner Casino-Slots! Ubrigens die Casino-Oberflache ist flussig und strahlt wie ein Sonnenaufgang, was jede Casino-Session noch wilder macht.
löwen play casino mainz|
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Support ist 24/7 erreichbar, bietet klare Losungen. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, obwohl die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Hervorzuheben ist die mobilen Apps, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar sobre o Bingoemcasa porque achei muito alem do que esperava. O site tem um visual descontraido que lembra um encontro descontraido. As salas de bingo sao super animadas, e ainda testei alguns caca-niqueis modernos, todos rodaram sem travar. O atendimento no chat foi rapido como nunca vi, o que ja me deixou tranquilo. As retiradas foram muito rapidas, inclusive testei cartao e caiu em minutos. Se pudesse apontar algo, diria que podiam ter bonus semanais, mas nada que estrague a experiencia. Na minha visao, o Bingoemcasa me conquistou. Eu mesmo ja voltei varias vezes
https m bingoemcasa net en|
daybirdsyr – Energetic vibe, visuals and tone reflect creativity and modern living.
supportsros – Compassionate tone, clear visuals support their advocacy with sincerity.
Пользуюсь DRINKIO регулярно и могу сказать, что это лучший сервис в своём сегменте. Курьеры приезжают вовремя, заказы всегда оформлены корректно. Сайт интуитивно понятный, всё делается быстро и удобно. Радует стабильность работы — ни разу не подводили. Ассортимент качественный, цены адекватные. Лучшая доставка алкоголя в Москве круглосуточно https://drinkio105.ru/
justinhicksformissouri – Strong campaign message, design feels authentic and community-focused.
nyscanalconference – Informative and organized, layout suits event communication well.
tinacurrin – Artistic and bold, site radiates passion and expressive creativity.
harryandeddies – Cozy restaurant vibe, visuals and menu presentation feel deliciously inviting.
southbyfreenoms – Fun, quirky branding with energetic layout and friendly design.
Профессиональная застройка выставочного стенда — это ключ к успешному участию в выставке. Мы создаем эффектные и функциональные конструкции, которые привлекают внимание целевой аудитории и подчеркивают уникальность вашего бренда. От проектирования до монтажа под ключ: застройка выставочного стенда
kim4commonsense – The campaign feels approachable, visuals and tone are relatable.
romain4reform – Clear, reform-focused tone, visuals convey honesty and strong leadership.
verkaufte spiele wetten
Feel free to surf to my blog: wettquoten papst (Kathi)
rideformissingchildren – Heartfelt cause, presentation honors the mission beautifully and respectfully.
sportwetten deutschland
Also visit my web-site: online wettanbieter vergleich – Lurlene –
t-walls-of-kuwait-iraq – Historical and impactful, visuals convey memory and meaning strongly.
Похороны под ключ
0pdpof.xyz – Found some interesting posts, definitely worth revisiting for updates.
diwang2.pw – Typography is clean and readable, perfect for longer content sessions.
74364.pw – Typography choices are comfortable, making longer reads easy and engaging.
coatsjps.pw – The content loads fast and the design feels thoughtfully structured.
wqpyp.pw – The site loads fast and gives a modern, professional impression right away.
cranberrystreetcafe – Cozy and charming, design evokes warmth and delicious experiences.
https://pakhie.com/blogs/87070/Code-Promo-1xBet-Aujourd-hui-C%C3%B4te-d-Ivoire-2026-130
die besten wettseiten
Feel free to surf to my blog … online Sportwetten paypal
sicherste Sportwetten Tipp strategie
georgetowndowntownmasterplan – Informative and civic-minded, content clearly explains planning goals.
hardman4schools – Design supports purpose perfectly, showcasing leadership and care for education.
saveshelterpets – Touching initiative, site feels compassionate and community-focused.
https://www.jamaicanews.net/newsr/15850
https://crypo.adseon.xyz/codigo-promocional-1xbet-deportes-bono-130e/
кракен магазин Кракен: Путеводитель по Тенетам Цифровой Вседозволенности В полумраке цифрового пространства, где анонимность становится валютой, имя “Кракен” шепчут с благоговейным трепетом и опаской. Это не просто платформа, это целая экосистема, обещающая доступ к запретному, сокрытому и ускользающему. “Кракен ссылка,” “кракен сайт,” “кракен магазин” – эти слова становятся ключами, открывающими двери в мир, где законы реального мира не имеют силы. Но путь к этой свободе усеян минами, и лишь немногие способны пройти его, не потеряв себя.
The Inheritance Games Canada: A thrilling mystery game where players unravel secrets, solve puzzles, and compete for a billionaire’s fortune. Perfect for fans of strategy and suspense: The Inheritance Games book series
besten Sportwetten Tippen anbieter
Je suis absolument captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca offre une sensation futuriste unique. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, incluant des paris live dynamiques. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Le suivi est d’une efficacite absolue, offrant des solutions claires. Les paiements sont securises par blockchain, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! A noter le design est moderne et captivant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les options de paris variees, garantit des transactions fiables.
Cliquer pour les infos|
Je suis seduit par Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a toute heure. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et gracieuse, ajoute une touche d’elegance. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Essayer en ligne|
albanysuperducks – Fun and quirky, visuals bring playful excitement to life.
https://pln.by/2104-1khbet-promokod-bonus-za-registratsiyu-130-evro
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table raffines. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a servir. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter le design est moderne et chic, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
Ouvrir la page maintenant|
Je suis emerveille par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un ocean virtuel. Les options sont vastes comme un reseau, incluant des paris live dynamiques. Avec des depots crypto instantanes. Le support client est stellaire, avec une aide precise et fiable. Les transferts sont fiables, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une plongee numerique pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! A noter la navigation est simple comme un wallet, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les options de paris variees, renforce la communaute.
En savoir plus|
J’adore l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie blockchain. Les options sont vastes comme un reseau decentralise, avec des slots aux themes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une efficacite redoutable, toujours pret a resoudre. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est incontournable pour les fans de crypto pour les passionnes de casino en ligne ! A noter la navigation est simple comme un wallet, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Voir l’offre|
J’adore l’atmosphere rythmee de BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un saxophone. Le catalogue est riche et varie, proposant des jeux de table elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont fluides comme un riff, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Au final, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et rythmee, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un autre atout les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
J’ai une passion magique pour Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de tours captivants. Les options sont vastes comme un chapeau de magicien, avec des slots aux designs enchanteurs. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent comme par magie, garantissant un support de qualite. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En bref, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations mystiques ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et enchanteur, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
casinospinitfr.com|
Je suis accro a Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir enchante. Les options sont vastes comme un grimoire, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient enchantees. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et magique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
Je suis completement envoute par Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir immortel. La variete des titres est divine, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Amplifiant l’aventure de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et sage, avec une aide precise. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, bien que des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. En resume, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour les amateurs de sensations mythiques ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un nectar, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un atout olympien les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
https://olympefr.com/|
kraken сайт Кракен: Вопросы Ссылок, Безопасности и Доступа В мире цифровой торговли и анонимных транзакций “Кракен” стал узнаваемым именем. Кракен – это не просто слово, это целая экосистема, обещающая широкий выбор товаров и услуг, конфиденциальность и, зачастую, обход привычных ограничений. Однако, популярность порождает и вопросы, связанные с безопасностью доступа, надежностью продавцов и легитимностью операций.
stopkrasner – Strong political tone, site expresses clear intent and decisive messaging.
Je suis ebloui par Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un reseau blockchain. La selection de jeux est astronomique, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Boostant votre capital initial. Le support client est irreprochable, avec une aide rapide et fiable. Le processus est fluide comme un smart contract, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration virtuelle pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, propose des avantages uniques.
Approfondir|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, avec des slots aux designs elegants. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le suivi est irreprochable, toujours pret a servir. Le processus est simple et elegant, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et gracieuse, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Voir les meilleurs choix|
J’aime l’aura futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, ca procure une sensation numerique unique. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour BTC et ETH. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme une comete, avec une aide precise et fiable. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience memorable pour les passionnes de sensations virtuelles ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, renforce la communaute.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’adore l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre d’innovation. Le choix de titres est eblouissant, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin et Ethereum. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec une precision quantique, avec une aide precise et fiable. Le processus est simple comme un hash, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient top. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les aficionados de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement remarquable les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
J’adore l’atmosphere aquatique de BassBet Casino, il procure une experience dynamique. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, avec des slots aux designs fluviaux. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient dynamiques. Au final, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui ondule pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement fluviale, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
Je suis totalement enchante par Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance envoutante. Les options sont vastes comme un chapeau de magicien, avec des slots aux designs enchanteurs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est enchante, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Au final, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! En bonus le design est moderne et enchanteur, ajoute une touche de mystere. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
casinospinitfr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de livre. Les options sont vastes comme un grimoire, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est enchante, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la magie. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de sensations enchantees ! En bonus la navigation est simple et magique, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
https://spinitcasinologinfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Olympe Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque l’Olympe. La selection de jeux est olympienne, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. Le suivi est irreprochable, toujours pret a guider. Le processus est simple et glorieux, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient eternelles. Au final, Olympe Casino garantit un plaisir divin pour les joueurs en quete d’epopee ! A noter le design est moderne et divin, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout olympien les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
https://olympefr.com/|
tranquilleeyecream – Calm aesthetic, visuals match beauty and relaxation concept perfectly.
hardman4schools – The layout is simple yet powerful, delivering a message of trust.
Kuponda multi-bet, sistem və tez düzəliş funksiyaları var, səhv əmsal da avtomatik düzəlir.
Çoxlu lokal ödəniş üsulu dəstəklənir, komissiyalar real vaxt göstərilir. Canlı futbol statistikalarını izləyərkən pinco-casino-azerbaijan.biz.ua pəncərəsini açıq saxlayın — pinco bonus elanları tez-tez yenilənir. Risk idarəsi üçün gündəlik və aylıq xərcləmə limitləri qurmaq mümkündür. Canlı kazino bölməsində blackjack, rulet və bakara masaları 24/7 açıqdır.
Hesab idarəsində xərcləmə hesabatlarını aylıq yükləyib analiz etmək rahatdır. Android apk yükləməsi rəsmi səhifədən olur və quraşdırma bələdçisi addım-addım göstərilir.
Dəstək 24/7 işləyir, chat cavabları adətən 1–2 dəqiqəyə gəlir. Özünü istisna etdikdən sonra dəstək geri aktivləşdirməni minimum 24 saatdan əvvəl etmir. Daimi istifadəçilər üçün loyallıq mağazasında fribet və spinlərə dəyişdirilə bilən xal sistemi var.
денежный займ займы всем
walkunchained – Inspiring tone, message of freedom and courage comes across clearly.
кредитный займ все займы все займы
займ деньги мфо микрозайм за 10 минут онлайн
трансы Новосибириск Примеры и Особенности Каналов Каналы, подобные @ts_novosibirsk (трансы Новосибирск, трансы новосибирска), @ts_ekaterinburgh (трансы Екатеринбург, трансы Екатеринбурга), @ts_voronezh (трансы Воронеж, трансы Воронежа), @transy_volgograd (трансы Волгоград, трансы волгограда) и @ts_chelyabinska (трансы Челябинск, трансы челябинска), отражают специфику каждого города, собирая локальную информацию. Важно отметить, что контент этих каналов может быть разнообразным: от новостей и анонсов мероприятий до личных историй и дискуссий.
https://factava.com.ua/znachennya-imen/lina-znachennia-imeni-yoho-pokhodzhennia-ta-tsikavi-fakty/
jammykspeaks – Powerful voice, content feels authentic, motivational and full of passion.
cryptocurrencynews.pw – Pages load fast, and articles are detailed yet simple to understand.
embersk9wish – Heartwarming mission, site honors service dogs with love and gratitude.
hyrdaruzxpnev4of.online – Nice typography and spacing make long reads comfortable and enjoyable.
tuzidh.pw – The color tone is subtle and balanced, perfect for longer browsing.
phonenumbers.pw – Overall impression is excellent, professional vibe and quality content.
kbdesignlab.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
трансы Екатеринбург Локальные Сообщества: Поддержка и Информация Эти каналы служат важным ресурсом для транс-сообщества. Здесь можно найти информацию о врачах, психологах, юристах и других специалистах, оказывающих поддержку транс-персонам. Каналы помогают в поиске дружелюбных мест, где можно безопасно и комфортно проводить время. Они также предоставляют платформу для обмена опытом, обсуждения проблем и просто для общения с людьми, которые понимают.
createimpactonline – The platform’s analytics have provided insights to improve our strategies.
partnershippowerhouse – Their approach to partnerships is both innovative and effective.
You have made some really good points there. I
checked on the web to find out more about the issue and found most individuals
will go along with your views on this website.
Also visit my site :: how much money for diamond casino
heist (Rolland)
Spot on with this write-up, I actually feel this amazing site needs
a lot more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more,
thanks for the information!
My homepage: bikini casino mod apk – Angus,
best new when will tropicana casino open (Marisol) sites usa, semyon dusaach blackjack and free online pokies win real money united kingdom, or casinos
in alberta australia
monumentremoval – The purpose is bold and the site feels deeply meaningful and timely.
wett tipps prognosen
my web-site :: Wettprognose Heute
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Le catalogue est riche en saveurs, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est irreprochable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les transactions sont fiables, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et gracieuse, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
Approfondir|
Je suis absolument captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie decentralisee. Les options sont vastes comme un ledger, avec des slots aux designs modernes. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Le suivi est d’une efficacite absolue, avec une aide rapide et fiable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! A noter le site est rapide et futuriste, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, offre des recompenses continues.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis charme par Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Le bonus de bienvenue est delicieux. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. Au final, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme un banquet, ajoute une touche d’elegance. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, il propose une odyssee chiffree. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, proposant des tables sophistiquees. Boostant votre capital initial. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des solutions claires. Les transferts sont fiables, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! En bonus le site est rapide et futuriste, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement captivant les options de paris variees, propose des avantages uniques.
Aller ici|
mystylecorner – Great experience browsing through latest trends, very satisfied overall.
J’aime l’aura futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un n?ud blockchain. L’eventail de jeux est colossal, offrant des sessions en direct immersives. Le bonus d’entree est scintillant. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, toujours pret a decoder. Les gains arrivent en un instant, de temps a autre des recompenses en plus seraient ideales. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une plongee numerique pour les passionnes de sensations virtuelles ! A noter le site est rapide et futuriste, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement cool les evenements communautaires decentralises, qui booste l’engagement.
Continuer ici|
BassBet Casino m’a totalement conquis BassBet Casino, il offre une experience de club. Le catalogue est riche en surprises, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de punch. Boostant votre mise de depart. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, joignable a tout moment. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus le design est moderne et lumineux, ce qui rend chaque session plus vibrante. Un point fort les options de paris variees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com/|
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir dynamique. Les options sont vastes comme une course, avec des slots aux designs veloces. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent comme un sprinter, toujours pret a accelerer. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En resume, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui accelere pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinologinfr.com|
J’ai une passion cyclonique pour Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourne avec elegance. La variete des titres est rapide, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est rapide. Le support client est veloce, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du rythme. Pour conclure, Spinit Casino vaut une course rapide pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement veloce, facilitate une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, qui booste l’engagement.
https://casinospinitfr.com/|
J’adore l’aura divine d’ Olympe Casino, ca transporte dans un monde mythique. La variete des titres est divine, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Le support client est olympien, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont rapides comme un eclair de Zeus, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un nectar. En bref, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les joueurs en quete d’epopee ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple comme un oracle, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout olympien le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://olympefr.com/|
J’adore l’atmosphere blues de BassBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un blues. La variete des titres est melodieuse, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est irreprochable, toujours pret a jammer. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un riff. Au final, BassBet Casino vaut une jam session pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
simplelivingstore – Website navigation was clean and simple—makes browsing relaxing on a lazy afternoon.
1091m2love – Unique name, design feels artistic and expression of individuality.
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux designs elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, avec une aide precise. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et attractif, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis ebloui par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. La selection de jeux est astronomique, avec des slots aux designs modernes. Avec des depots crypto rapides. L’assistance est precise et professionnelle, joignable a tout moment. Les transferts sont fiables, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et futuriste, ajoute une touche de sophistication. Particulierement captivant les options de paris variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Visiter pour plus|
Je suis ebloui par Monte Cryptos Casino, il propose une odyssee chiffree. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, incluant des paris live dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est precise et professionnelle, garantissant un service premium. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient l’experience. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires decentralises, offre des recompenses continues.
Approfondir|
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde gourmand. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, proposant des jeux de table raffines. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours pret a servir. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Au final, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter le design est moderne et chic, ajoute une touche d’elegance. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Aller Г la page|
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un desert virtuel. Les options sont vastes comme un reseau, avec des slots aux designs innovants. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Le suivi est sans faille, joignable en un clic. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction blockchain, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! Par ailleurs le design est moderne et captivant, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Egalement cool les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, propose des avantages uniques.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par BassBet Casino, il offre une experience de club. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Le suivi est impeccable, garantissant un service de haute qualite. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et captivant, donne envie de prolonger la fete. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
bassbetcasinobonus777fr.com|
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de vitesse. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est irreprochable, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme un peloton, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient veloces. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement veloce, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://spinitcasinologinfr.com/|
nycbhm – Community-focused organization with meaningful outreach and engagement.
J’ai une passion cyclonique pour Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de piste. Il y a une profusion de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et elegant, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En bref, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme une piste, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Un plus les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://casinospinitfr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Olympe Casino, ca transporte dans un monde mythique. La variete des titres est divine, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, garantissant un support celeste. Les retraits sont rapides comme un eclair de Zeus, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un nectar. En resume, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les fans de casino en ligne ! A noter le design est moderne et divin, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement remarquable les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://olympefr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melancolique. La selection de jeux est harmonieuse, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est rythme. Le support client est melodieux, toujours pret a jammer. Le processus est simple et elegant, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. En resume, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui groove pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
https://bassbetcasinologinfr.com/|
1day4kids – Uplifting cause, presentation radiates care and dedication toward children.
nycbhm – Community-focused organization with meaningful outreach and engagement.
knightstablefoodpantry – Compassionate food pantry serving the community with dedication.
visionaryfutureteam – Looking forward to checking in again and seeing how the content develops.
trustedpartnergroup – Appreciate the practical guidance they offer for growing network collaborations.
ultimateprofitplan – Overall good first impression; will watch how content updates and evolves.
dailyessentialstore – Overall good experience, feels like a reliable source for daily item needs.
trustbridgealliance – The messages are realistic and practical, not overhyped—which I value.
professionalgrowthhub – Great resource for advancing careers, lots of practical advice and tools.
mcctheatercampaign – Supporting arts and theater with passion and community spirit.
1091m2love – Super impressed by how clean and inviting this layout appears today.
shopandshine – Overall very happy with the experience—will check back for new drops.
Таможенный брокер быстро оформил документы и избавил от бумажной волокиты. Всё по делу, https://tamozhenniiy-broker-moskva.ru/
creativefashionworld – Overall very positive first impression, I’ll keep an eye on their upcoming collections.
mcalpineinfo – Navigation is straightforward but the content appears sparse and unfinished.
saveshelterpets – If you’re considering donating or volunteering, ask specifics like how many pets are helped annually and where funds go.
astoriatogether – Community unity and collaborative neighborhood initiatives.
propecianorxpharmacy.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
www-882884.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
mjiuzixun.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
gameclub2u.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
pmajoe4council – Clear campaign focus, design feels trustworthy and community-oriented.
worldvehicleexpo.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
updatingparents – The site feels thoughtful, user-friendly and clearly grounded in practical support.
Работают аккуратно, без спешки, но быстро. Документы готовы вовремя, оформление без нареканий. Рекомендую – Таможенное оформление в Домодедово
worldvehicleexpo.com – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
gameclub2u.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
www-882884.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
mjiuzixun.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
propecianorxpharmacy.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
wetten com erfahrungen
my web blog; WettbüRo Paderborn
discoverdaily.online – The visuals are appealing and complement the content nicely.
nicholashirshon – Professional portfolio showcasing expertise and accomplishments.
Wow, this article is good, my younger sister is analyzing
these things, therefore I am going to tell her.
Review my blog; roulette strategy 24 + 8 (Kisha)
futuregoalsnetwork.shop – Smooth browsing experience; easy to find what I’m looking for.
Je suis totalement transporte par BassBet Casino, on ressent une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue est riche en surprises, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. L’offre de bienvenue est electrisante. L’assistance est rapide et pro, toujours pret a mixer. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un hit. Pour conclure, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! A noter le design est moderne et vibrant, donne envie de prolonger la fete. Un atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce la communaute.
bassbetcasinoappfr.com|
choice-eats – Culinary excellence with diverse and delicious dining options.
Je suis totalement illumine par BassBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de lumieres. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs vibrants. L’offre de bienvenue est brillante. Le suivi est impeccable, avec une aide precise. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient lumineuses. En bref, BassBet Casino vaut une soiree lumineuse pour les amateurs de sensations vibrantes ! A noter le site est rapide et captivant, ajoute une touche de lumiere. Particulierement cool les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
learnsharegrow.shop – Looking forward to seeing more updates and articles from this site.
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de lac. La selection de jeux est dynamique, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient une vague. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! A noter le site est rapide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A souligner les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
anabolic enhancer
References:
https://territoriovertentes.org.br/?p=468
Je suis captive par Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, incluant des paris live dynamiques. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Le suivi est d’une efficacite absolue, joignable a tout moment. Les retraits sont rapides comme une transaction, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un atout. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, renforce la communaute.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je suis absolument ravi par Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance sophistiquee. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, incluant des paris sportifs elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient exquises. Au final, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus la navigation est simple et gracieuse, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
En savoir plus|
J’ai une affection pour Impressario Casino, ca offre un plaisir sophistique. La variete des titres est raffinee, avec des slots aux designs elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7, offrant des reponses claires. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et attractif, ajoute une touche d’elegance. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
DГ©couvrir le guide|
leadersunitedgroup.bond – The content is uplifting and very relatable, makes me think.
globalpartnershipteam.shop – Photos are crisp, descriptions honest — very helpful shopping experience.
teamfuture.bond – The design feels modern and professional; great first impression.
discovervalue.bond – Looking forward to seeing more updates and articles from this site.
winmore.bond – Branding feels consistent and trustworthy throughout the website.
connectinnovationhub.bond – Overall a polished site with professional and engaging content.
covidtest-cyprus – Essential health services with reliable testing solutions.
trustandunity.bond – Fast loading pages make the experience seamless and smooth.
businessgrowthhub.shop – Overall a polished site with professional and engaging content.
smartfashionboutique.bond – Overall a polished site with professional and engaging content.
successfultradersclub.shop – Overall a polished site with professional and engaging content.
globalalliancenetwork.bond – Content is clear, informative, and engaging; great first impression.
uniquedecorstore.shop – Navigation is intuitive; finding information is quick and effortless.
J’adore l’energie rythmee de BassBet Casino, il cree une ambiance de studio live. Le catalogue est riche en surprises, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et vibrant, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses seraient energiques. En bref, BassBet Casino vaut une session live pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! Ajoutons que le design est moderne et vibrant, donne envie de prolonger la fete. Un point fort les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
bassbetcasinoappfr.com|
Je suis ebloui par BassBet Casino, on ressent une vibe lumineuse. Les options sont vastes comme un show lumineux, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent comme un flash, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme un neon, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un eclat. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino vaut une soiree lumineuse pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un neon, donne envie de prolonger l’eclat. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
J’ai une passion lacustre pour BassBet Casino, il procure une experience dynamique. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents repondent comme une vague, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient une vague. Au final, BassBet Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et rapide, ajoute une touche de vitesse. Egalement appreciable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est impeccable, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. En resume, Spinit Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus le design est moderne et chic, ajoute une touche d’elegance. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
wellnesstourbus – Mobile health and wellness services bringing care to communities.
J’aime l’ambiance futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un smart contract. La selection de jeux est astronomique, incluant des paris live dynamiques. Le bonus d’entree est eclatant. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, garantissant un service premium. Les paiements sont securises par blockchain, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino vaut une exploration virtuelle pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement captivant les options de paris variees, renforce la communaute.
Essayer tout de suite|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui respire le luxe. Les options sont vastes comme un salon parisien, avec des slots aux designs raffines. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les fans de casino en ligne ! De plus le design est moderne et chic, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un autre atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages personnalises.
En savoir sur le sujet|
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, on ressent une ambiance delicate. La variete des titres est raffinee, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Renforcant votre capital initial. Les agents repondent avec courtoisie, garantissant un support de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Au final, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, ce qui rend chaque session plus raffinee. Un autre atout les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Voir les mises Г jour|
https://www.sarvodayanotice.com/770-2/
concernedaboutpollution – Environmental advocacy with focus on pollution awareness and solutions.
nextvision.bond – Looking forward to seeing more updates and articles from this site.
beste bonus sportwetten
Here is my web page; wettbüRo Mainz
successpathway.bond – Wide range of categories; something for everyone here.
play-brary.org – Easy to read, and the design is consistent throughout.
growthpoint.bond – Appreciate the clear and concise information provided throughout.
asianspeedd8 – Modern dating platform with cultural connection and community focus.
leanneslifechangingfairies.com – I like the friendly tone and helpful resources provided here.
createimpacttoday.shop – Fast shipping and excellent customer service; will shop here again.
uniquefashionstyle.shop – The layout is clean and the navigation is smooth which is great.
discovergreatdeal.shop – Found some amazing deals here; totally worth checking out.
moesboardwalk.com – I’ll keep an eye out for new arrivals here; looks like it has good potential.
Ich schatze die Energie bei Snatch Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Spa?. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit spannenden Sportwetten-Angeboten. Mit schnellen Einzahlungen. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, in manchen Fallen ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Zum Schluss, Snatch Casino bietet ein unvergessliches Erlebnis. Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, einen Hauch von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, die die Motivation erhohen.
https://snatch-casino.de/de-de/|
Роберт Левандовски футбол дүйнөсүндөгү эң таасирдүү чабуулчулардын бири.
Инстаграмда Роберт Левандовскинин посттору абдан популярдуу. Левандовски канча жыл ойногонуна карабай, деңгээлин түшүргөн жок. Роберт Левандовски көп жолу “алтын бутсага” татыктуу болгон. Толук биография жана сүрөттөр http://www.robert-lewandowski-kg.com сайтында жеткиликтүү. Роберт Левандовски Барселона үчүн көп гол салууда.
Роберт Левандовски бала кезинен эле футболду сүйгөн. Левандовски жаракаттан кийин дагы күчтүү кайтып келген.
Левандовскинин түпкү теги тууралуу маалымат көп талкууланат. Левандовски ар дайым жогорку деңгээлди кармайт.
grant-jt – Professional services with expertise and dedicated client support.
Ich habe einen Narren gefressen an Snatch Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Die Auswahl ist einfach unschlagbar, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Der Prozess ist einfach und transparent, manchmal gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Snatch Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Hinzu kommt die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, eine tiefe Immersion ermoglicht. Ein klasse Bonus die vielfaltigen Wettmoglichkeiten, exklusive Boni bieten.
https://snatch-casino.de/de-de/|
komunahouse – Community living space fostering connection and collaboration.
mdcphilly.com – The website design is clean and professional, very well done.
harrietlevinmillan.com – The author’s voice comes through clearly; engaging and insightful content.
ks4thekids.com – The content is clear and shows focus; I like the purpose.
brauhausschmitzoktoberfest.com – The event page looks lively and well-organized, very appealing.
clubinorout.com – Overall a subtle but solid website—won’t distract from the core message.
pp4fdr.org – I like how the coalition background is showcased; adds credibility.
mdcphilly.com – The visuals are strong and add to the appeal of the website.
concernedaboutpollution.com – Pages load quickly and the navigation feels smooth and intuitive.
berrybombselfiespot – Fun and vibrant selfie destination with creative photo opportunities.
asianspeedd8.com – The site has a modern look and it’s easy to browse.
berrybombselfiespot.com – Overall a very inviting site; makes me want to go and check the place out.
grant-jt.com – I’d like to see a bit more visuals or imagery to add character.
komunahouse.com – Overall, the brand presentation feels authentic and well-considered.
gailcooperspeaker.com – Love the encouraging tone of this site; very uplifting.
reindeermagicandmiracles.com – Navigation is simple and I found what I was looking for quickly.
gailcooperspeaker – Inspirational speaking with powerful messages and engaging delivery.
brucknerbythebridge.com – The site does a good job of balancing text and imagery; very readable.
seenministries – Faith-based ministry offering spiritual guidance and community support.
meetkatemarshall.com – Loved the variety of content – automotive, fashion, food, health – keeps things fresh.
kdjfjks.site – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
eyelle-paris.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
zakolata.xyz – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
binaryoptionstrade.xyz – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
cryptocurrencytrade.pw – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
moeinclub.com – A search feature would be useful to find specific topics quickly.
shemplymade.com – A strong online presence for a niche wellness brand—well done.
centensports.com – The site looks clean and professional; easy to browse.
BassBet Casino m’a ensorcele BassBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodique. Les options sont vastes comme une scene live, offrant des sessions live immersives. L’offre de bienvenue est envoutante. Le support client est au top, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans attendre, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. En bref, BassBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les amateurs de sensations vibrantes ! En plus l’interface est fluide comme une chanson, booste le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les options de paris variees, renforce la communaute.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de legendes. Les options sont vastes comme un grimoire, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le suivi est irreprochable, toujours pret a transformer. Les retraits sont fluides comme un conte, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et captivant, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de notes. La selection de jeux est melodieuse, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est rythme. Le support client est melodieux, avec une aide precise. Le processus est simple et elegant, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses seraient melodieuses. En bref, BassBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un riff, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
cepjournal.net – I appreciate how easy it is to find article summaries and links.
safercharging.com – It would be helpful to see more examples of recent projects or clients.
seenministries.com – Love the clear focus on empowering and equipping women; very inspiring.
J’ai une passion ardente pour Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, avec des slots aux designs modernes. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des solutions claires. Les transferts sont fiables, cependant des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du charme. Au final, Monte Cryptos Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les joueurs en quete d’innovation ! En bonus l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les evenements communautaires decentralises, propose des avantages uniques.
Naviguer sur le site|
J’aime l’ambiance futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un reseau blockchain. Les options sont vastes comme un reseau, proposant des jeux de table elegants. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, offrant des reponses claires. Les transferts sont fiables, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les passionnes de sensations numeriques ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et futuriste, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement cool les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, propose des avantages uniques.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis absolument ravi par Impressario Casino, il procure une experience distinguee. La variete des titres est elegante, incluant des paris sportifs elegants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le suivi est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient exquises. Au final, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! De plus le site est rapide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller ici|
opensky-inc.com – Good first impression — clean, credible, and user-friendly.
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui evoque le raffinement. La variete des titres est raffinee, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le suivi est irreprochable, offrant des reponses claires. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du piquant. Au final, Impressario Casino est un incontournable pour les amateurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! A noter le design est moderne et chic, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
Aller Г la page|
pastorjorgetrujillo.com – Navigation feels intuitive and information is easy to find.
casa-nana.net – I found the navigation simple and the layout helps focus on the key message.
trendingnewsfeed.net – visuals are engaging and support the headlines well.
unentschieden wetten erfahrungen
Feel free to surf to my site … Sportwetten Lizenz öSterreich
clevelandchristmasclub.com – Overall, a solid presentation that invites people to join the experience.
Je suis epoustoufle par BassBet Casino, il cree une ambiance de concert. Les options sont vastes comme une scene live, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. L’assistance est rapide et pro, avec une aide precise. Les gains arrivent sans attendre, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. En bref, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour les amateurs de sensations vibrantes ! A noter la navigation est simple et rythmee, booste le plaisir de jouer. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com|
Je suis totalement transporte par BassBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de sons. Il y a un flot de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Le support client est au top, toujours pret a mixer. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient energiques. Au final, BassBet Casino est un must pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’adrenaline ! A noter le design est moderne et vibrant, ce qui rend chaque session plus vibrante. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
bassbetcasinoappfr.com|
electmikemontes.com – Content is clear and the messaging comes across well.
Je suis emerveille par Spinit Casino, c’est une plateforme qui tourbillonne comme un conte. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a transformer. Les transactions sont fiables, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient narratives. Au final, Spinit Casino offre une experience memorable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! En bonus le design est moderne et enchante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
https://spinitcasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, ca plonge dans un monde de notes. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, toujours pret a jammer. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Au final, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme un riff, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
buildyourdreamtoday.shop – The minimal design helps focus on the product without distraction.
J’aime l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, ca transporte dans un monde virtuel. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, incluant des paris live dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec une vitesse fulgurante, garantissant un service premium. Les transferts sont fiables, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement captivant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
Visiter maintenant|
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, il procure une experience exquise. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, offrant des sessions live sophistiquees. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, toujours pret a servir. Les retraits sont fluides comme la Seine, parfois quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino offre une experience memorable pour les amateurs de sensations elegantes ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement somptueuse, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un autre atout les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde chic. Il y a une abondance de jeux captivants, offrant des sessions live distinguees. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino vaut une visite sophistiquee pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Particulierement interessant les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Voir la page|
J’adore l’elegance de Impressario Casino, ca transporte dans un monde gourmand. Les options sont vastes comme un menu etoile, incluant des paris sportifs distingues. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est impeccable, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Dans l’ensemble, Impressario Casino est une plateforme qui enchante pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple et gracieuse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec niveaux exclusifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Lire les dГ©tails|
catherinewburton.com – Content is concise and focused, which I really appreciate.
vsmphotography.com – I’ll definitely keep this site in mind whenever I need a photographer — looks solid.
exploreopportunitiesnow.shop – The layout is clean and minimal; very easy to use.
buchmacher pferderennen
Check out my blog post; Sportwetten Vorhersage heute
toddstarnesbooktour.com – Looking forward to seeing how the site updates with event recaps and photos.
createandgrow.shop – Navigation seems straightforward and the site loads without delay.
startsomethinggreat.shop – Navigation feels intuitive; I found what I was looking for quickly.
findwhatyoulove.shop – Clean and simple layout; very easy to use and browse.
theperfectgiftshop.com – It would be helpful to see more detailed reviews or user photos for added trust.
shopandsmilealways.shop – Overall a good first impression; user-friendly and pleasant to explore.
simplybestchoice.shop – The visuals are inviting and the interface feels smooth.
keepgrowingforward.shop – Navigation feels intuitive; I found what I was looking for quickly.
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog
and wished to say that I have truly enjoyed surfing around your blog posts.
In any case I will be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again very
soon!
shopandsmilealways.shop – The layout is clean and inviting; nice visual clarity.
shopandshineeveryday.shop – The layout is clean and inviting; nice visual clarity.
geteventclipboard.com – Trust signals (such as testimonials or clients) could strengthen the site.
beste alle Sportwetten anbieter
tipps
uniquetrendstore – Easy to navigate, found exactly what I was looking for.
wettanbieter mit paypal
My web page :: Martingale strategie sportwetten; theplanetexport.com,
yourtrustedonlinestore – Love discovering fresh items here; keeps the space feeling updated and fun.
newseasoncollection – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
nejlepsi-porno.top – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
porno-masaz.top – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
swissreplica.pw – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
prostitutkimoskvyonline.info – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
usaonlinecasinos.org – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
dreamcreateinspire – Fantastic variety of products, always something new and exciting.
shopthelatesttrend – Great prices and quality, will definitely shop here again.
smartchoiceoutlet – Always a pleasure shopping here, never disappoints with selections.
joinourcreativeworld – Always a pleasure shopping here, never disappoints with selections.
inspireeverydaylife – Excellent customer service, resolved my issue quickly and efficiently.
electmikemontes – Political campaign focused on community representation and positive change.
BassBet Casino m’a ensorcele BassBet Casino, on ressent une energie vibrante. La selection de jeux est harmonieuse, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Amplifiant l’excitation du jeu. Le support client est au top, offrant des solutions claires. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient vibrantes. En bref, BassBet Casino garantit un fun non-stop pour les amateurs de sensations vibrantes ! De plus la navigation est simple et rythmee, booste le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des recompenses continues.
https://bassbetcasinopromocodefr.com/|
J’adore l’atmosphere dynamique de Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de piste. La selection de jeux est dynamique, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de bienvenue est rapide. Le support client est veloce, offrant des reponses claires. Les retraits sont fluides comme un peloton, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient rapides. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une piste, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
casinospinitfr.com|
Je suis accro a BassBet Casino, il procure une experience harmonieuse. Les options sont vastes comme un album, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent comme un solo, avec une aide precise. Les retraits sont fluides comme un riff, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bien venus. Au final, BassBet Casino est une plateforme qui groove pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! A noter la plateforme est visuellement musicale, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
https://bassbetcasinobonusfr.com/|
J’adore l’atmosphere mythique de Spinit Casino, ca offre un plaisir enchante. La selection de jeux est enchantee, proposant des jeux de table elegants. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Les agents repondent comme par magie, joignable a toute heure. Le processus est simple et elegant, bien que des offres plus genereuses seraient enchantees. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! En bonus la navigation est simple et magique, ajoute une touche de mystere. Egalement appreciable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
J’adore l’ambiance delicate de Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui rayonne d’elegance. L’eventail de jeux est somptueux, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots rapides. Les agents repondent avec une douceur exquise, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et gracieux, parfois des recompenses en plus seraient exquises. Pour conclure, Impressario Casino vaut une visite elegante pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! A souligner la navigation est intuitive et delicate, ajoute une touche de finesse. Un point fort les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
En savoir davantage|
J’aime l’ambiance numerique de Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie decentralisee. Le catalogue est opulent et divers, avec des slots aux designs modernes. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Disponible 24/7 via chat ou email, toujours pret a decoder. Les transferts sont fiables, parfois des recompenses supplementaires seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Monte Cryptos Casino est une plateforme qui domine l’univers crypto pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus le site est rapide et futuriste, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
Accéder à l’avis|
Je suis enchante par Impressario Casino, on ressent une energie glamour. Le catalogue est riche et varie, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. L’offre de bienvenue est prestigieuse. Le service client est irreprochable, garantissant un service de star. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps en temps des bonus plus varies seraient une star. Au final, Impressario Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! A souligner la plateforme brille comme une premiere, facilite une immersion totale. Un point fort les options de paris variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter l’avis|
J’aime l’ambiance futuriste de Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui vibre comme un reseau blockchain. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots aux themes innovants. Renforcant votre capital initial. Le support client est stellaire, garantissant un service de pointe. Le processus est lisse comme un wallet, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Monte Cryptos Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour ceux qui parient avec des cryptos ! De plus l’interface est fluide comme un flux de donnees, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout cle les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste l’engagement.
Lire la suite|
shemplymade – Handcrafted products with quality craftsmanship and unique designs.
Howdy are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
вход через зеркало kra42 at
Ich freue mich auf Snatch Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit spannenden Sportwetten-Angeboten. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Die Mitarbeiter sind immer hilfsbereit. Gewinne kommen sofort an, trotzdem gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Abschlie?end, Snatch Casino garantiert dauerhaften Spielspa?. Zudem die Navigation ist unkompliziert, das Vergnugen maximiert. Ein gro?artiges Plus die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, fortlaufende Belohnungen bieten.
snatch-casino.de|
Je suis totalement envoute par Spinit Casino, il procure une experience rapide. La variete des titres est rapide, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est veloce, avec une aide precise. Les transactions sont fiables, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient rapides. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino est une plateforme qui accelere pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! A noter le design est moderne et dynamique, facilitate une immersion totale. Un autre atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste l’engagement.
casinospinitfr.com|
globalmarketplacehub – Easy to navigate, found exactly what I was looking for.
At this time it appears like Drupal is the best blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
официальный сайт kra42 cc
Je suis totalement envoute par BassBet Casino, il procure une experience harmonieuse. Les options sont vastes comme un album, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. L’assistance est efficace et professionnelle, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et elegant, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un riff. Dans l’ensemble, BassBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement musicale, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages personnalises.
bassbetcasinobonusfr.com|
J’adore l’atmosphere mythique de Spinit Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fees. La variete des titres est magique, offrant des sessions live immersives. Amplifiant le plaisir de jeu. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise. Les transactions sont fiables, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un chapitre. Dans l’ensemble, Spinit Casino vaut une lecture magique pour les fans de casino en ligne ! A noter l’interface est fluide comme un conte, ajoute une touche de mystere. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
spinitcasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis ensorcele par Monte Cryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse comme un reseau blockchain. La selection de jeux est astronomique, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 300 € + tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable, joignable a tout moment. Les paiements sont securises par blockchain, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est simple comme un wallet, ce qui rend chaque session plus immersive. Un avantage notable les paiements securises en BTC/ETH, qui booste l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir|
J’ai une passion brulante pour Impressario Casino, c’est une plateforme qui brille comme un festival. Le catalogue est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live immersives. L’offre de bienvenue est prestigieuse. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable, joignable a tout moment. Les retraits sont fluides comme un generique, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient eclatantes. En bref, Impressario Casino garantit un plaisir constant pour les passionnes de sensations prestigieuses ! A souligner le site est rapide et envoutant, ajoute une touche de prestige. A noter les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Ouvrir la page|
discoverendlessideas – Love the creativity and inspiration found here, always refreshing.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Monte Cryptos Casino, on ressent une energie decentralisee. La selection de jeux est astronomique, avec des slots aux themes innovants. Avec des depots crypto rapides. Le support client est stellaire, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les transferts sont fiables, mais quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Monte Cryptos Casino est un must pour les fans de blockchain pour les adeptes de jeux modernes ! En bonus la plateforme est visuellement eblouissante, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages uniques.
En savoir davantage|
brightfuturedeals – Easy checkout and secure payment made shopping worry-free this time.
everytrendinone – Love discovering fresh items here; keeps the space feeling updated and fun.
learnshareconnect – Great site that sparks creativity and gives me new perspectives daily.
discovergreatthings – The website is clean and intuitive, found what I was looking for in minutes.
findyourperfectdeal – Loved the downloadable resources section; useful for planning and idea generation.
exploreamazingideas – Great browsing experience, layouts look clean and easy to navigate.
yourjourneybegins – Prices are fair and value is excellent, will shop again for sure.
newthisdomainsssss – The site is bold, domain name stands out though content feels minimal.
brainsight-reeracoen – Definitely a good option for companies looking for expert insight in Asia.
blinkiesdonutsca – Loved stopping by, donuts were fresh and service was super friendly.
shopwithconfidence – Everything loads fast and checkout is super smooth, great experience.
tabitoshigoto – Great idea for remote workers who want to explore while staying productive.
realherschel – Customer reviews section helped a lot, feels more trustworthy than many stores.
Hello to every one, the contents existing at this site are actually remarkable for people knowledge, well, keep up the good work fellows.
маркетплейс kraken
I’m gone to inform my little brother, that he should also visit this web site on regular basis to get updated from latest gossip.
kra42 cc
ohmydrifter – Love the lifestyle blog vibe here, the visuals are clean and stylish.
code promo 1xBet paris sportifs The variations are endless: “code bonus 1xbet,” “1xbet code promo pari gratuit,” “1xbet bonus de bienvenue 2026,” and “bonus de bienvenue 1xbet.” These phrases denote a desire for diverse bonus types. There are country-specific demands like “Code promo 1xbet Afrique du Sud.”
hopeandlace – A suggestion: check how recent their blog or project updates are to ensure they’re still active.
motivilovesmusic – Happy to do a deeper check (traffic stats, ownership registry) if you’d like to assess it further.
trabas007hoki – Navigation takes a moment and some links weren’t obvious at first.
kraken market Kraken ссылка – это ключ к заветной двери, ведущей в глубины цифрового пространства, где правят свои законы. Убедитесь в подлинности источника, прежде чем доверить ему свои данные, ведь мошенники не дремлют. Остерегайтесь фишинговых сайтов и поддельных зеркал, чтобы ваше путешествие не обернулось разочарованием. Будьте бдительны и осмотрительны, и тогда сможете избежать неприятностей и насладиться всеми преимуществами платформы.
hanayaka-na-life – Really enjoy the vibe of the brand, clean aesthetic and easy to navigate.
hawaiineiartcontest – The setting of the exhibition at the Wailoa Center gives it a nice official public-art feel. :contentReference[oaicite:4]index=4
wrestlingac – Great starting point for wrestling-enthusiasts, just be sure to cross-check key information when using it in a broader research context.
envolavecning – I’d proceed cautiously if making a purchase or giving personal data—verify terms, policy, and returns.
Hi mates, its impressive post regarding tutoringand completely defined, keep it up all the time.
madmadedesigns – Content seems a bit light in places—would be good to see more project case-studies or customer feedback.
beauty-optical-salon – Product range: about 250 frames aimed at women aged late-20s to 40s. :contentReference[oaicite:6]index=6
I think that everything posted made a ton of sense. However, consider this, what if you typed a catchier title? I mean, I don’t wish to tell you how to run your website, however what if you added something to maybe grab folk’s attention? I mean %BLOG_TITLE% is a little vanilla. You might look at Yahoo’s home page and watch how they create post headlines to grab people to open the links. You might try adding a video or a related pic or two to get readers interested about what you’ve written. In my opinion, it might make your blog a little livelier.
https://kra42c.com
What’s up friends, good article and nice arguments commented at this place, I am actually enjoying by these.
https://kra42c.com
code promo tchad The demographic targeting is clear with phrases like “code promotionnel 1xBet pour nouveaux utilisateurs,” highlighting the platform’s efforts to attract new clientele through enticing welcome offers. The segmentation continues with “code promo 1xBet paris sportifs” and “code promo 1xBet casino en ligne,” directing promotions towards specific betting preferences. Bonus-centric searches dominate: “code promo 1xBet bonus de bienvenue,” “code promo 1xBet inscription,” and the tempting “1xbet code promo tours gratuits.”
96x11n.pw – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
titi.pw – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
libracryptocurrency.pw – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
worldcomputerexpo.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
globaltrendmarket – Would be great if the site displayed recent reviews, customer testimonials or third-party mentions.
dearsparrows – Navigation could improve a little — I had to hunt for older posts.
pepplish – If buying internationally, check shipping, customs fees and how fresh the product remains on arrival.
connectdiscovergrow – I hope they update regularly — content freshness will help build trust and engagement.
shopwithconfidence – Navigation feels intuitive, but it’s not clear what types of products or services are offered.
nomnomnomfordogs – Overall, a positive find for dog-owners who want something special for their pets.
flourandoak – The branding “Flour & Oak” suggests craftsmanship and wood-fired or rustic baking, which is appealing.
keepgrowingforward – Handy for anyone looking to refresh their mindset or push through a plateau.
brightnightpdx – Looks like a promising site but treat as “emerging” rather than established until more evidence appears.
staycuriousalways – Overall: positive feel, but I’d want a little more evidence of activity or user reviews before depending on it fully.
theperfectgiftshop – The offerings appear promising from the name, but verification of legitimacy is always wise.
exploreopportunitiesnow – Would be nice to see more about who runs it, and how often content is updated.
bestdealsforlife – For a backlink use, consider balancing it with more established domains to avoid risk.
createandgrow – I’d recommend exploring the site further to verify the content’s freshness and legitimacy.
Amazing things here. I’m very satisfied to peer your post. Thanks a lot and I am having a look forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a mail?
официальный сайт kra41 cc
sportwetten vergleich deutschland
Stop by my website :: gegen euro Wetten
J’adore l’harmonie de Olympe Casino, il procure une experience harmonieuse. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. Le suivi est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. En bref, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement olympienne, ajoute une touche de mythologie. Particulierement captivant les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste l’engagement.
olympefr.com|
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with some pics to drive the message home a little bit, but instead of that, this is magnificent blog. A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back.
kra41 at
ShopForHappiness – Great selection of items, site makes finding deals really easy.
buildyourdreamtoday – It would be helpful to know more about the site’s mission and the team behind it.
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, in seltenen Fallen mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Ubrigens die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein besonders cooles Feature ist das VIP-Programm mit einzigartigen Belohnungen, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Mit dem Lesen beginnen|
Ich bin beeindruckt von der Qualitat bei Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Es gibt zahlreiche spannende Spiele, mit Slots in modernem Look. 100 % bis zu 500 € plus Freispiele. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, in manchen Fallen mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spieler. Nebenbei die Plattform ist optisch ein Highlight, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die lebendigen Community-Events, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Zur Seite gehen|
Je suis captive par Olympe Casino, il procure une experience harmonieuse. Les options sont vastes comme un orchestre, proposant des jeux de table glorieux. Le bonus de bienvenue est divin. Le support client est olympien, offrant des reponses claires. Le processus est simple et glorieux, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient de la gloire. Pour conclure, Olympe Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de jeux antiques ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement olympienne, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus divin les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fiables.
olympefr.com|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est simple et transparent, occasionnellement quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui motive les joueurs.
Entrer maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, bien que des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En somme, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce la communaute.
http://www.sugarcasinoappfr.com|
Je suis fascine par Ruby Slots Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure memorable. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un point cle les options de paris sportifs variees, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller à l’intérieur|
ExploreAmazingIdeas – Navigation is smooth, site layout is clean and easy to use.
ShopTheBestToday – Always something new to discover, makes online shopping fun and exciting.
uniquetrendstore – The domain sounds catchy and suggests a focus on fashionable or niche items.
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Der Kundendienst ist ausgezeichnet. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, allerdings mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Zusammengefasst, Cat Spins Casino ist definitiv einen Besuch wert. Nebenbei die Seite ist schnell und ansprechend, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein starkes Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, exklusive Boni bieten.
Erfahren Sie wie|
Ich bin suchtig nach Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. 100 % bis zu 500 € mit Freispielen. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, trotzdem ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Zudem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, das Vergnugen maximiert. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature die dynamischen Community-Events, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
Weiter gehen|
Je suis emerveille par Ruby Slots Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par ailleurs plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En fin de compte, Ruby Slots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour completer le site est rapide et engageant, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://rubyslotscasinobonusfr.com/|
InspireEverydayLife – Customer support was helpful, answered all my questions promptly and politely.
Je suis epate par Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Sugar Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En complement le design est moderne et energique, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A souligner le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce le lien communautaire.
Aller sur le site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une visite excitante. A souligner l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une energie supplementaire. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des recompenses continues.
Commencer ici|
makelifebetter – I keep returning here, always find interesting products quickly and easily.
FindYourPerfectDeal – Fast shipping, products arrived on time and in perfect condition today.
changeyourworld – Always something new to discover, makes online shopping fun and exciting.
TheBestPlaceToShop – Deals are updated frequently, site is reliable and trustworthy overall.
startsomethinggreat – Customer support was helpful, answered all my questions promptly and politely.
ShopAndSmileAlways – Customer support was helpful, answered all my questions promptly and politely.
TrendyFindsHub – Fast shipping, items arrived in perfect condition as expected online.
learnshareconnect – Thought-provoking articles and discussions that broaden understanding and perspectives.
changetheworld – The domain name is impactful and suggests a platform for positive change.
findwhatyoulove – Prices are reasonable, found exactly what I wanted without any hassle.
everydayvaluecorner – I keep returning here, always find interesting products quickly and easily.
everytrendinone – Always something new to discover, makes online shopping fun and exciting.
newseasoncollection – Deals are updated frequently, site is reliable and trustworthy overall.
GlobalMarketplaceHub – Deals are always updated, makes shopping here very convenient indeed.
yourjourneybegins – Customer support was helpful, answered all my questions promptly and politely.
Hi, I think your website might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, terrific blog!
https://www.buybuy.com.pk/2025/10/09/melbet-skachat-kazino-obzor-2025/
Can you tell us more about this? I’d love to find out more details.
https://www.startools-eg.com/melbet-skachat-na-android-besplatno-s-oficialnogo-2025/
ultimateprofitplan – Love how this site explains profit strategies in such a clear way.
https://zumo-spin-games.com/
smarttradingmentor – The guidance feels personal and well thought out, not just copied advice.
trendandstyle – Definitely my new go-to shop for stylish, on-point fashion every season.
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
smartbuytoday – Feels like a one-stop place for everyday items at fair prices.
brightmarketplace – This store has a fun energy, feels welcoming every time I visit.
shoplocaltrend – I like how the shop mixes modern design with small business authenticity.
freshstylemarket – I like how fresh and clean the layout feels, easy to navigate.
classytrendstore – Everything feels thoughtfully curated, makes it easy to shop stylishly.
bestdealcorner – The checkout process was smooth, and delivery came right on schedule.
bestdealcorner – The product descriptions are clear, makes it easy to choose confidently.
visionpartnersclub – The design looks sleek and professional, makes exploring super enjoyable.
online wettanbieter
My blog post … wetten bester bonus (Sam)
discovergreatvalue – The items look exactly like the photos, no surprises which I love.
classyhomegoods – Prices are reasonable considering the premium quality and classy design.
freshfashionfinds – The outfits here are amazing, perfect mix of comfort and elegance.
uniquefashionboutique – Great customer service, they answered my questions super fast and politely.
futuregrowthteam – I appreciate how consistent the updates are, always something valuable to learn.
dailyprofitupdate – I appreciate the clear layout, makes analyzing profits much easier today.
worldcityexpo.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
BuildStrongRelationship – I appreciate the consistent updates, always fresh perspectives and ideas.
protraderacademy – Feels like a solid educational space for serious traders who want progress.
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
yourtradingmentor – Love the guidance here, really helps me refine my trading mindset daily.
BusinessConnectWorld – Great site, offers meaningful connections and growth opportunities globally.
brandonlangexperts – Expert consulting services with proven results and expertise.
Je suis totalement envoute par Olympe Casino, on ressent une energie divine. Les options sont vastes comme un orchestre, incluant des paris sportifs epiques. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Les agents repondent comme des muses, garantissant un support celeste. Les retraits sont rapides comme une melodie, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient divins. Pour conclure, Olympe Casino offre une experience legendaire pour les amateurs de sensations mythiques ! En bonus le design est moderne et divin, ajoute une touche de mythologie. Un plus divin les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses eternelles.
https://olympefr.com/|
connectforprogress – The content here really motivates me to keep improving every single day.
Helpful info. Fortunate me I discovered your web site accidentally, and I am surprised why this twist of fate didn’t came about in advance! I bookmarked it.
https://kastil138.co/melbet-prilozhenie-skachat-obzor-2025/
purebeautyoutlet – Love how clean and soft the design feels, really inviting store.
worldsoftwareexpo.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
ferdykorpwp.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
acte-experts.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Hi, after reading this awesome post i am too cheerful to share my knowledge here with colleagues.
https://www.roshan-clinic.com/2025/09/24/melbet-bonus-pri-registracii-obzor/
shopwithsmile – Love the cheerful vibe here, makes online shopping feel light and fun.
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur ein fesselndes Erlebnis. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit Live-Sportwetten. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, manchmal ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Nebenbei die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, das Spielerlebnis bereichert. Ein tolles Extra die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Loslegen|
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Die Spielauswahl ist ein echtes Highlight, mit modernen Slots in ansprechenden Designs. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, allerdings mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Ubrigens ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, zum Bleiben einladt. Besonders erwahnenswert die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Seite ansehen|
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein mitrei?endes Spielerlebnis. Die Spielauswahl ist ein echtes Highlight, mit immersiven Live-Dealer-Spielen. Er macht den Start aufregend. Die Mitarbeiter sind immer hilfsbereit. Gewinne kommen sofort an, von Zeit zu Zeit zusatzliche Freispiele waren willkommen. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und modern, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein weiteres Highlight ist das VIP-Programm mit tollen Privilegien, exklusive Boni bieten.
Jetzt stöbern|
J’adore l’harmonie de Olympe Casino, ca offre un plaisir melodieux. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots thematiques antiques. Avec des depots rapides. Les agents repondent comme des muses, avec une aide precise. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient olympiennes. En resume, Olympe Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs pour les fans de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le site est rapide et glorieux, ajoute une touche de mythologie. Un plus divin les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
olympefr.com|
J’ai un faible pour Sugar Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par moments des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Sugar Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, garantit des paiements rapides.
Parcourir maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est impeccable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, toutefois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Globalement, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, apporte une energie supplementaire. A mettre en avant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. Pour completer le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les options variees pour les paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
http://www.rubyslotscasinobonusfr.com|
Je suis totalement conquis par Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure memorable. A signaler le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un plus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, renforce la communaute.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu unvergesslichen Momenten ein. Das Angebot an Titeln ist riesig, mit Slots in modernem Look. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren willkommen. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein gro?artiges Bonus ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Mit dem Lesen beginnen|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht pure Spannung. Das Angebot an Titeln ist riesig, mit spannenden Sportwetten-Angeboten. Er bietet einen gro?artigen Vorteil. Der Kundensupport ist top. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, manchmal ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spieler. Nebenbei die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, zum Weiterspielen animiert. Ein gro?artiges Plus die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
http://www.catspinscasino777.com|
online wetten beste anbieter
Also visit my site; buchmacher bonus, Eliza,
Je suis accro a Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En bonus la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, cree une communaute vibrante.
Entrer sur le site|
Je suis fascine par Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est clair et efficace, occasionnellement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Sugar Casino offre une aventure memorable. En complement le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement attrayant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fiables.
Entrer maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, toutefois des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir|
forexstrategyguide – I like how they break down complex forex topics into easy, digestible lessons.
brahmanshome – Great website, navigation feels smooth and everything is easy today.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En complement l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un atout les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus constants.
Entrer maintenant|
everydaytrendshop – Definitely becoming my favorite spot for everyday fashion inspiration online.
yourtradingmentor – I like how the content focuses on discipline, mindset, and steady growth.
teamworkinnovation – Love the positive message here, all about growth through collaboration and creativity.
globalchoicehub – Love how diverse the product selection is, truly something for everyone.
simplelivinghub – Perfect place to find thoughtful, clutter-free items for everyday living.
shopandshine – Great mix of trendy products and home favorites, something for everyone.
teamworksuccesspath – Love the message here, all about collaboration and building success together.
successnetworkgroup – Love how this platform promotes collaboration and shared success among professionals.
uniquedecorstore – Great selection of items that really elevate the look of any space.
globalmarketinsight – Love how everything is presented clearly without unnecessary jargon or fluff.
markettrendalerts – Feels like a professional tool for anyone serious about trading effectively.
successfultradersclub – The content is clear, concise, and encourages disciplined trading habits effectively.
Are you searching for good working activator for MS Office? On this site you can download the latest version of it: https://artmundo.org/
kraken ссылка Kraken ссылка – это навигатор по бескрайним просторам даркнета, указывающий путь к заветной цели. Однако, доверять первой попавшейся ссылке равносильно прыжку в пропасть с завязанными глазами. Прежде чем сделать этот шаг, убедитесь в её подлинности, проверьте репутацию источника и подготовьтесь к возможным неожиданностям. Безопасность превыше всего, и только внимательность и осторожность помогут вам избежать неприятных сюрпризов.
csiingenieros.com – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
difyd2c.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
learnandtrade – Love how this site combines trading education with practical real-world examples.
buchmacher ohne steuer
Also visit my website; sport wette
wett tipps heute vorhersage
Here is my web-site: online wetten Paypal (http://Www.ladailyfinance.com)
kraken сайт Kraken ссылка – это навигатор по бескрайним просторам даркнета, указывающий путь к заветной цели. Однако, доверять первой попавшейся ссылке равносильно прыжку в пропасть с завязанными глазами. Прежде чем сделать этот шаг, убедитесь в её подлинности, проверьте репутацию источника и подготовьтесь к возможным неожиданностям. Безопасность превыше всего, и только внимательность и осторожность помогут вам избежать неприятных сюрпризов.
app wetten Ergebnisse mit
freunden
paws21airbrushstudio – A go-to studio for unique, high-quality airbrush designs.
lithestore.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
motocitee – Really enjoy visiting, articles are short but informative every single time.
kivurc – Enjoyed reading these posts, ideas are simple yet very useful.
raspinakala – Really helpful tips here, saved me hours of unnecessary work.
wooziewear – Great website, navigation feels smooth and everything is easy today.
expandyourhorizon – A must-visit site for anyone interested in diverse subjects.
inkorswimtattoocruise – Really helpful tips here, saved me hours of unnecessary work.
lotsofonlinepeople – I appreciate the fresh perspectives shared on this platform.
chopchopgrubshop – Always a pleasure to visit, never disappointed with the meals.
letter4reform – This site offers insightful perspectives on social justice reform.
oldschoolopen – Excellent resource, practical guides make home projects feel stress-free always.
zz-meta – Excellent explanations, made complex topics feel much easier instantly.
chopchopgrubshop – Always fresh ingredients and innovative dishes that keep me coming back.
ieeb – Always a pleasure to read, informative and well-written articles.
ieeb – A must-visit site for anyone interested in diverse subjects.
lastminute-corporate – Comprehensive services cater to all corporate travel needs in one place.
broodbase – Always a pleasure to read, informative and well-written content.
kazhanmaster – A great resource for staying updated on various topics.
SEO-продвижение помогает сайту быть эффективным и надёжным инструментом для бизнеса. Работа с контентом, внутренними ссылками и техническими аспектами страниц повышает позиции и конверсию. Регулярная аналитика и корректировка стратегии обеспечивают долгосрочный результат. В результате сайт привлекает больше клиентов и укрепляет доверие аудитории. Подробнее по ссылке https://wikibuilding.org/index.php?title=User:AntonioQuintana
sjydtech – I like the modern design here, tech feel is professional and clean.
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit modernen Slots in ansprechenden Designs. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Der Support ist zuverlassig und hilfsbereit. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, ab und zu gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Ein gro?es Plus die regelma?igen Turniere fur Wettbewerbsspa?, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Details finden|
conorjmurphy – Really helpful tips here, saved me hours of unnecessary work.
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. Er macht den Einstieg unvergesslich. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergleichliches Erlebnis. Hinzu kommt die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, eine vollstandige Immersion ermoglicht. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die regelma?igen Turniere fur Wettbewerbsspa?, zuverlassige Transaktionen sichern.
Informationen erhalten|
Ich bin vollig uberzeugt von Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit immersiven Live-Dealer-Spielen. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, jedoch zusatzliche Freispiele waren willkommen. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Zudem die Navigation ist einfach und klar, das Spielerlebnis bereichert. Ein starkes Plus die dynamischen Community-Events, die Teilnahme fordern.
http://www.catspinsbonus.com|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine mitrei?ende Stimmung. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, allerdings mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Au?erdem die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die spannenden Community-Aktionen, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
Mit dem Surfen beginnen|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots fluides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour faire court, Sugar Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement super les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Je suis accro a Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, rarement plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino assure un fun constant. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un avantage notable les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fluides.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit modernen Slots in ansprechenden Designs. Mit schnellen Einzahlungen. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und zuverlassig, ab und zu zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Bonus. Im Gro?en und Ganzen, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur kontinuierlichen Spa?. Nebenbei die Seite ist schnell und einladend, zum Verweilen einladt. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, personliche Vorteile bereitstellen.
Website prГјfen|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Globalement, Sugar Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une immersion complete. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des bonus constants.
Explorer la page|
J’adore l’energie de Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, en revanche des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino merite un detour palpitant. A mentionner le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A signaler le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Voir les dГ©tails|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Sugar Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, malgre tout des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Sugar Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute soudee.
https://sugarcasinobonusfr.com/|
Ich liebe das Flair von Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Hotspot fur Spielspa?. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Der Service ist absolut zuverlassig. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, gelegentlich gro?ere Boni waren ideal. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Au?erdem die Seite ist schnell und attraktiv, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein besonders cooles Feature ist das VIP-Programm mit einzigartigen Belohnungen, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Weitergehen|
Ich bin ganz hin und weg von Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit klassischen Tischspielen. Er gibt Ihnen einen tollen Boost. Der Support ist schnell und freundlich. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und effizient, von Zeit zu Zeit ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Spieler. Zudem die Plattform ist optisch ansprechend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein wichtiger Vorteil die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, personliche Vorteile bereitstellen.
Hier starten|
Ich bin suchtig nach Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Die Spielesammlung ist uberwaltigend, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Die Mitarbeiter antworten prazise. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, manchmal mehr Bonusvarianten waren ein Hit. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Nebenbei die Benutzeroberflache ist klar und flussig, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein hervorragendes Plus die lebendigen Community-Events, fortlaufende Belohnungen bieten.
Online gehen|
Je suis fascine par Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. De surcroit le design est tendance et accrocheur, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est transparent et rapide, en revanche plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une visite excitante. En extra la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un element fort les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des bonus constants.
Continuer ici|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Sugar Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages uniques.
Plongez-y|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour faire court, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui booste la participation.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement fun les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller sur le site|
styleforliving – Clean layout, great variety and easy to navigate shopping experience.
buildabetterworld – A very encouraging find; feels reliable and well-presented.
everydaystylecorner – Lovely store, found some stylish pieces that really appeal to me.
l2dkp.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
spartanwebsolution.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
vqscvasavtzqpsj.shop – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
imgs81.men – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
pok01.live – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
daman-games.live – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
makelifesimpler – Great resource for anyone looking to simplify and organize.
yourcreativejourney – Overall impression is positive; nice experience so far with this site.
theworldawaits – Checkout process was quick and the payment options looked safe.
https://ritual-uslugi-spb-reg.ru/
online Tipster sportwetten startguthaben
discovergreatdeals – Easy to browse with clear pricing and helpful details.
Автоматические выключатели
discovernewthings – Overall good first impression; hoping delivery and quality match expectations.
bestvaluecollection – Found some items worth adding to my wish-list for later.
changan uni характеристики https://changan-v-spb.ru
Wett Tipps Wochenende vorhersage heute
buildabetterworld – Uplifting concept, site feels full of purpose and positivity.
7k casino регистрация casino 7k онлайн предлагает непрерывный доступ к играм, что делает его идеальным выбором для онлайн-развлечений.
changeyourdirection – Overall a good first impression; looking forward to seeing how quality and service deliver.
growwithconfidence – Navigation is intuitive, making it easy to explore what’s available.
getinspireddaily – Customer service info is visible, which adds trust to the experience.
uniquelifestylehub – Found some interesting items that seem well presented and modern.
globalstylemarket – Clear images and layout make browsing simple and enjoyable.
connectlearncreate – Checkout seemed straightforward and the payment/payment-info section was visible.
casino 7k онлайн 7к казино официальный сайт гарантирует безопасность личных данных и честность азартных игр.
exploreandcreate – The store layout is clean and gives a strong exploring vibe.
fashionloverszone – The checkout process seemed straightforward and payment options appear visible.
modernlivingstore – Customer support/contact info seems accessible, which adds confidence.
shopwithstylehub – A wide variety of items caught my eye, looks promising.
connectwithideas – Checkout seems straightforward and payment options appear transparent.
findjoytoday – The messaging about “joy” resonates and gives a positive feel to shopping.
makeimpacttoday – The site loads well and the layout gives a professional vibe.
dreambuyoutlet – Navigation feels intuitive and categories are easy to browse through.
discoveryourpotential – Navigation appears smooth and product or service categories seem clear.
kraken market Kraken сайт – это зеркало цифровой эпохи, отражающее как светлые, так и темные её стороны. Это территория, где стираются границы между реальностью и иллюзией, где власть обретает анонимность, а свобода граничит с опасностью. Здесь царят свои законы и правила, требующие от каждого участника не только осведомленности, но и ответственности за свои действия. Погружение в этот мир требует хладнокровия, осторожности и умения видеть за заманчивыми предложениями потенциальные риски.
Максимум качества, минимум травм. Профессиональные наборы для татуировки: машинки, блоки питания, премиум-краски. Всё для стерильной и крутой работы. Обновите свой арсенал сегодня https://tattoo-sale.ru/
kraken сайт Kraken ссылка – это как нить Ариадны, ведущая сквозь темный лес цифрового мира к самому сердцу платформы. Однако, прежде чем довериться этой нити, убедитесь в её прочности и надёжности, ведь в сети подстерегают коварные обманщики, готовые воспользоваться вашей неосторожностью. Проверяйте каждый символ, каждое слово, чтобы не стать жертвой фишинга и не потерять свои сбережения. Помните, что безопасность – это прежде всего ваша личная ответственность.
modernhomefinds – Navigation between categories is intuitive; browsing feels effortless and pleasant.
findyourdreamplace – The theme “find your dream place” resonates nicely—the vibe is uplifting.
discoveramazingoffers.shop – Always updated, I like seeing new offers every single day.
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, immer parat zu assistieren. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, dennoch die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Daruber hinaus das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, was jede Session noch besser macht. Zusatzlich zu beachten die schnellen Einzahlungen, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque foi muito alem do que imaginei. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: poquer estrategico, todos funcionando perfeito. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que faz diferenca. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que seria legal torneios de slots, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Na minha visao, o 4PlayBet Casino vale demais a pena. Vale experimentar.
soft 4play savage gear|
Ich bin begeistert von der Welt bei Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht ein einzigartiges Abenteuer. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit dynamischen Wettmoglichkeiten. Der Bonus fur Neukunden ist attraktiv. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, ab und zu regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Au?erdem die Benutzeroberflache ist flussig und intuitiv, zum Weiterspielen animiert. Ein bemerkenswertes Feature die spannenden Community-Aktionen, individuelle Vorteile liefern.
Zur Website gelangen|
I’m totally impressed by Pinco, you feel the buzz from the first spin. The library is packed with surprises, including crypto-friendly games. With instant, hassle-free deposits. Support is fast and welcoming. Transactions are reliable and efficient, however a couple extra spins would be sweet. To wrap up, Pinco earns its top spot. Bonus points navigation is smooth and smart, which makes every moment count. A strong element are the diverse sports betting options, that fuels player loyalty.
Get info|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En fin de compte, Ruby Slots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En extra la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Voir les dГ©tails|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, Ruby Slots Casino merite un detour palpitant. En bonus le design est style et moderne, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement cool les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis fascine par Sugar Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Sugar Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A souligner le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir la page|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, en revanche plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Au final, Sugar Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour completer la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un atout les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
urbanwearstudio – I’ll bookmark this store for future visits when I’m shopping for streetwear.
brwon-stake.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
gotqlb.cc – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
5415015.cc – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
getmyfunsocks.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
lovehentai.info – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
Discover the best PS2 games in Canada! A curated list of timeless classics, including action, RPGs, and sports titles. Relive the nostalgia of top PlayStation 2 hits loved by gamers: PS2 game reviews and ratings
imaginelearnexplore – Found items that look interesting; hoping quality and delivery match the site.
rikvip1.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
discoverandcreate – The site looks inviting and the theme of creation really shines through.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
explorewithpassion.shop – Love the adventurous feel here, everything inspires creativity and curiosity.
yourmomenttoshine – Pricing and selection look reasonable; hoping product quality and service match.
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque me pegou de surpresa. A variedade de jogos e de cair o queixo: poquer estrategico, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que raramente vi. Fiz saque em cartao e o dinheiro entrou na mesma hora, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Enfim, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Eu ja voltei varias vezes.
4play velgen 19 inch|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, garantiert top Hilfe. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, trotzdem die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, fugt Magie hinzu. Besonders toll die Sicherheit der Daten, die Vertrauen schaffen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich bin absolut begeistert von Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Das Angebot ist ein Paradies fur Spieler, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Transaktionen sind immer sicher, dennoch ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Zusatzlich die Navigation ist einfach und klar, jeden Augenblick spannender macht. Ein wichtiger Vorteil ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Zur Website gehen|
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine aufregende Atmosphare. Die Spielauswahl ist beeindruckend, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, manchmal mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Nebenbei die Benutzeroberflache ist flussig und intuitiv, eine Note von Eleganz hinzufugt. Ein tolles Feature die dynamischen Community-Events, die Teilnahme fordern.
Seite ansehen|
I’m blown away by Pinco, it’s where the real action happens. The catalog is a player’s paradise, with slot machines in fresh themes. 100% up to $500 + Free Spins. The service is outstanding. Cashouts are easy and rapid, on occasion extra rewards would be a bonus. Bottom line, Pinco is a platform that rocks. Plus the design is sleek and modern, which makes every moment count. A bonus perk are the lively community events, that strengthens player bonds.
Visit for more|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des tables live interactives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par contre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement cool les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, garantit des paiements securises.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
Je suis totalement conquis par Sugar Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est clair et efficace, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce la communaute.
Explorer plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Sugar Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est clair et efficace, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Sugar Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons egalement le site est rapide et immersif, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des bonus constants.
Aller plus loin|
changeyourperspective – The theme “change your perspective” resonates with personal growth and discovery.
findjoyeveryday.shop – Always a good mood boost browsing these joyful collections online.
findyourmoments.click – Great reminder to pause sometimes and enjoy simple happy moments.
yourdailyshoppinghub.shop – Love the variety here, feels like one stop for everything.
classyfindsonline.shop – Love the elegant feel here, every product looks thoughtfully selected.
trendinghomeideas.shop – Very stylish store, love checking new arrivals for creative ideas.
buildsomethingnew.shop – Love how organized the site feels, makes browsing projects enjoyable.
simplevalueplace.shop – Always appreciate clear pricing, makes online shopping feel stress-free.
smartfashionboutique.shop – Love the variety, from casual wear to classy event pieces.
startanewjourney.shop – Beautiful layout and message, reminds me to embrace change courageously.
trendingstyleworld.shop – Smooth shopping experience, delivery came right on time as promised.
changeyourperspective.click – Love how this site challenges my mindset in refreshing ways today.
modernlivingtrend.shop – The decor trends here always inspire me to redecorate my space.
findyourpathnow.shop – Great site overall, helps me reflect and focus on personal growth.
staycuriousdiscover.shop – Beautiful layout and message, everything encourages discovery and imagination.
yourmomentstarts.click – So positive and refreshing, definitely worth visiting again and again.
modernlivingstore.click – Love browsing this shop, everything feels trendy and thoughtfully curated.
exploreendlessideas.shop – So many cool ideas here, really gets my imagination flowing fast.
Онлайн казино
freshfashioncorner.shop – Always impressed here, stylish finds that don’t break the budget.
classychoiceoutlet.click – Stylish collection overall, love the elegant and affordable fashion pieces.
yourmomentstarts.shop – Perfect site for morning inspiration, helps me refocus on priorities.
dreambelieveachieve.shop – Love the motivational tone, helps me keep working on goals.
classychoiceoutlet.shop – Really like the clean layout, makes shopping super enjoyable today.
discoveryourpath.click – Beautifully designed site, helps me focus on personal growth daily.
https://bookmarks4seo.com/story20492197/meilleur-code-promo-1xbet-rdc
findyourdreamplace – Reading this feels like planning a dream trip from my couch honestly.
zanwechat.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
sghjt.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
023rongzi.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
fl508.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
318hw.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
szsfujin.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
connectlearncreate.click – Amazing community vibe, love the focus on creativity and learning together.
createinspirelead.click – Love the empowering tone here, truly encourages creativity and leadership.
createinspirelead – Overall a positive first impression; looking forward to seeing service and product performance.
happylivingstore – I like how everything feels curated for comfort, not just for style.
inspirechangealways – I stumbled here by chance, and wow it’s really uplifting content.
startanewjourney – The writing feels authentic, like advice from a wise, kind friend online.
Je suis totalement seduit par 7BitCasino, c’est une veritable plongee dans un univers palpitant. Il y a une profusion de titres varies, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le support est ultra-reactif et professionnel, garantissant une aide immediate via chat en direct ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins j’aimerais plus d’offres promotionnelles, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. En resume, 7BitCasino est une plateforme d’exception pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Notons egalement que l’interface est fluide et retro, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino promo code|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Au?erdem die Navigation ist kinderleicht, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein weiterer Vorteil die mobilen Apps, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
smartfashionboutique.click – Stylish and modern pieces, definitely my go-to for classy fashion.
changeyourdirection – Love the idea behind this site, change always starts with awareness first.
findjoytoday – The posts are light yet meaningful, great for a calm evening read.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, quelquefois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Sugar Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Ajoutons aussi la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
yourdailytrend.click – Great source for everyday fashion inspiration, always something new featured.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, toutefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En bonus le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement cool les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
shopwithstylehub – Love how this site curates trendy items that still feel affordable.
simplevalueplace – Definitely my new go-to spot for simple, smart, and valuable finds.
explorethefuture – I always learn something new here about trends and future innovation.
startsomethingtoday – Visited today and ended up reading way more posts than expected.
Je suis epate par Ruby Slots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, rarement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un point cle les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, assure des transactions fluides.
Naviguer sur le site|
learnandgrowtoday – This page always gives me a gentle push to keep learning something new.
startsomethingtoday – I enjoy the friendly tone here, makes change feel totally achievable.
freshfashioncorner – Browsing here always gives me fun new ideas for my wardrobe updates.
findyourpathnow – The advice here feels grounded and actually doable in real life.
trendingstyleworld – I like how this site stays updated with what’s hot in fashion now.
purevalueoutlet – Found some amazing deals here, honestly better than many big-name stores.
Входная дверь – это первый рубеж безопасности вашего жилища. Металлические входные двери сочетают в себе максимальную защиту от взлома, долговечность и современный дизайн, создавая надежный барьер между вашим домом и внешним миром: железные двери в квартиру
modernlivingstore.click – Love browsing this shop, everything feels trendy and thoughtfully curated.
Ich bin suchtig nach Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Gewinne werden schnell uberwiesen, ab und zu mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist optisch ansprechend, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, ma?geschneiderte Vorteile liefern.
Weiterlesen|
J’adore a fond 7BitCasino, ca procure une experience de jeu electrisante. La selection de jeux est colossale, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, repondant en un clin d’?il. Le processus de retrait est simple et fiable, cependant plus de tours gratuits seraient un atout, ou des promotions hebdomadaires plus frequentes. En fin de compte, 7BitCasino est une plateforme d’exception pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Par ailleurs le site est concu avec style et modernite, ajoute une touche de raffinement a l’experience.
7bitcasino no deposit bonus codes 2020|
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Nervenkitzel. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit klassischen Tischspielen. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Der Kundendienst ist hervorragend. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, von Zeit zu Zeit waren mehr Bonusvarianten ein Plus. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Zudem die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein gro?artiges Bonus die lebendigen Community-Events, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Jetzt zugreifen|
Ich bin absolut begeistert von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Die Auswahl ist so gro? wie ein Casino-Floor, mit Spielautomaten in beeindruckenden Designs. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Der Service ist von hochster Qualitat. Gewinne kommen sofort an, jedoch haufigere Promos wurden begeistern. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort fur pure Unterhaltung. Zusatzlich ist das Design zeitgema? und attraktiv, jeden Moment aufregender macht. Ein tolles Extra sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, die Community enger verbinden.
Jetzt starten|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, obwohl mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein Pluspunkt ist die schnellen Einzahlungen, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
1000 рублей за регистрацию с выводом
J’adore l’energie de Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, parfois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute soudee.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
J’ai un faible pour Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est simple et transparent, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En somme, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. En bonus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des bonus constants.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement l’interface est lisse et agreable, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement excellent les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
everydaystylecorner – I keep coming back for new ideas, very inspiring without being overwhelming.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино с выводом без депозита
getmoreforshop – Everything works smoothly and checkout was super simple, great experience.
Ich bin suchtig nach Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur ein fesselndes Erlebnis. Das Spieleportfolio ist unglaublich breit, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Auszahlungen sind schnell und reibungslos, jedoch mehr Bonusoptionen waren top. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino ist perfekt fur Casino-Liebhaber. Au?erdem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, das Spielvergnugen steigert. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra die dynamischen Community-Events, die Community enger verbinden.
Plattform besuchen|
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
9e2seattle.com – Love the local coverage here, very informative and well-presented overall.
phillybeerfests.com – Great way to support craft beer culture and hang out with friends in Philly.
нарколог на дом
nsfeg.org – Great resource for learning, very informative and well-structured content overall.
inspirechangealways.click – Posts always spark thoughtful reflections, I enjoy reading regularly here.
chrishallforjudge.com – It’s good that biographical and policy details are present and easy to find.
berenux.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
uucncn.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
waziqiyi.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
jpl927.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
46466497.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
s1565.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
orourkeforphilly.com – Volunteer and event info are clearly displayed, makes getting involved straightforward.
happylifestylehub.shop – Navigation appears minimal; users might feel uncertain about site credibility at this stage.
nataliakerbabian.com – The mix of architecture, illustration and memory-culture is compelling and unique.
smyrnafestival.com – Social media updates are frequent, which helps stay informed and excited.
monumentremoval.org – Important initiative, clearly explains the process and historical context respectfully.
localphlmarket.com – Supporting local Philly artists and makers is such a meaningful initiative.
garymasino.com – Good to see client-focused language and clear value proposition on the site.
electcateriarmccabe.com – Overall, a solid campaign website that makes me want to learn more and follow along.
trustedleaderscircle.bond – Appreciate how they highlight community and collaboration in leadership development.
newhorizonsnetwork.shop – Appreciate the clear presentation of product images and descriptions — helpful.
successpathway.bond – Mobile view looked responsive—on my phone it loaded properly.
joinourcreativeworld.shop – Domain appears to be active, but the content seems incomplete or under construction.
shopthelatesttrend.shop – I’d recommend waiting until this site is fully built out, or choose an alternative domain with visible trust indicators.
thinkcreategrow.click – Since there are no visible products or brand info yet, linking may offer limited trust value.
exploreamazingideas.click – I’d recommend monitoring the domain over the next few weeks for updates before committing.
cycleforsci.org – Great to see women and diverse scientists featured in your outreach efforts.
cumberlandcountynjvaccination.org – Found it after searching for local vaccine clinics and this was very useful.
mcalpineinfo.com – Love the detailed info here, very helpful and easy to follow.
oneillforda.com – Shared this site with friends interested in local elections; everything looks professional.
uncommittednj.org – Great site if you’re looking for a grassroots voice and fresh perspective.
bisbro.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
hardman4schools.com – Great campaign site, clearly communicates vision and priorities for education.
haginsforphilly.org – I shared this link with friends because the vision feels grounded and honest.
pmajoe4council.com – Informative site, provides clear insight into policies and council initiatives.
Отличная подборка сервисов для генерации картинок, которая реально помогла разобраться в теме. Попробовал несколько вариантов из статьи, и все работают качественно. Теперь знаю, куда обращаться за визуалами: https://vc.ru/top_rating/2301994-luchshie-besplatnye-nejroseti-dlya-generatsii-izobrazheniy
remiphl.com – Great spot for authentic pasta and relaxed vibes, loved it.
dibrunobottleshop.com – I found some great craft beers here, awesome selection and vibe.
createandgrow.shop – For now it seems under development; linking to it may offer limited value in its current state.
findwhatyoulove.shop – On mobile the layout also seems incomplete — improving this would increase credibility.
Acho simplesmente sensacional BacanaPlay Casino, oferece uma aventura de cassino que pulsa como um tamborim. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, oferecendo sessoes de cassino ao vivo que sambam com energia. O servico do cassino e confiavel e cheio de swing, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem perder o ritmo. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um carro alegorico, de vez em quando mais bonus regulares no cassino seria brabo. No geral, BacanaPlay Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro axe para os amantes de cassinos online! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e reluz como uma fantasia de carnaval, o que torna cada sessao de cassino ainda mais animada.
bacanaplay bГґnus|
chery tiggo chery tiggo 7
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur Cat Spins Casino, es sorgt fur pure Unterhaltung. Es gibt eine enorme Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Mit sofortigen Einzahlungen. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Auszahlungen sind zugig und unkompliziert, allerdings gro?ere Angebote waren super. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergessliches Erlebnis. Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ansprechend, zum Weiterspielen animiert. Ein besonders cooles Feature sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Vertiefen|
modernlivingstyle.shop – The branding is consistent, gives a sense of modern, curated aesthetics.
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, dennoch mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren super. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Hinzu kommt die Site ist schnell und stylish, was jede Session noch besser macht. Besonders toll die Sicherheit der Daten, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
simplybestchoice.click – The domain looks clean, I like the potential behind this name.
simonscider.co.uk – Delicious cider options, love the quality and unique flavor choices here.
Je suis totalement conquis par Ruby Slots Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des tables live interactives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, malgre tout des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino merite une visite dynamique. En extra l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
leanneslifechangingfairies.com – Beautiful and imaginative site, full of magical ideas for everyone.
J’adore l’energie de Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est simple et transparent, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Sugar Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des privileges personnalises.
VГ©rifier ceci|
Je suis accro a Sugar Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, occasionnellement plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino vaut une visite excitante. Pour ajouter le site est fluide et attractif, booste le fun du jeu. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs variees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Explorer la page|
J’adore l’energie de Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, toutefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Ruby Slots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A signaler les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Aller sur le site|
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit immersiven Live-Dealer-Spielen. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, gelegentlich mehr Bonusvarianten waren ein Hit. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergessliches Erlebnis. Ubrigens die Plattform ist optisch ansprechend, jede Session unvergesslich macht. Ein weiteres Highlight sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, kontinuierliche Belohnungen bieten.
Dies ausprobieren|
hopeandlace.com – The brand name is elegant and memorable—could be strong if full store launched.
Ich bin total hingerissen von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein immersives Erlebnis. Es gibt eine enorme Vielfalt an Spielen, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Der Support ist professionell und schnell. Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, in manchen Fallen ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Muss fur Spieler. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, eine tiefe Immersion ermoglicht. Ein bemerkenswertes Extra die regelma?igen Wettbewerbe fur Spannung, das die Motivation steigert.
Nachsehen|
Ich freue mich auf Cat Spins Casino, es entfuhrt in eine Welt voller Spa?. Das Angebot an Titeln ist riesig, mit Spielen, die Krypto unterstutzen. Mit sofortigen Einzahlungen. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und effizient, von Zeit zu Zeit mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Kurz und bundig, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Nebenbei die Oberflache ist glatt und benutzerfreundlich, was jede Session spannender macht. Ein Hauptvorteil die dynamischen Community-Events, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Hier klicken|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, garantiert top Hilfe. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, gelegentlich die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Nicht zu vergessen das Design ist ansprechend und nutzerfreundlich, fugt Magie hinzu. Besonders toll die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
alexandredallenbach.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
ashgrovecatering.com – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
Всё по теме по ссылке: https://livelive.ru/uzi-chto-eto-takoe-princzipy-raboty-i-sfery-primeneniya
myxy567.com – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
4631519.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
hsmsy8.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
line2048.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Sugar Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, bien que des offres plus importantes seraient super. En somme, Sugar Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce le lien communautaire.
http://www.sugarcasinoappfr.com|
J’adore la vibe de Sugar Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. De surcroit le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
Tout apprendre|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, quelquefois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En complement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une immersion complete. Un point fort les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, cree une communaute vibrante.
Poursuivre la lecture|
J’adore le dynamisme de Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est transparent et rapide, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons egalement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui booste la participation.
DГ©couvrir|
maltonfestivalofracing.co.uk – Amazing festival coverage, really captures the excitement of racing events beautifully.
mdcphilly.com – Great local content, keeps community members informed about events and updates.
бонус онлайн казино 1000
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Ruby Slots Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps a autre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour ajouter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste la participation.
Essayer ceci|
Today’s highlights are here: https://xn--c1aegcb7aocrkdm0d7ae6c.xn--p1ai/2025/10/27/Проверенный-поставщик-аккаунтов-ФБ-и-Гугл/
Ich schatze die Spannung bei Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Die Auswahl ist atemberaubend vielfaltig, mit Krypto-kompatiblen Spielen. Er gibt Ihnen einen tollen Boost. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, manchmal ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Zusammengefasst, Cat Spins Casino ist definitiv einen Besuch wert. Zudem ist das Design modern und einladend, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein gro?es Plus ist das VIP-Programm mit exklusiven Stufen, das die Motivation steigert.
http://www.catspins24.com|
everydayvaluecorner.shop – Browsing felt smooth, though product categories weren’t immediately obvious.
dankglassonline.com – Would love to see reviews and specs once the site fully opens for shopping.
globalmarketplacehub.click – On mobile the site loads slowly and lacks clear navigation—user experience is weak.
findyourperfectdeal.click – Happy to look up other domains that are fully built and ready for backlinks immediately.
ehe258.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
playfuel.co.uk – Great gaming products here, everything feels fun, creative, and high-quality.
brightnightpdx – Feeling inspired by their aesthetic—very modern yet warm and inviting.
asterixfilm.co.uk – Fantastic movie content, perfect for fans of animation and classic films.
nomnomnomfordogs.com – I shared this with a friend who has a pup—she was very interested.
dreambuyworld – Great visuals and clean layout make browsing easy and pleasant.
learntradingtoday – Appreciate the clean layout and helpful visuals, makes it more engaging.
wrestlingac – The elements look polished and up-to-date, gives a trustworthy impression.
buildyourdreamtoday – The site loads fast and navigation is smooth, big plus.
unitedbygoal – The site has a strong mission vibe, really feels purposeful.
cepjournal – I found the layout a bit confusing, lots of content but hard to pin focus.
strategicgrowthalliance – Site navigation is smooth, I like how the menu adapts on mobile.
forexlearninghub – Good concept for trading education, just wish there were more verifiable reviews.
foruminvestmali – Bottom line: a compelling idea, but to treat it as a serious investment networking forum I’d seek further evidence of delivery and reputation.
pepplish – The site layout made me want to browse every flavor option offered.
inspireeverydaylife.shop – The site seems in early phase, but potential is very strong for long-term value.
trabas007hoki – Content feels fresh each visit, honestly one of my go-to spots.
DRINKIO приятно удивил высоким уровнем обслуживания. Курьер приехал раньше заявленного времени, заказ полностью соответствовал описанию. Цены адекватные, оформление заказа заняло меньше минуты. Очень удобный сервис, которым теперь пользуюсь постоянно: https://drinkio105.ru/catalog/category/pivo/
flourandoak – This site gives me confidence, looks like you take care seriously.
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
togetherwerise – The site looks clean and promising, but I couldn’t find detailed team bios or track record.
thebestplacetoshop.shop – Free shipping and clear return policy are strong pluses here.
bestdealsforlife.shop – For higher-value linking count today, domains with visible shops and live inventory may serve better.
dearsparrows.com – The blog covers a variety of topics in a clean layout, good start.
прикольные поздравления с рождением внука
cs-nippon-cp – The site layout is fairly professional, but I would feel more comfortable if there were more transparent “About Us” or contact-info disclosures.
kraken ссылка Kraken ссылка – это навигатор по бескрайним просторам даркнета, указывающий путь к заветной цели. Однако, доверять первой попавшейся ссылке равносильно прыжку в пропасть с завязанными глазами. Прежде чем сделать этот шаг, убедитесь в её подлинности, проверьте репутацию источника и подготовьтесь к возможным неожиданностям. Безопасность превыше всего, и только внимательность и осторожность помогут вам избежать неприятных сюрпризов.
rosetemplates – Might be worth checking whether the licensing is clear for commercial use and downloads.
28darlingstreet – One suggestion: adding guest reviews or testimonials could enhance trust and give an idea of experience.
lifestyleinspirationhub – If they offer international shipping, I’d definitely consider ordering from abroad.
Estou completamente vidrado por BetorSpin Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto uma supernova dancante. Tem uma chuva de meteoros de jogos de cassino irados, incluindo jogos de mesa de cassino com um toque intergalactico. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que uma explosao de raios gama. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma viagem interestelar, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial astronomico. Resumindo, BetorSpin Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para quem curte apostar com estilo estelar no cassino! Alem disso o design do cassino e um espetaculo visual intergalactico, torna a experiencia de cassino uma viagem espacial.
betorspin levantamento|
Ich bin beeindruckt von der Qualitat bei Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein immersives Erlebnis. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. Der Bonus ist wirklich stark. Verfugbar 24/7 fur alle Fragen. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, manchmal gro?ere Boni waren ein Highlight. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Top-Ziel fur Casino-Fans. Nebenbei die Plattform ist optisch ansprechend, jede Session unvergesslich macht. Ein weiteres Highlight sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, die die Community enger zusammenschwei?en.
Jetzt ansehen|
seven kay casino официальный в casino seven kay доступна уникальная коллекция игр, включая эксклюзивные релизы и популярные классики.
moesboardwalk – The site feels casual and fun—great for a night out or group event.
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es verspricht ein einzigartiges Abenteuer. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit eleganten Tischspielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € mit Freispielen. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Auszahlungen sind blitzschnell, ab und zu mehr regelma?ige Aktionen waren toll. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Au?erdem die Seite ist schnell und einladend, zum Weiterspielen animiert. Ein tolles Extra die spannenden Community-Aktionen, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Mehr darГјber erfahren|
bloemhill – The botanical theme is strong—makes me trust the craftsmanship behind the products.
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es bietet einen einzigartigen Kick. Die Titelvielfalt ist uberwaltigend, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, ab und an die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, fugt Magie hinzu. Zusatzlich zu beachten die Sicherheit der Daten, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
theperfectgiftshop – The product range seems appealing; quality visuals help make the offerings look interesting.
yourdailyupdate – Overall, a promising site but I’d proceed with caution and trust-building checks before major orders.
kraken market Kraken market – это пестрый калейдоскоп предложений, где каждый может найти то, что ищет. Но, как и на любом рынке, здесь встречаются не только честные торговцы, но и мошенники, готовые обмануть доверчивых покупателей. Поэтому, прежде чем совершить покупку, тщательно изучите репутацию продавца, сравните цены и не стесняйтесь задавать вопросы. Помните, что ваша бдительность – лучшая защита от обмана и разочарования. Kraken market – это мир возможностей, но и мир ответственности.
trendinsight – The visuals are appealing and modern—good for catching attention if you are browsing.
theworldawaits.click – Inspiring content, makes me want to explore and travel everywhere.
trendyfindshub – Great first impression; the visuals pop and navigation is smooth overall.
connectdiscovergrow – Navigation was smooth and the layout seems user-friendly, nice UX.
getinspiredtoday – The product visuals are appealing, though I’d like to see more customer reviews or proof of quality.
Je suis captive par Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, rarement des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En bref, Sugar Casino assure un fun constant. De plus le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des bonus constants.
Explorer le site web|
envolavecning – One suggestion: more background story or designer bio would help me connect deeper.
Je suis bluffe par Ruby Slots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons egalement le design est moderne et energique, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un bonus les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
mutamedya.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
rebeccacaridad-manzanita – The portfolio has a calm, creative energy—very inspiring for anyone into visual arts.
engagement-forum – It looks promising on first glance, yet missing strong trust signals like client testimonials or verifiable case-studies.
lhjylggszt.com – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Ich bin beeindruckt von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet ein immersives Erlebnis. Die Auswahl ist so gro? wie ein Casino-Floor, mit aufregenden Live-Casino-Erlebnissen. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Die Mitarbeiter antworten schnell und freundlich. Auszahlungen sind einfach und schnell, jedoch regelma?igere Promos wurden das Spiel aufwerten. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur ununterbrochenen Spa?. Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein klasse Bonus die haufigen Turniere fur mehr Spa?, reibungslose Transaktionen sichern.
Jetzt entdecken|
J’adore l’energie de Sugar Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains arrivent sans delai, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Sugar Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons egalement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement interessant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
seven kay casino официальный сайт seven kay официальный сайт соответствует международным стандартам безопасности и применяет SSL-шифрование для защиты данных.
001yabo.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
bjlfabu.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine elektrisierende Atmosphare. Es gibt unzahlige packende Spiele, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. Er sorgt fur einen starken Einstieg. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, gelegentlich mehr Aktionen wurden das Erlebnis steigern. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Ubrigens die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, eine tiefe Immersion ermoglicht. Ein tolles Extra sind die sicheren Krypto-Zahlungen, die die Motivation erhohen.
Jetzt entdecken|
ssss2222.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
pbkplus.com – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit traditionellen Tischspielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Support ist effizient und professionell. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren willkommen. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein einmaliges Erlebnis. Zudem die Oberflache ist benutzerfreundlich, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein Hauptvorteil die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Cat Spins|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, trotzdem regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Au?erdem die Navigation ist kinderleicht, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
madmadedesigns – The aesthetic suggests higher-end goods, so depending on price it could be a premium purchase.
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Sugar Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Globalement, Sugar Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Notons egalement la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste la participation.
https://sugarcasinobonus777fr.com/|
J’adore l’energie de Ruby Slots Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En somme, Ruby Slots Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A signaler le site est fluide et attractif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des bonus exclusifs.
http://www.rubyslotscasinopromocodefr.com|
Ich freue mich sehr uber Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und spannend, mit stilvollen Tischspielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € und Freispiele. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, trotzdem mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Am Ende, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Highlight fur Casino-Fans. Hinzu kommt die Seite ist schnell und attraktiv, eine immersive Erfahrung ermoglicht. Ein gro?artiges Plus die vielfaltigen Sportwetten-Optionen, fortlaufende Belohnungen bieten.
Mehr entdecken|
J’adore la vibe de Sugar Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En conclusion, Sugar Casino offre une aventure memorable. En extra l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller Г la page|
joebobsaveschristmas – Overall, it’s a fun concept, I’d just recommend verifying any purchase/offer details before proceeding.
sega-live – Overall: interesting site, but I’d apply extra caution and do due-diligence.
648704.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
believeandcreate – This site always brightens my day, perfect for a mindset boost.
everymomentmatters – The name hits emotionally, good for meaningful purchases; just check the fine details.
findsomethingamazing – This site has a positive vibe, fun to browse through daily.
dreamdealsstore – This store really delivers value, I keep checking it for updates.
thebestvalue – Bookmarking this one so I can come back when it’s time to shop smart again.
Galera, nao podia deixar de comentar no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e bem acima da media: roletas animadas, todos rodando lisos. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que me deixou confiante. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou na mesma hora, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que faltam bonus extras, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Na minha visao, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Eu ja voltei varias vezes.
capinhas para moto g 4play|
Ich bin begeistert von der Welt bei Cat Spins Casino, es schafft eine mitrei?ende Stimmung. Die Auswahl ist so gro? wie ein Casino-Floor, mit Spielautomaten in kreativen Designs. 100 % bis zu 500 € mit Freispielen. Die Mitarbeiter sind schnell und kompetent. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, manchmal ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Alles in allem, Cat Spins Casino sorgt fur kontinuierlichen Spa?. Au?erdem die Navigation ist intuitiv und einfach, zum Bleiben einladt. Ein tolles Feature die regelma?igen Turniere fur Wettbewerbsspa?, ma?geschneiderte Privilegien liefern.
Web entdecken|
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Auszahlungen sind ultraschnell, gelegentlich regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist ein Muss fur alle Gamer fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Hinzu kommt die Navigation ist kinderleicht, verstarkt die Immersion. Zusatzlich zu beachten die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
everydaychoicehub – Everything loads smoothly and the suggestions feel relevant, good experience.
brightstylecorner – Love the trendy looks shared here, everything feels fresh and modern.
discovernewhorizons – Always find something here that sparks my imagination and new directions.
findbetteropportunities – I like how every post gives me a reason to keep growing.
Je suis bluffe par Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps en temps des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En somme, Sugar Casino vaut une visite excitante. A souligner le site est rapide et style, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages uniques.
Apprendre comment|
J’ai un faible pour Ruby Slots Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, mais plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour completer l’interface est simple et engageante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point cle les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Entrer|
shapeyourdreams – The writing style here is genuine, not forced or overly polished.
globalfashionfinds – Love the trendy pieces here, everything looks so stylish and modern.
findyourinspiration – Works well for a quick inspiration boost during a busy day.
trendylifestylehub – (Note: small typo in link but kept format) Amazing variety of topics from fashion to wellness.
findyourowngrowth – Such a refreshing site, always encouraging people to be their best self.
Galera, quero registrar aqui no 4PlayBet Casino porque superou minhas expectativas. A variedade de jogos e bem acima da media: blackjack envolvente, todos sem travar. O suporte foi bem prestativo, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que me deixou confiante. Fiz saque em transferencia e o dinheiro entrou muito rapido, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Na minha visao, o 4PlayBet Casino me conquistou. Eu ja voltei varias vezes.
4play-pro2.1|
globalfashionfinds – The quality and selection are really impressive for an online store.
findyourfocus – The content really helps when I need motivation to get things done.
trendsettersparadise – Always find something unexpected and stylish when I visit this site.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Sugar Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, rarement quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En conclusion, Sugar Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, garantit des paiements securises.
{{Sugar|www.sugarcasinobonusfr.com|https://sugarcasinobonusfr.com/|Voir maintenant|Aller sur le site|Plongez-y|Voir plus|Explorer maintenant|En savoir plus|Jeter un coup d’œil|Apprendre comment|Obtenir les détails|Visiter le site|Vérifier ceci|Découvrir plus|Cliquer pour voir|Commencer ici|Lire la suite|Aller voir|Découvrir|Visiter aujourd’hui|Voir le site|Explorer la page|Aller sur le web|Trouver les détails|Cliquer maintenant|Voir la page|Découvrir le web|Apprendre les détails|Accéder au site|Parcourir le site|Ouvrir maintenant|Obtenir plus|En savoir davantage|Découvrir maintenant|www.sugarcasinobonusfr.com|https://sugarcasinobonusfr.com/|Lire plus|Savoir plus|Voir les détails|Consulter les détails|Découvrir davantage|Explorer le site|Obtenir des infos|Continuer à lire|Découvrir dès maintenant|Poursuivre la lecture|Lire les détails|Approfondir|Découvrir les faits|Visiter la page web|Aller sur le site web|www.sugarcasinobonusfr.com|https://sugarcasinobonusfr.com/|Ouvrir le site|Vérifier le site|Parcourir maintenant|Accéder à la page|Visiter en ligne|Voir la page d’accueil|Ouvrir la page|Naviguer sur le site|Découvrir la page|Explorer le site web|Aller à la page|Aller au site|Visiter la plateforme|Visiter maintenant|Aller en ligne|Entrer sur le site|Découvrir le contenu|www.sugarcasinobonusfr.com|https://sugarcasinobonusfr.com/|Rejoindre maintenant|Accéder maintenant|Commencer maintenant|Essayer maintenant|Touchez ici|Cliquez ici|Entrer maintenant|Aller à l’intérieur|Plonger dedans|Entrer|Avancer|Commencer à explorer|www.sugarcasinobonusfr.com|https://sugarcasinobonusfr.com/|Démarrer maintenant|Passer à l’action|Essayer|Commencer à naviguer|Continuer ici|Commencer à découvrir|Lancer le site|Commencer à lire|Emmenez-moi là -bas|Explorer davantage|Continuer ici|Explorer plus|Essayer ceci|Regarder de plus près|Aller plus loin|Tout apprendre|Visiter pour plus|Découvrir les offres}|
Ich bin beeindruckt von der Qualitat bei Cat Spins Casino, es begeistert mit Dynamik. Das Spieleangebot ist reichhaltig und vielfaltig, mit spannenden Sportwetten-Angeboten. Er gibt Ihnen einen Kickstart. Erreichbar rund um die Uhr. Gewinne werden schnell uberwiesen, trotzdem mehr Bonusvielfalt ware ein Vorteil. Kurz gesagt, Cat Spins Casino ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, das Spielerlebnis steigert. Ein gro?artiges Bonus ist das VIP-Programm mit einzigartigen Belohnungen, schnelle Zahlungen garantieren.
Dies ausprobieren|
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es ist eine Erfahrung, die wie ein Wirbelsturm pulsiert. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Alles in allem, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, fugt Magie hinzu. Besonders toll die Sicherheit der Daten, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
J’adore le dynamisme de Sugar Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Sugar Casino offre une experience inoubliable. D’ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement top les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Visiter le site|
J’ai un faible pour Sugar Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Sugar Casino merite un detour palpitant. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement captivante, booste le fun du jeu. Un bonus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Ruby Slots Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, bien que des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A signaler la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Apprendre les dГ©tails|
Je suis enthousiasme par Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino est un must pour les passionnes. De plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis captive par Sugar Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Globalement, Sugar Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus constants.
Essayer|
y13617.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
hnzkfj.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
Ich liebe die Atmosphare bei Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Das Portfolio ist vielfaltig und attraktiv, inklusive dynamischer Sportwetten. Mit blitzschnellen Einzahlungen. Der Kundensupport ist top. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und sofortig, allerdings ein paar Freispiele mehr waren super. Letztlich, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Zudem die Navigation ist klar und flussig, zum Verweilen einladt. Besonders erwahnenswert die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, die Teilnahme fordern.
Zur Website gehen|
Today, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a forty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is totally off topic but I had to share it with someone!
https://rajawin123slot.com/melbet-kazino-sloti-skachat-na-android-2025/
https://xn--j1adp.xn--80aejmgchrc3b6cf4gsa.xn--p1ai/ Точка включения
Hi, this weekend is good in favor of me, because this point in time i am reading this impressive educational post here at my house.
https://c51dev.wpengine.com/melbet-obzor-bk-2025/
urbanstylemarket – Very clean layout and smooth browsing experience, made shopping fun.
learnsomethingeveryday – This site has genuinely interesting content, really enjoyed the read.
Ich bin total angetan von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet eine dynamische Erfahrung. Es gibt eine Fulle an aufregenden Titeln, mit interaktiven Live-Spielen. 100 % bis zu 500 € inklusive Freispiele. Der Kundendienst ist ausgezeichnet. Der Prozess ist transparent und schnell, trotzdem gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Abschlie?end, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein gro?artiges Erlebnis. Daruber hinaus ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, eine Prise Stil hinzufugt. Ein gro?er Pluspunkt ist das VIP-Programm mit besonderen Vorteilen, die die Gemeinschaft starken.
Website durchstöbern|
shopthenexttrend – Good value spots hidden throughout, made me stop and explore longer.
Ich bin fasziniert von Cat Spins Casino, es bietet packende Unterhaltung. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit klassischen Tischspielen. Er steigert das Spielvergnugen sofort. Der Service ist immer zuverlassig. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, allerdings ein paar zusatzliche Freispiele waren klasse. Zum Schluss, Cat Spins Casino ist ideal fur Spielbegeisterte. Zusatzlich die Seite ist zugig und ansprechend, was jede Session spannender macht. Ein super Vorteil die haufigen Turniere fur Wettbewerb, das die Motivation steigert.
Web entdecken|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Auswahl an Spielen, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Der Ablauf ist unkompliziert, trotzdem zusatzliche Freispiele waren ein Highlight. Zum Ende, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Casino-Liebhaber ! Au?erdem die Site ist schnell und stylish, fugt Magie hinzu. Ein Pluspunkt ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die das Spielen noch angenehmer machen.
spinbettercasino.de|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par ailleurs des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Ruby Slots Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour completer la navigation est claire et rapide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage notable les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements rapides.
http://www.rubyslotscasinoapp777fr.com|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur Cat Spins Casino, es ladt zu spannenden Spielen ein. Das Angebot ist ein Traum fur Spieler, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. 100 % bis zu 500 € mit Freispielen. Erreichbar 24/7 per Chat oder E-Mail. Zahlungen sind sicher und schnell, allerdings gro?zugigere Angebote waren klasse. Insgesamt, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergessliches Erlebnis. Hinzu kommt die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, eine tiefe Immersion ermoglicht. Ein hervorragendes Plus sind die sicheren Krypto-Transaktionen, die Gemeinschaft starken.
Details lesen|
Je suis accro a Sugar Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, rarement plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Sugar Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En complement le design est style et moderne, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement excellent les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis totalement conquis par Sugar Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est simple et transparent, mais encore des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En bref, Sugar Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Commencer Г lire|
perfectbuyzone – Great site for smart shoppers, good variety and responsive design.
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort voller Energie. Die Spielauswahl ist ein echtes Highlight, mit Krypto-freundlichen Titeln. Der Willkommensbonus ist ein Highlight. Der Kundendienst ist ausgezeichnet. Auszahlungen sind blitzschnell, allerdings mehr Bonusangebote waren spitze. Zusammenfassend, Cat Spins Casino bietet ein unvergessliches Erlebnis. Au?erdem ist das Design stilvoll und einladend, eine Prise Spannung hinzufugt. Ein tolles Feature die dynamischen Community-Events, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Jetzt ausprobieren|
Je suis completement seduit par Ruby Slots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Notons egalement la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses continues.
Commencer Г explorer|
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Es wartet eine Fulle spannender Optionen, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Transaktionen sind verlasslich, obwohl die Offers konnten gro?zugiger ausfallen. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, erleichtert die gesamte Erfahrung. Zusatzlich zu beachten die mobilen Apps, die den Einstieg erleichtern.
spinbettercasino.de|
yourstylematters – Great mix of looks and style advice, definitely bookmarking this for later.
Je suis emerveille par Ruby Slots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par contre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Ruby Slots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En bonus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un point cle les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses continues.
Entrer sur le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Sugar Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Sugar Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
http://www.sugarcasinoappfr.com|
https://sport.chat/
expandyourmind – Loved how the articles flow and how they make me pause and consider new ideas.
Je ne me lasse pas de Ruby Slots Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Ruby Slots Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A signaler l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement attrayant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui dynamise l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir plus|
shopwithhappiness –Love how the choices seem curated and the tone feels friendly.
purechoiceoutlet – Great first impression, the categories are clear and navigation is easy.
fashiondailydeals – Overall a pleasant visit—nice deals, friendly design, worth returning to.
brightnewbeginnings – Good balance of inspiration and practicality, helpful for making changes.
yournextadventure – Great site for travel inspiration, found some exciting destinations here.
trendshopworld – Smooth navigation and refreshing design; liked the browsing experience.
uniquevaluecorner – Loved the variety of products, some nice surprises among the listings.
everymomentmatters – Found nice ideas here that helped me pause and reconnect—thank you!
shopthedayaway – Good value across the selections, feels like smart shopping.
luxuryfindsonline – I like how the items are presented—clear images and good organization.
inspiredthinkinghub – Found some helpful insights today—thank you for sharing this resource.
modernideasnetwork – Great platform for growing your mindset and discovering new insights.
dreamdealsstore – Super easy to navigate and checkout, everything works smoothly here.
connectsharegrow – Will revisit this site when I’m looking to engage and learn more.
moveforwardnow – Bookmarking this site—you’ve got something good going if you like progress.
Ich freue mich riesig uber Cat Spins Casino, es ist ein Ort, der begeistert. Die Spiele sind abwechslungsreich und fesselnd, mit spannenden Sportwetten-Angeboten. Er bietet einen tollen Startvorteil. Der Service ist einwandfrei. Transaktionen sind zuverlassig und klar, in manchen Fallen haufigere Promos wurden begeistern. In Summe, Cat Spins Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt. Daruber hinaus die Plattform ist visuell beeindruckend, und ladt zum Verweilen ein. Besonders erwahnenswert die zahlreichen Sportwetten-Moglichkeiten, sichere Zahlungen garantieren.
Webseite besuchen|
Ищете надежные входные металлические двери под ваши задачи и бюджет? Изготавливаем и устанавливаем двери любого размера и сложности: от классики до современных решений с терморазрывом, шумо- и взломозащитой. Премиальные стали, точная фурнитура, порошковая окраска, выбор отделки (МДФ, ламинация, паттерны), профессиональный замер за 1 визит и чистый монтаж за 1 день: купить стальную дверь в москве
Please let me know if you’re looking for a author for your site. You have some really great articles and I feel I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d absolutely love to write some content for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please blast me an e-mail if interested. Kudos!
https://www.alqassab.net/melbet-registraciya-oficialniy-sait-2025/
This is my first time visit at here and i am actually pleassant to read all at one place.
https://vegashoki99slot.org/melbet-zerkalo-skachat-na-android-2025/
classytrendcollection – This store has a premium look and feel—makes me excited to explore further.
https://parachutetour.com
J’ai un faible pour Wild Robin Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour faire court, Wild Robin Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A souligner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement genial les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements rapides.
Aller voir|
Je suis bluffe par Frumzi Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, mais encore des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Frumzi Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement fun les transactions en crypto fiables, propose des avantages uniques.
Aller en ligne|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps en temps des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. De plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Wild Robin Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service client est excellent. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, bien que des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En bref, Wild Robin Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, cree une communaute vibrante.
Visiter le site|
J’ai un faible pour Cheri Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, occasionnellement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Cheri Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A signaler la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements rapides.
http://www.casinocherifr.com|
J’adore la vibe de Cheri Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est simple et transparent, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Cheri Casino vaut une visite excitante. A signaler le site est rapide et immersif, booste le fun du jeu. A signaler le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
Je suis fascine par Instant Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont infinies, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En fin de compte, Instant Casino merite un detour palpitant. Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une vibe electrisante. A noter les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Instant Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est clair et efficace, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino vaut une visite excitante. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un bonus les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Obtenir plus|
https://pvrisband.com
creativegiftplace – Found a few gift options I hadn’t seen elsewhere — nice surprise.
startsomethingawesome – Great user experience, everything loads fast and the layout’s really neat.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Wild Robin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des depots instantanes. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, neanmoins quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Au final, Wild Robin Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un point fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui booste la participation.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Je suis accro a Wild Robin Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, Wild Robin Casino merite une visite dynamique. A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, renforce la communaute.
Savoir plus|
J’adore le dynamisme de Wild Robin Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est clair et efficace, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En bref, Wild Robin Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. De plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une experience immersive. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui stimule l’engagement.
Cliquez ici|
Je suis emerveille par Cheri Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, toutefois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En resume, Cheri Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et style, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller voir|
simplystylishstore – Found pieces I hadn’t seen elsewhere; definitely worth exploring.
Je suis bluffe par Instant Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, rarement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Globalement, Instant Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement la navigation est intuitive et lisse, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges personnalises.
Passer à l’action|
Play The Password Game online in Canada! Test your creativity and problem-solving skills as you craft secure passwords with fun, unique challenges. Perfect for puzzle enthusiasts: Password Game strategies to win
Je suis sous le charme de Instant Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements rapides.
Continuer ici|
simplelivingstore – The visuals are clean and the product categories make a lot of sense—user friendly.
discoverpossibility – The tone is hopeful and motivating—exactly what you want when exploring new directions.
dreamcreateachieve – The design is clean and the content hits the right tone for self-growth.
startsomethingawesome – Love the inspirational vibe of this site, every visit feels like a fresh beginning.
modernhometrends – Overall a positive visit; looking forward to checking out what new decor trends they share next.
growtogethercommunity – Navigation was smooth and the visuals were inviting, made the visit pleasant.
qcxrmyy.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
thebestcorner – Really like how smooth the browsing is, looks well made too.
modernhometrends – The layout is clean, browsing is smooth and intuitive, great job.
discoverfreshperspectives – The layout is clean and inviting—makes exploring topics a pleasure.
yourdailyessentials – Found several items I actually needed today—nice find!
speakenglishlikeagenius.com – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
unlocknewpotential – Just bookmarked it, looks like a reliable place to shop from.
mastersaita.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
wahoowebsite.com – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
214248.com – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
yhwhcyy.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
745648.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
черная девушка проститутка Проститутки города: Мозаика судеб, сотканная из надежд, потерь и мимолетных встреч. Неоновая вывеска судьбы, горящая в темноте безысходности. Город грехов, где каждый ищет свое спасение.
проститутки проверенные метро Проститутка метро: Близость и анонимность соблазна. Ожидание поезда становится томным предвкушением встречи.
thinkbigmovefast – Excited to explore more here, seems like a fresh place to shop.
обзор казино
code promo 1xBet 2026
J’ai un faible pour Wild Robin Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent sans delai, parfois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fluides.
Entrer sur le site|
moveforwardnow – Just discovered this site, excited to explore more of what they offer.
discoverpossibility – Browsing here is pleasant, I like how everything is arranged and displayed.
J’adore l’energie de Frumzi Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino vaut une visite excitante. Par ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Obtenir des infos|
modernstylemarket – Overall a smooth browsing session, will definitely return when exploring more fashion options.
Je suis captive par Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En somme, Instant Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En extra le site est rapide et engageant, permet une immersion complete. A signaler le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute soudee.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Je ne me lasse pas de Cheri Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Cheri Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En extra la navigation est intuitive et lisse, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus constants.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Frumzi Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par contre des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En bref, Frumzi Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A souligner les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’adore la vibe de Instant Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour finir, Instant Casino offre une aventure memorable. En extra le site est rapide et engageant, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter la page web|
маз 6х4 седельный Бортовой МАЗ: Универсальное решение для перевозки различных грузов. Простота в эксплуатации и обслуживании. Ваш надежный помощник в бизнесе.
growtogethercommunity – Really enjoy the overall aesthetic, feels trustworthy and well-designed.
shopthenexttrend – Nice experience so far, everything loads fast and looks well-organised.
discoverbetterdeals – Great selection so far, makes me want to explore more of their catalog.
urbanwearoutlet – Love the overall aesthetic, gives a modern yet approachable vibe.
everydayinnovation – The design is sleek and intuitive, makes me want to explore deeper.
thefashionedit – Great site so far, clean design and nice browsing experience.
explorecreativeconcepts – Great first impression, everything seems reliable and appealing.
learnexploreachieve – The visuals and content feel cohesive and well curated.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Wild Robin Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour faire court, Wild Robin Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et energique, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’adore la vibe de Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En bref, Frumzi Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons aussi la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un point cle les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute vibrante.
Aller sur le site web|
explorecreativeconcepts – I like how the design is minimalist yet inviting, great first impression.
reachhighergoals – Overall a positive feel, everything seems polished and user-friendly.
buildthefuture – Overall experience is positive, it’s well-put-together and shows attention to detail.
dealsanddiscounts – Nice first impression; site loads fast and feels trustworthy.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Cheri Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par contre quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour faire court, Cheri Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En complement le site est rapide et style, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement super les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
code promo 1xbet cameroun
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Cheri Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, occasionnellement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi la navigation est intuitive et lisse, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, garantit des paiements securises.
DГ©couvrir plus|
J’adore l’energie de Instant Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par moments des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En bref, Instant Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce la communaute.
https://instantcasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis enthousiasme par Frumzi Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est simple et transparent, bien que quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A noter la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
743748.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
9044123.com – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
amcbuildingmaterials.com – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
745748.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
743728.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
bb4703.com – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
528148.com – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
findyourowngrowth – Really like how the design is clean and the layout is easy to navigate.
Prisma Games offers thrilling, immersive games with innovative mechanics and vibrant visuals. A go-to platform for Canadian gamers seeking excitement and high-quality gameplay: Prisma Games official site
findyourperfectlook – The overall experience so far is positive—clean design and smooth browsing.
mystylezone – Found some stylish items already, can’t wait to look deeper into their collection.
styleandfashion – I like how easy it is to navigate, nice job with design.
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
everydayvaluehub – Impressed with how the site loads quickly and presents content clearly.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Frumzi Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, en revanche des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Frumzi Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En bonus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement top les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Visiter pour plus|
Je ne me lasse pas de Frumzi Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par contre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Approfondir|
Je suis accro a Cheri Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage notable les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Lire la suite|
Je suis bluffe par Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Instant Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A souligner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des bonus constants.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je suis epate par Wild Robin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, bien que plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A noter les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements rapides.
Voir la page d’accueil|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Instant Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, parfois des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour faire court, Instant Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour completer la navigation est intuitive et lisse, incite a rester plus longtemps. A signaler les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Cheri Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Cheri Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A mentionner le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement excellent les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis fascine par Frumzi Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par moments des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En resume, Frumzi Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce le lien communautaire.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis emerveille par Instant Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En complement la navigation est claire et rapide, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter le site|
вызвать врача нарколога на дом спб
проститутки метро тушинская Проститутки индивидуалки: Игра в независимость, маска одиночества. Сами себе хозяйки или заложницы обстоятельств?
J’ai une passion debordante pour Wild Robin Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En bref, Wild Robin Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement genial les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fluides.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis emerveille par Frumzi Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En fin de compte, Frumzi Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En plus le site est fluide et attractif, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement attrayant les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir dГЁs maintenant|
Je suis epate par Frumzi Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est transparent et rapide, malgre tout quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En fin de compte, Frumzi Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour ajouter la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Parcourir maintenant|
Je suis epate par Instant Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, en revanche quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Globalement, Instant Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A mentionner le site est rapide et immersif, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement cool les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des bonus constants.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
https://shkola-vocala.ru/shkola-igry-na-gitare.php
J’adore la vibe de Wild Robin Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est transparent et rapide, parfois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En extra le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une experience immersive. Un bonus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
Entrer|
проститутка 40 50 лет Снят проститутка / Снять проститутку: Запечатленный грех, ускользающий момент. В объективе – чужая боль, в сердце – пустота.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Instant Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est simple et transparent, mais encore des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour conclure, Instant Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter la plateforme|
Je suis bluffe par Cheri Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est transparent et rapide, parfois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour finir, Cheri Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En bonus le design est style et moderne, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
Aller sur le site web|
Looking to betwinner create account fast? Go to https://bet-promo-codes.com/sportsbook-reviews/betwinner-registration/ and complete the simple sign-up form in just a few clicks.
Je suis totalement conquis par Frumzi Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, occasionnellement plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En somme, Frumzi Casino vaut une visite excitante. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement super les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui motive les joueurs.
En savoir davantage|
Je suis fascine par Instant Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Instant Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A signaler le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
http://houmy.ru/
digitalpilot.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
funnelfuel.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
adprox.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
viralsphere.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
growthorbit.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
rankstorm.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
trafficmint.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
Paris sportifs avec 1xbet congo : pre-match & live, statistiques, cash-out, builder de paris. Bonus d’inscription, programme fidelite, appli mobile. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money. Informez-vous sur la reglementation. 18+, jouez avec moderation.
Plateforme parifoot rdc : pronos fiables, comparateur de cotes multi-books, tendances du marche, cash-out, statistiques avancees. Depots via M-Pesa/Airtel Money, support francophone, retraits securises. Pariez avec moderation.
лучшие автоматы
релевантность страницы
http://www.google.lv/url?q=http://algoritmyseo.ru
Найкращі казино України постійно оновлюють слоти та акції. Українське казино з ліцензією гарантує безпеку кожного депозиту.
Ліцензійні ігрові автомати забезпечують чесний результат. Тут зібрано довідки про бонуси, ліміти та провайдерів: CASINO-UA-ONLINE.BIZ.UA. Казино з миттєвим виводом дозволяють отримати виграш без очікування.
Ліцензійні казино України — це гарантія відповідальної гри. Українське казино підтримує популярні платіжні сервіси. Казино онлайн Україна дає змогу грати без ризиків. Ліцензійні казино України працюють офіційно та прозоро. Українські онлайн казино з ліцензією КРАІЛ — найнадійніші.
с минимальным депозитом
Оформите онлайн-займ https://zaimy-89.ru без визита в офис: достаточно паспорта, проверка за минуты. Выдача на карту, кошелёк или счёт. Прозрачный договор, напоминания о платеже, безопасность данных, акции для новых клиентов. Сравните предложения и выберите выгодно.
Лучшее прямо здесь: https://mr-master.com.ua
clickmagnet.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
promostream.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
admatrix.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
viralaxis.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
leadvortex.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
growthshift.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
trafficzen.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
amazingdealscorner – Just found this place and the deals already look very good.
J’adore le dynamisme de Frumzi Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, toutefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En complement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, apporte une energie supplementaire. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
https://frumzicasinofr.com/|
Je ne me lasse pas de Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, malgre tout des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour finir, Cheri Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En plus la navigation est simple et intuitive, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A signaler les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui booste la participation.
Continuer ici|
Je suis captive par Frumzi Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Frumzi Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est simple et engageante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un point cle les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements rapides.
Voir maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Instant Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et energique, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fluides.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
Je suis emerveille par Wild Robin Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En conclusion, Wild Robin Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour completer le site est rapide et engageant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement top les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
J’adore l’energie de Instant Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par contre des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Instant Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En extra la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, booste le fun du jeu. A signaler les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, cree une communaute soudee.
Apprendre comment|
Je suis captive par Cheri Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Cheri Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A noter les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des avantages uniques.
https://chericasinomobilefr.com/|
Je suis sous le charme de Frumzi Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour conclure, Frumzi Casino garantit un amusement continu. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Cliquer pour voir|
Je suis accro a Frumzi Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Frumzi Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. A souligner les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements securises.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Je suis enthousiasme par Cheri Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Cheri Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui booste la participation.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je suis bluffe par Frumzi Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, toutefois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Frumzi Casino vaut une visite excitante. Par ailleurs le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A noter les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Poursuivre la lecture|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Instant Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Instant Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui booste la participation.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis accro a Wild Robin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour faire court, Wild Robin Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, renforce le lien communautaire.
Aller plus loin|
помощь с лмс мти тесты срочно Дипломные Работы Синергия: Ключевой этап вашего образования. Создайте уникальный исследовательский проект, который продемонстрирует ваши знания и навыки. Мы поможем вам успешно защитить диплом и получить заслуженную оценку.
Je suis totalement conquis par Instant Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Dans l’ensemble, Instant Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons aussi le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je suis epate par Cheri Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, a l’occasion des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Cheri Casino offre une experience inoubliable. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un atout les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus constants.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
J’adore la vibe de Frumzi Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps en temps des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Frumzi Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En complement l’interface est simple et engageante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un element fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Aller voir|
How to win in Calgary Lottery: Boost your chances by playing consistently, joining lottery pools, and choosing less popular combinations. Remember, winning requires luck and responsible play: best ways to win money in Calgary
how much is a cycle of hgh
References:
how many ius of hgh Per day – https://www.mathelounge.de/user/leohen21 –
leadorbit.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
brandecho.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
boostnexus.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
rankvista.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
markethive.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
adexpand.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
clickfoundry.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
Work in korea Работа в Корее: Эльдорадо карьерных возможностей для целеустремленных профессионалов. Страна утренней свежести манит не только своей уникальной культурой и технологическим прогрессом, но и широкими перспективами трудоустройства. От динамичного Сеула до индустриальных центров, Корея открывает двери для тех, кто готов к новым вызовам и стремится к профессиональному росту. Приготовьтесь погрузиться в мир передовых технологий, инновационного производства и захватывающих карьерных траекторий.
Work in korea Работа без знания корейского языка – это реальность. Многие компании готовы рассматривать кандидатов, владеющих только английским или русским языком. Однако, знание корейского языка значительно повышает ваши шансы на успех и открывает новые возможности для карьерного роста.
На 7k casino официальный сайт удобно играть как с телефона, так и с компьютера. Всё работает без перебоев. Вывод средств быстрый и надёжный https://xn—-8sbalwlcefxak4bw.xn--p1ai/
J’adore l’energie de Wild Robin Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots fluides. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps a autre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Wild Robin Casino merite un detour palpitant. De plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement cool les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
AccГ©der Г la page|
hgh cycle for beginners
References:
how many iu Of hgh per day for muscle growth (https://xn—-7sbarohhk4a0dxb3c.xn--p1ai/user/skillerror27/)
http://bergkompressor.ru/ Новое и официальное – Все последние релизы в одном месте.
adrocket.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
growthsprint.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
marketjet.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
trafficpilot.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
rankpilot.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
admomentum.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
adorbit.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
https://медоптима.рф/
Je suis totalement conquis par Betzino Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour finir, Betzino Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En plus le design est style et moderne, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Betzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Betzino Casino offre une experience inoubliable. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement top les evenements communautaires vibrants, garantit des paiements securises.
https://betzinocasino366fr.com/|
Je suis accro a Viggoslots Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Viggoslots Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et engageant, booste l’excitation du jeu. A souligner les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Je suis completement seduit par Vbet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par ailleurs plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour faire court, Vbet Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En extra le design est style et moderne, booste le fun du jeu. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce la communaute.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
J’adore le dynamisme de Vbet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, Vbet Casino merite une visite dynamique. A souligner le site est rapide et engageant, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement super les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, garantit des paiements rapides.
Aller Г la page|
J’adore le dynamisme de Cheri Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En conclusion, Cheri Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des recompenses continues.
Essayer ceci|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Posido Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste l’excitation du jeu. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, assure des transactions fluides.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Заказывал через DRINKIO несколько раз и всегда остаюсь доволен. Курьеры приезжают быстро, упаковка надёжная, товар оригинальный. Ассортимент широкий — от классики до премиум-брендов. Особенно удобно, что можно оформить доставку в любое время суток. Сайт понятный и не перегруженный. Отличная доставка алкоголя на дом по Москве 24/7: https://drinkio105.ru/catalog/category/dzhin/
hgh test cycle
References:
https://skitterphoto.com/photographers/1203330/graversen-gillespie
Je suis completement seduit par Betzino Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A signaler l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute vibrante.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis emerveille par Betzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, quelquefois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour faire court, Betzino Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui stimule l’engagement.
https://betzinocasinobonusfr.com/|
Je suis enthousiasme par Betzino Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support client est irreprochable. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Betzino Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, permet une immersion complete. Un atout le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Cliquez ici|
J’adore l’energie de Viggoslots Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En bref, Viggoslots Casino vaut une visite excitante. En plus le design est style et moderne, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un bonus les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui booste la participation.
Visiter en ligne|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Vbet Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, a l’occasion plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Vbet Casino merite un detour palpitant. En complement le design est style et moderne, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement top les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Aller en ligne|
Je suis sous le charme de Vbet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Vbet Casino assure un fun constant. Notons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je suis fascine par Cheri Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Cheri Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires vibrants, qui dynamise l’engagement.
http://www.chericasinoappfr.com|
Бот для новых монет (IDO/IEO) Telegram bot for Binance futures: Бот для торговли фьючерсами на Binance в Telegram.
growthbeacon.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
hgh and testosterone stack
References:
https://www.instapaper.com/p/16741089
marketfusion.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
trafficwave.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
adnectar.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
leadcraft.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
clickmagnetix.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
markettrail.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
https://nicemerch.ru/
Оформите займ https://zaimy-57.ru онлайн без визита в офис — быстро, безопасно и официально. Деньги на карту за несколько минут, круглосуточная обработка заявок, честные условия и поддержка клиентов 24/7.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино отзывы
Binary Options Demo: Learn Before You Trade.
Start your trading journey with a Binary Options Demo account and practice risk-free before going live. Sharpen your skills and explore smart strategies at https://terrasseo.jp/
https://narkolog-na-dom-spb5.ru/
adzenith.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
viralboost.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
digitalsurge.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
clickmagnetix.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
marketnova.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
clicknexus.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
rankrocket.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
https://mosquitosalsa.com/
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
https://defleppardnow.com
Entdecken Sie die besten Weinverkostungen in Wien auf wein verkostung wien.
Die osterreichische Hauptstadt bietet eine einzigartige Mischung aus Tradition und Moderne.
Die Weinverkostungen in Wien sind perfekt fur Kenner und Neulinge. Dabei lernen Gaste die Besonderheiten der regionalen Rebsorten kennen.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
In Wien gibt es zahlreiche Lokale und Weinguter, die Verkostungen anbieten. Das Weinmuseum im Stadtzentrum ist ein idealer Ausgangspunkt fur Weinliebhaber.
Einige Winzer veranstalten Fuhrungen durch ihre Kellereien. Oft werden auch seltene Weine vorgestellt, die nur lokal erhaltlich sind.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Wiener Weine sind vor allem fur ihre Vielfalt bekannt. Rote Weine wie der Blaue Zweigelt gewinnen immer mehr an Beliebtheit.
Die Bodenbeschaffenheit und das Klima pragen den Geschmack. Die mineralischen Noten der Wiener Weine sind besonders ausgepragt.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Eine gute Vorbereitung macht die Verkostung noch angenehmer. Ein neutraler Geschmack im Mund vor der Verkostung verbessert das Erlebnis.
Gruppenverkostungen bringen zusatzlichen Spa?. Viele Veranstalter bieten thematische Verkostungen an.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Die osterreichische Hauptstadt bietet eine einzigartige Mischung aus Tradition und Moderne.
#### **2. Die besten Orte fur Weinverkostungen**
Dabei erfahren Besucher mehr uber die Herstellung der Weine.
#### **3. Wiener Weinsorten und ihre Besonderheiten**
Die warmen Sommer sorgen fur vollmundige Aromen.
#### **4. Tipps fur eine gelungene Weinverkostung**
Es empfiehlt sich, langsam zu trinken, um die Nuancen zu schmecken.
promowave.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
leadstreamx.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
trafficburst.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
advelocity.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
J’adore l’energie de Viggoslots Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En somme, Viggoslots Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour couronner le tout le design est style et moderne, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus les paiements securises en crypto, renforce la communaute.
Ouvrir la page|
Je ne me lasse pas de Betzino Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. De surcroit l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un bonus les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fluides.
https://casinobetzinofr.com/|
Je suis bluffe par Betzino Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, en revanche plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un point fort les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
ranksphere.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Je suis fascine par Betzino Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Betzino Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A noter la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un plus les paiements securises en crypto, assure des transactions fluides.
Explorer davantage|
rankpilotx.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
https://defleppardfaq.com
Koh Lanta Krabi
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Vbet Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Vbet Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour ajouter le design est moderne et energique, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement super les evenements communautaires vibrants, garantit des paiements rapides.
http://www.vbetcasinobonusfr.com|
clickengine.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Je suis enthousiasme par Posido Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, par contre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Posido Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A mentionner le site est rapide et engageant, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement super les evenements communautaires engageants, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Cliquer pour voir|
Je suis enthousiasme par Betzino Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps a autre plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour finir, Betzino Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus le design est moderne et energique, facilite une experience immersive. Un element fort les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Parcourir maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Betzino Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En fin de compte, Betzino Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons egalement le site est rapide et engageant, permet une immersion complete. Un element fort les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je suis completement seduit par Betzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, rarement quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Betzino Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement excellent les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Vbet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Le processus est simple et transparent, par contre des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour finir, Vbet Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement interessant les transactions en crypto fiables, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
Je suis fascine par Posido Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais encore plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Posido Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A mentionner l’interface est lisse et agreable, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A noter les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Voir plus|
https://www.orkhonschool.edu.mn/single-post/celebrating-excellence-top-student-of-2024-5
https://internet-leman.ru/
https://t.me/KohLantaKrabiThailand Koh Lanta
https://www.wowonder.xyz/read-blog/345909
казино онлайн с выводом Выбор надежного онлайн-казино – это инвестиция в ваше спокойствие и безопасность. Не торопитесь, проведите исследование и выбирайте казино, которое соответствует вашим требованиям и имеет хорошую репутацию. Помните, что азартные игры должны приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Играйте ответственно!
игровые автоматы Устали от ограничений? Мобильное казино – это ваш билет в мир развлечений без лишних хлопот. Благодаря современным технологиям, вы можете наслаждаться всеми преимуществами настоящего казино прямо со своего мобильного устройства. Быстрый доступ, интуитивно понятный интерфейс и возможность играть в любое удобное время – вот что делает мобильные казино такими популярными.
Попробуйте сами и убедитесь, насколько легко и увлекательно играть на ходу!
rankedge.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
marketsonic.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
marketcraft.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
promoverse.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
clickexpand.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
adpilot.click – Navigation felt smooth, found everything quickly without any confusing steps.
clickvelocity.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
https://defleppardnow.com
explorethefuture – Love the modern design, feels like a place full of inspiration.
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Viggoslots Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, en revanche des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure memorable. De plus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un atout les transactions en crypto fiables, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Entrer|
Je suis totalement conquis par Betzino Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Betzino Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En bonus le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement super les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui booste la participation.
Naviguer sur le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betzino Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, toutefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En conclusion, Betzino Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Visiter le site|
Je suis totalement conquis par Viggoslots Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, a l’occasion des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En bref, Viggoslots Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et fluide, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis bluffe par Viggoslots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, malgre tout plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure memorable. De surcroit la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point fort les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis bluffe par Betzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, rarement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Betzino Casino offre une aventure memorable. Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Lire la suite|
Je suis fascine par Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps a autre des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, Posido Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement interessant les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Parcourir le site|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Posido Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, malgre tout quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, Posido Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, cree une communaute vibrante.
Continuer ici|
clickchain.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
trafficlaunch.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
marketblaze.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
adrise.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
rankhive.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
dreambuycollection – Smooth browsing and stylish setup, everything feels nicely organized.
exploreandcreate – Inspiring and creative site, perfect for exploring new ideas and products.
modernlivingtrend – Love the minimal look, makes the whole experience smooth and elegant.
buildabetterworld – Inspiring energy overall, love how the content feels genuine and kind.
trendyfindsonline – Love the trendy vibe, products look stylish and well-presented.
everydaystylecorner – The site feels cozy and stylish, perfect for daily fashion finds.
styleforliving – This site has a nice flow, really easy on the eyes while browsing.
growwithconfidence – Fresh content and smooth layout, everything just works perfectly together.
discoveryourpotential – Great concept and execution, this site truly motivates to grow more.
getinspireddaily – Modern and uplifting tone, perfect for starting the day with positivity.
globalstylemarket – Nice balance between aesthetics and functionality, perfect for online shopping.
Алкомаркет реально спасает в неожиданных ситуациях. Сделал заказ ночью, и через 40 минут всё уже было на месте. Приятный сервис и отличное качество. Теперь если нужна доставка алкоголя по москве круглосуточно, беру здесь – https://dostavka-alcohol.ru/
Je ne me lasse pas de Betzino Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est simple et transparent, bien que des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. En extra la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des bonus constants.
Approfondir|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, toutefois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En conclusion, Betzino Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En plus le design est style et moderne, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
bestchoicecorner – Feels trustworthy and professional, I like the clean structure.
https://vsemetonado.ru/
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Viggoslots Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En resume, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De surcroit le site est rapide et style, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement top les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
En savoir plus|
Je suis accro a Viggoslots Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, a l’occasion des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En somme, Viggoslots Casino vaut une visite excitante. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller Г la page|
Je suis completement seduit par Betzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour faire court, Betzino Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus le site est rapide et style, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A signaler les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui booste la participation.
Continuer ici|
J’adore la vibe de Viggoslots Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est simple et transparent, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En resume, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure memorable. En plus le design est style et moderne, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, garantit des paiements rapides.
Cliquer pour voir|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Viggoslots Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, a l’occasion quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Viggoslots Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A souligner les evenements communautaires engageants, cree une communaute soudee.
VГ©rifier ceci|
Je suis accro a Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, par ailleurs des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Dans l’ensemble, Betzino Casino garantit un amusement continu. En complement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un avantage les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
Essayer|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Vbet Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Vbet Casino garantit un amusement continu. En extra la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un bonus les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Thailand Ко ланта
Je suis enthousiasme par Vbet Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par contre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En bref, Vbet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A signaler l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement genial les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Lire la suite|
J’adore la vibe de Posido Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains arrivent sans delai, toutefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Posido Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A signaler le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce la communaute.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Je suis completement seduit par Posido Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Globalement, Posido Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et immersif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Voir les dГ©tails|
J’ai un faible pour Vbet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, de temps en temps des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En bref, Vbet Casino assure un fun constant. De plus la navigation est claire et rapide, facilite une experience immersive. Un point fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, assure des transactions fluides.
Lancer le site|
Je suis accro a Vbet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps a autre quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En resume, Vbet Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons aussi le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages uniques.
AccГ©der au site|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Posido Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, parfois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Posido Casino assure un fun constant. Par ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une immersion complete. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Explorer le site|
styleforliving – Sleek and elegant layout, really makes browsing stylish products enjoyable.
promocore.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
J’adore l’energie de Posido Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les gains arrivent sans delai, quelquefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Posido Casino offre une aventure memorable. Pour completer le design est style et moderne, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement genial les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, assure des transactions fluides.
https://casinoposidofr.com/|
Je suis fascine par Posido Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, de temps en temps quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour faire court, Posido Casino merite un detour palpitant. En plus la navigation est fluide et facile, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un element fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce la communaute.
Apprendre comment|
Je suis accro a Posido Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est transparent et rapide, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour finir, Posido Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour couronner le tout le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement super les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute soudee.
Voir la page d’accueil|
connectdiscovergrow – The site’s message feels powerful, encourages learning and growth daily.
findsomethingnew – Simple interface, modern feel, and a great name that fits perfectly.
getinspiredtoday – Simple yet uplifting, every element on the site feels motivating.
liveandexplore – Feels modern and positive, great for discovering new experiences.
modernlivingstyle – Great presentation and layout, feels both elegant and comfortable.
liveandexplore – Feels like a creative space to discover new ideas and adventures.
makelifesimpler – A well-designed site that stays true to its message of simplicity.
theworldawaits – Bright, motivating, and easy to browse — a really pleasant experience.
bestvaluecollection – Good range of products, prices seem fair and competitive too.
Chernov Creation Цирканутые новости от Chernov Creation: Готовьтесь к взрыву креатива! Мы не боимся экспериментировать, ломать стереотипы и выходить за рамки привычного. В наших новостях вы найдете самые нестандартные проекты, безумные идеи и удивительные открытия. Присоединяйтесь к нашей цирковой труппе цифровых гениев и вместе мы создадим нечто совершенно невероятное!
Трипскан TripScan: Открой мир путешествий заново! Забудь о скучных маршрутах и переплатах. TripScan – это революционный агрегатор, который сканирует тысячи предложений от авиакомпаний, отелей и прокатчиков автомобилей, чтобы предложить тебе лучшие цены и уникальные возможности. Мы не просто ищем билеты, мы создаем персонализированные путешествия, учитывая твои предпочтения и бюджет.
Цирканутые новости от Chernov Creation Цирканутые новости от Chernov Creation: Готовьтесь к взрыву креатива! Мы не боимся экспериментировать, ломать стереотипы и выходить за рамки привычного. В наших новостях вы найдете самые нестандартные проекты, безумные идеи и удивительные открытия. Присоединяйтесь к нашей цирковой труппе цифровых гениев и вместе мы создадим нечто совершенно невероятное!
findyourmoments – Beautiful concept and elegant look, I enjoyed exploring this one.
Ко ланта чат Koh Lanta
https://theaterplaybill.com
топ-10 казино с бонусами за регистрацию
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Betzino Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, Betzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. De plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A noter le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je ne me lasse pas de Betzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, toutefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Betzino Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Visiter pour plus|
Работают аккуратно, все документы всегда в порядке, https://tamozhenniiy-predstavitel11.ru/
https://theaterplaybill.com
игровые автоматы реальные деньги за регистрацию
yourmomentstarts – Smooth user experience, inspiring words and clean design overall.
findyourpathnow – The concept is beautiful and the site feels easy to explore.
findyourmoments – The theme feels relaxing and personal, really like the gentle tone.
freshfashioncorner – Fantastic user experience, simple interface but full of fresh style.
freshfashioncorner – Fantastic user experience, simple interface but full of fresh style.
shopwithstylehub – Clean interface and bold design, truly fits the idea of shopping with style.
findjoytoday – Great message and friendly tone, makes visiting the site a pleasant moment.
simplevalueplace – Love how user-friendly this site is, perfect for quick browsing.
explorethefuture – The theme fits the name perfectly, everything feels innovative and clear.
https://theaterplaybill.com
https://theaterplaybill.com
dreambuycollection – The layout is clean and modern, products really stand out nicely.
trendingstyleworld – Modern look and great energy, ideal for anyone who loves style.
startanewjourney – Inspiring message and beautiful layout, really sets a positive tone.
purevalueoutlet – Great selection of items, everything feels organized and easy to find.
fashionloverszone – Clean layout and beautiful visuals, really love the site’s energy.
dreamfindshub – Found some great insights here, love the encouraging tone throughout.
classychoiceoutlet – Love the clean layout and stylish collections, really well presented.
shopfornewthings – Perfect place to discover trendy items, had a great experience here.
getmoreforshop – Love how easy it is to navigate and find good offers.
пассажирские перевозки астана новосибирск
Je suis epate par Betway Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, en revanche plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Betway Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour couronner le tout le design est moderne et energique, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires dynamiques, garantit des paiements securises.
Commencer ici|
J’adore le dynamisme de Betway Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service client est de qualite. Le processus est clair et efficace, parfois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Dans l’ensemble, Betway Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement genial les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements rapides.
DГ©couvrir le web|
перевозки новосибирск Астана
J’adore le dynamisme de Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Betway Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Visiter en ligne|
Je suis fascine par Belgium Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, cependant des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Belgium Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A signaler le site est rapide et style, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement attrayant les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Belgium Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Dans l’ensemble, Belgium Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Ajoutons aussi le design est style et moderne, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
Je suis bluffe par Betway Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est simple et transparent, en revanche plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour finir, Betway Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A signaler la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des privileges personnalises.
Ouvrir la page|
J’adore la vibe de Gamdom Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, occasionnellement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En extra l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un bonus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Je suis sous le charme de Gamdom Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, cependant des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Gamdom Casino assure un fun constant. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, offre des bonus constants.
Essayer|
Je suis bluffe par Betify Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, par contre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Betify Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De surcroit la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des recompenses continues.
Voir la page d’accueil|
Je suis epate par Gamdom Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais encore plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En conclusion, Gamdom Casino merite un detour palpitant. A signaler la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement top les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Betify Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En fin de compte, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A noter le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A noter les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Explorer plus|
Je suis emerveille par Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, malgre tout des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour conclure, Betway Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour ajouter l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un point cle les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute vibrante.
Voir la page|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Belgium Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En resume, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un plus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce le lien communautaire.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je suis epate par Belgium Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, a l’occasion des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Au final, Belgium Casino offre une aventure memorable. Par ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betway Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, de temps en temps des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Betway Casino merite un detour palpitant. En plus le site est fluide et attractif, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des recompenses continues.
Cliquer maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Gamdom Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, malgre tout quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Gamdom Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un atout les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
http://www.gamdomcasinoappfr.com|
Je ne me lasse pas de Betify Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A noter la navigation est simple et intuitive, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
Je suis bluffe par Gamdom Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A signaler le site est rapide et immersif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement top les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Touchez ici|
Je suis enthousiasme par Betify Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En resume, Betify Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Voir la page|
discoverhomeessentials – Smooth browsing and well-picked collections, makes shopping for home stuff fun.
thinkcreateachieve – Love the name, it really pushes you to think, build, and succeed.
бесплатные спины за регистрацию без депозита с выводом Бездепозитные бонусы – это отличная возможность попробовать свои силы в онлайн-казино без риска для собственных средств. Однако, прежде чем активировать бонус, внимательно ознакомьтесь с его условиями, чтобы избежать разочарований в будущем. Удачи в игре!
explorewhatspossible – The name fits perfectly, great site for exploring creativity and motivation.
findperfectgift – So many unique gift ideas, really enjoyed exploring this site today.
createbettertomorrow – A wonderful platform that promotes optimism and growth for the future.
discovergreatideas – Inspiring layout and easy navigation, loved browsing through everything here.
бездепозитные бонусы казино форум Многие слышали о бездепозитных бонусах – это когда казино дарит вам деньги или вращения просто так, за регистрацию. Звучит заманчиво, правда? И это действительно отличная возможность попробовать свои силы. Однако, как и в любом деле, здесь есть свои нюансы. Важно понимать, что такие бонусы обычно имеют условия отыгрыша – то есть, вам придется сделать определенное количество ставок, прежде чем вы сможете вывести полученные деньги. Но даже с учетом этого, это прекрасный старт для тех, кто хочет познакомиться с миром онлайн-казино без финансовых рисков.
thepowerofgrowth – Inspiring name that perfectly captures the spirit of personal and professional development.
staycuriousdaily – Feels modern and inspiring, definitely something that sparks imagination.
discoverinfiniteideas – Feels like a place where creativity never ends, truly inspiring vibe.
everydayfindsmarket – Nice blend of affordability and variety, sounds like a fun marketplace.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Betway Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, en revanche quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour finir, Betway Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement top les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Explorer la page|
Je suis totalement conquis par Betway Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour finir, Betway Casino merite un detour palpitant. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce le lien communautaire.
VГ©rifier le site|
discoveramazingfinds – Sounds trustworthy and fun, definitely a place I’d browse often.
groweverymoment – Perfect for personal development and staying mindful of daily achievements.
Je suis totalement conquis par Betway Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, quelquefois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Globalement, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. D’ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un bonus les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce le lien communautaire.
DГ©couvrir la page|
Je suis completement seduit par Belgium Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, quelquefois des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Dans l’ensemble, Belgium Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute soudee.
http://www.casinobelgium365fr.com|
J’adore le dynamisme de Gamdom Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est de qualite. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour conclure, Gamdom Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. A noter les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui booste la participation.
Essayer maintenant|
J’adore le dynamisme de Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Betway Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Pour ajouter le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Particulierement fun les paiements securises en crypto, qui motive les joueurs.
Cliquer pour voir|
Je suis enthousiasme par Betway Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est clair et efficace, malgre tout des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En resume, Betway Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Aller sur le site|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betify Casino, il cree une experience captivante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour finir, Betify Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement super les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Ouvrir le site|
Je suis totalement conquis par Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, de temps a autre plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En resume, Belgium Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. En plus le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui booste la participation.
http://www.casinobelgium365fr.com|
Je suis bluffe par Gamdom Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, mais encore des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Gamdom Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute soudee.
Entrer sur le site|
everydaystylemarket – Love the balance of comfort and fashion, feels fresh and versatile.
Je suis bluffe par Betway Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, mais des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Betway Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A signaler les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges personnalises.
Explorer plus|
Je suis completement seduit par Betify Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En fin de compte, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Notons egalement la navigation est intuitive et lisse, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce le lien communautaire.
Cliquez ici|
findyournextgoal – Love the message, perfect reminder to keep moving forward in life.
creativityneverends – Love the concept, it instantly sparks motivation and artistic energy.
simplefashioncorner – Great concept, simplicity in style always stands out beautifully.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betify Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des transactions rapides. Le support client est irreprochable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour conclure, Betify Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, offre des bonus exclusifs.
En savoir davantage|
findyourpath – Motivational and calm at the same time, truly love the energy it gives.
J’ai un faible pour Betify Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui booste la participation.
http://www.betifycasinoa366fr.com|
makeimpacteveryday – Such a positive message, encourages small actions that create big change.
learnsomethingnewtoday – The name instantly makes me want to explore and discover more.
dreambiggeralways – The name radiates confidence and motivation, really uplifting vibe overall.
Discover exquisite Austrian wines at wine tasting vienna and immerse yourself in Vienna’s vibrant wine culture.
Wien begeistert mit seiner langen Weintradition und zeitgenossischen Angeboten. Die Region ist bekannt fur ihren exzellenten Wei?wein, besonders den Grunen Veltliner. Die Weinkeller Wiens locken mit ihrem authentischen Charme und kostlichen Tropfen.
Das milde Klima und die mineralreichen Boden begunstigen den Weinbau. Daher gedeihen hier besonders aromatische Rebsorten.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
In Wien gibt es mehrere renommierte Weinregionen, wie den Nussberg oder den Bisamberg. Diese Gebiete sind fur ihre Spitzenweine international bekannt. Familiengefuhrte Weinguter bieten oft Fuhrungen und Verkostungen an. Dabei lernt man viel uber die Herstellung und Geschichte der Weine.
Ein Besuch im Weingut Wieninger oder im Mayer am Pfarrplatz lohnt sich. Diese Weinguter stehen fur hochste Qualitat und Handwerkskunft.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Weinverkostung**
Eine klassische Wiener Weinverkostung beginnt meist mit einer Kellertour. Oft werden historische Anekdoten zum Weinbau geteilt. Danach folgt die Verkostung unterschiedlicher Weine. Von frischen Wei?weinen bis zu kraftigen Rotweinen ist alles dabei.
Haufig werden die Weine mit lokalen Kasesorten oder Brot serviert. Es ist die perfekte Erganzung zum sensorischen Erlebnis.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
Um das Beste aus einer Weinverkostung in Wien herauszuholen, sollte man vorher buchen. Einige Anbieter bieten auch private Verkostungen an. Zudem lohnt es sich, auf die Jahreszeiten zu achten. Im Herbst finden oft Weinlesefeste statt.
Ein guter Tipp ist auch, ein Notizbuch mitzubringen. Es hilft, personliche Favoriten zu dokumentieren.
—
### **Spin-Template fur den Artikel**
#### **1. Einfuhrung in die Weinverkostung in Wien**
Jahrlich stromen Tausende von Besuchern in die Weinkeller der Stadt.
#### **2. Beliebte Weinregionen und Weinguter**
Hier verbinden sich Tradition mit innovativen Methoden.
#### **3. Ablauf einer typischen Wiener Weinverkostung**
Es ist die perfekte Erganzung zum sensorischen Erlebnis.
#### **4. Tipps fur unvergessliche Weinverkostungen**
So kann man sich die geschmacklichen Eindrucke leicht merken.
—
**Hinweis:** Durch Kombination der Varianten aus den -Blocken konnen zahlreiche einzigartige Texte generiert werden, die grammatikalisch und inhaltlich korrekt sind.
theartofgrowth – Inspiring and thoughtful layout, perfect for personal growth and learning.
казино фриспины за регистрацию и без депозита
kra44 at
фриспины без отыгрыша без депозита
Je suis totalement conquis par Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, toutefois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Betway Casino assure un fun constant. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, permet une immersion complete. Egalement excellent les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Commencer ici|
kra39 cc
J’adore l’energie de Betway Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Betway Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus le site est rapide et engageant, incite a rester plus longtemps. A mettre en avant les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, assure des transactions fluides.
Visiter la plateforme|
Топ-добірка у нас: https://dailyfacts.com.ua/transport.html
yourstylezone – Stylish, modern, and user-friendly, love the smooth browsing experience.
styleandchoice – Great mix of creativity, personality, and trend appeal.
simplebuyhub – Love how easy it is to shop here, very user-friendly layout.
бездепозитные бонусы без отыгрыша Мечтаете окунуться в мир азартных игр, но не хотите рисковать собственными деньгами? Онлайн-казино идут навстречу вашим желаниям, предлагая щедрые бездепозитные бонусы. Это отличная возможность познакомиться с игрой, протестировать новые слоты и, возможно, даже выиграть реальные деньги, не вложив ни копейки!
бесплатные вращения без депозита Бездепозитный бонус – это подарок от казино, который вы получаете просто за регистрацию или выполнение определенных условий, без необходимости пополнять свой игровой счет.
starttodaymoveforward – Perfect message for anyone aiming to improve and achieve more.
budgetfriendlypicks – I’m impressed with the variety and low prices available here.
trendywearstore – Fashion-forward choices that make shopping online really enjoyable.
discoverhiddenopportunities – Encourages people to think differently and chase unseen potential.
shopandsaveonline – Great deals and simple layout, makes online shopping quick and easy.
Je suis epate par Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, toutefois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Betway Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A noter le design est moderne et attrayant, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement super les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, assure des transactions fiables.
Lire les dГ©tails|
Je suis bluffe par Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des tables live interactives. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, mais encore des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Belgium Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour couronner le tout la navigation est intuitive et lisse, booste le fun du jeu. Un atout les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui motive les joueurs.
Aller plus loin|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Belgium Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, en revanche des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A souligner le site est rapide et immersif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un bonus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
AccГ©der Г la page|
Je suis captive par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, par contre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, booste le fun du jeu. Un avantage les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements securises.
Touchez ici|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Gamdom Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par ailleurs plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Gamdom Casino merite un detour palpitant. En plus le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Betify Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots fluides. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Betify Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs le design est style et moderne, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A noter les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des bonus exclusifs.
DГ©couvrir plus|
Je suis captive par Betify Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps a autre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Betify Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A mentionner l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une energie supplementaire. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Continuer ici|
J’adore l’energie de Belgium Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En resume, Belgium Casino merite une visite dynamique. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement excellent les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
http://www.casinobelgiumfr.com|
Je ne me lasse pas de Belgium Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour faire court, Belgium Casino offre une experience hors du commun. A signaler la plateforme est visuellement captivante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un element fort les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui booste la participation.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis epate par Gamdom Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En fin de compte, Gamdom Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En plus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui stimule l’engagement.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je suis bluffe par Gamdom Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Au final, Gamdom Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En extra le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г explorer|
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est clair et efficace, toutefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Globalement, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A souligner le design est moderne et energique, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Lancer le site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Betify Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, en revanche plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Betify Casino vaut une visite excitante. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement fun les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter pour plus|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Belgium Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour conclure, Belgium Casino assure un fun constant. A mentionner l’interface est simple et engageante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, renforce la communaute.
Explorer plus|
Je suis epate par Betify Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Pour faire court, Betify Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons aussi le design est tendance et accrocheur, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, cree une communaute vibrante.
http://www.betifycasino777fr.com|
Je suis captive par Betway Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les options de jeu sont infinies, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service client est excellent. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, mais encore des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Betway Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, assure des transactions fluides.
Lancer le site|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Betify Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le service client est excellent. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Betify Casino vaut une visite excitante. Notons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Particulierement fun les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des privileges sur mesure.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
J’adore la vibe de Betway Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En fin de compte, Betway Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Pour completer la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute soudee.
https://betwaycasino365fr.com/|
startfreshjourney – Uplifting and positive vibe, perfect for inspiration and fresh beginnings.
Затворы стальные Трубы ПНД (полиэтилен низкого давления) отличаются повышенной гибкостью и используются для прокладки кабельных сетей, систем водоснабжения и газопроводов.
connectwithpeople – The name itself gives warm, friendly, and community-driven vibes.
бездепозитные фриспины за регистрацию с выводом без пополнения Бездепозитные бонусы – это привлекательные предложения от онлайн-казино и букмекерских контор, которые позволяют игрокам начать играть, не внося собственных средств. Чаще всего они предоставляются за регистрацию нового аккаунта. Это может быть небольшая сумма денег на игровой счет или определенное количество бесплатных вращений для популярных игровых автоматов.
бездепозитные фриспины за регистрацию с выводом без пополнения Бездепозитные бонусы – это привлекательные предложения от онлайн-казино и букмекерских контор, которые позволяют игрокам начать играть, не внося собственных средств. Чаще всего они предоставляются за регистрацию нового аккаунта. Это может быть небольшая сумма денег на игровой счет или определенное количество бесплатных вращений для популярных игровых автоматов.
globalfashionzone – Awesome concept, love seeing fashion from different cultures here.
staycuriousdaily – Love the concept; it perfectly captures a mindset of lifelong learning.
groweverymoment – This name feels uplifting and perfectly balanced for a growth brand.
findyourbalance – Inspiring name that fits perfectly with healthy living and mindfulness.
чижик магазин каталог товаров и цены Чижик магазин каталог – это ваш гид по выгодным покупкам. Каталог помогает сориентироваться в ассортименте и выбрать наиболее интересные предложения.
где согласовать перепланировку квартиры https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-1.ru/ .
https://444-000.ru/
китайская туристическая виза Виза в Китай для россиян – это обязательный документ, позволяющий гражданам РФ въезжать на территорию Китая с различными целями: туризм, бизнес, учеба и т.д. Процедура оформления визы имеет свои особенности и нюансы.
без депозита бонус за регистрацию с выводом Бездепозитные бонусы в онлайн-казино – это как бесплатный билет в мир азартных игр. Они позволяют вам попробовать игры, оценить платформу и даже выиграть реальные деньги, не рискуя собственными средствами. Звучит слишком хорошо, чтобы быть правдой? Давайте разберемся, что это такое, как они работают и стоит ли ими пользоваться.
бездепозитные игровые автоматы Сегодня многие онлайн-казино привлекают новичков бездепозитными предложениями. Суть проста: игроку выдаются определённые средства или вращения без необходимости пополнения счёта. Это позволяет попробовать игры, познакомиться с платформой и оценить качество сервиса, не рискуя собственными деньгами. Но главное — такие бонусы задают тон всему игровому опыту: вы привыкнете к интерфейсу, ощутите динамику слотов или стратегию живой рулетки, а затем при желании переведёте часть интереса в реальные ставки.
шенгенская виза во Францию Оформление визы в Японию – процесс, сопряженный с определенными требованиями и нюансами японского консульства. Тщательная подготовка документов и понимание правил подачи заявки являются ключевыми факторами успеха.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betway Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, mais des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, Betway Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement excellent les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
urbanchoicehub – Great selection of city-style fashion and lifestyle products.
bestdailyoffers – Perfect site for anyone who enjoys finding value and discounts.
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Betway Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par contre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, Betway Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En complement le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
everydaystylemarket – The name says it all — everyday style made simple.
discoveramazingfinds – Impressive range of categories and deals to explore.
creativechoiceoutlet – A stylish and well-organized site with lots of creative finds.
exploreinnovativeideas – This site really gets my creativity flowing, so many cool ideas.
Je suis completement seduit par Belgium Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En resume, Belgium Casino merite un detour palpitant. D’ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement super les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
шкаф для строп Шкаф для 4-х бочек – это не просто складское оборудование, это продуманная система безопасности, призванная минимизировать риски, связанные с хранением химических веществ и горючих материалов. Разработанный в соответствии с самыми строгими отраслевыми стандартами, этот шкаф обеспечивает надежную защиту от утечек, разливов и несанкционированного доступа. Усиленная конструкция, выполненная из высококачественной стали, гарантирует долговечность и устойчивость к агрессивным средам. Встроенная система вентиляции предотвращает скопление опасных паров, создавая здоровую и безопасную рабочую среду. Замки с защитой от несанкционированного доступа обеспечивают дополнительный уровень безопасности.
J’adore le dynamisme de Betway Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, malgre tout des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En resume, Betway Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui motive les joueurs.
Continuer ici|
Je suis fascine par Gamdom Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de depart est top. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, quelquefois des offres plus importantes seraient super. En bref, Gamdom Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et style, booste l’excitation du jeu. A noter les paiements securises en crypto, offre des bonus constants.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
шкаф для строп Клеть для 9 баллонов – это надежная защита для ваших газовых баллонов. Прочная металлическая конструкция исключает возможность случайного повреждения баллонов, а специальные крепления обеспечивают их устойчивое положение. Клеть для 9 баллонов – это гарантия безопасности персонала и сохранности вашего имущества.
Je suis captive par Betify Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, rarement des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En conclusion, Betify Casino assure un fun constant. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, qui motive les joueurs.
Cliquer pour voir|
J’ai un faible pour Belgium Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, de temps en temps plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En somme, Belgium Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un atout les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des recompenses continues.
Commencer Г explorer|
Je suis emerveille par Betify Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est efficace et amical. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, parfois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, permet une immersion complete. Egalement genial les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, assure des transactions fiables.
Ouvrir la page|
Je suis captive par Belgium Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Belgium Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En extra l’interface est lisse et agreable, permet une immersion complete. Un plus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages uniques.
https://casinobelgiumfr.com/|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Gamdom Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par moments des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Gamdom Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A souligner le site est rapide et style, facilite une experience immersive. Particulierement cool les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Voir plus|
Je suis accro a Betify Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, malgre tout des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Au final, Betify Casino garantit un amusement continu. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Visiter le site|
https://aviator-game.com.ua/
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Belgium Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, quelquefois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Globalement, Belgium Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En bonus l’interface est simple et engageante, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г explorer|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Betify Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps a autre quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Globalement, Betify Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, renforce le lien communautaire.
Explorer le site web|
J’adore l’energie de Betify Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par moments des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour finir, Betify Casino offre une experience inoubliable. De surcroit l’interface est lisse et agreable, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un plus le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements rapides.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Je suis captive par Belgium Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps en temps quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Belgium Casino merite une visite dynamique. De plus la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une immersion complete. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui booste la participation.
Aller plus loin|
тележка для стружки Шкаф для бочек и еврокуба – это закрытые конструкции, обеспечивающие защиту содержимого от внешних воздействий и несанкционированного доступа. Часто используются для хранения опасных веществ.
корпоратив под ключ Заказать корпоратив – это доверить свой праздник профессионалам, которые воплотят ваши мечты в реальность.
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Изучая Афишу, откройте для себя не только известные достопримечательности, но и скрытые жемчужины города: тихие дворики, уютные кафе, необычные музеи. Погрузитесь в атмосферу Санкт-Петербурга, почувствуйте его ритм и вдохновение, и пусть каждое ваше посещение станет незабываемым приключением. Ведь Санкт-Петербург – это город, который постоянно удивляет и восхищает, город, в который хочется возвращаться снова и снова. А Афиша – ваш верный спутник на этом увлекательном пути
Je suis epate par Betify Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, bien que plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En bref, Betify Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement excellent les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages uniques.
Parcourir maintenant|
шкаф для бочек Металлический поддон – универсальное средство для хранения и транспортировки различных грузов. Изготавливаются из стали или алюминия, обеспечивая высокую прочность и устойчивость к воздействию окружающей среды. Металлические поддоны широко используются на складах, в логистических центрах и на производственных предприятиях, обеспечивая безопасное и эффективное перемещение товаров.
организация свадьбы под ключ Организация свадьбы под ключ – это комплексное решение, позволяющее вам полностью делегировать все заботы профессионалам. Мы берем на себя все этапы подготовки, начиная от разработки концепции и заканчивая координацией в день свадьбы. Наша команда экспертов продумает каждую деталь, чтобы ваше торжество прошло безупречно. Услуги по организации корпоративов – это симфония деталей, где каждая нота – это тщательно продуманный элемент, создающий неповторимую мелодию незабываемого события. Мы не просто организуем вечеринки, мы создаем впечатления, которые укрепляют командный дух, мотивируют сотрудников и оставляют яркие воспоминания. От разработки оригинальной концепции до воплощения самых смелых идей, мы берем на себя все хлопоты, освобождая ваше время для более важных задач. Наши опытные event-менеджеры, как искусные дирижеры, гармонично объединяют все составляющие идеального корпоратива: подбор площадки, кейтеринг, развлекательную программу, техническое обеспечение и многое другое.
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Афиша Санкт-Петербурга – это не просто список развлечений; это живое полотно, сотканное из тысяч культурных нитей, образующих неповторимый облик Северной столицы. Здесь каждый найдет что-то для себя, будь то поклонник классического искусства, ценитель современного авангарда или просто человек, ищущий ярких впечатлений. От балетных постановок в легендарном Мариинском театре, где эхо великих премьер до сих пор витает в воздухе, до модных выставок в креативных пространствах “Ткачей” и “Артмузы”, Санкт-Петербург предлагает бесконечный калейдоскоп возможностей для обогащения душевного мира. Благодаря Афише, вы всегда в курсе грядущих концертов мировых звезд, театральных фестивалей, кинопоказов и гастрономических событий. Это ваш персональный проводник по культурной жизни города, который поможет вам не пропустить самые интересные мероприятия и спланировать свой досуг наилучшим образом. Здесь можно найти информацию о мастер-классах, лекциях, экскурсиях и других образовательных программах, позволяющих расширить кругозор и узнать больше об истории и культуре Санкт-Петербурга.
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Афиша Санкт-Петербурга – это не просто сводка предстоящих событий, это портал в бурлящий мир искусства и развлечений Северной Венеции. Это путеводитель, раскрывающий перед вами двери в самые сокровенные уголки культурной жизни города, от помпезных дворцов до андеграундных клубов. Здесь анонсы оперных див соседствуют с новостями о независимых театральных постановках, а обзоры модных ресторанов перекликаются с репортажами с уличных фестивалей. Каждый день в Санкт-Петербурге рождаются новые идеи, открываются новые выставки, звучат новые мелодии. И Афиша – ваш надежный компас в этом океане культурных возможностей. С ней вы всегда будете в курсе последних тенденций, сможете спланировать свой досуг и открыть для себя что-то новое и захватывающее. Будь то грандиозный концерт на Дворцовой площади или камерный вечер поэзии в старинном особняке, Афиша поможет вам сделать правильный выбор и создать unforgettable memories.
Афиша Санкт Петербурга Афиша Санкт-Петербурга – это не просто список развлечений; это живое полотно, сотканное из тысяч культурных нитей, образующих неповторимый облик Северной столицы. Здесь каждый найдет что-то для себя, будь то поклонник классического искусства, ценитель современного авангарда или просто человек, ищущий ярких впечатлений. От балетных постановок в легендарном Мариинском театре, где эхо великих премьер до сих пор витает в воздухе, до модных выставок в креативных пространствах “Ткачей” и “Артмузы”, Санкт-Петербург предлагает бесконечный калейдоскоп возможностей для обогащения душевного мира. Благодаря Афише, вы всегда в курсе грядущих концертов мировых звезд, театральных фестивалей, кинопоказов и гастрономических событий. Это ваш персональный проводник по культурной жизни города, который поможет вам не пропустить самые интересные мероприятия и спланировать свой досуг наилучшим образом. Здесь можно найти информацию о мастер-классах, лекциях, экскурсиях и других образовательных программах, позволяющих расширить кругозор и узнать больше об истории и культуре Санкт-Петербурга.
бездепозит и фриспины при регистрации
https://dzen.ru/holstai
игровые автоматы без депозита
пирамида_оргонит Аквадиск: Аквадиск – это устройство, предназначенное для структурирования воды. Считается, что структурированная вода обладает улучшенными свойствами, которые благотворно влияют на организм человека. Аквадиски обычно изготавливаются из специальных материалов и имеют определенную форму, которая способствует созданию вихревого потока воды, структурирующего ее молекулы. Сторонники использования аквадисков утверждают, что структурированная вода улучшает гидратацию, повышает энергию и способствует общему оздоровлению. Различные размеры аквадисков используются для структурирования воды в разных объемах – от стакана до больших емкостей.
металлочерепица купить в спб Металлочерепица: Металлочерепица – это современный кровельный материал, имитирующий натуральную черепицу. Она изготавливается из оцинкованной стали с полимерным покрытием, что обеспечивает ей долговечность, устойчивость к коррозии и привлекательный внешний вид. Металлочерепица легка в монтаже, имеет небольшой вес и широкую цветовую гамму, что позволяет реализовать различные дизайнерские решения. Этот материал идеально подходит для кровли жилых домов, коттеджей и других зданий, придавая им эстетичный вид и надежную защиту от атмосферных воздействий.
discoverandbuy – Excellent product variety with great prices, definitely worth revisiting.
женский_талисман Вихреваякатушка: Вихреваякатушка – это устройство, создающее вихревые энергетические поля. Считается, что эти поля оказывают положительное влияние на окружающую среду и живые организмы. Вихревые катушки используются в различных областях, таких как сельское хозяйство, медицина и энергетика, для улучшения роста растений, оздоровления организма и повышения эффективности энергетических систем. Orgonite часто используют в сочетании с вихревыми катушками для усиления их энергетического воздействия.
сэндвич панели цена Панели для стен: Панели для стен – это современный и практичный способ отделки помещений. Они позволяют быстро и легко преобразить интерьер, скрыть неровности стен и создать стильный дизайн. Существует множество видов стеновых панелей: деревянные, пластиковые, МДФ, ПВХ и другие. Каждый вид имеет свои преимущества и недостатки, поэтому при выборе панелей необходимо учитывать назначение помещения, стиль интерьера и бюджет. Стеновые панели легко монтируются, не требуют сложной подготовки поверхности и могут использоваться для отделки как жилых, так и коммерческих помещений.
Je suis emerveille par Betway Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour faire court, Betway Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs le site est rapide et immersif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement attrayant les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Parcourir maintenant|
findnewinspiration – I always come away feeling motivated and ready to take action.
dreambiggeralways – Love the message, every visit gives me motivation to aim higher.
stayfocusedandgrow – Helpful insights for maintaining discipline and a positive mindset.
learnandimprove – Every post feels genuine and aimed at helping people grow smarter.
Je suis accro a Betway Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais encore plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Globalement, Betway Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Pour completer le design est style et moderne, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement excellent les options variees pour les paris sportifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Continuer Г lire|
Теперь не нужно контролировать каждую мелочь, специалисты делают всё за нас https://vsoprovozhdenie.ru/
глицин какая аминокислота
аспарагин
yourstylezone – Trendy site that really helps express personal fashion taste.
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, de temps a autre des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Au final, Azur Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un element fort le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis bluffe par Azur Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent sans delai, a l’occasion des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Azur Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Ajoutons aussi le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement attrayant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
https://azurcasino366fr.com/|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky 31 Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, parfois quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A noter le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A noter les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky 31 Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter l’interface est intuitive et fluide, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement interessant les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des bonus constants.
VГ©rifier ceci|
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
J’adore l’energie de 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les gains arrivent sans delai, par contre quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, 1xBet Casino merite un detour palpitant. En complement le design est moderne et attrayant, facilite une immersion totale. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Visiter aujourd’hui|
https://bsme-at.at
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Action Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des depots instantanes. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En resume, Action Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. A mentionner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis totalement conquis par Action Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, en revanche des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En conclusion, Action Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion totale. Un point fort les transactions en crypto fiables, garantit des paiements securises.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
https://lblsp.at
diplomova prace Psani seminarni prace / Napsani seminarni prace: (Viz vysvetleni vyse u “Seminarni prace.”)
казино с бонусом за регистрацию и без депозита на реальные деньги
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Azur Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Azur Casino assure un fun constant. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A mettre en avant les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, cree une communaute vibrante.
Touchez ici|
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию с выводом
Квалифицированное сопровождение импорта, четкий контроль каждого этапа https://vsoprovozhdenie.ru/
jak spravne napsat bakalarskou praci Bakalarska prace / Diplomova prace: (Viz vysvetleni vyse, jedna se o stejny pojem, pouze bez diakritiky)
средство от диабета
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est transparent et rapide, toutefois quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Pour faire court, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. De plus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, permet une immersion complete. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des bonus exclusifs.
https://azurcasino366fr.com/|
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par moments des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En bref, Azur Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. En bonus le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une immersion totale. Egalement excellent les paiements securises en crypto, cree une communaute soudee.
Trouver les dГ©tails|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky 31 Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, cependant des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et energique, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce la communaute.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par 1xBet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, toutefois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En resume, 1xBet Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A souligner le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Explorer le site|
Je ne me lasse pas de 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, a l’occasion des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En conclusion, 1xBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A noter les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Entrer|
J’adore le dynamisme de 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, 1xBet Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement fun les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis completement seduit par Lucky 31 Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement fun les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
http://www.lucky31casino365fr.com|
brightstylemarket – Love the modern vibe, bright visuals, and easy shopping flow.
Je suis fascine par Action Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, cependant des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Pour finir, Action Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement fun les options variees pour les paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Commencer Г lire|
growyourmindset – Love the motivational tone, makes self-improvement feel exciting and doable.
everydaytrendstore – Stylish products, great prices, and a smooth checkout process.
discovermoreideas – A must-visit site for daily inspiration and innovative ideas.
findyourstylehub – Great fashion ideas and inspiration, perfect for daily style updates.
learnandimprove – Every post feels genuine and aimed at helping people grow smarter.
https://s-nano-s.ru/
https://b2best.at
https://t.me/stalprofservice Лестница из металла в Москве – это современное и функциональное решение для многоуровневых помещений. Металлические лестницы отличаются прочностью, долговечностью и разнообразием дизайнерских решений. В Москве, где архитектурные стили сочетают в себе современность и классику, металлические лестницы пользуются большой популярностью. Они могут быть выполнены из различных материалов, таких как сталь, алюминий или чугун, и могут иметь различные формы и размеры. Металлические лестницы часто используются в квартирах, офисах, торговых центрах и других общественных зданиях, где важна безопасность, надежность и эстетичный внешний вид. Компании в Москве предлагают широкий выбор металлических лестниц, начиная от простых конструкций до сложных дизайнерских проектов.
J’ai un faible pour Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, Azur Casino vaut une visite excitante. A noter le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Savoir plus|
бонусы и акции в онлайн-казино на деньги
продвижение дзен Индивидуальные прогоны Хрумером, настроенные под Ваши критерии и задачи.
слоты без депозита с бонусом
Thank you for every other great article. The place else could anyone get that kind of information in such a perfect means of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I’m on the look for such info.
https://www.alyunaniya.com/melbet-2025-obzor-bonusov-stavok/
J’ai un faible pour Azur Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, bien que des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Azur Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un plus les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des recompenses continues.
Obtenir des infos|
https://bsme-at.at
антресольный этаж купить Металлоконструкциямосква: Металлоконструкциямосква – это металлоконструкция, спроектированная и изготовленная в Москве. В условиях активного строительства в Москве, металлоконструкции широко используются для создания каркасов зданий, промышленных сооружений и других объектов. При проектировании и изготовлении металлоконструкций в Москве необходимо учитывать местные строительные нормы и правила, а также требования безопасности. Многие компании в Москве специализируются на проектировании, изготовлении и монтаже металлоконструкций различных типов и сложностей.
J’adore le dynamisme de 1xBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, a l’occasion plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour faire court, 1xBet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. D’ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement fun les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir le site|
Hello there I am so grateful I found your site, I really found you by error, while I was researching on Digg for something else, Regardless I am here now and would just like to say thanks a lot for a remarkable post and a all round interesting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read through it all at the moment but I have bookmarked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read more, Please do keep up the awesome work.
https://www.angelinamargo.com/promocode-melbet-besplatno-2025/
Je suis bluffe par Lucky 31 Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, de temps a autre des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino merite une visite dynamique. De plus le design est moderne et energique, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement cool les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Commencer Г lire|
Je suis enthousiasme par 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est excellent. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Au final, 1xBet Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Notons egalement le design est style et moderne, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des avantages uniques.
Obtenir les dГ©tails|
Je suis bluffe par Lucky 31 Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La gamme est variee et attrayante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, a l’occasion plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino assure un fun constant. Notons egalement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A signaler les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Cliquer maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Action Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En fin de compte, Action Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A signaler la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement fun les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, cree une communaute soudee.
DГ©couvrir|
продвижение вконтакте Увеличение видимости в Google и Yandex, профессиональный опыт с 2011 года.
Мезонин Антресольныхэтажей: Антресольныхэтажей – это множественное число антресольного этажа, то есть несколько антресольных этажей в здании или комплексе зданий. Проектирование и строительство антресольныхэтажей требует учета общих архитектурных решений, функциональных требований и требований безопасности. Антресольныеэтажей позволяют увеличить полезную площадь здания и создать дополнительные возможности для использования пространства.
https://b2best.at
https://b2best.at
findbettervalue – Always impressed by how much value I get for every purchase.
simplechoiceoutlet – Great deals, simple layout, and quality products that never disappoint.
Je suis captive par Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, bien que des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Globalement, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. De surcroit la navigation est intuitive et lisse, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. A noter le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui booste la participation.
Visiter la page web|
Je ne me lasse pas de 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par contre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En fin de compte, 1xBet Casino offre une experience inoubliable. A mentionner le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a rester plus longtemps. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fluides.
Approfondir|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des tables live interactives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par ailleurs des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino garantit un amusement continu. En complement la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement interessant les transactions en crypto fiables, qui dynamise l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis fascine par 1xBet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En resume, 1xBet Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement interessant les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, garantit des paiements securises.
AccГ©der maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, mais encore des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Lucky 31 Casino merite une visite dynamique. En bonus l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. A noter les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui booste la participation.
http://www.lucky31casino365fr.com|
globalshoppingzone – Amazing deals and smooth checkout process, definitely worth visiting again.
J’adore la vibe de Action Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, toutefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Action Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A mentionner le site est rapide et engageant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, garantit des paiements rapides.
Aller à l’intérieur|
urbanwearzone – The site has that perfect mix of comfort, style, and attitude.
beststylecollection – Fantastic collection with great quality and affordable prices.
shopandsmiletoday – Great prices and smooth experience, really makes online shopping fun.
Aw, this was an exceptionally nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to produce a very good article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and never manage to get nearly anything done.
https://monpera888.net/melbet-2025-obzor-bukmekera/
музыкальный дует Elegant Duet Мы «Elegant Duet» Дарья Сулина — виолончель Любовь Морская — скрипка 26 лет мы играем на инструментах и являемся профессиональными музыкантами. За нашей спиной большой опыт работы в театре, филармонии, камерных коллективах и сольных выступлений! На сегодняшний момент мы создали сольный проект, дуэт » Elegant.duet «. Более 20 стран гастролей, в том числе с солистами Scorpions, лауреаты международных конкурсов, звание Гран-при. Степендиаты фондов Глазунова, фонда президента РФ Неоднократные презентации глянцевых журналов, в том числе look book, Премия года 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 FB, музыкальное сопровождение показов мод с звездными дизайнерами, сопровождение закрытых эксклюзивных показов. Репертуар многогранен, от Баха до твоих любимых хитов. С «Elegant Duet» Ваше мероприятие будет заряжено особой энергетикой и конечно же элегантностью и эстетикой «Elegant Duet» — дуэт под который можно танцевать.
Скачать Майнкрафт Мобильный Майнкрафт – это идеальное решение для тех, кто хочет играть в любимую игру в любое время и в любом месте. Благодаря оптимизации для мобильных устройств, вы можете наслаждаться полным функционалом Minecraft на своем смартфоне или планшете. Стройте замки в дороге, исследуйте шахты во время перерыва на работе и сражайтесь с монстрами, сидя в парке. Мобильный Minecraft предлагает удобное управление, адаптированное для сенсорных экранов, и возможность играть как в одиночку, так и с друзьями через интернет. Не упустите возможность погрузиться в мир Minecraft в любое время и в любом месте!
Последняя версия Майнкрафт Minecraft mod – это модификация, которая изменяет или расширяет оригинальную игру Minecraft, добавляя новые возможности и функции, которые не были предусмотрены разработчиками. Моды могут добавлять новые блоки, предметы, мобов, биомы, команды и даже целые игровые механики, полностью преображая геймплей и открывая новые горизонты для творчества и приключений. Они создаются талантливыми сторонними разработчиками и позволяют игрокам настроить Minecraft под свои личные предпочтения и создать уникальный игровой опыт. Существуют тысячи различных модов, от простых изменений интерфейса, которые делают игру более удобной и интуитивно понятной, до сложных модификаций, которые полностью меняют геймплей, добавляя новые измерения, задания и возможности. Установка модов может потребовать использования специальных программ, таких как Forge или Fabric, которые позволяют вам управлять модами и настраивать их параметры. Minecraft mod – это отличный способ вдохнуть новую жизнь в игру и получить уникальный игровой опыт, который будет соответствовать вашим интересам и предпочтениям.
What a information of un-ambiguity and preserveness of valuable know-how regarding unpredicted emotions.
https://www.linqubes.com/promokod-melbet-kazino-2025/
https://b2best.at
webmagnet.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
https://bsme-at.at
https://bs2-bs2web.at
yourdailyfinds – Convenient and fun to browse, always discovering something useful.
Официальный сайт Kraken https://kra44-cc.at безопасная платформа для анонимных операций в darknet. Полный доступ к рынку через актуальные зеркала и onion ссылки.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Скачать Майнкрафт Скачать Майнкрафт моды – это как открыть секретную дверь в мир бесконечных возможностей для кастомизации вашей любимой игры. Моды позволяют вам трансформировать Minecraft до неузнаваемости, добавляя новые элементы, механики, существа, измерения и целые миры, созданные талантливыми и креативными разработчиками. Хотите ли вы добавить в игру магию, технологии будущего, захватывающие приключения в новых биомах или просто улучшить графику, чтобы сделать мир более реалистичным, моды предоставляют вам все необходимые инструменты для этого. С их помощью вы можете создать уникальный игровой опыт, который будет идеально соответствовать вашим личным предпочтениям и интересам, делая каждое прохождение неповторимым. Погрузитесь в мир бесконечных модификаций, экспериментируйте с различными сочетаниями и сделайте свой Minecraft поистине неповторимым!
J’ai un faible pour Azur Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Azur Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De surcroit la navigation est simple et intuitive, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Entrer sur le site|
какую букмекерскую контору выбрать в россии
https://bsme-at.at
бк в москве
https://bs2-bs2web.at
https://bs2-bs2web.at
makeeverymomentcount – I enjoy visiting this page when I need a dose of positivity.
Je suis captive par Azur Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. De surcroit l’interface est intuitive et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
https://azurcasino365fr.com/|
globalshoppingzone – Love how easy it is to explore unique items here.
shopforvalue – Great place to find useful items at really fair prices.
dreamdiscovercreate – One of my favorite spots to find meaningful and inspiring items.
brightstylemarket – Definitely a go-to marketplace for stylish everyday essentials.
музыкальный дует Elegant Duet Мы «Elegant Duet» Дарья Сулина — виолончель Любовь Морская — скрипка 26 лет мы играем на инструментах и являемся профессиональными музыкантами. За нашей спиной большой опыт работы в театре, филармонии, камерных коллективах и сольных выступлений! На сегодняшний момент мы создали сольный проект, дуэт » Elegant.duet «. Более 20 стран гастролей, в том числе с солистами Scorpions, лауреаты международных конкурсов, звание Гран-при. Степендиаты фондов Глазунова, фонда президента РФ Неоднократные презентации глянцевых журналов, в том числе look book, Премия года 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 FB, музыкальное сопровождение показов мод с звездными дизайнерами, сопровождение закрытых эксклюзивных показов. Репертуар многогранен, от Баха до твоих любимых хитов. С «Elegant Duet» Ваше мероприятие будет заряжено особой энергетикой и конечно же элегантностью и эстетикой «Elegant Duet» — дуэт под который можно танцевать.
discoverandshop – Makes online shopping fun, efficient, and totally stress-free.
https://bs2-bs2web.at
лестница на антресольный этаж Строительство: Строительство – это процесс возведения зданий и сооружений, включающий в себя комплекс работ по подготовке площадки, устройству фундаментов, возведению стен и перекрытий, монтажу кровли, установке окон и дверей, прокладке инженерных сетей и выполнению отделочных работ. Строительство требует привлечения квалифицированных рабочих, инженеров, архитекторов и других специалистов. Строительство должно осуществляться в соответствии с проектной документацией, строительными нормами и правилами, а также требованиями безопасности и охраны окружающей среды.
https://b2best.at
https://bs2-bs2web.at
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Lucky 31 Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, de temps en temps quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A mentionner le site est rapide et immersif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des privileges personnalises.
Lucky 31|
Je suis enthousiasme par Azur Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots fluides. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Azur Casino assure un fun constant. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute soudee.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis bluffe par 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En complement le site est rapide et style, booste l’excitation du jeu. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Aller Г la page|
Je suis captive par Action Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, en revanche des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a rester plus longtemps. A souligner le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller voir|
vavada casino pl
Nabycie nieruchomosci w Beskidach to szansa na stworzenie wymarzonego miejsca na wakacje lub staly dom.
Dzieki rozwijajacej sie infrastrukturze i rosnacemu zainteresowaniu turystow, ceny dzialek stopniowo wzrastaja. Coraz wiecej osob docenia spokoj i piekno przyrody, jakie oferuja Beskidy.
#### **2. Gdzie szukac najlepszych ofert dzialek?**
Wybor odpowiedniej lokalizacji zalezy od indywidualnych potrzeb i budzetu. Warto sprawdzic profesjonalne strony internetowe, takie jak dzialki-beskidy.pl, ktore prezentuja sprawdzone oferty.
Przed zakupem nalezy dokladnie przeanalizowac dostepnosc mediow i warunki zabudowy. Wiele ofert zawiera szczegolowe informacje o mozliwosciach zagospodarowania terenu, co ulatwia podjecie decyzji.
#### **3. Jakie korzysci daje posiadanie dzialki w Beskidach?**
Nieruchomosc w gorach to nie tylko inwestycja finansowa, ale rowniez szansa na poprawe jakosci zycia. Dzialka w Beskidach moze stac sie zrodlem dochodu, jesli zdecydujemy sie na wynajem turystom.
Dodatkowo, region ten oferuje wiele atrakcji, takich jak szlaki turystyczne i stoki narciarskie. Beskidy to idealne miejsce dla tych, ktorzy cenia aktywny tryb zycia i bliskosc natury.
#### **4. Jak przygotowac sie do zakupu dzialki?**
Przed podjeciem decyzji warto skonsultowac sie z prawnikiem i geodeta. Profesjonalna pomoc pozwoli uniknac nieprzyjemnych niespodzianek zwiazanych z formalnosciami.
Wazne jest rowniez okreslenie swojego budzetu i planow zwiazanych z zagospodarowaniem terenu. Wiele osob decyduje sie na kredyt, aby sfinansowac zakup wymarzonej dzialki.
—
### **Szablon Spinu**
**1. Dlaczego warto kupic dzialke w Beskidach?**
– Malownicze krajobrazy Beskidow przyciagaja zarowno turystow, jak i przyszlych mieszkancow.
– Dzialki w Beskidach to coraz czesciej wybierana lokata kapitalu przez swiadomych inwestorow.
**2. Gdzie szukac najlepszych ofert dzialek?**
– Warto przegladac specjalistyczne portale, ktore skupiaja sie na nieruchomosciach w Beskidach.
– Przed zakupem nalezy zweryfikowac dostepnosc mediow i mozliwosci zabudowy.
**3. Jakie korzysci daje posiadanie dzialki w Beskidach?**
– Wlasny kawalek gorskiej przestrzeni pozwala na ucieczke od miejskiego zgielku.
– Region oferuje wiele aktywnosci, od wedrowek po gorach po jazde na nartach.
**4. Jak przygotowac sie do zakupu dzialki?**
– Warto dokladnie sprawdzic historie dzialki, aby upewnic sie, ze nie ma zadnych roszczen.
– Okreslenie budzetu i celow inwestycji ulatwi podjecie wlasciwej decyzji.
Je suis emerveille par Lucky 31 Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots fluides. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, de temps a autre quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. De plus la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir plus|
Je suis bluffe par 1xBet Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est clair et efficace, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, 1xBet Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En extra le site est rapide et immersif, permet une immersion complete. Particulierement interessant les transactions en crypto fiables, renforce le lien communautaire.
Voir les dГ©tails|
koh lanta Лонг Бич Ко Ланта: Один из самых популярных пляжей острова
Je suis emerveille par Action Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En somme, Action Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons aussi le site est rapide et engageant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Voir plus|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Lucky 31 Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, malgre tout plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et style, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute vibrante.
Aller à l’intérieur|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Action Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, cependant plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Dans l’ensemble, Action Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons que l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un atout les options de paris sportifs variees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Obtenir plus|
ко ланта таиланд отзывы Остров Ко Ланта Таиланд: Все, что нужно знать перед поездкой
пиастрикс вход
электронный кошелек piastrix регистрация
Je ne me lasse pas de Lucky 31 Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le service client est excellent. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, toutefois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure memorable. A signaler le site est rapide et style, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement attrayant les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements securises.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis bluffe par Azur Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, rarement des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A signaler le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce le lien communautaire.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis bluffe par Action Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Pour conclure, Action Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement captivante, facilite une immersion totale. Un plus les evenements communautaires dynamiques, propose des avantages uniques.
Cliquer maintenant|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky 31 Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce la communaute.
https://casinolucky31fr.com/|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de 1xBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est pro et accueillant. Le processus est transparent et rapide, bien que des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, 1xBet Casino assure un fun constant. Ajoutons que le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une immersion totale. Un atout le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des privileges sur mesure.
VГ©rifier ceci|
Je suis accro a Action Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En resume, Action Casino merite une visite dynamique. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Aller sur le site web|
advista.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
Je ne me lasse pas de Lucky 31 Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par contre des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Lucky 31 Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un element fort les options variees pour les paris sportifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Savoir plus|
Je suis sous le charme de Action Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, neanmoins des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En resume, Action Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A noter le site est rapide et style, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute vibrante.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support client est irreprochable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, parfois des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. En conclusion, Azur Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A signaler l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A signaler les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce la communaute.
VГ©rifier le site|
bahis sitesi 1xbet http://1xbet-7.com/ .
surewin casino https://surewin-online.com .
dreamfashionfinds – Excellent place to discover stylish looks at great prices.
growthflow.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
https://bs2-bs2web.at
classystylemarket – Perfect for anyone who loves sophisticated and stylish choices.
trendworldmarket – Great mix of modern, stylish, and trending items.
buildyourownfuture – A helpful hub for growth-minded individuals.
globalfindsoutlet – A smooth browsing experience with lots of great deals.
Je suis enthousiasme par Azur Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des tables live interactives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est simple et transparent, bien que des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour finir, Azur Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. D’ailleurs l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement genial le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, propose des avantages uniques.
Avancer|
https://lblsp.at
brightfashionhub – The clothing inspiration here made planning my weekend outfits much easier.
growtogethercommunity – Navigation was smooth, and each section offered something worth checking out.
fashionchoicehub – Great balance of stylish content and practical tips that actually make sense.
findnewdeals – Loved how simple it was to browse deals without feeling overwhelmed.
bestbuycollection – Found some great product picks here that felt genuinely worth checking out.
findnewhorizons – The layout felt simple and welcoming, making the experience very enjoyable.
консультация юристов онлайн Юрист онлайн консультация бесплатно В современном ритме жизни, когда скорость и доступность информации ценятся превыше всего, возможность получить квалифицированную юридическую консультацию онлайн бесплатно становится неоценимым преимуществом. Это шанс оперативно оценить ситуацию, понять свои права и обязанности, а также наметить дальнейшие шаги без каких-либо финансовых вложений.
Ко ланта Жизнь морских цыган (Chao Leh) на Ко Ланта: Сохраняя традиции предков. Ко Ланта – это не просто туристический остров, это также дом для морских цыган (Chao Leh), коренных жителей, которые на протяжении многих веков жили в гармонии с морем и сохраняли свои уникальные обычаи и культуру. Морские цыгане, также известные как “люди моря”, живут в небольших поселениях на восточном побережье Ко Ланта. Они традиционно занимаются рыболовством, сбором даров моря и строительством лодок. Их уникальный образ жизни неразрывно связан с морем, которое является для них источником существования и духовной связи. Морские цыгане придерживаются своей собственной религии, основанной на вере в духов природы и предков. Они проводят сложные церемонии и фестивали, чтобы просить у духов защиты и благословения. В последние годы культура и образ жизни морских цыган подвергаются влиянию современной цивилизации и туризма. Однако они прилагают все усилия для сохранения своих традиций и передачи их молодому поколению. Посещение поселений морских цыган предоставляет уникальную возможность познакомиться с их культурой и увидеть их традиционные ремесла.
https://speedwaymedia.com/2025/11/06/roulet-tino-a-full-review-for-nascar-and-motorsports-enthusiasts/
J’adore la vibe de Azur Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il donne un elan excitant. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, mais plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En conclusion, Azur Casino assure un fun constant. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et engageant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A noter les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Continuer ici|
J’ai un faible pour Lucky 31 Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Lucky 31 Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Notons egalement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un bonus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des avantages uniques.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Azur Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Azur Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En bonus le design est moderne et attrayant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un plus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fiables.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je suis sous le charme de Action Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Globalement, Action Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En extra la navigation est simple et intuitive, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement super le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus constants.
Essayer|
Je ne me lasse pas de 1xBet Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les gains arrivent sans delai, neanmoins des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour faire court, 1xBet Casino merite une visite dynamique. Pour ajouter l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un atout les evenements communautaires dynamiques, renforce le lien communautaire.
Parcourir le site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky 31 Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, quelquefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En fin de compte, Lucky 31 Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. De plus l’interface est lisse et agreable, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Explorer davantage|
Je suis captive par Lucky 31 Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, quelquefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. D’ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement cool les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des recompenses continues.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, parfois des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour conclure, 1xBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A mentionner le design est moderne et attrayant, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un bonus les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, renforce la communaute.
Parcourir le site|
Je suis fascine par Action Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, rarement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, Action Casino assure un fun constant. De plus le site est rapide et engageant, facilite une immersion totale. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
http://www.casinoactionfr.com|
Купить ИЖС в Нижегородской области. Помогу купить участок в Нижегородской области Нижегородская область, с ее бескрайними полями, живописными лесами и богатым культурным наследием, манит возможностью обустроить собственный уголок, вдали от городской суеты. Мечтаете о просторном участке для строительства дома, дачи или фермерского хозяйства? Я, как опытный эксперт в сфере недвижимости Нижегородской области, помогу вам реализовать эту мечту. Тщательный подбор участков, соответствующих вашим запросам по местоположению, площади, коммуникациям и бюджету. Полное юридическое сопровождение сделки, от проверки документов до оформления прав собственности. Сделайте первый шаг к жизни на своей земле!
Je suis totalement conquis par Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, quelquefois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Azur Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement captivante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un atout le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, cree une communaute vibrante.
Naviguer sur le site|
J’adore la vibe de Action Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des depots fluides. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par moments plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Globalement, Action Casino offre une experience hors du commun. Pour ajouter le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un avantage les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des bonus constants.
Obtenir plus|
Купить дом в Нижегородской области Помогу купить участок в Нижегородской области Мечтаете о собственном уголке земли в живописном уголке России? Нижегородская область – это регион с богатой историей, прекрасной природой и развитой инфраструктурой, идеальное место для строительства загородного дома или ведения личного подсобного хозяйства. Я помогу вам найти идеальный участок, учитывая ваши предпочтения по местоположению, площади, коммуникациям и бюджету. Сопровождение на всех этапах сделки, от поиска до оформления документов.
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky 31 Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En fin de compte, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour completer la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un plus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Ouvrir la page|
Je suis fascine par Azur Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour finir, Azur Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De plus le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement attrayant les transactions en crypto fiables, assure des transactions fiables.
http://www.azurcasinoappfr.com|
Clarte Nexive se demarque comme une plateforme d’investissement crypto revolutionnaire, qui utilise la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour offrir a ses utilisateurs des avantages concurrentiels decisifs.
Son IA analyse les marches en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et execute des strategies complexes avec une precision et une vitesse inatteignables pour les traders humains, maximisant ainsi les potentiels de profit.
Je suis enthousiasme par Action Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Action Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Notons egalement le design est tendance et accrocheur, booste le fun du jeu. A mettre en avant les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
Lire la suite|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de 1xBet Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, occasionnellement plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, 1xBet Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus exclusifs.
https://1xbetcasino365fr.com/|
Je suis captive par Lucky 31 Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, occasionnellement des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour faire court, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et immersif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un plus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Obtenir des infos|
консультация юриста бесплатно онлайн круглосуточно Бесплатная юридическая консультация онлайн Воспользуйтесь уникальной возможностью получить бесплатную юридическую консультацию, не рискуя своими финансами. Это идеальный вариант для тех, кто хочет разобраться в своих правах и обязанностях, получить общее представление о проблеме и определить дальнейший план действий.
Je suis fascine par Lucky 31 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, a l’occasion plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour conclure, Lucky 31 Casino merite un detour palpitant. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui stimule l’engagement.
Visiter maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par 1xBet Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il donne un elan excitant. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, 1xBet Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. A souligner la navigation est claire et rapide, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Visiter la page web|
J’adore la vibe de Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Le bonus de depart est top. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, Action Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus la navigation est fluide et facile, apporte une touche d’excitation. A mettre en avant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui motive les joueurs.
Continuer ici|
консультация юриста бесплатно онлайн Бесплатная юридическая консультация онлайн Воспользоваться бесплатной юридической консультацией онлайн – это разумный шаг для тех, кто хочет разобраться в правовых аспектах своей ситуации, не неся при этом финансовых затрат. Многие платформы предлагают такую возможность, позволяя задать вопрос юристу и получить ответ в кратчайшие сроки. Это отличный способ получить общее представление о проблеме и понять, стоит ли обращаться за платной юридической помощью.
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Le processus est simple et transparent, rarement quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Action Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A noter le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement super les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Essayer|
heaps of wins casino no deposit bonus heaps of wins casino no deposit bonus .
trendyvaluezone – Another solid visit with updated products that felt modern and practical.
займ онлайн на карту казахстан
changeyourmindset – This place always gives me something thoughtful to reflect on daily.
все займы онлайн
discovermoreideas – Browsing brought a few fresh insights that helped me plan my week.
dreambuildachieve – The content felt clear and uplifting, perfect for a quick mindset boost.
learnsomethingincredible – Learned a new concept that actually helped me think differently today.
dreamshopworld – Found some great items today that genuinely caught my attention quickly.
newstesting12112 – A simple, updated and reader-friendly website for quick information.
Современное Искусство Моделирование в цифровой скульптуре – это процесс создания виртуального прототипа будущего объекта. Художник, подобно скульптору прошлого, формирует форму, добавляет текстуру и детали, уделяя особое внимание анатомическим особенностям (если речь идет о создании фигур человека или животных). От точности и мастерства моделирования зависит конечный результат – качество и реалистичность 3D-печатной копии.
Value Hub Picks – The organization of items made finding things simple and fast.
Современное Искусство Миниатюра в эпоху цифровой скульптуры переживает ренессанс. Авторские фигурки, коллекционные модели, винтажные статуэтки – все это обретает новую жизнь благодаря возможностям 3D печати. Точность, детализация и возможность воспроизведения сложных форм делают этот процесс незаменимым для создания уникальных и востребованных произведений искусства. Спрос на 3dпечать фигурок, особенно в крупных городах, таких как Спб, постоянно растет.
Hey! I understand this is kind of off-topic but I had to ask. Does building a well-established blog like yours require a massive amount work? I am brand new to operating a blog however I do write in my journal on a daily basis. I’d like to start a blog so I can easily share my personal experience and thoughts online. Please let me know if you have any kind of recommendations or tips for brand new aspiring blog owners. Appreciate it!
RUSSIAN PIDOR
кухни на заказ санкт петербург https://www.kuhni-spb-10.ru .
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Azur Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est clair et efficace, de temps en temps plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Azur Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. En bonus le site est fluide et attractif, booste l’excitation du jeu. Egalement excellent le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, qui booste la participation.
Entrer maintenant|
Ко ланта Жизнь морских цыган (Chao Leh) на Ко Ланта: Сохраняя традиции предков. Ко Ланта – это не просто туристический остров, это также дом для морских цыган (Chao Leh), коренных жителей, которые на протяжении многих веков жили в гармонии с морем и сохраняли свои уникальные обычаи и культуру. Морские цыгане, также известные как “люди моря”, живут в небольших поселениях на восточном побережье Ко Ланта. Они традиционно занимаются рыболовством, сбором даров моря и строительством лодок. Их уникальный образ жизни неразрывно связан с морем, которое является для них источником существования и духовной связи. Морские цыгане придерживаются своей собственной религии, основанной на вере в духов природы и предков. Они проводят сложные церемонии и фестивали, чтобы просить у духов защиты и благословения. В последние годы культура и образ жизни морских цыган подвергаются влиянию современной цивилизации и туризма. Однако они прилагают все усилия для сохранения своих традиций и передачи их молодому поколению. Посещение поселений морских цыган предоставляет уникальную возможность познакомиться с их культурой и увидеть их традиционные ремесла.
findhappinessdaily – Uplifting messages and helpful tips that brighten my day instantly.
J’adore la vibe de Azur Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En somme, Azur Casino est un must pour les passionnes. A mentionner le site est fluide et attractif, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, garantit des paiements rapides.
Visiter le site|
юридическая консультация бесплатная онлайн без регистрации Бесплатная юридическая консультация онлайн Многие юридические платформы предлагают бесплатные онлайн консультации для привлечения клиентов и демонстрации своей компетенции. Это отличная возможность оценить квалификацию юриста, задать общие вопросы и понять, подходит ли он вам для дальнейшего сотрудничества. Не стоит упускать шанс получить бесплатную консультацию, чтобы сориентироваться в своей правовой ситуации.
консультация онлайн юриста Бесплатная юридическая консультация онлайн Многие юридические платформы предлагают бесплатные онлайн консультации для привлечения клиентов и демонстрации своей компетенции. Это отличная возможность оценить квалификацию юриста, задать общие вопросы и понять, подходит ли он вам для дальнейшего сотрудничества. Не стоит упускать шанс получить бесплатную консультацию, чтобы сориентироваться в своей правовой ситуации.
Моделирование Цифровая Скульптура являет собой революцию в мире искусства, предлагая художникам невиданную ранее свободу самовыражения и технические возможности. Виртуальное пространство становится холстом, на котором мастер может создавать сложные формы и детали, не ограниченные тяжестью материалов или сложностью ручной обработки. Этот вид искусства стирает границы между реальностью и фантазией, позволяя воплощать в жизнь самые смелые и неординарные идеи.
startsomethingnewtoday.click – Site layout is clean, everything organized perfectly for easy browsing today.
globalfindsoutlet.click – Love browsing new arrivals, everything is organized and looks professional.
3DПечать 3D Печать и DLP Печать — это технологии, которые позволяют перенести цифровую скульптуру в физический мир. 3D печать, в частности, позволяет создавать объекты из различных материалов, включая пластик, смолы и металлы. DLP печать, с другой стороны, предлагает более высокую точность и детализацию, что особенно важно при создании миниатюр и коллекционных фигурок.
Ko Lanta Ко Ланта: Гармония тайского гостеприимства и островов-близнецов. Ко Ланта, расположенный в провинции Краби на юге Таиланда, представляет собой архипелаг, где самые крупные острова – Ко Ланта Ной (малый) и Ко Ланта Яй (большой) – соединены мостом. Это место, где традиционное тайское гостеприимство встречается с нетронутой красотой природы, создавая уникальную атмосферу для отдыха. В отличие от более шумных туристических центров, Ко Ланта предлагает спокойствие и уединение, сохраняя при этом доступность современных удобств. Оба острова обладают своим неповторимым характером. Ко Ланта Ной, ближе к материку, является административным и логистическим центром, а Ко Ланта Яй – основной туристический остров, где сосредоточены пляжи, отели и рестораны. Здесь можно найти как роскошные курорты, так и уютные бунгало, утопающие в зелени тропических садов. Главная достопримечательность Ко Ланта Яй – это его западное побережье, усеянное длинными песчаными пляжами, омываемыми Андаманским морем. Ко Ланта – это не только пляжный отдых. Остров предлагает множество активностей: от дайвинга и снорклинга на близлежащих коралловых рифах до исследования национального парка Му Ко Ланта с его густыми джунглями и впечатляющим маяком. Вечером путешественников ждут уютные бары и рестораны с видом на закат, где можно насладиться свежайшими морепродуктами и традиционными тайскими блюдами.
happylifestylemarket.click – Found unique items I couldn’t get anywhere else locally.
discovernewcollection.click – Checkout was fast, site layout makes everything easy to follow.
urbantrendstore.click – Prices are fair, offers are really worth exploring this time.
learnsomethingincredible.click – Loved the tutorials here, learning new things feels simple and fun.
J’ai un faible pour Azur Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des transactions rapides. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, mais plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Azur Casino offre une aventure memorable. A signaler la navigation est fluide et facile, apporte une touche d’excitation. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, cree une communaute soudee.
https://casinoazurfr.com/|
Je ne me lasse pas de Azur Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Au final, Azur Casino offre une experience hors du commun. De plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un element fort les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, cree une communaute vibrante.
Aller sur le site|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Lucky 31 Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est simple et transparent, a l’occasion des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, Lucky 31 Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce la communaute.
Aller sur le site web|
J’adore le dynamisme de Action Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est efficace et amical. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Action Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. De surcroit la navigation est claire et rapide, apporte une energie supplementaire. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour la competition, cree une communaute vibrante.
Explorer maintenant|
Je suis accro a 1xBet Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, malgre tout des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Globalement, 1xBet Casino garantit un plaisir constant. De surcroit le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un point cle les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Essayer ceci|
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky 31 Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, cependant des offres plus importantes seraient super. En somme, Lucky 31 Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus le design est style et moderne, booste le fun du jeu. A signaler le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, qui motive les joueurs.
http://www.lucky31casino365fr.com|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour 1xBet Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, mais des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En bref, 1xBet Casino offre une aventure memorable. D’ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je suis emerveille par Action Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des depots fluides. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, par contre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Au final, Action Casino merite un detour palpitant. D’ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, facilite une immersion totale. A souligner les options de paris sportifs variees, renforce le lien communautaire.
Cliquer maintenant|
Je suis accro a Azur Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, de temps a autre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En resume, Azur Casino est un must pour les passionnes. En complement la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Aller voir|
J’ai un faible pour Azur Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, malgre tout des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Au final, Azur Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En complement le site est rapide et immersif, incite a rester plus longtemps. A noter le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, garantit des paiements securises.
Aller sur le site web|
Je suis emerveille par Azur Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La gamme est variee et attrayante, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, toutefois des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Pour conclure, Azur Casino est un must pour les passionnes. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une immersion complete. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fluides.
Commencer ici|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Lucky 31 Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Globalement, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure memorable. A noter le site est rapide et style, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des privileges sur mesure.
AccГ©der au site|
Je suis accro a Action Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent sans delai, mais des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En conclusion, Action Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour couronner le tout le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un plus le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui stimule l’engagement.
Voir plus|
Je suis totalement conquis par 1xBet Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour finir, 1xBet Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A souligner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un atout les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je suis accro a Lucky 31 Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En somme, Lucky 31 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. A noter le site est fluide et attractif, apporte une energie supplementaire. A souligner les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, cree une communaute soudee.
Explorer le site|
Je suis sous le charme de 1xBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des slots aux designs captivants. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, toutefois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. Au final, 1xBet Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. De plus la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un avantage les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir le web|
Je suis bluffe par Action Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, en revanche plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, Action Casino garantit un plaisir constant. A signaler le design est moderne et energique, facilite une experience immersive. Un avantage les transactions en crypto fiables, cree une communaute vibrante.
http://www.casinoaction365fr.com|
Слушеть Рэп онлайн Благодаря платформам, таким как Spotify, YouTube, и Apple Music, слушатели могут получить доступ к обширной библиотеке музыки, включая как классические хиты, так и новинки от молодых исполнителей.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Azur Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, en revanche des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Globalement, Azur Casino garantit un amusement continu. De surcroit le design est moderne et attrayant, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un bonus les evenements communautaires vibrants, assure des transactions fluides.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Слушеть Рэп онлайн Combining rhythm, rhyme, and powerful lyrics, rap artists convey their experiences and perspectives, making it a dynamic storytelling medium.
Explore Dadasdas – Informative and well-crafted articles jo quickly read ho jate hain.
bestpickshub.click – Website design is clean, easy to explore and find products.
Rap musik Подписывайтесь на любимые каналы, создавайте свои плейлисты и открывайте для себя новые треки — мир рэпа предлагает безграничные возможности для открытий и наслаждения. Rap musik
bestbuycollection.click – Found exactly what I needed, checkout process was quick and simple.
Rap musik В его основе лежит ритмичное чтение текста, позволяющее артистам передавать свои мысли, эмоции и переживания.
Je suis accro a Casinozer Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le suivi est impeccable. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par ailleurs des offres plus importantes seraient super. Pour faire court, Casinozer Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que le site est rapide et immersif, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un point cle les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements rapides.
Parcourir maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Casinozer Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, offrant des tables live interactives. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Dans l’ensemble, Casinozer Casino garantit un plaisir constant. En complement le design est moderne et attrayant, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. A signaler les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui motive les joueurs.
Approfondir|
Je suis fascine par Casinozer Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Le processus est clair et efficace, a l’occasion quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino merite un detour palpitant. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, facilite une immersion totale. A noter les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses continues.
Poursuivre la lecture|
Je suis epate par Mystake Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est simple et transparent, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. En fin de compte, Mystake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. A souligner le design est tendance et accrocheur, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement top les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, offre des recompenses continues.
VГ©rifier le site|
Je suis captive par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Globalement, Mystake Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons aussi le site est rapide et immersif, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Egalement super les evenements communautaires engageants, cree une communaute vibrante.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
J’adore l’energie de Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus de depart est top. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, parfois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En bref, Pokerstars Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi la navigation est intuitive et lisse, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est clair et efficace, en revanche quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. De surcroit le site est rapide et immersif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement super les paiements securises en crypto, propose des avantages uniques.
Avancer|
Je suis totalement conquis par Stake Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, de temps en temps des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En fin de compte, Stake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est fluide et facile, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un atout les evenements communautaires dynamiques, offre des recompenses continues.
Passer à l’action|
геотекстиль дорнит “ПОЛИСИНТЕЗ” предлагает армированную пленку различной плотности и с различным типом армирования, обеспечивая гибкость выбора для различных применений, таких как укрытия для строительных площадок, теплицы, навесы и бассейны. Наша армированная пленка характеризуется высокой устойчивостью к ультрафиолетовому излучению и долговечностью, что гарантирует длительный срок службы. отражающая изоляция
Je suis captive par Casinozer Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection est riche et diversifiee, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus initial est super. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, de temps a autre des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Casinozer Casino garantit un plaisir constant. Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et intuitive, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un point cle les paiements securises en crypto, qui booste la participation.
Emmenez-moi lГ -bas|
Je suis completement seduit par Casinozer Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est clair et efficace, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En somme, Casinozer Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. A mentionner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste le fun du jeu. A signaler le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des avantages uniques.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par moments plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En resume, Casinozer Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De surcroit la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs variees, cree une communaute vibrante.
DГ©couvrir les faits|
Je ne me lasse pas de Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, quelquefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Globalement, Mystake Casino garantit un amusement continu. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement super les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Commencer maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Pokerstars Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour completer la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires vibrants, cree une communaute soudee.
Aller sur le site web|
J’ai un faible pour Stake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Le processus est transparent et rapide, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En bref, Stake Casino offre une experience hors du commun. En extra le site est rapide et style, booste le fun du jeu. Un point cle les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
J’ai un faible pour Stake Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. En somme, Stake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Pour ajouter le site est rapide et immersif, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Aller à l’intérieur|
fashiondailycorner.click – Prices look fair, quality seems solid based on what I saw today.
бесплатные фриспины без депозита
бесплатные вращения без депозита
отражающая изоляция Наша компания специализируется на производстве и поставке полиэтиленовых пленок, армированных пленок, отражающей изоляции, геотекстиля дорнит и тентов, отвечающих самым высоким стандартам качества.
Лига ставков Лига ставок – это мост между вами и миром спортивных состязаний, где каждое событие – это шанс испытать свою интуицию и знания. Это больше, чем просто букмекерская контора; это платформа, где страсть к спорту встречается с азартом прогнозирования, создавая уникальную атмосферу напряжения и предвкушения. Здесь каждый, от начинающего любителя до опытного аналитика, может найти свой способ участия и, возможно, сорвать куш.
1win официальный Лига Ставок: История, Надежность и Современные Возможности Лига Ставок – это одна из старейших и наиболее авторитетных букмекерских компаний на российском рынке, зарекомендовавшая себя как надежный партнер для любителей спортивных ставок. Бренд узнаваем, имеет богатую историю и продолжает активно развиваться, предлагая клиентам современные решения и широкие возможности для игры. История и Развитие Компания была основана в 2008 году и с тех пор прошла долгий путь, став одним из лидеров индустрии. Лига Ставок – это легальный букмекер, работающий на основании лицензии ФНС, что гарантирует игрокам честность и прозрачность финансовых операций. За годы работы компания накопила огромный опыт и экспертизу в области спортивного беттинга. Широкий Спектр Ставок и Событий Лига Ставок предлагает своим клиентам обширную линию спортивных событий, включающую как популярные виды спорта (футбол, хоккей, баскетбол, теннис), так и менее известные дисциплины. Компания предоставляет возможность делать ставки на результаты матчей, тоталы, форы, индивидуальные показатели игроков и другие события. Особое внимание уделяется Live-ставкам, позволяющим игрокам делать прогнозы в режиме реального времени во время матча. Технологии и Удобство Пользования Лига Ставок активно внедряет современные технологии, чтобы обеспечить клиентам максимальный комфорт и удобство. Компания предлагает удобный и функциональный веб-сайт, а также мобильные приложения для устройств на базе iOS и Android. Интерфейс интуитивно понятен и позволяет легко найти нужную информацию и сделать ставку. Круглосуточная служба поддержки оперативно отвечает на вопросы и помогает решить любые проблемы. Бонусная Программа и Акции Лига Ставок предлагает привлекательную бонусную программу для новых и действующих клиентов. Новые игроки могут получить приветственный бонус при регистрации и первом депозите. Постоянные клиенты участвуют в программе лояльности, накапливая бонусы за активные ставки. Компания регулярно проводит акции и конкурсы с ценными призами, что делает игру еще более интересной и выгодной.
кайт хургада
Je suis sous le charme de Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour faire court, Pokerstars Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement top le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, garantit des paiements securises.
AccГ©der au site|
ко ланта
J’adore le dynamisme de Pokerstars Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots fluides. Le support client est irreprochable. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par moments plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Pour finir, Pokerstars Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En extra l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement excellent les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller Г la page|
ко ланта
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Stake Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, de temps a autre des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. Globalement, Stake Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A souligner l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un atout les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Obtenir plus|
Je suis accro a Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, mais encore des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Mystake Casino merite une visite dynamique. A souligner la navigation est intuitive et lisse, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. A souligner les evenements communautaires dynamiques, qui dynamise l’engagement.
https://mystakecasino365fr.com/|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Casinozer Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est efficace et amical. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Globalement, Casinozer Casino offre une aventure memorable. Notons aussi le design est tendance et accrocheur, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste la participation.
Lancer le site|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En somme, Mystake Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Ajoutons aussi le design est moderne et attrayant, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement super les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, cree une communaute vibrante.
Tout apprendre|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. En bref, Casinozer Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons egalement le site est rapide et immersif, facilite une immersion totale. A mettre en avant les tournois reguliers pour la competition, propose des privileges personnalises.
Commencer ici|
Global Shop Picks – Spent a moment browsing and noticed a few useful products.
Лига ставок Лига Ставок: История, Надежность и Современные Возможности Лига Ставок – это одна из старейших и наиболее авторитетных букмекерских компаний на российском рынке, зарекомендовавшая себя как надежный партнер для любителей спортивных ставок. Бренд узнаваем, имеет богатую историю и продолжает активно развиваться, предлагая клиентам современные решения и широкие возможности для игры. История и Развитие Компания была основана в 2008 году и с тех пор прошла долгий путь, став одним из лидеров индустрии. Лига Ставок – это легальный букмекер, работающий на основании лицензии ФНС, что гарантирует игрокам честность и прозрачность финансовых операций. За годы работы компания накопила огромный опыт и экспертизу в области спортивного беттинга. Широкий Спектр Ставок и Событий Лига Ставок предлагает своим клиентам обширную линию спортивных событий, включающую как популярные виды спорта (футбол, хоккей, баскетбол, теннис), так и менее известные дисциплины. Компания предоставляет возможность делать ставки на результаты матчей, тоталы, форы, индивидуальные показатели игроков и другие события. Особое внимание уделяется Live-ставкам, позволяющим игрокам делать прогнозы в режиме реального времени во время матча. Технологии и Удобство Пользования Лига Ставок активно внедряет современные технологии, чтобы обеспечить клиентам максимальный комфорт и удобство. Компания предлагает удобный и функциональный веб-сайт, а также мобильные приложения для устройств на базе iOS и Android. Интерфейс интуитивно понятен и позволяет легко найти нужную информацию и сделать ставку. Круглосуточная служба поддержки оперативно отвечает на вопросы и помогает решить любые проблемы. Бонусная Программа и Акции Лига Ставок предлагает привлекательную бонусную программу для новых и действующих клиентов. Новые игроки могут получить приветственный бонус при регистрации и первом депозите. Постоянные клиенты участвуют в программе лояльности, накапливая бонусы за активные ставки. Компания регулярно проводит акции и конкурсы с ценными призами, что делает игру еще более интересной и выгодной.
Je ne me lasse pas de Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. La gamme est variee et attrayante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Les agents repondent avec efficacite. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, malgre tout des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Au final, Pokerstars Casino offre une experience inoubliable. En complement le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, propose des privileges sur mesure.
Commencer Г explorer|
Success Explorer – Engaging content that encourages looking at new opportunities with confidence.
Je suis totalement conquis par Stake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, a l’occasion des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, Stake Casino offre une aventure memorable. En bonus l’interface est intuitive et fluide, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Particulierement cool le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui booste la participation.
https://stakecasinobonusfr.com/|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour conclure, Pokerstars Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un point cle les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, qui booste la participation.
Visiter la plateforme|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection de jeux est impressionnante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les gains arrivent en un eclair, en revanche des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour faire court, Pokerstars Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires engageants, assure des transactions fiables.
Aller sur le web|
слоты бонус за регистрацию
Je suis captive par Stake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des sessions live immersives. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est excellent. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. Pour faire court, Stake Casino est un endroit qui electrise. D’ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour la competition, qui booste la participation.
Commencer Г dГ©couvrir|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Mystake Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, rarement plus de promos regulieres ajouteraient du peps. Globalement, Mystake Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs le design est moderne et energique, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Egalement top les options variees pour les paris sportifs, renforce la communaute.
Cliquer maintenant|
J’adore la vibe de Casinozer Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le suivi est impeccable. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps a autre des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Ajoutons que le design est tendance et accrocheur, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Egalement top les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages uniques.
Visiter maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Casinozer Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options de jeu sont infinies, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, occasionnellement des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En resume, Casinozer Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point fort les evenements communautaires engageants, cree une communaute vibrante.
Voir les dГ©tails|
J’ai un faible pour Casinozer Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont toujours fiables, par ailleurs quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino est un endroit qui electrise. D’ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. A noter les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, garantit des paiements securises.
Essayer ceci|
бездепозит и фриспины при регистрации
Thanks , I have just been searching for information about
this subject for a while and yours is the greatest I have
found out till now. However, what in regards to the bottom line?
Are you sure concerning the supply?
freshstyleboutique.click – Found unique pieces easily, navigation was smooth and user friendly overall.
подробнее kraken зеркало
fashiondailycorner.click – Fashion picks look impressive, enjoyed scrolling through the updated collection today.
1 win официальный сайт winline, Fonbet, Бетсити, Betboom, Мелбет – конкуренты 1win Фрибет – это бонус, который можно использовать для бесплатных ставок.
ко ланта
Бетсити 1 ставка – это момент истины, первый шаг в игре, где интуиция, анализ и удача переплетаются, чтобы определить исход пари. Ставки на спорт – это не просто игра на деньги, это погружение в мир спорта, это возможность проявить себя как эксперта, это страсть, которая объединяет миллионы людей по всему миру.
ко ланта
TurkPaydexHub se distingue comme une plateforme d’investissement en crypto-monnaies revolutionnaire, qui met a profit la puissance de l’intelligence artificielle pour fournir a ses clients des avantages decisifs sur le marche.
Son IA scrute les marches en temps reel, detecte les occasions interessantes et met en ?uvre des strategies complexes avec une precision et une vitesse inaccessibles aux traders humains, maximisant ainsi les perspectives de gain.
промокоды 1 хбет Вводите актуальный промокод на http://www.google.com.nf/url?q=https://bergkompressor.ru/news/artcles/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_5.html и получите бонус до 32 500 рублей, чтобы получить стартовый капитал для игры.
1xBet бонус код Воспользуйтесь бонусом при регистрации на http://www.google.md/url?q=https://bergkompressor.ru/news/artcles/?1xbet_promokod_pri_registracii_bonus_5.html и получите 32 500 рублей + бонус 100%, чтобы получить дополнительное преимущество.
Je suis sous le charme de Pokerstars Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, bien que quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Pokerstars Casino vaut une visite excitante. En complement la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Particulierement interessant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, garantit des paiements rapides.
http://www.pokerstarscasino365fr.com|
1win официальный 1 ставка – это отправная точка, первый шаг на пути к выигрышу. Это момент истины, когда знания, интуиция и удача сливаются воедино, чтобы определить исход игры. Ставки на спорт – это не просто способ заработать деньги, это стиль жизни, наполненный адреналином и предвкушением. Это возможность почувствовать себя частью глобального спортивного сообщества, где каждый матч – это повод для обсуждения и анализа.
Лига ставков ставки Ставки на спорт спорт ставков – это сложная система, требующая постоянного обучения и адаптации. Это игра, в которой выигрывает тот, кто умеет анализировать, прогнозировать и держать руку на пульсе событий. Ставки прогнозы – это искусство предвидения, основанное на кропотливом анализе статистики, новостей и экспертных оценок. Это ключ к успешным ставкам и стабильному выигрышу.
бездепозит и фриспины при регистрации
бездепозитный бонус игровые автоматы
Je suis bluffe par Pokerstars Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, parfois quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Pour faire court, Pokerstars Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Pour completer le site est rapide et style, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. A signaler les evenements communautaires engageants, qui motive les joueurs.
Rejoindre maintenant|
globaltrendstore.click – Great site layout, product descriptions were helpful and made choosing easier today.
changeyourfuture.click – Practical tips provided, implementing changes seems simple and very achievable today.
сюда kra43 сс
J’adore la vibe de Stake Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, par moments des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour conclure, Stake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une immersion complete. Un bonus les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, renforce la communaute.
DГ©couvrir plus|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, cependant des offres plus importantes seraient super. Globalement, Pokerstars Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. En extra l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, booste l’excitation du jeu. Un point fort les options de paris sportifs variees, assure des transactions fiables.
En savoir davantage|
Je suis completement seduit par Stake Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est toujours au top. Le processus est clair et efficace, en revanche quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Dans l’ensemble, Stake Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Ajoutons aussi le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, renforce la communaute.
Visiter la page web|
Je suis fascine par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus initial est super. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. Pour faire court, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires vibrants, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Entrer maintenant|
Je suis totalement conquis par Mystake Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Le bonus initial est super. Le service client est excellent. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, en revanche plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Mystake Casino est un endroit qui electrise. A noter la navigation est fluide et facile, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un point cle le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Naviguer sur le site|
Je suis completement seduit par Mystake Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est efficace et amical. Les transactions sont toujours securisees, par ailleurs quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En somme, Mystake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En complement le site est rapide et immersif, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement top les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, garantit des paiements securises.
Cliquer pour voir|
Je suis enthousiasme par Casinozer Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, mais des bonus plus varies seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Casinozer Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En plus la navigation est fluide et facile, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, renforce la communaute.
Entrer|
What’s up mates, how is all, and what you desire to say on the topic of this piece of writing, in my view its truly amazing designed for me.
Купить iPhone в Митино
Je suis captive par Stake Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des sessions live immersives. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, neanmoins des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En resume, Stake Casino garantit un amusement continu. En complement l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires dynamiques, assure des transactions fiables.
Rejoindre maintenant|
Je suis emerveille par Stake Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, occasionnellement plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Dans l’ensemble, Stake Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Egalement top les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses regulieres.
Entrer maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par Pokerstars Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les options de jeu sont incroyablement variees, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, par contre plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. Au final, Pokerstars Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons aussi l’interface est simple et engageante, permet une immersion complete. Un point cle les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fiables.
DГ©couvrir maintenant|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Pokerstars Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, proposant des jeux de table classiques. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, en revanche quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Globalement, Pokerstars Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Par ailleurs l’interface est lisse et agreable, donne envie de continuer l’aventure. Un element fort les evenements communautaires engageants, qui stimule l’engagement.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Stake Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les options de jeu sont infinies, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, quelquefois des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En somme, Stake Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A souligner le site est fluide et attractif, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un point fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, propose des avantages uniques.
http://www.stakecasino366fr.com|
Je suis bluffe par Mystake Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, cependant des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Globalement, Mystake Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un plus les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, renforce la communaute.
En savoir davantage|
Je suis emerveille par Mystake Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, toutefois plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En bref, Mystake Casino offre une aventure memorable. En complement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. A mettre en avant les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui dynamise l’engagement.
DГ©marrer maintenant|
Je suis fascine par Mystake Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, quelquefois plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Dans l’ensemble, Mystake Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Ajoutons aussi l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Egalement super les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Commencer maintenant|
Je suis completement seduit par Casinozer Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, par contre quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Globalement, Casinozer Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Un plus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, cree une communaute soudee.
http://www.casinozercasino777fr.com|
beef casino обман или нет
Hi there, after reading this remarkable piece of writing i am also happy to share my experience here with colleagues.
Купить iPhone в Митино
Онлайн-казино Vavada гарантирует быстрый вход даже при блокировках.
Актуальные адреса сайта работают корректно круглосуточно.
Слоты, турниры и лайв-игры адаптированы под мобильные устройства.
Создание аккаунта происходит мгновенно, а интерфейс остаётся понятным и удобным.
Если вам нужно актуальный рабочий адрес, используйте vavada online casino — там всегда доступна актуальная информация.
Сохраняйте баланс, чтобы процесс оставался комфортным.
Site Elephant Bet https://elephantbet-mz.com/
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Pokerstars Casino, il cree une experience captivante. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent sans delai, a l’occasion des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Au final, Pokerstars Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A mentionner la navigation est simple et intuitive, facilite une experience immersive. Un bonus les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Visiter pour plus|
findyournextgoal.click – Really helpful tips, encourages consistent progress toward personal growth every single day.
globaltrendstore.click – Great site layout, product descriptions were helpful and made choosing easier today.
содержание vodkabet
веб-сайт водка бет
Creative Exploration Spot – Hands-on ideas and tips to bring new projects to life.
findyourstyle.shop – Loved exploring new trends, fashion pieces here look modern and fresh.
learnwithoutlimits.shop – Great tutorials provided, makes understanding complex concepts much easier and quicker today.
Все документы переведём – срочный перевод документов. Перевод корпоративных документов. Самарское бюро. Нотариальное заверение. Срочно и качественно. Юридическая точность.
Je suis totalement conquis par Pokerstars Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, occasionnellement des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Dans l’ensemble, Pokerstars Casino est un choix parfait pour les joueurs. Par ailleurs la navigation est claire et rapide, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un bonus les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, propose des avantages uniques.
Visiter le site|
J’adore le dynamisme de Pokerstars Casino, on ressent une ambiance de fete. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il rend le debut de l’aventure palpitant. Le support client est irreprochable. Le processus est simple et transparent, rarement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En conclusion, Pokerstars Casino offre une aventure memorable. A signaler le design est moderne et energique, apporte une touche d’excitation. A signaler les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fiables.
Plonger dedans|
J’ai un veritable coup de c?ur pour Stake Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. La bibliotheque est pleine de surprises, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains arrivent sans delai, occasionnellement des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. En conclusion, Stake Casino garantit un amusement continu. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est lisse et agreable, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement top les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir davantage|
Je ne me lasse pas de Mystake Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Les options de jeu sont infinies, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, quelquefois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Globalement, Mystake Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A mentionner l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Egalement super les paiements en crypto rapides et surs, qui stimule l’engagement.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Casinozer Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, toutefois quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. En bref, Casinozer Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Notons egalement l’interface est intuitive et fluide, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement attrayant le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, garantit des paiements securises.
Consulter les dГ©tails|
J’adore la vibe de Mystake Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, bien que plus de promotions frequentes boosteraient l’experience. En conclusion, Mystake Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A noter le site est rapide et immersif, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un avantage notable les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, garantit des paiements securises.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
Je suis epate par Casinozer Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des sessions live immersives. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service d’assistance est au point. Le processus est clair et efficace, mais encore quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. En somme, Casinozer Casino merite un detour palpitant. En extra le site est rapide et style, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement top les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fluides.
Aller au site|
позавчера слушать Рок группа “Позавчера” – это не просто коллектив музыкантов, это семья, объединенная общей любовью к музыке и стремлением создавать что-то значимое. Их концерты – это ритуал, где каждый зритель становится частью этой семьи.
узнать больше Здесь https://cerberus-veitrf.ru/
музыка позавчера Рок группа “Позавчера” – это не просто коллектив музыкантов, это семья, объединенная общей любовью к музыке и стремлением создавать что-то значимое. Их концерты – это ритуал, где каждый зритель становится частью этой семьи, сопричастным к магии творчества.
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Stake Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Avec des depots instantanes. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, bien que des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. En somme, Stake Casino est un endroit qui electrise. De surcroit l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Un element fort les tournois reguliers pour s’amuser, assure des transactions fiables.
Commencer Г lire|
рок группа позавчера Музыка “Позавчера” – это источник вдохновения, способный пробудить в человеке дремлющие таланты и мечты. Это музыка, которая помогает верить в себя и не бояться идти своим путем.
J’ai un faible pour Pokerstars Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. Le catalogue de titres est vaste, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il offre un coup de pouce allechant. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, mais des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En resume, Pokerstars Casino merite un detour palpitant. Notons egalement le site est fluide et attractif, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Passer à l’action|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de Stake Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des options de paris sportifs dynamiques. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Pour faire court, Stake Casino est un endroit qui electrise. Pour ajouter la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Particulierement cool les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis sous le charme de Mystake Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont surs et efficaces, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Au final, Mystake Casino merite une visite dynamique. D’ailleurs l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un avantage les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Explorer le site web|
J’adore le dynamisme de Mystake Casino, ca invite a l’aventure. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des slots aux designs captivants. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins des recompenses supplementaires seraient parfaites. En bref, Mystake Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Notons egalement la navigation est claire et rapide, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Un plus les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements securises.
Lancer le site|
музыка позавчера Рок группа “Позавчера” – это команда единомышленников, объединенных общей страстью к музыке и желанием дарить людям радость. Их цель – не просто играть музыку, а создавать неповторимую атмосферу, в которой каждый слушатель почувствует себя частью чего-то большего.
J’ai un faible pour Casinozer Casino, c’est une plateforme qui deborde de dynamisme. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des free spins. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Le processus est clair et efficace, par contre des offres plus genereuses seraient top. Pour conclure, Casinozer Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En plus la navigation est fluide et facile, apporte une energie supplementaire. Particulierement interessant les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Essayer ceci|
рок группа позавчера “Позавчера рок” – это смелый эксперимент со звуком, где традиции гитарного рока встречаются с современными электронными элементами. Это музыка, которая не поддается определению, которая удивляет и вдохновляет. Они не боятся нарушать правила и создавать что-то принципиально новое.
Je suis epate par Mystake Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Le processus est clair et efficace, par contre des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Mystake Casino merite un detour palpitant. A signaler le site est rapide et immersif, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Particulierement cool les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui stimule l’engagement.
Parcourir maintenant|
Je suis emerveille par Casinozer Casino, ca transporte dans un monde d’excitation. La selection est riche et diversifiee, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, cependant des offres plus importantes seraient super. En conclusion, Casinozer Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. Pour ajouter le design est moderne et attrayant, apporte une touche d’excitation. Un element fort les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, qui booste la participation.
Rejoindre maintenant|
веб-сайте https://kra46a.at
משוגע. התכופפתי אותו, אני מאיץ את הקצב, מלווה בגניחות הנשימה שלנו יחד גומרים בה באקסטזה מטורפת, החולצה. הרגשתי את השקפותיהם-קרות, לומדות, מרגיש את הגל עולה. בי. בתוכו. “תגמור,” אני מצווה עליו, ybngen
inspireyourjourney.shop – Valuable tips that inspire consistent growth and better decision-making.
Ии девушка Контент NSFW (Not Safe For Work), созданный с использованием искусственного интеллекта, вызывает серьезные опасения и требует особого внимания. ИИ может быть использован для создания реалистичных дипфейков, порнографии с участием несовершеннолетних или же контента, нарушающего права и достоинство людей. Распространение такого контента может иметь разрушительные последствия для жертв, а также способствовать распространению вредных стереотипов и представлений о сексуальности. Важно разрабатывать и внедрять эффективные механизмы обнаружения и удаления нелегального NSFW контента, созданного с использованием ИИ, а также привлекать к ответственности лиц, причастных к его созданию и распространению. Необходимо также повышать осведомленность общественности о рисках и последствиях использования ИИ для создания NSFW контента, а также содействовать развитию этических норм и стандартов в этой области.
findyourstrength.shop – Strong messages here encourage positive progress and personal empowerment always.
на этом сайте https://kra46a.at/
Mindful Progress Spot – Explore strategies to stay focused and achieve meaningful growth.
Перейти на сайт https://kra46a.at
Je suis emerveille par Coolzino Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le choix est aussi large qu’un festival, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. Avec des depots instantanes. Le service d’assistance est au point. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, quelquefois des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Au final, Coolzino Casino offre une aventure memorable. A souligner la navigation est claire et rapide, permet une immersion complete. Un point fort les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, assure des transactions fiables.
Voir les dГ©tails|
Elephant Bet Apostas Online https://elephantbet-mz.com/
J’ai un faible pour Coolzino Casino, ca offre un plaisir vibrant. Les jeux proposes sont d’une diversite folle, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par ailleurs des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. En somme, Coolzino Casino merite un detour palpitant. Ajoutons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, incite a rester plus longtemps. Particulierement cool les nombreuses options de paris sportifs, qui motive les joueurs.
DГ©couvrir les offres|
J’adore l’ambiance electrisante de Coolzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Avec des depots fluides. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est clair et efficace, occasionnellement des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. En bref, Coolzino Casino vaut une visite excitante. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ce qui rend chaque session plus palpitante. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires engageants, garantit des paiements securises.
En savoir plus|
Je suis enthousiasme par MonteCryptos Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. 100% jusqu’a 500 € avec des spins gratuits. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, parfois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En resume, MonteCryptos Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En extra la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Egalement super les competitions regulieres pour plus de fun, assure des transactions fluides.
En savoir plus|
J’ai une passion debordante pour Lucky8 Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Le service client est de qualite. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, par moments des bonus varies rendraient le tout plus fun. Au final, Lucky8 Casino offre une experience inoubliable. D’ailleurs la navigation est intuitive et lisse, permet une immersion complete. Egalement super les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, qui motive les joueurs.
Obtenir des infos|
Je suis emerveille par Coolzino Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le bonus de depart est top. Le service est disponible 24/7. Les gains arrivent sans delai, bien que plus de promotions variees ajouteraient du fun. Pour faire court, Coolzino Casino est un incontournable pour les joueurs. A mentionner le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un bonus le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Continuer Г lire|
Je suis emerveille par Lucky8 Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. La selection est riche et diversifiee, offrant des tables live interactives. Avec des transactions rapides. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, a l’occasion quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Au final, Lucky8 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Egalement genial les options variees pour les paris sportifs, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Continuer Г lire|
Je ne me lasse pas de NetBet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. 100% jusqu’a 500 € plus des tours gratuits. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En fin de compte, NetBet Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A mentionner la navigation est claire et rapide, booste le fun du jeu. Particulierement attrayant les options de paris sportifs variees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Regarder de plus prГЁs|
Je suis bluffe par NetBet Casino, ca transporte dans un univers de plaisirs. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, avec des machines a sous visuellement superbes. Il donne un elan excitant. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les retraits sont ultra-rapides, occasionnellement quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En somme, NetBet Casino est un endroit qui electrise. En plus la navigation est intuitive et lisse, apporte une touche d’excitation. Egalement top les paiements securises en crypto, propose des privileges personnalises.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
Je suis totalement conquis par Coolzino Casino, il offre une experience dynamique. Le catalogue est un paradis pour les joueurs, offrant des tables live interactives. Le bonus initial est super. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, parfois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Pour finir, Coolzino Casino est un must pour les passionnes. Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, apporte une energie supplementaire. Un plus les transactions en crypto fiables, cree une communaute vibrante.
Ouvrir maintenant|
Je suis enthousiaste a propos de MonteCryptos Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est fiable et reactif. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par moments plus de promos regulieres dynamiseraient le jeu. En conclusion, MonteCryptos Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. En bonus le site est rapide et engageant, ajoute une touche de dynamisme. Un atout le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, offre des bonus constants.
Savoir plus|
Je suis completement seduit par MonteCryptos Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Il y a une abondance de jeux excitants, incluant des paris sportifs pleins de vie. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, quelquefois des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. En bref, MonteCryptos Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En plus la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. A noter les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, renforce la communaute.
https://montecryptoscasino777fr.com/|
J’adore le dynamisme de Lucky8 Casino, on y trouve une vibe envoutante. Les options sont aussi vastes qu’un horizon, proposant des jeux de table classiques. Il donne un avantage immediat. Le service client est excellent. Les paiements sont surs et fluides, par contre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. En somme, Lucky8 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A noter l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Particulierement fun le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, offre des bonus exclusifs.
Essayer maintenant|
Je suis enthousiasme par NetBet Casino, il procure une sensation de frisson. La selection est riche et diversifiee, incluant des paris sur des evenements sportifs. Il donne un elan excitant. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, cependant des recompenses supplementaires dynamiseraient le tout. En somme, NetBet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En bonus l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, incite a rester plus longtemps. Un point fort le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, qui motive les joueurs.
http://www.netbetcasino366fr.com|
Je suis bluffe par NetBet Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, offrant des sessions live palpitantes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont rapides et pros. Les gains sont transferes rapidement, par contre des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Dans l’ensemble, NetBet Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. A souligner la navigation est fluide et facile, booste le fun du jeu. A signaler le programme VIP avec des avantages uniques, renforce la communaute.
Ouvrir maintenant|
findpurposeandpeace.click – Calm and inspiring content helps discover purpose and maintain peace today.
happyshoppingcorner.click – Shopping here feels smooth, navigation is easy and products look great.
tripscan Tripscan – это инновационная платформа, позволяющая спланировать идеальное путешествие, учитывая все ваши предпочтения и бюджет. Она анализирует миллионы вариантов перелетов, отелей и развлечений, предлагая персонализированные маршруты и самые выгодные предложения.
NeoSpin Australia https://casino-neospin.org/
J’ai un faible pour Coolzino Casino, on y trouve une energie contagieuse. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il donne un avantage immediat. Les agents sont toujours la pour aider. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, parfois des bonus diversifies seraient un atout. Pour finir, Coolzino Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. En plus le design est tendance et accrocheur, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un avantage notable les evenements communautaires pleins d’energie, assure des transactions fluides.
Aller Г la page|
Je suis captive par Coolzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Il y a un eventail de titres captivants, avec des machines a sous aux themes varies. Le bonus initial est super. Le suivi est d’une fiabilite exemplaire. Les gains sont verses sans attendre, en revanche quelques free spins en plus seraient bienvenus. Dans l’ensemble, Coolzino Casino merite une visite dynamique. Ajoutons que le design est moderne et attrayant, permet une plongee totale dans le jeu. Un point fort les transactions en crypto fiables, qui stimule l’engagement.
Commencer Г naviguer|
Trendy Styles Hub – Discover the latest fashion trends and update your wardrobe effortlessly.
smartbuyzone.click – Smooth navigation throughout, helpful for quick shopping and exploring new items.
J’adore la vibe de Coolzino Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de table sophistiques. Le bonus de depart est top. Le suivi est d’une precision remarquable. Le processus est simple et transparent, par moments quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient cool. Globalement, Coolzino Casino est un lieu de fun absolu. Par ailleurs la plateforme est visuellement captivante, incite a prolonger le plaisir. Un plus les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, propose des privileges personnalises.
Obtenir des infos|
modernfashionworld.click – Impressive fashion styles, browsing through outfits felt smooth and enjoyable today.
Je suis fascine par MonteCryptos Casino, il cree une experience captivante. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le support est fiable et reactif. Le processus est fluide et intuitif, occasionnellement des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En somme, MonteCryptos Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. Notons egalement la plateforme est visuellement vibrante, donne envie de prolonger l’aventure. Un element fort les evenements communautaires vibrants, renforce la communaute.
Ouvrir maintenant|
J’adore l’energie de MonteCryptos Casino, ca donne une vibe electrisante. La gamme est variee et attrayante, comprenant des jeux crypto-friendly. Il booste votre aventure des le depart. Le support est rapide et professionnel. Les paiements sont securises et instantanes, toutefois des offres plus genereuses seraient top. En conclusion, MonteCryptos Casino est un immanquable pour les amateurs. Notons egalement le design est moderne et attrayant, booste le fun du jeu. Egalement genial les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le lien communautaire.
https://montecryptoscasino777fr.com/|
J’adore la vibe de Lucky8 Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Les titres proposes sont d’une richesse folle, comprenant des jeux optimises pour Bitcoin. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + tours gratuits. Disponible a toute heure via chat ou email. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, malgre tout quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. En bref, Lucky8 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. A mentionner le site est fluide et attractif, facilite une immersion totale. Un bonus les transactions crypto ultra-securisees, qui dynamise l’engagement.
Essayer ceci|
Je suis fascine par Lucky8 Casino, il cree un monde de sensations fortes. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, avec des slots aux graphismes modernes. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Les agents repondent avec rapidite. Les retraits sont simples et rapides, par ailleurs des offres plus consequentes seraient parfaites. Globalement, Lucky8 Casino garantit un amusement continu. Notons aussi l’interface est lisse et agreable, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement excellent les evenements communautaires engageants, qui booste la participation.
Visiter le site|
Je suis enthousiasme par NetBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, comprenant des titres adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Il offre un demarrage en fanfare. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les paiements sont securises et rapides, rarement des recompenses additionnelles seraient ideales. Dans l’ensemble, NetBet Casino vaut une visite excitante. Notons aussi la plateforme est visuellement electrisante, amplifie l’adrenaline du jeu. Un plus les options de paris sportifs diversifiees, garantit des paiements rapides.
http://www.netbetcasino366fr.com|
J’adore le dynamisme de NetBet Casino, on ressent une ambiance festive. On trouve une gamme de jeux eblouissante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Avec des transactions rapides. Le service client est de qualite. Les transactions sont d’une fiabilite absolue, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits en plus seraient geniaux. Dans l’ensemble, NetBet Casino assure un divertissement non-stop. En extra la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ce qui rend chaque moment plus vibrant. Particulierement interessant le programme VIP avec des privileges speciaux, propose des avantages sur mesure.
Commencer Г naviguer|
ко ланта ко ланта
продолжить https://kra43-cc.at/
Je suis bluffe par Coolzino Casino, il propose une aventure palpitante. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de cartes elegants. Le bonus d’inscription est attrayant. Le support est pro et accueillant. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, neanmoins des bonus plus frequents seraient un hit. Pour conclure, Coolzino Casino offre une experience inoubliable. Pour ajouter l’interface est fluide comme une soiree, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Egalement genial les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le lien communautaire.
AccГ©der Г la page|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour MonteCryptos Casino, ca invite a plonger dans le fun. La variete des jeux est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs en direct. Le bonus de bienvenue est genereux. Le support est efficace et amical. Le processus est transparent et rapide, par contre quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Pour faire court, MonteCryptos Casino est une plateforme qui pulse. D’ailleurs le design est style et moderne, ce qui rend chaque session plus excitante. Particulierement interessant les transactions en crypto fiables, qui stimule l’engagement.
Jeter un coup d’œil|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky8 Casino, ca offre une experience immersive. Le choix de jeux est tout simplement enorme, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Avec des depots rapides et faciles. Disponible 24/7 par chat ou email. Les retraits sont fluides et rapides, quelquefois des offres plus genereuses rendraient l’experience meilleure. En bref, Lucky8 Casino offre une aventure inoubliable. Pour couronner le tout l’interface est intuitive et fluide, permet une immersion complete. Un avantage notable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fluides.
Commencer Г lire|
J’ai une affection particuliere pour Lucky8 Casino, ca pulse comme une soiree animee. Le catalogue est un tresor de divertissements, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il amplifie le plaisir des l’entree. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les transactions sont fiables et efficaces, mais encore des offres plus importantes seraient super. En somme, Lucky8 Casino est une plateforme qui fait vibrer. En bonus la plateforme est visuellement captivante, ce qui rend chaque partie plus fun. Un avantage notable le programme VIP avec des recompenses exclusives, offre des bonus constants.
AccГ©der au site|
J’ai une passion debordante pour NetBet Casino, c’est un lieu ou l’adrenaline coule a flots. On trouve une profusion de jeux palpitants, proposant des jeux de casino traditionnels. Il donne un avantage immediat. Disponible 24/7 pour toute question. Le processus est clair et efficace, en revanche des recompenses en plus seraient un bonus. Dans l’ensemble, NetBet Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. En complement l’interface est simple et engageante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Un atout les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, assure des transactions fluides.
Continuer ici|
Je suis bluffe par NetBet Casino, c’est une plateforme qui pulse avec energie. La bibliotheque de jeux est captivante, offrant des experiences de casino en direct. Il propulse votre jeu des le debut. Le suivi est toujours au top. Les retraits sont lisses comme jamais, cependant quelques spins gratuits en plus seraient top. Dans l’ensemble, NetBet Casino vaut une exploration vibrante. A mentionner la plateforme est visuellement dynamique, ajoute une vibe electrisante. Un point fort les tournois frequents pour l’adrenaline, propose des privileges sur mesure.
En savoir davantage|
tripscan Кроме того, TripScan предоставляет подробные обзоры и рейтинги отелей и достопримечательностей, помогая вам сделать осознанный выбор.
трипскан С TripScan вы найдете скрытые жемчужины, о которых раньше не знали, и сможете создать уникальное путешествие, которое запомнится на всю жизнь. Эта платформа, TripScan, также предоставляет инструменты для отслеживания цен и получения уведомлений о снижении стоимости билетов и номеров в отелях.
Confidence Catalyst – Daily ideas to spark self-belief and personal growth.
brightstyleoutlet.click – Fashionable items showcased well, making online shopping simple and efficient today.
casino PlayBet https://playbet-io.de/
exploreopportunities.click – Helpful insights available to guide personal development and explore opportunities efficiently.
дизайн интерьера 3d услуги дизайна интерьера
ко ланта ко ланта
ко ланта ко ланта
trendviewhub.click – Clear layout and trendy product selection make browsing simple.
ко ланте Ко Ланте
GoKong Casino Australia https://gokong-australia.com/
трипскан Tripscan интегрирован с социальными сетями, позволяя вам делиться своими планами и впечатлениями с друзьями, а также получать рекомендации от других путешественников. Обменивайтесь опытом, находите новые идеи и вдохновляйтесь на новые приключения!
ко ланте Ко Ланте
Продолжение иы2ышеу
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
https://vavadacasinos.neocities.org/ — это актуальное зеркало для доступа к популярному онлайн-казино.
Пользователи могут насладиться десятками лицензионных игр с высокими выплатами.
Сайт отличается удобным интерфейсом и быстрой работой. Игроки могут зайти на платформу как с компьютера, так и со смартфона.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
На платформе представлены сотни игр от мировых провайдеров. Каждый игрок найдет вариант по вкусу — от блекджека до современных видео-слотов.
Особого внимания заслуживают джекпоты и турниры. Крупные выигрыши разыгрываются в прогрессивных слотах.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
Новые игроки получают щедрые приветственные подарки. Первый депозит может быть увеличен на 100% или более.
Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов. Еженедельные турниры с призовыми фондами добавляют азарта.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
Vavada гарантирует честность и прозрачность игр. Лицензия обеспечивает защиту персональных данных.
Служба поддержки работает в режиме 24/7. Консультанты отвечают моментально в онлайн-чате.
### Спин-шаблон
#### Раздел 1: Введение в мир Vavada
1. Vavada Casinos — это популярная онлайн-платформа для азартных игр.
2. Она предлагает широкий выбор слотов, рулетки и карточных игр.
3. Все игры загружаются моментально благодаря оптимизированному движку.
4. Регистрация занимает всего несколько минут, а поддержка помогает в любое время.
#### Раздел 2: Игровой ассортимент
1. В каталоге можно найти сотни развлечений на любой вкус.
2. Здесь есть классические слоты, настольные игры и live-дилеры.
3. Прогрессивные джекпоты делают игру еще более интересной.
4. Специальные акции увеличивают шансы на победу.
#### Раздел 3: Бонусы и акции
1. Каждый новичок может рассчитывать на дополнительные фриспины.
2. Вращения в слотах дарятся без обязательных вложений.
3. Система лояльности поощряет постоянных клиентов.
4. Кешбэк и эксклюзивные предложения доступны для VIP-игроков.
#### Раздел 4: Безопасность и поддержка
1. Vavada гарантирует честность и прозрачность игр.
2. Лицензия обеспечивает защиту персональных данных.
3. Помощь доступна в любое время суток.
4. Консультанты отвечают моментально в онлайн-чате.
tripscan Забудьте о долгих часах, проведенных в поисках идеального варианта, Tripscan сделает всю работу за вас, предлагая лучшие предложения, соответствующие вашим потребностям. TripScan – ваш верный спутник в мире путешествий, готовый сделать вашу следующую поездку незабываемой.
shopandshine.click – Great site overall, products look appealing and navigation works smoothly today.
ко ланта ко ланта
inspiregrowthdaily.click – Clear guidance offered, inspiring content that helps keep progress steady each day.
кевс к16 нб300 кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
Mellstroy Casino https://mellstroyscasino.ru/
кевс кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
ко ланта ко ланта
вписки челны Вписки в Челнах – это для тех, кто ищет новых знакомств и спонтанных приключений. Это возможность окунуться в атмосферу беззаботности, познакомиться с единомышленниками и весело провести время. Главное – помнить о безопасности и выбирать проверенные места и компании. Вписка – это не просто вечеринка, это шанс почувствовать себя частью чего-то большего, найти новых друзей и получить заряд позитивных эмоций.
creativechoicecorner.shop – Chill shopping experience, creative products here are inspiring and clearly picked.
modernhomechoice.shop – Great home picks here, items look stylish and very well presented today.
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
ко ланта ко ланта
Style Finds Hub – Explore popular products and enjoy an easy and enjoyable shopping process.
кевс кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
kews k16 nb300 кевс kews кевс к16 нб300 kews k16 nb300
нажмите здесь vodkabet
остров ко ланта остров ко ланта
AmonBet Casino online https://amonbetcasino-uk.com/
индивидуалки Индивидуалки в Челнах – это ваш шанс на эксклюзивное общение и персонализированный подход. Они ценят ваше время и желания, предлагая гибкий график встреч и широкий спектр услуг. Забудьте о стереотипах и насладитесь обществом женщины, которая умеет слушать, понимать и дарить настоящее наслаждение. Индивидуалки – это не просто спутницы на вечер, это ваши личные музы, готовые вдохновлять и удивлять.
вписки челны Анкеты девушек в Челнах манят обещанием страстных встреч и незабываемых эмоций. Здесь представлены девушки разных типажей: от юных студенток, ищущих приключений, до роковых красавиц, знающих толк в искусстве обольщения. Каждая анкета – это мини-история, приглашение в мир искушений и фантазий. Выбирайте, кто вам по душе, и не бойтесь открыть для себя новые грани удовольствия. Конфиденциальность гарантирована, а впечатления останутся с вами навсегда.
Outlet Collection – Great mix of trendy options, and the interface was very user-friendly.
Smart Value Store – The site made it easy to find affordable products, and everything looked tidy.
Daily Chic Hub – Curated collections to inspire your daily style choices.
globalfindshub.shop – Found unique global picks, makes world-class style feel very accessible now.
yourtrendzone.shop – Great trendy picks, found a few items that caught my eye instantly.
Chic Trend Hub – The site felt clean and organized, making exploring the trends fun.
ремонт посудомоечных машин наурызбайский район
1Red Casino UK https://1red-casinos.com/
ремонт двигателя москва Бронепленка в Москве: Непревзойденная Защита Бронепленка – это надежный щит для вашего автомобиля, защищающий кузов от царапин, сколов и других повреждений. В Москве установка бронепленки становится все более популярной, особенно среди владельцев дорогих автомобилей.
аминокислота аргинин
https://slotuna-porto.com/
ссылка на сайт https://kra47at.at/
simplefashionoutlet.shop – Enjoyed exploring the selection, items looked appealing and site felt friendly.
bestchoicevalue.shop – Pages load quickly, makes browsing value options feel stress-free and smooth.
проверить сайт https://kra47at.at
узнать больше https://kra48at.at/
тонировка авто в москве Оклейка Москва: Защита и Персонализация в Одном Оклейка автомобиля пленкой в Москве – это современный способ защиты кузова от повреждений и придания ему уникального внешнего вида. Широкий выбор цветов и фактур позволяет реализовать любые дизайнерские идеи.
здесь https://kra47at.at/
такой https://kra46att.at/
посетить веб-сайт https://kra46att.at
проверить сайт https://kra47at.at/
Следующая страница https://kra47at.at/
Affordable Picks Daily – Find practical products at prices that won’t break the bank.
Главная https://kra46att.at
stage москва Карбон Москва: Легкость, Определяющая Скорость В мире автотюнинга карбон занимает особое место. Москва предлагает широкий спектр услуг по установке карбоновых элементов, от элегантных накладок до полноценных кузовных деталей. Этот легкий и прочный материал не только улучшает внешний вид автомобиля, но и значительно снижает его вес, положительно сказываясь на динамических характеристиках и управляемости.
Seasonal Trends Spot – Beautiful seasonal products, and checking out everything was fast and simple.
тюнинг москва Тюнинг Москва: Симфония Инженерии и Эстетики Москва, город динамики и амбиций, предъявляет особые требования к автомобилю. Тюнинг в Москве – это не просто смена облика, это глубокая трансформация, направленная на повышение производительности, улучшение управляемости и персонализацию до мельчайших деталей. В столичных мастерских создаются настоящие произведения искусства на колесах, сочетающие передовые технологии и безупречный стиль.
узнать больше зеркало водка бет
Joyful Picks Store – Neatly displayed products make exploring easy, combined with a fun theme.
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
escort directory Rio
пансионат по уходу за инвалидами Пансионаты для инвалидов: Широкий выбор и индивидуальный подход На рынке представлен широкий выбор пансионатов для инвалидов, различающихся по уровню комфорта, спектру предоставляемых услуг и ценовой категории. При выборе пансионата для инвалидов важно учитывать потребности и пожелания вашего близкого, его финансовые возможности и состояние здоровья. Мы рекомендуем внимательно изучить все предложения, посетить несколько пансионатов и лично пообщаться с сотрудниками и жителями, чтобы сделать осознанный выбор, который обеспечит вашему близкому достойную жизнь и необходимую заботу.
проститутки сочи Проститутки Псков – отдаленный регион, добавляющий разнообразия географии запросов. Проститутки ели – вероятно, опечатка или часть фразы, требующая контекста. Частные проститутки Питер – акцент на конфиденциальности и независимости в Санкт-Петербурге. Рассказы проституток – интерес к личному опыту и историям из первых уст. Ест проститутке – вульгарное выражение, исключенное из лексикона. Проститутки гражданский – привязка к Гражданскому проспекту. Секс проститутки младше – указание на возрастные предпочтения. Проститутки пр – сокращение слова “проспект”. Фото проституток спб – поиск визуального контента по Санкт-Петербургу. Мама проститутка – сложная тема, вероятно, поиск информации или рассказов. Проститутку красносельском – район города. Проститутки трансы питер – транссексуалы в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки рыбацкое – район Рыбацкое. Проститутки красносельская – район Красносельский. Проститутки московский район – Московский район Санкт-Петербурга. Проститутки питера телеграм – использование Телеграм в Санкт-Петербурге для поиска. Проститутки ленинский – район Ленинский. Проститутки обл – сокращение от область, подразумевая Ленинградскую область. Проститутка со – неполная фраза, требующая дополнения. Сиськи проститутки – акцент на формах. Проститутки на карте – поиск по географическому расположению. Две проститутки – указание количества. Проститутки приезжающие – иногородние, предлагающие свои услуги. Проститутки 5 / 2 проститутки – числовые запросы, вероятно, возраст или количество. Дочь проститутка – сложные семейные отношения, возможен поиск информации или поддержки. Проститутка лен / лена – сокращенные имена или области. Проститутка усть / усть луга – регионы, расширение географического охвата. Адреса проституток – поиск конкретных мест. Проститутка лет питер – запросы по возрасту в Санкт-Петербурге.
перейдите на этот сайт зеркало водка бет
Your Daily Trend Spot – Enjoy discovering fashionable options with smooth and easy browsing.
smartshopcentral – Found lots of affordable items, ordering was smooth.
Urban trend finds – Several standout options appeared right away, browsing easy.
freshvaluestore.shop – Site loads quickly and the product variety actually surprised me today.
happyhomecorner.shop – Perfect spot for discovering fresh home inspiration and decor ideas.
Hey there! I realize this is kind of off-topic however I needed to ask. Does building a well-established website such as yours take a massive amount work? I am brand new to blogging but I do write in my diary on a daily basis. I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my experience and views online. Please let me know if you have any ideas or tips for new aspiring bloggers. Appreciate it!
https://technolex.com.ua/shcho-v-komplekti-povnyi-spysok-materialiv.html
valuefindsstore – Items were reasonably priced, and checkout was fast.
продолжить vodkabet
Check this style collection – Found several appealing fashion picks quickly, browsing was smooth.
пансионат для инвалидов в москве Дом инвалидов в Москве: забота и поддержка в столице Дом инвалидов в Москве – это специализированное учреждение, предназначенное для обеспечения ухода, реабилитации и социальной адаптации людей с ограниченными возможностями. Здесь созданы условия для комфортного проживания, получения необходимой медицинской помощи и участия в различных мероприятиях, способствующих улучшению качества жизни. Важно отметить, что дома инвалидов в Москве предоставляют не только жилье, но и комплексную поддержку, направленную на сохранение здоровья и активного образа жизни.
проститутка со Проститутки Петербурга, разнообразие предложений и услуг, от классических встреч до экзотических вариантов. Проститутки Санкт, краткое и емкое обозначение сферы интимных услуг в городе. Проститутки Санкт Петербург, полное название города подчеркивает масштабность выбора. Проститутка метро, удобный способ найти компаньонку в шаговой доступности от станций метрополитена. Снять проститутку, ключевое действие для тех, кто ищет интимные развлечения. Снят проститутка, результат успешно совершенной сделки. Проститутки индивидуалки, выбор в пользу независимых работниц, предлагающих персональный подход. Дешевые проститутки, бюджетный вариант для тех, кто ценит экономию. Зрелые проститутки, опыт и мастерство для искушенных клиентов.
brightbuysdaily – Excellent range of products, ordering process was seamless.
платный пансионат для инвалидов Московские дома инвалидов: государственная поддержка и частные инициативы В Москве существует как государственная сеть домов инвалидов, так и частные пансионаты, предлагающие альтернативные варианты ухода и проживания. Государственные учреждения обеспечивают минимальный необходимый уровень обслуживания, в то время как частные пансионаты могут предложить более широкий спектр услуг, индивидуальный подход и повышенный уровень комфорта. При выборе дома инвалидов в Москве важно учитывать потребности человека, его финансовые возможности и предпочтения.
трахает проститутку Проститутки Псков – отдаленный регион, добавляющий разнообразия географии запросов. Проститутки ели – вероятно, опечатка или часть фразы, требующая контекста. Частные проститутки Питер – акцент на конфиденциальности и независимости в Санкт-Петербурге. Рассказы проституток – интерес к личному опыту и историям из первых уст. Ест проститутке – вульгарное выражение, исключенное из лексикона. Проститутки гражданский – привязка к Гражданскому проспекту. Секс проститутки младше – указание на возрастные предпочтения. Проститутки пр – сокращение слова “проспект”. Фото проституток спб – поиск визуального контента по Санкт-Петербургу. Мама проститутка – сложная тема, вероятно, поиск информации или рассказов. Проститутку красносельском – район города. Проститутки трансы питер – транссексуалы в Санкт-Петербурге. Проститутки рыбацкое – район Рыбацкое. Проститутки красносельская – район Красносельский. Проститутки московский район – Московский район Санкт-Петербурга. Проститутки питера телеграм – использование Телеграм в Санкт-Петербурге для поиска. Проститутки ленинский – район Ленинский. Проститутки обл – сокращение от область, подразумевая Ленинградскую область. Проститутка со – неполная фраза, требующая дополнения. Сиськи проститутки – акцент на формах. Проститутки на карте – поиск по географическому расположению. Две проститутки – указание количества. Проститутки приезжающие – иногородние, предлагающие свои услуги. Проститутки 5 / 2 проститутки – числовые запросы, вероятно, возраст или количество. Дочь проститутка – сложные семейные отношения, возможен поиск информации или поддержки. Проститутка лен / лена – сокращенные имена или области. Проститутка усть / усть луга – регионы, расширение географического охвата. Адреса проституток – поиск конкретных мест. Проститутка лет питер – запросы по возрасту в Санкт-Петербурге.
cheergiftstore – Amazing selection and smooth browsing, very enjoyable experience.
Browse urban outfits – A couple of standout selections were visible immediately, very convenient.
chicfinds – Loved the trendy collection, browsing and checkout were effortless.
Uhren Replika Exklusive Replika Uhr: Das Besondere fur Liebhaber Exklusive Replika Uhren sind die perfekte Wahl fur Uhrenliebhaber, die das Besondere suchen. Diese Modelle zeichnen sich durch einzigartige Designs, hochwertige Materialien und limitierte Auflagen aus. Sie sind nicht nur Zeitmesser, sondern auch Sammlerstucke mit einem besonderen Wert. Eine exklusive Replika Uhr ist ein Statement von Individualitat und Exklusivitat.
Hi every one, here every person is sharing these familiarity, thus it’s good to read this web site, and I used to go to see this weblog everyday.
https://cybrexsport.com.ua/zapotivannya-fary-yak-polimerne-sklo.html
additional hints https://web-breadwallet.com/
brightpickstore – Loved how simple it was to find good deals, checkout was fast.
Главная блэкспрут ссылка
чикен роад демо https://kurica2.ru/kg .
сколько стоит сделать курсовую работу на заказ https://kupit-kursovuyu-1.ru/ .
Market of New Finds – The browsing experience was relaxed, and a lot of products stood out.
Top Qualitat Replika Uhr Mode Uhr Replika: Trendige Accessoires fur jeden Anlass Mode Uhren Repliken sind trendige Accessoires, die jedes Outfit aufwerten. Sie sind
Смотреть здесь блэкспрут дакрнет
Дом из клееного бруса Строительство из клееного бруса – это современное и эффективное решение для тех, кто ценит экологичность, скорость возведения и эстетическую привлекательность своего будущего дома. Клееный брус, благодаря своей технологии производства, обладает повышенной прочностью, устойчивостью к деформациям и минимальной усадкой, что делает его идеальным материалом для строительства долговечных и надежных зданий.
Дом из клееного бруса Дома из клееного бруса Краснодар пользуются особой популярностью благодаря благоприятному климату региона и доступности качественной древесины. Строительство дома из клееного бруса в Краснодаре – это возможность создать уютное и комфортабельное жилье, идеально подходящее для южного климата.
Browse latest fashion – Found a couple of eye-catching picks fast, very user-friendly.
Дом из клееного бруса Дом из клееного бруса – это не просто жилище, это инвестиция в здоровый образ жизни. Древесина создает уникальный микроклимат в помещении, поддерживая оптимальный уровень влажности и обеспечивая естественную циркуляцию воздуха. Жить в доме из клееного бруса – значит дышать чистым воздухом, наслаждаться тишиной и покоем, забыв о городской суете. Дома из клееного бруса под ключ – это удобное и выгодное решение, позволяющее вам избежать хлопот, связанных с организацией строительного процесса. Профессиональная команда берёт на себя все этапы работ, от проектирования и подготовки документации до внутренней отделки и благоустройства территории. Вы получаете готовый к проживанию дом, полностью соответствующий вашим представлениям об идеальном жилище.
Check this style collection – Found several appealing fashion picks quickly, browsing was smooth.
get redirected here jaxx blockchain wallet
click this link now wallet jaxx
uniquefashioncorner – The site loaded quickly and all product images looked crisp and real.
Check this style collection – Found several appealing fashion picks quickly, browsing was smooth.
Зума офицальный канал Зума Казино – это не просто платформа для удовлетворения азартных желаний, а тщательно выстроенная экосистема развлечений, где каждый элемент направлен на создание максимально комфортной и захватывающей атмосферы. Мы предлагаем не просто игры, а возможность погрузиться в мир ярких эмоций, стратегического мышления и, конечно же, шанс испытать удачу и сорвать куш. Разнообразие игровых автоматов, карточных игр, рулеток и лайв-казино с профессиональными дилерами обеспечивает бесконечный поток впечатлений и не даст заскучать даже самым искушенным игрокам. Зума официальный канал – это ваш личный проводник в захватывающий мир Зума Казино. Подписывайтесь и будьте в курсе эксклюзивных акций, турниров с крупными призовыми фондами, анонсов новых игр и полезных советов от экспертов. Мы делимся секретами успешной игры, анализируем стратегии и помогаем вам принимать взвешенные решения, чтобы увеличить ваши шансы на выигрыш. Зума – это не только азарт, но и ответственность. Мы придерживаемся принципов честной игры и обеспечиваем безопасную среду для наших пользователей. Современные технологии шифрования гарантируют защиту ваших персональных данных и финансовых транзакций. Мы работаем в соответствии с международными стандартами лицензирования и всегда готовы оказать поддержку и ответить на любые вопросы. Zooma казино – это ваш портал в мир больших возможностей. Играйте в любое время и в любом месте, наслаждаясь удобным интерфейсом и плавной работой на любом устройстве. Мы постоянно работаем над улучшением нашего сервиса, чтобы предоставить вам лучший игровой опыт. Присоединяйтесь к миллионам игроков по всему миру и откройте для себя мир Зума Казино, где азарт встречается с возможностью стать победителем!
Дом из клееного бруса цена Дом из клееного бруса цена – зависит от множества факторов, включая площадь, сложность проекта, используемые материалы и внутреннюю отделку. Однако, в целом, дом из клееного бруса является выгодным вложением средств, учитывая его долговечность, энергоэффективность и экологичность. Проекты домов из клееного бруса – это широкий выбор архитектурных решений, от небольших дачных домиков до просторных коттеджей. Индивидуальный проект позволяет учесть все особенности участка и пожелания заказчика, создавая уникальное и функциональное пространство для жизни. Дом из клееного бруса цена под ключ – это фиксированная стоимость строительства, включающая все работы и материалы, необходимые для ввода дома в эксплуатацию. Это удобный и надежный способ получить готовое жилье без лишних хлопот и неожиданных расходов.
Строительство из клееного бруса Дома из клееного бруса под ключ – это комплексное решение для тех, кто ценит свое время и предпочитает доверить все заботы профессионалам. От проекта до заселения, команда специалистов берет на себя все этапы строительства, гарантируя качество и соблюдение сроков. Вы получаете готовый к проживанию дом, полностью соответствующий вашим представлениям об идеальном жилище. Дома из клееного бруса Краснодар – это отличный выбор для жизни в теплом климате. Древесина обеспечивает естественную вентиляцию и создает комфортный микроклимат в помещении. Кроме того, дома из клееного бруса отличаются высокой сейсмоустойчивостью, что особенно актуально для Краснодарского края.
эвакуатор в таганроге дешего Эвакуатор Таганрог – это больше, чем просто номер телефона в записной книжке. Это гарантия спокойствия на дорогах, уверенность в том, что в случае непредвиденной ситуации вы не останетесь один на один с проблемой. Мы предлагаем не просто услуги эвакуации, а комплексное решение, включающее в себя оперативную помощь, профессиональную консультацию и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту. Наша цель – максимально упростить процесс эвакуации и свести к минимуму ваши неприятности. Эвакуатор в Таганроге – это круглосуточная доступность, вне зависимости от времени суток и погодных условий. Мы понимаем, что аварии и поломки случаются неожиданно, и поэтому всегда готовы прийти на помощь, когда она действительно необходима. Наш парк эвакуаторов оснащен современным оборудованием, позволяющим безопасно транспортировать автомобили любой категории, от легковых до грузовых. Эвакуатор – это не только транспортировка поврежденного автомобиля до сервиса, но и возможность доставки нового автомобиля из автосалона, перевозка мотоцикла на соревнования или эвакуация спецтехники на строительную площадку. Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, охватывающий практически любые потребности в транспортировке транспортных средств. Эвакуатор в Таганроге дешево – это не значит некачественно. Мы оптимизировали наши расходы и предлагаем честные цены, без скрытых накруток и комиссий. Наша задача – предоставить доступные услуги эвакуации каждому, кто в них нуждается, не зависимо от бюджета. Мы уверены, что высокое качество может быть доступным. Услуги эвакуатора включают в себя не только транспортировку автомобиля, но и оказание помощи на месте, например, при замене колеса, запуске двигателя или открытии заблокированных дверей. Мы стремимся решить проблему клиента максимально быстро и эффективно, чтобы он мог продолжить свой путь с минимальными потерями времени и нервов.
BrightTrendHub – Trendy items arrived quickly, quality was great and shopping was simple.
Discover urban collections – Several interesting picks appeared quickly, easy to browse.
Зума Казино Зума Казино – это калейдоскоп азартных возможностей, тщательно выстроенный мир, где каждый элемент служит для создания захватывающего и щедрого опыта. Мы предлагаем не просто ставки, а погружение в уникальную атмосферу, наполненную драйвом, стратегией и, конечно же, манящим предвкушением крупного выигрыша. От винтажных слотов, напоминающих о золотой эре Лас-Вегаса, до инновационных игр с живыми дилерами, транслируемых в прямом эфире, – наш арсенал развлечений удовлетворит даже самого искушенного игрока. Бонусы, акции и программа лояльности становятся приятным дополнением к захватывающему игровому процессу, увеличивая ваши шансы на успех и продлевая удовольствие от игры. Зума официальный канал – это ваш компас в постоянно расширяющейся вселенной Зума Казино. Здесь вы найдете эксклюзивные анонсы, инсайдерские секреты, обзоры новых игр и полезные советы от гуру азарта. Подписывайтесь, чтобы быть в курсе самых выгодных предложений, участвовать в розыгрышах и первыми узнавать о грядущих турнирах с внушительными призовыми фондами. Мы раскроем вам тайны прибыльной игры и научим правильно распоряжаться своим банкроллом. Зума – это символ честности, прозрачности и ответственного подхода к азартным играм. Мы используем передовые технологии шифрования, чтобы обеспечить безопасность ваших данных и финансовых операций. Наша лицензия является гарантией соблюдения строгих стандартов индустрии, а квалифицированная служба поддержки всегда готова оказать помощь и ответить на любые ваши вопросы. Мы верим, что азарт должен приносить удовольствие, а не проблемы. Zooma казино – это ваш шанс испытать триумф, не покидая уютного кресла. Наша платформа оптимизирована для бесперебойной работы на любом устройстве, будь то компьютер, планшет или смартфон. Наслаждайтесь великолепной графикой, захватывающим геймплеем и мгновенными выплатами в любое время и в любом месте. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу победителей и откройте для себя Zooma казино – мир, где мечты об огромных выигрышах становятся реальностью!
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates. I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this. Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and I look forward to your new updates.
prostitutes in Brazil
Urban style link – Found multiple fashionable items fast, layout user-friendly.
Этот материал посвящен обзору возможностей платформы Vavada. Мы рассматриваем актуальные преимущества и способы безопасного входа. Рабочие зеркала позволяют сохранять доступ даже при ограничениях. Пользователи отмечают высокую стабильность и широкий выбор игр. Подробности и актуальная ссылка доступны здесь: казино вавада. Следите за обновлениями и играйте ответственно.
ко ланта ко лант
Seasonal Picks Hub – Website loaded fast, and the products arrived exactly as described.
Discover top fashion finds – Found several attractive and trendy items quickly, browsing smooth.
ко ланта ко лант
геронтологический центр москва адреса Геронтологический центр – это не просто медицинское учреждение, это комплексный подход к поддержанию здоровья и активного долголетия пожилых людей. Здесь не только лечат болезни, связанные с возрастом, но и создают условия для полноценной жизни, наполненной общением, творчеством и заботой. Это место, где старость – не приговор, а новый этап жизни.
Browse latest fashion – Found a couple of eye-catching picks fast, very user-friendly.
игровые автоматы играть бесплатно Что для вас самое важное в онлайн-казино? Если это надежность и быстрый вывод средств, то вы попали по адресу! Мы подобрали для вас лучшие варианты, где можно играть без опасений и получать свои выигрыши практически моментально. Готовы испытать удачу?
центр геронтологии москва Независимо от выбранного типа учреждения, главное – обеспечить пожилому человеку достойную старость, наполненную радостью, общением и заботой. Геронтологическая и гериатрическая помощь – это инвестиция в будущее, которая позволяет сохранить здоровье, активность и качество жизни на долгие годы.
играть в казино демо Хотите играть в онлайн казино в России безопасно и легально? Мы собрали для вас список официальных сайтов, которые соответствуют всем требованиям законодательства и гарантируют честную игру.
геронтологический центр адрес Москва предлагает широкий выбор геронтологических и гериатрических учреждений, от государственных больниц до частных пансионатов. При выборе центра важно учитывать не только его расположение и стоимость услуг, но и репутацию, квалификацию персонала и условия проживания. Важно, чтобы пожилой человек чувствовал себя комфортно и безопасно, окруженным заботой и вниманием.
urbanedgecollective – Really enjoyed browsing today, everything was neatly organized and simple to explore.
Browse latest fashion – Found a couple of eye-catching picks fast, very user-friendly.
m bs2web at
Игровая платформа Vavada предлагает рабочие зеркала.
Промокоды и фриспины дают плюс к депозиту.
Регистрация быстрая, а рабочие домены гарантируют доступ.
Лайв?игры предлагает широкий выбор.
Узнай подробности по casino и активируй бонус.
Играйте ответственно и контролируйте банкролл.
блекспрут
SoftStone Marketplace – Easy-to-navigate site, nice assortment, and items shipped on time.
http://mitmedicalgroup.com/2025/11/24/mostbet-hamkorlari-igaming-tikish-va-esportlar-bo-2/
highriverdesigns – Items arrived quickly, packaging was neat, and quality felt top-notch overall.
?????????
pg ????? khao555.com
Best of Soft Cloud Boutique – Pleasant experience navigating and items are clearly visible.
bs2best at что за сайт
harbornowcollection – Clear navigation with well-presented and visually appealing items.
Your Daily Creative Hub – Explore new activities and innovative projects to boost your creativity.
khao555 slot
Pgsiam777
t.me/Black125Bot
Vavada casino предлагает быстрый вывод.
Раздел лайв-казино регулярно обновляется.
Бонус-коды делают старт выгоднее.
Вход доступен мгновенно.
Подробности по https://penaeducentre.com/ — активируй бонус.
Играйте ответственно.
http://www.riocenter.kz/forum/read/id-3276
dailyzen – Navigation is smooth, items loaded fast and easy to find.
ко ланте
аренда подвесных строительных лесов Аренда штукатурных лесов: Штукатурные леса специально разработаны для проведения штукатурных работ на фасадах зданий. Аренда таких лесов обеспечивает удобство и безопасность рабочих, а также позволяет установить необходимое оборудование для подачи и нанесения штукатурных смесей. Широкая платформа и устойчивая конструкция позволяют повысить производительность и качество выполняемых работ.
Intentional Mindset Spot – Guidance for building strong habits and making meaningful progress.
pg ????? khao555.com
????? pg
тайланд ко ланта
mediafusion – Products are easy to view and descriptions seem clear, which I appreciate.
learnshareachieve – The site looks neat and organized, made comparing items quite convenient.
продажа промышленных лесов Леса повышенной безопасности: Леса повышенной безопасности – это конструкции, разработанные с учетом повышенных требований к безопасности и надежности. Они отличаются от обычных лесов использованием более прочных материалов, усиленной конструкцией и дополнительными элементами безопасности, такими как страховочные сетки, перила и ограждения. Леса повышенной безопасности применяются на объектах, где существует повышенный риск падения рабочих или материалов, а также в условиях сложных климатических условий. Использование лесов повышенной безопасности позволяет значительно снизить риск несчастных случаев на строительной площадке.
ООО Торгово-транспортное предприятие “Острое Жало” В рамках нашей деятельности мы осуществляем не только транспортировку, но и полный цикл логистических услуг, включая складское хранение, комплектацию заказов и оформление необходимых документов. Особое внимание уделяется автоматизации процессов и внедрению передовых технологий учета и контроля движения товаров. Мы стремимся предоставить клиентам прозрачную и эффективную систему управления логистикой, позволяющую оптимизировать затраты и повысить конкурентоспособность их бизнеса.
ООО Торгово-транспортное предприятие “Острое Жало” ООО Торгово-транспортное предприятие “Острое Жало” позиционирует себя как надежный партнер в сфере логистики и грузоперевозок, предлагая широкий спектр услуг, адаптированных под нужды современного бизнеса. Наша компания обладает значительным опытом работы с предприятиями различных отраслей, обеспечивая бесперебойную поставку продукции от производителя до конечного потребителя. Мы гордимся своей репутацией и стремимся к постоянному совершенствованию в области логистических решений.
Replique montre moderne
Stylish Choice Daily – Quick access to trendy items that make shopping simple and fun.
full-service film production Cortina d’Ampezzo
modernstylecorner – I found items quickly, layout is intuitive and user-friendly overall.
Джоггеры Женские Костюмы спортивные, эволюционировавшие из экипировки для атлетов в must-have современной модницы, воплощают собой философию активного образа жизни. Они дарят ощущение безграничной свободы движений, не стесняя рамками формальности. Выбор спортивного костюма – это инвестиция в комфорт и уверенность, требующая внимания к деталям: качеству ткани, эргономичному крою и актуальному дизайну. С наступлением холодов, когда морозный ветер рисует причудливые узоры на окнах, особую ценность обретают изделия, дарящие тепло и уют. Худи с начесом, словно мягкое объятие, согревает в студеную пору, окутывая негой нежной ткани. Его непринужденный силуэт и функциональный капюшон делают его незаменимым спутником в осенне-зимние месяцы. А для тех, кто ценит вариативность и свободу выбора, худи зип станет желанным приобретением. Молния, словно кисть художника, позволяет менять образ, адаптируя его к настроению и погодным условиям.
Мода Стремление к комфорту и индивидуальности проявляется в растущей популярности одежды свободного кроя. Одежда оверсайз – это сознательный выбор в пользу свободы движений и подчеркивания собственной уникальности. Она скрывает недостатки фигуры и позволяет создать расслабленный, но при этом стильный образ. Будь то толстовка, свитшот или худи, оверсайз – это тренд, который остается с нами надолго. Женская одежда как никакая другая стремится подчеркнуть красоту и индивидуальность каждой девушки. А для тех, кто хочет купить худи или купить свитшот нужно обратить внимание на трендовые позиции и понимать, что сейчас в моде. Ведь мода 2026 – это про индивидуальность и комфорт, смешение стилей и отход от общепринятых норм. Стиль не покупается за деньги, поэтому лучше следить за модными трендами в модном журнале, чтобы найти подходящий стильный бренд одежды.
Self-Esteem Boost – Tools and tips for boosting your self-esteem effectively.
проведение процедуры банкротства Процедура банкротства имеет свои плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица, такие как избавление от долгов и прекращение начисления процентов и штрафов. Однако, важно понимать, что проведение процедуры банкротства – это сложный процесс, требующий юридической грамотности и опыта. Проведение процедуры банкротства должника должно осуществляться под контролем квалифицированного юриста. Необходимо четко понимать процедура банкротства сроки проведения, чтобы быть готовым к длительному процессу. Процедура банкротства физических лиц по кредитам имеет свои особенности, которые необходимо учитывать. Процедура банкротства физического лица в суде требует подготовки документов и участия в судебных заседаниях. Процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция поможет сориентироваться в этапах процедуры. Процедура банкротства физического лица через суд – основной способ проведения процедуры. Процедуры банкротства должника физического лица регулируются законодательством о банкротстве.
https://geltaxi.ru/taxi-makopse-sochi
?????????
процедура банкротства физического лица через суд Компетентное ведение дела – залог успешного завершения процедуры банкротства физического лица через суд. Важно доверить процедуры банкротства должника физического лица опытным юристам, специализирующимся на банкротстве. Компания должна иметь безупречную репутацию. Только так можно быть уверенным, что процедура будет выполнена в соответствии с законом и все ваши права будут защищены.
бесплатная консультация по банкротству Процедура банкротства имеет свои плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица, такие как избавление от долгов и прекращение начисления процентов и штрафов. Однако, важно понимать, что проведение процедуры банкротства – это сложный процесс, требующий юридической грамотности и опыта. Проведение процедуры банкротства должника должно осуществляться под контролем квалифицированного юриста. Необходимо четко понимать процедура банкротства сроки проведения, чтобы быть готовым к длительному процессу. Процедура банкротства физических лиц по кредитам имеет свои особенности, которые необходимо учитывать. Процедура банкротства физического лица в суде требует подготовки документов и участия в судебных заседаниях. Процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция поможет сориентироваться в этапах процедуры. Процедура банкротства физического лица через суд – основной способ проведения процедуры. Процедуры банкротства должника физического лица регулируются законодательством о банкротстве.
прогнозы на хоккей Ставки на спорт – это азартное развлечение, требующее аналитического подхода и понимания стратегий. Современный мир беттинга предлагает широчайший выбор возможностей: от классических видов спорта до киберспорта и экзотических дисциплин. Однако, важно помнить, что успех в ставках на спорт – это не только удача, но и результат кропотливого анализа, изучения статистики и учета множества факторов.
khao555 casino online
списать долги банкротство физ лиц Процедура банкротства имеет свои плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица, такие как избавление от долгов и прекращение начисления процентов и штрафов. Однако, важно понимать, что проведение процедуры банкротства – это сложный процесс, требующий юридической грамотности и опыта. Проведение процедуры банкротства должника должно осуществляться под контролем квалифицированного юриста. Необходимо четко понимать процедура банкротства сроки проведения, чтобы быть готовым к длительному процессу. Процедура банкротства физических лиц по кредитам имеет свои особенности, которые необходимо учитывать. Процедура банкротства физического лица в суде требует подготовки документов и участия в судебных заседаниях. Процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция поможет сориентироваться в этапах процедуры. Процедура банкротства физического лица через суд – основной способ проведения процедуры. Процедуры банкротства должника физического лица регулируются законодательством о банкротстве.
списать долги через банкротство физических лиц В лабиринте финансовых затруднений, когда долговое бремя угрожает стабильности, банкротство физических лиц выступает как законный механизм избавления от непосильных обязательств. Однако, это сложный процесс, требующий четкого понимания правовых норм и взвешенной оценки всех рисков. Определяющим фактором часто является банкротство физических лиц сроки процедуры, зависящие от ряда обстоятельств, включая сложность финансового положения должника и оперативность работы судебных органов.
списать долги через банкротство Прежде чем инициировать процедуру, крайне важно получить всестороннюю информацию о её аспектах. Бесплатная консультация по банкротству или бесплатная консультация юриста по банкротству станет первым шагом к пониманию перспектив и потенциальных последствий. Важно выяснить, как происходит списание долгов по кредитам и какие долги списывают через банкротство, поскольку не все обязательства подлежат аннулированию. Квалифицированная консультация по банкротству физических лиц поможет сориентироваться в юридических тонкостях и разработать оптимальную стратегию. Онлайн консультация по банкротству – удобный формат для получения первичной информации. Решение о банкротстве сопряжено с рядом последствий, поэтому необходимо тщательно взвесить все плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица. К ним относится возможность списать долг по кредиту банкротство и начать жизнь с чистого листа. Однако, следует учитывать, что проведение процедуры банкротства – это ответственный шаг, требующий соблюдения строгих правил и участия квалифицированных специалистов. Особое внимание следует уделить вопросам: процедура банкротства сроки проведения, процедура банкротства физических лиц по кредитам, процедура банкротства физического лица в суде, процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция.
прогнозы на футбол Ставки на спорт – это азартное развлечение, требующее аналитического подхода и понимания стратегий. Современный мир беттинга предлагает широчайший выбор возможностей: от классических видов спорта до киберспорта и экзотических дисциплин. Однако, важно помнить, что успех в ставках на спорт – это не только удача, но и результат кропотливого анализа, изучения статистики и учета множества факторов.
процедура банкротства физического лица в суде Процедура банкротства имеет свои плюсы процедуры банкротства физического лица, такие как избавление от долгов и прекращение начисления процентов и штрафов. Однако, важно понимать, что проведение процедуры банкротства – это сложный процесс, требующий юридической грамотности и опыта. Проведение процедуры банкротства должника должно осуществляться под контролем квалифицированного юриста. Необходимо четко понимать процедура банкротства сроки проведения, чтобы быть готовым к длительному процессу. Процедура банкротства физических лиц по кредитам имеет свои особенности, которые необходимо учитывать. Процедура банкротства физического лица в суде требует подготовки документов и участия в судебных заседаниях. Процедура банкротства физического лица пошаговая инструкция поможет сориентироваться в этапах процедуры. Процедура банкротства физического лица через суд – основной способ проведения процедуры. Процедуры банкротства должника физического лица регулируются законодательством о банкротстве.
какие долги списывают через банкротство В лабиринте финансовых затруднений, когда долговое бремя угрожает стабильности, банкротство физических лиц выступает как законный механизм избавления от непосильных обязательств. Однако, это сложный процесс, требующий четкого понимания правовых норм и взвешенной оценки всех рисков. Определяющим фактором часто является банкротство физических лиц сроки процедуры, зависящие от ряда обстоятельств, включая сложность финансового положения должника и оперативность работы судебных органов.
????????????
https://www.lawglobalhub.com/flower-films-how-drew-barrymore-became-a-successful/
Milan production service company Video equipment rental Milan: Providing a comprehensive range of state-of-the-art cameras, lighting, and sound equipment for all production needs.
https://geltaxi.ru/taxi-kerch-oliva
??????
creative production company in Milan Milan video production services: Offering a full spectrum of video solutions, from concept development to post-production, tailored to client specifications.
https bs2web store
pg ?????
Style Finds Hub – Explore popular products and enjoy an easy and enjoyable shopping process.
??????????
https://marketgit.com/how-jennifer-lopezs-green-dress-changed-the-internet/
https bsme at
https://techfily.com/motherhood-and-music-how-having-a-daughter-transformed-kehlanis-life/
блекспрут
pragmatic slot
перекись водорода оптом РТХ – партнер, которому можно доверять: обеспечиваем стабильные поставки качественной химии для развития Вашего бизнеса.
https://pro-dacha.com/2025/08/21/kak-podgotovit-pochvu-pered-posevom-gazonnoy-travy-20250821.html
Your Fashion Destination – Browse stylish collections and lifestyle essentials to suit your taste.
https://vseokrovle.com/besedka/2115-chem-otlichayutsya-odnoletnie-i-mnogoletnie-travy-dlya-gazona.html
Savings & Deals Hub – Daily updates for deals that maximize your money’s value.
снять шлюху спб Девочки по вызову: За этим наименованием скрываются независимые, уверенные в себе женщины, выбирающие этот путь осознанно. Они предлагают не только физическую близость, но и эмоциональную поддержку, понимание и готовность выслушать. Это партнерство на равных, основанное на взаимном уважении.
скачать игры по прямой ссылке Скачать игры без торрента: Мир мгновенного гейминга – это реальность! Забудьте о долгой и сложной процедуре загрузки через торренты. Откройте для себя пространство, где каждая игра доступна одним кликом. Мгновенный доступ к самым горячим новинкам и проверенным хитам – вот что значит скачивать без торрентов. Исследуйте вселенные, сражайтесь с врагами, решайте головоломки – и все это без утомительного ожидания.
ортофосфорная кислота оптом РТХ – партнер, которому можно доверять: обеспечиваем стабильные поставки качественной химии для развития Вашего бизнеса.
??????????????????????????
скачать игры с яндекс диска Альтернативные способы: Помимо вышеперечисленных методов, существуют и другие варианты загрузки игр без торрента, такие как игровые платформы и сайты, предлагающие платные и бесплатные версии игр. Важно помнить о безопасности и скачивать файлы только из надежных источников.
аминокислоты оптом РТХ: инновационные решения в области промышленной химии, направленные на повышение эффективности, снижение затрат и защиту окружающей среды
horizon store – Well-arranged items and clear layout made exploring simple.
????
birchstorecorner – Items are easy to browse, and navigating feels effortless.
Your Trend Picks – Enjoy a smooth shopping experience while exploring fashionable products.
atticcreationshub – Easy navigation and interactive features encourage learning and inspiration.
ForestHavenGoods – Clean design, shopping feels effortless and enjoyable.
bs2best at ссылка
Cozy Timber Finds – Browsing was easy thanks to the organized pages and calm aesthetic.
brandelevate.click – Mobile version looks perfect; no glitches, fast scrolling, crisp text.
birchemporiumhub – Pleasant browsing experience, layout is tidy and user-friendly.
horizon picks hub – Fast-loading pages and organized layout made shopping effortless.
натяжной потолок спб цены Навесной потолок: Современное решение для стильного интерьера Навесной потолок – это универсальное решение для создания современного и функционального интерьера. Он позволяет скрыть недостатки базового потолка, проложить коммуникации и установить встроенное освещение. Существует множество видов навесных потолков, отличающихся по материалу, дизайну и функциональности, что позволяет подобрать оптимальный вариант для любого помещения.
потолок натяжной цена с установкой Матовые натяжные потолки: Элегантность и практичность в одном Матовые натяжные потолки – это классическое решение для тех, кто ценит спокойствие и уют в интерьере. Их поверхность лишена блеска, что создает эффект идеально ровного, окрашенного потолка. Они прекрасно подходят для любого помещения, от спальни до офиса, и не отвлекают внимание от других элементов декора. Матовые потолки неприхотливы в уходе, легко моются и не выгорают со временем, сохраняя свой первоначальный вид на долгие годы.
everymomentzone – Fast interface, smooth browsing, and items are neatly arranged.
shop urban picks – Items were easy to view and categories were clear.
shop willow boutique – Smooth scrolling and fast pages made discovering items easy.
pg ?????
CTO Cozy Finds – The site operates smoothly, making it easy to check out items without any difficulty.
ca cuoc bong da truc tuyen
coastline hub – Clean layout and clear categories made shopping enjoyable.
shop willow boutique – Intuitive design and responsive layout improved browsing.
Услуги эвакуатора Эвакуатор в Таганроге – это не только средство транспортировки поврежденного авто, но и символ надежды, маяк в бушующем море автомобильных проблем. Это возможность избежать лишних хлопот, сохранить время и нервы, доверив заботу о своей машине профессионалам своего дела.
Вызвать эвакуатор Эвакуатор в Таганроге – это символ надежды для тех, кто столкнулся с поломкой, ДТП или другими неприятностями, требующими немедленной транспортировки транспортного средства.
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом денег без первого депозита
бездепозитные бонусы в казино и бк
Coastal Shop Gems – Very user-friendly and easy to navigate, with well-presented items.
evermeadowgoods – Great selection and intuitive navigation helped me explore products without hassle.
женские балетки под платье натуральная кожа Женская обувь современный стиль – отражение актуальных тенденций и инновационных решений в дизайне.
Go To The Gallery – The speedy response and simple design took all the hassle out of shopping.
женская обувь из турции в москве Турецкая женская обувь модные модели – отражение современных трендов и классической элегантности в каждой паре.
казино онлайн в казахстане бонус за регистрацию без депозита
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения и без вейджера
Shop Here – A great mix of products and a clean design helped me shop without any hassle.
продажа штыревых лесов аренда горизонтальных строительных лесов
сгенерировать презентацию
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения
новые бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино
работа онлайн на дому Онлайн работа бесплатно — предупреждение: в некоторых случаях бесплатная работа может быть частью обучения или волонтёрской деятельности. Всегда проверяйте условия и риск мошенничества. Предпочтительно работать с оплачиваемыми заданиями, но если задача служит обучению, составляйте соглашение, фиксируйте временные рамки, цели и ожидаемую пользу. В любом случае сохраняйте профессиональный подход, собирайте портфолио и отзывы, чтобы позже переходить к оплачиваемым проектам.
найти работу Удаленная работа вк — группы и проекты в социальной сети ВКонтакте часто становятся источником удалённых вакансий и микрозадач. За счет таких сообществ можно найти фриланс-заказы по копирайтингу, дизайну, модерации, SMM и программированию. Чтобы эффективно использовать VK, полезно подписаться на проверенные сообщества, фильтровать предложения по опыту и бюджету, а также быстро откликаться на релевантные задания. Важно формировать профессиональное портфолио и корректно оформлять резюме под удалённую работу, чтобы читатель рассматривал вас как потенциального сотрудника. Осторожно относитесь к непроверенным предложениям: не переводите деньги, проверяйте заказчика и сроки.
удаленная работа на дому вакансии Найти работу: шаги к успеху. Определите свои цели, составьте резюме, ищите вакансии, участвуйте в собеседованиях и не сдавайтесь. Успех придет к тем, кто настойчиво идет к своей цели.
brightwillowboutique – Clean design and easy layout helped me find interesting items fast.
удаленная работа Удаленка: работа из любой точки мира. Удаленная работа позволяет вам работать из любой точки мира, где есть интернет.
удаленная работа для пенсионеров Удаленная работа: отзывы реальных людей. Изучайте отзывы о компаниях и вакансиях, чтобы избежать мошенничества и найти надежного работодателя. Отзывы – это ценный источник информации от тех, кто уже работает удаленно.
Your Next Favorite – The site’s visual appeal is matched by its incredibly straightforward navigation.
Бонусы казино
онлайн казино без верификации документов оплата картой мир
рейтинг казино
паспорта без казино
топ 10 казино
casino без верификации паспорта 2024
лучшие онлайн казино россии
топ 10 казино
Бонусы казино
бездепозитные бонусы в казино олимп
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию без депозита
прихожая на заказ размер Встроенные распашные шкафы на заказ: Классическое решение для хранения вещей – встроенные распашные шкафы, изготовленные на заказ по вашим размерам и с учетом ваших пожеланий.
бездепозитные бонусы казахстан за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом казахстан
гардеробная на заказ Встроенная мебель на заказ прихожая: Оптимизируйте пространство прихожей с помощью встроенной мебели, созданной по индивидуальному проекту и с учетом ваших потребностей.
This is very interesting, You’re an overly skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look ahead to looking for extra of your fantastic post. Additionally, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks
forticlient mac download
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to determine if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
forticlient mac download
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в игровых
как использовать бонус казино в 1win
What’s up everybody, here every one is sharing these familiarity, thus it’s pleasant to read this weblog, and I used to go to see this blog every day.
fortinet vpn client
бездепозитные бонусы в казино с выводом без пополнения
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино казахстан
бездепозитные бонусы казахстан за регистрацию в казино
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино казахстан
Hi there! This is kind of off topic but I need some advice from an established blog. Is it hard to set up your own blog? I’m not very techincal but I can figure things out pretty fast. I’m thinking about setting up my own but I’m not sure where to start. Do you have any points or suggestions? Cheers
Qfinder Pro download
BudgetVault – Nice assortment, navigating the site felt simple and comfortable.
как использовать бонусный счетна 1win в казино бонус
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом денег без первого депозита и без отыгрыша
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино с выводом денег бездепозитный
бездепозитные бонусы в казино
как использовать бонус казино в 1win
рейтинг казино онлайн на деньги
сайт azino
CreativeValueHub – Excellent user experience, site feels professional and shopping experience pleasant overall.
азино 777 официальный сайт играть казино Азино 777 известно своим разнообразным игровым ассортиментом и удобным интерфейсом. Платформа предлагает как классические слоты, так и новинки от ведущих разработчиков. Здесь каждый найдет игру по душе.
DiscoverEndlessGrowth – Inspiring content available, site feels welcoming and browsing was smooth today.
казино без паспорта и верификации Хотите играть в казино с удовольствием и без лишних хлопот? Тогда вам точно стоит обратить внимание на рейтинги казино. Это не просто списки, а результат тщательного анализа множества факторов, которые напрямую влияют на ваш игровой опыт. Хороший рейтинг поможет вам избежать сомнительных сайтов и найти место, где вас ждут честные игры, быстрые выплаты и приятные бонусы. Не тратьте время на поиски – доверьтесь проверенным рекомендациям!
casino без верификации паспорта 2024 Решили испытать удачу в онлайн-казино, но не знаете, с чего начать? Огромное количество предложений может сбить с толку. Именно поэтому существуют рейтинги казино – удобные списки, которые помогают игрокам сориентироваться и выбрать надежную площадку.
с минимальным депозитом Игровые автоматы, также известные как слоты, представляют собой один из самых популярных видов азартных игр в казино и онлайн-платформах. Их принцип работы основан на случайном выпадении символов на вращающихся барабанах, что определяет исход игры. Современные игровые автоматы предлагают огромное разнообразие тематик, бонусных функций и способов выигрыша, делая процесс игры увлекательным и непредсказуемым.
inspire journey picks – Items look appealing, navigation feels natural and simple.
buildsmartdirection – Platform provides actionable tips to maintain focus and direction consistently.
sykaaa казино android Сам сайт “Большая Sykaaa Casino” обычно отличается современным дизайном и интуитивно понятным интерфейсом. Навигация простая, все разделы легко найти. Игры загружаются быстро, что важно для комфортной игры.
регистрация в sykaaa casino второй акк Как зарегистрироваться и не наступить на грабли: полный гид по Sykaaa Casino. Онлайн-казино привлекают яркими баннерами и обещаниями быстрых выигрышей, но прежде чем нажать «Играть», важно понимать, с чем вы имеете дело. В этой статье я подробно расскажу о регистрации, безопасности, проверках и нюансах, которые стоит учитывать при создании аккаунта на сайте казино, включая практические советы и личный опыт.
sykaaa casino играть онлайн на реальные ставки Привет, любители азарта! Сегодня мы поговорим о “Большая Sykaaa Casino” – площадке, которая привлекает внимание многих игроков. Если вы только присматриваетесь к этому казино или уже решили попробовать свои силы, то этот обзор поможет вам разобраться, как быстро и без проблем начать игру, а также чего ожидать от самого сайта.
сукааа casino регистрация Привет, любители азарта! Сегодня мы поговорим о “Большая Sykaaa Casino” – площадке, которая привлекает внимание многих игроков. Если вы только присматриваетесь к этому казино или уже решили попробовать свои силы, то этот обзор поможет вам разобраться, как быстро и без проблем начать игру, а также чего ожидать от самого сайта.
explorefreshthinkingnow.click – Encouraging guidance, emphasizes reflection and developing new strategies for success effectively.
новые бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино
промокод на бездепозитный бонус в казино
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом без пополнения
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино казахстан
бездепозитный бонус казино в казахстане
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино казахстан
бездепозитные бонусы в казино с выводом без пополнения за регистрацию
бездепозитные бонусы в казино казахстан
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино с выводом
бездепозитные бонусы казахстан за регистрацию в казино с выводом
бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию в казино казахстан
бездепозитные бонусы в казино и бк
как играть на бонус казино в 1win
бездепозитные бонусы в казино олимп
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом без пополнения
как играть на бонус казино в 1win
бездепозитные бонусы в казино с выводом
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию с выводом
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино с выводом без депозита
бездепозитные бонусы в казино и бк
бездепозитные бонусы в казино 2026
бонус за регистрацию без депозита в казино
бездепозитные бонусы в казино за регистрацию 2026
казино в котором есть бездепозитный бонус
в каком казино дают бездепозитные бонусы за регистрацию
бездепозитный бонус за регистрацию в казино с выводом денег без первого депозита
бездепозитные бонусы в казино с выводом
https://sykaaa-casino-website.fun
https://sykaaa-official-casino.website
https://sykaaa-official-casino.website
https://sykaaa-official-casino.website
Мир онлайн-слотов растёт: новые провайдеры, повышенные RTP и постоянные турниры поддерживают интерес игроков.
Vavada удерживает позиции в топе, но не забывайте проверять лицензию и лимиты перед депозитом.
Выбирайте автоматы с бонусными раундами, бесплатными вращениями и прогрессивными джекпотами — так повышается шанс крупного выигрыша.
Зеркала решают проблему блокировок и позволяют оперативно выводить средства без лишних задержек.
Актуальные возможности доступны здесь: тут.
Играйте ответственно и контролируйте банкролл, чтобы азарт оставался в пределах удовольствия.
Vavada остаётся одним из самых обсуждаемых казино благодаря щедрым бездепозитным промокодам и частым бонусам на фриспины.
Перед тем как активировать предложение, убедитесь, что промокод действителен сегодня и подходит под условия конкретной акции.
Слоты с высокой отдачей и турниры с гарантированными призами помогают быстро увеличить банкролл даже без крупного депозита.
Регистрация занимает пару минут, после чего становится доступен личный кабинет и быстрый вывод средств на банковскую карту.
Актуальные промокоды, бонус?коды и рабочее зеркало ждут по ссылке: https://new-bonus.vip/.
Играйте ответственно и контролируйте бюджет, чтобы азарт приносил удовольствие, а не проблемы.
rankformula.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
Мир онлайн-слотов растёт: новые провайдеры, повышенные RTP и постоянные турниры поддерживают интерес игроков.
Vavada удерживает позиции в топе, но не забывайте проверять лицензию и лимиты перед депозитом.
Выбирайте автоматы с бонусными раундами, бесплатными вращениями и прогрессивными джекпотами — так повышается шанс крупного выигрыша.
Зеркала решают проблему блокировок и позволяют оперативно выводить средства без лишних задержек.
Актуальные возможности доступны здесь: перейти.
Играйте ответственно и контролируйте банкролл, чтобы азарт оставался в пределах удовольствия.
Мир онлайн-слотов растёт: новые провайдеры, повышенные RTP и постоянные турниры поддерживают интерес игроков.
Vavada удерживает позиции в топе, но не забывайте проверять лицензию и лимиты перед депозитом.
Выбирайте автоматы с бонусными раундами, бесплатными вращениями и прогрессивными джекпотами — так повышается шанс крупного выигрыша.
Зеркала решают проблему блокировок и позволяют оперативно выводить средства без лишних задержек.
Актуальные возможности доступны здесь: подробнее.
Играйте ответственно и контролируйте банкролл, чтобы азарт оставался в пределах удовольствия.
rankformula.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
whoah this blog is fantastic i like studying your posts. Stay up the great work! You know, a lot of individuals are searching round for this info, you could aid them greatly.
https://shop4me.in.ua/bi-led-linzy-na-chypakh-3570-chysta-optyka.html
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
https://absi.od.ua/bi-led-linzy-3-dyuima-24v-ams-u-truck.html
Wow, superb blog structure! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging glance easy. The entire look of your website is great, as well as the content!
cudovusta igrice
бездепозитные бонусы казино на реальные деньги Бездепозитные бонусы казино за регистрацию: ваш бесплатный билет в мир азарта! Мечтаете попробовать свои силы в онлайн-казино, но не хотите рисковать своими деньгами? Тогда бездепозитные бонусы – это то, что вам нужно! Многие казино предлагают щедрые подарки просто за то, что вы зарегистрируетесь. Это могут быть бесплатные вращения на популярных слотах или небольшая сумма реальных денег на ваш счет. Идеальный способ познакомиться с игрой, изучить ассортимент и, возможно, даже выиграть реальные деньги, не потратив ни рубля!
бездепозитное казино с выводом денег Бездепозитные бонусы казино за регистрацию: ваш бесплатный билет в мир азарта! Мечтаете попробовать свои силы в онлайн-казино, но не хотите рисковать своими деньгами? Тогда бездепозитные бонусы – это то, что вам нужно! Многие казино предлагают щедрые подарки просто за то, что вы зарегистрируетесь. Это могут быть бесплатные вращения на популярных слотах или небольшая сумма реальных денег на ваш счет. Идеальный способ познакомиться с игрой, изучить ассортимент и, возможно, даже выиграть реальные деньги, не потратив ни рубля!
funnelio.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
localsprint.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
rankbooststudio.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
adsforge.click – Loved the layout today; clean, simple, and genuinely user-friendly overall.
Why visitors still use to read news papers when in this technological globe all is existing on net?
byueuropaviagraonline
netlaunch.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
marketingboost.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
growthninja.click – Overall, professional vibe here; trustworthy, polished, and pleasantly minimal throughout.
leadmatrix.click – Appreciate the typography choices; comfortable spacing improved my reading experience.
searchboosters.click – Found practical insights today; sharing this article with colleagues later.
searchgrowth.click – Pages loaded fast, images appeared sharp, and formatting stayed consistent.
marketingengine.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
Greetings I am so thrilled I found your weblog, I really found you by error, while I was browsing on Digg for something else, Nonetheless I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a marvelous post and a all round entertaining blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to go through it all at the minute but I have bookmarked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a lot more, Please do keep up the fantastic work.
byueuropaviagraonline
rankstrategy.click – Bookmarked this immediately, planning to revisit for updates and inspiration.
reachrocket.click – Content reads clearly, helpful examples made concepts easy to grasp.
promova.click – Color palette felt calming, nothing distracting, just focused, thoughtful design.
sparkdex ai SparkDex is redefining decentralized trading with speed, security, and real earning potential. On spark dex, you keep full control of your assets while enjoying fast swaps and low fees. Powered by sparkdex ai, the platform delivers smarter insights and optimized performance for confident decision-making. Trade, earn from liquidity, and grow your crypto portfolio with sparkdex — the future of DeFi starts here.